EDITORIAL
Published on 22 Apr 2024
Editorial: Flavonoids and chronic metabolic diseases
doi 10.3389/fnut.2024.1403863
- 515 views
4,492
Total downloads
22k
Total views and downloads
Select the journal/section where you want your idea to be submitted:
EDITORIAL
Published on 22 Apr 2024
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 22 Dec 2023
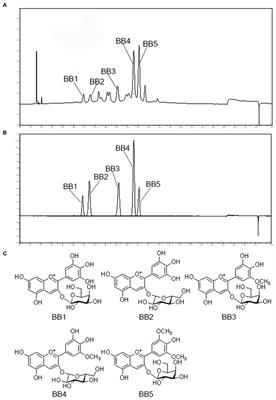
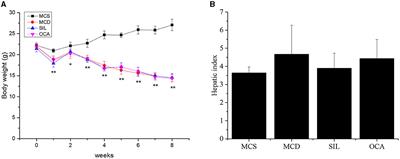
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 06 Oct 2023
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Published on 12 Jul 2023

REVIEW
Published on 31 May 2023

BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT
Published on 18 May 2023