EDITORIAL
Published on 01 Nov 2021
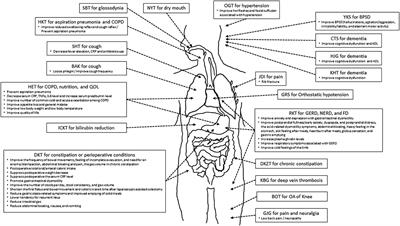
Editorial: Ageing-Related Symptoms, Kampo Medicine, and Treatment
doi 10.3389/fnut.2021.749320
- 1,308 views
14k
Total downloads
70k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 01 Nov 2021
CASE REPORT
Published on 29 Apr 2021

CASE REPORT
Published on 14 Apr 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 04 Feb 2021

CASE REPORT
Published on 27 Jan 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 21 Jan 2021
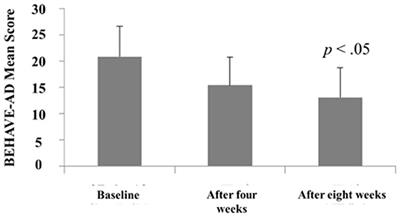
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 09 Oct 2020

CASE REPORT
Published on 11 Sep 2020

CASE REPORT
Published on 14 Aug 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 31 Jul 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 17 Jul 2020

REVIEW
Published on 15 Jul 2020