- 1Department of Agricultural Sciences, University of Naples Federico II, Portici, Italy
- 2Interdepartmental Research Centre on the “Earth Critical Zone”, University of Naples Federico II, Portici, Naples, Italy
Wheat, a staple crop, faces numerous challenges due to climate change and the increasing demand for sustainable practices. Biostimulants, which enhance plant growth and resilience, have gained attention for their potential to improve wheat productivity in an environment-friendly manner. This study presents a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of field-based research on wheat's response to biostimulants under field conditions from 2000 to 2024. Analyzing 222 studies, the bibliometric analysis reveals a significant rise in research publications on biostimulants, with an annual growth rate of 15.6%. Asia leads with the largest share of publications (59.4%), followed by Europe (18.1%) and Africa (11.6%). North America, South America and Oceania have fewer contributions. Additionally, research institutions in Pakistan, India and Egypt rank as the most productive on this topic. Saudi Arabia stands out with the highest percentage of international collaboration, at 91.7% between countries and 100% among institutions. The findings reveal that biostimulants significantly improve wheat's ability to withstand abiotic stress, optimize nutrient uptake, and enhance overall plant health. Research is transitioning from traditional organic methods and microbial inoculants to advanced biostimulant formulations, improved nutrient management, and reduced environmental impact. However, gaps remain, particularly in understanding the combined effects of multiple biostimulants and their long-term impact on wheat and soil health. This synthesis of research trends lays the groundwork for advancing sustainable wheat production, supporting food security and agricultural resilience amidst environmental challenges.
1 Introduction
Wheat (Triticum spp.) is one of the most widely cultivated crops globally, serving as a staple food for over half of the global population (Shiferaw et al., 2013). It is grown in many countries, the largest producers being China, India, Russia, the United States, Canada, and Pakistan, with an estimated annual production of approximately 136.59, 110.55, 91.00, 49.31, 33.82 and 28.00 million tons, respectively (Statista, 2024). Wheat is a crucial pillar of food security, providing around 15–25% and 20% of protein and daily caloric intake globally, respectively (Gooding, 2023; Deswal et al., 2023; Bin Safdar et al., 2023). However, wheat cultivation faces numerous challenges, particularly due to climate change (Rizwan et al., 2024), soil degradation (Campos-Avelar et al., 2023), and the growing demand for sustainable agricultural practices that reduce dependence on chemical inputs (Wang et al., 2024; Soares et al., 2024).
The quest for innovative, environment-friendly methods to enhance wheat's resilience and productivity has triggered interest in biostimulants. Biostimulants have become valuable tools in modern agriculture due to their ease of application and environment-friendly composition (Servalesa, 2023; Zulfiqar et al., 2024). Multiple definitions and classifications of biostimulants have emerged since their introduction. A biostimulant is defined as a vegetal or microbial based- substances/product that, when applied to plants or the rhizosphere, enhances nutritional efficiency, abiotic stress tolerance, and/or plant quality traits, without being a direct source of nutrients (du Jardin, 2015). Biostimulants encompass a wide range of natural compounds (e.g., humic substances, seaweed extracts, protein hydrolysates) and microbial inoculants, such as plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) and mycorrhizal fungi, which play a crucial role in improving plant health, resilience, and overall productivity. Despite the growing body of research on biostimulants, the complex interactions between these substances, wheat plants, and the environment are not yet fully elucidated. As global demand for wheat continues to rise, understanding the effects of biostimulants on wheat growth and productivity is crucial for optimizing crop yields and ensuring food security (Moreno-Moraga et al., 2024). According to Ayed et al. (2022), various factors can influence the efficacy of biostimulants, including the type of biostimulant (e.g., microbial inoculants, seaweed extracts, amino acids, etc.), the specific wheat cultivar, application methods, dosage, and timing (Maignan et al., 2021), and prevailing environmental conditions (e.g., drought, salinity, temperature fluctuations, etc.) (Ma et al., 2022; Radzikowska-Kujawska et al., 2022).
Over the past two decades, numerous field-based studies have investigated the effects of biostimulants on wheat growth and development (Popko et al., 2018; Radzikowska-Kujawska et al., 2022). These studies have employed a range of biostimulants, including naturally derived plant growth regulators (Dyadiuchenko et al., 2020), and beneficial microorganisms (Lamlom et al., 2023), exploring their effects on various aspects of wheat physiology, including seed germination, root growth, leaf development, and grain yield (Shahrajabian et al., 2021; Marta et al., 2023). Notably, humic substances and seaweed extracts have been shown to enhance nutrient use efficiency and stimulate photosynthetic activity, resulting in significant improvements in both yield and grain quality (Maignan et al., 2020). Furthermore, microbial biostimulants, including plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) and mycorrhizal fungi, have demonstrated the ability to enhance root system development and improve water-use efficiency, thereby conferring resilience to abiotic stresses such as drought and salinity (Tanveer et al., 2024; Kibret et al., 2024). Additionally, these microbial agents have been found to delay leaf senescence during the grain-filling stage, sustaining higher chlorophyll content for extended periods and potentially contributing to increased photosynthetic productivity (Aburri, 2022).
Due to technological development, research, and practical interest, the number of publications on the effect of biostimulants on wheat is changing. Moreover, in recent years, the interests of national and international policy organizations have drawn special attention to the marketability of biostimulants (European Commission, 2019; Davidson, 2024). Despite the growing body of evidence, a comprehensive review of the existing literature is needed to synthesize the findings and identify key trends, patterns, and gaps in research on wheat's response to biostimulants.
Bibliometric analysis is a quantitative research method that systematically examines scientific publications to uncover patterns, relationships, and trends in literature. By employing statistical techniques to analyze metrics such as citation counts, publication frequencies, and authorship patterns, this method provides valuable insights into research impact and collaboration. It is particularly useful for assessing productivity and quality across various disciplines, guiding funding decisions, informing policymaking, and offering a powerful tool for evaluating the current state of knowledge on a topic (Salinas-Ríos and García López, 2022).
Several bibliometric studies have been conducted on biostimulants, each with distinct objectives and focus areas. Lau et al. (2025) conducted a bibliometric analysis covering a 5-year period (2019–2024) using data from a single database (Scopus), focusing on biostimulants' role in enhancing plant resilience to abiotic stress, particularly physiological and biochemical responses to drought, salinity, and heat stress. However, this study does not analyze the global research landscape nor track how scientific focus has evolved over time (e.g., from individual biostimulants to integrated applications across different cropping systems). Meena et al. (2025) conducted a bibliometric analysis spanning 2010–2024 using the Web of Science database, adopting a sustainability-driven approach by assessing how biostimulant research contributes to reducing chemical inputs, improving resource efficiency, and promoting eco-friendly agricultural practices. However, it lacks an in-depth network analysis of research collaborations and the impact of policy-driven trends on biostimulant adoption.
Additionally, Gallegos-Cedillo et al. (2024) explored biostimulant applications in vegetable seedling and transplant production, emphasizing their contributions to early plant development and nutrient uptake. However, it omits insights into cereal crops like wheat, failing to analyze biostimulant responses in field conditions for staple crops under different environmental stresses. Miranda et al. (2024) focused specifically on microalgae-based biostimulants, analyzing their commercial potential, technological challenges, and research trends. However, its scope is limited as it exclusively examines microalgal-derived products, overlooking other major biostimulant categories such as humic substances, seaweed extracts, or microbial inoculants. Furthermore, the study lacks crop-specific analysis, making it difficult to assess the direct impact of microalgal biostimulants on wheat and other staple crops. It also fails to explore global research collaborations, interdisciplinary trends, and policy-driven factors influencing biostimulant adoption. While it addresses formulation methods and market trends, it provides minimal assessment of agronomic field performance, long-term soil health impacts, and regulatory challenges.
Corsi et al. (2022) performed a bibliometric analysis focusing on the physiological and biochemical mechanisms of biostimulants but does not explore their long-term agronomic impact, economic feasibility in field applications, or the evolution of research focus over time. Additionally, it does not track publication growth or research collaborations, limiting its ability to assess global research trends in biostimulant science.
These gaps underscore the necessity for a comprehensive bibliometric analysis that specifically addresses wheat biostimulant research over an extended period (2000–2024), incorporating a multi-database approach to capture global publication trends, interdisciplinary collaborations, research evolution, and policy influences. Our study aims to fill this void by mapping research trajectories, identifying emerging themes, and assessing institutional and geographical contributions, providing a more holistic understanding of biostimulant applications in wheat production.
Our analysis provides insights into the current state of knowledge on wheat's response to biostimulants, discusses the limitations and challenges of existing research, and highlights areas for future research.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Methodology
The search for relevant literature was conducted on October 18, 2024, using bibliometric analysis as a statistical tool to evaluate the scientific literature in this field. Notably, bibliometric analysis has gained prominence in the agricultural and biological sciences, with approximately 1,917 related articles published between 2000 and 2024 in these fields, according to the Scopus database. Of these, a substantial 82.68% were published in the last 5 years (2020–2024), highlighting the method's growing importance.
2.2 Data source and search criteria
The bibliometric analysis conducted in this study adheres to the protocol established by the Collaboration for Environmental Evidence (CEE), as specified by Pullin et al. (2022), thus ensuring the validity and reliability of the results. To ensure a rigorous selection process, specific inclusion and exclusion criteria were applied for selecting papers for the analysis. Three key selection criteria were established: (I) studies must be conducted exclusively under field conditions, excluding laboratory, greenhouse, and pot experiments; (II) studies must focus on durum wheat and common wheat, and (III) studies must investigate the application of biostimulants. Additionally, the research question guiding this bibliometric analysis—'How does wheat respond to biostimulants?'—was formulated using the PICOL (Population/Intervention, Comparator/Outcome, and Location) model, as detailed in Table 1 of the CEE protocol.
The PICOL framework was employed to integrate the terms “field”, “biostimulants”, “wheat”, “yield”, “quality”, and “diseases” into the ‘topic words' of the literature collected through the Scopus and ISI Web of Science databases. The following search query was used to identify relevant literature:
(({field conditions} OR {field experiment} OR {plot}) AND (Wheat OR (Triticum AND (aestivum* OR turgidum*))) AND (biostimul* OR PGPB OR PGPR OR (plant AND growth AND promot*) OR AMF OR (arbuscular AND mycorrhizal AND fung*) OR ((humic OR fulvic) acid*) OR (Silicon OR zeolite) OR (seaweed* OR *algae OR nodosum) OR chitosan) OR ({Amino Acid*} OR {Protein Hydrolysate*}) AND (yield OR quality OR protein OR gluten OR disease)).
This search was further refined to include only articles published in English between 2000 and 2024, focusing on peer-reviewed journals in the subject areas of Agricultural and Biological Sciences, Environmental Science, Immunology and Microbiology, Biochemistry, Earth and Planetary Sciences, and Multidisciplinary Studies.
2.3 Screening
The initial search identified 791 articles, which were imported into EndNote software (Version 20.2.1, Clarivate Analytics). The selection process for these articles is illustrated in Figure 1. Upon application of the established inclusion criteria to evaluate titles, abstracts, and full-text studies, 569 articles were excluded. Consequently, 222 articles met the eligibility criteria and were retained for bibliometric analysis.
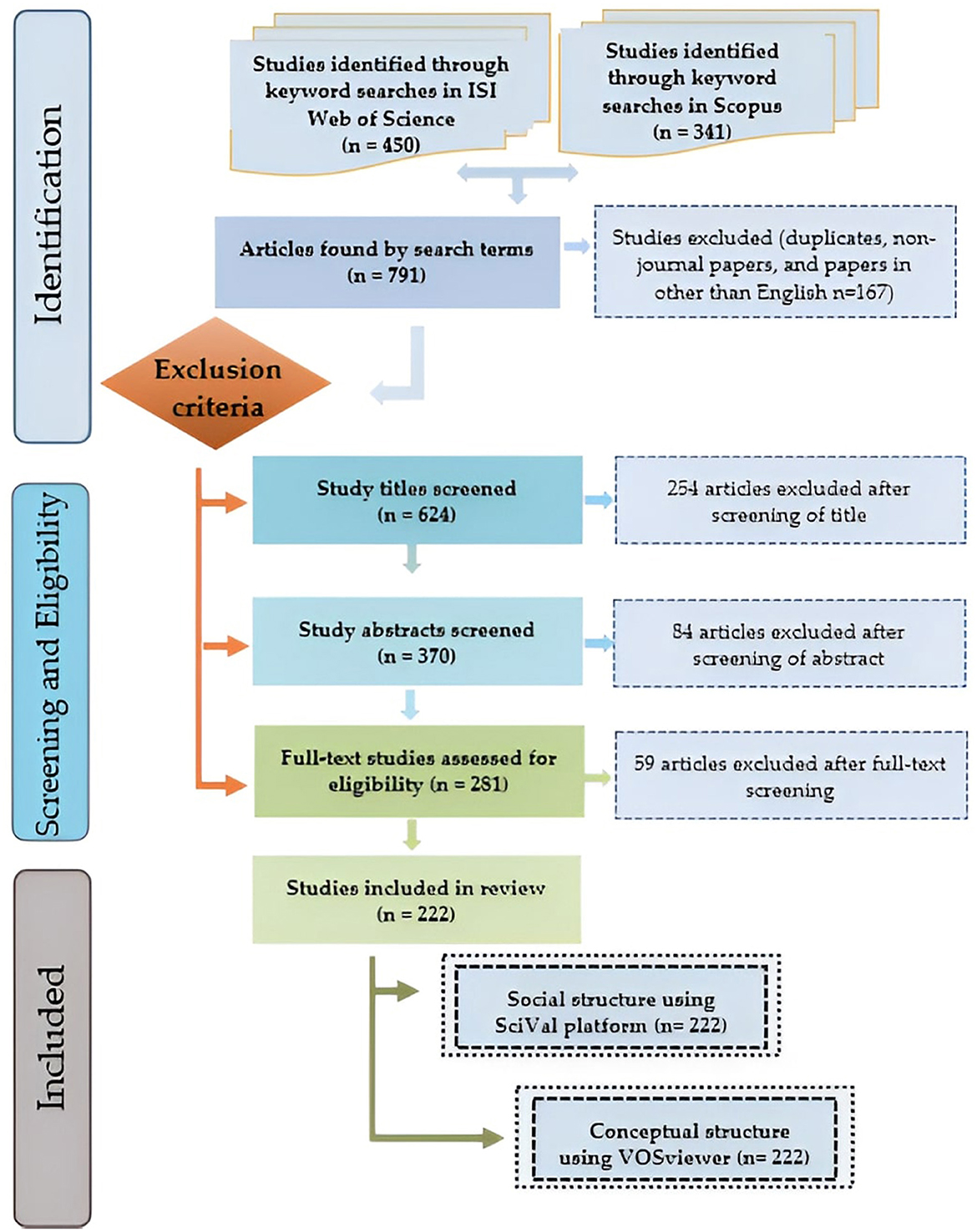
Figure 1. Selection of articles for inclusion in the bibliometric analysis (n represents the number of articles).
2.4 Data analysis
This study conducted a retrospective analysis of 222 scientific papers published between 2000 and 2024 which explore the effects of biostimulants on wheat, and examines the trajectory of research in this area over the past 25 years. To this end, a range of bibliometric indicators were employed, including the number of publications per scholar, citation counts, the number of contributing countries, institutions, and journals, journal impact factors, and co-occurrence analysis of terms across different time frames.
The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) was calculated using the formula:
where P is the value of publications. n: The number of years between the start and end periods.
The quantitative analysis was conducted using the SciVal platform, developed by Elsevier, which assesses research performance, identifies collaboration opportunities, and uncovers emerging trends in the field (Vardell et al., 2011; Dresbeck, 2015). Additionally, VOSviewer (V1.3.20) was used to create a term co-occurrence network (Van Eck and Waltman, 2009), while Citescpace (V6.4.R1) was employed to generate a co-cited reference network (Chen, 2006).
3 Results
3.1 Progression of research findings
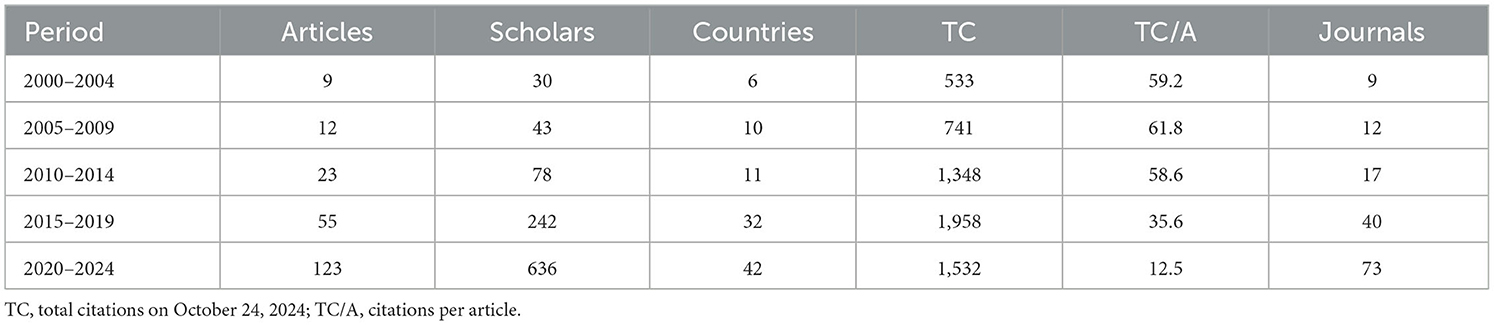
A rigorous selection process was adopted to identify 222 research articles examining wheat's response to biostimulants under field conditions. These studies were selected based on predefined eligibility, inclusion, and exclusion criteria, to enable a robust bibliometric analysis. Table 2 illustrates the development of scientific studies on wheat's response to biostimulants under field conditions across 25 years (2000–2024). This analysis, highlighting key attributes in the biostimulant-related literature, is organized into five 5-year intervals.
The data indicate a substantial growth in research focus on wheat's response to biostimulants under field conditions throughout the analyzed period. This trend is especially pronounced in the latest 5-year interval (2020–2024), accounting for over 55.4% of the total scientific publications on this topic. Conversely, the fourth interval (2015–2019) contributed over 32% of all citations, reflecting the impact of studies published during this span. Compared to the initial 5-year period (2000–2004), the most recent period has seen over a 14-fold increase in the number of articles and a three-fold rise in total citations. The scientific output in this area has shown a strong annual growth rate of 15.6%, following a clear exponential trend in publication activity from 2000 to 2024 (Figure 2).
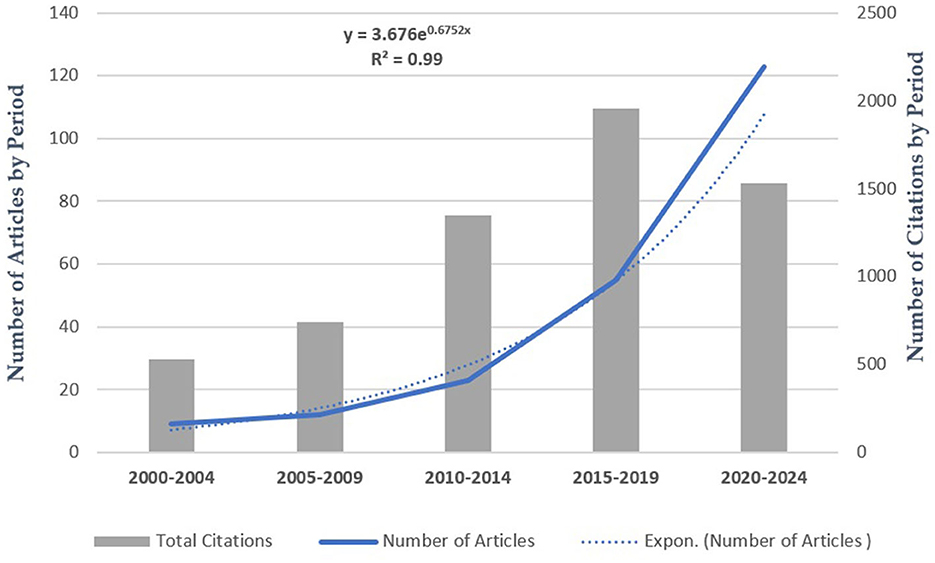
Figure 2. Trends in the number of articles, total citations, and polynomial variation over time: the dotted line represents the fitted exponential curve for the number of articles.
In the past 25 years, the number of research papers published peaked in 2021, 2022, and 2024, with 28, 29, and 28 publications, respectively. Total citations have fluctuated over time, reaching a high of 681 in 2019 before declining notably (data not shown).
Despite the significant increase in the total number of articles and citations, a contrasting trend has emerged in citations per document, particularly following the second interval (2005–2009). Over the past 5 years, the average citations per article markedly declined by 80% vis-a-vis the aforementioned interval (Table 2).
A total of 960 authors contributed to the 222 published articles, resulting in an average of 4.3 authors per document. Notably, six scholars produced single-author papers, while the average co-authorship per article was 5.12. As illustrated in Figure 3, 89.5% of scholars published only one article over the 25-year study period, with 7.7% publishing two articles, and just 0.8% publishing three or more. In the early period (2000–2004), author participation was relatively modest, with 30 authors contributing to publications, yielding an average of three authors per article (Table 2). In contrast, during the most recent five-year period, the number of contributing authors increased 21 times (Table 2) which is further evidenced by an increase in the average number of authors per article, which has reached five authors per publication during the latest period.
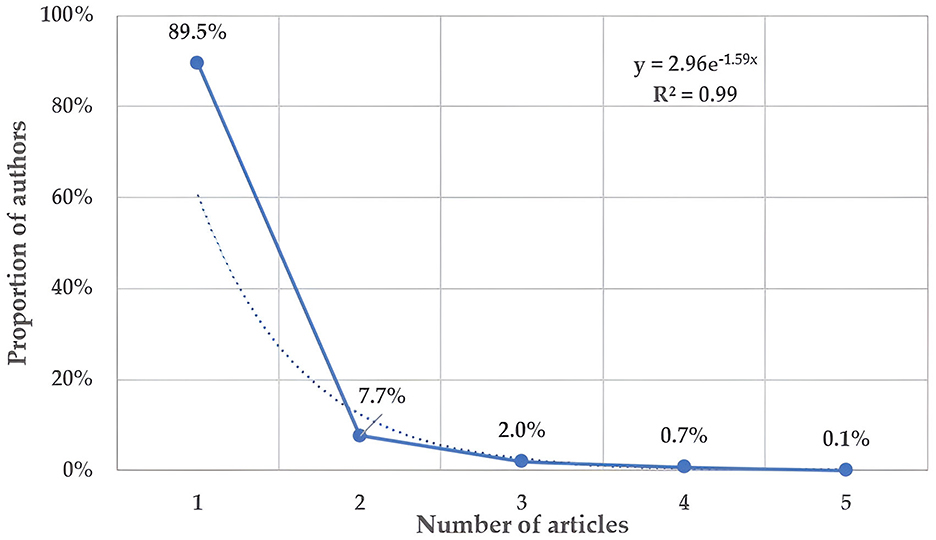
Figure 3. Frequency distribution of author scientific productivity: the dotted line represents the fitted exponential curve for the number of articles.
Over the 25-year study period, a total of 51 countries contributed to publications in this research area. This number expanded significantly, rising from just 6 in the initial period (2000–2004) to over seven times that number in the most recent period.
Finally, the documents were published across 117 distinct sources from 2000 to 2024, rising from 9 sources in the initial five-year period (2000–2004) to 73 sources in the 2020–2024 period. This reflects an over eightfold increase in the number of unique publication sources, highlighting the broadening dissemination of research in this field.
3.2 Analysis of scientific production
3.2.1 Most pertinent journals
Our analysis of 222 articles revealed that they were cited in 117 distinct sources, with 53.85% thereof being open-access journals. According to Bradford's Law, only 11 journals were identified as the core sources, collectively accounting for 75 publications, representing approximately one-third of the total articles (Table 3). In 2023, 55% of the top 11 journals with the highest scientific output in our research field were ranked in the first quartile (Q1) of the SCImago Journal Rank (SJR), with impact factors ranging from 2.66 for the “Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science” to 4.1 for “Frontiers in Plant Science”. The remaining 45% of these leading journals were distributed across quartiles Q2 to Q4, according to SJR rankings.
Notably, 54.5% of these journals are based in Europe, primarily in Switzerland, while 27.3% originate from Asia, with India being a significant contributor. In contrast, 18.2% of the journals are based in North America, with the United States being the primary location. Within our study period, we identified two key journals, “Agronomy” and “Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis”, which collectively contributed 11.26% and 9.70% of all published articles and total citations related to our research topic, respectively, boasting the highest H-index (8) for publications on this topic. However, “The Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science” achieved the highest average citation per article at 39.3, followed by “Agronomy” and “Biology and Fertility of Soils” with 28.8 and 27 citations per article, respectively. Over the last 5 years (2020–2024), 45 articles on the topic of wheat's response to biostimulants were published in these leading 11 journals, a substantial increase from just three across three journals in the early 2000s (2000–2004). This trend highlights the growing scholarly interest and a wider array of journals for research on biostimulants' impact on wheat.
3.2.2 Most productive authors
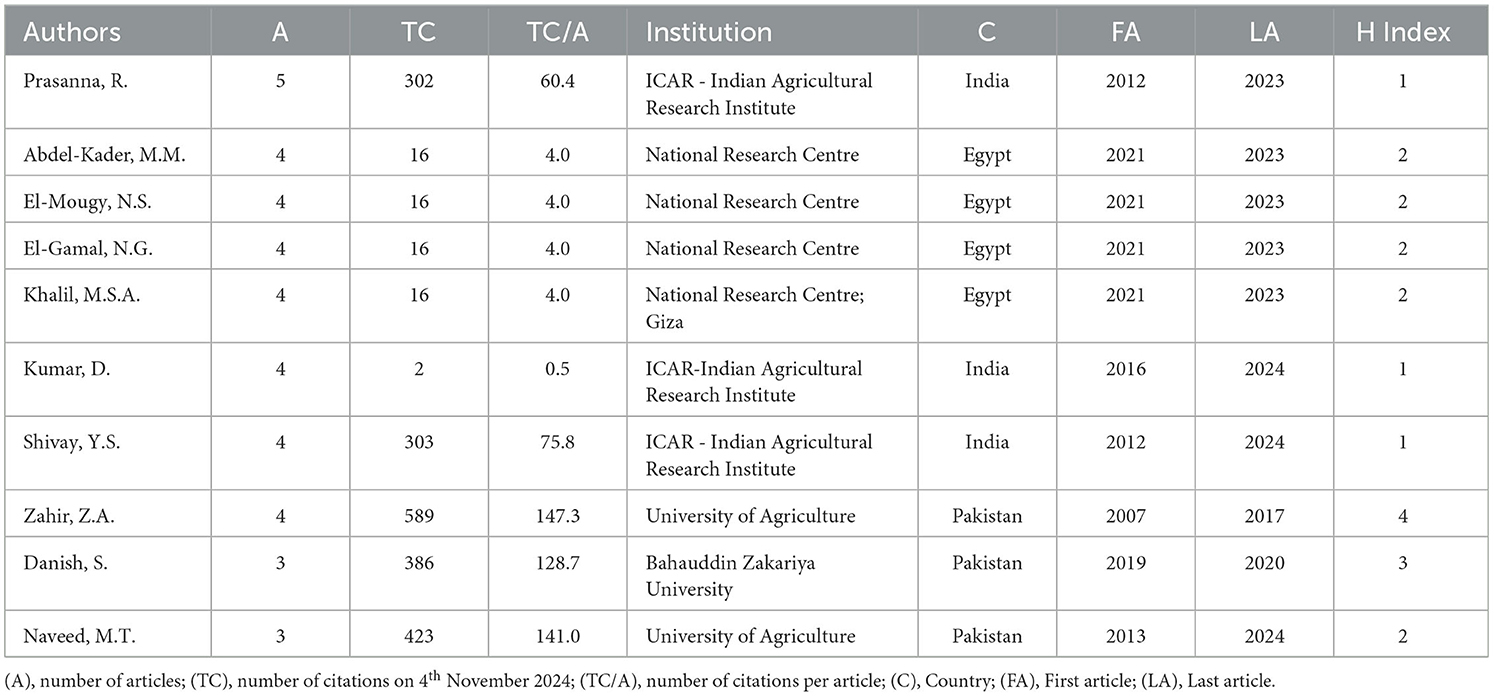
Table 4 presents the top 10 prolific authors in our research area, evaluated through bibliometric indicators such as the total number of publications, total citations, and average citations per article. Collectively, these authors have contributed 39 articles and a total of 2,069 citations, representing 17.57% of all publications and 33.85% of total citations in this field. The significant contribution from authors of Asian origin, with scholars from India and Pakistan each constituting 30% of the most productive group, is noteworthy. Africa too is well-represented, particularly by Egypt, which accounts for 40% of the top authors.
The leading contributor, Prasanna R. from the ICAR-Indian Agricultural Research Institute, stands out with five publications over 11 years (2012–2023), accumulating 302 citations and achieving the highest H-index of 1. Four Egyptian scholars follow closely (Abdel-Kader M.M., El-Mougy N.S., El-Gamal N.G., and Khalil M.S.A), all affiliated with the Plant Pathology Department of the National Research Centre. Each of these researchers has published four articles, receiving a total of 16 citations per author and maintaining an H-index of 2 (Table 4).
Further, three prominent authors from Pakistan, Zahir Z.A. and Naveed M.T. from the University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, along with Danish S. from Bahauddin Zakariya University, exhibit higher citation metrics, with an impressive average of 466 citations and 139 citations per article (Table 4). Lastly, among the top 10 most prolific authors, only three from Pakistan demonstrated a notable percentage of international co-authorship over the analyzed period (2000–2024), with values ranging between 25% and 100% (Table 5).
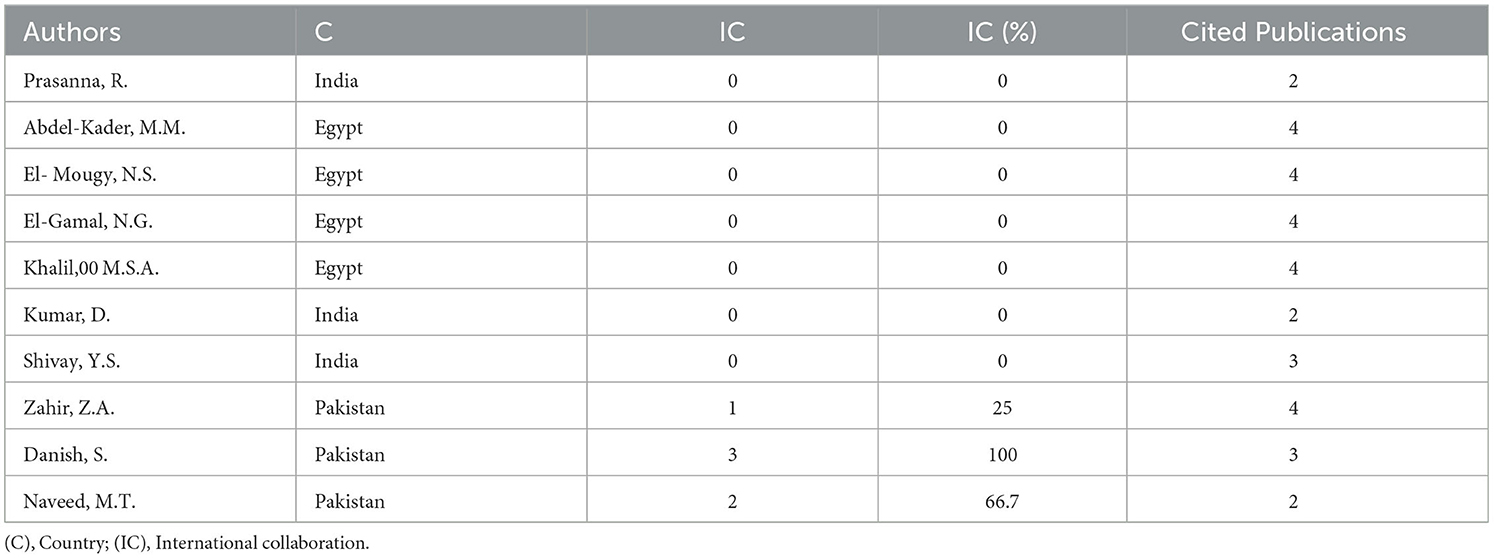
Table 5. International co-authorship of top 10 most relevant authors on the effects of biostimulants on wheat from 2000 to 2024.
3.2.3 Most productive countries and affiliations
Only 26.4% of the world's countries (52 nations) have actively engaged in this research subjects of the current study. As illustrated in Figure 4, Asia accounts for the largest share of publications, contributing 59.4% (184 articles), followed by Europe with 18.1% (56 articles) and Africa with 11.6% (36 articles). Collectively, these three continents represent a substantial 89.0% of all publications focused on research on wheat's response to biostimulants. In contrast, our bibliometric analysis highlights that North America, South America, and Oceania have considerably fewer publications, with only 17, 14, and 3 articles, respectively.
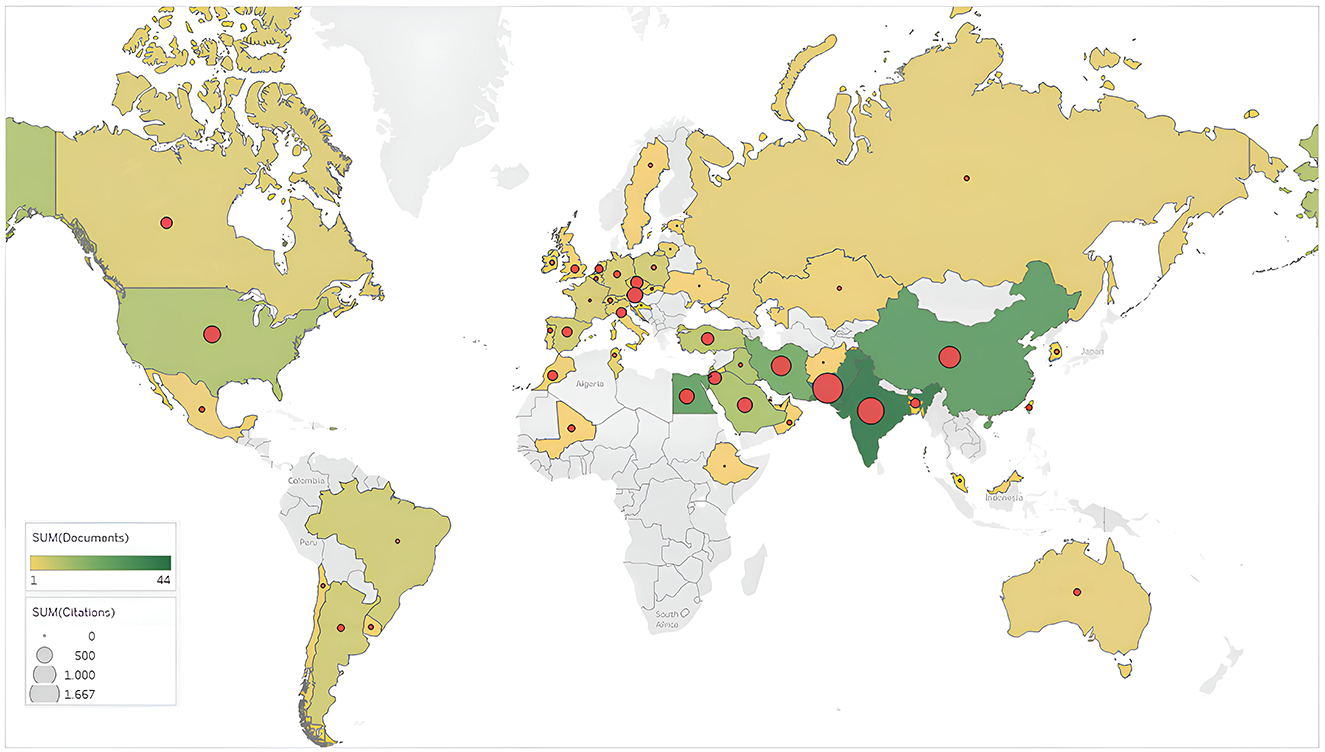
Figure 4. Global map illustrating the geographic distribution of research publications and cumulative citations by country. Source: Tableau.
India, Pakistan, and China are the leading countries in the wheat response to biostimulants research field, publishing 44, 41, and 30 articles, respectively. They also have the highest number of citations, with Pakistan having 1,672, India 1,302, and China 842. These countries have the top H-index values, scoring 20 for Pakistan and 15 each for India and China, indicating the major role these three countries play in advancing research in this area, comprising 37% of all published articles (Table 6).
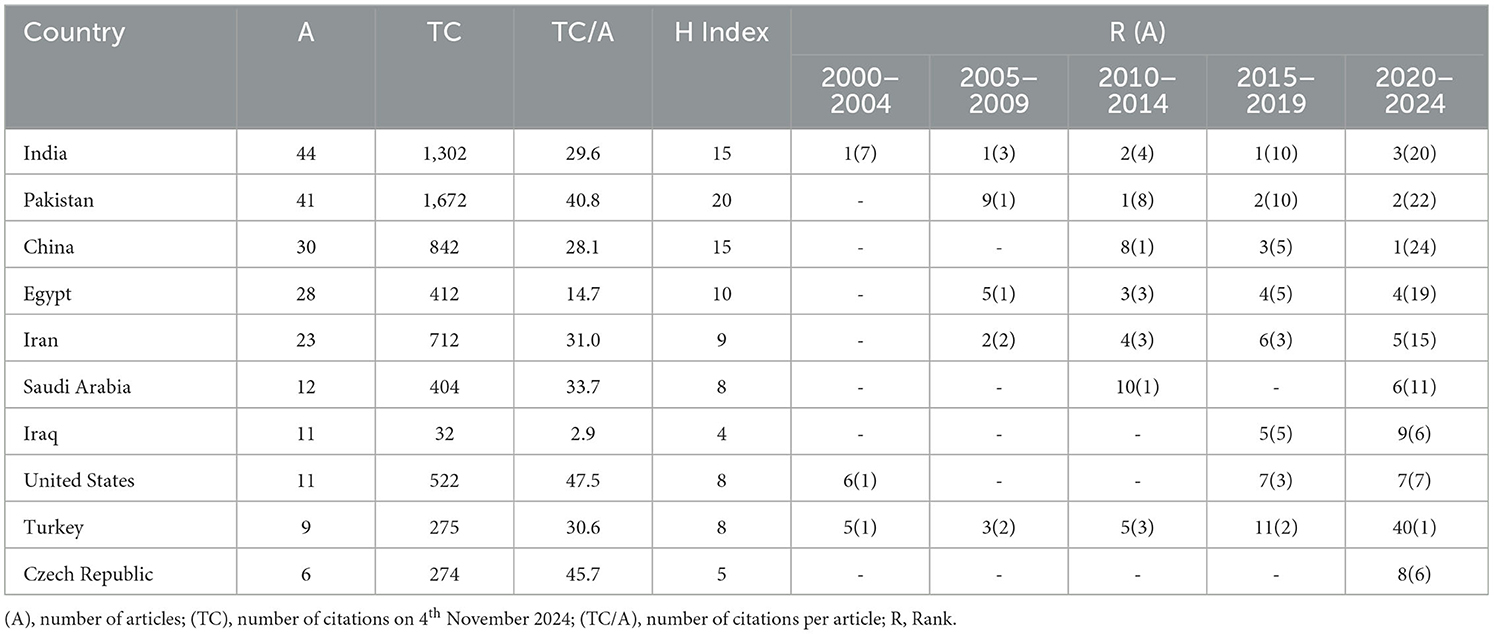
Table 6. Top 10 most productive countries on the effects of biostimulants on wheat from 2000 to 2024.
Meanwhile, the United States and the Czech Republic rank first and second for the average number of citations per article, with 47.5 and 45.7, respectively. India and Turkey have consistently published research articles throughout the analyzed periods (2000–2024). China joined this research field in the third 5-year period (2010–2014), while Iraq started contributing only after 2015, as did the Czech Republic, in the 2020–2024 period (Table 6).
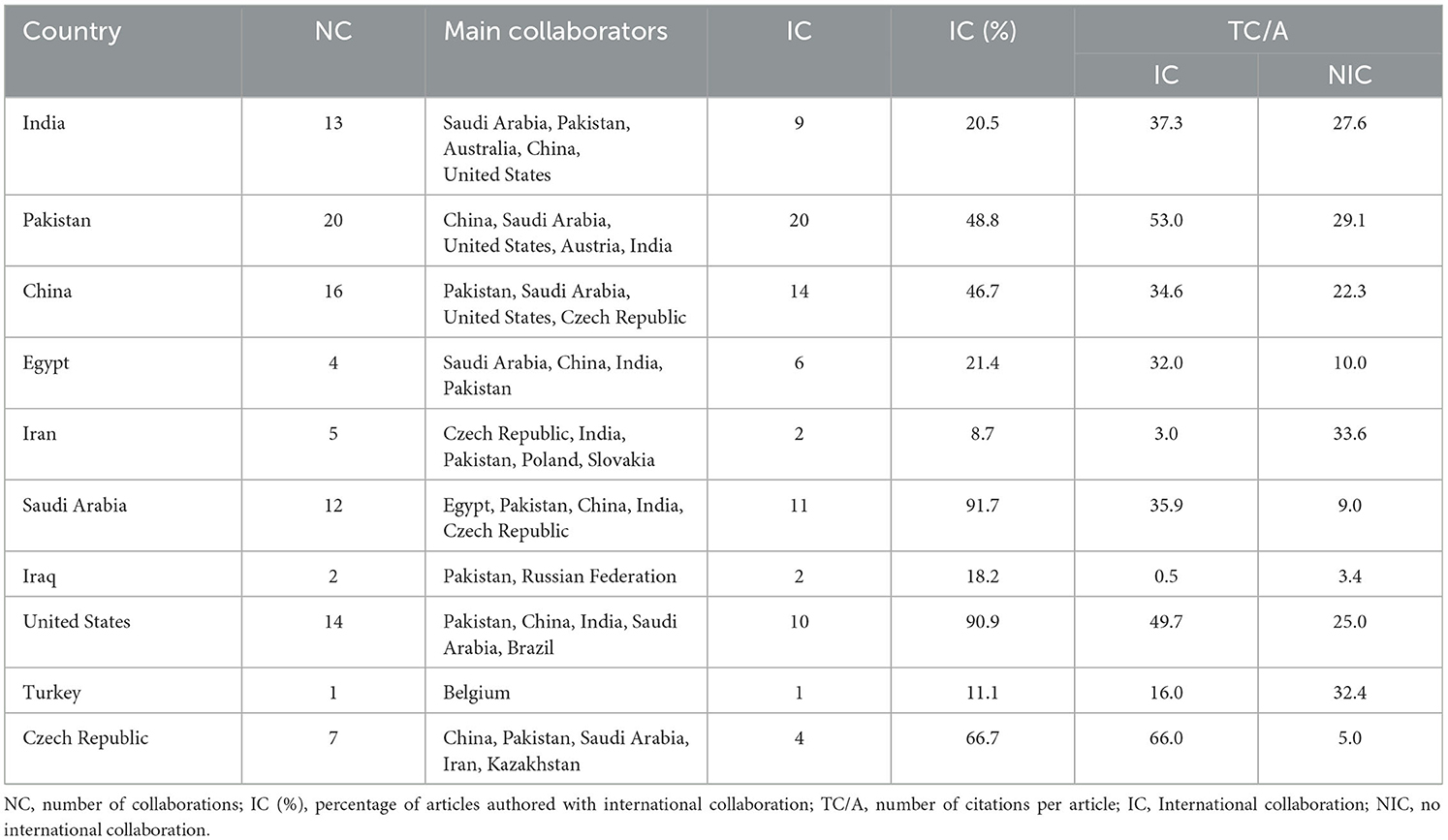
Table 7 reveals that Saudi Arabia has the highest level of international collaboration, with 91.7% of its research articles (11 out of 12) being co-authored with researchers from other countries. The United States follows with a collaboration rate of 90.7% (10 articles), while the Czech Republic shows a moderate collaboration rate of 66.7% (4 articles). Iran, Turkey, and Iraq have relatively low levels of international collaboration, with respectively only 8.7% (2 articles), 11.1% (1 article), and 18.2% (2 articles) of their research being produced collaboratively.
Figure 5 presents the international collaboration network among major countries, constructed through a co-authorship analysis, where each country has contributed to at least one article. Despite the substantial body of literature on wheat's response to biostimulants, international research collaboration in this field remains moderate, encompassing only 25.2% of the total publications (56 out of 222 articles). According to Figure 5, international cooperation is confined to 48 countries, organized into eight distinct clusters based on their specific collaborative networks. The proximity of countries on the map reflects the frequency and strength of their collaborative efforts.
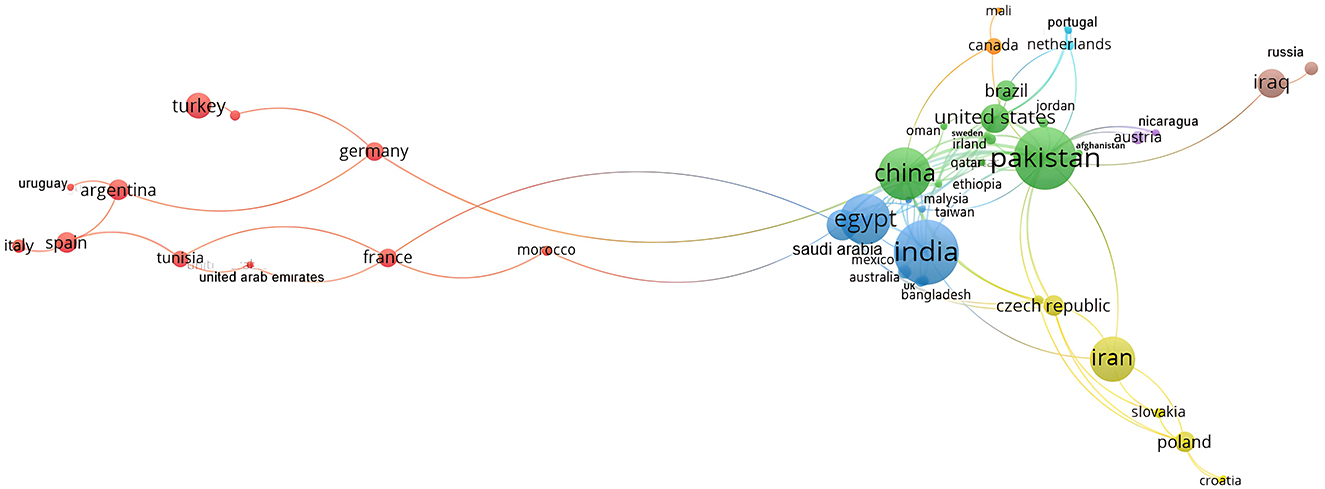
Figure 5. Global collaboration network visualization map. Color: represents a cluster of country collaboration in the wheat response to biostimulants research field; Nodes: represent countries (node size proportional to publication output); Links: indicate collaborative relationships between countries. Source: VOSviewer (resolution 0.5; minimum cluster size 1; small clusters not merged).
A notable example of international cooperation is Pakistan's collaborative cluster (highlighted in green), which includes partnerships with countries such as Afghanistan, Brazil, China, Ethiopia, Ireland, Sweden, Jordan, Oman, Qatar, and the United States. This cluster accounts for 31.19% of all published articles. The next significant cluster, shown in blue and led by India, consists of collaborations with nine countries, contributing 95 articles or 30.55% of the total publications, featuring countries such as Australia, Bangladesh, Egypt, Malaysia, Mexico, Saudi Arabia, Taiwan, and the United Kingdom.
The research topic examining the impact of biostimulants on wheat over the past 25 years (2000–2024) has involved contributions from more than 200 affiliations. According to Table 8, the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR, India) stands out as the most prolific institution, having published 17 articles, garnered 556 citations, and achieved the H-index of 8 in this research area. Notably, 11.8% of the publications from this university involved international co-authorship. Pakistan and India emerged as leading contributors, each represented by three affiliated institutions.
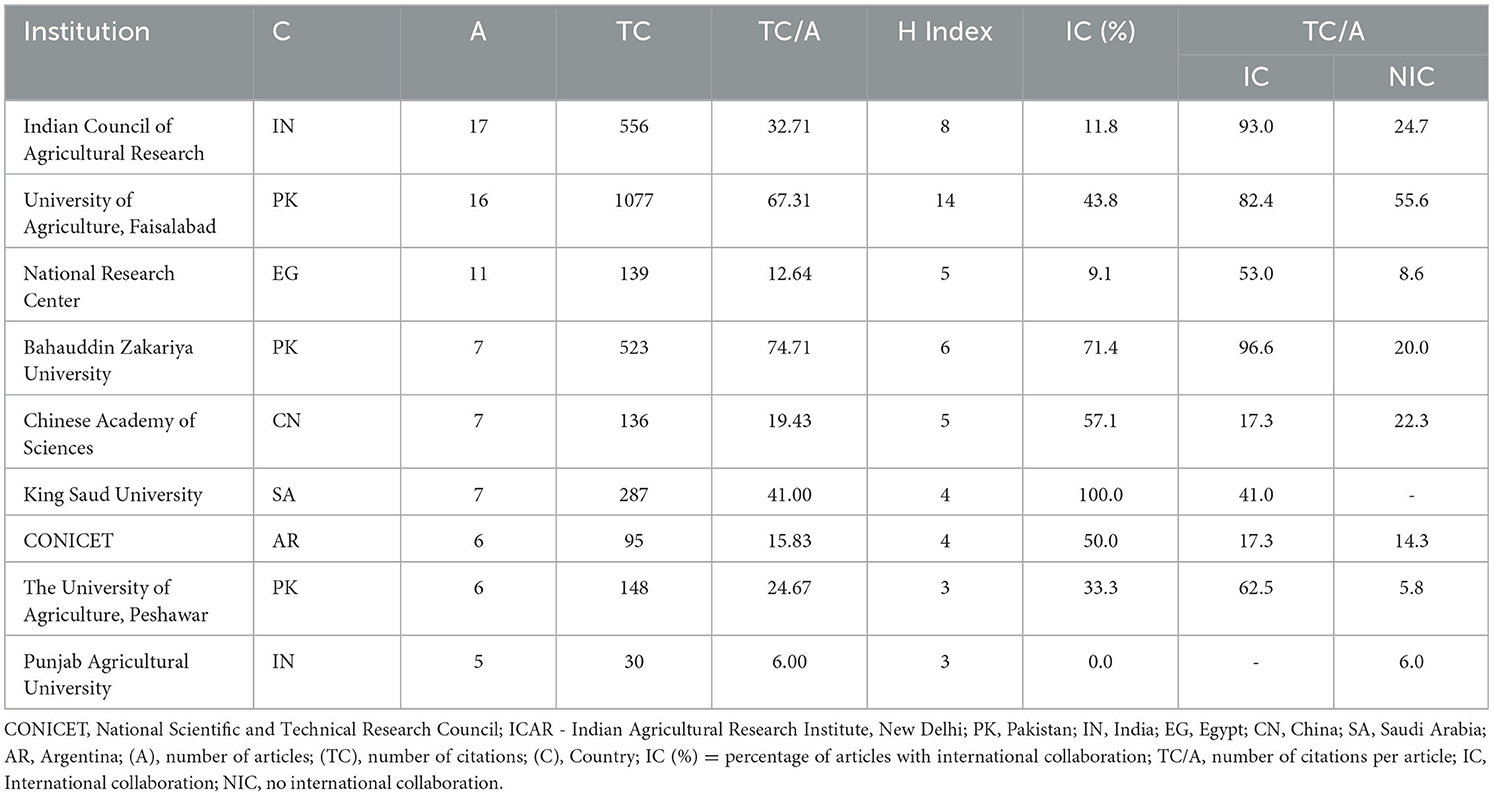
Table 8. Top 9 most productive affiliations on the effects of biostimulants on wheat from 2000 to 2024.
The University of Agriculture, Faisalabad (Pakistan) ranks second in output, with 16 publications achieving 1,077 citations and the highest H-index (16) in this field. This institution also demonstrates strong global engagement, with 43.8% of its publications involving international collaboration. Meanwhile, Bahauddin Zakariya University (Pakistan) claims third place in total citations (523) and leads in average citations per article (74.71), alongside a robust collaboration rate of 71.4% across five co-authored studies. In contrast, King Saud University in Saudi Arabia has an impressive collaboration rate of 100%, contributing seven articles, while Bahauddin Zakariya University in Pakistan maintains a substantial collaboration rate of 71.4%, reflected in five co-authored articles. In contrast, one prominent Indian institution, such as Punjab Agricultural University, did not engage in international collaboration (Table 8).
Importantly, except for one Argentine, one Indian, and one Chinese institution, all of the top nine most productive affiliations displayed higher citation rates per article when resulting from international collaborations, compared to articles without such partnerships (Table 8).
3.2.4 Document citation analysis
The top 10 most-cited publications in the research field of wheat response to biostimulants are depicted in Figure 6. Notably, 40% of these publications were disseminated through open-access journals. Collectively, these top 10 articles account for 33.53% of the total citations in the field, amounting to 6,150. The tenth most cited publication, titled “Mitigation of Salinity-Induced Negative Impact on the Growth and Yield of Wheat by Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria in Naturally Saline Conditions”, garnered 135 citations. The most highly cited publication is “Field Response of Wheat to Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi and Drought Stress”, with 316 citations, followed closely by “Biofortification of Wheat Through Inoculation of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria and Cyanobacteria”, which received 302 citations.
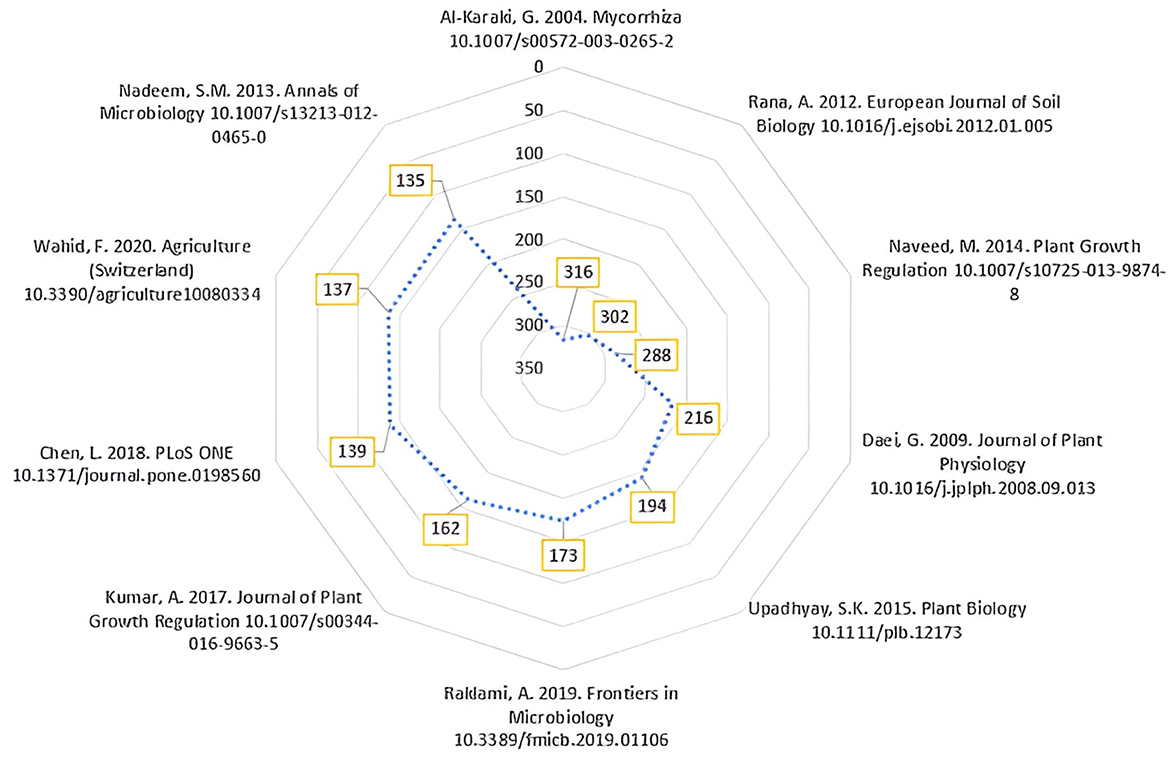
Figure 6. The top 10 cited articles in the wheat response to biostimulants research field. Authors of top 10 cited articles, publication year, journal, and DOI; Radar scale of number of citations. Source: Scival.
These top-cited publications span four key research themes, as categorized by SciVal. The first theme, “Plant Growth; Microorganism; Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria”, encompasses five of the top-cited works and investigates the various mechanisms through which bacteria enhance plant growth. This includes studies on the effects of bacterial interactions under biotic and abiotic stress, improvements in soil fertility, and responses to metal contamination. The second research theme, “Arbuscular Mycorrhiza; Antioxidant; Water Stress”, includes three highly cited articles. This theme explores how arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) bolster plant stress tolerance, particularly under conditions of salinity, drought, and water stress. It examines the influence of AMF on plant growth, nutrient absorption, antioxidant activity, and gene expression under diverse stressors.
The third theme, “Bacilli; Lipopeptide; Biological Control,” is represented by a single publication that focuses on the diverse roles of lipopeptides produced by Bacillus strains in agricultural contexts. It highlights the structural variety, biocontrol properties, production methods, and genomic aspects of these lipopeptides. The final theme, “Solubilization; Plant Growth; Soil Microbiology,” also includes one cited work. This research emphasizes the role of phosphorus solubilization in enhancing plant growth and yield. It covers studies on different phosphate sources, the effects of bacterial and fungal strains on nutrient uptake and root development, and the metabolic pathways involved in the solubilization of insoluble phosphorus. It also discusses the potential of bioinoculants in agricultural practices to boost crop productivity.
3.3 Term co-occurrence network analysis
Figure 7a presents a term co-occurrence network analysis based on 324 of the most relevant terms, each appearing at least thrice in the titles and abstracts of 222 articles. The network consists of 324 nodes, 3,995 links, and a total link strength of 20,519. In this network, each node represents a term, with its size indicating its frequency of appearance. Terms that frequently co-occur in literature are positioned proximally, forming clusters that reveal thematic relationships and distinct research areas in biostimulant studies.
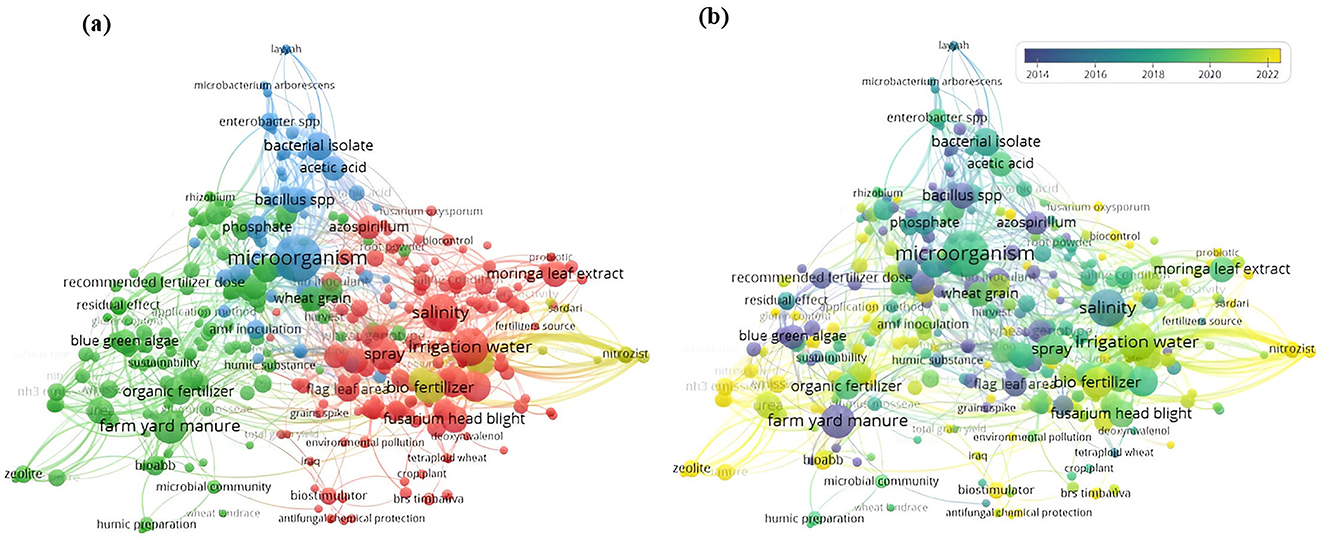
Figure 7. (a) Co-occurrence network visualization of the 324 most frequently occurring terms, each appearing at least three times across 222 articles. Color: represents a cluster of related terms (refer to the text for further explanation); Nodes: denote individual terms, with node size corresponding to term frequency; (b) Temporal evolution of the authors' terms on the research topic from 2014 to 2022. Source: VOSviewer (resolution 0.5; minimum cluster size 1; small clusters not merged).
This analysis reveals four primary clusters, each focused on a unique research theme in the field. Notably, the red cluster, with 144 terms, centers on Environmental Stress Tolerance in Wheat, marking it a “motor theme” due to its well-developed nature and relevance (Supplementary Table 1). This cluster explores how biostimulants enhance wheat's resilience to various environmental stresses, with frequent mention of terms like “salinity,” “disease severity”, and “irrigation water”(Supplementary Table 1). Key biostimulants, such as chitosan, moringa leaf extract, and seed coatings, are highlighted for their dual role in activating defense mechanisms and protecting against abiotic and biotic stresses, ultimately promoting yield stability and crop health in challenging conditions. Research in this area focuses on identifying biostimulant combinations that enhance wheat's ability to thrive in harsh environments, thus contributing to sustainable crop production.
The green cluster, which ranks second in term density with 121 terms, focuses on Sustainable Nutrient Management (Supplementary Table 1). It emphasizes optimizing nutrient availability and efficiency for wheat, which is crucial for sustainable agriculture. Frequently occurring terms, such as “farmyard manure,” “urea,” and “organic fertilizer,” indicate research into nutrient sources that enhance soil fertility while reducing dependence on synthetic inputs (Supplementary Table 1). This cluster also investigates the synergistic use of biostimulants with organic and inorganic fertilizers to improve nutrient uptake and assimilation, maximize yield, and reduce environmental impact. Sustainable nutrient management through biostimulants plays an essential role in maintaining long-term soil productivity, aligning with global goals for food security. This theme is classified as “fundamental and pertinent.”
Represented by blue and consisting of 48 terms, the third cluster explores Beneficial Microorganisms for Growth Promotion (Supplementary Table 1). This cluster focuses on the use of microbial biostimulants to enhance wheat growth, with terms like “microorganism,” “bacterial isolate,” “Bacillus spp.,” and “arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi” highlighting the role of beneficial microbes in improving nutrient availability and root health. These microorganisms promote phosphate uptake, root colonization, and nutrient cycling, fostering an environment conducive to wheat growth. Research in this area seeks to identify microbial strains that establish symbiotic relationships with wheat roots, boosting productivity and resilience. This theme is considered an “isolated theme” within biostimulant research.
Finally, the yellow cluster (comprised of 11 terms) focuses on Next-Gen Biostimulants for Root Structure (Supplementary Table 1). This underdeveloped and emerging area investigates advanced biostimulants aimed at promoting root architecture and enhancing water-use efficiency in wheat. Terms such as “biofertilizer,” “seaweed,” “mycorrhiza,” and “root volume” reflect interest in biostimulants that improve root structure, allowing wheat to access water and nutrients more effectively, particularly under dry or semi-arid conditions. Research on next-generation biostimulants, including seaweed extracts and root-focused formulations, emphasizes increasing the adaptability of wheat to moisture fluctuations and reducing irrigation needs. This theme is classified as a “marginal and underdeveloped” area but presents valuable potential for improving wheat productivity under resource-limited conditions.
In Figure 7b, we show how certain terms have changed in the co-occurrence network from 2014 to 2022. Before 2014, research focused on terms like “farmyard manure,” “blue green algae,” “arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi,” and “bio inoculant”. This indicates that earlier studies were centered on traditional organic methods and microbial inoculants to boost nutrient uptake and wheat productivity. These terms suggest that early research efforts were concentrated on fundamental biostimulant applications and basic fertility improvements.
After 2022, new terms like “bioabb,” “NH3 emission”, “biostimulator”, “bulk blend fertilizer,” and “supplementary irrigation” emerged. This shift points to a growing interest in advanced biostimulant formulations, better nutrient management, and reducing environmental impacts. The emergence of terms like “resilience,” “sodium silicate”, and “reactive oxygen species” shows a broader focus on making wheat more resilient to environmental stresses and optimizing its physiological processes in the field. This evolution highlights a trend toward more advanced and multifunctional biostimulants that not only promote growth but also enhance resilience and sustainability in wheat farming.
3.4 Co-cited reference network
In this study, we highlight how the co-cited reference technique complements term co-occurrence analysis to deepen our understanding of our research topic. The co-citation network includes 11,479 references from the 222 research subjects of the current study, covering the years from 2000 to 2024. This network contains 1,085 nodes, each representing an individual reference, and 3,653 links showing their co-citation relationships (Figure 8).
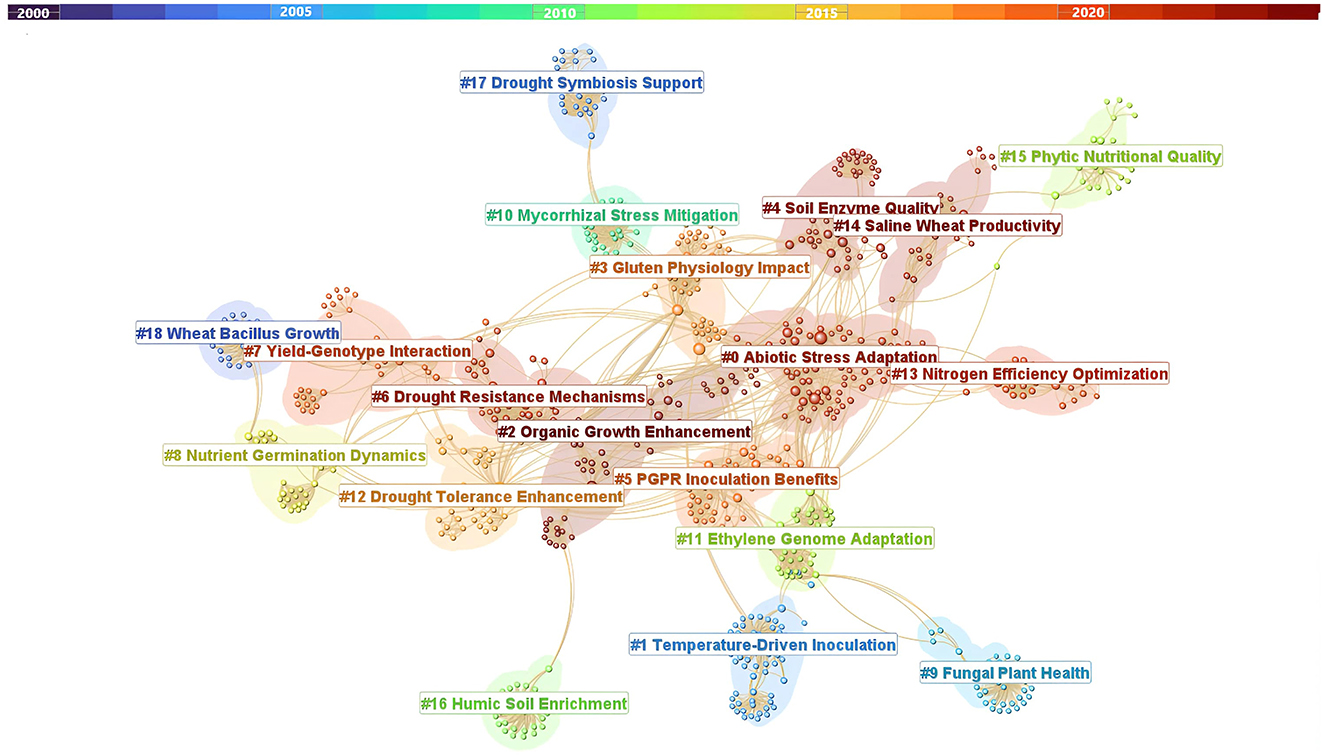
Figure 8. Co-cited reference network in wheat response to biostimulants under field conditions (2000–2024) with cluster labels. Node: represents reference articles (node size based on the total citation of the references); Colors: represent the temporal orders of co-occurrence links between reference articles. Modularity Q index = 0.903, mean silhouette score (S) = 0.948. Source: CiteSpace (Configuration LRF = 3, LBY = 1, e = 1.0 g index (k = 50). Network = 1,085 nodes and 3,653 co-citation links).
Table 9 lists the top 10 most frequently cited references, with only three directly related to biostimulants. Among them, the review by Calvo et al. (2014), titled “Agricultural uses of plant biostimulants,” stands out with 10 citations, making it the fifth most cited reference. In eighth place, “Plant biostimulants: definition, concept, main categories, and regulation” by du Jardin (2015) has 8 citations, followed by Adesemoye et al. (2009), “Plant growth-promoting Rhizobacteria allow reduced application rates of chemical fertilizers,” with 7 citations.
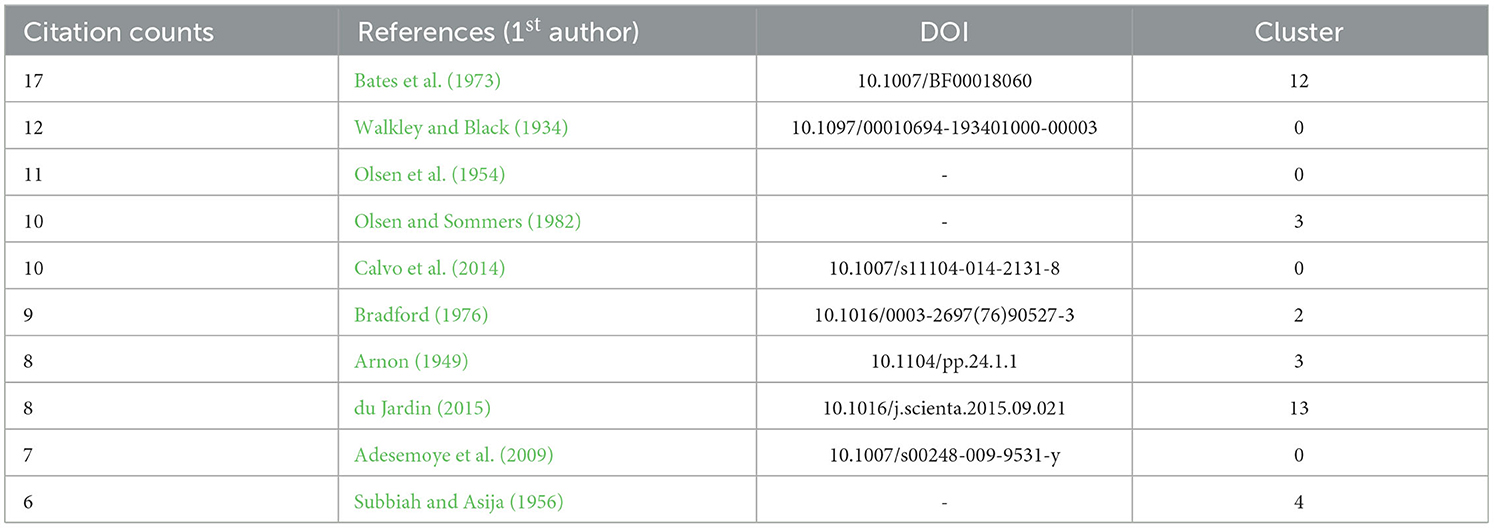
Table 9. The top 10 most co-cited references in the wheat response to biostimulants research field from 2000 to 2024.
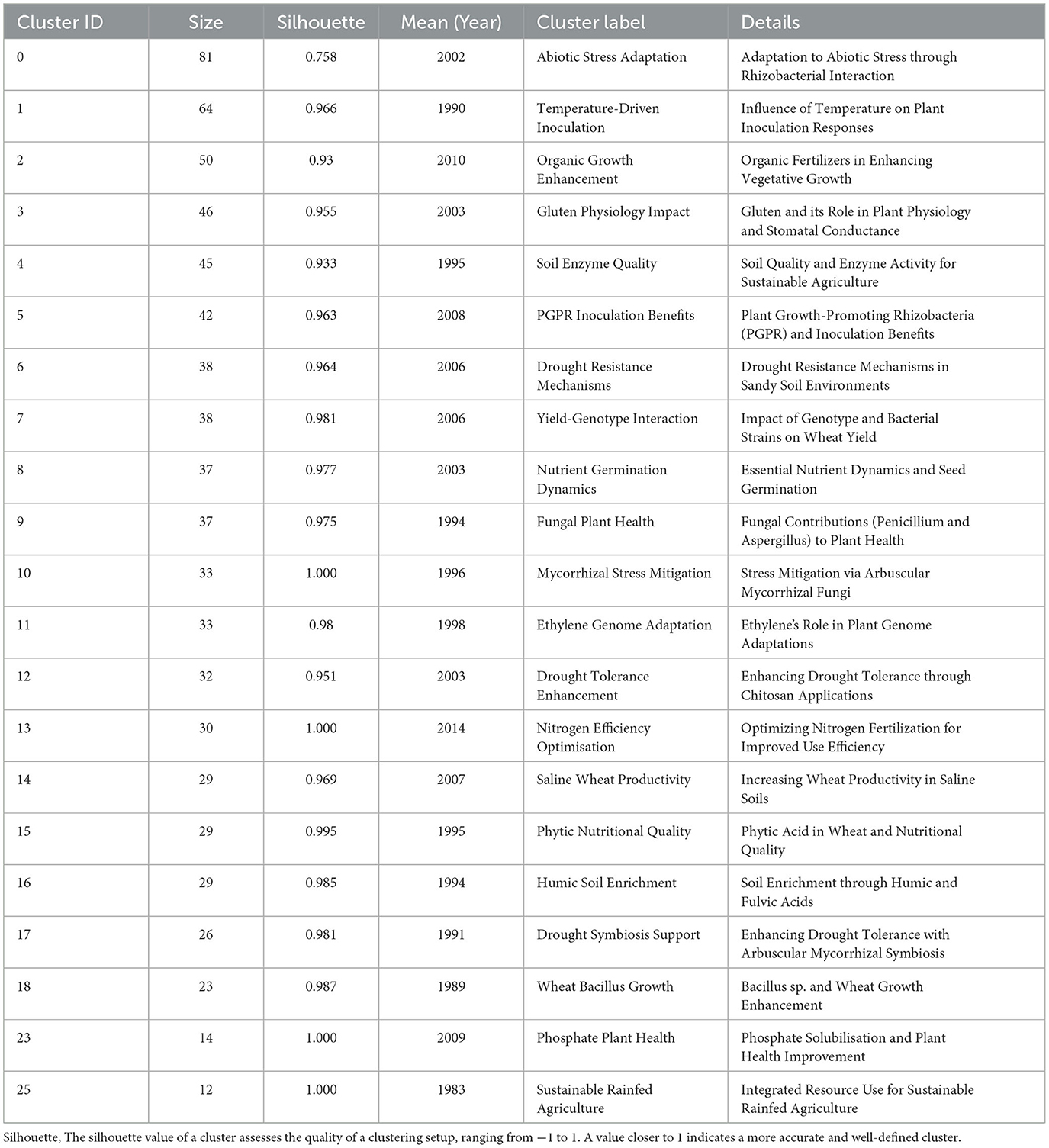
The co-cited reference network identified 21 unique research areas in the field of biostimulants (Figure 8). Figure 8 displays the top 19 clusters while Table 10 provides detailed metrics for each cluster, including size, silhouette values (which indicate clustering quality), and the average duration of research activity in years.
Among the 21 clusters shown in Figure 8 and Table 10, Cluster #0, titled “Adaptation to Abiotic Stress through Rhizobacterial Interaction,” is the largest, containing 81 references and a silhouette score of 0.758, which indicates a diverse mix of biostimulant citations. The average publication year for this cluster is 2002. Cluster #1, titled “Influence of Temperature on Plant Inoculation Responses,” includes 64 references with a notably high silhouette score of 0.966, reflecting strong internal cohesion, with an average publication year of 1990. The third largest cluster, “Organic Fertilizers in Enhancing Vegetative Growth,” comprises 50 references, averaging the publication year of 2010. This cluster, along with others with high silhouette scores, represents well-defined and cohesive scientific communities frequently citing each other's work.
Table 10 highlights smaller clusters like Cluster #23 and Cluster #25, which, while high in silhouette scores, are relatively minor in their impact on our main research focus. Cluster #23 emphasizes how biostimulants improve phosphorus availability through phosphate solubilization, supporting wheat growth and resilience. Cluster #25 addresses sustainable resource use in rainfed agriculture, emphasizing efficient water and nutrient management. Together, these clusters contribute to our understanding of nutrient optimization and sustainable practices, guiding effective biostimulant use to enhance wheat performance in practical, field-based conditions.
4 Discussion
According to the findings of a quantitative analysis reveals a significant rise in the number of studies published on our research topic over the past 5 years (2020-2024). The increasing research interest in biostimulants aligns with major international initiatives promoting sustainable agriculture, climate resilience, and reduced chemical dependency. Programs such as the European Green Deal and Farm to Fork Strategy (European Commission, 2020) emphasize the reduction of chemical inputs, supporting biostimulants as eco-friendly alternatives. Similarly, the UN Food Systems Summit (United Nations, 2021) and the FAO's Sustainable Plant Production Framework (FAO, 2022) recognize biostimulants as critical tools for enhancing crop resilience, soil health, and nutrient efficiency. Additionally, international climate conferences such as COP26 and COP27 have stressed the need for climate-adaptive agricultural practices, further accelerating biostimulant research. Moreover, disruptions in global fertilizer supply chains have highlighted the urgency of finding alternatives to synthetic fertilizers, reinforcing the role of biostimulants in sustainable wheat production and reducing environmental impact. These global initiatives underscore the relevance of biostimulants in ensuring food security and advancing sustainable farming systems, thus driving further research and innovation in the field. Regarding their role in crop production, biostimulants primarily act as complements rather than direct alternatives to chemical fertilizers by improving nutrient use efficiency, plant physiological responses, and stress tolerance. Unlike fertilizers, which supply essential nutrients, biostimulants enhance nutrient uptake, root development, and microbial interactions, enabling crops to optimize available resources. However, in specific contexts, biostimulants can partially or fully replace fertilizers. For example, in nutrient-rich soils, biostimulants reduce the need for high fertilizer applications by improving nutrient assimilation. In organic farming systems, biostimulants such as humic substances, seaweed extracts, and microbial inoculants can sustain plant growth without synthetic fertilizers. In addition, in low input farming systems, they can be useful for reducing chemical fertilizer dose without negatively affecting plant growth and yield. Additionally, under abiotic stress conditions (e.g., drought, salinity, extreme temperatures), biostimulants help maintain crop productivity by modulating stress-related physiological pathways. Therefore, while biostimulants alone may not fully replace fertilizers in intensive farming systems, they significantly reduce fertilizer dependency, promote sustainable agriculture, and contribute to environmentally responsible crop production.
However, despite the considerable rise in the number of articles published in recent years, the average citations per article remain low. This phenomenon can be attributed to several factors, including heightened competition among researchers. With the increase in the volume of published articles, the pool of potential citations per article also expands, thereby complicating the ability of any single work to garner a substantial number of citations. Additionally, as research areas become more specialized, scholars tend to cite fewer articles, focusing mainly on those that are most relevant to their specific subfields. This creates smaller and more focused citation networks. It's important to note that a decrease in the number of citations per article doesn't mean the research is of lower quality or less important. Instead, it shows changes in how researchers communicate and the growing size of the research community.
The bibliometric indicators also reveal the increasing significance of this field over the past 25 years. This momentum underscores the critical role of biostimulant research in addressing pressing agricultural and environmental challenges, particularly in the early decades of the 21st century. The distribution of scientific literature further highlights the concentration of key research in a limited number of core journals, as outlined by Bradford's Law (1976). This law describes the asymmetrical distribution of scientific output, where a small number of journals contain most of the relevant research, while a larger number of journals contribute fewer pertinent articles. This concept is crucial for understanding how research findings are disseminated in academic fields (Yeung et al., 2017). Over the past 25 years, 11 journals were identified as the core sources for wheat's response to biostimulants, with other journals publishing less frequently on this topic.
Evaluating these core journals requires attention to their trustworthiness and reliability. According to Sorenson (2016), this is a critical step in bibliometric studies. In 2023, 55% of the top 11 journals in this field were ranked in the first quartile (Q1) of the SCImago Journal Rank (SJR), indicating high scientific credibility. The remaining 45% were distributed across quartiles Q2 to Q4. This diversity in journal rankings reflects a range of research interests and methodologies within the field. While higher-ranked journals may publish more influential or generalizable studies, lower-ranked journals often offer niche perspectives, emerging trends, and unique insights that might not be covered elsewhere. Consequently, readers are encouraged to explore a wide range of journals to gain a holistic understanding of wheat's response to biostimulants, capturing valuable contributions from diverse academic sources.
Asian scholars and institutions have played a leading role in this field, contributing 59.4% of all academic publications over the past 25 years. These contributions have garnered the highest total number of citations (2,496), equivalent to 40.84% of the total citations received within this timeframe. This dominance can be attributed to Asia's significant agricultural output, environmental challenges, and the growing emphasis on sustainable farming practices. These nations are among the world's top wheat producers, with India ranking the second-largest wheat producer globally, following China (Pérez-Pérez et al., 2024). This significant agricultural output necessitates continuous research into innovative methods to improve yield and ensure long-term sustainability. The extensive scale of wheat production in these countries has created a demand for advanced agricultural practices, including the use of biostimulants, considered essential for enhancing crop productivity and resilience (Kumar and Urmila, 2018).
These regions are affected by environmental challenges, such as drought and heavy metal contamination, making the exploration of biostimulants particularly valuable (Fakhar et al., 2022; Radzikowska-Kujawska et al., 2022; Sellami and Terribile, 2023). Research efforts are heavily focused on improving wheat's tolerance to these stressors, which is critical for maintaining food security vis-a-vis climate variability (Fakhar et al., 2022; Radzikowska-Kujawska et al., 2022). There is also a growing emphasis on sustainable agriculture, with an increasing need for eco-friendly inputs to reduce dependency on chemical fertilizers and pesticides (Arshad and Iqbal, 2022). Biostimulants are considered a viable alternative, promoting plant growth and resilience while supporting global shifts toward more sustainable and environmentally responsible farming practices (Yahya et al., 2022).
Further, research and development are advancing rapidly in these countries, with the integration of cutting-edge techniques such as metabolomics to study the effects of biostimulants on wheat (Hamade et al., 2024).
Despite Asia's leadership in publication output, the international impact of research on wheat's response to biostimulants remains constrained. Limited global collaboration and regional focus often restrict the international visibility of these studies. Factors such as inadequate funding for cross-border research projects and challenges in publishing in high-impact journals further obstruct the global reach of Asian research outputs. Additionally, the rigorous standards of high-impact journals, coupled with resource constraints, make it challenging for some researchers to publish work that meets international expectations. These barriers highlight the need for greater investment in collaborative research initiatives and equitable access to high-impact publication platforms.
Although Asia currently leads this research field, there is a growing global interest in biostimulants, with other regions beginning to recognize their potential to address agricultural challenges. This trend portends the emergence of a more balanced distribution of research efforts in the future as interest and investment in sustainable agricultural practices increase worldwide.
The term co-occurrence analysis provides a quantitative and systematic approach to examine, interpret, and visualize the organization and content of academic literature (Lin et al., 2020; Zhou et al., 2022). It enables researchers to identify patterns and insights in extensive collections of scholarly work, aiding in knowledge discovery (Sedighi, 2016). In fields such as wheat response to biostimulants, where the volume of research has grown significantly in recent years, this tool is invaluable for organizing and understanding complex information. The strength of term co-occurrence analysis lies in its ability to deliver a broad, unbiased, and thorough examination of textual content, making it highly effective for uncovering the conceptual structure in a research area (Jalal, 2019; Kirtania, 2023). This approach enables researchers to detect emerging trends and grasp the semantic relationships between concepts, which are essential for comprehensive bibliometric studies (Zhou et al., 2022; Kirtania, 2023). Through term co-occurrence analysis, researchers can reveal complex connections and observe thematic developments over time, deepening their understanding of the evolution and future directions in fields like wheat biostimulant research.
Early studies in our field of research focused on traditional organic methods and microbial inoculants, as evidenced by terms such as “farmyard manure,” “blue-green algae,” and “arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi.” Over time, research shifted to more contemporary topics, including “biostimulator,” “NH3 emission,” and “supplementary irrigation,” reflecting advances in biostimulant formulations and nutrient management and reducing environmental impacts. More recently, terms like “resilience,” “sodium silicate,” and “reactive oxygen species” indicate a focus on enhancing wheat's resilience to environmental stressors and optimizing its physiological responses. This progression illustrates the field's trajectory toward multifunctional biostimulants that integrate growth promotion, stress tolerance, and environmental sustainability.
While term co-occurrence analysis reveals how themes are connected by tracking how often specific terms appear together, the co-cited reference technique examines the relationships between studies frequently cited together and helps us identify influential studies in the field (Trujillo and Long, 2018). By examining these co-citation patterns, we can find clusters of related research topics and see studies that have significantly shaped our area of research. This approach also reveals gaps in current research, pointing to areas where further investigation could be valuable. Together, the co-cited reference technique and term co-occurrence analysis provide a clearer view of the key studies and ideas driving advances in soil health research, enriching our understanding of the field's structure and evolution (Chen, 2006).
The modularity Q and mean silhouette scores are essential metrics for analyzing the network's structural characteristics. Modularity Q, as explained by Chen et al. (2010), measures the extent to which a network can be divided into distinct groups, indicating the clarity of the network's overall structure. On the other hand, the mean silhouette score assesses the quality and internal consistency of each cluster. In our analysis, we found a modularity Q value of 0.903, suggesting a well-defined separation between clusters with minimal overlap. The high silhouette score of 0.948 shows that, on average, these clusters are internally consistent and cohesive (Figure 8). Numerous research fields are highly isolated from one another. The number of clusters, in this case, was determined to be 21, indicating that the diversity of research topics in biostimulants reflect changing research interests and focus over time.
The cluster analysis highlights key trends in wheat-biostimulant research, with a strong focus on abiotic stress adaptation, drought tolerance, nutrient optimization, and overall plant health. The potential of mycorrhizal fungi, PGPR, and other biostimulants like chitosan, silicon, and algae in supporting plant growth, resilience, and nutrient uptake is well recognized. However, a significant research gap persists in understanding the combined effects of multiple biostimulants, their long-term impacts on soil ecosystems, and the best strategies for maximizing wheat productivity and sustainability.
The evolution of research themes in our research topic reflects a dynamic shift in focus over the past two decades, showcasing the field's progression toward addressing increasingly complex agricultural challenges. Early investigations (2000–2004) predominantly centered on the effects of individual biostimulants, such as arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, Penicillium chrysogenum, and microbial inoculants like Bacillus spp., on plant health and nutrient uptake. These studies provided foundational insights into the role of specific biostimulants in enhancing crop performance.
In recent years (2020–2024), research has broadened to explore the integrated use of multiple biostimulants to tackle complex challenges. This includes investigating biostimulant effects on wheat quality (such as gluten content), optimizing yield for specific genotypes, and enhancing plant resilience to various stresses. Recent studies also emphasize using biostimulants to mitigate drought and salinity stress by improving plant water-use efficiency and nutrient uptake. This shift signals a deeper understanding of biostimulants' potential to boost wheat productivity and sustainability vis-a-vis increasing environmental pressures. By unraveling the complex interactions among biostimulants, plant physiology, and soil microbiome, researchers aim to develop innovative strategies for optimized wheat production and enhance food security in a changing climate.
5 Conclusions
Over the past few decades, the study of biostimulants in wheat cultivation has garnered significant attention in both political and scientific fields. Our findings reveal several key areas where biostimulants have shown substantial impact, including enhancing wheat's ability to cope with abiotic stress, optimizing nutrient uptake, and promoting overall plant health. Studies have demonstrated that mycorrhizal fungi, PGPR, and other biostimulants such as chitosan and algae can significantly improve wheat growth by enhancing nutrient uptake and helping plants withstand stress factors like drought and salinity. This trend reflects a broader shift toward more sustainable agricultural practices that reduce reliance on chemical inputs, aligning with global efforts to promote environmentally responsible food production.
However, this study has some limitations in the current research landscape and points to important gaps for future work. Notably, most studies focus on individual biostimulants, whereas the effects of combined or sequential biostimulant applications remain underexplored. Though these combinations could offer synergistic benefits, their impacts on soil health, microbial communities, and long-term crop productivity are not well understood. Many studies are also of limited duration, making it difficult to assess the full lifecycle impact of biostimulants on soil ecosystems and nutrient cycles.
Another area for future exploration is the development of standardized protocols for biostimulant application under field conditions. Variability in application methods, dosages, and timing can lead to inconsistent results, underscoring the need for optimized guidelines that consider local environmental factors and crop requirements. Further, advancing our understanding of biostimulants' interactions with the soil microbiome could lead to innovations in product formulation and application techniques, enhancing biostimulant efficacy and sustainability.
Future research should also consider the economic feasibility of biostimulant use, especially for small farmers in regions facing severe environmental stresses. Studies that integrate field-based research with economic assessments can identify effective and accessible biostimulant practices. Addressing these research gaps and optimizing biostimulant use is essential for maximizing wheat productivity and resilience in a changing climate, contributing to global food security and sustainable agriculture.
Author contributions
MHS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. IDM: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. MM: Methodology, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fsufs.2025.1543981/full#supplementary-material
References
Aburri, N. S. (2022). Effects of a New Biostimulant on Vegetational Indexes, Yield and Quality in Common Wheat (dissertation/master's thesis). [Padova (IT)]: University of Padova.
Adesemoye, A. O., Torbert, H. A., and Kloepper, J. W. (2009). Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria allow reduced application rates of chemical fertilizers. Microb. Ecol. 58, 921–929. doi: 10.1007/s00248-009-9531-y
Arnon, D. I. (1949). Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 24, 1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1
Arshad, N., and Iqbal, M. S. (2022). Improving morphological and biochemical characters, yield attributes and aphid mortality in wheat (Triticum aestivum l.) by biostimulants. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 20, 5103–5123. doi: 10.15666/aeer/2006_51035123
Ayed, S., Bouhaouel, I., Jebari, H., and Hamada, W. (2022). Use of biostimulants: towards sustainable approach to enhance durum wheat performances. Plants. 11:133. doi: 10.3390/plants11010133
Bates, L. S., Waldren, R. P., and Teare, I. D. (1973). Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil. 39, 205–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00018060
Bin Safdar, L., Foulkes, J., Kleiner, F. H., Searle, I., Bhosale, R., Fisk, I. D., et al. (2023). Challenges facing sustainable protein production: opportunities for cereals. Plant Commun. 4, 100716–100716. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2023.100716
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999
Calvo, P., Nelson, L., and Kloepper, J. W. (2014). Agricultural uses of plant biostimulants. Plant Soil. 383, 3–41. doi: 10.1007/s11104-014-2131-8
Campos-Avelar, I., Montoya-Martínez, A. C., Villa-Rodríguez, E. D., Valenzuela-Ruiz, V., Ayala Zepeda, M., Parra-Cota, F. I., et al. (2023). The mitigation of phytopathogens in wheat under current and future climate change scenarios: next-generation microbial inoculants. Sustainability 15:15250. doi: 10.3390/su152115250
Chen, C. (2006). CiteSpace II: detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. JASIST. 57, 359–377. doi: 10.1002/asi.20317
Chen, C., Ibekwe-SanJuan, F., and Hou, J. (2010). The structure and dynamics of co- citation clusters: a multiple-perspective co-citation analysis. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 61, 1386–1409. doi: 10.1002/asi.21309
Corsi, S., Ruggeri, G., Zamboni, A., Prinsi, B., Espen, L., Ferrante, A., et al. (2022). A bibliometric analysis of the scientific literature on biostimulants. Agronomy 12, 1257–1257. doi: 10.3390/agronomy12061257
Davidson, P. (2024). Plant biostimulant state regulatory update. Available online at: https://www.bpia.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/AAPFCO-Biostimulant-Update-.pdf (accessed October 31, 2024).
Deswal, K., Munjal, R., and Swami, P. (2023). “Wheat's radiation stress response and adaptive mechanisms,” in Abiotic Stresses in Wheat, eds. M. K. Khan, A. Pandey, M. Hamurcu, O. P. Gupta, Sait Gezgin (London, United Kingdom: Academic Press), 283–295. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-95368-9.00008-4
du Jardin, P. (2015). Plant biostimulants: definition, concept, main categories and regulation. Sci. Hortic. 196, 3–14. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2015.09.021
Dyadiuchenko, L., Taranenko, V., Muraviev, V., and Dmitrieva, I. (2020). The study of natural essential oils as growth regulators of winter wheat. BIO Web Conf. 21:00023. doi: 10.1051/bioconf/20202100023
European Commission (2019). Regulation (EU) 2019/1009 of the European parliament and of the council laying down rules on making available on the market of EU fertilizing products and amending regulations (EC) no 1069/2009 and (EC) no 1107/2009 and repealing regulation (EC) no 2003/2003. Available online at: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32019R1009andrid=1 (accessed October 31, 2024).
European Commission (2020). Farm to fork strategy. Available online at: https://food.ec.europa.eu/horizontal-topics/farm-fork-strategyen (accessed October 31, 2024).
Fakhar, A., Gul, B., Rafique, M., and Ortas, I. (2022). “Use of biostimulants to increase heavy metal tolerance in cereals,” in Sustainable Remedies for Abiotic Stress in Cereals, ed. A. A. H. Abdel Latef (Singapore: Springer), 575–598. doi: 10.1007/978-981-19-5121-3_22
FAO (2022). Global conference on sustainable plant production. FAOEvents. Available online at: https://www.fao.org/events/detail/global-conference-on-sustainable-plant-production/en (accessed October 31, 2024).
Gallegos-Cedillo, V. M., Nájera, C., Signore, A., Ochoa, J., Gallegos, J., Egea-Gilabert, C., et al. (2024). Analysis of global research on vegetable seedlings and transplants and their impacts on product quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 104, 4950–4965. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.13309
Gooding, M. J. (2023). “Wheat”, in ICC Handbook of 21st Century Cereal Science and Technology, eds. P. R., Shewry, H. Koksel, R. N. John (Taylor, Academic Press, London, United Kingdom), 121–130. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-95295-8.00027-7
Hamade, K., Fliniaux, O., Fontaine, J.-X., Molinié, R., Petit, L., Mathiron, D., et al. (2024). NMR and LC-MS-based metabolomics to investigate the efficacy of a commercial bio stimulant for the treatment of wheat (Triticum aestivum). Metabolomics. 20:58. doi: 10.1007/s11306-024-02131-0
Jalal, S. K. (2019). Co-authorship and co-occurrences analysis using bibliometrix r-package: a case study of India and Bangladesh. Ann. Lib. Inf. Stud. (ALIS) 66, 57–64.
Kibret, M., Devkota, K. P., Ben Bakrim, W., Ezzariai, A., Terefe, H., Karouach, F., et al. (2024). Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria mitigate drought and salinity stresses, and improve the physiological and agronomic performances in crops: a systematic review. Cab Rev. Perspect. Agric. Vet. Sci. Nutr. Nat. Resour. 19. doi: 10.1079/cabireviews.2024.0025
Kirtania, D. K. (2023). Network visualization of ChatGPT research: a study based on term and keyword co-occurrence network analysis. SSRN Electron. J. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.4406624
Kumar, A., and Urmila (2018). Impact of biofertilizers in enhancing growth and productivity of wheat: A review. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 6, 360–362.
Lamlom, S. F., Irshad, A., and Mosa, A. (2023). The biological and biochemical composition of wheat (Triticum aestivum) as affected by the bio and organic fertilizers. BMC Plant Biol. 23:111. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04120-2
Lau, S.-E., Wei, L., Hamdan, M. F., Chan, C., Saidi, N. B., Ong-Abdullah, J., et al. (2025). Enhancing plant resilience to abiotic stress: the power of biostimulants. Phyton 94, 1–10. doi: 10.32604/phyton.2025.059930
Lin, M., Chen, Y., and Chen, R. (2020). Bibliometric analysis on pythagorean fuzzy sets during 2013–2020. Int. J. Intell. Comput. Cybern. 14, 104–121. doi: 10.1108/IJICC-06-2020-0067
Ma, Y., Freitas, H., and Dias, M. C. (2022). Strategies and prospects for biostimulants to alleviate abiotic stress in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 13:1024243. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1024243
Maignan, V., Bernay, B., Géliot, P., and Avice, J.-C. (2020). Biostimulant effects of glutacetine® and its derived formulations mixed with n fertilizer on post-heading n uptake and remobilization, seed yield, and grain quality in winter wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 11:607615. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.607615
Maignan, V., Géliot, P., and Avice, J.-C. (2021). Glutacetine® biostimulant applied on wheat under contrasting field conditions improves grain number leading to better yield, upgrades n-related traits and changes grain ionome. Plants. 10:456. doi: 10.3390/plants10030456
Marta, A. E., Slabu, C., Covasa, M. M., Motrescu, I., and Jitareanu, C. D. (2023). Comparative analysis of the influence of different biostimulators on the germination and sprouting behaviour of four wheat varieties. J. Appl. Life Sci. Environ. 55, 377–390. doi: 10.46909/alse-554071
Meena, D. C., Birthal, P. S., and Kiran, M. (2025). Biostimulants for sustainable development of agriculture: a bibliometric content analysis. Discover Agric. 3:2. doi: 10.1007/s44279-024-00149-5
Miranda, A. M., Hernandez-Tenorio, F., Villalta, F., Vargas, G. J., and Sáez, A. A. (2024). Advances in the development of biofertilizers and biostimulants from microalgae. Biology 13, 199–199. doi: 10.3390/biology13030199
Moreno-Moraga, A., Sánchez-Rodríguez, A. R., Guerrero-Criado, J. J., González-Sánchez, E. J., and Márquez-García, F. (2024). Amino acids and slow-release urea based biostimulants to enhance yield and grain quality on durum wheat under no-tillage in a semi-arid region. SSRN. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.4853719
Olsen, S., Cole, C., Watanabe, F., and Dean, L. (1954). Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. Circ. U S Dep. Agric. 939, 1–18.
Olsen, S. R., and Sommers, L. E. (1982). “Phosphorus”, in Methods of Soil Analysis Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties, ed. A. L. Page (Madison: American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America), 403–430. doi: 10.2134/agronmonogr9.2.2ed.c24
Pérez-Pérez, M., Ribeiro, M., Fdez-Riverola, F., and Igrejas, G. (2024). Insights into wheat science: a bibliometric review using unsupervised machine learning techniques. J. Cereal Sci. 118, 103960–103960. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2024.103960
Popko, M., Michalak, I., Wilk, R., Gramza, M., Chojnacka, K., and Górecki, H. (2018). Effect of the new plant growth biostimulants based on amino acids on yield and grain quality of winter wheat. Molecules 23:470. doi: 10.3390/molecules23020470
Pullin, A. S., Frampton, G., Livoreil, B., and Petrokofsky, G. (2022). Guidelines and standards for evidence synthesis in environmental management: version 5.1. Available online at: https://environmentalevidence.org/information-for-authors/ (accessed October 10, 2024).
Radzikowska-Kujawska, D., John, P., Piechota, T., Nowicki, M., and Kowalczewski, P. Ł. (2022). Response of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum l.) to selected biostimulants under drought conditions. Agriculture 13:121. doi: 10.3390/agriculture13010121
Rizwan, M., Aman, M. K., Haider, M. J., Hafiz; Saqib, M., and Malik, A. (2024). Wheat under pressure: assessing the influence of climate change on Pakistan's agricultural landscape. Authorea. doi: 10.22541/au.171142989.95052132/v1
Salinas-Ríos, K., and García López, A. J. (2022). Bibliometrics, a useful tool within the field of research. J. Basic Appl. Psychol. Res. 3, 9–16. doi: 10.29057/jbapr.v3i6.6829
Sedighi, M. (2016). Application of word co-occurrence analysis method in mapping of the scientific fields (case study: the field of Informetrics). Libr. Rev. 65, 52–64. doi: 10.1108/LR-07-2015-0075
Sellami, M. H., and Terribile, F. (2023). Research evolution on the impact of agronomic practices on soil health from 1996 to 2021: a bibliometric analysis. Soil Syst. 7:78. doi: 10.3390/soilsystems7030078
Servalesa (2023). Biostimulants, the key for modern agriculture. Available online at: https://servalesa.com/en/biostimulants-the-key-for-modern-agriculture/ (accessed October 31, 2024).
Shahrajabian, M. H., Chaski, C., Polyzos, N., and Petropoulos, S. A. (2021). Biostimulants application: a low input cropping management tool for sustainable farming of vegetables. Biomolecules. 11:698. doi: 10.3390/biom11050698
Shiferaw, B., Smale, M., Braun, H.-J., Duveiller, E., Reynolds, M., and Muricho, G. (2013). Crops that feed the world 10, past successes and future challenges to the role played by wheat in global food security. Food Secur. 5, 291–317. doi: 10.1007/s12571-013-0263-y
Soares, S., Pérez-Gregorio, R., Vilaça, R., Carvalho, S. M. P., Izs,ó, T., and Kasza, G. (2024). Microbiomes for the future of sustainable wheat production. Open Access Gov. 43, 398–399. doi: 10.56367/OAG-043-11507
Sorenson, M. E. (2016). Beyond the Google search bar: evaluating source credibility in contemporary research. Commun. Teach. 30, 82–86. doi: 10.1080/17404622.2016.1139150
Statista (2024). World wheat production by country 2018/2019. Available online at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/237912/global-top-wheat-producing-countries/ (accessed November 5, 2024).
Subbiah, B. V., and Asija, G. L. (1956). A rapid procedure for the estimation of available nitrogen in soils. Current Sci. 25, 259–260.
Tanveer, Y., Yasmin, H., Nosheen, A., Farah, M. A., and Altaf, M. M. (2024). Synergizing Bacillus halotolerans, Pseudomonas sihuiensis and Bacillus atrophaeus with folic acid for enhanced drought resistance in wheat by metabolites and antioxidants. BMC Plant Biol. 24:1003. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05609-0
Trujillo, C. M., and Long, T. M. (2018). Document co-citation analysis to enhance transdisciplinary research. Sci. Adv. 4:e1701130. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1701130
United Nations (2021). Food systems summit 2021 EN. Available online at: https://www.un.org/en/food-systems-summit (accessed November 5, 2024).
Van Eck, N. J., and Waltman, L. (2009). How to normalize co-occurrence data? An analysis of some well-known similarity measures. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 60, 1635–1651. doi: 10.1002/asi.21075
Vardell, E., Feddern-Bekcan, T., and Moore, M. (2011). SciVal experts: a collaborative tool. Med. Ref. Serv. Q. 30, 283–294. doi: 10.1080/02763869.2011.603592
Walkley, A., and Black, I. A. (1934). An examination of the degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 37, 29–38. doi: 10.1097/00010694-193401000-00003
Wang, X., Cui, C., Xu, M., Cheng, B., and Zhuang, M. (2024). Key technologies improvements promote the economic-environmental sustainability in wheat production of China. J. Clean. Prod. 443:141230. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.141230
Yahya, M., Rasul, M., Sarwar, Y., Suleman, M., Tariq, M., Hussain, S. Z., et al. (2022). Designing synergistic biostimulants formulation containing autochthonous phosphate-solubilizing bacteria for sustainable wheat production. Front. Microbiol. 13:889073. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.889073
Yeung, A. W. K., Goto, T. K., and Leung, W. K. (2017). The changing landscape of neuroscience research, 2006–2015: a bibliometric study. Front. Neurosci. 11:120. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00120
Zhou, X., Zhou, M., Huang, D., and Cui, L. (2022). A probabilistic model for co-occurrence analysis in bibliometrics. J. Biomed. Inform. 128:104047. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2022.104047
Keywords: biostimulants, wheat, bibliometric analysis, sustainable agriculture, environmental stresses
Citation: Sellami MH, Di Mola I and Mori M (2025) Evaluating wheat response to biostimulants: a 25-year review of field-based research (2000–2024). Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1543981. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1543981
Received: 12 December 2024; Accepted: 10 March 2025;
Published: 28 March 2025.
Edited by:
Boon Chin Tan, University of Malaya, MalaysiaReviewed by:
Zina Flagella, University of Foggia, ItalyStefania Astolfi, University of Tuscia, Italy
Dinesh Meena, National Institute for Agricultural Economics and Policy Research (NIAP), India
Copyright © 2025 Sellami, Di Mola and Mori. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ida Di Mola, aWRhLmRpbW9sYUB1bmluYS5pdA==
 Mohamed Houssemeddine Sellami
Mohamed Houssemeddine Sellami Ida Di Mola
Ida Di Mola Mauro Mori
Mauro Mori