- 1College of Economics and Management, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China
- 2Academy of Global Food Economics and Policy (AGFEP), China Agricultural University, Beijing, China
- 3Shanghai Midu Information Technology Co., Ltd, Shanghai, China
Major animal epidemics can significantly disrupt the pork market. Understanding how consumer network attention, triggered by these epidemics, impacts pork price fluctuations is of great significance for maintaining market stability and ensuring food security. This study focuses on exploring this complex relationship, with a particular emphasis on the roles of information dissemination and emotion transmission. Taking African Swine Fever (ASF) as a case study, monthly provincial panel data from June 2021 to November 2022 were collected. Web scraping techniques and social network analysis were employed. Weibo user repost and emotion transmission networks were constructed, integrating social network structures into the analytical framework to comprehensively analyze the problem. The study reveals several important findings. Firstly, consumer network attention significantly intensifies pork price volatility during major epidemics, and there is notable heterogeneity across different information environments. Secondly, both information dissemination and emotion transmission play moderating roles. Specifically, the media information index negatively moderates the relationship between consumer attention and pork price fluctuations. The betweenness centrality of the Weibo repost network also has a negative moderating effect, indicating that “opinion leaders” on social media can mitigate the impact of consumer attention on price fluctuations through selective information dissemination. In contrast, the closeness centrality of the emotion transmission network has a positive moderating effect, highlighting the amplifying effect of rapid emotion propagation on market reactions. This research highlights the economic implications of the relationship between consumer network attention, information dissemination, emotion transmission, and pork price fluctuations during food safety incidents. It emphasizes the importance of understanding these dynamics for maintaining food market stability.
1 Introduction
In the context of globalization, the spread of animal diseases is no longer restricted by geographical boundaries. The outbreak of African Swine Fever (ASF) in China is particularly noteworthy. Its rapid spread has caused significant damage to China's livestock and poultry industry, leading to severe fluctuations in the national pork market. Pork, as the primary source of meat for both urban and rural residents in China, accounts for 73% of the country's total meat consumption, and China's pork consumption represents 49.3% of the global total. Therefore, the stability of the pork market is not only crucial to China's economy but also has far-reaching implications for the global supply chain. The supply and demand dynamics of the pork market are influenced by various factors, including long-term factors such as household income levels, population growth, and changes in consumption patterns; short-term factors involve seasonal dietary habits, epidemics, food safety issues, and consumer substitution effects. Major swine epidemics, such as the H7N9 avian flu in 2013, ASF in 2018, and H5N1 avian flu in 2024, pose threats not only to livestock production but also spread rapidly through the internet, altering consumer behavior and decision-making. In the digital economy era, this impact is particularly significant as consumers react swiftly to online public opinion regarding major public events. On the one hand, this directly influences market consumption decisions and price fluctuations; on the other hand, the spread of online information may have lasting effects on market demand, thereby reshaping consumer behavior and market response in the long term.
In recent years, frequent incidents involving fresh agricultural products, especially major animal epidemics, have caused drastic fluctuations in agricultural product prices. Studies have found that, in addition to the fundamental factors of supply and demand, information asymmetry and the disturbances caused by unexpected events significantly impact the mechanisms behind agricultural price shocks (Zhang et al., 2013; Zhao et al., 2013). Particularly for significant animal epidemics like ASF, characterized by sudden outbreaks, high transmission rates, and high morbidity and mortality, they have become one of the main factors affecting livestock product prices. The rapid development of the internet has alleviated information asymmetry but also introduced the problem of information overload. In the digital economy era, information about major animal epidemics spreads rapidly through the internet, originating from either official media or individuals. The exponential growth of information dissemination on the internet greatly reduces market information asymmetry while increasing consumer attention to these events. The fast development of the internet empowers consumers to actively search for and engage with information that interests them, forming consumer network attention. According to behavioral economics theory, consumer attention to a particular event can significantly influence price fluctuations by affecting their decision-making behavior (Liang et al., 2017; Ma et al., 2023; Li et al., 2024; Li, 2024).
Information about major animal epidemic events quickly proliferates on the internet, creating online public opinion. Media, as a key entity in online public opinion, not only serves as the main information source for consumers to learn about major animal epidemics but also largely determines the volume of information consumers can access, thereby influencing information transparency. Thus, the extent of consumer network attention's impact on pork price fluctuations may vary under different levels of media reporting intensity. In the context of major animal epidemics, online public opinion spreads rapidly among consumers, often triggering “group polarization” (Chen et al., 2020; Lu, 2021; Jia et al., 2024) and further amplifying the emotional transmission among consumers. Consumer attention is spread through behaviors such as reposting and commenting on social media, forming a broad network of information dissemination where the emotions carried by this information also spread quickly. The “spiral of silence” effect further intensifies the transmission of certain negative emotions, leading to a generally pessimistic outlook among consumers regarding market prospects (Soon, 2020; Kubin and von Sikorski, 2021; Zhang and Wang, 2022). As information is repeatedly disseminated and emotions continue to escalate, consumer purchasing decisions change accordingly, resulting in severe price fluctuations due to demand changes in the market (Duan et al., 2024). In this context, consumer network attention has a significant impact on pork price fluctuations, but this relationship is neither one-way nor linear. Media reporting intensity, information dissemination, and emotional transmission play crucial moderating roles in this process, either amplifying or mitigating the effect of consumer network attention on market prices. This paper explores these mechanisms: how does consumer network attention, under the shock of major animal epidemics, affect pork price fluctuations? How do media reporting intensity, information dissemination, and emotional transmission moderate the relationship between consumer network attention and pork price fluctuations?
Compared to previous studies, the main contribution of this paper lies in its consideration of the profound impact of weak relationship networks on consumer behavior. Based on textual data from China's largest social media platform, Weibo,1 this study employs social network analysis to construct Weibo user repost networks and emotion transmission networks. By integrating weak relationship networks into the analytical framework, this paper not only reveals how information and emotions spread and evolve among consumers but also demonstrates how pork prices respond to the dissemination of information and emotions. Particularly in the context of major swine epidemics, the interaction patterns of consumers on the Weibo platform provide valuable insights into understanding the rapid changes in market sentiment and their impact on market prices. This research offers a unique perspective for comprehensively assessing how consumer attention influences their purchasing decisions, ultimately leading to fluctuations in pork prices.
The structure of this artcle is as follows: the first section is the introduction; the second section presents the theoretical analysis and research hypotheses; the third section focuses on model construction and variable selection; the fourth section analyzes the empirical results; and the fifth section concludes with policy recommendations.
2 Theoretical analysis and research hypothesis
Pork prices result from the interaction between supply and demand, and sudden major swine epidemic shocks can disrupt this balance, causing abnormal fluctuations in pork prices (Zhang and Zhang, 2011). On the supply side, sudden swine epidemics cause multiple damages to the pig industry, leading to supply shortages and a retaliatory rise in prices. On the demand side, such epidemics significantly impact market demand (Bakhtavoryan et al., 2014; Liu and Niyongira, 2017). In the internet era, consumers are surrounded by various online information sources. When sudden events are disseminated online, they attract consumer attention. According to the theory of bounded rationality, consumers gather information through online attention and make decisions, affecting their attitudes, perceptions, and purchasing choices (Bakhtavoryan et al., 2014; Peng, 2015; Ovca et al., 2018; Li et al., 2024).
When a sudden swine epidemic occurs, consumers' limited understanding of the disease and its potential consequences diminishes their sense of control (Fritsche et al., 2017; Kakkar and Sivanathan, 2017). Driven by a motive to regain control, consumers significantly increase their attention to the event to obtain more market information for their purchasing decisions (Landau et al., 2015; Yu et al., 2022; Carrieri and Principe, 2022). Therefore, event information needs to influence purchasing decisions through consumer online attention, which subsequently triggers changes in market effective demand and leads to price fluctuations (Li et al., 2024).
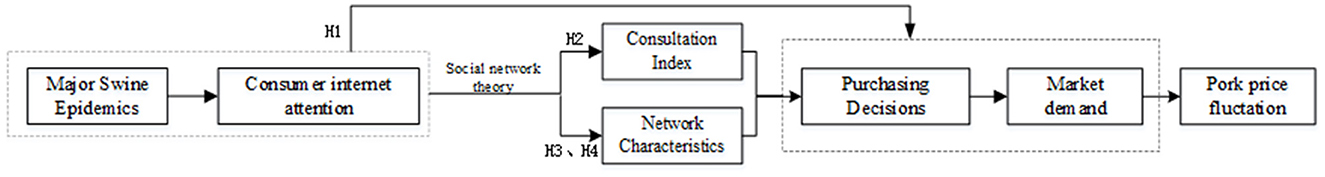
Based on the above analysis (Figure 1), this paper argues that consumer online attention triggered by sudden animal epidemic events influences purchasing decisions. When the swine supply side experiences a severe shock, the supply volume drastically decreases. Given the long growth cycle of pigs, it is not possible to replenish the stock in the short term, resulting in a low and stable supply volume for a brief period. In this context, changes in consumer purchasing decisions lead to variations in effective market demand, ultimately manifesting as fluctuations in pork price volatility. Accordingly, the following hypothesis is proposed for validation:
H1: Information from sudden animal epidemic events triggers consumer online attention, which in turn influences purchasing decisions. When supply volume remains low in the short term, changes in purchasing decisions impact effective demand, leading to increased pork price volatility.
Portals and social platforms are the primary channels through which consumers obtain information, helping to reduce information asymmetry and enabling more rational decision-making (Simeone and Scarpato, 2020). However, with the explosion of news on portals and information on social platforms, consumers face challenges in processing information, leading to phenomena like the “information cocoon” and “perceptual overload.” Consumer online attention, as an active behavior influenced by external information stimuli, is regulated through portals and social platform information, impacting consumer behavior through complex “demonstration effects” and “linkage effects.”
Regarding the impact of portal news, according to the strong and weak tie theory in social networks, portals, as part of a strong tie network, have an information advantage, allowing them to capture and publish authoritative information promptly (e.g., Baidu). In this study, we use the reading, comments, reposts, and likes on Baidu to construct a consultation index to measure the intensity of information transmission from portals to consumers. When the consultation index is higher, consumers are more likely to make decisions based on authoritative information, thus affecting pork price fluctuations. Accordingly, the following hypothesis is proposed:
H2: The consultation index has a negative moderating effect on the relationship between consumer online attention and pork price fluctuations, meaning that an increase in authoritative information can mitigate the impact of consumer attention on price volatility.
Secondly, consumers at the lower end of the information pyramid face constraints like fewer information sources and limited interpretation ability. The rapid development of social platforms in the WEB2.0 era helps fill this gap. The weak ties in consumer online social networks discussed in this study differ from traditional offline networks based on social relationships. The theory of weak ties, first proposed by American scholar Granovetter, measures the strength of connections between nodes based on four dimensions: interaction frequency, trust, intimacy, and reciprocal exchange. The findings show that, in social relationships, weak ties are often the ones that significantly influence individual behavior. The reason is that when two nodes share a weak tie, their social circles overlap less, allowing for more effective information exchange. Weak ties link different social circles and facilitate the transmission of information across groups. Thus, compared to strong ties, weak ties are more effective in transmitting information between individuals and further influencing consumer purchasing decisions.
In the WEB2.0 era, consumers increasingly use social platforms for social interaction, which breaks the limitations of time and space, greatly enhancing the speed and breadth of information dissemination. When major animal epidemics occur, users interact through likes, reposts, and comments on related news to express agreement, opposition, or sharing. According to Granovetter's definition of strong and weak ties, most reposting users do not share close ties; instead, they form weak tie networks around significant animal epidemic events. Therefore, the weak tie networks formed by user reposts and comments strengthen information exchange among consumers from different social circles, creating “demonstration effects” and “linkage effects” on a broader scale, leading to convergence in purchasing decisions (Giacomo, 2020; Pavlova et al., 2014).
In a social network, nodes with higher centrality play a more crucial role. Consumers who occupy important positions in the network not only gain market information earlier but also disseminate it to more consumers. In other words, the centrality of a social network structure moderates the impact of consumer online attention on pork price fluctuations. When network centrality is high, more information is transmitted to consumers through the network, and consumers are more influenced by the “demonstration effect” and “linkage effect,” leading them to adjust their purchasing decisions. When supply remains relatively stable, changes in effective demand ultimately manifest as fluctuations in pork price volatility. Accordingly, the following hypothesis is proposed:
H3: The centrality of the repost network negatively moderates the relationship between consumer online attention and pork price fluctuations.
Lastly, whether official media or individuals publish event information on social platforms, they often use biased wording and expressions to convey emotions to their audience. However, in the fast-evolving internet era, consumers, surrounded by an overload of information, find it challenging to discern the truth due to their limited information-processing capacity. Many unreliable online media outlets and self-media, seeking traffic, fabricate news stories, misreport events, or exaggerate emotions, leading to public misjudgment and misinformation. Additionally, government information disclosure delays in response to public emergencies, combined with competition among online media for the first release of event information, weaken the government's role as a gatekeeper. Fragmented and fast-paced reading habits among netizens also lead to misinformation spreading and amplifying on social platforms.
The “distortion of information” caused by this misinformation triggers group polarization, leading to sudden shifts in the emotions surrounding major animal epidemic information on social platforms. Consumers, as both recipients and transmitters of information, react to external stimuli by adjusting their purchasing decisions, which eventually causes pork price fluctuations through changes in effective demand.
The WEB2.0 era further intensifies the group polarization effect. On the one hand, the anonymity, equality, timeliness, and interactivity of social platforms encourage individuals to freely express their opinions. On the other hand, social platforms easily form “information cocoons,” where individuals are exposed primarily to biased or false information, using it as the basis for expressing their views. Lastly, some self-assured opinion leaders on social platforms eventually shape mainstream opinions. This means that the emotions conveyed by event information on social platforms can shift during transmission, influenced by factors such as opinion leaders, information cocoons, and time. Changes in consumer emotions, in turn, lead to adjustments in their purchasing decisions.
Therefore, in emotion transmission networks, emotions that occupy critical positions exert greater influence over public opinion. In other words, emotional nodes with high centrality in the emotion transmission network are more likely to dominate the final direction of public sentiment. When the centrality of emotional nodes is high, the number of consumers sharing the same emotions increases. Influenced by the “demonstration effect” and “linkage effect,” consumers form expectations based on the emotional information and adjust their purchasing decisions accordingly. When supply remains relatively stable, changes in effective demand ultimately manifest as fluctuations in pork price volatility. Accordingly, the following hypothesis is proposed:
H4: The centrality of the emotion transmission network negatively moderates the relationship between consumer online attention and pork price fluctuations.
3 Research design
3.1 Variable description and data sources
3.1.1 Pork price volatility
Pork price volatility serves as an indicator that provides a tangible representation of the fluctuation trend in pork prices. This study selects pork price volatility as a proxy variable for pork price fluctuations. The data is sourced from the BRIC database. The formula for calculating pork price volatility in this study is as follows:
Here, Pi, t−1 represents the pork price in region i at period t−1, and Pi, t represents the pork price in region i at period t. Based on this, the original values are processed using logarithmic differencing to obtain the pork price volatility price_voli, t.
3.1.2 Consumer attention
Based on the previous analysis, consumer internet attention serves as a crucial proxy for measuring consumer purchasing behavior. In the digital age, consumers gather information of interest and express their opinions and emotions online. These activities are recorded as digital data, forming a vast information repository. This study selects consumer internet attention as the primary indicator for measuring responses to the African Swine Fever (ASF) event. Online search data, due to its low cost, timeliness, and broad coverage, has been proven effective for predicting socio-economic behavior (Ginsberg et al., 2008). Scholars first applied this method in the healthcare sector and subsequently extended it to various economic fields. For example, Venkataraman et al. (2018) used Google search volumes to predict housing price changes in India. Yang and Lü (2014) employed the Baidu Search Index to explore the relationship between sudden events and stock market fluctuations, finding that the attention given to these events significantly explained stock price volatility. Liang et al. (2017) also used Google Trends data to investigate the correlation between online attention and grain prices. Li et al. (2024) assessed the impact of abnormal consumer attention on pork price fluctuations using the Baidu Index.
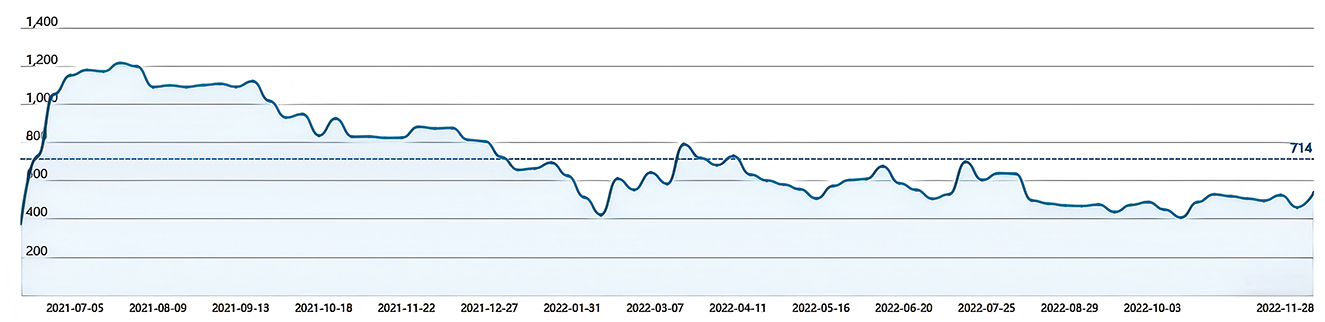
In this study, using web scraping technology, we collected Baidu Search Index data from the Baidu Index website (http://www.baiduindex.com) for the period from June 2012 to November 2022, with “African Swine Fever” as the keyword, to construct consumer internet attention as the core variable. This index is based on user search volumes on Baidu, using the keyword as the statistical object. It scientifically analyzes and calculates the weighted frequency of keyword searches on Baidu's web search platform. Depending on the data source, the search index is divided into PC search index and mobile search index. By aggregating the search frequencies from both PC and mobile users for the specified keyword, it reflects the level of public attention to the event over specific time periods. Specifically, Baidu standardizes and weights keyword search volumes to ensure the comparability of data across different time periods. To ensure the timeliness and representativeness of the data, the daily search frequencies were aggregated on a monthly basis, forming the consumer attention indicator. This indicator not only captures the public's interest fluctuations regarding sudden events (such as African Swine Fever) but also effectively reflects trends in information demand changes.
Figure 2 shows the trend of the Baidu Search Index for the keyword “African Swine Fever” from June 2021 to November 2022. The index peaked in July 2021 and gradually declined thereafter, indicating changes in public attention. This study selects consumer internet attention as the core explanatory variable to explore how consumer attention influences pork price fluctuations.
3.1.3 Information index
As analyzed previously, media serves as a critical conduit for market information, influencing agricultural product prices by acting as an “information bridge” among market participants, government agencies, and consumers. As an intermediary, media significantly enhances the efficiency of information dissemination, achieving leaps in speed and reach in the digital era. Research indicates that media can substantially impact product price fluctuations by improving the efficiency of market information dissemination (Zhang and Wang, 2022; Lin et al., 2024). Consumers rely on media-provided market information to make purchasing decisions, and the intensity of media coverage directly influences the quantity and quality of market information consumers receive. Media coverage intensity not only directly affects the quantity and quality of information received by consumers but also modulates the influence of consumer network attention on pork price fluctuations by broadening and accelerating information transmission. In this study, the information index is used as a moderating variable to explore how media coverage intensity regulates consumer behavior and market responses.
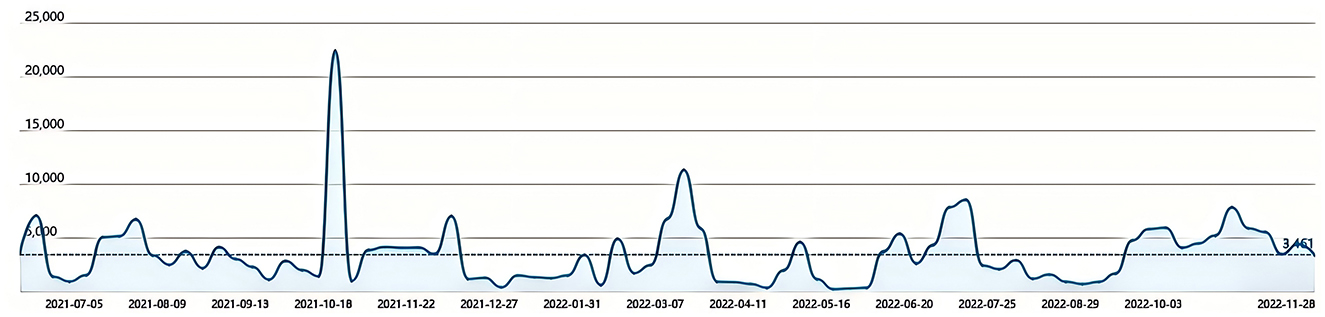
Using web scraping technology, this study collected information index data for the keyword “African Swine Fever” from June 2021 to November 2022 and aggregated the daily data into monthly totals. The information index is calculated based on intelligent distribution and recommendation mechanisms, incorporating user behaviors such as reading, commenting, reposting, liking, and disliking, with each behavior weighted accordingly. This index comprehensively reflects the coverage and influence of media reports, with the data sourced from http://www.baiduindex.com.
In summary, the information index effectively reflects the breadth and intensity of media coverage, thereby illustrating the role of media in information dissemination. It accurately captures the intensity of market information received by consumers and its impact on their purchasing decisions. Figure 3 shows the nationwide trend of the Baidu information index for the keyword “African Swine Fever” during the sample period. The average value of the index during this period was 3,415, with significant fluctuations, peaking at 22,370 in mid-October 2021. This peak corresponds to the zero-reporting of African Swine Fever cases in China in October 2021, which led to an increase in media coverage, further intensifying the transmission of information.
3.1.4 Construction of the user repost network and emotion transmission network
Major animal epidemics refer to outbreaks with high pathogenicity or high mortality rates that occur suddenly, spread rapidly, and pose a serious threat to livestock production safety, potentially endangering public health and safety. These events are characterized by sudden occurrence, rapid spread, and high incidence or mortality rates. In recent years, the deep integration of social media in the public opinion field has led to significant events rapidly disseminating and evolving into nationwide waves of public discourse. The public nature of these events can trigger fluctuations in public's emotions, and under the amplification of collective emotions, public opinion quickly escalates. In the previous discussion, this article examined the regulatory effects of user retweet networks and emotional transmission networks on consumer attention and pork price fluctuations. Therefore, in the context of significant animal epidemic events, it is important to understand the network relationships among individuals and whether the transmission of emotions between different individuals undergoes changes. In this study, we selected “African swine fever” as the research object to address these questions.
3.1.4.1 Sample selection and data description
For this study, a total of 24,786 randomly selected Weibo users who published original posts were tracked, and their posts were analyzed to collect 140,000 posts related to “African swine fever” along with their associated sentiment orientations.2 The retweet volume of these original Weibo posts was examined, revealing that the majority of authors were news media and government agencies, contributing significantly to the retweet volume. The top five Weibo accounts based on retweet volume were @CCTV News (40,960), @Beijing Evening News (33,260), @Headline News (2,206), and @CCTV Finance (1,084). The data spanned from June 1, 2021, to November 17, 2022. The data was further refined by removing duplicate samples and irrelevant Weibo posts, including those with voting mechanisms, formatting errors, and missing key fields.
This section's discussion aims to analyze information dissemination and emotional transmission patterns among online users regarding significant animal epidemics. Therefore, original Weibo posts related to “African swine fever” with only comments and no retweets are not considered in the analysis. The distinction between first-level retweets and multi-level retweets is determined based on the presence of the expression “//@username: comment content” in the retweet field. If the expression is absent, it is considered a first-level retweet directly from the original Weibo user. If the expression appears once or multiple times, the user mentioned in the first expression is regarded as the superior node user.
3.1.4.2 Measurement of network characteristic indicators
Network structural characteristics can be depicted using centrality, clustering coefficient, and network density. This study focuses on the importance of each node; thus, degree centrality, closeness centrality, and betweenness centrality are chosen to measure the significance of nodes.
Degree centrality is derived from the concept of the degree. The larger the degree of a node, the more important that node is. In a network containing N nodes, the maximum possible degree is N-1. The degree centrality of a node with degree d can be expressed as follows:
Betweenness centrality is an indicator that describes the importance of a node based on the number of shortest paths passing through it. It is defined as follows:
Where gst represents the number of shortest paths from node s to node t, and is the number of those cc shortest paths from node ss to node tt that pass through node ii. Betweenness centrality measures the control node ii has over the information flow between pairs of nodes along the shortest paths in the network. The higher the betweenness centrality of a node, the more significant its position in the network, and the greater its influence on information transmission within the network.
3.1.4.3 Network construction
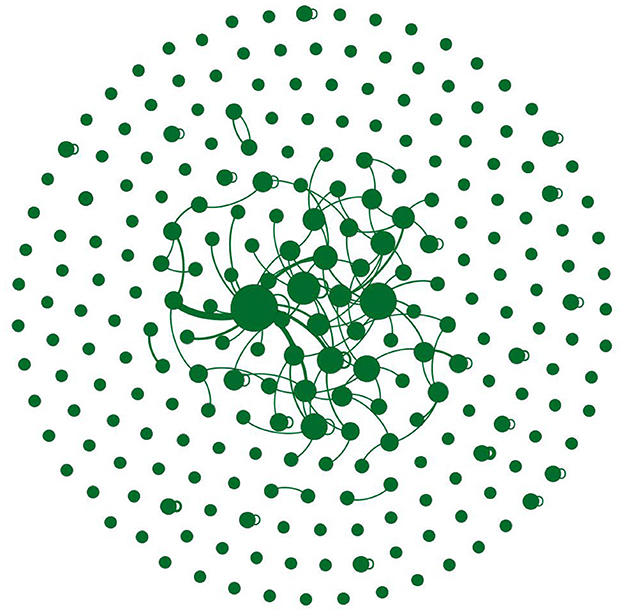
To visually represent the retweet relationships among different nodes, this study selected key nodes to construct a local network graph. The user retweet relationship network graph was generated using Gephi software, as depicted in Figure 4. Larger nodes in the graph indicate higher degree centrality, signifying their greater importance in the network. The observation reveals that both official media and individual users carry equal significance in the user retweet relationship network, suggesting that information from both official media and individual users has an impact on consumers. Additionally, each node is connected to itself, indicating instances where users retweet their own original Weibo posts, consistent with the earlier analysis.
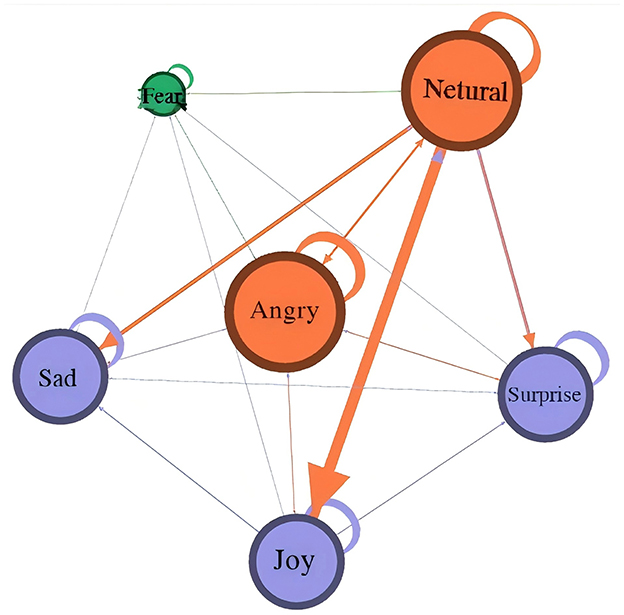
Likewise, this study establishes an emotion transmission network using six types of emotions as nodes to investigate whether changes occur during the emotion transmission process. Figure 5 illustrates that nodes representing neutral and anger emotions hold particular significance. Neutral emotions are situated at the network's periphery, serving as the initial point for emotion transmission. They subsequently transition into anger, joy, sadness, and surprise emotions, with anger being the most frequent transition. Moreover, each emotion is connected to itself, indicating that some emotions remain unchanged during transmission. This occurs because in the online discourse surrounding major animal epidemic events, if the “group polarization” effect is triggered without control or guidance of the event, coupled with the timely elimination of the public's panic about food safety, the situation can easily escalate, leading to a comprehensive collapse of online sentiment and the emergence of a “snowball effect.” Major animal epidemic events have extensive and enduring impacts. Even a minor issue can generate various voices and discussions. Combined with the ease of social media dissemination, this information can rapidly spread, ferment, and experience explosive growth, resulting in consequences more severe and lasting than the events themselves.
3.1.5 Control variables
This study selects population density, consumer confidence index, pig slaughter volume, and the price volatility of beef, chicken, and lamb as control variables. Population density and consumer confidence index are used to reflect market demand, pig slaughter volume indicates supply, while the price volatilities of beef, chicken, and lamb represent the price fluctuations of substitutes. Population density data is sourced from the China Statistical Yearbook, the consumer confidence index from the National Bureau of Statistics, and the pig slaughter volume, beef, chicken, and lamb price volatility data are sourced from the BRIC database.
3.2 Descriptive statistics
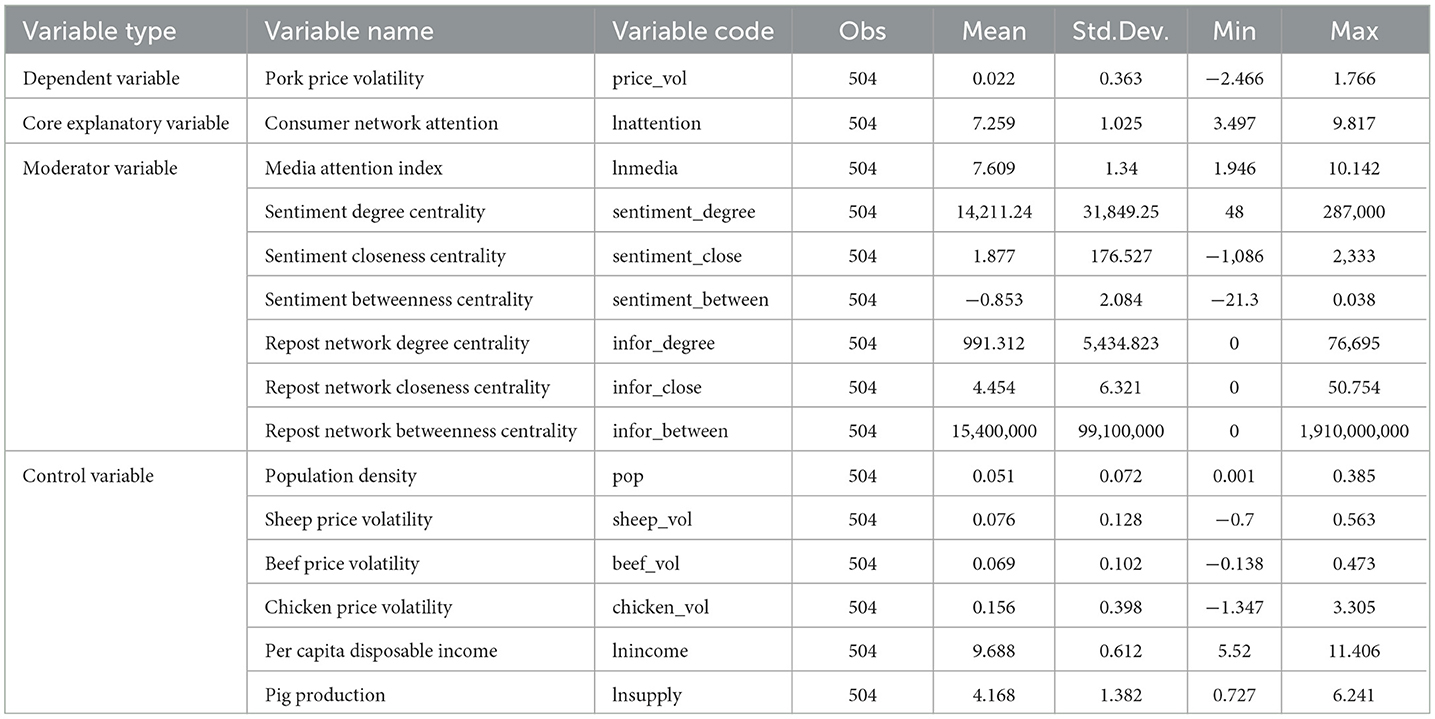
Table 1 presents the descriptive statistics of the variables, highlighting notable variations. Pork price volatility exhibits a wide range, with values from −2.466 to 1.766 and a mean of 0.022, indicating significant fluctuations and an overall downward trend in pork prices. The primary variable, consumer network attention, shows noticeable differences between its minimum and maximum values, but its relatively small standard deviation (1.025) suggests stable attention levels over the study period. In contrast, the media attention index has a larger range and higher standard deviation (1.34), reflecting more substantial fluctuations in media coverage intensity related to African Swine Fever. This suggests that while consumer attention remained relatively consistent, media reports varied significantly in intensity, underscoring the media's critical role in supplying information and shaping market responses.
4 Empirical analysis
4.1 Baseline regression
To address the question of how consumer network attention affects pork price volatility under the impact of major animal epidemics, this study designs the following baseline model to examine the influence of consumer network attention on pork price volatility. The baseline model is constructed as follows:
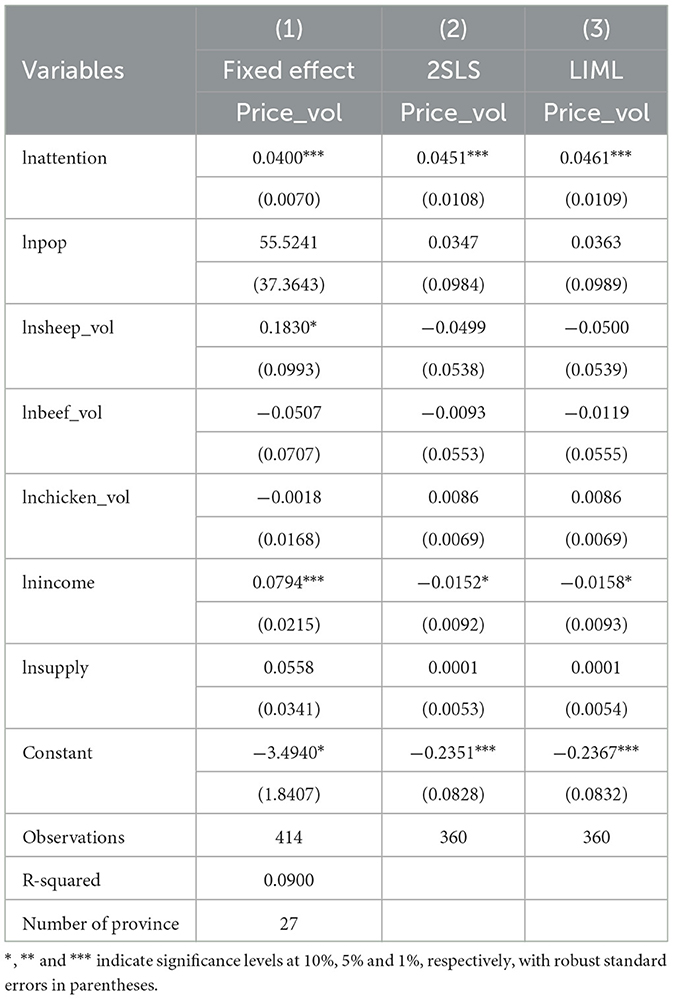
Among them, Price_volit represents the volatility of pork prices, lnattentionit represents the natural logarithm of consumer network attention, and Xit represents the control variables. This study selected population density, disposable income of residents, pig production volume, beef price volatility, chicken price volatility, and lamb price volatility as control variables. If hypothesis H1 is valid, the regression coefficient of the main explanatory variable should be significantly positive, indicating that higher consumer network attention leads to more pronounced pork price volatility, while the opposite suggests smaller price fluctuations.
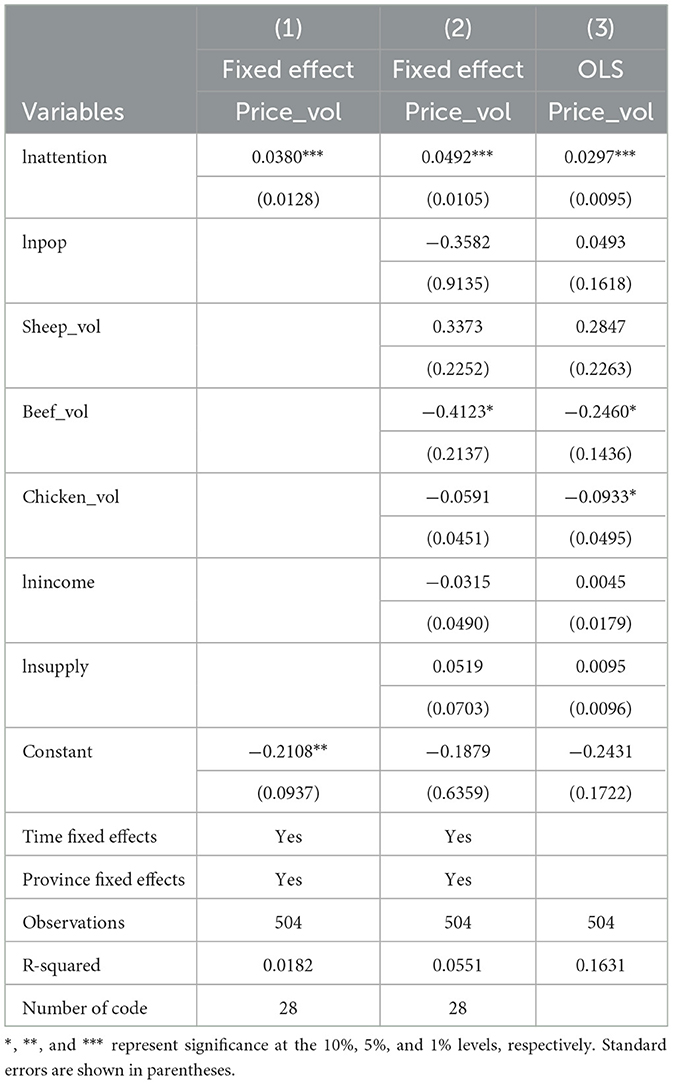
Table 2 presents the results of the benchmark regression. As can be seen from the table, consumer attention (lnattention) has a significant positive impact on pork price volatility (price_vol), consistently significant at the 1% level across all three models. This suggests that as consumer network attention increases, pork price volatility also rises. The reasoning behind this is that higher consumer attention leads to increased access to market information, which stabilizes or even boosts pork demand as consumers are less likely to change their purchasing decisions out of panic. During periods when pork supply has not yet fully recovered, stable or increased demand can exacerbate price fluctuations.
Additionally, the control variables reveal some notable trends. First, beef price volatility (beef_vol) has a significant negative effect on pork price volatility, reflecting the substitution effect between different types of meat: a decrease in beef prices may drive an increase in pork prices. Although the price volatility of lamb and chicken does not show significant effects in the model, they may still have some influence on the pork market. Furthermore, while population density (lnpop) and income levels (lnincome) do not show significant impacts on price volatility in this model, their effects could manifest through indirect mechanisms. This article underscores the importance of consumer attention and cross-market dynamics in shaping pork price volatility, particularly in contexts of major animal disease outbreaks.
4.2 Moderating effects analysis
To further elucidate the mechanism behind the impact of consumer network attention on pork price volatility, this study examines the moderating effects of the media consultation index and social network characteristics. Drawing on existing literature, we construct Equation 5 based on Equation 4 to test the moderating effects of these two factors on the relationship between consumer network attention and pork price volatility.
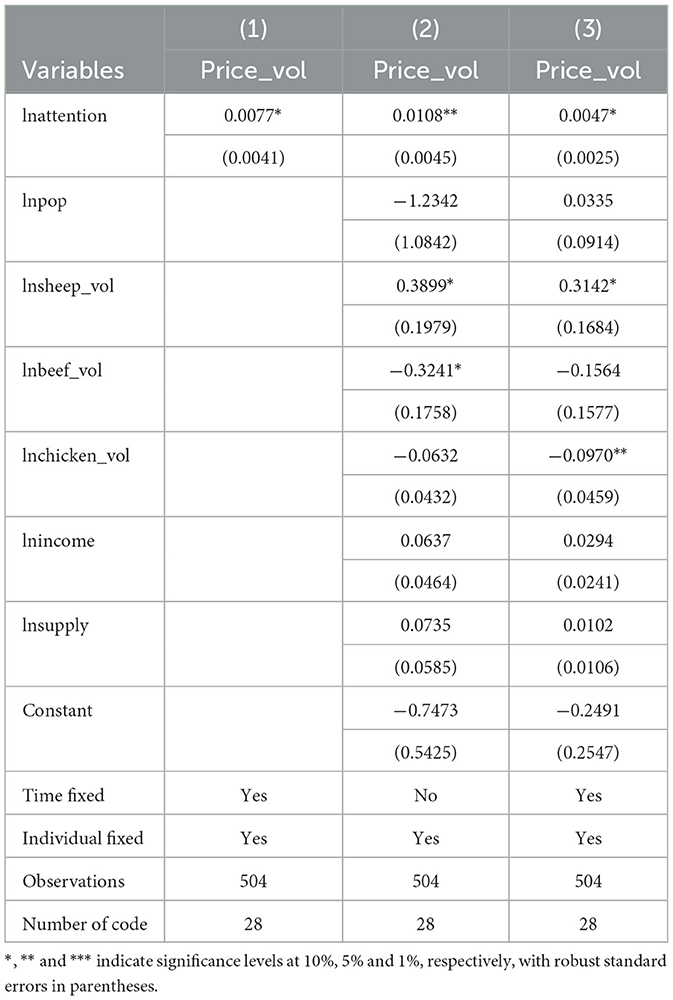
In Equation 5, Modit represents the moderating variable, while the remaining variables are set the same as in Equation 4. For this study, the media information index, characteristics of the repost network and characteristics of the emotion transmission network were selected as moderator variables. The consultation index is used to measure the level of attention and coverage of news information on specific keywords on the Internet, reflecting the weighted sum of internet users' behaviors such as reading, commenting, sharing, and liking during period t. In the process of constructing the indicator, the specific consultation index is log-transformed after adding 1. Social network characteristics can influence consumer decision-making. This study selects degree centrality, closeness centrality, and betweenness centrality indicators from the social network to characterize the features of the retweet relationship network and emotion transmission network. The necessary raw data for calculating these variables mainly come from the official website of Baidu Index and the Micro Data Research Institute. If the coefficients α2 and α3 in Equation 5 are statistically significant, it indicates that the Mod variable plays a moderating role in the relationship between consumer network attention and pork price volatility.
4.2.1 The moderating role of media consultation index
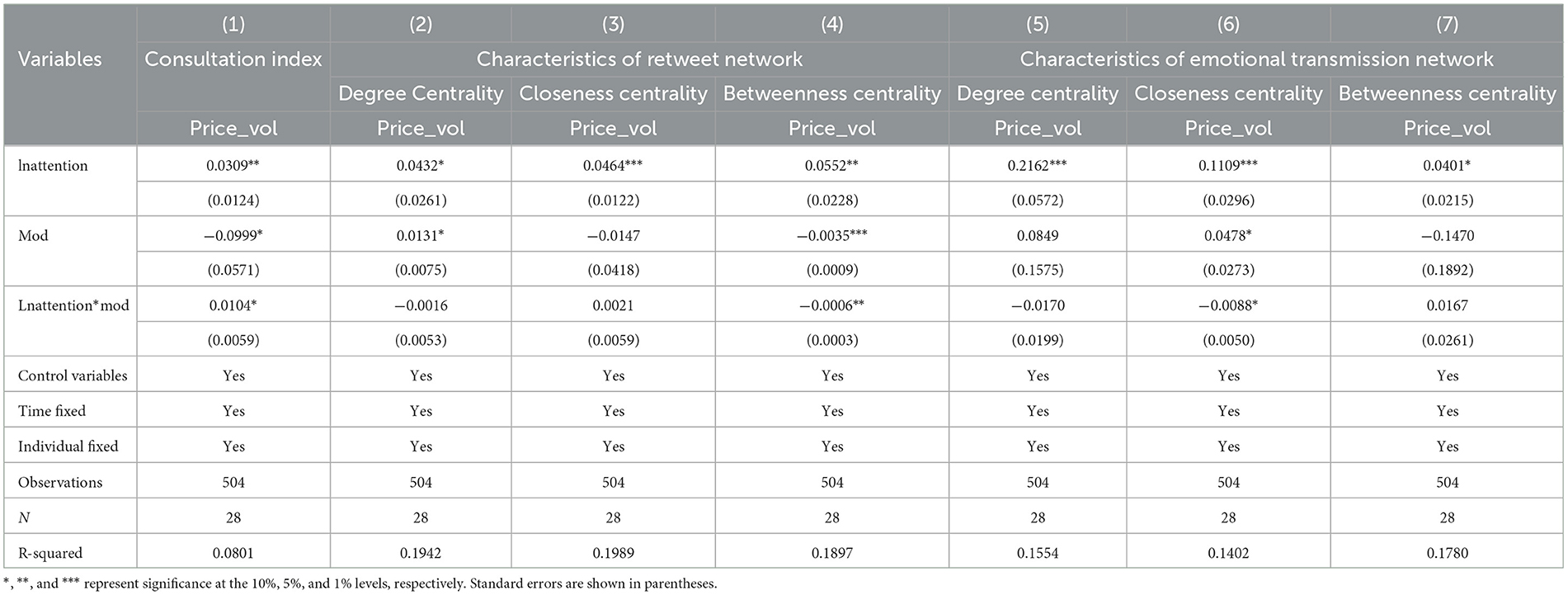
In the first column of Table 3, at a significance level of 5%, the media consultation index negatively moderates the relationship between consumer network attention and pork price volatility. As the media consultation index increases, the exacerbating effect of consumer network attention on pork price volatility is strengthened. The Spiral of Silence theory suggests that, to avoid isolation, people tend to express opinions that align with the majority while remaining silent about divergent opinions. This results in a spiral-like process where one opinion becomes increasingly vocal while the other gradually becomes silent. The internet amplifies individuals' voices, and personal opinions can surpass those of official media, turning individuals into “opinion leaders.” Consequently, the information consumers obtain from the internet often carries strong personal emotions, influencing their behavioral decisions. In this context, based on subjective market information, consumers may make panic-driven decisions to hoard pork, increasing their purchases for a certain period. When the supply remains relatively stable, the rise in effective demand exacerbates pork price volatility. The Perceptual Load theory suggests that, due to limited information processing capacity, consumers selectively process information when faced with a massive amount of information. After the outbreak of a major animal epidemic, the media, as an essential information dissemination channel, plays a role in guiding public opinion and correcting negative phenomena. It largely serves as a supplier of market information, prompting consumers to prioritize purchasing decisions based on the information provided by the media. On one hand, the media continuously conveys information about major animal epidemics to consumers, enabling them to understand relevant information and alleviate information asymmetry in the agricultural product market, leading to more rational purchasing decisions. On the other hand, through official media, false information or inflammatory remarks in the market are promptly countered and controlled, reducing consumer panic. Some consumers may adopt a wait-and-see attitude, leading to the maintenance or reduction of pork purchases. When the supply remains relatively stable, unchanged or decreased effective demand ultimately leads to a decrease in pork price volatility.
Consumers are likely to increase their online attention to ASF due to changing sentiment in the traditional media and consumer pessimism. That is, there may be inverse causality between the core explanatory variables and the mediating variables, which would lead to an endogeneity problem. In this article, we use the Granger causality test to verify whether there is inverse causality between variables. The empirical findings of this study are consistent with the Perceptual Load theory, which may be related to the adaptive differences between the Spiral of Silence and Perceptual Load theories. During the outbreak of a major animal epidemic, although “opinion leaders” in the online space may be social individuals rather than official media, consumers, constrained by their information processing capacity, prioritize the processing of authoritative media information. That is, based on authoritative media information, they maintain or reduce their pork purchases. When the supply remains relatively stable, unchanged or decreased effective demand eventually mitigates pork price volatility. Therefore, in the research context of this study, the consultation index exhibits a negative moderating effect.
4.2.2 Moderating effects of social network structure
4.2.2.1 Characteristics of forwarding network structure
In columns (2)–(4) of Table 3, at a significance level of 5%, the betweenness centrality of the forwarding network negatively moderates the relationship between consumer online attention and pork price fluctuations. With an increase in betweenness centrality, the amplifying effect of consumer online attention on pork price fluctuations is weakened.
Based on the analysis of the spiral of silence and cognitive load theories presented earlier, the moderating effects of the repost network characteristics in the regression results are consistent with the cognitive load theory., which may be related to the adaptive differences between the Spiral of Silence and Perceptual Load theories. During the outbreak of major animal epidemics, consumers, limited by their information processing capacity, prioritize the processing of market information they encounter first, most of which comes from official news media reports. Based on the information provided by official news media, consumers do not engage in panic-driven stockpiling, but rather maintain or reduce their pork purchases. When the pork supply is relatively stable, the unchanged or decreased effective demand ultimately mitigates pork price fluctuations. Therefore, in the context of this study, the betweenness centrality index in the forwarding network exhibits a negative moderating effect.
4.2.2.2 Characteristics of emotional transmission networks
In Table 3, columns (5)–(7), at a significance level of 5%, the closeness centrality of emotional transmission networks positively moderates the relationship between consumer network attention and pork price fluctuations. As the closeness centrality increases, the intensifying effect of consumer network attention on pork price fluctuations will be weakened.
Based on the previous analysis of the spiral of silence and cognitive load theories, the moderating effect of the emotional transmission network characteristics in the regression results aligns with the spiral of silence theory. During the outbreak of a major animal epidemic, consumer emotions are influenced by the emotions of “opinion leaders,” who may be individuals with more extreme views. At this time, consumers adjust their expectations and make purchasing decisions under the influence of “opinion leaders”' emotions. If the closeness centrality corresponding to the emotions of the opinion leaders is low, the likelihood of emotional mutation due to information distortion is also low. In such cases, consumers tend to stockpile pork in large quantities due to their extreme emotions, resulting in increased pork purchases. When the pork supply is relatively stable, unchanged or increased effective demand ultimately exacerbates pork price fluctuations. Therefore, in the context of this study, the closeness centrality index in the emotional transmission network exhibits a positive moderating effect.
4.3 Endogeneity and robustness tests
4.3.1 Endogeneity issues
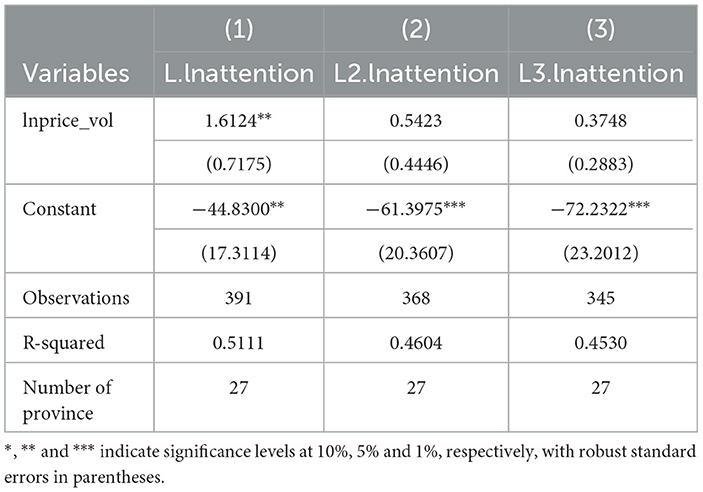
This study aims to explore the impact of consumer network attention on pork price fluctuations, inherently encountering a challenge of reverse causality. Specifically, consumer attention to sudden animal epidemic events may not solely originate from the outbreak of major animal epidemics. Some consumers may increase their attention to such events due to abnormal pork price fluctuations. Therefore, using the aforementioned economic indicators as dependent variables in the empirical analysis may introduce endogeneity issues. To address this concern, this study adopts the approaches proposed by Shao and Li (2017) and Aghion et al. (2016) regarding the timing of variables. The model is constructed with consumer network attention as the dependent variable and pork price volatility as the independent variable. Additionally, both the dependent variable and control variables are lagged by one period to observe whether the changes in explanatory variables in the future can predict the changes in the dependent variable in the current period. The results, as shown in Table 4, indicate that when considering the same control variables, only lagged consumer network attention as the dependent variable exhibits a significant coefficient with pork price volatility. This suggests a reverse causal relationship between pork price volatility and future consumer network attention.
To address the endogeneity issue caused by reverse causality, this study adopts the approaches proposed by Zhang C. et al. (2023), Zhang W. Q. et al. (2023) and Cheng et al. (2022). Lagged consumer network attention at two and three periods is introduced as instrumental variables into the model. The analysis utilizes two-stage least squares and maximum likelihood methods for a reexamination of the baseline model through regression analysis. The results, as presented in Table 5, indicate that the coefficients of consumer network attention remain consistent and significant at the 1% level of significance in both the two-stage least squares and maximum likelihood regression outcomes. In comparison to the baseline regression results, the introduction of instrumental variables maintains a significant positive coefficient for consumer network attention, with a slight increase in its magnitude. This suggests that the endogeneity resulting from mutual causality has led to an underestimation of the coefficient.
4.3.2 Robustness test
In the preceding section, we employed web scraping techniques to collect Baidu Index as an indicator of consumer network attention. Similarly, we used web scraping techniques to gather Weibo posts related to the keyword “African swine fever” during the sample period. The total number of reposts, comments, and likes for these Weibo posts were aggregated to represent consumer network attention for robustness testing. The results, as presented in Table 6, revealed that even when restricting the information platform to Weibo, consumer network attention still significantly intensifies pork price fluctuations.
5 Conclusions and policy implication
5.1 Conclusions
Utilizing a panel model approach and provincial-level monthly data collected through web scraping techniques, this study examines the impact of consumer internet attention triggered by major animal disease events on pork price fluctuations. We focus on the largest developing market, China, and take African Swine Fever as a case study to analyze how information related to significant animal disease outbreaks influences pork prices. No prior research has comprehensively explored the relationship between consumer internet attention and pork price volatility within the context of major disease outbreaks in such a large developing market. Our findings contribute to the understanding of digital information dissemination's role in agricultural market dynamics and offer policy insights for other developing economies facing similar challenges.
This study utilizes social network theory to investigate the underlying mechanisms linking consumer network attention triggered by major animal epidemic events and China's pork price fluctuations, using African swine fever as an illustrative example. Monthly provincial panel data from June 2021 to November 2022 were collected through web scraping and social network analysis. By constructing a Weibo user repost network and an emotion transmission network, social network characteristics are integrated into the analysis framework to explore the impact and mechanisms of consumer network attention on pork price fluctuations resulting from major animal epidemic event information. The article contributes significantly by examining the influence of weak relationship networks on consumer behavior, offering a comprehensive analysis of how consumer network attention shapes purchasing decisions and contributes to fluctuations in pork prices. Through the use of web crawlers and social network analysis, the research builds Weibo user repost and emotion transmission networks, incorporating the features of weak relationship networks into the analytical framework.
The study's findings are as follows: Firstly, from the perspective of demand-side behavior, consumer network attention triggered by major animal epidemic events significantly amplifies China's pork price fluctuations. Secondly, considering the moderating effects of the media information index and social network characteristics, it is found that the media information index negatively moderates the relationship between consumer network attention and pork price fluctuations. As the media information index increases, the intensifying effect of consumer network attention on pork price fluctuations is enhanced. The intermediary centrality of the repost relationship network negatively moderates the relationship between consumer network attention and pork price fluctuations, and as the intermediary centrality increases, the intensifying effect of consumer network attention on pork price fluctuations is weakened. The closeness centrality of the emotion transmission network positively moderates the relationship between consumer network attention and pork price fluctuations. As the closeness centrality increases, the intensifying effect of consumer network attention on pork price fluctuations is strengthened.
Our study has some limitations. First, the panel data used in this research spans only from June 2021 to November 2022, which provides a relatively short time frame that may not fully capture the long-term impacts of major animal epidemics, such as African Swine Fever, on pork price fluctuations. Furthermore, the data is primarily sourced from Chinese social media platforms, such as Weibo and Baidu, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to other international contexts or cultural settings. Second, while the study employs social network analysis (SNA) to construct repost and emotion transmission networks, it may not fully account for the nonlinear dynamics of emotion propagation, such as emotional polarization or random shocks. Additionally, the exclusive reliance on Weibo data overlooks the potential influence of other social media platforms, such as WeChat or TikTok, which could underestimate the complexity of cross-platform information dissemination.
5.2 Policy implication
Our results have implications apropos the Consumer Internet Attention and its Post-epidemic Impact on China's Pork Price Fluctuations. Firstly, the government should strengthen information supervision and guidance, fully leveraging the role of official information dissemination in guiding public opinion during sudden epidemic outbreaks. As consumer network attention significantly amplifies pork price fluctuations, especially following major animal disease outbreaks, the government should enhance its regulation and guidance of online information. This includes the timely release of accurate and authoritative information to stabilize market expectations and reduce unnecessary panic. Secondly, it is crucial to enhance the quality of media information to ensure timely, sufficient disclosure by official media. This study finds that as the media information index increases, the intensifying effect of consumer network attention on pork price fluctuations also strengthens. Therefore, improving the quality and credibility of media reports and ensuring the accuracy, timeliness, and comprehensiveness of information are important measures to stabilize pork price fluctuations. Thirdly, make full use of social media. This study finds that the characteristics of the user repost relationship network and the emotional transmission network both play a moderating role in the impact of consumer network attention on pork price fluctuations. The government needs to recognize the key role of “opinion leaders” on social media platforms in disseminating information to slow the spread of panic and enhance the dissemination of beneficial information. Finally, focus on the development of public opinion monitoring tools to monitor and analyze the dissemination of information on social media and its impact on the market, enabling more effective and rapid responses to market price fluctuations.
Data availability statement
The raw data underpinning the study contains highly sensitive personal information. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
XL: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JJ: Data curation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Postdoctoral Fellowship Program, grant numbers GZC20233025.
Conflict of interest
JJ was employed by Midu Technology Co., Ltd.
The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
1. ^Weibo holds a strong position within China's social media ecosystem, particularly playing a crucial role in information dissemination and public discussions. As of 2023, Sina Weibo has 517 million users, encompassing a wide range of user groups, including the general public, celebrities, government agencies, and media outlets, making it a vital channel for information transmission and public opinion formation.
2. ^The data is sourced from the Microdata Research Institute, which categorizes textual sentiment into six types: sadness, fear, anger, neutrality, surprise, and joy.
References
Aghion, P., Dechezleprêtre, A., Hémous, D., Martin, R., and Van Reenen, J. (2016). Carbon taxes, path dependency, and directed technical change: evidence from the auto industry. J. Polit. Econ. 124, 1–51. doi: 10.1086/684581
Bakhtavoryan, R., Capps, O., and Salin, J. (2014). The impact of food safety incidents across brands: the case of the Peter Pan Peanut Butter recall. J. Agricult. Appl. Econ. 4, 559–573. doi: 10.1017/S1074070800029102
Carrieri, V., and Principe, F. (2022). WHO and for how long? an empirical analysis of the consumers' response to red meat warning. Food Policy 108:102231 doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2022.102231
Chen, T., Li, Q., Fu, P., Yang, J., Xu, C., Cong, G., et al. (2020). Public opinion polarization by individual revenue from the social preference theory. Int. J. Environm. Res. Public Health 17, 946–975. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17030946
Cheng, M., Han, J., and Yang, W. (2022). Economic growth, urban-rural income gap, and shared prosperity. Res. Finan. Trade 33, 1–17.
Duan, C., Liu, L., and Yi, L. (2024). the impact of sudden epidemics and online public opinion on pork price fluctuations: evidence from dual epidemic shocks. J. Agricult. Technol. Econ. 2024, 110–125. doi: 10.13246/j.cnki.jae.2024.05.005
Fritsche, I., Moya, M., Bukowski, M., Jugert, P., de Lemus, S., Decker, O., et al. (2017). The great-recession and group-based control: converting personal helplessness into social class in group-trust and collective action. J. Soc. Issues 73, 117–137. doi: 10.1111/josi.12207
Giacomo, F. A. (2020). Consumption network effects. Rev. Econ. Stud. 87, 130–163. doi: 10.1093/restud/rdz026
Ginsberg, J., Mohebbi, M., Patel, R., Brammer, L., Smolinski, M., and Brilliant, L. (2008). Detecting influenza epidemics using search engine query data. Nature 457, 1012–1014. doi: 10.1038/nature07634
Jia, R., Wang, X., and Wang, N. (2024). Risk Assessment of group polarization in network public opinion during emergencies. Library Inform. Serv. 68, 83–92. doi: 10.13266/j.issn.0252-3116.2024.06.008
Kakkar, H., and Sivanathan, N. (2017). When the appeal of a dominant leader is greater than a prestige leader. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 114, 6734–6739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1617711114
Kubin, E., and von Sikorski, C. (2021). The role of (Social) media in political polarization: a systematic review. Ann. Int. Commun. Assoc. 45, 188–206. doi: 10.1080/23808985.2021.1976070
Landau, M. J., Kay, A. C., and Whitson, J. A. (2015). Compensatory control and the appeal of a structured world. Psychol. Bullet.141, 694–722. doi: 10.1037/a0038703
Li, X. (2024). Spiral of silence: consumer attention, media emotion, and pork price fluctuations. Agriculture 14:2021. doi: 10.3390/agriculture14112021
Li, X., Tao, J. P., and Tu, T. T. (2024). Information on sudden animal epidemics and pork price fluctuations—from the perspective of consumer internet attention. J. Agricult. Technol. Econ. 2024, 73–95.
Liang, Z., Kuang, Y., Fu, Z., and Li, Y. L. (2017). Dynamic correlation study on grain price volatility and public online attention. Econ. Forum 2017, 108–115.
Lin, W., Ma, B., and Liang, J. (2024). Price response to government disclosure of food safety information in developing markets. Food Policy 12, 100–120. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2024.102602
Liu, A., and Niyongira, R. (2017). Chinese consumers' food purchasing behaviors and awareness of food safety. Food Control. 9, 185–191. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.03.038
Lu, Y. (2021). Research on Food Safety Online Public Opinion and Government Response Strategies. Zhongnan University of Economics and Law.
Ma, C., Tao, J., Tan, C., Liu, W., and Li, X. (2023). Negative media sentiment about the pig epidemic and pork price fluctuations: a study on spatial spillover effect and mechanism. Agriculture 13, 658. doi: 10.3390/agriculture13030658
Ovca, A., Jevsnik, M., Kavcic, M., and Raspor, P. (2018). Food safety knowledge and attitudes among future professional food handlers. Food Control. 2, 345–353. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.08.011
Pavlova, M. K., Silbereisen, R. K., and Sijko, K. (2014). Social participation in poland: links to emotional well-being and risky alcohol consumption. Soc. Indicat. Res. 1, 29–44. doi: 10.1007/s11205-013-0332-9
Peng, Y. (2015). The effects of food safety issues released by we media on consumers' awareness and purchasing behavior: a case study in China. Food Policy. 51, 44–52. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2014.12.010
Shao, Y., and Li, Z. (2017). Spatial Agglomeration, Firm Dynamics, and Economic Growth: An Analysis Based on China's Manufacturing Industry. China Indus. Econ. 5–23.
Simeone, M., and Scarpato, D. (2020). Sustainable consumption: how does social media affect food choices? J. Cleaner Prod. 277:124036. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124036
Soon, J. M. (2020). Consumers' awareness and trust toward food safety news on social media in Malaysia. J. Food Prot. 83, 452–459. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-19-415
Venkataraman, M., Panchapagesan, V., and Jalan, E. (2018). Does internet search intensity predict house prices in emerging markets? A case of India[J]. Prop. Manage. 36.
Yang, X., and Lü, B. F. (2014). Emergencies, investor attention and stock market volatility: Empirical evidence from online search data[J]. Econo. Manage. 36, 147–158.
Yu, X., Yu, Z., and Zheng, S. (2022). Risk, trust, and consumer purchase intention recovery: a case study of the new wholesale market food rumor event. J. Agro-Tech. Econ. 2022, 4–18. doi: 10.13246/j.cnki.jae.2022.01.008
Zhang, C., Wu, H., Cai, G., and Xu, X. (2023). Media coverage, analyst forecasts, and stock price volatility. Southern Econ. J. 36:101317.
Zhang, L., and Wang, P. (2022). Public attitude and opinion leaders: mapping chinese discussion of the EU's energy role on social media. JCMS: J. Common Market Stud. 60, 1777–1796. doi: 10.1111/jcms.13350
Zhang, L., Wang, X., and Li, Y. (2013). Interactive effects of China's monetary policy and stock price volatility based on SVAR model. Managem. Rev. 25, 10–19.
Zhang, L., and Zhang, X. (2011). Impact of external shocks on price volatility of agricultural products in China: a perspective from the agricultural industry chain. Managem. World 2011, 71–81.
Zhang, W. Q., Dong, J. R., Zhang, H. T., and Luo, J. H. (2023). Mechanisms, challenges, and strategies of environmental policies promoting green total factor productivity enhancement in China: a perspective of innovation mode selection. Econ. Rev. 1, 126–143.
Keywords: pork price fluctuation, consumer internet attention, social network analysis, African Swine Fever, asymmetric information
Citation: Li X and Ji J (2025) Price response to consumer attention during major animal epidemics in developing markets: perspectives from the influence of information and emotion contagion. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1518012. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1518012
Received: 27 October 2024; Accepted: 31 December 2024;
Published: 04 February 2025.
Edited by:
Chiedza Tsvakirai, University of South Africa, South AfricaReviewed by:
Siphe Zantsi, Agricultural Research Council of South Africa (ARC-SA), South AfricaWenyu Wan, Huazhong Agricultural University, China
Copyright © 2025 Li and Ji. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xia Li, bGVleEBjYXUuZWR1LmNu
 Xia Li
Xia Li Jing Ji3
Jing Ji3