- 1College of Applied Technology, Shenyang University, Shenyang, China
- 2Shengyang Polytechnic College, Shenyang, China
- 3Department of Economics and Management, Shenyang Agricultural University, Shenyang, China
Enhancing farmers’ well-being is a key focus in China’s “Three Rural Issues” (agriculture, rural areas, and farmers) work. Exploring the impact of nature reserve establishment on the subjective well-being of surrounding farmers is of great significance for creating a better and happier life for farmers. By constructing a theoretical framework of “Nature Reserve—Ecological Awareness— Multidimensional Well-being,” and based on survey data from 1002 farmers inside and outside six nature reserves in Liaoning Province, China, this study uses benchmark regression models and mediating effect models to investigate the impact of nature reserve establishment on the multidimensional well-being of surrounding farmers. The research results indicate that the establishment of nature reserves has a significant positive impact at the 5% statistical level on life satisfaction and positive emotional well-being of farmers within nature reserves, with coefficients of 0.308 and 0.164, respectively. It also has a negative impact at the 1% statistical level on negative emotional well-being, with a coefficient of -0.153. Robustness tests confirm these findings. Mediating effect analysis reveals that the ecological environment cognition does not have a statistically significant mediating effect on the well-being of farmers around nature reserves. However, the perception of ecological value has a mediating effect on life satisfaction, positive affect, and negative affect. The perception of ecological policies of nature reserves has a mediating effect on life satisfaction but is not statistically significant for other well-being dimensions. Nature reserve management should enhance oversight and efficiency while promoting ecological civilization principles to address villagers’ misconceptions, encouraging farmers to diversify their reliance on ecosystem services and excluding densely populated villages from core conservation areas, provided ecosystem services are maintained.
1 Introduction
Nature reserves are not only natural habitats for precious endangered species and natural relics but also key areas for maintaining ecological welfare for the people (Wang, 2018). The construction of nature reserves offers an important material basis for the sustainable development of the economy and society as well as the safeguarding of long-term human interests, and it plays an irreplaceable part in maintaining the earth’s ecological security. The Chinese government places great importance on the construction of nature reserves, prohibiting or restricting activities that impact the ecological environment of these protected areas. This policy has played a significant role during the rescue phase of the Chinese ecosystem, while also profoundly affecting the surrounding farmers who originally depended on forestry resources for their livelihood (Liu et al., 2020; Duan and Ouyang, 2020). Subjective well-being is an important measure of social development and national governance levels (Andrew, 2019). President Xi Jinping has repeatedly emphasized the need to continuously enhance people’s happiness. As China’s natural ecosystem protection enters a new phase of being “healthy, stable, and efficient,” ensuring the welfare of farmers around nature reserves is not compromised and actively exploring ways to improve the well-being of these farmers is a crucial issue in the construction of ecological civilization. It is also a key topic in the process of turning “lucid waters and lush mountains” into “gold and silver mountains.”
The primary measurement indicator for the quantitative analysis of subjective well-being is life satisfaction, which expresses individuals’ subjective evaluation of their overall long-term living conditions. With the ongoing deepening of happiness research, measurement indicators of well-being have also been continuously improved. Diener et al. (2003) proposed the concept of emotional well-being, which refers to daily feelings or emotions and comprises two dimensions: positive affect and negative affect. These are temporary and fluctuating personal emotional states (Diener et al., 2003). While life satisfaction and emotional well-being are biologically related, the same factor may have different effects on them (Kahneman and Deaton, 2010). Schimmack et al. (2002) suggested that immediate information can influence respondents’ emotional experiences, and habitual users of emotional information may have their life satisfaction perceptions change with emotional fluctuations. Therefore, well-being measurement should not only adopt a single static dimension but also consider the dynamic dimension of emotional changes (Andrew et al., 2015).
Ecological awareness is part of social consciousness, comprising a mixture of information and beliefs about ecology and the environment. It represents people’s understanding and perception of ecological and environmental issues, creating and disseminating behavioral patterns in individuals and groups within society. Ecological awareness can guide and sustain harmony between society and the environment and typically includes people’s ecological environment cognition and ecological value perception (Xu et al., 2020). Justyna et al. (2021) argue that ecological awareness should also include the perception of ecological policies, as ecosystem protection is often accompanied by policy guidance and support, with different stakeholders perceiving these policies heterogeneously. Good ecological awareness ensures eco-friendly national development and is a necessary condition for sustainable ecological development. Ecological perception plays an indispensable role in the implementation of environmental policies and management and deserves research attention.
Based on the above analysis, this article attempts to make contributions from the following aspects: first, the research perspective is novel. There are few studies on the well-being of farmers around nature reserves in China, and this paper enriches the subject of well-being research. Second, the research framework is innovative. This paper establishes a theoretical framework of “Nature Reserve—Ecological Awareness—Multidimensional Well-being,” studying the impact of nature reserve construction on the well-being of surrounding farmers and exploring the mechanism of ecological perception’s influence on this impact, thus providing insights and suggestions for improving related policies. Third, it introduces the theory of ecological awareness. Current research mainly focuses on ecological value perception (Ma et al., 2016), with few studies addressing ecological policy perception. This paper divides ecological awareness into three dimensions: ecological environment cognition, ecological value perception, and ecological policy perception, broadening the scope of ecological perception research and supplementing relevant studies. Fourth, it uses multidimensional well-being measurement indicators. There are few empirical studies in China employing multidimensional well-being indicators. This paper constructs well-being indicators from multiple dimensions, including life satisfaction, positive affect, and negative affect, which helps to more accurately assess the impact of nature reserve establishment on the well-being of surrounding farmers.
This paper uses micro-survey data from 1,002 households around nature reserves to explore the impact of nature reserve establishment on the subjective well-being of surrounding farmers. Through the intermediary variable of ecological awareness, it investigates the mechanism of this influence, revealing the intrinsic relationship between nature reserve construction and residents’ well-being. This has significant theoretical and practical implications for creating a better and happier life for people. The second part of this article is theoretical analysis and research hypotheses; the third part introduces data sources, variable descriptions, and model settings; the fourth part analyzes the empirical results, tests the robustness, and examines the mediating effect mechanism; the fifth part is for discussion; the sixth part is policy recommendations; the seventh part is the conclusion, shortcomings, and prospects.
2 Theoretical analysis and research hypotheses
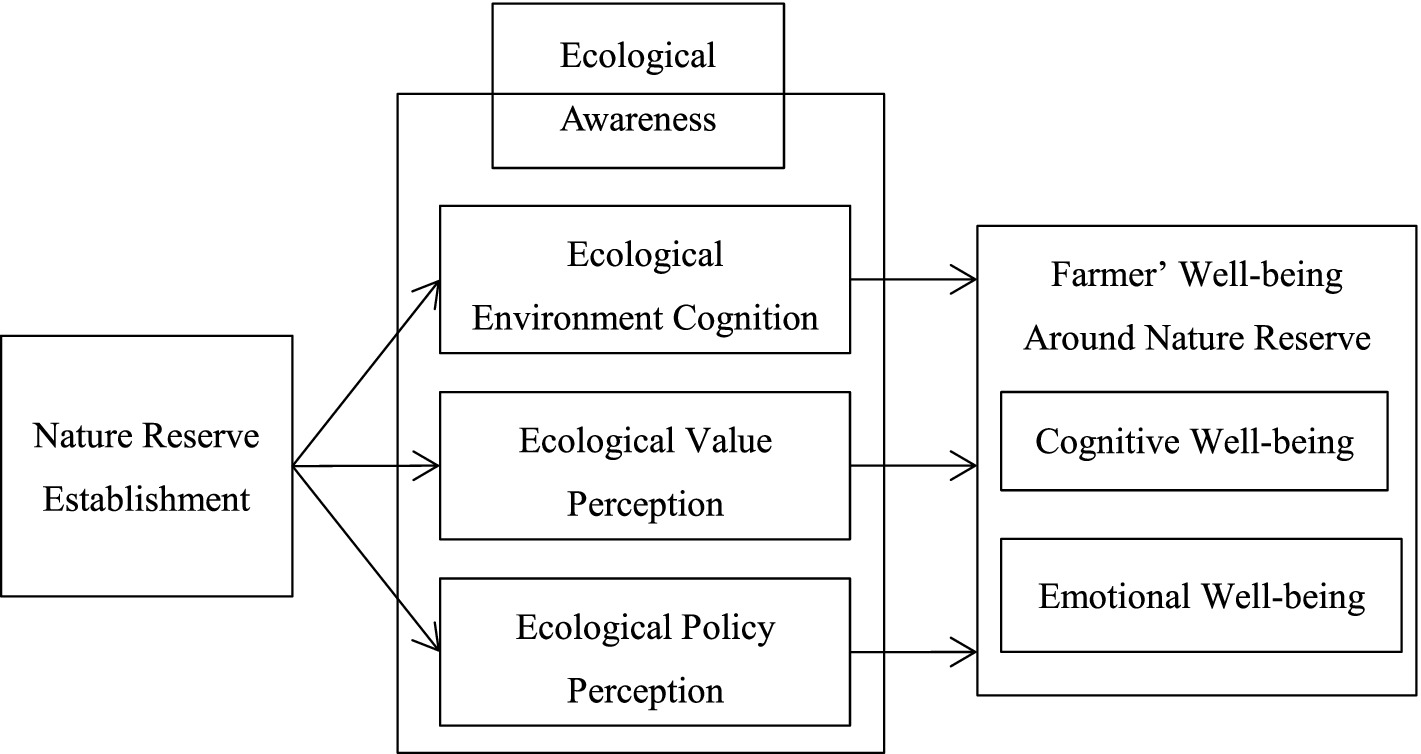
Ecological awareness mainly consists of three basic elements. First are the cognitive elements. It is generated based on people’s certain understanding of natural resources and ecosystems. Secondly, there is the ecological Value Perception. Ecological value perception includes a series of perceptions of social, economic, psychological, and other aspects brought about by ecology. Thirdly, there is ecological policy perception. Ecological awareness also involves the perception of norms and policies related to nature and its resources (Justyna et al., 2021; Sladjana et al., 2022). Ecological awareness is an important symbol of human civilization in modern society. While focusing on the ecological environment, it also pays attention to human physical health and spiritual well-being. Subjective well-being is a broad and multidimensional concept, encompassing cognitive well-being and emotional well-being (Fu et al., 2024). Cognitive well-being refers to individuals’ life satisfaction; emotional well-being includes two relatively independent dimensions: positive and negative affect. This paper constructs a theoretical analysis framework of “Nature Reserve—Ecological Awareness—Multidimensional Well-being” from three dimensions: ecological environment cognition, ecological value perception, and ecological policy perception (Figure 1). This framework clearly and intuitively reflects the relationships among these three elements.
2.1 Impact of nature reserve establishment on farmers’ subjective well-being
The establishment of nature reserves provides essential ecosystem service functions necessary for human survival, and the improvement of these services directly affects the well-being of surrounding farmers (Guo and Xiao, 2016). The United Nations’ Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MA) report clearly indicates that the ecosystem services of protected areas are vital sources of human well-being, significantly impacting both the “living conditions” and the spiritual “life status” of individuals. Ecosystem services can improve human well-being in the long run and exert a positive influence on society and ecology (Ketema and Wei, 2021). Besides providing human welfare products and services, ecosystems can also contribute to human life welfare and pleasure value through market exchange (Zhang, 2022). There is a close relationship between ecosystem service functions and human happiness (Ma et al., 2021). Based on the above analysis, research hypothesis H1 is proposed.
H1. The establishment of nature reserves enhances the cognitive well-being and emotional well-being.
2.2 The relationship between nature reserves, ecological environment cognition, and farmers’ subjective well-being
2.2.1 Establishment of nature reserves and ecological environment cognition of farmers
Ecological environment cognition refers to the process of ecosystem changes and the impact of human activities on the natural environment that people understand, and belongs to the cognitive level of ecological perception (Justyna et al., 2021). Nature reserves implement strict resource acquisition control policies, significantly enhancing ecosystem services such as water conservation, water quality purification, soil and vegetation improvement, and air quality enhancement, thereby improving the ecological environment (Zheng et al., 2020). The restoration of ecological elements can lead to alterations in people’s views and preferences regarding the ecological environment. Thus, farmers around nature reserves can exhibit a positive perception of ecological performance (Zhang et al., 2024).
2.2.2 Ecological environment cognition and farmers’ subjective well-being
Satisfying people’s various needs does not necessarily directly generate residents’ sense of well-being. The emergence of subjective well-being also demands the cognitive and evaluative processes of residents regarding the fulfillment of their own needs (Pan and Chen, 2021). Environmental cognition can stimulate individuals’ psychological emotions, and positive environmental cognition has a significant positive impact on farmers’ subjective well-being (Schebella et al., 2019). Fu et al. (2024) argue that landscape elements in urban parks directly affect the life satisfaction of users. National parks have excellent natural landscapes and beautiful natural environments that can help people overcome negative emotions, recover from unfavorable situations and effectively enhance people’s emotional well-being (Pan and Chen, 2021). Based on the above analysis, research hypothesis H2 is proposed.
H2. The establishment of nature reserves indirectly enhances farmers’ cognitive and emotional well-being through their understanding of the ecological environment.
2.3 The relationship between nature reserves, ecological value perception, and farmers’ well-being
2.3.1 Establishment of nature reserves and ecological value perception of farmers
Value perception is the balance between perceived benefits and contributions. Ecological value perception includes a series of intertwined social, economic and psychological value perceptions, which are expressed in this article as egoistic value perception, altruistic value perception, and psychological value perception (Justyna et al., 2021). Firstly, a significant proportion of collective forest land in China is located within nature reserves. These collective forests are not only important ecological resources but also primary production factors and livelihood sources for farmers. The establishment of nature reserves restricts the rights of surrounding farmers to access collective forest land, forcing them to change traditional livelihoods and seek alternative sources of income. Additionally, inadequate ecological compensation and wildlife damage further harm farmers’ interests to varying degrees (Zhao et al., 2024; Xie et al., 2024). However, while bearing the costs of protection, surrounding farmers also benefit from opportunities brought by nature reserve construction, such as participation in ecotourism, engagement in ecological protection work, and the possibility of earning higher wages through labor migration (Duan et al., 2022; He et al., 2023a, 2023b). Thus, farmers, based on their individual resource endowments and capabilities, exhibit different “self-interested” value balances (Achieng et al., 2020). Secondly, as practitioners of ecological environmental protection, farmers around nature reserves experience firsthand the Chinese government’s commitment to and investment in ecological protection. They also recognize the critical importance of the ecological environment for human societal development, embodying an “altruistic” value perception (Ma et al., 2016). Finally, the establishment of nature reserves disrupts farmers’ original attachment to and satisfaction with their local areas, providing them with new identity construction and regional recognition (Liu, 2012). This leads to a psychological value perception of local pride, due to the significant ecological positioning and renowned geographic identity of the nature reserves (Peng et al., 2024).
2.3.2. Ecological value perception and farmers’ subjective well-being
The social representation theory focuses on the shared values, perspectives, and behavioral systems of a certain group. In the perspective of social representation theory, perceived value is not only an independent individual response, but also reflects an individual’s social and cultural response, and is an important factor in residents’ subjective well-being (Li et al., 2023). Scholars from different fields are attempting to establish research on the correlation between perceived value and well-being. Lin et al. (2014) found that the perceived value of customer service in nursing institutions is closely related to their subjective well-being. Ren et al. (2021) analyzed consumer behavior on social networking platforms and found that consumers’ perceived value of the platform has a positive impact on their subjective well-being. Fu and Wang (2021) found that the experiential value of accommodation hotels has a significant positive impact on tourists’ sense of well-being. It can be seen that the ecological perception value of farmers around the nature reserve has a positive impact on their subjective well-being. Based on the above analysis, research hypothesis H3 is proposed.
H3. The establishment of nature reserves indirectly enhances farmers’ well-being through their perception of ecological value.
2.4 The relationship between nature reserves, ecological policy perception, and farmers’ subjective well-being
2.4.1 Establishment of nature reserves and ecological policy perception of farmers
Ecological policy perception refers to the standards of action and a series of regulations and prohibitions involving social, ecological, economic, legal, and ethical aspects within ecological spaces that provide ecosystem services. This falls under the normative perception dimension (Chen et al., 2020; Justyna et al., 2021). In 1994, the Chinese government promulgated the “Regulations of the People’s Republic of China on Nature Reserves” (hereinafter referred to as “Nature Reserve Regulations”), which divided nature reserves into core areas, buffer zones, and experimental zones. The regulations stipulate that the core area is “prohibited from any unit and individual entry”; the buffer zone and experimental zone strictly control scientific research, living, and business projects. Production operations must meet environmental protection standards, and the construction of production facilities is entirely prohibited in these ecological spaces. Additionally, the Nature Reserve Regulations specifically list 10 prohibited activities, including logging, grazing, hunting, fishing, collecting herbs, reclamation, burning, mining, quarrying, and sand extraction. Enterprises and individuals violating these regulations will have their illegal gains confiscated, be ordered to stop illegal activities, and be required to restore the original state within a prescribed period or take other remedial measures. Especially since 2015, the Chinese government has implemented the “strictest protection” policy for the management of nature reserves, and farmers around nature reserves have a deep perception of ecological policies.
2.4.2 Ecological policy perception and farmers’ subjective well-being
There are few research results on environmental regulation from a perceptual perspective and the mechanism of its impact on farmers’ subjective well-being. Existing research focuses on the influence of environmental regulation policies on people’s subjective well-being. There is a threshold effect of environmental regulation on residents’ subjective well-being. When the environmental regulation reaches the threshold value, the higher the environmental regulation, the higher the subjective well-being (Wang, 2023). Environmental governance has regional, urban–rural, and income heterogeneity effects on residents’ subjective well-being, with a significant improvement effect on residents’ subjective well-being in urban areas and high-income groups, but no significant impact on rural areas and low-income groups (Shi and Yi, 2020). Based on the above analysis, research hypothesis H4 is proposed.
H4. The impact of ecological policy perception on farmers’ subjective well-being through the establishment of nature reserves needs to be tested.
3 Data source and variable selection
3.1 Data source
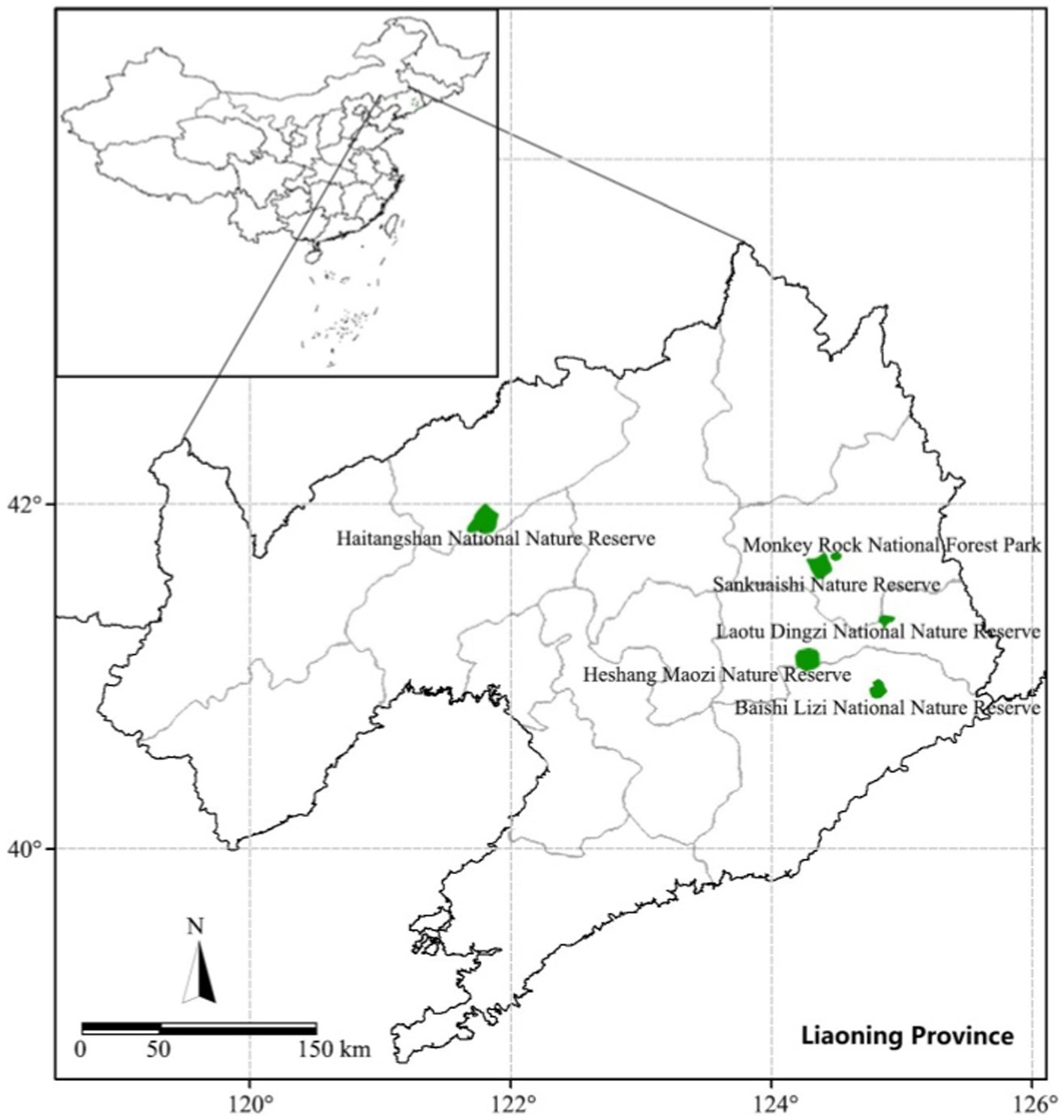
The study area focuses on nature reserves in Liaoning Province, which hosts 18 national-level and 27 provincial-level nature reserves, serving as crucial ecological support for maintaining the ecological security of Northeast China. Data collection took place from July 2021 to August 2021. Participants in the survey were teachers, doctoral students, and graduate students from the discipline of agricultural and forestry economics and management, all with a strong interest and experience in research. They also received systematic training on survey questionnaires and data collection.
The survey questionnaire primarily comprises 10 parts, including basic household information, household asset status, household production and operation income and expenditure, farmers’ perception and behavior, farmers’ non-economic welfare situation, participation in ecotourism, household energy consumption situation, and ecological compensation. Regarding sensitive issues such as household income and operating costs for farmers, the survey questionnaire is used to verify the logic before and after by examining the consumption situation of family members, striving to ensure the accuracy of the survey data. All the data needed for this study were retrieved from the survey questionnaire.
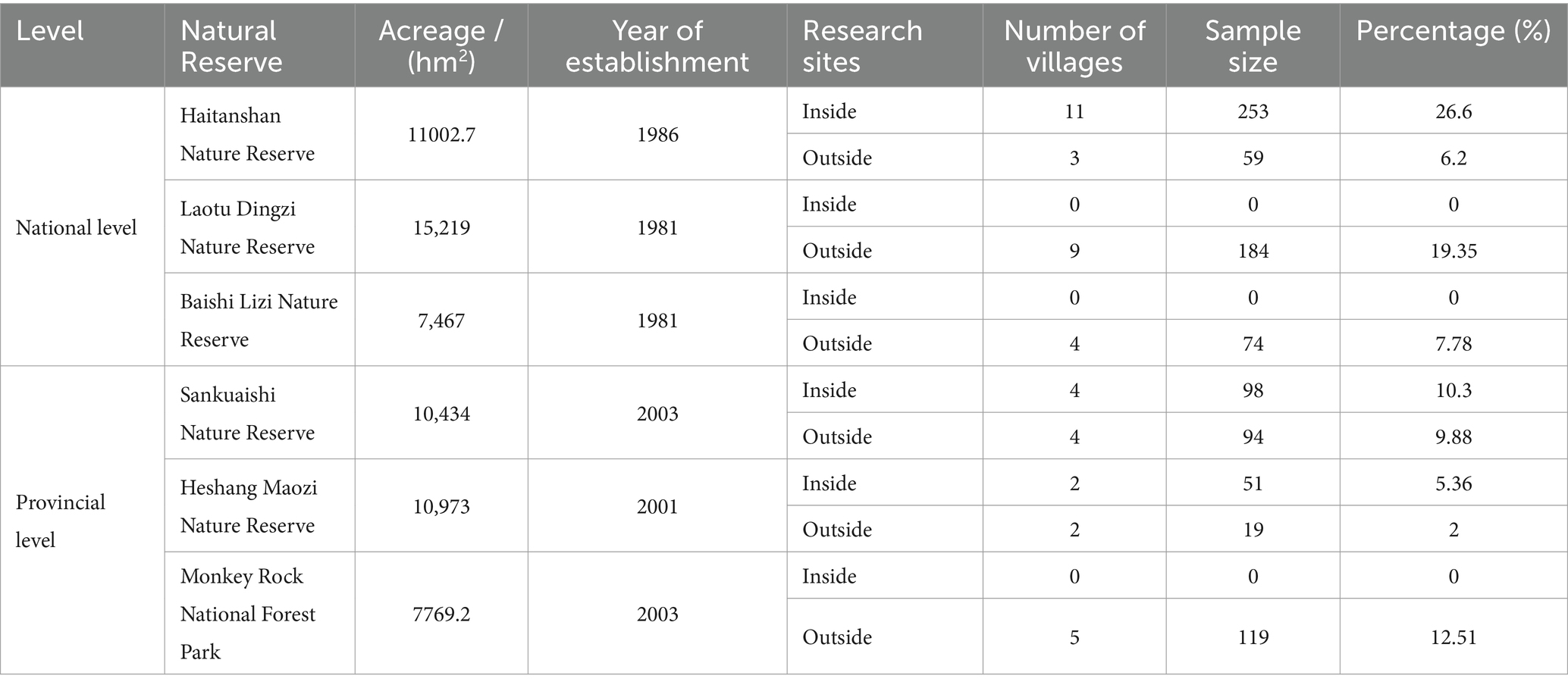
The sampling of sample farmers adopts a stratified random sampling approach. First, three national and three provincial nature reserves within Liaoning Province are selected, as depicted in Figure 2. Second, based on the list of villages inside and outside the nature reserves provided by the local township governments where the nature reserves are located, 25 villages within the reserves and 25 villages outside the reserves are randomly chosen. It is required that the villages outside the nature reserves are within 20 km of the reserves and their livelihoods are not under the control of the nature reserves (Nikoleta et al., 2020). Due to the completion of ecological migration in the villages within the Monkey Stone National Forest Park, Laotudingzi, and Baishilazi Nature Reserves, the actual number of surveyed villages is 17 within the nature reserves and 27 outside the nature reserves. Finally, on average, 25–30 households of villagers are randomly selected from each village, and respondents are requested to try to meet the requirements of being the head of the household or the spouse of the head of the household and being familiar with the family’s life, production income, and expenses.
In the field investigation, to ensure the reliability of information, the research team members completed the survey questionnaire by conducting face-to-face interviews with the interviewed farmers. At the start of the survey, a statement regarding the confidentiality clause was made to inform the respondents that the data used in this survey was only for academic research and would be kept strictly confidential, thus dispelling potential concerns of the farmers. Small gifts were given to boost the enthusiasm of the surveyed farmers. However, due to conflicts between the research plan and the working hours of some individual farmers, these farmers were unable to participate in the survey. Also, because of the limited number of village officials, it was impossible to explain the research plan in detail to every farmer, leading to low cooperation from some of them. Consequently, the number of valid questionnaires among farmers in each village varied. Final, after excluding invalid questionnaires with missing data or unclear writing that could not be revisited, a total of 951 valid questionnaires were obtained, yielding an effective rate of 94.91%, as shown in Table 1.
3.2 Variable selection
3.2.1 Dependent variable: farmers’ well-being around nature reserves
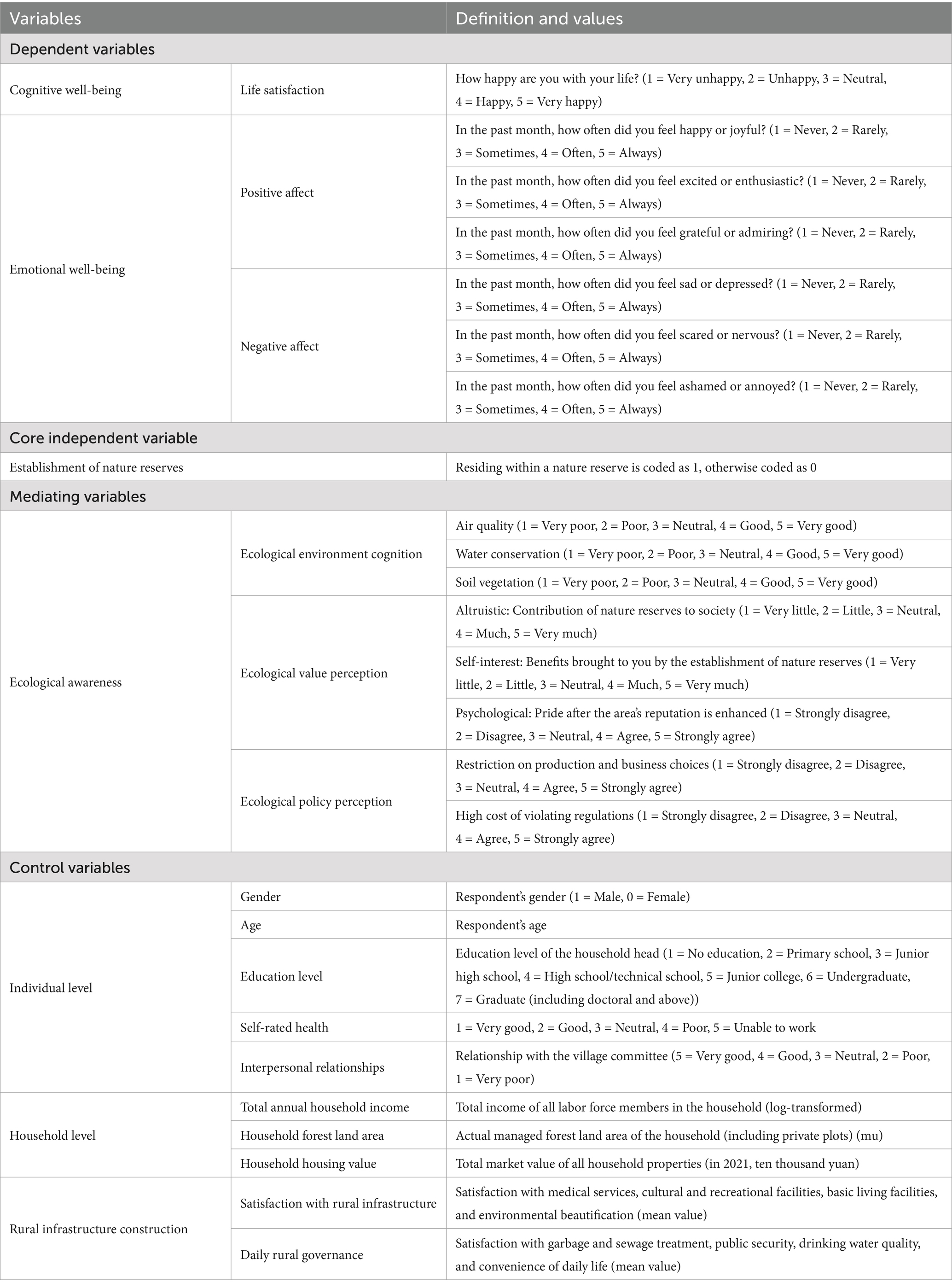
Subjective well-being encompassing cognitive well-being and emotional well-being. Cognitive well-being is measured by asking respondents, “Do you feel happy with your life?” Respondents can choose from five levels: very unhappy, unhappy, neutral, happy, and very happy, rated from 1 to 5. Drawing on Watson’s Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS), and based on the educational level and pre-survey conditions of farmers around nature reserves, the measurement of emotional well-being was adaptively modified. Emotional well-being can be an immediate emotional state or an overall emotional experience over a period (ranging from a day to a year). Immediate emotional experiences are prone to the “peak-end rule,” while long-term emotional experiences may suffer from recall distortion and memory bias. Thus, the period for overall emotional perception was set to the previous month from the time of the interview. Emotional experiences have attributes of intensity and frequency, with frequency being more important for overall well-being (Diener et al., 1991; Qiu, 2011). Therefore, the frequency options for emotional well-being are “never, occasionally, sometimes, often, always,” corresponding to ratings from 1 to 5, with higher ratings indicating greater frequency. The mean values of positive and negative affect were used as indicators, with equal weights assigned to multiple dimensions of well-being.
3.2.2 Core variable: establishment of nature reserves
For the long-term establishment of nature reserves, changes in farmers’ well-being may be influenced not only by the establishment of the reserves but also by other contemporaneous factors. To accurately measure the impact of nature reserve establishment on farmers’ well-being, a 0/1 variable indicating whether the farmer resides inside or outside the nature reserve was chosen to represent the core variable, thus excluding the interference of contemporaneous factors.
3.2.3 Mediating variables: ecological environment cognition, ecological value perception, and ecological policy perception
Based on the research findings of Zhao and Zhang (2006), Li (2015), and Hao et al. (2020), and considering the suitability of micro-level farmer evaluations, the relative consistency of topography and climate in the survey area, and the logical relevance of special cases in nature reserves, three indicators were chosen to represent ecological environment cognition: air quality, water conservation, and soil vegetation conditions. Drawing from the research of Duan et al. (2015) and Ren et al. (2018), self-interested value perception, altruistic value perception, and psychological perception were selected to express ecological value perception including individual benefit and cost perception, socio-economic value perception, and regional pride (Han, 2021; Schebella et al., 2019). According to the “Nature Reserve Regulations,” the perception of restricted production and operation choices and the perception of the cost of penalties for violations were chosen as indicators of ecological policy perception. All mediating variables were measured using a five-point Likert scale.
3.2.4 Control variables: control variables encompass a range of individual and household characteristics
Individual characteristics include gender, age, health status, education level, and interpersonal relationships. Household characteristics include household income, house value, and forestland management area. Additionally, China is actively improving rural living environments, significantly enhancing rural infrastructure and addressing issues such as sewage and garbage disposal, thereby increasing farmers’ well-being (Zhang et al., 2022). To minimize the interference of current rural living environment construction on farmers’ well-being, related indicators were included as control variables. The variable names, definitions, and value ranges are detailed in Table 2, while the indicators, means, and standard deviations of the dependent and mediating variables are shown in Table 3.
4 Model specification
4.1 Baseline model
To test whether the establishment of nature reserves significantly affects the well-being of farmers within the reserves, the following baseline model is specified:
where Yit represents the well-being of the i-th farmer, with t taking values of 1–3, corresponding to life satisfaction, positive emotional well-being, and negative emotional well-being, respectively. PAi is the core variable representing the location of the i-th farmer’s residence, where farmers living within the nature reserve are assigned a value of 1 (treatment group) and others are assigned a value of 0 (control group). Xi includes control variables for the i-th farmer’s well-being. α1 and α2 are parameters to be estimated, and ε1 is the random disturbance term for the i-th farmer. Life satisfaction is an ordinal discrete variable, and the hypothesis is tested using the Ordered Probit (OProbit) method. The indices for positive and negative emotional well-being are calculated using equal weighting, and the hypothesis is tested using the Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) method.
4.2 Entropy method
To reduce subjectivity in evaluation and to verify the accuracy of the regression results and the reliability of the conclusions, the entropy method is employed to assign weights to the indicators of emotional well-being.
First, normalization of the data is necessary due to differences in units or directions of the indicators to ensure accuracy.
For positive indicators:
For negative indicators:
where i represents the farmer, j represents the emotional well-being indicator, Yij is the original value of the indicator, indicating n evaluation indicators of emotional happiness for the i-th farmer, and Zij is the normalized value.
Second, the entropy method determines the weight of each indicator. The proportion Pij of the weight for the i-th evaluation object under the j-th indicator is calculated as follows:
The entropy value Eij of the j-th indicator is calculated as follows:
The weight ωj of the j-th indicator is calculated as follows:
Finally, the standardized values Zij and ωj are weighted and averaged to calculate each type of indicator and the comprehensive evaluation index:
4.3 Mediating effect model
To identify how the establishment of nature reserves indirectly affects farmers’ well-being through ecological awareness, the improved mediating effect testing process by Wen and Ye (2014) is adopted, with 1,000 bootstrap repetitions. The regression equations are constructed as follows:
where Mih represents the mediating variables of ecological awareness, with ℎ taking values of 1–3, corresponding to ecological environment cognition, ecological value perception, and ecological policy perception. α, β, and γ are parameters to be estimated, and ε1–ε3 represents random error terms. Other variables and symbols have the same meaning as in Equation 8.
5 Results and analysis
5.1 The total effect of nature reserve establishment on farmers’ well-being
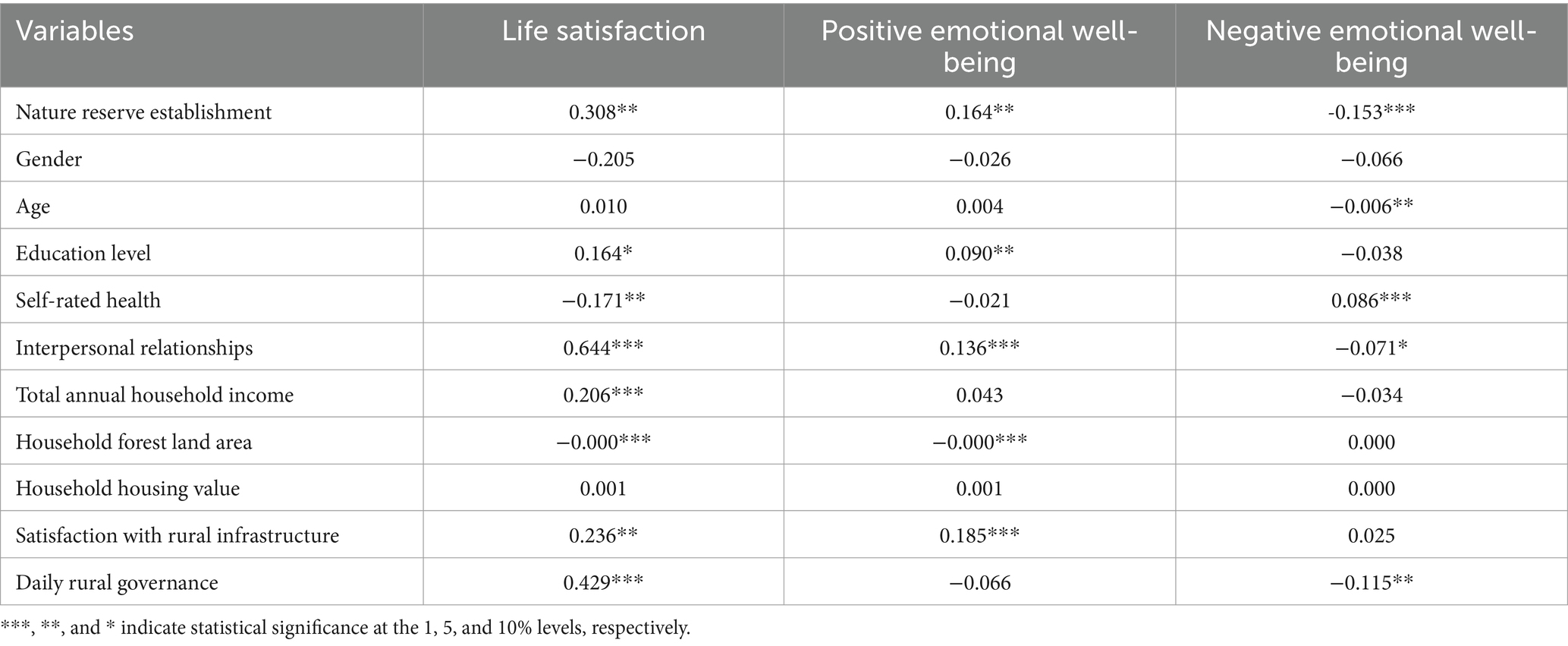
The total effect of the establishment of nature reserves on the well-being of farmers around nature reserves (Equation 1) is shown in Table 4. The establishment of nature reserves has a significant positive impact on the life satisfaction and positive emotional well-being of farmers within the reserves at the 5% statistical level and a significant negative impact on negative emotional well-being at the 1% statistical level, thus confirming hypothesis H1. It is evident that farmers within nature reserves experience greater life satisfaction, more positive affect, and fewer negative affect.
Among the control variables, age has no significant effect on life satisfaction and positive emotional well-being but has a significant negative impact on negative affect; the older the age, the fewer the negative affect. According to socioemotional selectivity theory, as age increases and wisdom accumulates, individuals tend to retain more emotionally satisfying events and view matters more objectively and peacefully, which can offset the increase in negative affect (Deaton and Stone, 2016). Educational attainment has a positive effect on life satisfaction and positive emotional well-being. Education can enhance human capital and bring more confidence, respect, and opportunities, thereby improving life satisfaction and fostering more positive affect in daily life (Oreopoulos and Salvanes, 2011). Good self-rated health promotes greater life satisfaction among farmers, while poorer self-rated health exacerbates negative affect. Interpersonal relationships significantly affect both life satisfaction and emotional well-being, playing a crucial role in farmers’ well-being, consistent with the findings of Li and Chen (2012). Rural China is a “relationship” society based on kinship and locality, where social networks function as informal insurance mechanisms that facilitate emotional exchanges between people, thereby enhancing self-identity and significantly impacting farmers’ well-being (Zheng et al., 2021). Household income affects life satisfaction but does not significantly enhance or reduce emotional well-being, which is consistent with the findings of Kahneman and Deaton (2010). While household income can enhance life satisfaction, its relationship with emotional well-being is weaker, confirming the differential impact of income on life satisfaction and emotional well-being (Kahneman and Deaton, 2010). Larger household forestland areas are associated with lower life satisfaction and positive emotional well-being among farmers. This can be explained by the increasing difficulty of obtaining logging quotas due to a series of national measures to strengthen rural ecological construction, resulting in greater opportunity cost losses for farmers with larger forestland areas, thereby reducing their well-being. Improvements in rural infrastructure and environment can enhance farmers’ life satisfaction and positive emotional well-being. Daily governance of the rural environment can significantly improve farmers’ life satisfaction but may also lead to more negative affect. The reason is that while daily environmental governance provides a better living environment, it currently remains detached from farmers’ values and lifestyles, and waste management, a high-cost governance project, negatively impacts farmers’ positive emotional well-being (Han, 2021).
5.2 Robustness tests
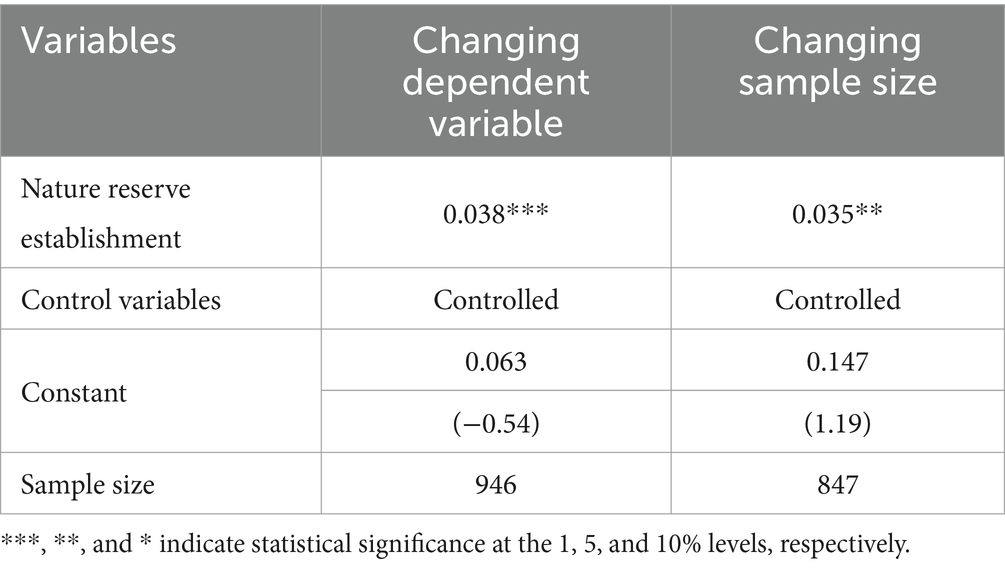
To verify the accuracy of the regression results and the reliability of the conclusions, this study conducted two robustness tests. Firstly, the well-being indicators were replaced. The entropy method was used to measure the intensity of well-being, and its various dimensions (Equations 2–7), and the processed well-being indicators were estimated using the OLS model. Secondly, the sample size was altered. The well-being intensity measured by the entropy method was ranked from highest to lowest, and the top and bottom 5% of the data were removed. The processed samples were then estimated using the OLS model. The specific results are shown in Table 5. Table 5 presents the regression results after replacing the dependent variable and changing the sample data. The estimated coefficients of the effect of nature reserve establishment on farmers’ well-being remain significantly positive with values of 0.038 *** and 0.035 ** respectively, indicating that the establishment of nature reserves is positively correlated with farmers’ well-being. This result is consistent with the baseline regression results, demonstrating the robustness of the baseline regression results.
5.3 Mediating effect testing
To verify whether the establishment of nature reserves indirectly affects farmers’ well-being through ecological awareness variables, an empirical test was conducted based on the mediating effect testing process and model of Wen and Ye (2014). According to Table 4, the establishment of nature reserves has a significant impact on both the life satisfaction and emotional well-being of farmers, suggesting the presence of mediating effects.
Comparing the direct influence coefficients (γ1) of nature reserve establishment in the regression results with the indirect influence coefficients (β1 × γ2) of nature reserve establishment (Equations 9, 10) if the signs are the same, it indicates the presence of a partial mediating effect; if the signs are different, it indicates the presence of a suppression effect.
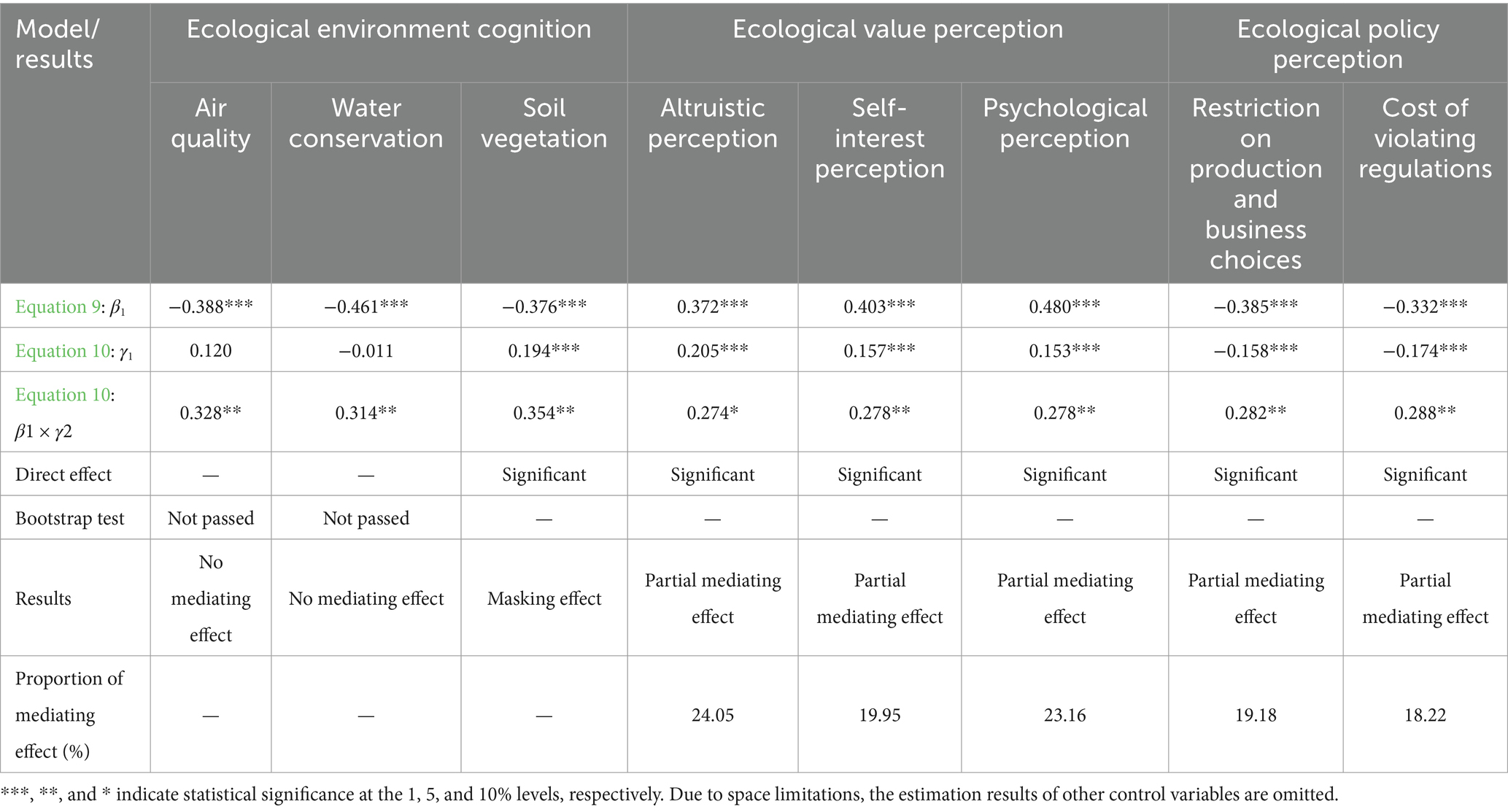
1. Mediating effect of ecological environment cognition. The mediating effect of ecological environment cognition on the influence of nature reserve establishment on farmers’ life satisfaction and emotional well-being is not statistically significant. Thus, hypothesis H2 is not supported.
2. Mediating effect of ecological value perception. The establishment of nature reserves has a significant positive impact on farmers’ ecological value perception. After controlling for the direct effect of nature reserve establishment, ecological value perception has a significant positive impact on farmers’ life satisfaction and positive emotional well-being, indicating that stronger ecological value perception among farmers within nature reserves enhances their life satisfaction and positive emotional well-being. After controlling for the direct effect of nature reserve establishment, ecological value perception has a significant negative impact on farmers’ negative emotional well-being, indicating that ecological value perception can suppress negative emotional well-being. The path of ecological value perception mediating the impact of nature reserve establishment on farmers’ life satisfaction and emotional well-being shows partial mediating effects, thus supporting hypothesis H3. The mediating effect of ecological value perception on negative emotional well-being accounts for the largest proportion of the total effect, at 35.36, 28.26, and 29.66%, respectively, while its mediating effect on positive emotional well-being accounts for the smallest proportion of the total effect, at 16.23, 18.48, and 11.40%, respectively.
3. Mediating effect of ecological policy perception. The establishment of nature reserves has a significant negative impact on farmers’ ecological policy perception. After controlling for the direct effect of nature reserve establishment, ecological policy perception has a significant negative impact on farmers’ life satisfaction and positive emotional well-being, indicating that a stronger ecological policy perception among farmers within nature reserves reduces their life satisfaction and positive emotional well-being, with the mediating effect accounting for 19.18 and 18.22%, respectively. After controlling for the direct effect of nature reserve establishment, ecological policy perception has no mediating effect on farmers’ positive emotional well-being; however, the perception of restricted production and operation choices has a positive impact on negative emotional well-being, indicating that stronger perception of restricted production and operation choices exacerbates negative emotional well-being among farmers within nature reserves, showing partial mediating effects. Thus, hypothesis H4 is verified (see Tables 6–8).
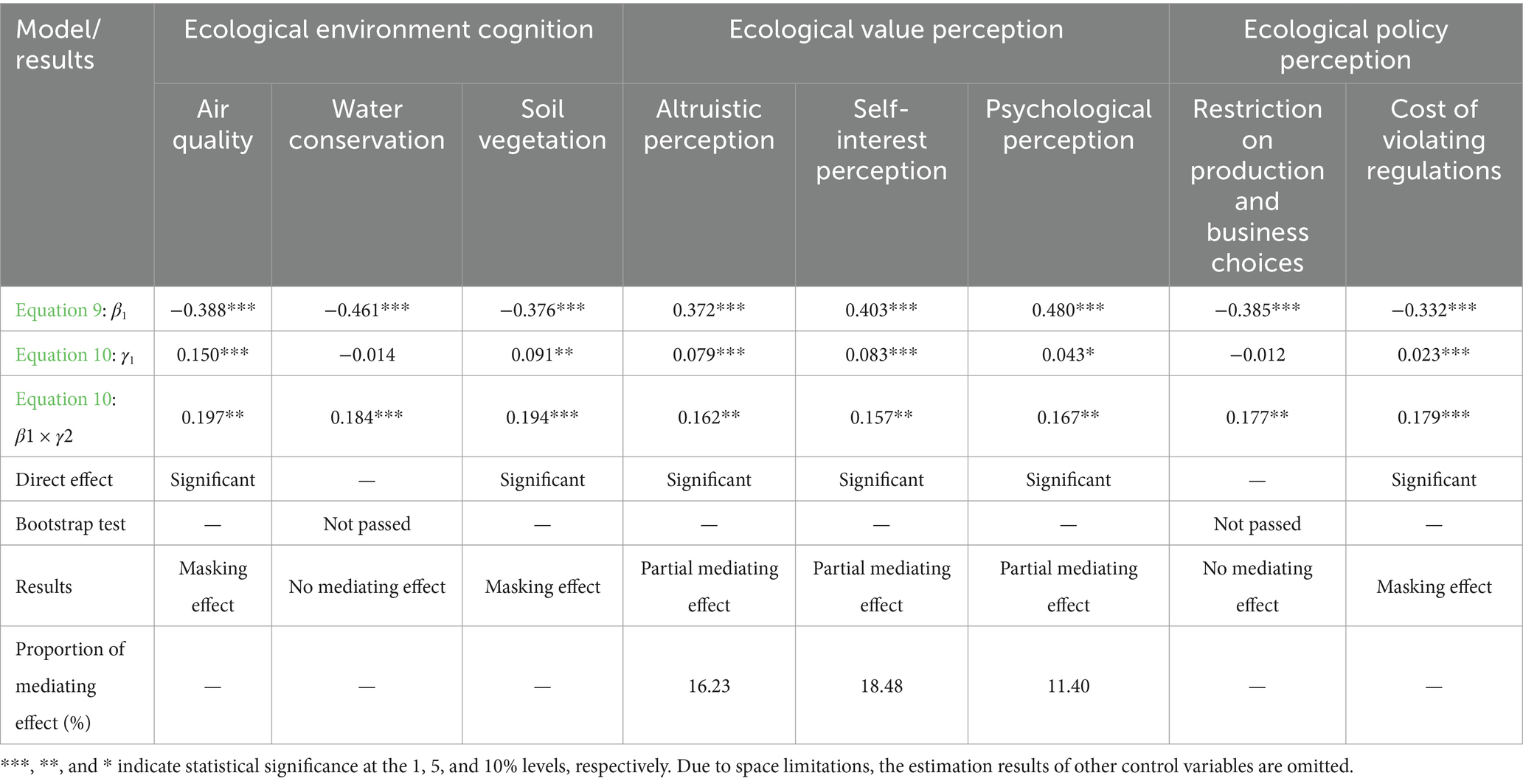
Table 7. The mediating effect of nature reserve establishment on farmers’ positive emotional well-being.
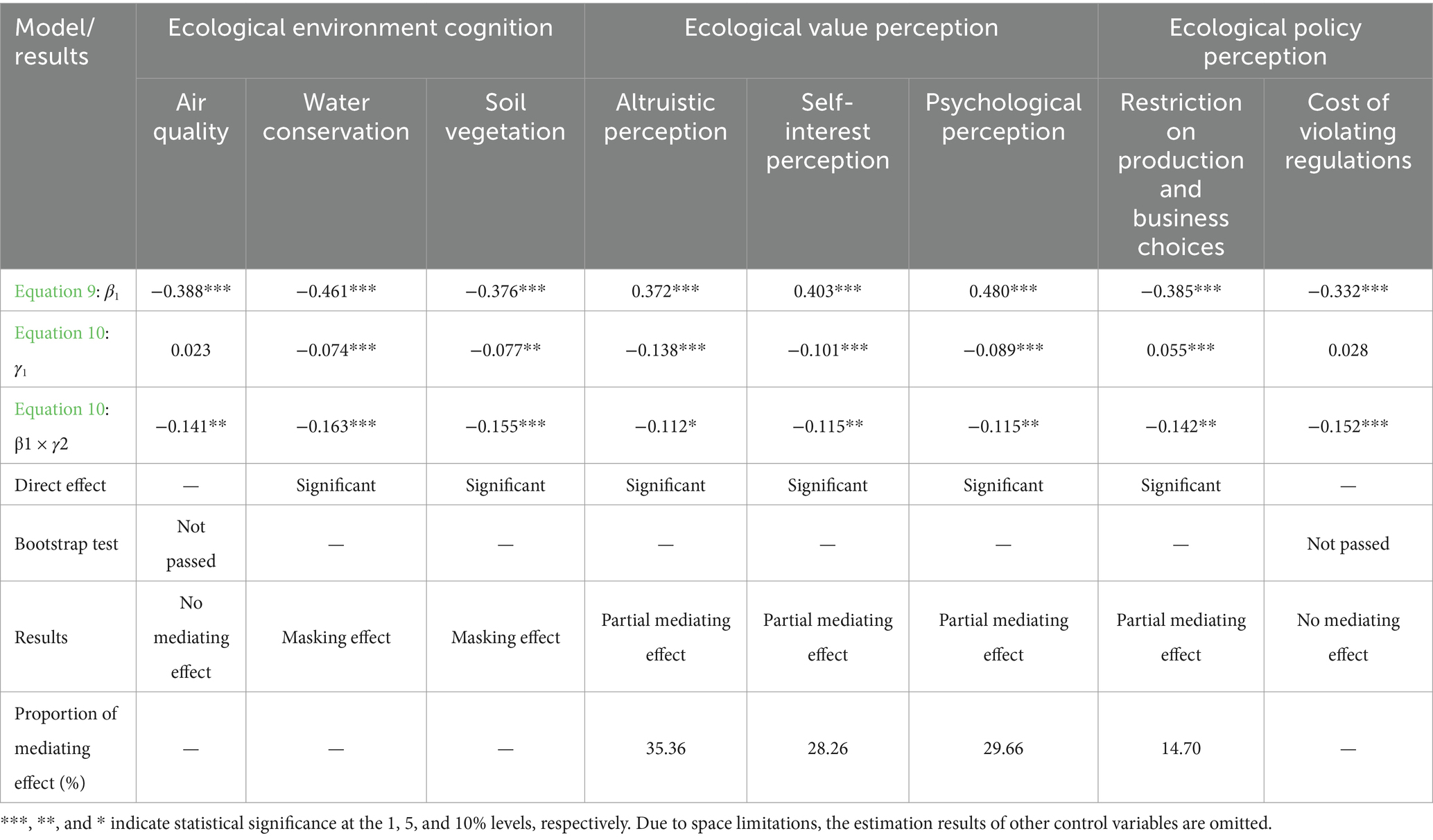
Table 8. The mediating effect of nature reserve establishment on farmers’ negative emotional well-being.
6 Discussion
The establishment of nature reserves can improve the subjective well-being of surrounding farmers. Enhancing farmers’ well-being is a key focus in China’s “Three Rural Issues” (agriculture, rural areas, and farmers). The impact of economic income on well-being is a classic topic in subjective well-being research. According to the project team’s field survey, the total household income of farmers within nature reserves (89,197 RMB) is higher than that of farmers outside the reserves (87,528 RMB). After controlling for the impact of total household income on well-being, it was found that farmers within nature reserves have higher life satisfaction, more positive affect, and fewer negative affect compared to those outside the reserves. This indicates that, over a long period of time, the construction of nature reserves has a positive impact on the well-being of surrounding farmers, consistent with the findings of Loveridge et al. (2021).
The hypothesis of the mediating effect of ecological environment perception is not valid. The establishment of nature reserves negatively impacts air quality, water conservation, and soil vegetation, implying lower satisfaction with the ecological environment among farmers within the reserves. However, relevant studies have shown that nature reserves protect 85% of China’s terrestrial ecosystem types and 85% of the nation’s key protected wild plant and animal species, and the ecological effects of nature reserves are increasingly positive (Andrew, 2019). A possible explanation for this is that, with the deep-rooted concept of ecological protection among the public, the stringent ecological protection policies lead to higher expectations of ecological protection outcomes among farmers within the reserves. However, persistent environmental violations and the tendency for information distortion in local communities result in loss aversion among these farmers, leading to biased ecological environment cognition. Secondly, Peng et al. (2023) found in ecological monitoring of nature reserves that the ecological environment quality of the core area is higher compared to the buffer zone and experimental zone of the nature reserve. Ecotourism construction is allowed in the experimental area. Ecotourism has caused certain damage to the ecological environment due to changes in land use, and a large number of tourists visiting during holidays have also brought environmental problems to the nature reserve. The villagers in the nature reserve mainly live in the experimental area and are not allowed to enter the core area, resulting in a deviation in ecological environment perception. Thirdly, Schebella et al. (2019) believe that natural parks have the best impact on users’ well-being, as different attributes of the ecological environment significantly affect people’s emotional well-being at different thresholds. Among them, vegetation cover attributes have the strongest correlation with psychological benefits (Schebella et al., 2019), which is consistent with the results of this study. It can be seen that ecological environment perception contributes to the improvement of people’s subjective well-being (Welsch, 2006), but for farmers who already live in nature reserves, ecological environment perception is not the key mechanism for their subjective well-being improvement.
The establishment of nature reserves enhances farmers’ subjective wellbeing through ecological value perception. Firstly, regarding the mediating effect of self-interest value perception. The establishment of nature reserves promotes interaction with the outside world and the development of ecotourism, providing opportunities for labor mobility and trade freedom, thereby meeting farmers’ basic needs for material wealth based on their personal capital. In the survey, we also found that 78.21% of the farmers firmly expressed their unwillingness to accept the destruction of ecosystems, regarding the natural environment as a significant factor in promoting personal well-being. Secondly, regarding the mediating effect of altruistic value perception. The theory of self-transcendence values suggests that individuals can achieve a more lasting and stable sense of well-being by transcending their immediate interests and desires and harmoniously connecting with others and society, even if this comes at a certain cost and lacks external recognition (Qin et al., 2017; Liu et al., 2022). The perceived value of altruism among farmers enhances their sense of happiness. Thirdly, the mediating effect of psychological value perception. Farmers in nature reserves undertake the social responsibility of constructing ecological barriers. Their innate connection with nature reserves forms a unique identity and local sentiment, alleviating the anxiety and restlessness brought about by relative deprivation and bringing about a sense of satisfaction and pride (Zhu and Liu, 2011). Pride is a positive and optimistic spirit, and inspiring cultural pride within the nature reserve can result in higher subjective well-being (Zhang and Feng, 2009; Li et al., 2023). Therefore, ensuring the comprehensive progress and spiritual enrichment of farmers is key to the long-term growth of well-being. Enhancing farmers’ well-being from the perspective of ecological value perception has significant theoretical and practical implications.
The establishment of nature reserves has reduced farmers’ cognitive well-being through ecological policy perception, through ecological policy perception, but has not had a mediating effect on positive emotions. This indicates that the same factor has heterogeneous effects on long-term life satisfaction and immediate emotional well-being, demonstrating the empirical significance and research value of multidimensional well-being studies. The “man-land relationship” remains a key conflict in nature reserve construction. The regulation of ecological space usage exacerbates welfare imbalances between different regulated areas and different interest groups. The regulated and non-regulated areas, respectively, as ecological service providers and beneficiaries, present a mismatch of ecological service function spillovers and “free-riding,” reducing the well-being of farmers around nature reserves (Song and Jin, 2019).
The establishment of nature reserves has intensified the negative emotions of farmers within them through the perception of ecological policies, and there is a mediating effect. Farmers have a strong sense of being restricted, meaning that they have ideas and plans for their family’s livelihood or life, yet they are under ecological control and thus unable to implement these plans or face difficulties in implementation. After investigation, it was found that nature reserves are highly sensitive regarding the approval of new tourism projects. It is difficult to obtain approval from the reserve management department for the construction and repair of tourism infrastructure within the reserve. Also, approval cannot be obtained for the renovation of civilian housing within the reserve. Commercial forests planted before the establishment of the nature reserve cannot obtain logging permits either.
7 Policy implications
Drawing from the findings of the study, this paper presents the following policy recommendations:
Firstly, the management department of nature reserves should strengthen supervision and enhance the effectiveness of governance mechanisms to reduce the occurrence of illegal environmental damage and improve the management efficiency of nature reserves. A sound economic compensation system for nature reserves should be established to promote coordinated governance and benefit sharing. Link the arrangement of ecological protection compensation funds to the assessment results of ecological environment quality improvement indicators and sign a commissioned protection management compensation agreement. Adopt the method of pre-allocation and settlement to increase positive incentives for achieving ecological protection goals and improve ecological performance.
Secondly, adjust the dependence structure of farmers on ecosystem services and encourage a shift from highly dependent supply services to a combination of supply, regulation, and cultural services. Deeply explore the connotation of ecological culture, utilize abundant forest resources, leverage the advantages of protected areas, and actively cultivate green and prosperous industries for the people. Carry out green projects such as “protected areas + nature education,” “protected areas + forest health care,” “protected areas + ecological agriculture,” “protected areas + artistic creation,” etc. This will enhance farmers’ awareness and capacity to engage in green industries, broaden their livelihood channels, stimulate their perception of self-interest value, and reduce their sense of limitation. Based on the green and prosperous industry, actively conduct marketing and promotion to draw traffic, shape brand features, boost local pride among farmers, and thereby improve their sense of well-being.
Thirdly, by making use of social welfare organizations to promote the concept of ecological civilization construction, we can rectify villagers’ cognitive biases regarding ecological performance. Continuously intensify the promotion of natural resource conservation and highlight policy objectives, enabling farmers to recognize that protecting nature is a means to increase natural value and capital, and thus enhancing farmers’ sense of policy identification.
Fourthly, during the planning and compilation process of nature reserves, villages with population aggregation should be excluded from the nature reserve scope on the premise of ensuring no decline in ecosystem service functions. Farmers within the nature reserves can establish new villages and towns through ecological migration, thereby achieving the goal of coordinated development. Meanwhile, reasonable livelihood security policies should be formulated to minimize farmers’ losses and ensure that their rights to production and operation are not violated.
8 Conclusion, shortcomings, and prospects
This paper constructs a theoretical analysis framework of nature reserve establishment—ecological awareness—farmers’ well-being, using survey data from 1,002 farmers within and outside six nature reserves in Liaoning Province, China, collected in 2021. The study empirically analyzes the impact of nature reserve establishment on farmers’ well-being and explores the underlying mechanisms using a mediating effect model. The results show that the establishment of nature reserves has a significant impact on both the life satisfaction and emotional well-being of farmers. Among the ecological awareness variables, the mediating effect of ecological environment cognition is not statistically significant; the mediating effect of ecological value perception on both life satisfaction and emotional well-being is statistically significant; and the mediating effect of ecological policy perception on life satisfaction is statistically significant.
This study has the following shortcomings: firstly, the ecological awareness of farmers of different ages and educational levels is heterogeneous, and it is necessary to discuss the mediating effect of ecological awareness under different demographic statistics. Due to limitations in the use of natural resources, the livelihoods of farmers have had to change, resulting in a large number of labor force transfers. Some young and middle-aged people choose to work outside to solve their livelihood problems, leading to an increasing number of left behind elderly people in the village. The respondents from rural households are mainly aged 50 and above, with primary or junior high school education. The data does not have normal distribution conditions, which affects the depth of the research. Secondly, the selection of ecological awareness variables, especially the perception of ecological policies, cannot fully reflect farmers’ understanding and perception of nature reserve policies. There is significant room for improvement in the selection of ecological awareness indicators.
The economic valuation of ecosystems and their influence on people’s subjective well-being have attracted widespread attention. However, research on the impact of nature reserve construction on the well-being of surrounding farmers has not received the attention it deserves, and scholars need to explore the mechanisms and pathways through which it affects subjective well-being. Whether the path of perceived value on residents’ multidimensional well-being has universal significance requires more scholars to conduct research from different fields and professions. The impact of subjective ecological policy perception on their sense of well-being requires a more detailed analysis.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because the questionnaire belongs to the research group of the National Social Science Foundation. The questionnaire also involves related data and research topics of other team members, so it is not convenient to disclose them. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to TZ, enR0c3lkeEBzeXUuZWR1LmNu.
Author contributions
TZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YG: Software, Writing – review & editing. DH: Resources, Writing – original draft. KC: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Social Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 20BGL173).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the 1,002 interviewees that were interviewed voluntarily and appreciate the cooperation and assistance of the regional Natural Resource administrations and grassroots workers.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Achieng, T., Maciejewski, K., Dyer, M., and Biggs, R. (2020). Using a social-ecological regime shift approach to understand the transition from livestock to game darming in the Eastern Cape, South Africa. Land 9:97. doi: 10.3390/land9040097
Andrew, S. (2019). Happiness and health. Ann. Rev. Public Health. 40, 339–359. doi: 10.1146/annurev-publhealth-040218-044150
Andrew, S., Deaton, A., and Stone, A. A. (2015). Subjective wellbeing, health, and ageing. Lancet 385, 640–648. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61489-0
Chen, Y., Yue, W. Z., Zhang, L., Xia, H. X., and Hou, B. (2020). Theoretical thinking on ecological space zoning from the perspective of territorial space planning. China Land Sci. 34, 1–9. doi: 10.11994/zgtdkx.20200730.100813
Deaton, A., and Stone, A. A. (2016). Understanding context effects for a measure of life evaluation: how responses matter. Oxf. Econ. Pap. 68, 861–870. doi: 10.1093/oep/gpw022
Diener, E., Oishi, S., and Lucas, R. E. (2003). Personality, culture, and subjective well-being: emotional and cognitive evaluations of life. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 54, 403–425. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.54.101601.145056
Diener, E., Sandvik, E., and Pavot, W. (1991). “Happiness is the frequency, not the intensity, of positive versus negative affect” in Assessing well-being. Social indicators research series. ed. E. Diener (Dordrecht: Springer), 119–139.
Duan, W., Jiang, Y. C., and Ouyang, B. (2022). Trend of conflict between community livelihoods and nature reserves: based on the intergenerational differences of rural households’ natural resource utilization behavior. Resour. Sci. 44, 1267–1279. doi: 10.18402/resci.2022.06.13
Duan, W., and Ouyang, B. (2020). Impacts of protected areas on multidimensional poverty of surrounding rural households: analysis of the intermediary effect based on social capita. Resour. Sci. 42, 1074–1086. doi: 10.18402/resci.2020.06.06
Duan, W., Zhao, Z., Ma, B., and Wen, Y. L. (2015). Perceptions of rural household surrounding the protection area on protection benefits and losses. Resour. Sci. 37, 2471–2479.
Fu, H. P., Guan, J. X., and Zhong, Q. L. (2024). Landscape elements, ecosystem services and users’ happiness: an indicator framework for park management based on cognitive appraisal theory. Ecol. Indic. 165:112209. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2024.112209
Fu, Y. K., and Wang, Y. J. (2021). Experiential value influences authentic happiness and behavioural intention: lessons from Taiwan’s tourism accommodation sector. Tour. Rev. 76, 289–303. doi: 10.1108/TR-06-2019-0228
Guo, L., and Xiao, Y. Z. (2016). Spatial-temporal change and trade-off/synergy relationships among multiple ecosystem services in Three-River-Source National Park. Nanjing Soc. Sci. 8, 74–81. doi: 10.15937/j.cnki.issn1001-8263.2016.08.013
Han, Y. X. (2021). New dilemma and breakthrough of rural grass-roots governance under rural revitalization strategy—taking improvement of human settlements as an example. J. Yunnan Minzu Univ. 38, 48–56. doi: 10.13727/j.cnki.53-1191/c.2021.02.006
Hao, Q., Shan, J. J., and Deng, L. (2020). Evaluation on natural suitability of human settlement in the context of territorial space planning. China Land Sci. 34, 86–93. doi: 10.11994/zgtdkx.20200512.101919
He, D., Wang, J., Liu, X., Shi, X., Xu, Z., Wang, Y., et al. (2023a). The impact of farm household tourism operations on poverty reduction and conservation under the control policies of China’s protected areas. Front. Environ. Sci. 11:1294060. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2023.1294060
He, D., Wang, J., Zhang, T., Xu, Z., Wang, Y., Liu, S., et al. (2023b). The impact of tourism on farmers’ household income in the context of China’s regulatory policies of protected areas. Front. For. Glob. Change 6:1144116. doi: 10.3389/ffgc.2023.1144116
Justyna, C., Krzysztof, R., and Aleksandra, L. (2021). The anthropocene and ecological awareness in Poland: the post-socialist view. Anthr. Rev. 10, 494–523. doi: 10.1177/20530196211051205
Kahneman, D., and Deaton, A. (2010). High income improves evaluation of life but not emotional well-being. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107, 16489–16493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1011492107
Ketema, H., and Wei, W. (2021). Ecosystem service variation and its importance to the wellbeing of smallholder farmers in contrasting agro-ecological zones of East African Rift. Food Energy Secur. 10:4. doi: 10.1002/fes3.310
Li, M. J. (2015). Environmental pollution, governmental regulation and the happiness sense of residents: an empirical analysis based on CGSS (2008) micro-survey data. Mod. Econ. Sci. 37, 59–68.
Li, S., and Chen, G. (2012). Can relationships bring happiness?—Empirical evidence from rural China. Chin. Rural Econ. 8, 66–78.
Li, Y. Q., Shi, J. W., and Luo, X. Y. (2023). Mechanism of change in residents’ subjective well-being in rural tourism communities: the turning point of happiness from the development stage to the consolidation stage. Prog. Geogr. 42, 1514–1526. doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2023.08.006
Lin, J. S., Hsiao, C. T., and Glen, R. (2014). Perceived service quality, perceived value, overall satisfaction and happiness of outlook for long-term care institution residents. Health Expect. 17, 311–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-7625.2012.00769.x
Liu, C. K. (2012). The influence of pride, government preference and the supply of basic public services in urban and rural areas. J. Manage. Word. 9, 174–175. doi: 10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2012.09.019
Liu, X. M., Fu, Z., Wen, R. H., Jin, C. P., Wang, X. F., and Wang, C. (2020). Characteristics of human activities and the spatio-temporal changes of national nature reserves in China. Geogr. Res. 39, 2391–2402. doi: 10.11821/dlyj020200458
Liu, P., Zhang, R., and Li, D. (2022). The effect and mechanisms of self-transcendence values on durable happiness. Adv. Psychhol. Sci. 30, 660–669. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2022.00660
Loveridge, R., Sallu, S. M., and Marion, P. (2021). Certified community forests positively impact human wellbeing and conservation effectiveness and improve the performance of nearby national protected areas. Conserv. Lett. 14:e12831. doi: 10.1111/conl.12831
Ma, L., Qin, Y. T., Zhang, H., Zheng, J., Hou, Y. l., and Wen, Y. L. (2021). Improving well-being of farmers using ecological awareness around protected areas: evidence from Qinling region, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18:9792. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18189792
Ma, B., Shen, J. Y., Ding, H. M., and Wen, Y. L. (2016). Farmer protection attitudes and behavior based on protection perception perspective for protected areas. Resour. Sci. 38, 80–86. doi: 10.18402/resci.2016.11.12
Nikoleta, J., Chrisovalantis, M., Apostolos, K., and Dimitrakopoulos, P. G. (2020). The role of location and social impacts of protected areas on subjective wellbeing. Environ. Res. Lett. 15:114030. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/abb96e
Oreopoulos, P., and Salvanes, K. G. (2011). Priceless: the nonpecuniary benefits of schooling. J. Econ. Perspect. 25, 159–184. doi: 10.1257/jep.25.1.159
Pan, H. L., and Chen, H. X. (2021). Empirical research on the effect mechanism of ecological environment on residents’ happiness in China. Chin. J. Environ. Manage. 1, 156–161. doi: 10.16868/j.cnki.1674-6252.2021.01.156
Peng, J., Qi, Y. Y., and Yang, Y. (2024). Mechanism for impact of national park tourism on local residents’ nature conservation attitude: a case study of Shennongjia Pilot National Park. Acta Ecol. Sin. 44, 7461–7475. doi: 10.20103/j.stxb.202309041901
Peng, X., ZhanG, S., Peng, P., Chen, A., Li, Y., Wang, J., et al. (2023). Unraveling the ecological tapestry: a comprehensive assessment of changtang nature reserve’s ecological and environmental using RSEI and GEE. Land 12:1581. doi: 10.3390/land12081581
Qin, Z. Q., Wei, Z. X., and Xie, Z. Y. (2017). The correlation research among core values identity, psychological well-being and successful intelligence—based on the data validation of knowledge talents. J. Guizhou Univ. Finance Econ. 5, 20–29.
Ren, L., Gan, C. L., Wu, M., and Chen, Y. R. (2018). A study on farmers’ land investment behavior in resettlement area based on PVT. Resour. Sci. 40, 1539–1549. doi: 10.18402/resci.2018.08.05
Ren, J. F., Yang, J. L., and Zhu, M. Y. (2021). Relationship between consumer participation behaviors and consumer stickiness on mobile short video social platform under the development of ICT: based on value co-creation theory perspective. Inform. Technol. Dev. 27, 697–717. doi: 10.1080/02681102.2021.1933882
Schebella, M. F., Weber, D., Schultz, L., and Weinstein, P. (2019). The wellbeing benefits associated with perceived and measured biodiversity in Australian urban green spaces. Sustainability 11:802. doi: 10.3390/su11030802
Schimmack, U., Diener, E., and Oishi, S. (2002). Life-satisfaction is a momentary judgment and stable personality characteristic: the use of chronically accessible and stable sources. J. Pers. 70, 345–384. doi: 10.1111/1467-6494.05008
Shi, H. P., and Yi, M. L. (2020). Environmental governance, high-quality development and residents’ happiness—empirical study based on CGSS (2015) micro survey data. Manag. Rev. 32, 18–33. doi: 10.14120/j.cnki.cn11-5057/f.2020.09.002
Sladjana, V., Maja, C., and Zorana, N. (2022). The development of ecological awareness in the republic of Serbia. Int. Rev. 1, 51–59. doi: 10.5937/intrev2202059V
Song, M., and Jin, G. (2019). Differentiated eco-compensation for cultivated land protection in the context of planning regulation: retrospect and prospect. Issues Agric. Econ. 12, 77–85. doi: 10.13246/j.cnki.iae.2019.12.008
Wang, C. H. (2018). The construction and management of China’s nature reserves in the past forty years of reform and opening-up: achievements, challenges and prospects. Chin. Rural Econ. 10, 93–106. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2014.10.10
Wang, Z. M. (2023). Research on the impact of environmental regulation on residents’ subjective well-being. Shandong: Shandong University of Finance and Economics.
Welsch, H. (2006). Environment and happiness: valuation of air pollution using life satisfaction data. Ecol. Econ. 58, 801–813. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2005.09.006
Wen, Z. L., and Ye, B. J. (2014). Analyses of mediating effects: the development of methods and models. Adv. Psychhol. Sci. 22, 731–745. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2014.00731
Xie, H. L., Liu, Q., Chen, B., Chen, Q. R., and Zeng, H. S. (2024). Value realization of ecological products in national parks: basic logic, core mechanism and typical model. Econ. Geogr. 44:169. doi: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2024.08.018
Xu, X., Wang, S., and Yu, Y. (2020). Consumer’s intention to purchase green furniture: do health consciousness and environmental awareness matter? Sci. Total Environ. 704:135275. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135275
Zhang, J. H. (2022). Research on the impact of perceived value of ecosystem cultural services on tourists’ happiness. Shanghai: Shanghai Normal University.
Zhang, X. K., and Feng, X. H. (2009). A review on the feeling of pride: the concept, function and influencing factors. Psychol. Sci. 32, 1398–1340. doi: 10.16719/j.cnki.1671-6981.2009.06.016
Zhang, T. T., He, D., Kuang, T., and Chen, K. (2022). Effect of rural human settlement environment around nature reserves on farmers’ well-being: a field survey based on 1002 farmer households around six nature reserves in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19:6447. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19116447
Zhang, Y., Lou, Y., Shu, Q. F., and Li, S. Z. (2024). A performance comparison of different governance types of protected areas in China: from the perspective of local communities. J. Nat. Resour. 39, 2364–2382. doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20241007
Zhao, X. N., Chen, Q., and Chen, T. (2024). Risk assessment of human-animal conflict in Sanjiangyuan National Park. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 36, 39–46. doi: 10.12375/ysdwxb.20240118
Zhao, S. D., and Zhang, Y. M. (2006). Ecosystems and human well-being: the achievements, contributions and prospects of the millennium ecosystem assessment. Adv. Earth Sci. 21, 895–902.
Zheng, D. F., Hao, S., and Lv, L. T. (2020). Spatial-temporal change and trade-off/synergy relationships among multiple ecosystem services in Three-River-Source National Park. Geogr. Res. 39, 64–78. doi: 10.11821/dlyj020180898
Zheng, W. L., Hong, W. J., and Luo, B. L. (2021). Enhancing farmers’ happiness in common prosperity: analysis based on economic income-social network-ecological welfare framework. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 21, 140–151. doi: 10.19714/j.cnki.1671-7465.2021.0095
Keywords: nature reserve, well-being, emotional well-being, ecological awareness, ecological policy perception, mediating effect
Citation: Zhang T, Guo Y, He D and Chen K (2025) Impact of nature reserve establishment on the subjective well-being of surrounding farmers: an analysis based on the mediating effect of farmers’ ecological awareness. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1517453. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1517453
Edited by:
Rahim Maleknia, Lorestan University, IranReviewed by:
Ashkan Nabavi-Pelesaraei, Technical University of Denmark, DenmarkMoslem Savari, Khuzestan University of Agricultural Sciences and Natural Resources, Iran
Ahmad Bazgir, Razi University, Iran
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Guo, He and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tingting Zhang, enR0c3lkeEBzeXUuZWR1LmNu; Ke Chen, Y2hlbmtlQHN5YXUuZWR1LmNu
 Tingting Zhang
Tingting Zhang Yuanyuan Guo
Yuanyuan Guo Dan He
Dan He Ke Chen3*
Ke Chen3*