
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Sustain. Food Syst., 05 March 2025
Sec. Water-Smart Food Production
Volume 9 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2025.1500907
This article is part of the Research TopicGreen Approaches Towards Pollutants Amputation for Water Footprint Sustainability in Food SystemsView all 4 articles
 Aroosha Saif1
Aroosha Saif1 Syeda Itrat Rizvi1
Syeda Itrat Rizvi1 Zarneen Shaukat1
Zarneen Shaukat1 Mamoona Saif1
Mamoona Saif1 Sobia Tabassum2
Sobia Tabassum2 Rizwan Khalid1
Rizwan Khalid1 Fahad Javed3
Fahad Javed3 Nazih Y. Rebouh4
Nazih Y. Rebouh4 Faiza Hassan5*
Faiza Hassan5* Qamar uz Zaman6*
Qamar uz Zaman6*Introduction: Effective wastewater management remains a significant challenge in Pakistan, with conventional methods often falling short in addressing the release of harmful pollutants into water bodies.
Method: This study explores the use of a novel composite photocatalyst combining biochar, zinc oxide (ZnO), and copper diphenylamine (Cu-DPA) to improve wastewater treatment under visible light. The composite was prepared by varying the Cu-DPA content in ZnO, with ratios of 50%, 40%, 30%, and 17%, alongside standard biochar ZnO and Cu-DPA formulations. Characterization techniques, including FTIR, XRD, and UV-visible spectroscopy were used to analyze the composite's properties. Photocatalytic performance was assessed by degrading Methylene Blue, a common dye pollutant, under visible light.
Results: The results showed that while ZnO alone achieved 78% degradation, the composites with different Cu-DPA ratios demonstrated varying efficiencies, with the biochar-enhanced ZnO/Cu-DPA composite achieving the highest degradation rate of 97% in 80 min.
Discussion: This composite exhibited good reusability over seven cycles. This research highlights the potential of the biochar ZnO/Cu-DPA composite as an effective, eco-friendly solution for wastewater treatment, offering significant improvements in photocatalytic performance and sustainability.
Water encompasses a significant portion of Earth's surface, accounting for three-fourths of its total area (Mostacedo-Marasovic et al., 2022). Of all the water on Earth, around 97.5% is saltwater found primarily in oceans, while the remaining 2.5% is freshwater. Freshwater sources include rivers, lakes, groundwater, and ice caps. For instance, the United Nations reports that nearly 2 billion people globally lack access to safe drinking water, with countries like India and South Africa facing acute water shortages and pollution challenges. In India, 70% of surface water is contaminated, while in South Africa, 30% of the population experiences water scarcity. These examples emphasize the critical need for innovative solutions, such as photocatalytic materials, for effective water treatment and management, thereby aligning with the study's objective. Of all the water on Earth, around 97.5% is saltwater found primarily in oceans, while the remaining 2.5% is freshwater. Freshwater sources include rivers, lakes, groundwater, and ice caps (Khan et al., 2023). This limited freshwater supply is essential for human consumption, agriculture, industry, and maintaining ecological balance (Stewart-Koster et al., 2023). Ensuring a secure future for humanity has become a pressing need, as our world grapples with environmental degradation and pollution (Zhou and Gu, 2024; Gupta and Suhas, 2009). With rapid population growth and technological advancements, water demand has surged across agriculture, industry, and households, leading to substantial wastewater generation (Gupta and Suhas, 2009). This escalating trend of growth and population, highlighted in reports like the United Nations World Water Development Report, emphasizes the urgent need for wastewater treatment and management (Mujtaba et al., 2024). Studies project that by 2050, global population growth will further strain clean water systems, with agriculture, industries, and municipalities collectively contributing to water scarcity (Ahsan et al., 2023). The severity of environmental challenges is evident in alarming statistics from the World Health Organization, which reported millions of deaths attributed to unhealthy environments, particularly due to air and water pollution (Haso et al., 2022; Kumari et al., 2023). The growing scarcity of water resources is exacerbated by factors like population migration, industrialization, and climate change, driving an ever-increasing demand for water (Dunphy and Rustum, 2024). The gravity of these issues cannot be overstated. Every day, vast amount of waste pollutants are discharge into the pubic-water systems, posing significant health risks and contributing to avoidable deaths (Edo et al., 2024; Yan et al., 2021).
Industrial wastewater contains a variety of pollutants, including biodegradable organic matter, total suspended solids, pathogens, nutrients, heavy metals, non-biodegradable organics, total dissolved solids, and dyes (Bogale et al., 2024). Dyes are considered a major pollutant present in water bodies. Dyes are substances which chemically attach to a substrate on which they are interacting (Chellapandi and Madhumitha, 2023). Each year, approximately 700,000 tons of various dyes are manufactured from about 100,000 commercially available options (Kusumlata et al., 2024). However, a significant environmental concern arises as most used dyes are disposed of without proper treatment, leading to the presence of dye effluents in water bodies (Dutta et al., 2024). The discharge of dye effluents into the environment is linked to the following four primary industries: The textile industry, dyeing industry, paper and pulp, tannery, and paint (Kumari et al., 2023; Katheresan et al., 2018; Kamati et al., 2024). These sectors are acknowledged for their role in releasing dye effluents, which may lead to environmental consequences, if not appropriately handled (Rahman and Tabassum, 2024). Among these industries, the Textile industry stands out as the largest user of dyestuff globally, utilizing approximately 10,000 tons per year (Periyasamy, 2024). This industry also produces the highest volume of dye effluent, estimated at around 100 tons annually, highlighting the substantial impact of dye-related wastewater (Katheresan et al., 2018). The extensive use of dyestuff in textile processes contributes significantly to the generation of large quantities of dye wastewater, aggravated by the industry's substantial water demands (Kallawar and Bhanvase, 2024).
Dyes from industrial operations pose significant risks, including respiratory issues (Yadav et al., 2014), skin irritation (Hassaan et al., 2017), and serious health conditions from long-term exposure (Ramamurthy et al., 2024). Environmentally, dye effluents harm aquatic life (Donkadokula et al., 2020), disrupt ecosystems, and reduce water quality (Kolya and Kang, 2024). Soil contamination from improper disposal affects fertility (Vikrant et al., 2018) and plant health (Bhatia et al., 2017), with potential risks to groundwater (Slama et al., 2021; Eseoghene et al., 2024). The removal of dyes is very important because when industries use dyes, they create a lot of pollution (Lanjwani et al., 2024). They store the waste from dyes and then release it into the water, which makes the water dirty and colored (Tolkou et al., 2024). This is a big concern for the environment and people's health, because these dyes can be harmful and toxic (Ikhlaq et al., 2024). It is very difficult to degrade the dyes due to their complex chemical structure because they usually contain numerous aromatic rings (Ikhlaq et al., 2021). It is thus important to find better ways to deal with dye waste. Waste should be treat before letting it go into the environment or even reuse it in their processes (Date and Jaspal, 2024). This is better for the environment and can save money too. Various treatment methods are available to combat wastewater pollution, including physical, chemical, and biological approaches (Lotha et al., 2024). Developing sustainable processes for color removal is crucial for advancing water treatment technologies and reducing environmental impact. Among all other techniques available, the Photocatalytic degradation is considered one of the most widely used techniques for treating dye-containing wastewater (Khan et al., 2024). Photocatalytic dye degradation employs three mechanisms: dye sensitization through charge injection, indirect dye degradation via oxidation/reduction, and direct photolysis. In dye sensitization, light excites electrons, creating radicals that degrade dyes into water and carbon dioxide. Indirect degradation generates hydroxyl radicals, which mineralize dyes completely. Direct photolysis, a slower process, degrades dyes under UV light without a catalyst (Saeed et al., 2022).
Different types of photocatalysts, including homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts, are used in wastewater treatment. When light, whether UV or visible, falls on a catalyst, an electron is excited from the valence band to the conduction band, creating a positive hole (Raashid et al., 2023). These photo-induced electrons and holes react with dyes, initiating a series of reactions that ultimately generate hydroxyl radicals, which are strong oxidizing agents that completely mineralize the dye into subsequent products (Saeed et al., 2022). Single metal oxides photocatalysts are effective but limited to UV light and have high electron-hole recombination rates (Liu et al., 2013). To improve performance, techniques such as the addition of functional groups and doping with metals and non-metals (Raizada et al., 2021) can significantly increase the photocatalytic performance by reducing the bandgap and enhancing visible light activity. Zinc oxide is a highly efficient semiconductor photocatalyst because of its non-toxic nature, cost effectiveness and widely availability, great photosensitivity, and chemical stability (Binjhade et al., 2022). Apart from its advantages, there is a significant limitation of using ZnO. ZnO has a higher bandgap of 3.2 eV which makes it difficult to absorb visible light. That's why it can only work under UV light (Chantes and Jarusutthirak, 2015). Unfortunately, sunlight produces only 4%−5% of UV radiation (Xu et al., 2010; Koe et al., 2020). As a result, harnessing solar energy efficiently through photocatalytic techniques is still problematic. To enhance the photocatalytic activity of semiconductor photocatalysts, doping with narrow-band gap materials are widely used (Sun et al., 2024). One technique to boost the photocatalytic activity is to increase the stability of charges or radical lifetime, because these are the main components which initiate the photocatalytic reaction. As soon as the radical lifetime ends, the reaction stops, and no further dye will be degraded. So, the addition of functional groups can significantly increase the photocatalytic performance (Navidpour et al., 2023). A metal complex is formed when the metal cation interacts with the organic ligand (Wu et al., 2024). Because of its characteristics having low density, large surface area and significant pore sizes, this metal complex will boost the photocatalytic activity under visible light. The photocatalytic activity of ZnO and other semiconductors can significantly increase when combined with the metal complexes according to recent research (Berehe et al., 2023). Although metal complexes are available in a vast variety, but metal complexes containing copper are usually more prioritized because copper is available in a vast variety as well as the complex's wide surface area and significant pore sizes (Pathak et al., 2024). In the year 2020, Samira and her team created four mononuclear copper-II complexes with demonstrated photocatalytic activity against dyes including RB, CR, CV, MO, and MB. In the year 2020, four mononuclear copper-II complexes with demonstrated photocatalytic activity against dyes including Rhodamine B, Congo Red, Crystal Violet, Methylene Orange, and Methylene Blue (Carvalho et al., 2020). It was investigated the synthesis of a Cu(II)–Quinoline complex supported on silica as a catalyst for the removal of methylene blue dye. The study reported that the Cu(II) coordination complex functioned as a photo-Fenton-like catalyst, achieving an impressive 95% dye degradation efficiency under solar irradiation within 2.5 h (Khudkham et al., 2022). The utilization of hydrogen peroxide as an oxidant facilitated the complete degradation (100%) of methylene blue dye by all tested complexes within 90 min. In a separate study, a Cu(II)-pyridyl complex catalyst demonstrated remarkable efficiency, degrading 95% of methylene blue dye (16 mg/L) and 93.7% of Rhodamine B (24 mg/L) within 35 min (Jain et al., 2019).
Considering the concepts discussed previously, a Biochar ZnO/Cu-DPA nanocomposite was suggested, which was demonstrated to have higher photocatalytic performance than ZnO or Cu-DPA alone. Biochar has been highly important in photocatalysis due to its splendid characteristics like acting as a good support material, improving the chances of reusability efficiency, and increasing the surface area of the photocatalyst and availability of many surface-active sites. It also serves the purpose of a shield that saves the photocatalyst from degradation in unfavorable conditions (Rasouli et al., 2023). The current work focused on the synthesis of Biochar-based nanocomposites with different proportions of Cu-DPA (17%, 30%, 40%, and 50%), achieved through a mechanical grinding process. The prepared catalysts' photocatalytic activities were analyzed by observing the degradation of methylene blue when subjected to visible light. Besides, catalyst characterization, operational optimization, and catalyst reusability analysis were also performed.
Ethanol 99% concentrated (Merck chemicals), Potassium hydroxide KOH (Sigma chemicals), Zinc sulfate hexahydrate (AnalaR chemicals), Diphenylamine (Merck chemicals), and Copper sulfate pentahydrate (Sigma chemicals). Additionally, Bagasse was sourced from the locally from outskirts of Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan.
By using the precipitation method for the synthesis of the Cu-DPA complex, firstly 3 gm of diphenylamine were dissolved in 15 mL of ethanol and 3 g of copper sulfate pentahydrate (CuSO4·5H2O) were dissolved in 15 ml of distilled water. Then the solutions were thoroughly mixed with a magnetic stirrer at room temperature for 2 h until a homogeneous solution was obtained. Subsequently, the solution was left undisturbed for 3 days to facilitate the creation of blue precipitates. After the precipitates were formed, these were washed 4 times with distilled water and one time with ethanol to remove any impurities. Finally, the precipitates were dried in hot air oven at 40°C for 24 h.
This composite was prepared through the sol-gel method. The first step of this method is to prepare 0.2 mol/L aqueous solution of zinc sulfate hexa-hydrate (ZnSO4·6H2O) and 0.4 mol/L potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution. To form a white suspension, a solution of KOH was introduced slowly into the ZnSO4 solution while stirring continuously at ambient temperature. For 20 min, the mixture was then centrifuged at 4,700 rpm. Subsequently, the off-white substance underwent two washes with distilled water and one wash with pure ethanol to remove any impurities. This was followed by calcination at 500°C for 3 h (Berehe et al., 2023; Ghorbani et al., 2015).
Before starting the pyrolysis process, it is important to do the pre-treatment. Pre-treatment involves washing the biomass to remove any dust particles because this can affect the performance of the pyrolysis process. After the pretreatment step, it was moved into the furnace to be pyrolyzed. The furnace temperature was maintained at 200°C for the process to be effective (Kamali et al., 2021). After the 2-h pyrolysis period, the pyrolyzed biomass (biochar) was cooled down inside the furnace so that rapid temperature change could not affect the properties of biochar. Once cooled, the biochar was taken out of the furnace and should be stored in containers for later use.
Different mixtures of synthesized ZnO nanoparticles with varying amounts of copper diphenylamine (e.g., 50%, 40%, 30%, and 17%) were prepared using a simple grinding method. Pestle and mortar were used for the uniform distribution of the composite and the final product was calcined at 300°C for 1 h (Berehe et al., 2023). Then the desired quantity of Biochar and photocatalyst nanoparticles of ZnO/Cu-DPA were gathered corresponding to the composite ratio and transferred into a grinding stage which is done by ball mill. The mixture of biochar and the Photocatalyst nanoparticles was placed inside a 500 ml jar with 4 pcs of the steel balls to aid the grinding process. The machine crushed the mixture to the finest extent and thoroughly mixed it to form a homogeneous compound. Such a process pays attention to maintaining a uniform particle size distribution and preventing an overheating or the crusher from out-of-levelness. After completing the grinding process, the obtained mixture was calcined at 150°C for 1 h for the synthesized Biochar-ZnO/Cu-DPA composite.
Structural analysis of the synthesized materials was performed using a Shimadzu X-ray diffractometer (Model: XRD-7000). The morphological characteristics were examined through scanning electron microscopy (SEM) using a JSM-JEOL 6390 instrument. Functional groups present in the samples were identified using Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy (PerkinElmer). Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue (MB) dye was conducted in a tungsten lamp reactor (60 W, Japan), with the degradation process monitored via a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Shimadzu UV-3600 Plus).
The photocatalytic experiment was conducted using a prepared methylene blue solution by dissolving 10 mg of methylene blue in 1,000 ml distilled water. Take 125 ml of the methylene blue solution and to ensure the adsorption/desorption equilibrium, the solution were stirred in the dark for approximately 30 min. Add 25 mg of each catalyst preparation, including those with different amounts of Cu-DPA mixed with ZnO and the biochar-based photocatalyst. The beaker was positioned on a stirrer which is magnetized, the lowering of the temperature was achieved with the help of water. The setup was irradiated by using a 60 W tungsten lamp and positioned at a height of 10 cm above the beaker. Stirring of the mixture was continuously performed during the irradiation, to obtain even exposure to light.
After 80 min of time intervals, 7 ml of the solution was withdrawn and passed through a centrifugation process at 4,700 revolutions per minute. A UV-visible spectrophotometer is used to measure the absorbance of the clear liquid where the wavelength of the dye has its maximal absorbance (λmax), typically observed at a wavelength of ~663 nm. The sample's absorbance was measured before irradiation namely Ao and the absorbance of sample was measured after irradiation namely At (Berehe et al., 2023; Zelekew et al., 2021).
After the treatment was over, the Biochar ZnO/Cu-DPA photocatalyst underwent a recycling process. This involves washing of the catalyst using distilled water and acetone alternately to remove any leftover solution. The washed and dried catalyst was then immersed in a new MB solution with the same MB concentration (10 ppm) for the next run. These procedures were implemented in a series of cycles in order to determine the reusability of the catalyst and its stability over time. Similarly, an assessment of catalyst performance in MB degradation under visible light was done to ensure its consistent performance with the testing conditions and catalyst integrity maintained throughout the experiment (Ramadevi et al., 2023).
This section presents the experimental results, their interpretations, and conclusions derived from the experiments.
X-ray diffraction is used to identify the materials crystallinity. Zinc oxide has a hexagonal crystalline structure so to find out the crystallographic nature of zinc oxide we employed the X-ray diffraction technique. From Figure 1, we analyzed that there are 10 peaks formed at 2θ angles of 31.7°, 33.9°, 36.1°, 38.2°, 47.6°, 56.5°, 59.7°, 62.8°, 67.9°, and 69.10°. These peaks confirm the hexagonal crystalline structure of the zinc oxide nanoparticles. Moreover, the sharp peaks in this graph confirm the crystalline structure of zinc oxide nanoparticles (Berehe et al., 2023). The peak intensities suggest a high degree of crystallinity and potentially a preferred orientation along specific planes. This XRD pattern helps confirm the successful synthesis of Zinc oxide nanoparticles and the phase purity of the material, as there are no significant impurity peaks observed.
The morphological and structural characteristics of the synthesized ZnO particles were analyzed using SEM. The SEM image, presented in Figure 2, confirms that the Zinc Oxide particles exhibit a rod-like morphology, which is a typical structural feature of ZnO synthesized via the sol gel method. The uniformity and well-defined shape of the rods suggest a controlled growth process, contributing to enhanced surface properties. These structural attributes play a crucial role in determining the material's photocatalytic efficiency and potential applications in environmental remediation (Chen et al., 2017).
FTIR analysis was used to investigate the functional groups present in the samples. To analyze the functional groups and chemical bonding in the material, Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy was performed. FTIR of ZnO is shown in Figure 3A. The absorption peak at 3,400 cm−1 shows the stretching vibration of the O-H bond, while the peak at around 2,300 cm−1 shows the bond between carbon dioxide that may absorbed from environment during the synthesis of catalyst. The peak at around 1,400 cm−1 shows the stretching of the carbon-carbon double bond while the significant absorption peaks at around 1,000 and 500 cm−1 show the stretching vibration between zinc and oxygen (Hoseinpour et al., 2017). FTIR spectra of Cu-DPA is shown in Figure 3B. The absorption peaks at around 3,400, 1,300, and 500 cm−1 show the stretching vibration between nitrogen and hydrogen while the significant peak at around 1,000 cm−1 shows the bond between copper and diphenylamine. This solid line indicates the presence of our prepared catalyst. At 500 cm−1, a peak with Cu2O functional groups indicates impurities or byproducts produced during the reaction, but these byproducts will mineralize after a certain time period, so no harmful effect of these byproducts was observed (Thirumala Rao et al., 2011). Figure 3C shows the combined spectra of zinc oxide with copper diphenylamine. This graph shows the similar functional group as in ZnO and Cu-DPA. The peak at 3,500 cm−1 shows the stretching vibration of NH bond while the peak at 900 cm−1 shows the bond between copper and diphenylamine ligands. At 500 cm−1, the absorption peak shows the presence of zinc oxide nano particles.
The results, shown in Figures 4A–F, demonstrate that the prepared catalysts were effective in degrading methylene blue. The figure indicates that the degradation efficiency of methylene blue increase as the concentration of copper diphenylamine decreases when the solution is irradiated under visible light. Samples were collected at 20-min intervals to measure the degradation percentage using UV-Visible spectroscopy. It was observed that the degradation of methylene blue increases by decreasing the concentration of Cu-DPA, up to 17%. Beyond this limit, further reduction didn't increase the percentage degradation. Among all the prepared catalysts, the Biochar ZnO/Cu-DPA exhibited the highest degradation percentage after 80 min, outperforming all other synthesized catalysts. Figures 4A–F also show that after 80 min, the dye solution containing Biochar ZnO/Cu-DPA has the lowest absorbance, in contrast to the dye solution with all other synthesized samples.
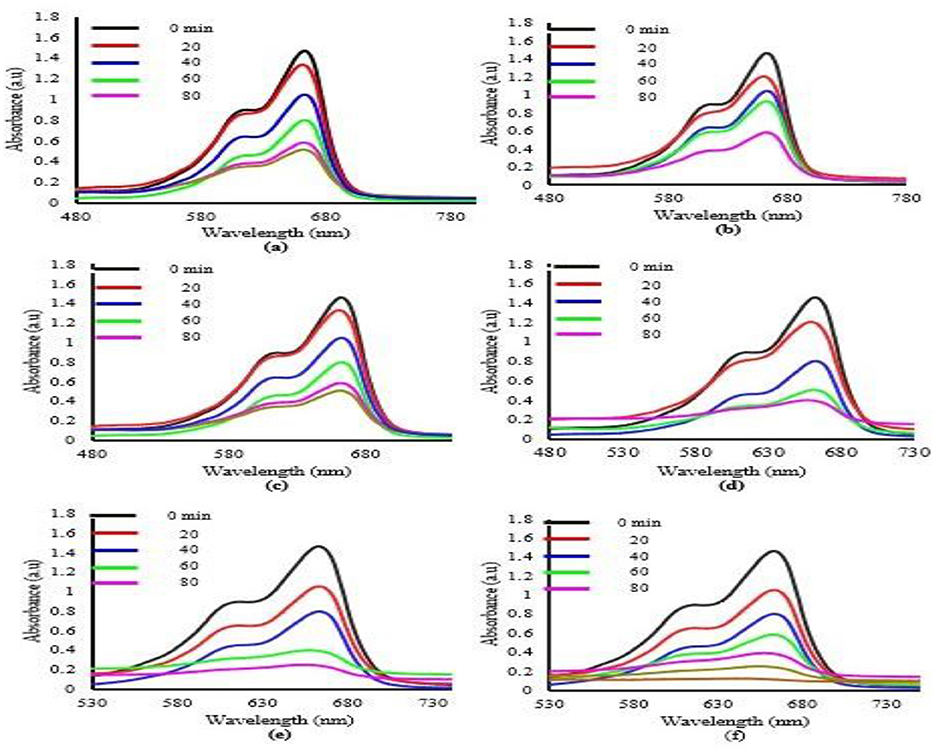
Figure 4. UV-Visible spectra depicting the absorption of methylene blue at various exposure intervals using (A) ZnO, (B) ZnO with 50% Cu-DPA, (C) ZnO with 40% Cu-DPA, (D) ZnO with 30% Cu-DPA, (E) ZnO with 17% Cu-DPA, and (F) Biochar ZnO and Cu-DPA.
The calculated % of degradation is 71, 97, 87, 78.5, 77.1, and 66% for ZnO, Biochar ZnO & Cu-DPA, and ZnO incorporating with 17% Cu-DPA, ZnO with 30% Cu-DPA, ZnO combined with 40% Cu-DPA and ZnO with 50% Cu-DPA, respectively. Every composite, apart from ZnO/50% Cu-DPA (as shown in Figure 4), achieved greater degradation efficiency than ZnO by itself. Figure 4 shows the percentage degradation of methylene blue in different irradiation times. Among all the prepared samples, Biochar ZnO/Cu-DPA has a high percentage degradation as per Figure 4. The reduced efficacy of ZnO nanoparticles can be attributed to their relatively large bandgap of 3.2 eV.
The concentration of dye greatly affects the performance of photocatalytic degradation. Figure 5 shows the relationship between percentage degradation and dye concentration. Different concentrated solutions (10 ppm, 20 ppm, 30 ppm, and 40 ppm) were prepared, and their degradation efficiency was observed using efficient photocatalyst (Biochar ZnO/Cu-DPA) under visible light irradiation for 80 min. The results shows that as concentration increases, the percentage degradation decreases. The calculated percentage degradation is 97%, 83%, 73%, and 61% for 10, 20, 30, and 40 ppm solutions. Generally, when dye concentration is increased, it increases the rate of reaction. However, on the other hand, an increase in dye concentration will decrease the degradation efficiency (Saeed et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2016). The major reasons behind this are decrease in the ratio of active sites of the photocatalyst, decrease in the ratio of OH radicals to the dye molecules and absorbance of light by dye molecules rather than creating photo-induced electron-hole pairs.
Besides achieving the highest percentage with our prepared catalyst Biochar ZnO/Cu-DPA, we can also reuse it. Figure 6 shows the percentage degradation after each cycle. The calculated percentage degradation is 97%, 89%, 83%, 78%, 75%, 71%, and 66% after 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th, 6th, and 7th cycle respectively. In the first cycle, the material exhibits the highest degradation efficiency, close to 100%. However, as the number of cycles increases, there is a gradual decline in degradation performance. By the 3rd and 4th cycles, the degradation efficiency drops to around 85% and 75%, respectively. This trend continues, and by the 7th cycle, the efficiency falls to about 65%. This behavior suggests that the material's activity diminishes with repeated use, possibly due to factors like catalyst deactivation, surface entangling, structural changes, or the loss of active sites. Despite this decrease, the catalyst still retains a significant level of activity after seven cycles, indicating a degree of reusability, though efficiency declines with time.
The experimental results underscore the pivotal role that Cu-DPA plays in enhancing the photocatalytic activity of ZnO, especially under visible light irradiation. The significant improvement in degradation efficiency observed with the Biochar ZnO/Cu-DPA composite can be attributed to the synergistic effects between ZnO and Cu-DPA. The inclusion of biochar further amplifies this synergy, likely due to its high surface area and ability to act as an adsorbent, facilitating better interaction between the catalyst and dye molecules. The superior photocatalytic performance of Biochar ZnO/Cu-DPA compared to pristine ZnO suggests that Cu-DPA enhances the visible light absorption capability, extending the photocatalysts operational range beyond the UV spectrum. This is consistent with prior studies, where metal ion-doped or ligand-modified ZnO composites demonstrated increased activity due to improved charge separation and longer electron-hole lifetimes, reducing recombination rates. However, the decline in photocatalytic efficiency with increasing dye concentrations can be attributed to several factors. First, the higher concentration of dye molecules could block active sites on the catalyst surface, reducing the number of available sites for the catalytic reaction. Second, excessive dye molecules might absorb the incident light, limiting the photons available to activate the ZnO catalyst, thus diminishing the overall photocatalytic performance. This indicates that there is an optimal dye concentration for achieving the highest degradation efficiency, beyond which the performance is hindered. Visible light photocatalytic performance of the novel composite catalyst containing renewable biochar, zinc oxide (ZnO), and copper diphenylamine was evaluated for the degradation of methylene blue under varying temperatures and pH conditions. The temperature played a crucial role in influencing the rate of photocatalysis. At elevated temperatures, the degradation efficiency increased due to enhanced molecular collisions and improved adsorption of methylene blue onto the catalyst surface. However, extremely high temperatures may lead to the deactivation of the active sites or desorption of reactants, reducing efficiency. The pH of the solution significantly impacted the surface charge of ZnO and the catalyst's interaction with methylene blue molecules. At acidic pH, the protonation of functional groups on biochar and ZnO could hinder dye adsorption, while at highly alkaline pH, excessive OH− ions could scavenge photogenerated holes, reducing photocatalytic efficiency. Optimal degradation was achieved at neutral to slightly basic pH, where a balance between adsorption and reactive species generation was maintained. These results demonstrate the synergistic effect of temperature and pH on the composite catalyst's performance, ensuring efficient dye removal under visible light. The reusability tests show that while Biochar ZnO/Cu-DPA retains good activity over several cycles, a gradual decrease in efficiency is inevitable. This can be explained by potential catalyst deactivation due to surface fouling or clogging by residual dye molecules, structural changes to the catalyst, or a partial loss of active Cu-DPA sites over multiple cycles. This behavior, however, still reflects a promising level of reusability, suggesting that with proper regeneration techniques, the catalyst could maintain its performance over an extended period. Future work should explore the optimization of the Cu-DPA concentration to maximize the visible light absorption and enhance charge carrier dynamics further. Additionally, varying the types of biochar used in the composite may offer further improvements, as different biochar materials possess unique surface properties and porosities that could influence catalytic performance. The incorporation of other co-catalysts or dopants could also be investigated to boost activity further and reduce the rate of catalyst deactivation. Composite catalyst, combining renewable biochar, zinc oxide (ZnO), and copper diphenylamine exhibits enhanced photocatalytic efficiency due to its unique synergy. Biochar improves electron transfer and dye adsorption, while copper compounds increase visible-light absorption and catalytic activity. This sustainable catalyst significantly outperforms traditional catalysts, effectively degrading methylene blue under mild visible-light conditions (Deepika et al., 2022). Moreover, a more detailed analysis of the degradation process is necessary to ensure that the byproducts formed are fully mineralized into harmless end products. This is crucial for the practical application of photocatalysts in environmental remediation. Long-term stability tests, under varied environmental conditions, will also be essential to evaluate the robustness and feasibility of Biochar ZnO/Cu-DPA for industrial-scale applications. This discussion expands on the initial findings, offering insights into potential causes of performance trends and suggesting avenues for future research and optimization.
In summary, we have successfully synthesized Biochar ZnO/Cu-DPA for degrading methylene blue. The degradation of methylene blue was done using different ratios of photocatalysts under visible light for 80 min. The degradation efficiencies were measured as follows: ZnO achieved 78%, the mixture with 50% Cu-DPA achieved 66%, the catalyst with 40% Cu-DPA exhibited 77.1%, the 30% Cu-DPA showed 78.5%, the one with 17% Cu-DPA showed 87%, and the biochar-enhanced ZnO with Cu-DPA exhibit 97%. The results declared that biochar ZnO & Cu-DPA show the highest percentage of degradation irradiated under visible light. By using the best photocatalyst (Biochar ZnO & Cu-DPA), the effect of dye concentration was observed, and the results declared that with an increase in dye concentration, the degradation percentage decreased. In the last, the reusability of the highly efficient photocatalyst (Biochar ZnO & Cu-DPA) was observed. In the first cycle, the percentage degradation of methylene blue was observed to be 97%, but in the 7th cycle, the percentage degradation decreased to 66%. As a whole, the percentage degradation of methylene blue decreases by 30% after the 7th cycle. Biochar ZnO/Cu-DPA was deemed the best choice for remediating wastewater that contains dyes.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
AS: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. SR: Investigation, Writing – original draft. ZS: Investigation, Writing – original draft. MS: Data curation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. ST: Software, Writing – review & editing. RK: Investigation, Writing – original draft. FJ: Writing – original draft. NR: Software, Writing – review & editing. FH: Software, Writing – review & editing. QZ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This paper has been supported by the RUDN University Strategic Academic Leadership Program.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Ahsan, A., Jamil, F., Rashad, M. A., Hussain, M., Inayat, A., and Akhter, P. (2023). Wastewater from the textile industry: Review of the technologies for wastewater treatment and reuse. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 40, 2060–2081. doi: 10.1007/s11814-023-1475-2
Berehe, B. A., Assen, A. H., Kumar, A. S. K., Ulla, H., Duma, A. D., Chang, J. Y., et al. (2023). Highly efficient visible light active ZnO/Cu-DPA composite photocatalysts for the treatment of wastewater contaminated with organic dye. Sci. Rep. 13:16454. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43842-z
Bhatia, D., Sharma, N. R., Singh, J., and Kanwar, R. S. (2017). Biological methods for textile dye removal from wastewater: a review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47, 1836–1876. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2017.1393263
Binjhade, R., Mondal, R., and Mondal, S. (2022). Continuous photocatalytic reactor: critical review on the design and performance. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 10:107746. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2022.107746
Bogale, F. M., Teffera, B., and Aragaw, T. A. (2024). Recent developments in integrated anaerobic/aerobic (A/O) process for textile industry wastewater treatment: a review. J. Hazardous Mater. Adv. 15:100438. doi: 10.1016/j.hazadv.2024.100438
Carvalho, S. S. F., Rodrigues, A. C. C., Lima, J. F., and Carvalho, N. M. F. (2020). Photocatalytic degradation of dyes by mononuclear copper(II) complexes from bis-(2-pyridylmethyl)amine NNN-derivative ligands. Inorganica Chim. Acta 512:119924. doi: 10.1016/j.ica.2020.119924
Chantes, P., and Jarusutthirak, C. (2015). “A comparison study of photocatalytic activity of TiO2 and ZnO on the degradation of real batik wastewater,” in International Conference on Biological, Environment and Food Engineering (BEFE-2015) May 15-16, 2015 (Singapore).
Chellapandi, T., and Madhumitha, G. (2023). A short review of recent discoveries in montmorillonite-based photocatalysts for organic dye water pollutant degradation. Environ. Quality Manag. 33, 105–116. doi: 10.1002/tqem.22021
Chen, X., Wu, Z., Liu, D., and Gao, Z. (2017). Preparation of ZnO photocatalyst for the efficient and rapid photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 12, 1–10. doi: 10.1186/s11671-017-1904-4
Date, M., and Jaspal, D. (2024). Dyes and heavy metals: removal, recovery and wastewater reuse—a review. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 10:90. doi: 10.1007/s40899-024-01073-8
Deepika, D., Manpreet, H., Singh, K., and Malik, A. K. A. (2022). Novel composite of zinc-based metal organic framework embedded with SnO2 nanoparticle as a photocatalyst for methylene blue dye degradation as well as fluorometric probe for nitroaromatic compounds detection. J. Fluoresc. 33, 613–629. doi: 10.1007/s10895-022-03055-5
Donkadokula, N. Y., Kola, A. K., Naz, I., and Saroj, D. (2020). A review on advanced physico-chemical and biological textile dye wastewater treatment techniques. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 19, 543–560. doi: 10.1007/s11157-020-09543-z
Dunphy, E., and Rustum, R. (2024). “Challenges faced by developing economics to mitigate the impacts of climate change on water resources,” in Living with Climate Change, 149–172. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-443-18515-1.00026-5
Dutta, S., Adhikary, S., Bhattacharya, S., Roy, D., Chatterjee, S., Chakraborty, A., et al. (2024). Contamination of textile dyes in aquatic environment: adverse impacts on aquatic ecosystem and human health, and its management using bioremediation. J. Environ. Manage. 353:120103. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.120103
Edo, G. I., Itoje-akpokiniovo, L. O., Obasohan, P., Ikpekoro, V. O., Samuel, P. O., et al. (2024). Impact of environmental pollution from human activities on water, air quality and climate change. Ecol. Front. 44, 874–889. doi: 10.1016/j.ecofro.2024.02.014
Eseoghene, K., Uwaga Monica, A., Emmanuel Olurotimi, O., and Nko Okina, S. (2024). Groundwater quality and agricultural contamination: a multidisciplinary assessment of risk and mitigation strategies. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 22, 1772–1784. doi: 10.30574/wjarr.2024.22.2.1607
Ghorbani, H., Mehr, F., Pazoki, H., and Rahmani, B. (2015). Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by precipitation method. Oriental J. Chem. 31, 1219–1221. doi: 10.13005/ojc/310281
Gupta, V. K., and Suhas. (2009). Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal–a review. J. Environ. Manage. 90, 2313–2342. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.11.017
Haso, H. W., Dubale, A. A., Chimdesa, M. A., and Atlabachew, M. (2022). High performance copper based metal organic framework for removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Front. Mater. 9:840806. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2022.840806
Hassaan, M. A., El Nemr, A., and Hassaan, A. (2017). Health and environmental impacts of dyes: mini review. Am. J. Environ. Sci. Eng. 1, 64–67. doi: 10.11648/j.ajese.20170103.11
Hoseinpour, V., Souri, M., Ghaemi, N., and Shakeri, A. (2017). Optimization of green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by Dittrichia graveolens (L.) aqueous extract. Health Biotechnol. Biopharma 1, 39–49. doi: 10.22034/HBB.2017.10
Ikhlaq, A., Parveen, S., Raashid, M., Masood, Z., Rizvi, O. S., and Al Johani, T. A. (2024). Methylene blue (MB) removal from aqueous solution by alum; catalytic ozonation process. Discover Chem. Eng. 4, 1–17. doi: 10.1007/s43938-024-00046-9
Ikhlaq, A., Raashid, M., Akram, A., Kazmi, M., and Farman, S. (2021). Removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solutions by adsorption in combination with ozonation on iron loaded sodium zeolite: role of adsorption. Desalin. Water Treat 237, 302–306. doi: 10.5004/dwt.2021.27744
Jain, H., Joshi, A., Ramachandran, C. N., and Kumar, R. (2019). Synthesis of a highly efficient multifunctional copper (II)-pyridyl complex for adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes. ChemistrySelect 4, 4952–4961. doi: 10.1002/slct.201900498
Kallawar, G. A., and Bhanvase, B. A. (2024). A review on existing and emerging approaches for textile wastewater treatments: challenges and future perspectives. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 31, 1748–1789. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-31175-3
Kamali, M., Appels, L., Kwon, E. E., Aminabhavi, T. M., and Dewil, R. (2021). Biochar in water and wastewater treatment - a sustainability assessment. Chem. Eng. J. 420:129946. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.129946
Kamati, S. N., Yan, J., and Fan, J. (2024). A review on progresses in reactive dye-containing wastewater treatment. Water Pract. Technol. 19, 2712–2733. doi: 10.2166/wpt.2024.142
Katheresan, V., Kansedo, J., and Lau, S. Y. (2018). Efficiency of various recent wastewater dye removal methods: a review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 6, 4676–4697. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2018.06.060
Khan, F. S., Khaliq, A., Akram, M., Nasim, N., and Kausar, S. (2023). A review on future water resources, environmental and future prospects. Planta Animalia 2, 27–39.
Khan, S., Noor, T., Iqbal, N., and Yaqoob, L. (2024). Photocatalytic dye degradation from textile wastewater: a review. ACS Omega 9, 21751–21767. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c00887
Khudkham, T., Channei, D., Pinchaipat, B., and Chotima, R. (2022). Degradation of methylene blue with a Cu(II)-quinoline complex immobilized on a silica support as a photo-fenton-like catalyst. ACS Omega 7, 33258–33265. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c03770
Koe, W. S., Lee, J. W., Chong, W. C., Pang, Y. L., and Sim, L. C. (2020). An overview of photocatalytic degradation: photocatalysts, mechanisms, and development of photocatalytic membrane. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 27, 2522–2565. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-07193-5
Kolya, H., and Kang, C. W. (2024). Toxicity of metal oxides, dyes, and dissolved organic matter in water: implications for the environment and human health. Toxics 12:111. doi: 10.3390/toxics12020111
Kumari, H., Sonia, Suman, Ranga, R., Chahal, S., Devi, S., et al. (2023). A review on photocatalysis used for wastewater treatment: dye degradation. Water Air Soil Pollut. 234:349. doi: 10.1007/s11270-023-06359-9
Kusumlata Ambade, B., Kumar, A., and Gautam, S. (2024). Sustainable solutions: reviewing the future of textile dye contaminant removal with emerging biological treatments. Limnol. Rev. 24, 126–149. doi: 10.3390/limnolrev24020007
Lanjwani, M. F., Tuzen, M., Khuhawar, M. Y., and Saleh, T. A. (2024). Trends in photocatalytic degradation of organic dye pollutants using nanoparticles: a review. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 159:111613. doi: 10.1016/j.inoche.2023.111613
Liu, F., Leung, Y. H., Djurišić, A. B., Ng, A. M. C., and Chan, W. K. (2013). Native defects in ZnO: effect on dye adsorption and photocatalytic degradation. J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 12218–12228. doi: 10.1021/jp403478q
Lotha, T. N., Sorhie, V., Bharali, P., and Jamir, L. (2024). Advancement in sustainable wastewater treatment: a multifaceted approach to textile dye removal through physical, biological and chemical techniques. ChemistrySelect 9:e202304093. doi: 10.1002/slct.202304093
Mostacedo-Marasovic, S. J., Mott, B. C., White, H., and Forbes, C. T. (2022). Towards water literacy: an interdisciplinary analysis of standards for teaching and learning about humans and water. Discip. Interdisc. Sci. Educ. Res. 4:25. doi: 10.1186/s43031-022-00065-y
Mujtaba, G., Shah, M. U. H., Hai, A., Daud, M., and Hayat, M. (2024). A holistic approach to embracing the United Nation's Sustainable Development Goal (SDG-6) towards water security in Pakistan. J. Water Proc. Eng. 57:104691. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2023.104691
Navidpour, A. H., Abbasi, S., Li, D., Mojiri, A., and Zhou, J. L. (2023). Investigation of advanced oxidation process in the presence of TiO2 semiconductor as photocatalyst: property, principle, kinetic analysis, and photocatalytic activity. Catalysts 13:232. doi: 10.3390/catal13020232
Pathak, R., Punetha, V. D., Bhatt, S., and Punetha, M. (2024). A review on copper-based nanoparticles as a catalyst: synthesis and applications in coupling reactions. J. Mater. Sci. 59, 6169–6205. doi: 10.1007/s10853-024-09546-z
Periyasamy, A. P. (2024). Recent advances in the remediation of textile-dye-containing wastewater: prioritizing human health and sustainable wastewater treatment. Sustainability 16:495. doi: 10.3390/su16020495
Raashid, M., Kazmi, M., Ikhlaq, A., Iqbal, T., Sulaiman, M., Zafar, A. M., et al. (2023). Degradation of sulfoxaflor pesticide in aqueous solutions utilizing photocatalytic ozonation with the simultaneous use of titanium dioxide and iron zeolite catalysts. Water 15:1283. doi: 10.3390/w15071283
Rahman, M., and Tabassum, Z. (2024). Biotechnological approach to treat textile dyeing effluents: a critical review analysing the practical applications. Textile Leather Rev. 7, 125–152. doi: 10.31881/TLR.2023.189
Raizada, P., Soni, V., Kumar, A., Singh, P., Khan, A. A. P., Asiri, A. M., et al. (2021). Surface defect engineering of metal oxides photocatalyst for energy application and water treatment. J. Materiom. 7, 388–418. doi: 10.1016/j.jmat.2020.10.009
Ramadevi, P., Shanmugavadivu, R., Venkatesan, R., Mayandi, J., and Sagadevan, S. (2023). Photocatalytic dye degradation efficiency and reusability of aluminium substituted nickel ferrite nanostructures for wastewater remediation. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 150:110532. doi: 10.1016/j.inoche.2023.110532
Ramamurthy, K., Priya, P. S., Murugan, R., and Arockiaraj, J. (2024). Hues of risk: investigating genotoxicity and environmental impacts of azo textile dyes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 31, 33190–33211. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-33444-1
Rasouli, K., Rasouli, J., Mohtaram, M. S., Sabbaghi, S., Kamyab, H., Moradi, H., et al. (2023). Biomass-derived activated carbon nanocomposites for cleaner production: a review on aspects of photocatalytic pollutant degradation. J. Clean. Prod. 419:138181. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.138181
Saeed, M., Muneer, M., Haq, A., and Akram, N. (2022). Photocatalysis: an effective tool for photodegradation of dyes—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29, 293–311. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-16389-7
Slama, H. B., Chenari Bouket, A., Pourhassan, Z., Alenezi, F. N., Silini, A., and Cherif-Silini, H. (2021). Diversity of synthetic dyes from textile industries, discharge impacts and treatment methods. Appl. Sci. 11:6255. doi: 10.3390/app11146255
Stewart Koster, B., Bunn, S. E., Green, P., Ndehedehe, C., Andersen, L. S., Armstrong McKay, D. I., et al. (2023). Living within the safe and just Earth system boundaries for blue water. Nature Sustain. 7, 53–63. doi: 10.1038/s41893-023-01247-w
Sun, N., Si, X., He, L., Zhang, J., and Sun, Y. (2024). Strategies for enhancing the photocatalytic activity of semiconductors. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 58, 1249–1265. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2024.01.319
Thirumala Rao, G., Babu, B., Joyce Stella, R., Pushpa Manjari, V., and Ravikumar, R.V. S. S. N. (2011). Spectral Investigations on Cu2+-Doped ZnO nanopowders. Appl. Magn. Resonance 41, 69–78. doi: 10.1007/s00723-011-0234-4
Tolkou, A. K., Tsoutsa, E. K., Kyzas, G. Z., and Katsoyiannis, I. A. (2024). Sustainable use of low-cost adsorbents prepared from waste fruit peels for the removal of selected reactive and basic dyes found in wastewaters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 31, 14662–14689. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-31868-3
Vikrant, K., Giri, B. S., Raza, N., Roy, K., Kim, K.-H., Rai, B. N., et al. (2018). Recent advancements in bioremediation of dye: current status and challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 253, 355–367. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.01.029
Wu, L., Garg, S., and Waite, T. D. (2024). Electrochemical treatment of wastewaters containing metal-organic complexes: A one-step approach for efficient metal complex decomposition and selective metal recovery. J. Hazard. Mater. 466:133526. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.133526
Xu, C., Cao, L., Su, G., Liu, W., Liu, H., Yu, Y., et al. (2010). Preparation of ZnO/Cu2O compound photocatalyst and application in treating organic dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 176, 807–813. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.11.106
Yadav, A. K., Jain, C., and Malik, D. (2014). Toxic characterization of textile dyes and effluents in relation to human health hazards. J. Sustain. Environ. Res 3, 95–102. doi: 10.1146/annurev-environ-100809-125342
Yan, X., Feng, J., Li, P., Li, J., Ren, B., Gao, S., et al. (2021). Fast and efficient removal of mercury ions using zirconium-based metal–organic framework filter membranes. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 131:108796. doi: 10.1016/j.inoche.2021.108796
Zelekew, O. A., Fufa, P. A., Sabir, F. K., and Duma, A. D. (2021). Water hyacinth plant extract mediated green synthesis of Cr(2)O(3)/ZnO composite photocatalyst for the degradation of organic dye. Heliyon 7:e07652. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07652
Zhang, A. Y., Wang, W. K., Pei, D. N., and Yu, H. Q. (2016). Degradation of refractory pollutants under solar light irradiation by a robust and self-protected ZnO/CdS/TiO2 hybrid photocatalyst. Water Res. 92, 78–86. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.01.045
Keywords: visible photocatalysis, methylene blue, advanced oxidation process, biochar, wastewater
Citation: Saif A, Rizvi SI, Shaukat Z, Saif M, Tabassum S, Khalid R, Javed F, Rebouh NY, Hassan F and Zaman Qu (2025) Development of composite catalyst containing renewable biochar blended with zinc oxide and copper diphenyl amine for visible light photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1500907. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1500907
Received: 24 September 2024; Accepted: 13 January 2025;
Published: 05 March 2025.
Edited by:
Shoomaila Latif, University of the Punjab, PakistanReviewed by:
Amita Shakya, Amity University, Chhattisgarh, IndiaCopyright © 2025 Saif, Rizvi, Shaukat, Saif, Tabassum, Khalid, Javed, Rebouh, Hassan and Zaman. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qamar uz Zaman, cWFtYXIuemFtYW4xQGVudnMudW9sLmVkdS5waw==; Faiza Hassan, ZmFpemEuaGFzc2FuQGNoZW0udW9sLmVkdS5waw==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.