- 1Wageningen Livestock Research, Wageningen University & Research, Wageningen, Netherlands
- 2Wageningen Bioveterinary Research, Wageningen University & Research, Lelystad, Netherlands
- 3Darling Ingredients International, Son en Breugel, Netherlands
- 4Netherlands Metabolomics Centre, Leiden University, Leiden, Netherlands
- 5Department of Analytical Biosciences, Leiden University, Leiden, Netherlands
This study investigates the effects of dietary spray-dried plasma (SDP) supplementation on the gut and health of growing pigs using an advanced “FeedOmics” approach. This integrative methodology employs a range of omics-based techniques to analyze microbial and molecular “signatures” associated with the dietary impact of SDP. Sixteen male growing pigs (34.9 ± 3.4 kg, 10–11 week old; n = 8/treatment group) were randomly assigned to receive one of two experimental diets for three weeks. These diets were prepared with one of the following protein sources containing (as fed basis): soybean meal (SBM, 343 g/kg), or SDP protein (SDPP, 196 g/kg). At the end of the trial, pigs were euthanized to collect jejunal and ileal mucosal tissues for gene expression analysis, jejunal and ileal digesta for microbiota profiling, blood plasma for systemic metabolomic assessment, and serum for cytokine and chemokine quantification. The SBM-based diet group was used as the reference. Findings indicate that SDPP influences the jejunum more than the ileum, where it causes a significant reduction in bacterial alpha diversity (P < 0.05) compared to SBM. We report a significant (P < 0.05) decrease in the relative abundance of the Sarcina genera in the small intestine, an effect comparable to pharmaceutical concentrations of zinc oxide (ZnO). Transcriptomic analysis identified 319 genes with altered expression in the jejunal mucosal tissue. Notably, SDPP upregulated tight junction receptors in the jejunum, which suggests it improves intestinal integrity by strengthening the gut barrier. We measured metabolites like threonine, taurine, and glutamine/glutamate in the blood of SDPP-fed pigs. These metabolites act as distinctive “fingerprints,” contributing to gut health by providing cellular energy, restoring tight junctions, and orchestrating immune responses in the small intestine mucosa. Overall, our results highlight the nutritional and functional value of SDP as functional dietary protein source.
1 Introduction
The increasing global demand for sustainable and efficient animal protein production necessitates the exploration of alternative protein sources. Traditional protein sources, such as soybean meal (SBM) and fishmeal, face challenges related to environmental impact, supply chain volatility, and potential human health concerns. To address these issues, researchers are investigating novel protein sources, including plant-based, insect-based, and microbial proteins (Kar, 2017; Kar et al., 2020, Kar et al., 2021a; Roques et al., 2022). Among these alternatives, spray-dried plasma (SDP) has emerged as a promising functional protein source for pig nutrition (Perez-Bosque et al., 2016; Roques et al., 2022). Spray dried plasma, derived from porcine or bovine blood plasma, is a rich source of high-quality protein, essential amino acids, growth factors, and immunoglobulins. By SDP in pig diets, it is possible to enhance growth performance, intestinal health, and immune function. Furthermore, the production of SDP aligns with the principles of a circular economy, as it utilizes a valuable byproduct from the slaughterhouse, thereby reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
Dietary SDP is widely used in nursery pig diet due to its nutritional value (high protein content with a high digestibility and a balanced amino acid profile) and its functional properties in relation to gut health. Improved growth performance was recorded as a response of weaned piglets to dietary SDP (Bikker et al., 2004; Kim et al., 2022). Additional research findings indicate that the inclusion of SDP enhances the health and growth performance of piglets, safeguarding the histological integrity and functionality of the small intestine (Moreto and Perez-Bosque, 2009; Gao et al., 2011).
From previous research, it is known that dietary protein sources can have profound effects on host-microbe interactions, both local (small intestine) and systemic (blood) levels (Kar et al., 2017a, Kar et al., 2017b). Spray dried plasma may support gut health and productivity in young pigs due to its functional value, enhanced by bioactive proteins like immunoglobulins (Balan et al., 2021) and bioactive peptides (Kar et al., 2016), which regulate factors affecting intestinal microbiota and mucosal immunity. However, information is missing on understanding the intricate interactions at the microbial and molecular level in the lumen and tissues of the gut that highlights the functional value of SDP. To fully evaluate SDP’s functional value, it is essential to understand how dietary protein sources impact digestive physiology through gut microbiota, intestinal mucosal response, and systemic nutrient metabolism in pigs. The functional value of dietary proteins from insects fed to pigs after weaning was determined by a FeedOmics approach (Kar et al., 2021a). Using ~ omics techniques within the FeedOmics approach, relevant data can be generated, allowing to gain a deep and thorough insight into the biological responses to differences in diet composition. However, such an approach has not yet been used in relation to diets containing SDP as a protein source for pigs.
Using a FeedOmics approach, we evaluated the effects of diets formulated with either soybean meal (SBM) as a reference protein source or SDP protein (SDPP) in pigs, focusing on both local (small intestine) and systemic (blood) responses. Data were collected across multiple biological levels to assess the functional value of SDP as a dietary protein source. Specifically, transcriptomic analyses of intestinal tissues and microbial profiling of the jejunal and ileal digesta were conducted to investigate gut functionality. Systemic effects were evaluated through blood amine profiling, while cytokine and chemokine concentrations in serum were measured to assess the immune and health status of the pigs.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Protein sources and experimental diets
The following protein sources were evaluated in the experimental diets, 1) soybean meal (SBM), commodity batch obtained via Research Diet Services, Wijk bij Duurstede, the Netherlands, and 2) SDP, obtained from Darling Ingredients B.V., the Netherlands. The evaluated nutrient composition of the SDP batch is as follows- Dry Matter (DM, as in) 915 g/kg; Protein 875 g/kg of DM; Ash content 78 g/kg of DM; Total fat 5 g/kg of DM and Gross energy 22 kJ/g of DM. The SDP sourced from Darling Ingredients is a reliable and high-quality ingredient for animal feed, meeting stringent processing and safety standards in compliance to the ‘Good Manufacturing’ Practices meeting industrial standards (Blazquez et al., 2020). The experimental diets were formulated to be iso-proteinaceous (CP, 160 g/kg as-fed basis) and included as single protein sources in the two experimental diets. Both diets were produced as mash by Research Diet Services (Wijk bij Duurstede, the Netherlands).
2.2 Animals and housing
All experimental procedures were conducted in compliance with the ARRIVE guidelines and received approval from the Animal Experimentation Board of Wageningen University & Research Centre (approval number 2014099.b). All methods performed here adhered to the relevant guidelines and regulations governing animal research. The full experimental design has already been described (Kar, 2017), a schematic representation can be seen in Supplementary Figure 1. The experimental design and the measured biomolecular parameters have been thoroughly detailed in a previous publication (Kar et al., 2021a). However, the key methodologies are outlined below for clarity. A total of 16 growing pigs (boars) (Topigs 20 × Tempo from Van Beek, Lelystad, the Netherlands) with an average initial body weight of 34.9 ± 3.4 kg (10–11-week-old) on the day (d) of arrival were included in the study. Pigs were blocked on litter and pigs within a block were randomly allocated to one of the experimental diets with eight pigs per experimental diet. The pigs were housed individually in metabolic cages (1.3 x 1.3 m or 2.0 x 1.0 m) with a tender foot floor. The ambient temperature was kept at 24°C on d 1 and 2, at 23°C on d 3, and constant at 22°C from d 4 and onwards. This helps pigs acclimate to the ambient temperature in the experimental unit. During d 1 to 27, the lights were turned on between 5.30 h till 19.00 h. During d 28 to 30, the lights were turned on between 2.30 h till 19.00 h. Adjustments to feeding strategies on dissection days (detail below), combined with modifications to light timing, ensured synchronized feeding of all experimental pigs. This approach maintained consistent conditions for digestion kinetics and nutrient metabolism, enabling the collection of representative biological samples during dissection. Body weight of animals was measured every week throughout the experimental period.
2.3 Feeding
First an adaptation period of one week was installed, where all pigs were adapted to the experimental diet (Table 1). From week 0 and onwards, pigs were fully on the experimental diets, where these diets were provided in a mash form and mixed with water (ratio 1:2). Water consumption was limited, and an extra 0.3 L of water was provided after each feeding. The feeding level was 2.5 times the net energy (NE) requirement for maintenance (293 kJ NE/kg BW0.75). During week 0 to 3, the daily feed allowance was divided into two equal amounts, fed at 8.00h and 16.00h. During week 3 till the moment of dissection at the end of the experimental period, the daily feed allowance was divided into 6 equal amounts, fed starting at 5.30 h at intervals of 3h.
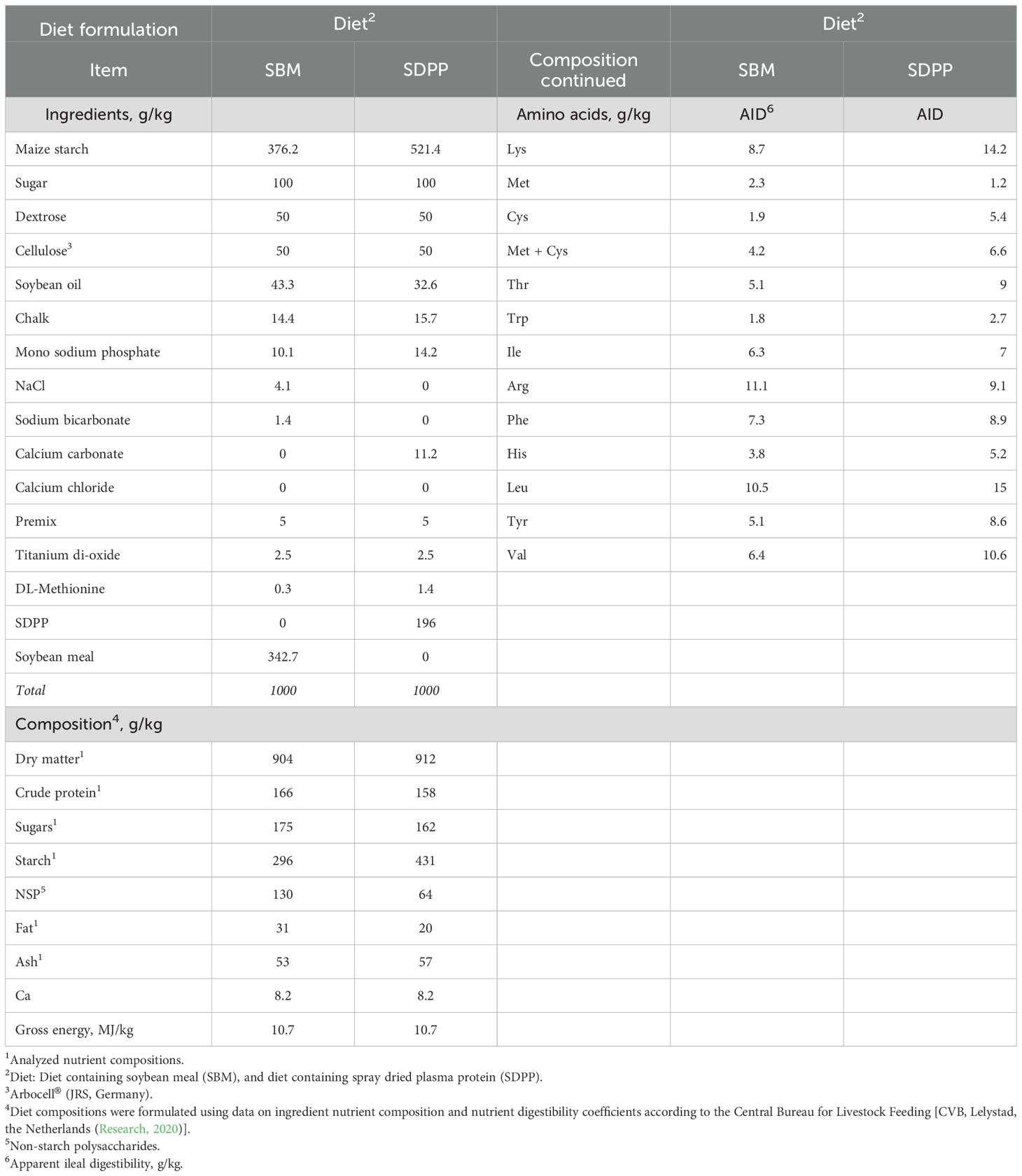
Table 1. Ingredient and calculated or analyzed1 nutrient composition of the experimental diets for pigs (as fed basis).
2.4 Sample collection and dissection procedure
Blood samples were collected via the ear-vein for serum and plasma preparation on d 7 and at dissection days (d28-29) after the morning meal ingestion. For serum, blood samples were collected in sterile Vacuette tubes containing Z-serum separator clot activator (Greiner Bio-One B.V., Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands), tubes were gently inverted and allowed to clot for at least 30 min. All tubes were centrifuged at 2,200x g for 15 min at 20°C and serum was extracted. For plasma, blood samples were collected in sterile Vacuette tubes containing lithium-heparin and immediately centrifuged at 3,000x g for 10 min at 4°C and plasma was extracted. Both serum and plasma were stored at -80°C for further analysis on levels of systemic cytokine and chemokines as well as systemic amine metabolite profiles, respectively.
On dissection days, pigs were euthanized following anesthesia induced with pentobarbital (Pentobarsol™, Dechra, Fort Worth, USA), administered via injection into the ear vein at a dosage recommended by the manufacturer relative to their body weight, before being sacrificed by bleeding. The small intestine was separated from the stomach and the large intestine. Jejunum and ileum were divided into three equal segments and two sub-segments of the same location of each tissue were sampled for intestinal mucosal layer and resident microbiota. For the intestinal mucosal layer, one of the sub-segments was cut open longitudinally along the lumen and washed with sterile normal saline solution. With a sterile glass slide the mucosal layer was collected, snap frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80°C for further analysis of genome-wide gene expression profiling. From another sub-segment, luminal digesta was collected to perform a community-scale analysis of the gut microbiota.
2.5 Chemical analysis of the diet
Representative samples of dried and ground diets were chemically analyzed for dry matter (DM) (ISO-6496, 1999; by four hours’ drying at 104°C); sugar (ISO 15914-1, I, 2004); starch (van Vuuren et al., 1993); ash (ISO-5984, 2002; after three hours’ ashing at 550°C); ether extract (ISO-6492, 1999; by extraction with petroleum ether); and nitrogen (N) (ISO-5983-2, 2009; by Kjeldahl method) and crude protein (CP) (calculated as Nx6.25). The results are shown in Table 1.
2.6 Small intestinal genome-wide transcriptome profiling
From each individual pig, jejunal and ileal tissue samples were collected, subsequently total RNA extraction was performed. Total RNA from individual samples from each intestinal tissue was extracted using trizol reagent (Life Technologies, California, United States) as recommended by the manufacturer. Homogenized tissue samples were dissolved in 5ml of trizol reagent (ThermoFisher Scientific, Lelystad, NL). After centrifugation, the supernatant was transferred to a fresh tube. Subsequently a phase separation with chloroform was performed as described by the manufacturer. The RNA was precipitated and dissolved, thereafter quantified by absorbance measurements at 260 nm. Quality check of the RNA samples was performed with the Agilent Bioanalyzer (Agilent, CA, USA). Details of biological replicates per treatment are shown in Supplementary Table 1. One RNA sample from ileum belonging to SDPP group failed to pass the QC performed with the Agilent Bioanalyzer. Downstream handling of the samples, i.e. labeling, hybridization, scanning, feature extraction, and QC by statistical analysis was performed as described previously (Schokker et al., 2014). Briefly, labeling was done as recommended by Agilent Technologies using the One-Color Microarray-Based Gene Expression Analysis Low Input Quick Amp Labelling. The input was 200 ng of total RNA and 600 ng of labelled cRNA was used on the 8-pack array. Hybridization was performed as described in the One-Color Microarray-Based Gene Expression Analysis Low Input Quick Amp Labelling protocol from Agilent in the hybridization oven (G2545A hybridization Oven Agilent Technologies). The hybridization temperature was 65°C with rotation speed 10 rpm for 17 hours. After 17 hours the arrays were washed as described in the One-Color Microarray-Based Gene Expression Analysis Low Input Quick Amp Labelling protocol from Agilent. The porcine Agilent microarray slides, G2519F Sus scrofa (035953), harbouring 43,803 probes, were used, and scanned using the DNA microarray scanner with Surescan high resolution Technology (Agilent Technologies). Agilent Scan Control with resolution of 5 µ, 16 bits and PMT of 100%. Feature extraction was performed using protocol 10.7.3.1 (v10.7) for 1 color gene expression.
The files generated by the feature extraction software were loaded in the Gene Expression Omnibus from NCBI with the accession number GSE98261, in which a log2-transformation and quantile normalization was carried out as described (Schokker et al., 2018), by executing different packages, including LIMMA (Smyth, 2005) within R. Thereafter, principal component analysis (PCA; unsupervised) was performed. In the first approach, transcripts were defined as significantly differentially expressed when the log fold-change (FC) between the treatment groups for both intestinal locations was > 1 or < − 1 and the adjusted P-value (false discovery rate) of LIMMA was < 0.05. The files generated by the feature extraction software were loaded in the Gene Expression Omnibus from NCBI with the accession number GSE98261, in which a log2-transformation and quantile normalization was carried out as described (Schokker et al., 2018), by executing different packages, including LIMMA (Smyth, 2005) within R. Thereafter, principal component analysis (PCA; unsupervised) was performed. In the first approach, transcripts were defined as significantly differentially expressed when the log fold-change (FC) between the treatment groups for both intestinal locations was > 1 or < − 1 and the adjusted P-value (false discovery rate) of LIMMA was < 0.05.
For a ‘data-driven’ approach, the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were used as input to identify enriched pathways, using the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) collection. In addition, also a ‘biology-driven’ approach was used, targeting specific pathways involved in gut functionality. To get better insight and proper interpretation of the transcriptomics data, we have superimposed the gene expression values from the genome-wide transcriptomes to KEGG pathways. The selected KEGG pathways encompass the ‘Intestinal Immune Network for IgA Production’, identified through a data-driven methodology (Table 2), and the ‘Tight Junction Pathway,’ which serves as an indicator of gut barrier integrity and was chosen based on a biology-driven approach to directly reflect gut health.

Table 2. Enriched biological pathways1 in small intestinal tissue (jejunum and ileum) of pigs fed a SBM or SDPP based diet.
2.7 Small intestinal microbiota profiling
2.7.1 Microbial DNA extraction
Details on the number of replicate samples per treatment per type of analysis are shown in Supplementary Table 1. The number of replicates ranged from 5 to 8 animals per treatment group due to non-availability of sufficient luminal digesta in some cases. Luminal digesta of each small intestinal location was mixed 1:1 with Phosphate Buffered Solution and vortexed, spun for 5 min (300x g) at 4°C. DNA was extracted from small intestinal digesta by the repeated bead beating method (Yu and Morrison, 2004) using QIAamp PowerFecal DNA Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to manufacturer’s instructions. PowerBead solution (750 μl) was added to the 5ml Eppendorf tube containing small intestinal digesta approximately 200 mg of luminal digesta (wet weight) was used for microbial DNA extraction. The quality and quantity of extracted DNA samples were checked by gel electrophoresis (only representative samples) and Nanodrop (Agilent, CA, USA), respectively.
2.7.2 16S rRNA gene-based amplicon sequencing
Library construction of the V3 hypervariable region (from 16S rRNA gene) followed by sequencing on an Illumina MiSeq platform (paired end reads; 2*300 bp) were performed. Amplicons of the V3 hypervariable region of the 16S rRNA gene, were generated using the primer set V3_F (CCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG) and reverse primer V3_R (ATTACCGCGGCTGCTGG). Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) conditions were as follows: 2 min at 98°C, 15× (10 s at 98°C, 30 s at 55°C, and 10 s at 72°C), and 7 min at 72°C. The PCR products were mixed with the same volume of 1x loading buffer (contained SYBR green) and were detected by electrophoresis on 2% agarose gel. Prior to library preparation, the PCR products were mixed in equimolar ratio and purified using Qiagen Gel Extraction Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). Samples were sequenced by targeted amplicon 16S sequencing using the MiSeq sequencer (Illumina, San Diego, California, United States). Subsequently, the sample-specific barcodes and primer sequences were trimmed from the Illumina raw reads and the file generated were uploaded in sequence read archive from NCBI with the accession number PRJNA1139701.
2.7.3 16S based amplicon sequencing data analysis
The trimmed paired end reads were imported into the CLC Genomics Workbench version 20.0.4 and were processed using the CLC Microbial Genomics Module version 2.5.1 (CLC bio, Arhus, Denmark). The paired end reads were merged into one high quality representative sequence using CLC default parameters (Mismatch cost = 1, Minimum score = 40, Gap Cost = 4, Maximum unaligned end mismatches = 5). The sequences were then clustered into operational taxonomic unit (OTUs) at 97% identity threshold, followed by taxonomic annotation using SILVA database v138.1 (Quast et al., 2013). The OTU table is further filtered by removing OTUs with low abundance (Minimum combined count = 10), to get a final abundance table for each sample. Using the relative abundance of matched OTUs at genus level, principle component analysis (PCA; unsupervised) was performed (released on Dec 13, 2017) (Quast et al., 2013). The OTU table is further filtered by removing OTUs with low abundance (Minimum combined count = 10), to get a final abundance table for each sample. Using the relative abundance of matched OTUs at genus level, principle component analysis (PCA; unsupervised) was performed using Canoco 5 (v5.10) according to software developer’s instructions (Ter Braak and Smilauer, 2018).
The phylogenetic tree was constructed using Maximum Likelihood Phylogeny tool based on a Multiple Sequence Alignment of the OTU sequences (top 100 most abundant OTUs) generated by MUSCLE (Multiple Sequence Comparison by Log- Expectation) tool (Edgar, 2004) in the workbench. The Maximum Likelihood Phylogeny tool determines the probability of the sequences in the tree, using Neighbour Joining as construction method and Jukes Cantor as Nucleotide substitution model. Abundance analysis, such as alpha- and beta- diversity, PERMANOVA analysis as well as differential abundance analysis (DAA) were performed using CLC- Microbial Genomics Module. Alpha- and beta-diversity measures were calculated with the relative abundance of matched OTU at genus level. To show whether genus abundance profiles of replicate samples for each dietary treatments taken from different locations i.e. jejunum and ileum, varied significantly according to the dietary treatments within a location or not. Comparison of the alpha-diversity measures i.e. Observed species and Shannon indices; considering the number of species and the evenness of the species was performed by a Mann Whitney U-test (non-parametric) or Student’s T-test (parametric) in GraphPad Software (8.1.1). Bray-Curtis’s measure was used to calculate distance matrices for the beta diversity. To visualize the beta diversity results, Principal Coordinate Analysis (PCoA) was performed on the dissimilarity matrices. Additionally, to measure the effect size and significance on beta-diversity (i.e. Bray Curtis) of the replicate digesta samples for each dietary treatments within a location, permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA) analysis, also known as non-parametric MANOVA (Anderson, 2001), was performed using OTU abundance profiles. Furthermore, we focused on the taxonomic distribution of the abundant bacteria derived from the 16S rRNA gene sequences in jejunal and ileal digesta of pigs fed either SDPP or SBM based diets. Multivariate redundancy analysis (RDA) was employed to identify microbial signatures (with response score > ± 0.5) in different dietary treatment groups within each small intestinal location using CANOCO 5. Additionally, the DAA tool of CLC- Microbial Genomics Module was used to characterize the microbial differences at genus level with False Discovery Rate (FDR)<0.05 with fold change > 5, between the digesta samples for the dietary treatment groups collected from each small intestinal location. Heat maps were constructed by hierarchical clustering of microbial families (selected from DAA) in Perseus software (version 1.6.14.0; available at: http://www.maxquant.org/), where relative abundance values were normalized by z-score transformation. For hierarchical clustering, Euclidean distance was utilized to measure the distance and clustering was conducted using the average linkage method.
2.8 Systemic metabolomics profiling
2.8.1 Assay description
The amine profiling was performed as described previously (Noga et al., 2012). Briefly, 5 µL of each sample was spiked with an internal standard solution (Supplementary Table 2), thiol amines are released from proteins and converted to a reduced form using Tris-(2-Carboxyethyl)phosphine (TCEP). Then proteins were precipitated by the addition of MeOH. The supernatant was transferred to an Eppendorf tube (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) and dried in a speedvac (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany). The residue was reconstituted in borate buffer (pH 8.5) with AQC reagent (Waters, Etten-Leur, The Netherlands). After reaction, the vials were transferred to an autosampler tray (Waters, Etten-Leur, The Netherlands) and cooled to 10°C prior to injection. For amine metabolite analysis, 1 µL of the reaction mixture was injected into the UPLC-MS/MS system using an Accq-Tag Ultra column (Waters, Etten-Leur, The Netherlands).
2.8.2 Equipment
We employed an ACQUITY UPLC system with autosampler (Waters, Etten-Leur, The Netherlands) was coupled online with a Xevo Tandem Quadrupole mass spectrometer (Waters, Etten-Leur, The Netherlands) operated using QuanLynx data acquisition software (version 4.1; Waters, Etten-Leur, The Netherlands). The Xevo Tandem Quadrupole was used in the positive-ion electrospray mode and all analytes were monitored in multiple reaction monitoring using nominal mass resolution.
2.8.3 Data processing and quality check of metabolomics data
Acquired data were evaluated using TargetLynx software (Waters, Etten-Leur, The Netherlands), by integration of assigned MRM peaks and normalization using proper internal standards. For analysis of AA, their 13C15N-labeled analogues were used and for other amines, the closest-eluting internal standard was employed (Supplementary Table 2). Blank samples were used to correct for background, and in-house developed algorithms were applied using the pooled quality check (QC) samples to compensate for shifts in the sensitivity of the mass spectrometer over the batch analysis (van der Kloet et al., 2009). We could detect 58 amines that comply with the acceptance criteria of QC corrections. The data are represented as relative response ratios (amine target area/area of internal standard; unit free) of these metabolites (after QC) are available online: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.13285418.
2.8.4 Metabolomics data analysis
To get more insight into the variability in the amine metabolomics data, PCA was performed using the intensities of the identified amine metabolites from plasma sample of pigs fed with either SBM or SDPP-based diets. To assess the contribution of metabolites to the differences observed between dietary treatments, we conducted a Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA), followed by the generation of a Variable Importance in Projection (VIP) plot (Figure 1A). The VIP score quantifies the significance of each variable in modeling both the predictor (X) and response (Y) variables. In this context, variables with VIP scores greater than 1 were considered highly influential within the PLS-DA model. Employing the statistical module of MetaboAnalyst 4.0 (Chong et al., 2019), the heat map graphic distances were measured using Euclidean distances and the clustering algorithm using a Ward dendrogram. The amine metabolites data was normalized by the pooled sample from group SBM and thereafter log transformation to the data was performed. To retain the most contrasting patterns among the treatment groups, the top 25 metabolites ranked by Student’s T-tests were displayed in the heat-map. Additionally, fold changes of the amine metabolites were calculated using the statistic suits of MetaboAnalyst 4.0. Metabolic pathway analysis module of MetaboAnalyst 4.0 (Chong et al., 2019) was employed to determine the amine metabolism that was affected by the SDPP diet compared to the SBM diets. All the compound names of the metabolites were matched with the human metabolome database (HMDB). To normalize the data, a log transformation was performed. Thereafter, the human pathway library was selected, and a reference metabolome based on our technical platform was uploaded. The analysis includes pathway enrichment analysis and topological analysis. Based on the topology analysis, the threshold values were set at 0.4 for pathway impact and 4 for the log(p)-value of pathway enrichment to identify the most relevant metabolic pathways (Kar et al., 2017b).
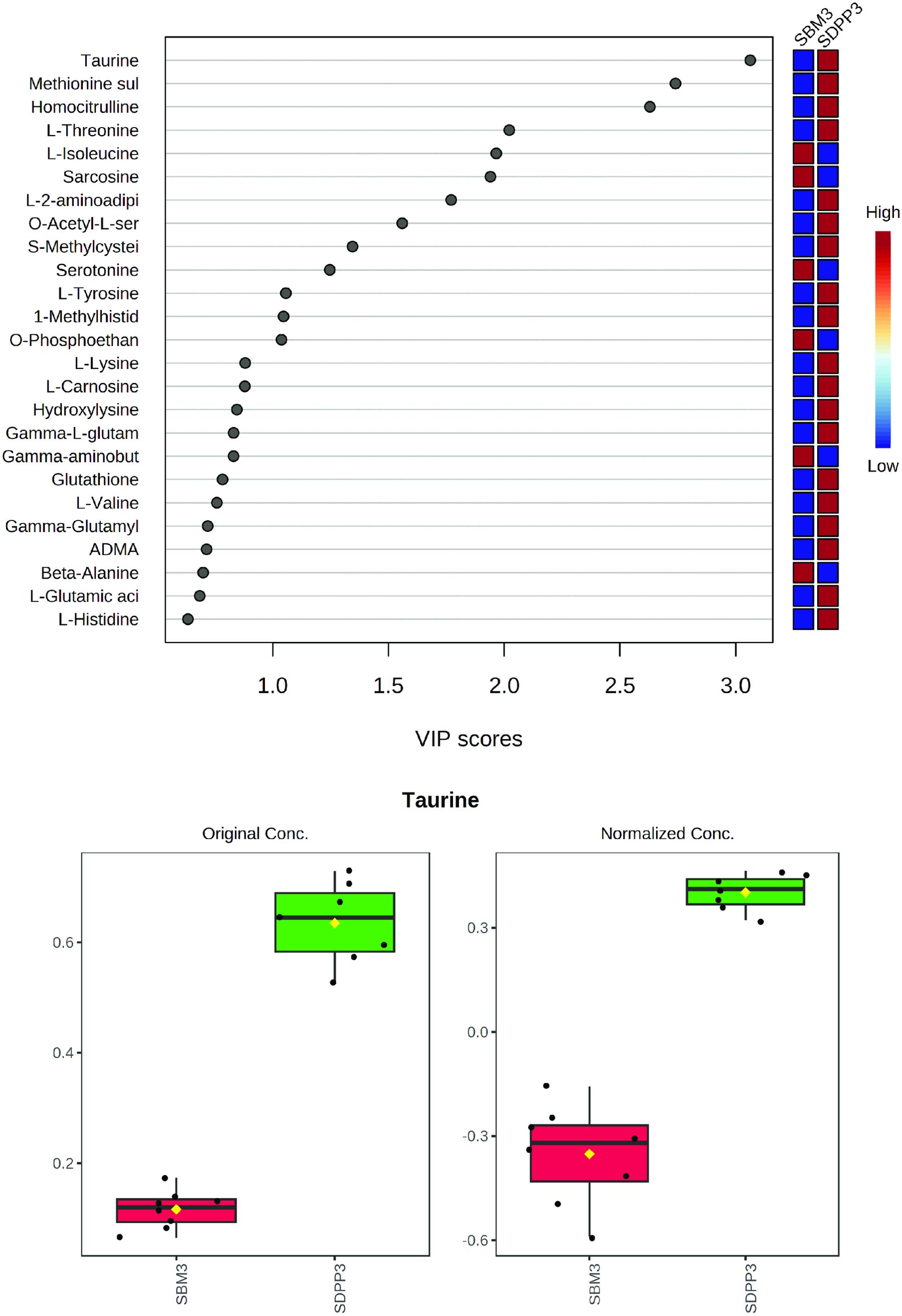
Figure 1. Profile of amines in plasma of pigs fed a diet with either soybean meal (SBM) or spray-dried plasma protein (SDPP) as single protein source. Panel (A) shows the Variable Importance Plot (VIP) scores of the plasma amine metabolites. Panel (B) depicts the concentration of the metabolites having the highest (top 5) VIP scores, all having a VIP > 2.
2.8.5 Systemic inflammatory marker profiling
Serum cytokine and chemokine concentrations (pg/ml) were measured using a ProcartaPlex Porcine kit (Affymetrix, eBIOscience, Vienna, Austria). Calibration curves from recombinant cytokine and chemokine standards were prepared for the 8-point standard dilution set with 4-fold dilution steps in sterile PBS. The samples were measured using a Bio-Plex MagPix Multiplex Reader (Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc. by the Luminex Corporation, The Netherlands). The Bio-Plex Manager software’s five-parameter logistic curve fitting (5PL) method was used for raw data analysis and calculation of cytokine concentrations. Cytokine concentration levels are presented as means ± Standard Error of the Mean. Statistical analysis was performed by Student’s T-test to calculate P value (two-tailed) using GraphPad prism (v5.03) for Windows Vista (GraphPad Software, San Diego, California, USA). P value <0.05 was considered significant.
3 Results
The diet was not entirely nutritionally balanced as the study was not intended to assess growth performance. Consequently, growth performance is not a primary outcome of this study, therefore no statistical test was performed on BW data. At the start of the experiment (time 0) the pigs weighed approximately 33 kg, whereas at the end, i.e., week 3, the average body weight was increased to approximately 45 kg.
Principle component analysis (PCA) was performed to get more insight into the variability of different responses measured by the ~omics based technologies. The plots of microbiota composition and gene expression in the jejunum, along with amine metabolites in the blood, showed distinct clustering of pigs fed either the experimental diet with SBM or SDPP. The first two axes explained 52.9% of the variance in microbiome composition for the jejunum and 51.2% for the ileum (Figure 2A). Furthermore, the genome-wide gene expression responses revealed that the first two axes accounted for 36.4% of the variance for the jejunum and 32.5% for the ileum (Figure 2B). Among the various responses measured by ~omics based technologies, the highest proportion of variance explained by dietary treatment was observed for amine metabolites in blood plasma, with the first two axes explaining 52.6% of the variance (Figure 2C).
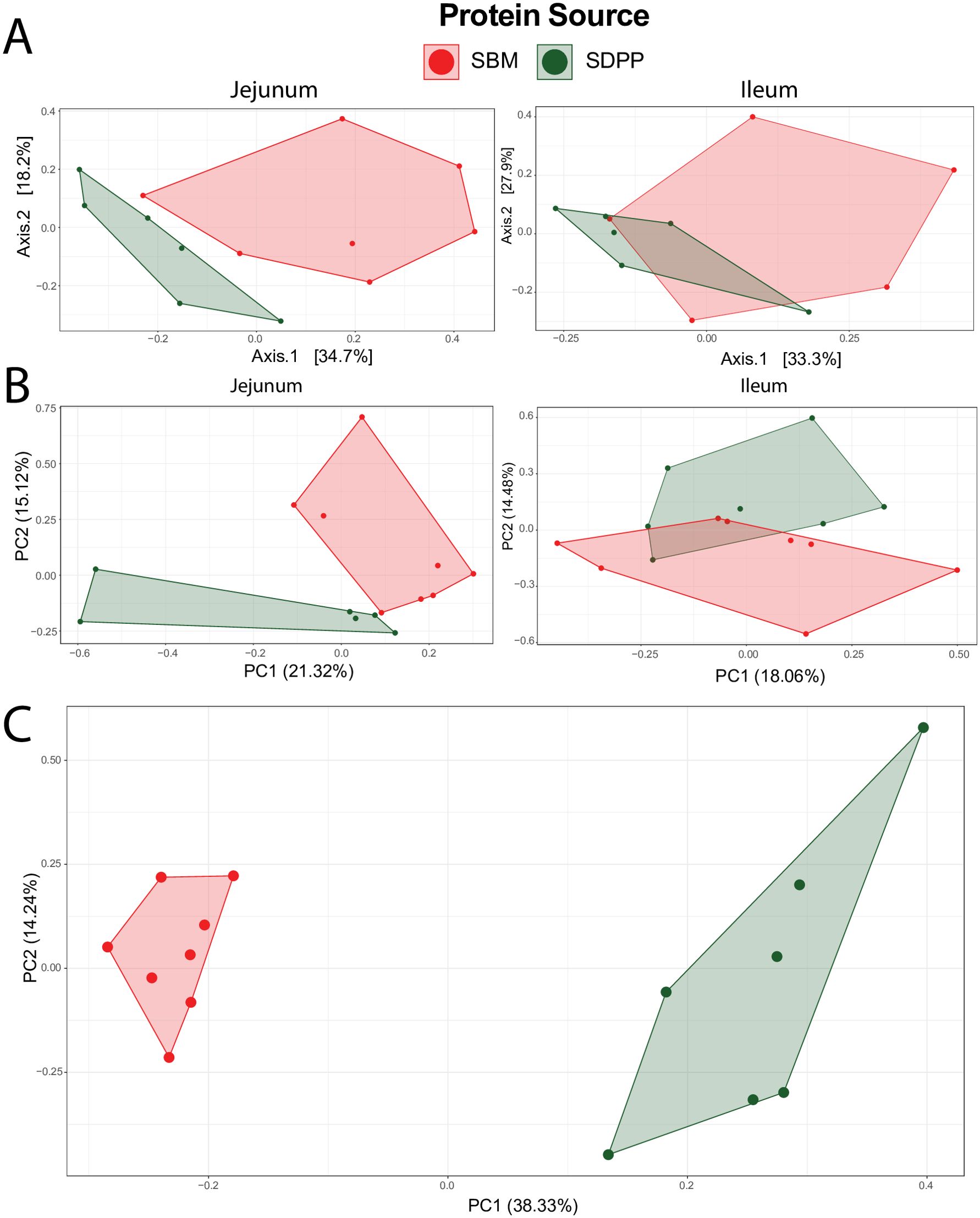
Figure 2. Principal component analysis (PCA) plot illustrating the variability in responses measured by omics-based technologies in pigs fed either a diet with soybean meal (SBM, red) or spray-dried plasma protein (SDPP, green), as single protein source. Panel (A) shows the small intestinal microbiota response, panel (B) shows whole-genome transcriptome response of the small intestine mucosa, and panel (C) shows plasma amine metabolite profile.
3.1 Small intestinal microbiota response
Sequencing of the 16S rRNA (V3 region) amplicons generated on average more than 441,000 high-quality reads that were classified into Operational Taxonomy Units (OTUs) with an average of more than 255,000 reads in OTU for both jejunum and ileum.
The alpha diversity measures calculated were Total number of species (Richness), Chao1, and Shannon entropy (Table 3). For jejunum statistically significant differences were observed for all three measures, were the SDPP group had lower values compared to the SBM group. The experimental diet with SBM included approximately 2,200 species, while the diet with SDPP included around 1,100 species, with Shannon entropy values of 7.8 and 5.6, respectively (Supplementary Figure 2). In the ileum, no significant differences were observed; however, the SDPP group exhibited numerically lower values compared to the SBM group. Beta diversity measures revealed no significant differences in the variability of the microbiome composition in jejunum or ileum digesta (Table 3).
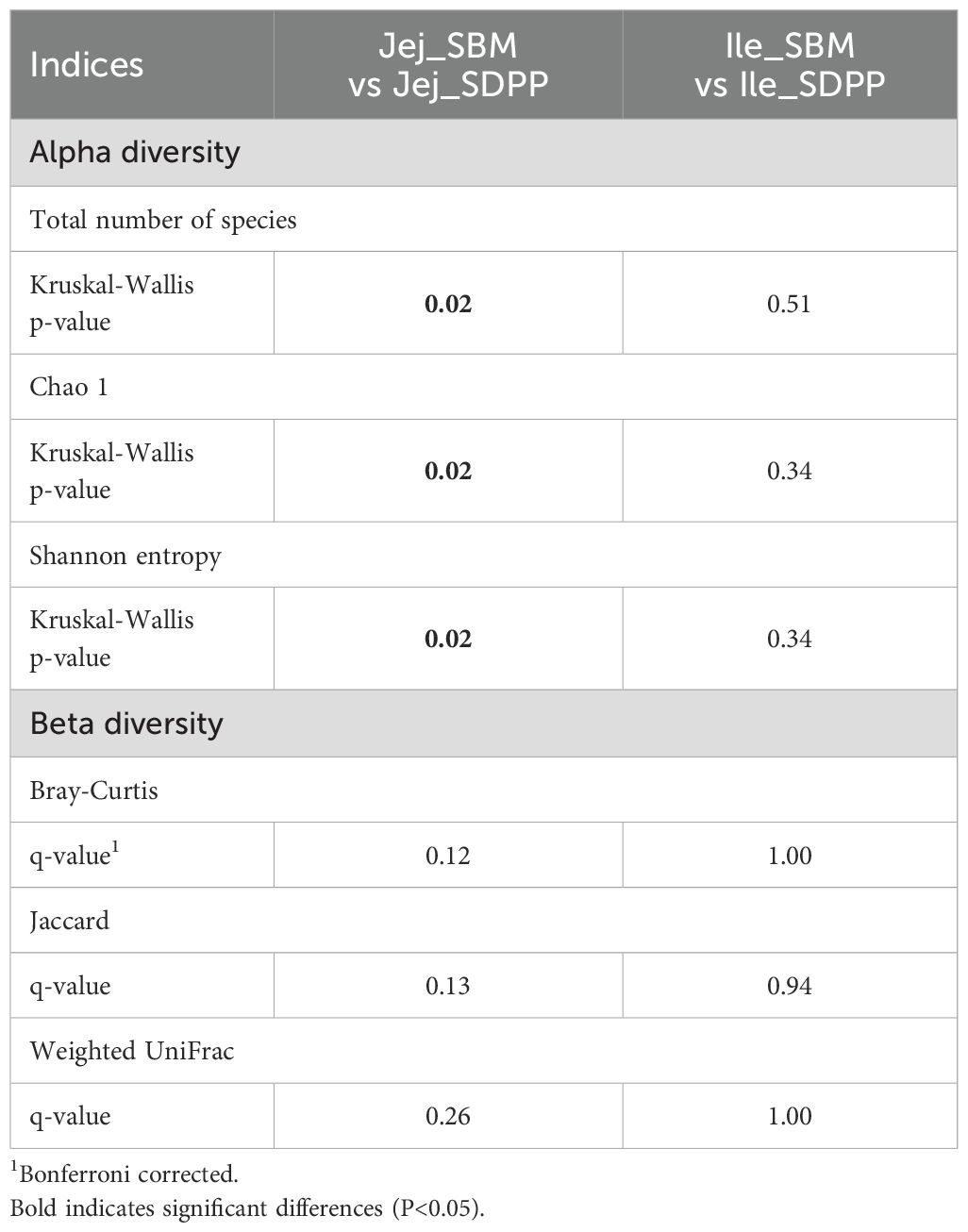
Table 3. Alpha diversity and beta diversity of microbiota in jejunal and ileal digesta of pigs fed diets with soybean meal (SBM) or spray-dried porcine plasma (SDPP) as single protein source.
Figure 3 shows the relative abundance of the identified microbiota composition at the genus level (see Supplementary Figure 3 for Phyla and Class). In the jejunum, Streptococcus, Lactobacillus, and Veillonella were the predominant genera, while in the ileum, Streptococcus, Escherichia-Shigella, Turicibacter, and Romboutsia were most prevalent. When comparing the experimental diets, a significant shift in the genus Sarcina was observed in the jejunum; the average relative contribution in the SBM group was approximately 0.13, which decreased to nearly zero in the SDPP group. A similar pattern was observed in the ileum, where the average relative contribution of Sarcina in the SBM diet was about 0.03, decreasing to almost zero in the SDPP fed group.
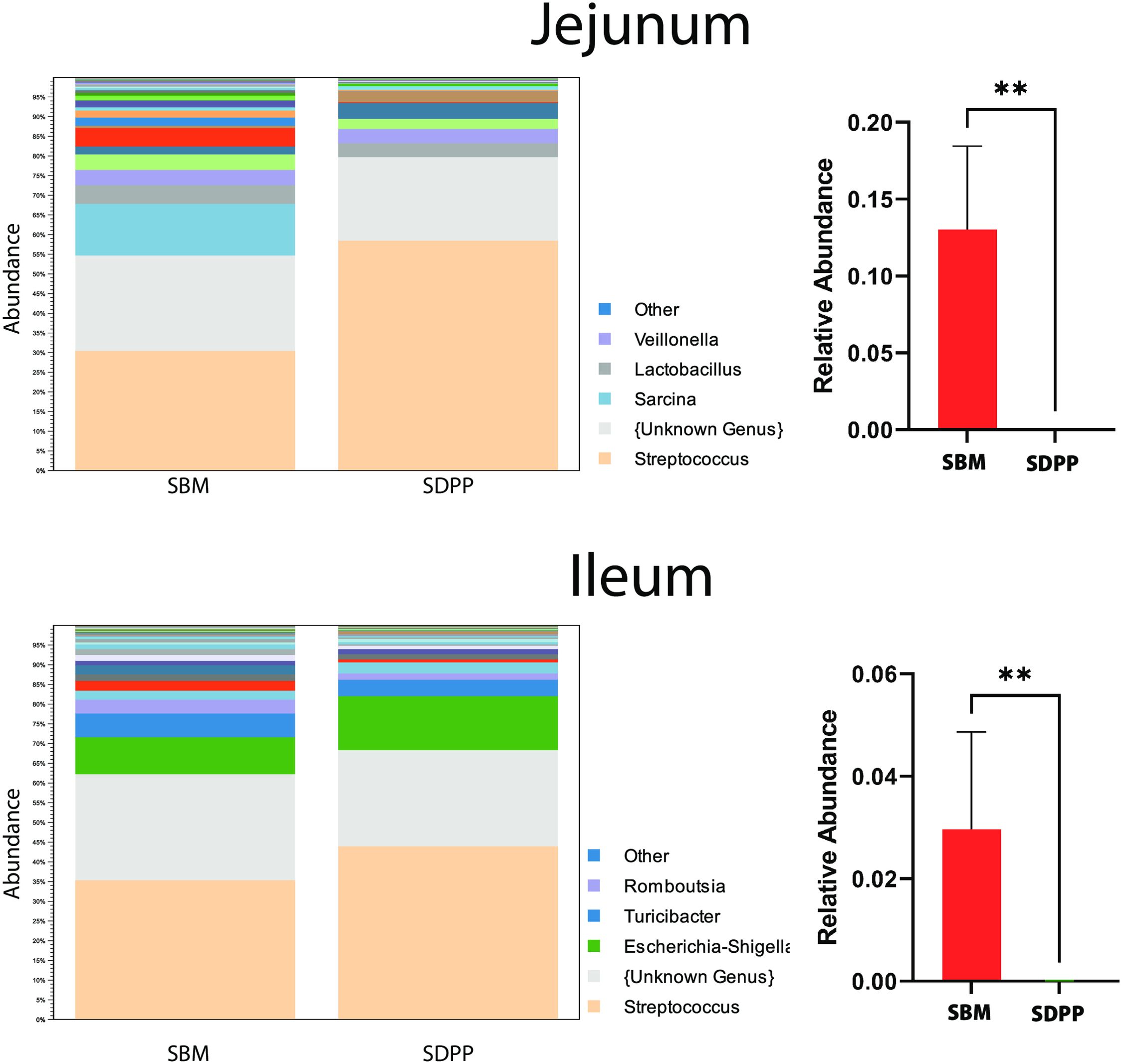
Figure 3. Stacked bar plots to illustrate the microbiota composition on genus level of jejunal and ileal microbiota comparing effects of soybean meal (SBM) and spray-dried porcine plasma (SDPP) based diets in pigs. The left panels depict the top 10 genera in jejunum (top-left) or ileum (bottom-left), where each color represents a different genus. The right panels show an example of statistically significant genera, i.e. Sarcina, when comparing the SBM (red) to the SDPP (green) based treatment. The y-axis represents the average relative abundance in jejunum (top-right) and ileum (bottom-right). **P<0.001.
3.2 Whole-genome transcriptome response of the small intestine mucosa
To gain insight into the biological significance of SDPP-induced changes in the small intestinal transcriptome, we used a data-driven approach to first identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Differences between the treatment groups, i.e., SBM and SDPP, were shown to be greater in jejunum compared to ileum as displayed in the PCA (Figure 2B). We observed more DEGs for jejunum, 319 (262 down- and 57 up-regulated) compared to ileum 40 (27 down- and 13 up-regulated) (Table 4). Pathway enrichment analysis was conducted to obtain an unbiased assessment of changes in biological processes associated with these DEGs when comparing the experimental diets containing SBM and SDPP (Table 2). Results showed seven significant enriched pathways for jejunum, i.e., intestinal immune network for IgA production, viral protein interaction with cytokine and cytokine receptor, cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, chemokine signaling pathway, complement and coagulation cascades, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, and ECM-receptor interaction. For ileum four enriched pathways were observed, i.e., steroid biosynthesis, cholesterol metabolism, mineral absorption, and bile secretion.
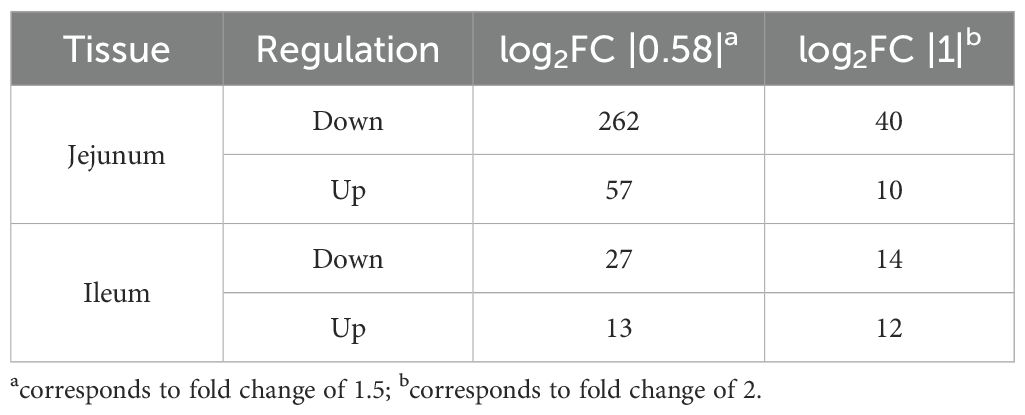
Table 4. Number of differentially expressed genes in jejunum and ileum tissue from pigs fed a SBM or SDPP based diet.
Overlaying the treatment-induced changes in jejunal and ileal transcriptome responses within KEGG pathways has significantly enhanced the visualization and understanding of the intricate gene expression networks that modulate various biological processes. Specifically, we highlight the ‘Intestinal Immune Network for IgA Production’ as a significantly enriched pathway (Table 2 and Supplementary Figure 4), showcasing its role in immune function. Additionally, the intestinal ‘Tight Junctions’ pathway (Supplementary Figure 5) is emphasized for its critical contribution to the barrier function of the small intestine, underscoring its importance in maintaining intestinal integrity. This approach serves as a powerful example of a data-driven methodology for interpreting biological results.
3.3 Post-absorptive plasma amine metabolomic responses
The PCA plot of amine plasma metabolites showed a clear separation of the dietary treatments. Here, we observed 13 metabolites with a VIP score above 1, and for the top 5 metabolites, i.e., taurine, methionine sulphate, homocitrulline, L-threonine, and L-isoleucine, VIP scores were above 2 (Figure 1A). Furthermore, the diet containing SDPP exhibited higher concentrations of taurine (Figure 1B), methionine sulphate, homocitrulline, and L-threonine compared to the diet containing SBM.
Plasma amine metabolites which differed in concentration between SBM and SDPP treatment groups were mapped to the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) metabolic pathways. This revealed seven metabolic pathways that were modulated by dietary treatment (Table 5). The enriched KEGG pathways were, 1) glycine, serine, and threonine metabolism, 2) taurine and hypotaurine metabolism, 3) arginine and proline metabolism, 4) phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan biosynthesis, 5) alanine, aspartate, and glutamate metabolism, 6) histidine metabolism, and 7) beta alanine metabolism.
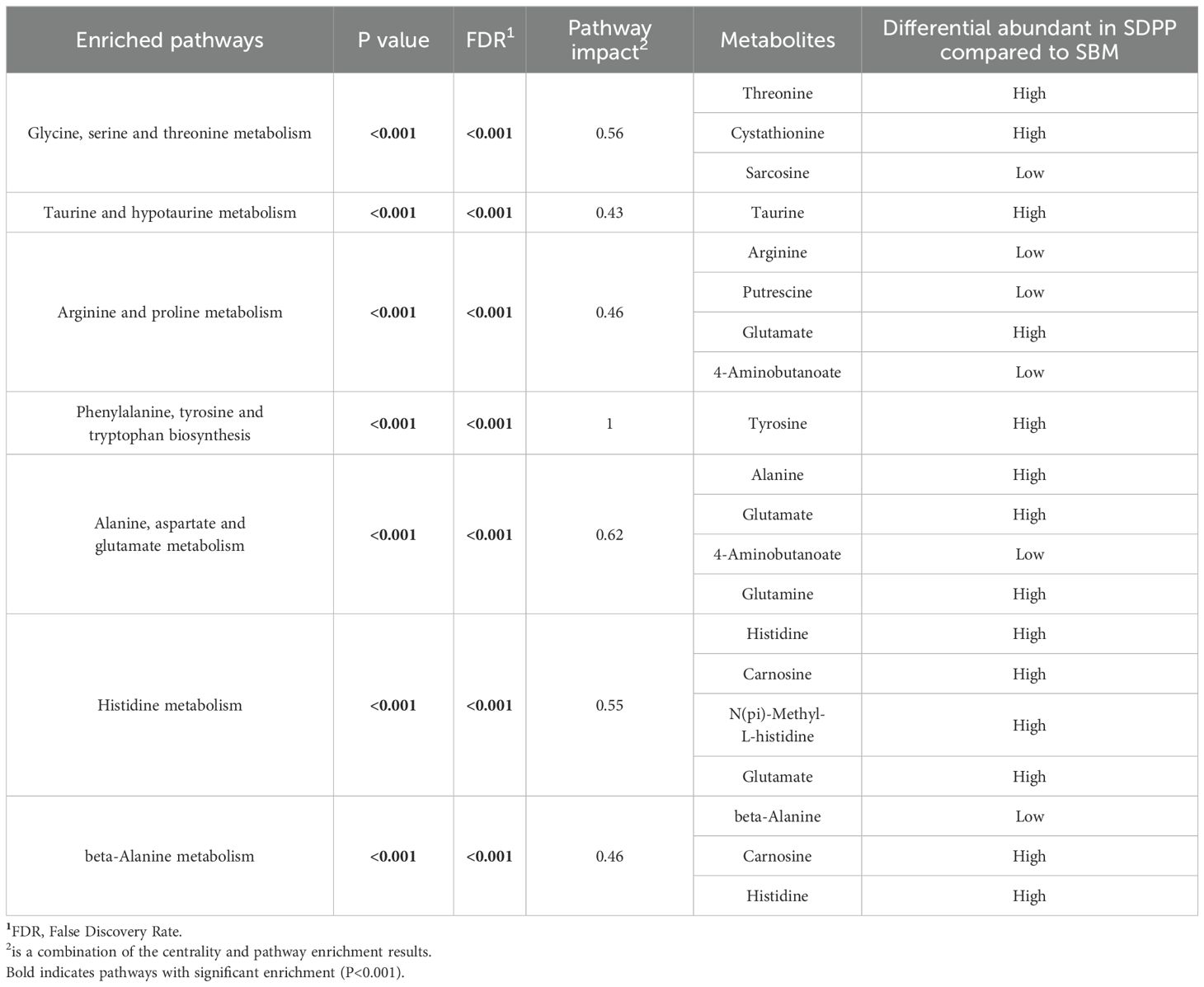
Table 5. Metabolic pathways involving amine metabolites in blood plasma differently present in pigs receiving a SBM or SDPP based diet.
3.4 Systemic inflammatory marker response
A specific panel of systemic inflammatory markers were measured and did not show significant differences between dietary treatments (see Supplementary Figure 6).
4 Discussion
In pigs, insect proteins are emerging as a potential alternative protein source and show promise for the future among other options (Kar et al., 2021a). While insect proteins are rich in essential amino acids and sustainable, they are not yet as widely studied or utilized as spray dried plasma. Issues such as palatability, variability in composition, potential allergenic compounds, production scalability and broader acceptance need to be addressed before they can match the performance and reliability of spray dried plasma. Spray-dried plasma remains a superior choice for young pigs, particularly during the critical post-weaning period, due to its exceptional nutritional, functional, and health-promoting properties (Kats et al., 1994; Zhang et al., 2015; Kim et al., 2022). In this study, we investigated the bio-functional properties of spray dried plasma as a functional protein source and its role in enhancing gut health in post-weaned pigs. The compositional disparities in the experimental diets, notably in NSP and fat content, induced by the protein sources, likely influenced the intestinal microbiome and host (intestinal) responses. We employed the FeedOmics approach, which combines various ~omics-based techniques to evaluate how dietary protein sources impact host physiology (Leibold et al., 2004; Kar, 2017; Kar et al., 2017a). It is important to note that the diets were not fully balanced in terms of essential amino acid concentrations relative to the pig’s requirements, as the study was not designed to assess growth performance. Consequently, growth and productive performance metrics are not the primary focus of this study. Instead, we illustrate how the FeedOmics approach offers mechanistic insights into how dietary SDPP, as a functional protein source, affects biological responses and promotes gut health in post-weaned pigs. The following sections discuss the effects of feeding SDPP to young growing pigs, focusing on gut responses and systemic effects.
4.1 Effect of SDPP on small intestinal microbiota
The analysis of the small intestinal microbiome showed that, regardless of the dietary treatment, the most prevalent phyla were Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, and Actinobacteria, with the respective classes Bacilli, Clostridia, and Gammaproteobacteria being dominant in the jejunal and ileal digesta of pigs. This finding aligns with previous research (Zhao et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2016; Li et al., 2017; McCormack et al., 2017; Crespo-Piazuelo et al., 2018; Li et al., 2018; Jin et al., 2019), which also identified Firmicutes and Actinobacteria as the predominant phyla in pigs, indicating their core role in the porcine intestinal microbiota Additionally, the ileal microbiome profile is consistent with other studies (Quan et al., 2018), particularly concerning the genera Escherichia-Shigella and Romboutsia. Our analysis of the taxonomic distribution revealed a significant fraction of bacteria in both intestinal locations classified as ‘unknown taxon or N/A,’ likely due to limitations of the SILVA SSU version 138.1 database (https://www.arb-silva.de/projects/ssu-ref-nr/) used for the OTU table. Despite this, we observed similar diet-specific microbial groups in the jejunum and ileum, suggesting that dietary treatment has a stronger influence on microbiota composition than location-specific variations (Holman et al., 2017).
Incorporating SDPP into the diet of post-weaned pigs reduces microbiota richness. The SDPP-based diet significantly altered the small intestinal microbiota compared to the SBM-based diet, leading to a notable reduction in microbial diversity and changes in microbial abundance at both the phylum and genus levels. While some studies report increased gut microbiota diversity with age (Niu et al., 2015; Shao et al., 2021), our findings show reduced diversity with SDPP, consistent with Han et al. (2018) for finishing pigs. Despite the lower diversity, there was no increase in pathogenic microbes such as Escherichia-Shigella, Clostridium, or Corynebacterium (Supplementary Figure 7), and Clostridium levels were significantly lower in SDPP-fed pigs compared to those fed SBM. Thus, while SDPP reduces bacterial diversity, it does not lead to higher pathogenic load, mirroring the microbiota profile observed in finishing pigs (Han et al., 2018).
Inclusion of SDPP in pig diets markedly decreased Sarcina, a Firmicutes genus, in the small intestine. Sarcina, a Gram-positive anaerobic coccus that thrives in acidic conditions, was more abundant in the jejunum compared to the ileum, indicating its preference for the upper gastrointestinal tract (Lam-Himlin et al., 2011; Savic Vukovic et al., 2021). We hypothesize that the alkaline environment associated with the SDPP diet may have contributed to the reduced Sarcina levels, although this remains unverified due to the absence of pH measurements. Conversely, the SBM diet, with its higher content of plant-derived fibers and oligosaccharides (130 g/kg vs. 64 g/kg non-starch polysaccharides; Table 1), likely supported luxuriant Sarcina growth, as these microbes rely on carbohydrate fermentation for energy (Lowe et al., 1989; Worrall et al., 2022).
Interestingly, a previous study found that the inclusion of zinc oxide (ZnO) at pharmaceutical levels significantly reduced the abundance of Sarcina, suggesting a similar effect of ZnO and SDPP on gut microbiota (Vahjen et al., 2010). Following the European Commission’s 2022 ban on ZnO (European Parliament, 2001, European Parliament, 2004) to address antimicrobial resistance and environmental concerns, and the earlier 2006 ban on growth-promoting antibiotics (Millet and Maertens, 2011), SDPP has emerged as a viable alternative. Our study, along with others (Zhe et al., 2021), supports the potential of SDPP to replace ZnO and antibiotics, possibly due to its antimicrobial bioactive peptides. While this hypothesis needs further validation, our results indicate that SDPP promotes a dynamic microbiome with limited potential for pathogenic microbe proliferation is indicative of a healthy, functional microbiome simultaneously offers antimicrobial benefits compared to traditional protein sources like SBM.
4.2 Effect of SDPP on global transcriptome profile of small intestinal mucosa
Our study reveals significant differences in small intestinal transcriptomics between pigs fed SDPP versus SBM, even when using stringent criteria (adjusted P-value < 0.05 and Fold Change |1|). This robust transcriptome response contrasts with the subtle changes often observed using less stringent methods in studies (Kar et al., 2017a) on other sole protein sources like insect proteins (Leibold et al., 2004). The pronounced changes in differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the jejunum compared to the ileum (Table 4) align with previous findings showing a greater number of DEGs in the jejunum of pigs fed Cyberlindnera jadinii yeast (Håkenåsen et al., 2020). This effect may be due to differences in protein digestion kinetics (Chen et al., 2019) and the higher protein and amino acid digestibility of SDPP relative to SBM (Mateo and Stein, 2007; Almeida et al., 2013), suggesting enhanced jejunal functionality.
The SDPP diet appears to induce an “early” release of bio-functional components such as immunoglobulins and bioactive peptides (Kar et al., 2016), which are well-documented for their health benefits (Coffey and Cromwell, 1995; Moreto and Perez-Bosque, 2009; Balan et al., 2021). Gao et al. (2011) further supported this by demonstrating that SDPP enhances antioxidant capacity in pigs, as indicated by improved enzyme activities and reduced malondialdehyde levels. Our transcriptomic analysis corroborates these findings, showing that DEGs in the jejunum of SDPP-fed pigs are associated with immunoregulation and defense pathways. Enrichment in “complement and coagulation” pathways underscores SDPP’s role in maintaining jejunal homeostasis and supporting local immune responses.
Previous studies have shown reduced immune cell numbers in SDPP-fed piglets, including lymphocytes in mucosa and gut-associated lymphoid tissues such as Peyer’s patches and lamina propria (Perez-Bosque et al., 2004, Perez-Bosque et al., 2008). Similarly, a study in mice revealed downregulation of key genes involved in mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathways in the ileum when fed SDPP (Kar et al., 2017b). Our findings also showed enrichment of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Protein Kinase B (PI3K-Akt) pathway in DEGs, which is crucial for cell cycle regulation and immune modulation (Van Laethem et al., 2013; Leopold Wager et al., 2014; Scheeren et al., 2014; Siggs et al., 2015). The parallel results from both mice and pigs suggest that SDPP may modulate immune responses by influencing the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, warranting further investigation using in vitro intestinal models and co-culture systems (Kar et al., 2021b; Saleri et al., 2021; Andrani et al., 2023).
Moreover, the enrichment of the “Intestinal Immune Network for IgA Production” pathway, with downregulated genes such as CCR10, CXCL12, CCL28, and MadCAM-1, suggests reduced leukocyte trans-endothelial migration in SDPP-fed pigs. This reduction may indicate lower intestinal tissue damage from stressors compared to SBM-fed pigs, supporting SDPP’s role in promoting intestinal health. Additionally, higher expression of tight junction receptors in the jejunum of SDPP-fed pigs, with minimal differences in the ileum, suggests improved gut barrier function and overall gut health in SDPP-fed pigs (Bischoff et al., 2014).
4.3 Effect of SDPP on amine metabolites in blood
Dietary protein digestion generates various metabolites that enter the bloodstream and affect different tissues. Utilizing the amine-based ‘endophenotype’ concept, our study explored how different dietary proteins impact host-microbe interactions by analyzing blood plasma amine profiles (Kar et al., 2017b). We identified threonine, taurine, and glutamine/glutamate as key metabolites distinguishing between SDPP and SBM diets.
Threonine, essential for mucosal protein synthesis and energy (Le Floc'h and Seve, 2005; Wen et al., 2020b), was found at higher plasma levels in SDPP-fed pigs, reflecting its greater dietary content (9 g/kg vs. 5 g/kg). This suggests enhanced absorption and potential benefits for gut barrier function and immune regulation through tight junctions and mTOR signaling (Singh et al., 2023; Wen et al., 2020a). Additionally, threonine modulates lymphocyte activity and IgA secretion, affecting intestinal inflammation (Tang et al., 2021). Taurine, abundant in SDPP, protects the intestinal mucosa by regulating immune responses and maintaining tight junction integrity (Wen et al., 2020a). Its antioxidant properties further mitigate oxidative stress (Hamard et al., 2010; Wang et al., 2010; Koo et al., 2020). Elevated blood glutamate levels in SDPP-fed pigs indicate increased glutamate metabolism, with glutamine conversion to glutamate supporting gut energy needs (Burrin and Stoll, 2009). Consistent with this, previous research showed that glutamate improves gut health and reduces diarrhea (Rezaei et al., 2013). Overall, SDPP’s benefits may stem from its effects on threonine, taurine, and glutamate metabolism, enhancing gut health and functionality.
4.4 Effect of SDPP on health indices in blood
To determine if the SDPP-based diet impacted systemic immunity, we assessed a panel of cytokines and chemokines in pig blood, including pro- and anti-inflammatory markers like IFNα, IFNγ, IL-1β, IL-10, IL-12p40, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, and TNFα. Previous research in mice suggests that dietary proteins can influence systemic cytokine levels (Kar et al., 2017b). Our results revealed no significant differences in these cytokines between dietary treatments, consistent with similar findings in pigs fed black soldier fly or SBM (28). We also evaluated the tryptophan (TRP) and kynurenine (KYN) ratio, which is indicative of systemic immune activity (Schefold et al., 2009; Harper et al., 2018). Changes in this ratio reflect immune activation, where a higher KYN–TRP ratio suggests increased immune response (Suzuki et al., 2010). Thus, immune activation leads to the formation of KYN and the reduction of tryptophan-TRP, and a higher KYN–TRP ratio indicates a systemic immune response (Suzuki et al., 2010). However, our results showed that the KYN–TRP ratio was stable across diets, aligning with the stable cytokine levels. These findings suggest that the SDPP-based diet does not significantly alter systemic immune responses, likely due to the healthy status of the experimental pigs.
Our findings offer new insights into the role of spray-dried plasma (SDP) as a functional protein source in promoting intestinal functionality and gut health in pigs under non-challenging conditions. The results corroborate the positive effects of SDP on gut health reported in previous studies, even at lower dietary inclusion levels, which were often conducted under the stress conditions of weaning (Torrallardona et al., 2003; Nofrarías et al., 2007; Moreto and Perez-Bosque, 2009; Gao et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2015). The FeedOmics approach employed in this study demonstrated the functional effects of SDPP compared to SBM as a dietary protein source, impacting the small intestinal microbiome, gut tissue transcriptome, and amine metabolite profiles in blood plasma. The functional properties of SDP provide added value in relation to supporting gut health and function in pigs and potentially other animal species.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. This data can be found here: NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus, accession GSE98261 and Sequence Read Archive, accession PRJNA1139701; and Zenodo, DOI https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.13285418.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by the Animal Experimentation Board of Wageningen University & Research Centre (approval number 2014099.b). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
SK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DS: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CV: Writing – review & editing. HV: Writing – review & editing. AH: Data curation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. LK: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. MS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. AJ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The authors acknowledge the financial support from the Wageningen University & Research “IPOP Customized Nutrition” program (grant no. 4417801270). The study was partly funded by grants from The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development (ZonMw), grant no. 435002020.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
This project received partial funding from Darling Ingredients via “IPOP Customized Nutrition” program grant no. 4417801270. The funder had no involvement in the study’s design, data collection, analysis, or interpretation. However, funder-affiliated authors participated in the final approval of the version submitted for publication.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fanim.2025.1532914/full#supplementary-material
References
Almeida F. N., Htoo J. K., Thomson J., Stein H. H. (2013). Comparative amino acid digestibility in US blood products fed to weanling pigs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 181, 80–86. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2013.03.002
Anderson M. J. (2001). A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol. 26, 32–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-9993.2001.01070.pp.x
Andrani M., Borghetti P., Ravanetti F., Cavalli V., Ferrari L., De Angelis E., et al. (2023). Acetate and propionate effects in response to LPS in a porcine intestinal co-culture model. Porcine Health Manag 9, 23. doi: 10.1186/s40813-023-00316-y
Balan P., Staincliffe M., Moughan P. J. (2021). Effects of spray-dried animal plasma on the growth performance of weaned piglets-A review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. (Berl) 105, 699–714. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13435
Bikker P., van Dijk A. J., Dirkzwager A., Fledderus J., Ubbink-Blanksma M., Beynen A. C. (2004). The influence of diet composition and an anti-microbial growth promoter on the growth response of weaned piglets to spray dried animal plasma. Livestock Production Sci. 86, 201–208. doi: 10.1016/j.livprodsci.2003.07.003
Bischoff S. C., Barbara G., Buurman W., Ockhuizen T., Schulzke J. D., Serino M., et al. (2014). Intestinal permeability–a new target for disease prevention and therapy. BMC Gastroenterol. 14, 189. doi: 10.1186/s12876-014-0189-7
Blazquez E., Rodriguez C., Rodenas J., Segales J., Pujols J., Polo J. (2020). Biosafety steps in the manufacturing process of spray-dried plasma: a review with emphasis on the use of ultraviolet irradiation as a redundant biosafety procedure. Porcine Health Manag 6, 16. doi: 10.1186/s40813-020-00155-1
Burrin D. G., Stoll B. (2009). Metabolic fate and function of dietary glutamate in the gut. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 90, 850S–856S. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2009.27462Y
Chen M. X., Wang S. Y., Kuo C. H., Tsai I. L. (2019). Metabolome analysis for investigating host-gut microbiota interactions. J. Formos Med. Assoc. 118 Suppl 1, S10–S22. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2018.09.007
Chong J., Wishart D. S., Xia J. (2019). Using metaboAnalyst 4.0 for comprehensive and integrative metabolomics data analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinf. 68, e86. doi: 10.1002/cpbi.86
Coffey R. D., Cromwell G. L. (1995). The impact of environment and antimicrobial agents on the growth response of early-weaned pigs to spray-dried porcine plasma. J. Anim. Sci. 73, 2532–2539. doi: 10.2527/1995.7392532x
Crespo-Piazuelo D., Estelle J., Revilla M., Criado-Mesas L., Ramayo-Caldas Y., Ovilo C., et al. (2018). Characterization of bacterial microbiota compositions along the intestinal tract in pigs and their interactions and functions. Sci. Rep. 8, 12727. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30932-6
Edgar R. C. (2004). MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, 1792–1797. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh340
European Parliament (2001). Directive 2001/82/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 6 November 2001 on the Community code relating to veterinary medicinal products. Ed. Parliament E. (Brussels, Belgium: European Parliament).
European Parliament (2004). Regulation (EC) No 726/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 31 March 2004 laying down Union procedures for the authorisation and supervision of medicinal products for human and veterinary use and establishing a European Medicines Agency. Ed. Parliament E. (Brussels, Belgium: European Parliament).
Gao Y. Y., Jiang Z. Y., Lin Y. C., Zheng C. T., Zhou G. L., Chen F. (2011). Effects of spray-dried animal plasma on serous and intestinal redox status and cytokines of neonatal piglets. J. Anim. Sci. 89, 150–157. doi: 10.2527/jas.2010-2967
Håkenåsen I. M., Øverland M., Ånestad R., Åkesson C. P., Sundaram A. Y. M., Press C. M., et al. (2020). Gene expression and gastrointestinal function is altered in piglet small intestine by weaning and inclusion of Cyberlindnera jadinii yeast as a protein source. J. Funct. Foods 73, 104118. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2020.104118
Hamard A., Mazurais D., Boudry G., Le-Huerou-Luron I., Seve B., Le Floc'h N. (2010). A moderate threonine deficiency affects gene expression profile, paracellular permeability and glucose absorption capacity in the ileum of piglets. J. Nutr. Biochem. 21, 914–921. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2009.07.004
Han G. G., Lee J. Y., Jin G. D., Park J., Choi Y. H., Kang S. K., et al. (2018). Tracing of the fecal microbiota of commercial pigs at five growth stages from birth to shipment. Sci. Rep. 8, 6012. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24508-7
Harper K. M., Mutasa M., Prendergast A. J., Humphrey J., Manges A. R. (2018). Environmental enteric dysfunction pathways and child stunting: A systematic review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 12, e0006205. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006205
Holman D. B., Brunelle B. W., Trachsel J., Allen H. K. (2017). Meta-analysis to define a core microbiota in the swine gut. mSystems 2 (3), e00004-17. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00004-17
ISO 15914-1, I (2004). Animal feeding stuffs-Enzymatic determination of total starch content (Geneva, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization).
ISO-5983-2 (2009). Animal feeding stuffs — Determination of nitrogen content and calculation of crude protein content — Part 2: Block digestion and steam distillation method (Geneva, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization).
ISO-5984 (2002). Animal feeding stuffs — Determination of crude ash (Geneva, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization).
ISO-6492 (1999). Animal feeding stuffs — Determination of fat content (Geneva, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization).
ISO-6496 (1999). Animal feeding stuffs — Determination of moisture and other volatile matter content (Geneva, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization).
Jin J., Zhang L., Jia J., Chen Q., Yuan Z., Zhang X., et al. (2019). Effects of maternal low-protein diet on microbiota structure and function in the jejunum of huzhu bamei suckling piglets. Animals. 9 (10), 713. doi: 10.3390/ani9100713
Kar S. K. (2017). FeedOmics, An Approach to Evaluate the Functional Properties of Protein Containing Feed Ingredients. (Wageningen, The Netherlands: Wageningen University and Research).
Kar S. K., Jansman A. J. M., Benis N., Ramiro-Garcia J., Schokker D., Kruijt L., et al. (2017a). Dietary protein sources differentially affect microbiota, mTOR activity and transcription of mTOR signaling pathways in the small intestine. PLoS One 12, e0188282. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188282
Kar S. K., Jansman A. J. M., Boeren S., Kruijt L., Smits M. A. (2016). Protein, peptide, amino acid composition, and potential functional properties of existing and novel dietary protein sources for monogastrics1,2. J. Anim. Sci. 94, 30–39. doi: 10.2527/jas.2015-9677
Kar S. K., Jansman A. J. M., Schokker D., Kruijt L., Harms A. C., Wells J. M., et al. (2017b). Amine metabolism is influenced by dietary protein source. Front. Nutr. 4. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2017.00041
Kar S. K., Schokker D., Harms A. C., Kruijt L., Smits M. A., Jansman A. J. M. (2021a). Local intestinal microbiota response and systemic effects of feeding black soldier fly larvae to replace soybean meal in growing pigs. Sci. Rep. 11, 15088. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-94604-8
Kar S. K., van der Hee B., Loonen L. M. P., Taverne N., Taverne-Thiele J. J., Schokker D., et al. (2020). Effects of undigested protein-rich ingredients on polarised small intestinal organoid monolayers. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 11, 51. doi: 10.1186/s40104-020-00443-4
Kar S. K., Wells J. M., Ellen E. D., Te Pas M. F. W., Madsen O., Groenen M. A. M., et al. (2021b). Organoids: a promising new in vitro platform in livestock and veterinary research. Vet. Res. 52, 43. doi: 10.1186/s13567-021-00904-2
Kats L. J., Nelssen J. L., Tokach M. D., Goodband R. D., Hansen J. A., Laurin J. L. (1994). The effect of spray-dried porcine plasma on growth performance in the early-weaned pig. J. Anim. Sci. 72, 2075–2081. doi: 10.2527/1994.7282075x
Kim H., Lee S. H., Kim B. G. (2022). Effects of dietary spray-dried plasma protein on nutrient digestibility and growth performance in nursery pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 100 (1), skab351. doi: 10.1093/jas/skab351
Koo B., Choi J., Yang C., Nyachoti C. M. (2020). Diet complexity and l-threonine supplementation: effects on growth performance, immune response, intestinal barrier function, and microbial metabolites in nursery pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 98 (5), skaa125. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaa125
Lam-Himlin D., Tsiatis A. C., Montgomery E., Pai R. K., Brown J. A., Razavi M., et al. (2011). Sarcina organisms in the gastrointestinal tract: a clinicopathologic and molecular study. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 35, 1700–1705. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31822911e6
Le Floc'h N., Seve B. (2005). Catabolism through the threonine dehydrogenase pathway does not account for the high first-pass extraction rate of dietary threonine by the portal drained viscera in pigs. Br. J. Nutr. 93, 447–456. doi: 10.1079/bjn20051375
Leibold M. A., Holyoak M., Mouquet N., Amarasekare P., Chase J. M., Hoopes M. F., et al. (2004). The metacommunity concept: a framework for multi-scale community ecology. Ecol. Lett. 7, 601–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2004.00608.x
Leopold Wager C. M., Hole C. R., Wozniak K. L., Olszewski M. A., Wormley F. L. Jr (2014). STAT1 signaling is essential for protection against Cryptococcus neoformans infection in mice. J. Immunol. 193, 4060–4071. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1400318
Li K., Xiao Y., Chen J., Chen J., He X., Yang H. (2017). Microbial composition in different gut locations of weaning piglets receiving antibiotics. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 30, 78–84. doi: 10.5713/ajas.16.0285
Li L., Chen S., Li X., Wan D., Liu G., Liu Y., et al. (2018). Intestinal microbiota in growing pigs: effects of stocking density. Food Agric. Immunol. 29, 524–535. doi: 10.1080/09540105.2017.1409195
Lowe S. E., Pankratz H. S., Zeikus J. G. (1989). Influence of pH extremes on sporulation and ultrastructure of Sarcina ventriculi. J. Bacteriol 171, 3775–3781. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3775-3781.1989
Mateo C. D., Stein H. H. (2007). Apparent and standardized ileal digestibility of amino acids in yeast extract and spray dried plasma protein by weanling pigs. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 87, 381–383. doi: 10.4141/CJAS06011
McCormack U. M., Curiao T., Buzoianu S. G., Prieto M. L., Ryan T., Varley P., et al. (2017). Exploring a possible link between the intestinal microbiota and feed efficiency in pigs. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 83 (15), e00380-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00380-17
Millet S., Maertens L. (2011). The European ban on antibiotic growth promoters in animal feed: from challenges to opportunities. Vet. J. 187, 143–144. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2010.05.001
Moreto M., Perez-Bosque A. (2009). Dietary plasma proteins, the intestinal immune system, and the barrier functions of the intestinal mucosa. J. Anim. Sci. 87, E92–100. doi: 10.2527/jas.2008-1381
Niu Q., Li P., Hao S., Zhang Y., Kim S. W., Li H., et al. (2015). Dynamic distribution of the gut microbiota and the relationship with apparent crude fiber digestibility and growth stages in pigs. Sci. Rep. 5, 9938. doi: 10.1038/srep09938
Nofrarías M., Manzanilla E. G., Pujols J., Gibert X., Majó N., Segalés J., et al. (2007). Spray-dried porcine plasma affects intestinal morphology and immune cell subsets of weaned pigs. Livestock Sci. 108, 299–302. doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2007.01.103
Noga M. J., Dane A., Shi S., Attali A., van Aken H., Suidgeest E., et al. (2012). Metabolomics of cerebrospinal fluid reveals changes in the central nervous system metabolism in a rat model of multiple sclerosis. Metabolomics 8, 253–263. doi: 10.1007/s11306-011-0306-3
Perez-Bosque A., Miro L., Polo J., Russell L., Campbell J., Weaver E., et al. (2008). Dietary plasma proteins modulate the immune response of diffuse gut-associated lymphoid tissue in rats challenged with Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B. J. Nutr. 138, 533–537. doi: 10.1093/jn/138.3.533
Perez-Bosque A., Pelegri C., Vicario M., Castell M., Russell L., Campbell J. M., et al. (2004). Dietary plasma protein affects the immune response of weaned rats challenged with S. aureus Superantigen B. J. Nutr. 134, 2667–2672. doi: 10.1093/jn/134.10.2667
Perez-Bosque A., Polo J., Torrallardona D. (2016). Spray dried plasma as an alternative to antibiotics in piglet feeds, mode of action and biosafety. Porcine Health Manag 2, 16. doi: 10.1186/s40813-016-0034-1
Quan J., Cai G., Ye J., Yang M., Ding R., Wang X., et al. (2018). A global comparison of the microbiome compositions of three gut locations in commercial pigs with extreme feed conversion ratios. Sci. Rep. 8, 4536. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22692-0
Quast C., Pruesse E., Yilmaz P., Gerken J., Schweer T., Yarza P., et al. (2013). The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 41, D590–D596. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1219
Research W. L. (2020). Voedernormen varkens en voederwaarden voedermiddelen voor varkens (Lelystad: Central Bureau for Livestock Feeding (CVB).
Rezaei R., Knabe D. A., Tekwe C. D., Dahanayaka S., Ficken M. D., Fielder S. E., et al. (2013). Dietary supplementation with monosodium glutamate is safe and improves growth performance in postweaning pigs. Amino Acids 44, 911–923. doi: 10.1007/s00726-012-1420-x
Roques S., Koopmans S. J., Mens A., van Harn J., van Krimpen M., Kar S. K. (2022). Effect of Feeding 0.8% Dried Powdered Chlorella vulgaris Biomass on Growth Performance, Immune Response, and Intestinal Morphology during Grower Phase in Broiler Chickens. Anim. (Basel) 12 (9), 1114. doi: 10.3390/ani12091114
Saleri R., Borghetti P., Ravanetti F., Andrani M., Cavalli V., De Angelis E., et al. (2021). A co-culture model of IPEC-J2 and swine PBMC to study the responsiveness of intestinal epithelial cells: the regulatory effect of arginine deprivation. Anim. (Basel) 11 (9), 2756. doi: 10.3390/ani11092756
Savic Vukovic A., Jonjic N., Bosak Versic A., Kovac D., Radman M. (2021). Fatal Outcome of Emphysematous Gastritis due to Sarcina ventriculi Infection. Case Rep. Gastroenterol. 15, 933–938. doi: 10.1159/000518305
Scheeren F. A., Kuo A. H., van Weele L. J., Cai S., Glykofridis I., Sikandar S. S., et al. (2014). A cell-intrinsic role for TLR2-MYD88 in intestinal and breast epithelia and oncogenesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 16, 1238–1248. doi: 10.1038/ncb3058
Schefold J. C., Zeden J. P., Fotopoulou C., von Haehling S., Pschowski R., Hasper D., et al. (2009). Increased indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) activity and elevated serum levels of tryptophan catabolites in patients with chronic kidney disease: a possible link between chronic inflammation and uraemic symptoms. Nephrol. Dial Transplant. 24, 1901–1908. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfn739
Schokker D., Fledderus J., Jansen R., Vastenhouw S. A., de Bree F. M., Smits M. A., et al. (2018). Supplementation of fructooligosaccharides to suckling piglets affects intestinal microbiota colonization and immune development1. J. Anim. Sci. 96, 2139–2153. doi: 10.1093/jas/sky110
Schokker D., Zhang J., Zhang L. L., Vastenhouw S. A., Heilig H. G., Smidt H., et al. (2014). Early-life environmental variation affects intestinal microbiota and immune development in new-born piglets. PLoS One 9, e100040. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100040
Shao M., Wang Z., He Y., Tan Z., Zhang J. (2021). Fecal microbial composition and functional diversity of Wuzhishan pigs at different growth stages. AMB Express 11, 88. doi: 10.1186/s13568-021-01249-x
Siggs O. M., Miosge L. A., Daley S. R., Asquith K., Foster P. S., Liston A., et al. (2015). Quantitative reduction of the TCR adapter protein SLP-76 unbalances immunity and immune regulation. J. Immunol. 194, 2587–2595. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1400326
Singh P., Gollapalli K., Mangiola S., Schranner D., Yusuf M. A., Chamoli M., et al. (2023). Taurine deficiency as a driver of aging. Science 380, eabn9257. doi: 10.1126/science.abn9257
Smyth G. K. (2005). “limma: linear models for microarray data,” in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions Using R and Bioconductor. Eds. Gentleman R., Carey V. J., Huber W., Irizarry R. A., Dudoit S. (Springer New York, New York, NY), 397–420.
Suzuki Y., Suda T., Furuhashi K., Suzuki M., Fujie M., Hahimoto D., et al. (2010). Increased serum kynurenine/tryptophan ratio correlates with disease progression in lung cancer. Lung Cancer 67, 361–365. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2009.05.001
Tang Q., Tan P., Ma N., Ma X. (2021). Physiological functions of threonine in animals: beyond nutrition metabolism. Nutrients 13 (8), 2592. doi: 10.3390/nu13082592
Ter Braak C. J. F., Smilauer P. (2018). Canoco reference manual and user’s guide: Software for ordination, version 5.10 (Ithaca, USA: Microcomputer Power).
Torrallardona D., Conde M. R., Badiola I., Polo J., Brufau J. (2003). Effect of fishmeal replacement with spray-dried animal plasma and colistin on intestinal structure, intestinal microbiology, and performance of weanling pigs challenged with Escherichia coli K99. J. Anim. Sci. 81, 1220–1226. doi: 10.2527/2003.8151220x
Vahjen W., Pieper R., Zentek J. (2010). Bar-coded pyrosequencing of 16S rRNA gene amplicons reveals changes in ileal porcine bacterial communities due to high dietary zinc intake. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76, 6689–6691. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03075-09
van der Kloet F. M., Bobeldijk I., Verheij E. R., Jellema R. H. (2009). Analytical error reduction using single point calibration for accurate and precise metabolomic phenotyping. J. Proteome Res. 8, 5132–5141. doi: 10.1021/pr900499r
Van Laethem F., Tikhonova A. N., Pobezinsky L. A., Tai X., Kimura M. Y., Le Saout C., et al. (2013). Lck availability during thymic selection determines the recognition specificity of the T cell repertoire. Cell 154, 1326–1341. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.08.009
van Vuuren A. M., van der Koelen C. J., Valk H., de Visser H. (1993). Effects of partial replacement of ryegrass by low protein feeds on rumen fermentation and nitrogen loss by dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 76, 2982–2993. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(93)77637-7
Wang W., Zeng X., Mao X., Wu G., Qiao S. (2010). Optimal dietary true ileal digestible threonine for supporting the mucosal barrier in small intestine of weanling pigs. J. Nutr. 140, 981–986. doi: 10.3945/jn.109.118497
Wen C., Guo Q., Wang W., Duan Y., Zhang L., Li J., et al. (2020a). Taurine alleviates intestinal injury by mediating tight junction barriers in diquat-challenged piglet models. Front. Physiol. 11. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00449
Wen C., Li F., Guo Q., Zhang L., Duan Y., Wang W., et al. (2020b). Protective effects of taurine against muscle damage induced by diquat in 35 days weaned piglets. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 11, 56. doi: 10.1186/s40104-020-00463-0
Worrall E. B., Chhaparia A., Carpenter D., Neuschwander-Tetri B. A. (2022). A rare cause of upper gastrointestinal bleeding: sarcina ventriculi. ACG Case Rep. J. 9, e00846. doi: 10.14309/crj.0000000000000846
Yang H., Huang X., Fang S., Xin W., Huang L., Chen C. (2016). Uncovering the composition of microbial community structure and metagenomics among three gut locations in pigs with distinct fatness. Sci. Rep. 6, 27427. doi: 10.1038/srep27427
Yu Z., Morrison M. (2004). Improved extraction of PCR-quality community DNA from digesta and fecal samples. Biotechniques. 36 (5), 808–812. doi: 10.2144/04365ST04
Zhang Y., Chen D. W., Yu B., He J., Yu J., Mao X. B., et al. (2015). Spray-dried chicken plasma improves intestinal digestive function and regulates intestinal selected microflora in weaning piglets. J. Anim. Sci. 93, 2967–2976. doi: 10.2527/jas.2014-8820
Zhao W., Wang Y., Liu S., Huang J., Zhai Z., He C., et al. (2015). The dynamic distribution of porcine microbiota across different ages and gastrointestinal tract segments. PLoS One 10, e0117441. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117441
Keywords: feedomics, gut health, immune system, microbiome, pig, spray dried plasma protein, transcriptome
Citation: Kar SK, Schokker D, van Vuure C, van Iersel H, Harms AC, Kruijt L, Smits MA and Jansman AJM (2025) Microbial and molecular signatures for enhanced gut health in pigs fed a diet with spray-dried plasma as functional protein source. Front. Anim. Sci. 6:1532914. doi: 10.3389/fanim.2025.1532914
Received: 22 November 2024; Accepted: 14 February 2025;
Published: 03 March 2025.
Edited by:
Rayudika Aprilia Patindra Purba, Airlangga University, IndonesiaReviewed by:
Ravikanth Reddy Poonooru, University of Missouri, United StatesYuwen Dong, University of Pennsylvania, United States
Copyright © 2025 Kar, Schokker, van Vuure, van Iersel, Harms, Kruijt, Smits and Jansman. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Soumya K. Kar, c291bXlhLmthckB3dXIubmw=
 Soumya K. Kar
Soumya K. Kar Dirkjan Schokker
Dirkjan Schokker Carine van Vuure3
Carine van Vuure3 Amy C. Harms
Amy C. Harms Alfons J. M. Jansman
Alfons J. M. Jansman