REVIEW
Published on 22 Jan 2020
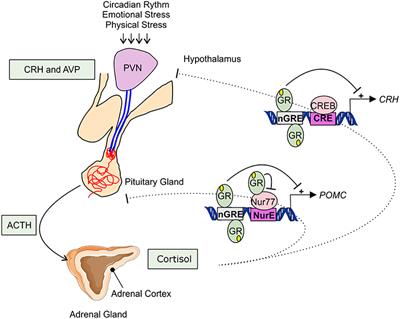
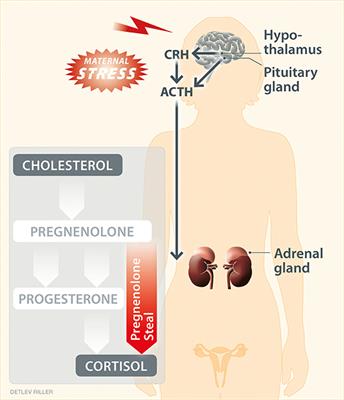
Steroids, Pregnancy and Fetal Development
doi 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03017
- 43,317 views
- 115 citations
62k
Total downloads
347k
Total views and downloads
Select the journal/section where you want your idea to be submitted:
REVIEW
Published on 22 Jan 2020

MINI REVIEW
Published on 13 Sep 2019
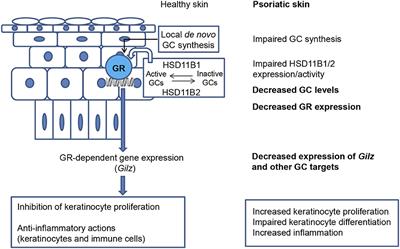
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 09 Aug 2019
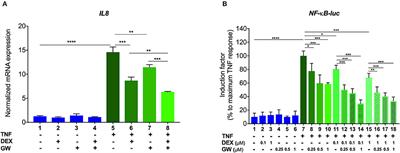
MINI REVIEW
Published on 07 Aug 2019
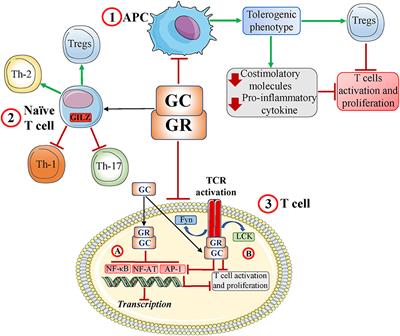
REVIEW
Published on 07 Aug 2019
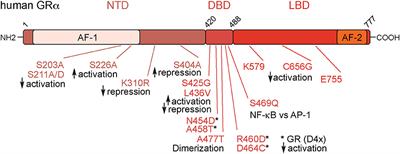
REVIEW
Published on 24 Jul 2019
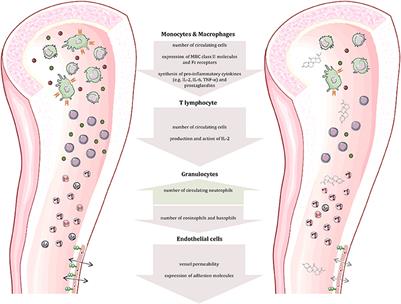
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 23 Jul 2019
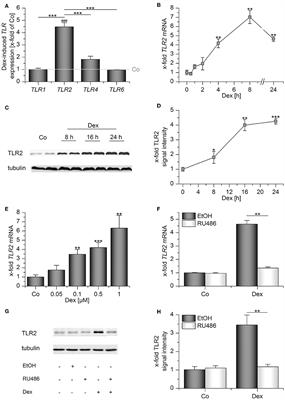
REVIEW
Published on 17 Jul 2019
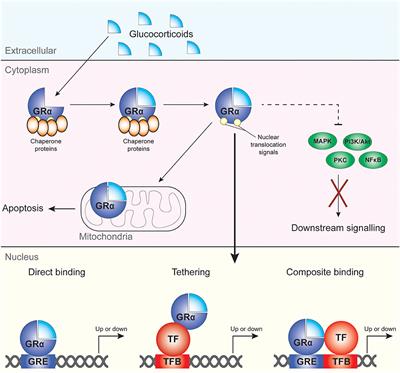
REVIEW
Published on 17 Jul 2019
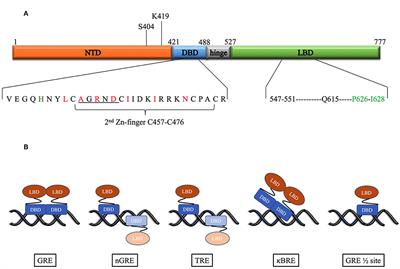
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 10 Jul 2019
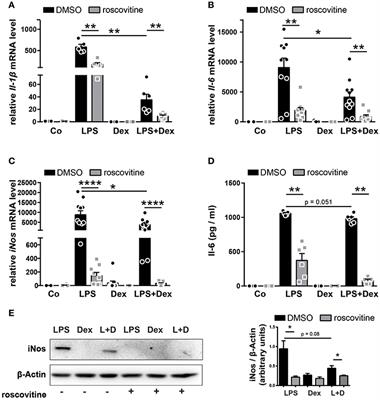
MINI REVIEW
Published on 09 Jul 2019

REVIEW
Published on 04 Jul 2019