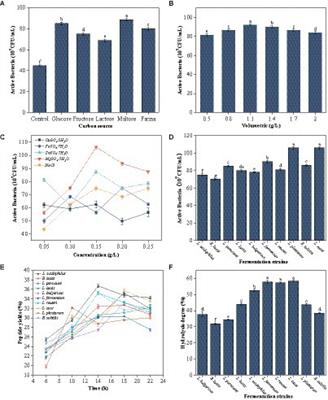
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 27 Jun 2024
Association between the C-reactive protein/albumin ratio and mortality in older Japanese patients with dysphagia
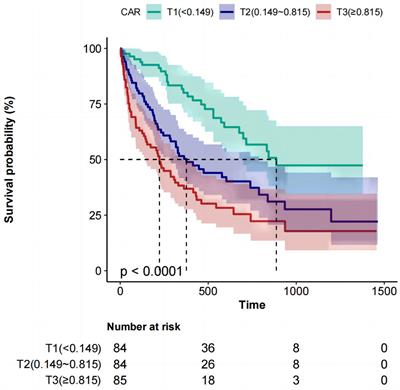
doi 10.3389/fnut.2024.1370763
- 912 views
3,127
Total downloads
22k
Total views and downloads
Select the journal/section where you want your idea to be submitted:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 27 Jun 2024

SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Published on 14 Jun 2024
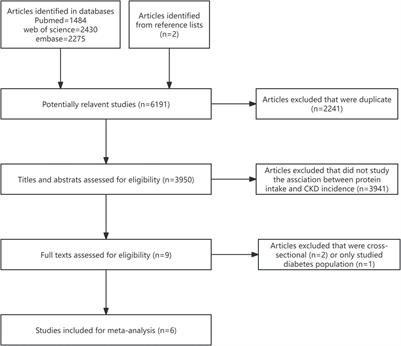
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 06 Jun 2024
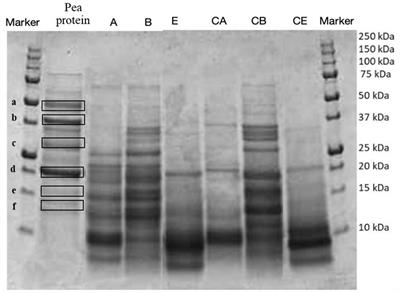
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 31 May 2024
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 13 Feb 2024