EDITORIAL
Published on 15 Jun 2022
Editorial: Sensory Stimulation and Oxytocin: Their Roles in Social Interaction and Health Promotion
doi 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.929741
- 3,920 views
- 15 citations
45k
Total downloads
236k
Total views and downloads
Select the journal/section where you want your idea to be submitted:
EDITORIAL
Published on 15 Jun 2022
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 14 Mar 2022
OPINION
Published on 09 Jul 2021
HYPOTHESIS AND THEORY
Published on 05 Jul 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 01 Jul 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 29 Jun 2021
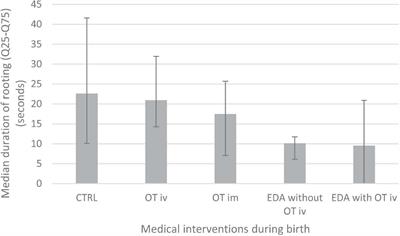
REVIEW
Published on 29 Apr 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 12 Feb 2021
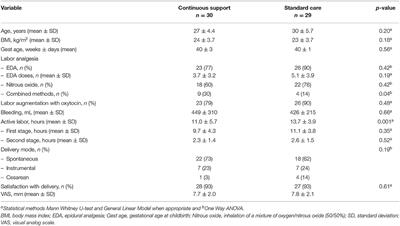
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 08 Feb 2021

REVIEW
Published on 18 Jan 2021
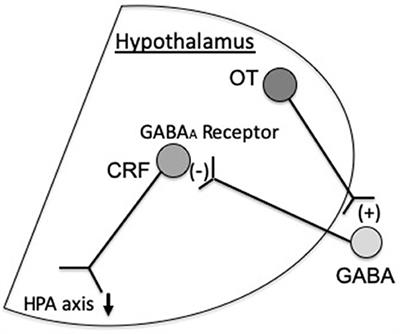
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 14 Jan 2021
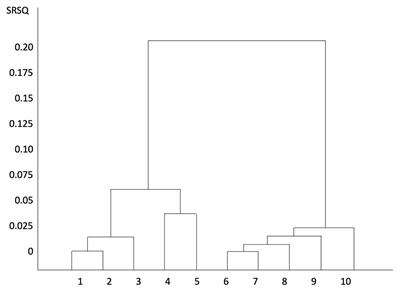
MINI REVIEW
Published on 05 Jan 2021

Frontiers in Endocrinology
Frontiers in Neuroscience
Frontiers in Psychiatry