REVIEW
Published on 04 Jun 2024
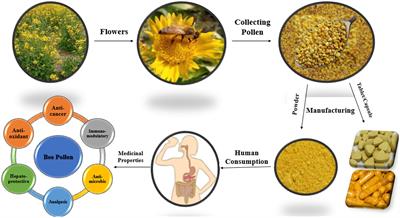
Bee pollen as a food and feed supplement and a therapeutic remedy: recent trends in nanotechnology
doi 10.3389/fnut.2024.1371672
- 7,839 views
- 1 citation
2,740
Total downloads
10k
Total views and downloads
Submit your idea
You will be redirected to our submission process.
Manuscripts can be submitted to this Research Topic via the main journal or any other participating journal.
Submit your idea
You will be redirected to our submission process.