- 1Centre for Management and Social Sciences, Riga Technical University Liepaja Academy, Liepaja, Latvia
- 2Faculty of Educational Sciences and Psychology, University of Latvia, Rīga, Latvia
- 3Faculty of Medicine and Life Sciences, University of Latvia, Rīga, Latvia
- 4Centre for Humanities and Arts, Riga Technical University Liepaja Academy, Liepaja, Latvia
Aim: The aim of the research is to identify and to analyse the possibilities of early school leaving support and predictive factors related to emotional and learning support and classroom organization.
Methods: Based on the Teaching through Interactions Framework, the study analyses the socio-emotional and methodological factors of early school leaving – emotional and learning support and classroom organization. In the analysis of theoretical scientific literature, a Systematic Review has been carried out, where the scientific articles included in internationally cited databases Web of Science, Scopus and Ebsco have been analysed by key words. Correlation and regression analysis in the SPSS environment of the program for processing quantitative data has been performed in a correlative study.
Results: The findings of the correlation analysis show that there are statistically significant negative correlations between early school leaving and emotional and learning support, as well as classroom organization. The selected six articles are mostly focused on the emotional support provision. As a result of the regression analysis, the most significant factor predicting early school leaving has been identified - the lack of emotional support.
Conclusion: Scientific articles included in the WoS, Scopus and Ebsco databases do not use a holistic approach to preventing early school leaving. The lower the emotional, classroom organization and instructional support, the higher the risk of early school leaving. Teacher’s empathy and sensitivity to the academic, socio-emotional and developmental needs of individual students and the whole class are the most important predictors of early school leaving.
Introduction
In the European Union, including in Latvia, early termination of education and school leaving has become one of the biggest problems, and one of the most complex challenges in education is the early identification or mitigation of its risks, which affects areas such as cognitive well-being; psychological well-being; physical well-being; social well-being and material well-being (Govorova et al., 2020; Rambla and Scandurra, 2021).
In the context of the study, exogenous (individual (health), related to family and peers (socio-economic)); endogenous or school factors (academic achievements and delays); relationships with classmates and peers (no friends, experiencing mobbing), teachers (pedagogical approaches, resources) and school (school environment), as well as cognitive, behavioural and socio-emotional engagement factors have been highlighted (González-Rodríguez et al., 2019; Tarabini et al., 2019; Montero-Sieburth and Turcatti, 2022).
Explaining the emotional consequences of early school leaving from a subjective perspective, learning problems and disorders, inability to adapt to circumstances, behavioural problems including violence and classroom behavior, social rejection, lack of belonging to a peer group, and problems related to home and family have been identified as the causes. This is in line with the studies where all causes of school dropout are divided into four main categories: problems related to the young person’s personality, behavior, academic abilities and relationships with the environment. Factors related to the personality of young people are especially emphasized, including low educational achievements over a long period of time, learning difficulties, behavioral and discipline problems, frequent and long-term absence, low self-esteem, unclear concept of the future, problems in interpersonal communication, use of psychoactive substances, social alienation, social isolation, involvement in criminal behavior, feeling of alienation from the educational environment. In terms of development, ESL learners lack the emotional, cognitive, functional, and social development required for normative adult life (Arkin and Cojocaru, 2020).
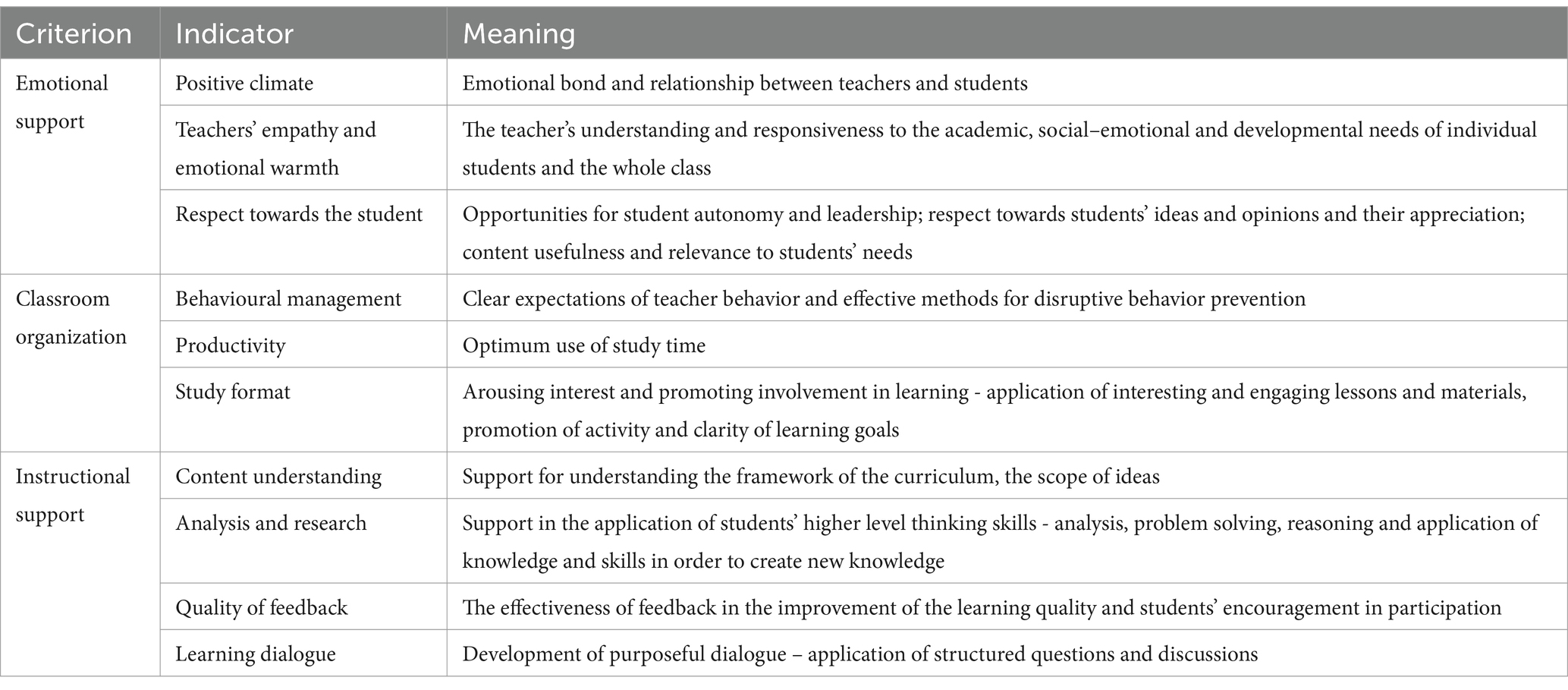
The Covid-19 pandemic has raised the need for a holistic approach to student support (Montero-Sieburth and Turcatti, 2022), and in the context of early school leavers, the theoretical model of Teaching Through Interactions Framework (Hamre et al., 2013; Hafen et al., 2015) in the process of learners’ teaching and learning, which consists of 3 domains, is topical:
• Emotional support in the dimensions of positive climate, teachers’ empathy and emotional warmth and respect towards the learner;
• Classroom management in the dimensions of behavior management, productivity and teaching and learning format;
• Instructional instructional support in the dimensions of content understanding, analysis and research, quality of feedback and learning dialogue.
A multidimensional intervention is needed, not only addressing psychological and social factors, but also increasing young people’s trust in the intervention offer when seeking support (Guerrero-Puerat and Guerrero, 2023).
Emotional support involves the expression of positive emotions, such as concern, empathy, understanding, respect, trust, and encouragement towards others; it promotes student engagement in learning and academic achievement; its effectiveness is influenced by a supportive environment, where the relationship between the supporter and the supported is decisive (Pan and Ye, 2024). Classroom management, on the other hand, is characterized by the actions that teachers take to create an environment that supports and facilitates both academic and social–emotional learning and includes teachers’ efforts to manage instructional time, student behavior, teacher-student relationships, and classroom organizational features (e.g., expectations, rules, routines) (Show et al., 2023). Emotional support behavior positively affects students’ academic achievement (O’Hare et al., 2020), so it is important to include emotional support alongside educational support to motivate students, especially in a negative emotional environment (He et al., 2023).
Strategies used by teachers in order to improve social and emotional skills are an important support for students in the learning process and mitigation of the school dropout risks (Main and Whatman, 2016).
One of the biggest challenges when developing a preventive strategy is to take into account the different learning needs of young people. This necessitates individualization of the learning process. To this end, a learning environment must be created that promotes social change and includes all types of learning, elevating the social status of learners in the classroom. To promote learning outcomes, educators must create competency-oriented learning situations that support learners’ professional development and career planning, leading to positive learning experiences in emotional, cognitive and social aspects. Learning in relation to real-life situations promotes the development of critical thinking among learners. This is particularly useful for at-risk groups such as early school leavers. In preventing early school leaving, measures are needed to reorient the traditional learning process from memorizing the content of learning to the development of critical thinking in the acquisition of content, including abilities to compare, analyze, synthesize and generalize (Maslo et al., 2015). Positive relationships between educators and learners from at-risk groups create a sense of belonging (Burke et al., 2016), motivate them (Zepke and Leach, 2010), promote intellectual development and achievements (Halawah, 2006).
The sense of belonging has a positive effect on the academic achievements and motivation of learners. Through the sense of belonging, the learner acquires such qualities as courage, optimism, self-confidence. The learners, who feel they belong to their group, see more clearly the importance of their work input and they have higher self-esteem. Research surveys, assessing students’ choices in favour of an educational institution, revealed that the ability of the educational institution to create and maintain a sense of belonging plays an important role in making the decision for further education (Verschelden, 2017).
Bondere (2017), citing leading research, highlights four factors that contribute to a student’s sense of belonging at school: support from adults (showing interest and providing emotional support), connection to a positive peer group, confidence in the value of their education (believing the school cares about their future), and a positive school environment (both physically and psychologically).
The sense of safety in an educational institution is formed by clear rules: good behavior is a guarantee of physical safety, while predictable requirements promote emotional safety. Class or group rules are designed with the aim of creating a safer, more supportive environment for each learner, where they are co-responsible for it (Gudeta, 2016).
When teaching to cooperate, different techniques can be applied in the pedagogical process; agreement and division of responsibility for assigned tasks mark the division of work and synergy of efforts:
1. Learning listening skills allows you to create a space to share ideas, listen to them;
2. The skill to ask questions, especially free and directed towards thinking, facilitates the expansion of knowledge and promotes progress towards better solutions;
3. Practicing and demonstrating the skills of conversation - patient listening, flexibility, an opinion presentation clearly point by point and the ability to think clearly under pressure - are useful in any life situation (Fadels et al., 2017).
Effective classroom organization with the goal of a safe learning environment creation, engaging students and mitigating disruptive behavior is the key prerequisite for good academic achievement (Black, 2016).
In order to achieve the goal of the study - to analyse the possibilities of early school leaving support and predictive factors related to emotional and learning support and classroom organization, three research questions have been raised:
• What support options for young people to mitigate the risks of early school leaving are analysed in scientific publications indexed by Web of Science, SCOPUS and EBSCO?
• What is the relation between early school leaving, emotional and learning support, and classroom organization in STEM education?
• What are the predictors of ESL related to emotional and learning support and classroom organization in STEM education?
Methods
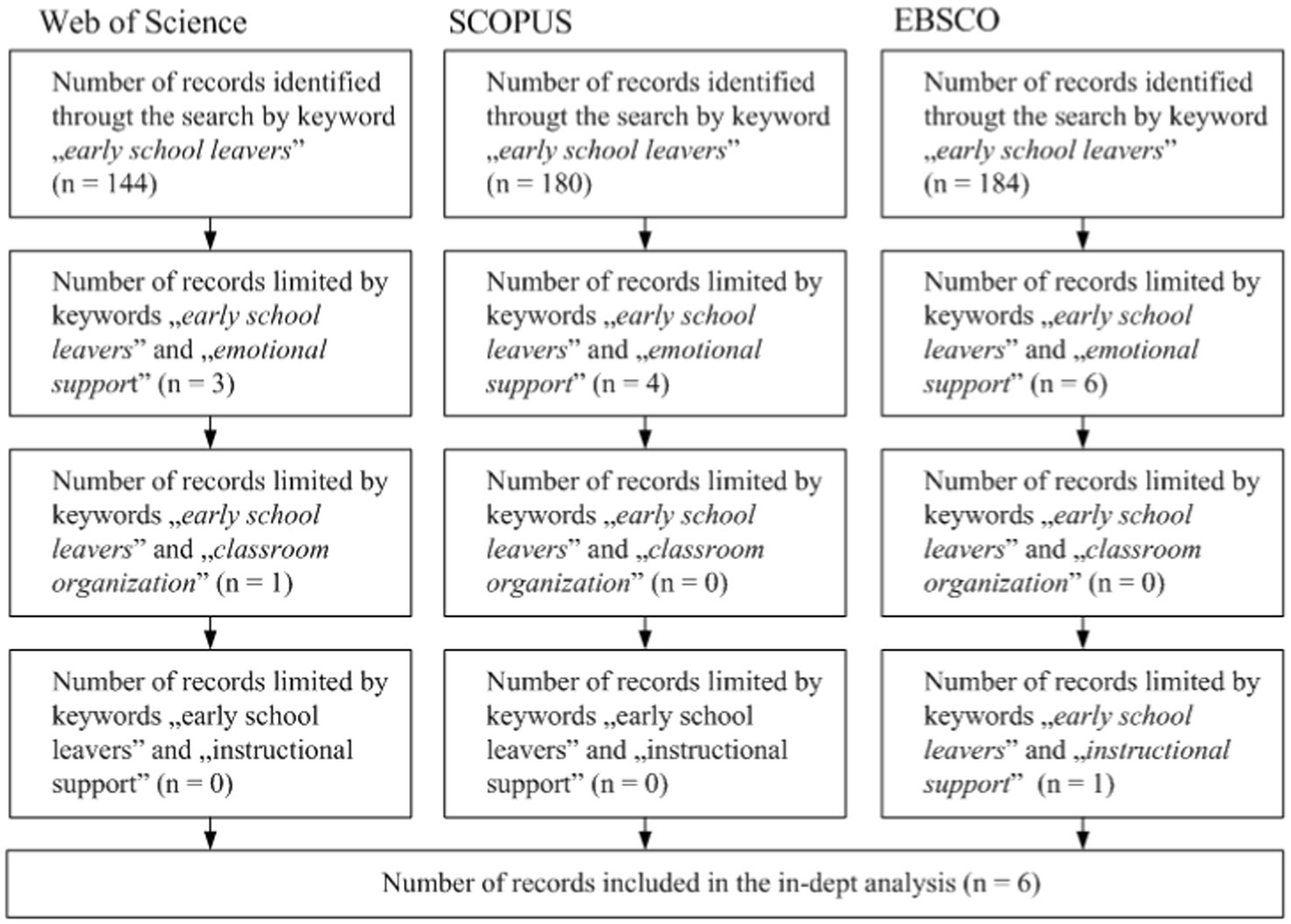
In order to answer the first research question and to find out what support options for keeping early school leavers (ESL) in school have been analysed in the scientific literature, a systematic review has been conducted, carrying out quantitative and qualitative research in the Web of Science, SCOPUS and EBSCO databases. The keywords “early school leavers,” “emotional support,” “classroom organization” and “instructional support” have been chosen to search for information.
The time of publication of the articles to be used in the systematic review (2000–2024), the language (English), the selected databases (Web of Science, SCOPUS, and EBSCO) have been defined as limiting criteria, excluding those articles that are in two databases (n = 3), and full-text availability and studied education at the school level (n = 3). In the end, 6 scientific articles have been used for more profound analysis. The selection scheme of systematic review scientific articles is shown in Figure 1.
In order to answer the second and third research question, as a result of the theoretical literature analysis, criteria and indicators of support for the prevention of early school leaving risks have been identified (see Table 1).
Within the framework for the analysis of socio-emotional and methodological support for the mitigation of early school leaving, based on the criteria and indicators identified as a result of the theoretical analysis, a questionnaire was developed, the structure of which has been created by substantive closed questions about the possibility of leaving school and the availability of support.
A correlational research design (Ilomaki and Tolppanen, 2019) and a data collection method – a questionnaire (Cleave, 2023) have been chosen for the study, where respondents are asked to answer 11 closed questions on a 4-point Likert scale (1 = disagree; 2 = rather disagree; 3 = rather agree; 4 = agree). The questionnaire is structured in 4 parts: on the possibility of early school leaving – question 1, on the availability of emotional support – questions 2–4, on classroom organization – questions 5–7, on the availability of learning support – questions 8–11.
Eighty seven teachers who implement general secondary and vocational secondary education programs in Latvia voluntarily participated in the study.
The research was conducted in accordance with the ethical requirements of the regulations of the Education Quality State Service and the international and national ethical standards observing the Code of Ethics for a Scientist of the Latvian Academy of Sciences (Code of Ethics for Scientists, 2017) within the framework of the project “Support for Early School Leaving Mitigation.”
Processing of the quantitative data obtained in the study has been carried out in the SPSS environment of the program for processing quantitative data.
Cronbach’s alpha coefficient for test reliability (α = 0.85) shows good internal consistency.
In order to answer the research question No 2, “What is the relation between early school leaving, emotional and learning support, and classroom organization?,” a correlational analysis has been conducted. As the results of the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test for the determination of the empirical distribution show that it does not correspond to the normal distribution (p > 0.05), which has determined the application of non-parametric methods, Spearman’s correlation coefficient has been used to determine relations/connections.
In order to answer the research question No 3 “What are the predictors of early school leaving in relation to emotional and learning support and classroom organization?,” a stepwise or sequential regression analysis has been performed.
Results and discussion
After having conducted a systematic review, it has been found that there is no simultaneous connection of all three keywords “emotional support,” “classroom organization” or “instructional support” with the keyword “early school leavers,” therefore the information has been searched in pairs “early school leavers” and “emotional support,” “early school leavers” and “classroom organization,” and “early school leavers” and “instructional support.”
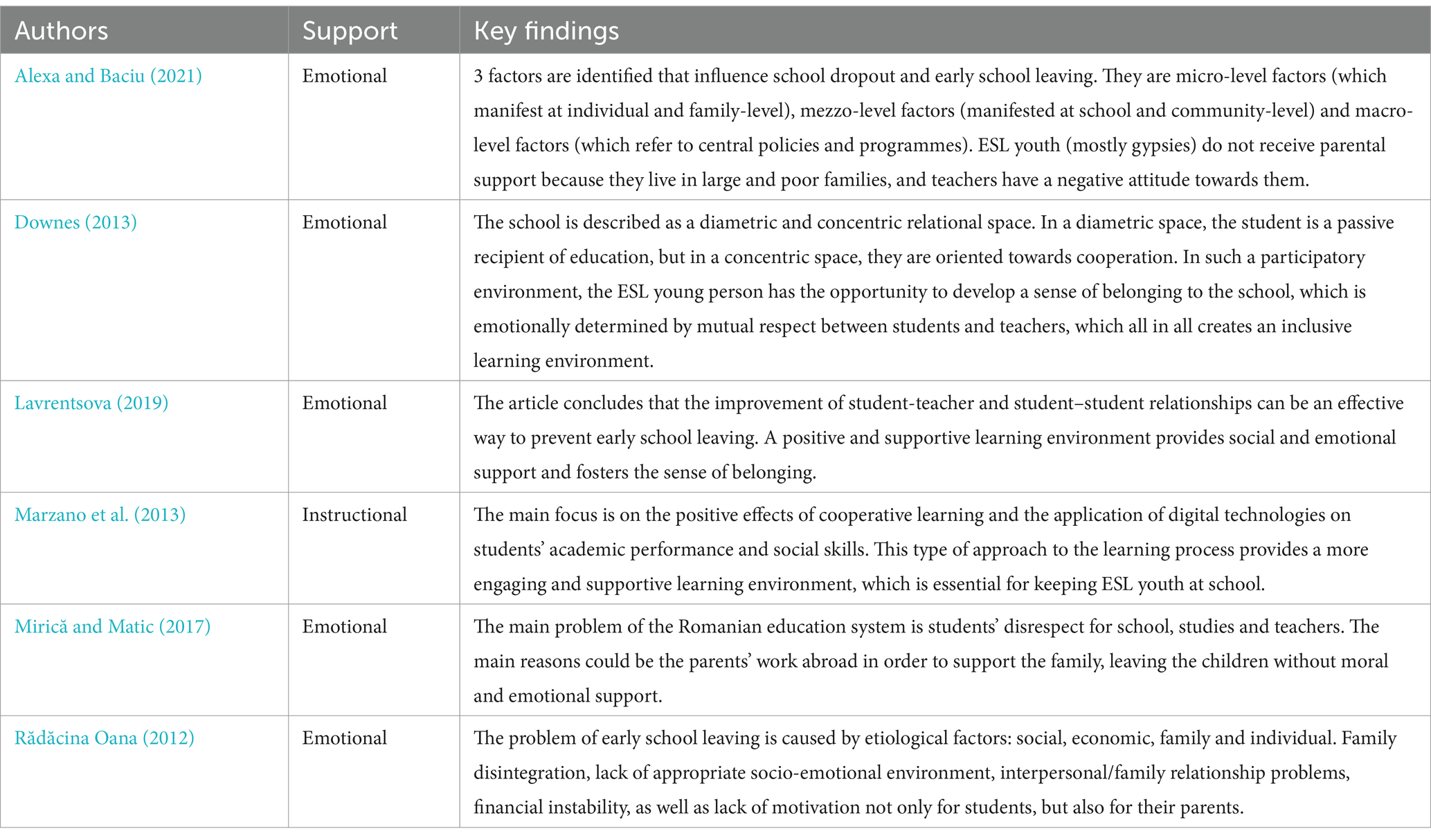
By conducting a more detailed analysis of the articles, it has been discovered that the selected articles are mostly focused on the emotional support provision, indicating the importance of a positive school atmosphere and teacher-student, student–student and parent–child mutual relationships (Table 2). In almost all articles, in parallel with the provision of emotional support, other problems related to the provision of this support are highlighted, for instance at micro-, mezzo- and macro- levels (Alexa and Baciu, 2021), the student’s place in diametric and concentric relational spaces (Downes, 2013), the role of the family (Alexa and Baciu, 2021; Mirică and Matic, 2017; Rădăcina Oana, 2012). An inclusive learning environment determined by student-teacher and student–student relationships can prevent early dropout and build a sense of student belonging (Downes, 2013; Lavrentsova, 2019), thus engaging learning methods such as cooperative learning and application of digital technologies (Marzano et al., 2013) could engage ESL more in an active learning process (see Table 2).
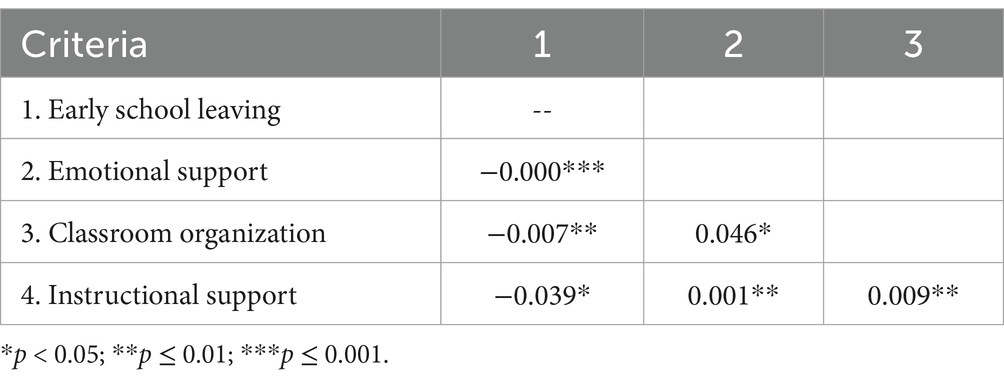
There is a statistically significant strong negative correlation between ESL and emotional support (rs = −0.00), this means that as emotional support increases, early school leaving decreases; a statistically significant medium negative correlation exists between ESL and classroom organization (rs = −0.007), this means that better classroom organization is associated with less early school leaving; and a statistically significant weak negative correlation exists between early school leaving and learning support (rs = −0.039), this means that greater instructional support is associated with less early school leaving (see Table 3).
There is a statistically significant strong negative correlation(rs = −0.000) between early school leaving and emotional support, which is manifested in the school environment through positive interpersonal intractions among students, teacher empathy, emotional warmth, and a respectful attitude displayed by teachers towards their students.
A statistically significant medium negative correlation exists between early school leaving and classroom organization(rs = −0.007), where the determining characteristics are student behavior in response to teacher expectations and methods for preventing disruptive behavior; optimal time management during the lesson; the availability of resources for student engagement and clear articulation of learning objectives.
A statistically significant weak negative correlation is observed between early school leaving and learning support (rs = −0.039), which is implemented in the school environment through the facilitation of content acquisition, development of critical thinking skills, organization of meaningful discussions and provision of constructive feedback.
Overall, these results indicate that emotional support, classroom organization, and instructional support are important factors that can influence early school leaving. Better emotional support and classroom organization are associated with a lower likelihood of early school leaving.
In order to answer the research Question 3, a stepwise or sequential regression analysis has been conducted—two separate regression analysis procedures. The first includes summary indicators—emotional support, classroom management and learning support—as predictors of early school leaving.
The backward stepwise regression results show that the model is statistically significant (F(1;87) = 197.31, p ≤ 0.001).
The results of the regression analysis show that the most important predictor of early school leaving is emotional support (β = −0.81; p = 0.000) – the lower the emotional support, the higher the risk of early school leaving. Instructional support (rs = −0.10; p = 0.039) is the least predictive of early school leaving (see Table 4).
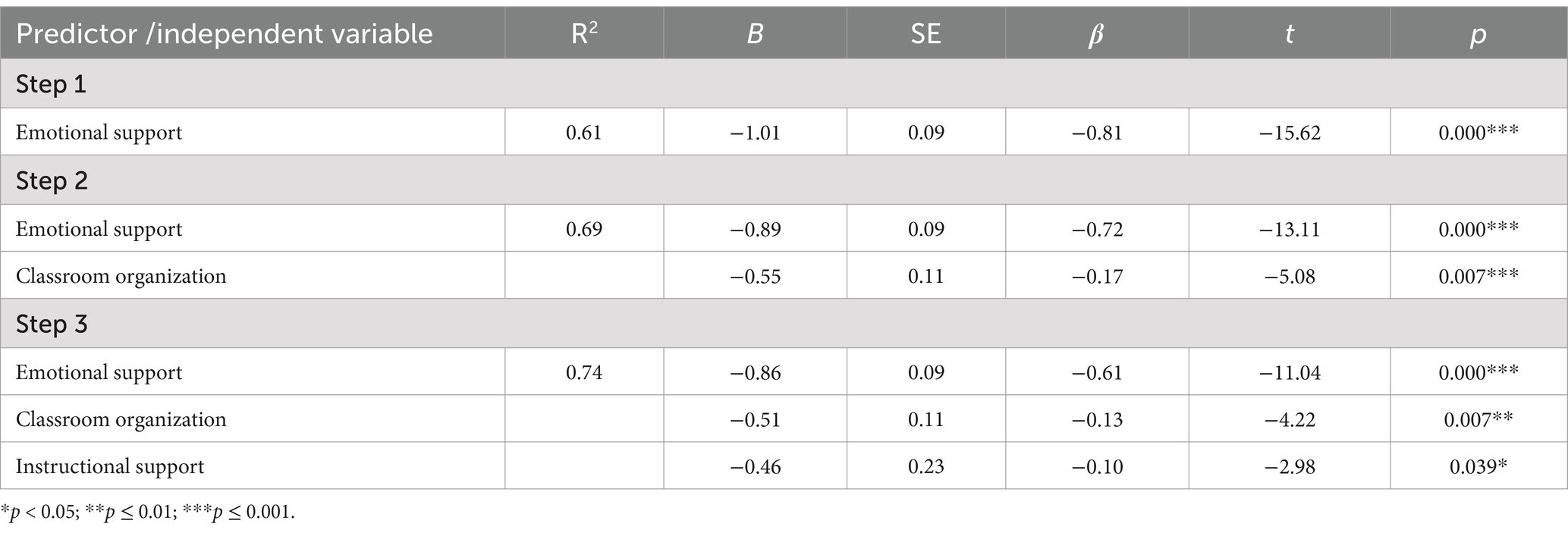
Table 4. Results of the regression analysis with early school leaving as the depend variable and emotional support, classroom organization and instructional support as independent variables (N = 87).
In order to identify the predictors of early school leaving at the subscale level, the second regression analysis has been conducted, including as predictors such emotional support indicators as positive climate, teachers’ empathy and emotional warmth, as well as respect towards the student; classroom organization indicators behavioral management, productivity and study format; as well as instructional support indicators such as content understanding, analysis and research, quality of feedback and learning dialogue.
Also, the second model, which identifies specific emotional and academic support factors, as well as classroom management elements that predict early school leaving, is statistically significant (F(1;87) = 171.06, p ≤ 0.001).
All determinants of early school leaving demonstrate an inverse relation with its occurrence: the less pronounced these factors are, the higher the risk and likelihood of early school leaving. The most crucial predictor of early school leaving is teacher empathy and emotional warmth (β = −0.61; p = 0.000), which is reflected in a teacher’s ability to understand and respond to the academic, socio-emotional, and developmental needs of individual students and the class as a whole. This factor has an inverse relation with early school leaving: the less a teacher considers and addresses these needs, the higher the risk of students leaving school early. The results can be interpreted similarly regarding the learning format (β = −0.27; p = 0.017), which encompasses the strategic application of educational resources in order to encourage student engagement and interest, as well as the setting of adequate learning goals aligned with students’ learning needs, and the provisin of high-quality, effective feedback (β = −0.19; p = 0.045) to enhance the learning process (see Table 5).
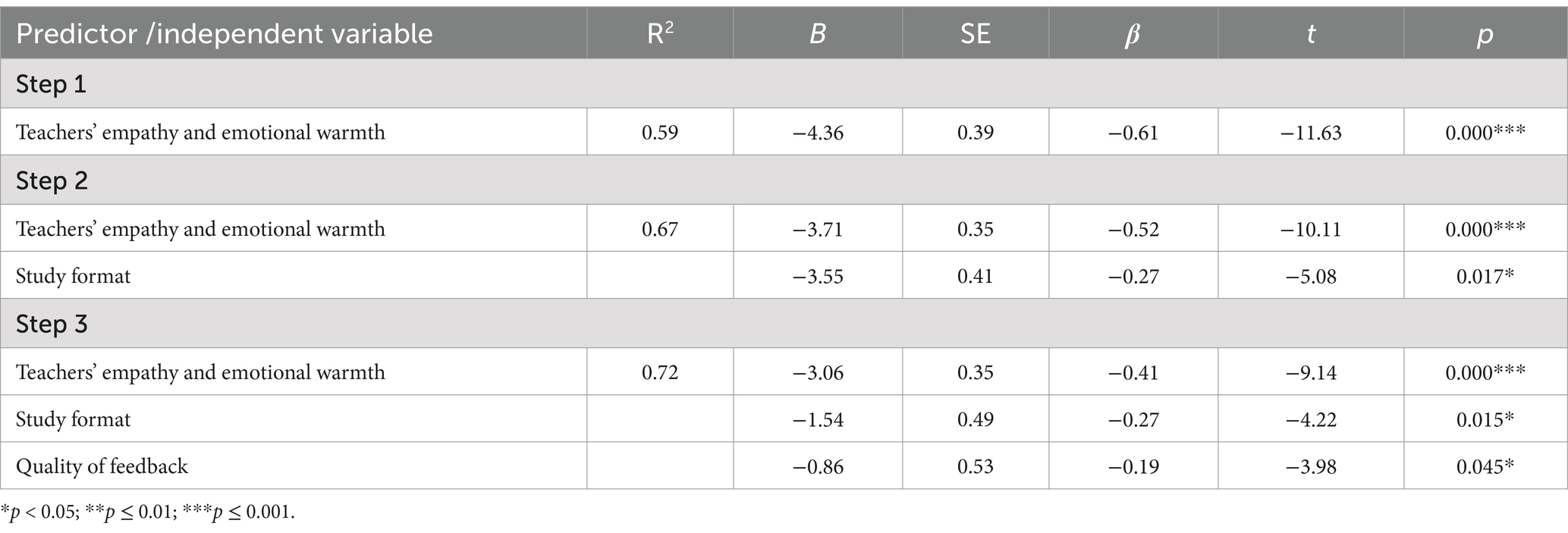
Table 5. Results of the regression analysis with early school leaving as the depend variable and the independent variables being indicators of the emotional support, classroom organization and instructional support (N = 87).
The results of our study do not contradict the results of other studies, which emphasize the need for a holistic approach in reducing early school leaving (Ozmusul, 2016; Jones et al., 2024).
The strengths of the study are the use of theoretical research findings and a framework developed by scientists in the context of early school leaving; the involvement, experience and cooperation of several Latvian university scientists (leading researchers and doctoral students) in conducting an interdisciplinary (in the field of education and psychology) research related to the validity of methods, results and data interpretation; carried out at the national level, but actualized in the context of the global problem of early school leaving and provides scientific views for the solution of the problem.
Limitations of the study were the sample size (only 87 respondents who voluntarily chose to participate in the study and whose responses may differ from those teachers who did not choose to participate in the study); data collection methods (only quantitative data were obtained in the study, it would be desirable to supplement them with qualitative data); involving a larger number of respondents, not only correlative, but also other research design types could be conducted.
Conclusion
1. Meta-analytical studies show that scientific articles included in the WoS, Scopus and Ebsco databases do not use a holistic approach to preventing early school leaving, analysing emotional and instructional support, as well as classroom organization, but emotional support predominates.
2. The most important predictor of early school leaving is emotional support, followed by classroom organization and instructional support. Emotional support is the main factor in students leaving school early, and improving it along with classroom organization and instructional support can help prevent early school leaving. The lower the emotional, classroom organization and instructional support, the higher the risk of early school leaving.
3. Of the indicators identified by the Teaching Through Interactions Framework, the most important predictors of early school leaving are teacher’s empathy and sensitivity to the academic, socio-emotional and developmental needs of individual students and the whole class, creating interest and promoting engagement in learning - using interesting and engaging lessons and teaching materials, promoting activity and clarity of learning objectives, and the effectiveness of feedback in improving the quality of learning and encouraging students to participate. These indicators are inversely proportional to early school leaving.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
AM: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft. TP: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Visualization, Writing – original draft. RB: Data curation, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. IP: Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Resources, Investigation, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alexa, S., and Baciu, E. L. (2021). School dropout and early school leaving in Romania: tendencies and risk factors. Rev. Roman. Educ. Multidimen. 13, 18–38. doi: 10.18662/rrem/13.2/408
Arkin, N., and Cojocaru, S. (2020). Future orientation of dropout youth in the context of future studies and education. Soc. Res. Rep. 12, 9–21. doi: 10.33788/srr12.1.1
Bondere, K. (2017). Par skolēnu piederības izjūtu skolai. Pieejams: Skolas Vārds. Available at https://skolasvards.lv/sleja/viedokli/par-skolenu-piederibas-izjutu-skolai (Accessed December 11, 2024).
Burke, P., Bennett, A., Burgess, C., Gray, K., and Southgate, E. (2016). Capability, belonging and equity in Higher Education: Developing inclusive approach. Centre of Excellence for Equity in Higher Education, University of Newcastle, Australia.
Cleave, P. (2023). Advantages of questionnaires in online research. Available online at: https://www.smartsurvey.co.uk/blog/advantages-of-questionnaires-in-online-research (Accessed November 17, 2024).
Code of Ethics for Scientists. (2017). Code of Ethics for Scientists. Available online at: https://www.lza.lv/images/Documents/2_Code_Of_Ethics_For_Scientists_ENG.pdf (Accessed September 9, 2024).
Downes, P. (2013). Developing a framework and agenda for Students' voices in the school system across Europe: from diametric to concentric relational spaces for early school leaving prevention. Eur. J. Educ. 48, 346–362. doi: 10.1111/ejed.12035
González-Rodríguez, D., Vieira, M. J., and Vidal, J. (2019). Factors that influence early school leaving: a comprehensive model. Educ. Res. 61, 214–230. doi: 10.1080/00131881.2019.1596034
Govorova, E., Benítez, I., and Muñiz, J. (2020). Predicting student well-being: network analysis based on PISA 2018. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17:4014. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17114014
Gudeta, J., (2016). Atbildība kā vērtība skolā. Kā veicināt skolēna atbildību pret mācībām, sevi un citiem? Pieejams: Available online at: https://www.visma.lv/blogs/atbildiba-ka-vertiba-skola-ka-veicinat-skolena-atbildibu-pret-macibam-sevi-un-citiem/ (Accessed October 5, 2024).
Guerrero-Puerat, L. M., and Guerrero, M. A. (2023). Exploring the relationship between early leaving of education and training and mental health among youth in Spain. Societies 13:103. doi: 10.3390/soc13050103
Hafen, C. A., Hamre, B. K., Allen, J. P., Bell, C. A., Gitomer, D. H., and Pianta, R. C. (2015). Teaching through interactions in secondary school classrooms: revisiting the factor structure and practical application of the classroom assessment scoring system–secondary. J. Early Adolesc. 35, 651–680. doi: 10.1177/0272431614537117
Halawah, I. (2006). The impact of student-faculty informal interpersonal relationships on intellectual and personal development. Coll. Stud. J. 40, 670–678.
Hamre, B. K., Pianta, R. C., Downer, J. T., DeCoster, J., Mashburn, A. J., and Hamagami, A. (2013). Teaching through interactions: testing a developmental framework of teacher effectiveness in over 4,000 classrooms. Elem. Sch. J. 113, 461–487. doi: 10.1086/669616
He, S., Zhu, R., and Hu, X. (2023). The influence of educational and emotional support on e-learning acceptance: an integration of social support theory and TAM. Educ. Inf. Technol. 28, 11145–11165. doi: 10.1007/s10639-023-11648-1
Ilomaki, J., and Tolppanen, A. M. (2019). “Methodological challenges in epidemiological studies” in Encyclopedia of pharmacy practice and clinical pharmacy (Mosby: Elsevier), 382–390.
Jones, R., Kreppner, J., Marsh, F., and Hartwell, B. (2024). Supporting behaviour and emotions in school: an exploration into school staff perspectives on the journey from punitive approaches to relational-based approaches. Emot. Behav. Diffic. 29, 82–98. doi: 10.1080/13632752.2024.2354021
Lavrentsova, E. (2019). The effects of student-teacher and student-student relationship on school engagement: an empirical research in Bulgaria. Педагогика 91, 320–331.
Main, K., and Whatman, S. (2016). Building social and emotional efficacy to (re)engage young adolescents: Capitalising on the ‘window of opportunity’. Int. J. Incl. Educ. 20, 1054–1069. doi: 10.1080/13603116.2016.1145265
Marzano, A., Tammaro, R., Notti, A. M., D'Alessio, A., and De Angelis, M. (2013). Cooperative learning, digital technologies and academic performance: an experience in the field. 5th international conference on education and new learning technologies proceedings of EDULEARN13 conference 1st-3rd July 2013, Barcelona, Spain, 3624–3631.
Maslo, I., Rubene, I., Surikova, S., Pīgozne, T., and Lasmane, I.. (2015). Izaicinājumi un iespējas 18-24-gadīgo jauniešu priekšlaicīgas mācību pārtraukšanas prevencijai: informatīvais ziņojums Nr. 2: 201. Available online at: http://www.lu.lv/par/projekti/es/2007-2013/esf/atbalsts-petijumiem/atbalsts-izglitibas-petijumiem/izaicinajumi2/nc/ (Accessed October 21, 2024).
Mirică, Ș. C., and Matic, A. E. (2017). The contribution of deontological rules to the efficient exercise of the right to education. Perspect. Law Public Admin. 6, 147–153.
Montero-Sieburth, M., and Turcatti, D. (2022). Preventing disengagement leading to early school leaving: pro-active practices for schools, teachers and families. Intercult. Educ. 33, 139–155. doi: 10.1080/14675986.2021.2018404
O’Hare, A., Powell, R. B., Stern, M. J., and Bowers, E. P. (2020). Influence of educator’s emotional support behaviors on environmental education student outcomes. Environ. Educ. Res. 26, 1556–1577. doi: 10.1080/13504622.2020.1800593
Ozmusul, M. (2016). School climate as a predictor of early school leavers. Croatian J Educ. 18, 491–517. doi: 10.15516/cje.v18i2.1355
Pan, J., and Ye, M. (2024). A comprehensive review on emotional support: delving into concepts, functions, influential factors, and theoretical frameworks. Int. Theory Pract. Hum. Soc. Sci. 1, 144–161. doi: 10.70693/itphss.v1i1.120
Rădăcina Oana, E. (2012). Avoidable school abandonment. Todays Children Tomorrows Parents 33, 73–82.
Rambla, X., and Scandurra, R. (2021). Is the distribution of NEETs and early leavers from education and training converging across the regions of the European Union? Eur. Soc. 23, 563–589. doi: 10.1080/14616696.2020.1869282
Show, J. C., Sayers, R., Yang, F., Granger, K. L., McCuilough, S., Kingsbery, C., et al. (2023). A systematic Meta-review of measures of classroom management in school settings. Assess. Eff. Interv. 49, 60–72. doi: 10.1177/153450842312086
Tarabini, A., Curran, M., Montes, A., and Parcerisa, L. (2019). Can educational engagement prevent early school leaving? Unpacking the School’s effect on educational success. Educ. Stud. 45, 226–241. doi: 10.1080/03055698.2018.1446327
Verschelden, C. (2017). Bandwidth recovery. Helping students reclaim cognitive resources lost to poverty, racism, and social marginalization. New York: Routledge.
Keywords: early school leaving, teaching through interactions framework, emotional support, instructional support, classroom organization
Citation: Medveckis A, Pigozne T, Birzina R and Pelnena I (2025) Predictors of early school leaving in within teaching through interaction framework. Front. Educ. 10:1563356. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2025.1563356
Edited by:
Emilio Jesús Lizarte, University of Granada, SpainReviewed by:
Ana Isabel Cisneros-Gimeno, University of Zaragoza, SpainAntonio Rodríguez Fuentes, University of Granada, Spain
Carmen Galván, University of Granada, Spain
Copyright © 2025 Medveckis, Pigozne, Birzina and Pelnena. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Arturs Medveckis, YXJ0dXJzLm1lZHZlY2tpc0BydHUubHY=
†ORCID: Arturs Medveckis, orcid.org/0000-0001-9290-2914
Tamara Pigozne, orcid.org/0000-0002-4518-7644
Rita Birzina, orcid.org/0000-0002-6124-1073
Ivita Pelnena, orcid.org/0000-0001-9099-4106
 Arturs Medveckis
Arturs Medveckis Tamara Pigozne
Tamara Pigozne Rita Birzina3†
Rita Birzina3†