CONCEPTUAL ANALYSIS
Published on 03 Sep 2024
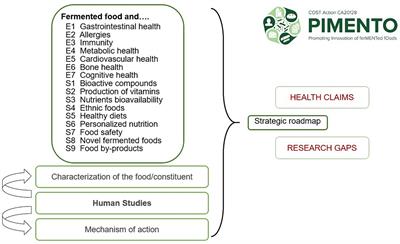
Health benefits and risks of fermented foods—the PIMENTO initiative
doi 10.3389/fnut.2024.1458536
- 13,300 views
- 4 citations
1,605
Total downloads
15k
Total views and downloads
Submit your idea
You will be redirected to our submission process.
Manuscripts can be submitted to this Research Topic via the main journal or any other participating journal.
Submit your idea
You will be redirected to our submission process.