- 1School of Public Administration and Policy, Shandong University of Finance and Economics, Jinan, China
- 2China Aero Geophysical Survey and Remote Sensing Center for Natural Resources, Beijing, China
The harmonization of rural human -land relations, centered on the interaction between rural livelihoods and land use, is crucial for sustainable rural development. This study explores the relationship between rural households’ livelihood capital status and land use effects (LUEs) in Qufu City, Shandong Province, China. The analysis is based on data collected through a triangulation method, combining quantitative (questionnaire) and qualitative (interview) approaches. Using a coupling degree (CD) model and a coupling coordination degree (CCD) model within a human -land system framework, this study evaluates the coupling and coordination between rural households’ livelihoods and land use as subsystems. It also examines the impact of LUE and CCD on rural households’ livelihood strategies through Skinner’s reinforcement theory. Results indicate variable CD and CCD across households with different livelihood strategies. In particular, the CD for the four household types ranged from 0.9 to 1, denoting a high-level coupling stage, with off-farm employment-oriented households registering the highest degree of 0.996. In CCD, professional households achieved a high degree of 0.761, whereas the others displayed a medium coupling coordination stage between 0.5 and 0.7. Professional households and balanced households showed superior LUE and CCD, with more than 50% of these households planning to maintain their original strategies. By contrast, households with off-farm employment-oriented or conventional strategies exhibited low LUE and CCD, with fewer than 50% of these households planning to retain their initial strategies. Professional agriculture-based livelihood strategies help improve the livelihood levels of farmers and promote the rational use of cultivated land resources, thereby making them particularly attractive to households engaged in agricultural production. This research contributes insights valuable for promoting the sustainable development of rural households’ livelihoods and land use.
1 Introduction
The harmonization of human–land relations is crucial for sustainable development (Rounsevell et al., 2012). The study of this relationship has gained increasing scholarly attention as global problems such as rapid population growth, geographical and temporal imbalance in resource supply, and expanding environmental pollution have intensified (Verburg et al., 2013; Chen et al., 2021; Nielsen et al., 2019). The human–land relationship is the interaction of human society and its activities with the geographical environment; it is also a fundamental pair of relationships accompanying the evolution of human development (Wu, 2008). In rural areas, the human–land relationship unfolds within the rural livelihood–land use system, which is a typical socioecological system. The household livelihood and land use systems are its two main subsystems, which change in an intertwined manner. The interaction between rural household livelihoods and land use is the core of rural human–land relations and a key issue for rural development.
Since the 1980s, rural households no longer rely on traditional agricultural production as their only livelihood strategy and have started to develop toward nonfarm, part-time work and agricultural specialization as a result of China’s rapid industrialization and urbanization and the implementation of land transfer policy (Zheng and Liu, 2018). As the main subject of farmland management, the livelihood changes in rural households are closely related to their farmland utilization status (Bradstock, 2005). A harmonious human–land relationship helps achieve harmony between social productivity and natural productivity, economic regeneration and natural regeneration, and economic system and ecosystem; moreover, harmonious coexistence between humans and nature can be realized (Li et al., 2021). Therefore, the interrelationship between the livelihood status and land use status of farmers with different livelihood strategy types must be explored in the context of the industrialization and urbanization of China to achieve sustainable development of rural households’ livelihoods and rational use of land resources.
Regarding the relationship between rural households’ livelihoods and land use, scholars have conducted a series of studies focusing on the effects of changes in rural households’ livelihood strategies on land use, such as the impact of transformation of farmers’ livelihood strategies (Lyu et al., 2022), livelihood diversification (Tittonell et al., 2010), and nonfarm livelihood (Su et al., 2018) on land use types, scale, and efficiency (Wang and Yang, 2012). They have also focused on the reverse effects of land use changes on rural households’ livelihood, such as the effects of land transfer (Zhao et al., 2017), land reform (Vista et al., 2012; Scoones et al., 2012), reversion to wetlands (Zhao et al., 2017), and cropping types (Djanibekov et al., 2013; Kamwi et al., 2015; Zhen et al., 2014) on livelihood strategies. Existing studies have mostly taken the perspective of livelihood strategy change and land use change by using one as the driver of the other, but the coupled symbiotic relationship between the two is scarcely studied. In recent years, some scholars have begun to pay attention to the symbiotic relationship between rural households’ livelihood and land use (Carr and McCusker, 2009; McCusker and Carr, 2006). They argued that the two are not independent but have a complex coupling relationship (Pensuk and Shrestha, 2008). However, systematic research on the coupling relationship between the two is lacking. In addition, the integrated objectives of the sustainable development of farmers’ livelihoods and sustainable use of land resources cannot be easily supported by studying only the changes in farmers’ livelihood strategies and land use. The perspective of changes in farmers’ livelihood strategies cannot reflect the overall status of farmers’ livelihoods and their sustainability, whereas the perspective of land use changes cannot cover the comprehensive requirements of sustainable land use. The actual livelihood status and land use status of farmers must be understood from the perspective of sustainable development objectives.
Based on existing studies, this study intends to make marginal contributions in the following aspects: First, this study constructs a conceptual framework for the sustainable development of farmers’ livelihoods–land use systems from a coupled coordination perspective based on the concepts of farmers’ sustainable livelihoods and sustainable land use. Second, it empirically analyzes the coupling degree (CD) of farmers’ livelihoods and land use systems under different livelihood strategies and the coupling coordination degree (CCD) by using Qufu City, Shandong Province, as a case area. As the hometown of Confucious, Qufu has seen a rapid differentiation of rural households’ livelihood strategies in the context of industrialization and urbanization. Moreover, the resulting rural households’ livelihood status and land use status have a strong representative and research significance. Therefore, this study classifies rural households’ livelihood strategies into six types [off-farm employment-oriented type (OFO), balanced type (BA), off-farm type (OF), idle type (IDL), professional type (PRO), and conventional type (CON)] by taking Qufu as an example. We analyzed the CD and CCD between the livelihood capital status (LCS) and land use effects (LUEs) for rural households with different livelihood strategies to reveal the mutual adaptability between them. On this basis, Skinner’s reinforcement theory is introduced to analyze the feedback mechanism of the coupled coordination degree of farmers’ livelihoods and land use systems on their livelihood strategies, thereby providing a reference for achieving sustainable development of farmers’ livelihoods and land use.
2 Conceptual framework for sustainable development of farmers’ livelihood–land use systems
Farmers’ livelihood–land use system includes two subsystems: farmers’ livelihood and land use. Therefore, this study constructs a conceptual framework for the sustainable development of farmers’ livelihoods–land use systems based on the conceptual connotations of sustainable livelihoods and sustainable land use. Based on the concept of sustainable livelihoods, the sustainability of farmers’ livelihoods, expressed in the form of strong resilience to disruptions in the context of vulnerability (Ashley and Carney, 1999; Guo and Zhang, 2013), is mainly achieved by having additional livelihood capital (including natural capital, human capital, physical capital, financial capital, and social capital) (DFID, 1999). Based on the concept of sustainable land use, the sustainability of farmers’ land use, expressed as rational land use, is achieved mainly through a high level and balanced development of LUE (ecological, economic, and social) (Yang et al., 2019). However, farmers’ livelihood system and the land use system are not independent of each other. Instead, they have a complex coupling relationship, wherein they interact and influence each other. Only a harmonious symbiosis between farmers’ livelihoods and land use can promote the sustainable development of this typical rural socioecological system.
From a synoptic perspective, the sustainable development of a farmer’s livelihood–land use system is the development process of this system from disorder to order. In this regard, disorder refers to the absence of regular connections, movements, and transformations among the system components, and it represents randomness and contingency; order refers to regular connections, movements, and transformations among the system components, and it represents rationality and forward movement (Wu et al., 2008). Therefore, we consider the state of sustainable development of farmers’ livelihoods–land use system as ordered. On this basis, the sustainable development of the farmers’ livelihood–land use system means that the farmer livelihood and land use, as two subsystems, form an ideal combination under the synergistic effect to reach an optimal state that promotes each other in a coordinated manner and achieve the sustainable development goal of the farmers’ livelihood-land use system.
The synergy between subsystems in a complex open system is the internal driving force for the formation of an orderly structure of the system; this synergy can cause a qualitative change in the system at a critical point to produce a synergistic effect that can change the system from disorder to order and produce some kind of stable structure from chaos (Haken, 1989). The degree of coupling coordination is a measure of the degree to which the elements within a system or system are in harmony with one another in the process of development. Thus, it reflects the tendency of the system to move from disorder to order. The degree of coupling coordination is precisely a measure of the synergistic effect. It is used in this study to indicate the degree of sustainable development of the livelihood–land use system of farmers.
In conclusion, the LCS and LUE of farmers reflect the operation status of their livelihood system and land use system, respectively. The synergistic relationship between them reflects the operation status of farmers’ livelihood–land use system. For farmers with different livelihood strategies, their LCS is bound to be different. Under different livelihood strategies, farmers’ land use objectives and approaches also differ, resulting in different LUEs. Moreover, does a difference in the degree of coupling and coordination between the livelihood level and LUE of farmers exist under different livelihood strategies? In this study, the above conceptual framework of sustainable development of farmers’ livelihood–land use system is empirically analyzed by taking Qufu City as an example.
3 Study area and data sources
3.1 Study area
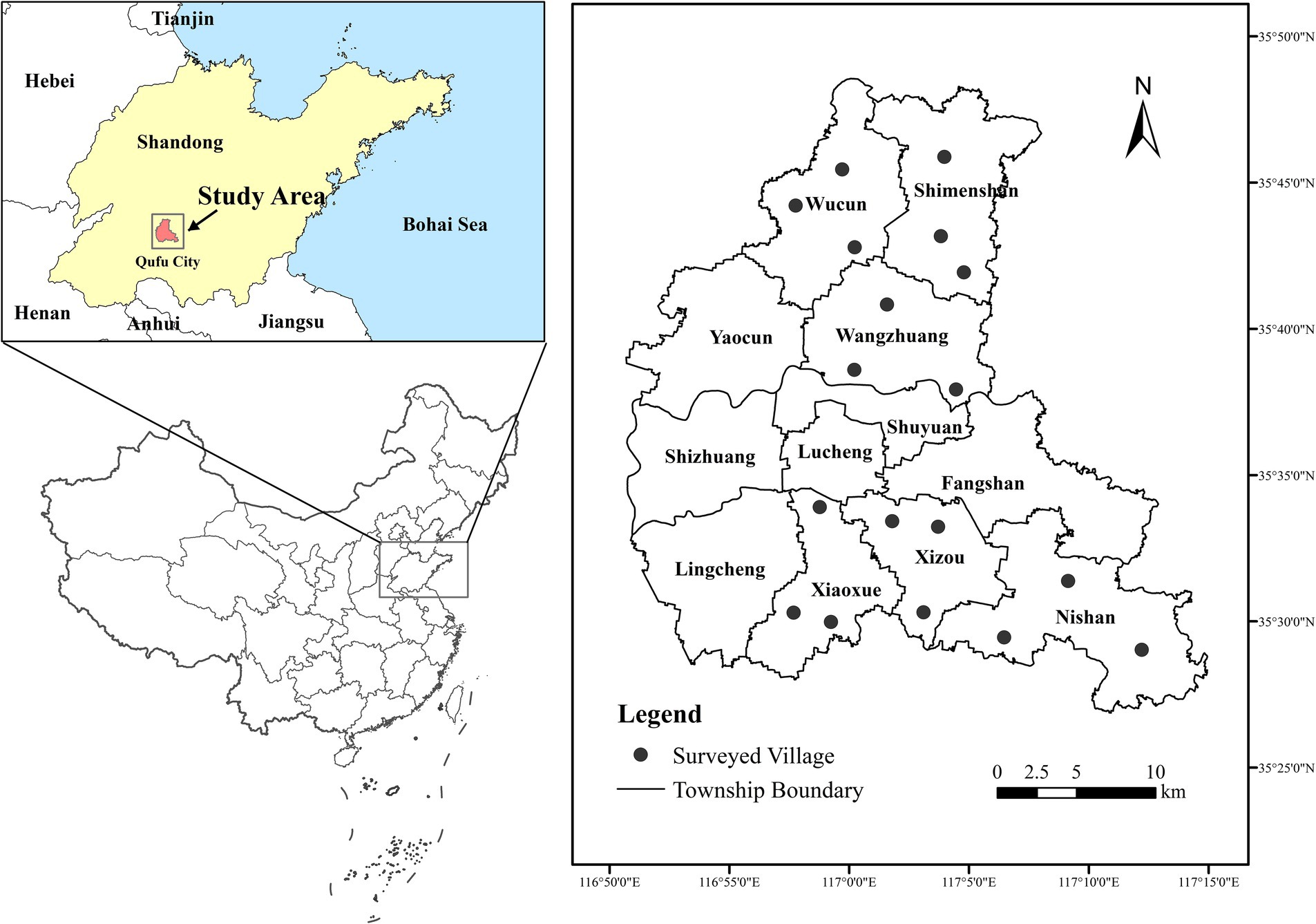
Considering the level of economic development, the actual condition of agricultural development, and the convenience of conducting surveys and interviews, Qufu City in Shandong Province was selected as the study area. Qufu is located in the southwest of Shandong Province (116°51′ to 117°13′E, 35°29′ to 35°49′N) (Figure 1). It has a total area of 815 km2, with low hills, plains, and depressions accounting for 22, 71, and 7% of the total area, respectively. Qufu has a warm temperate monsoon climate, with dry spring and autumn, rainy summer, dry and cold winter, and an average precipitation of 698 mm per year, making the agriculture industry highly developed. Qufu City has four streets, namely, Lucheng, Shuyuan, Shizhuang, and Xiaoxue. It also has eight towns, namely, Wucun Town, Yao Village Town, Lingshen Town, Nishan Town, Xizou Town, Wangzhuang Town, Shimenshan Town, and Fangshan Town, with 416 administrative villages. According to statistics, Qufu has 4.71 × 104 hm2 of arable land, accounting for 57.52% of the total land area of the region, with 0.13 hm2 of arable land per capita. In 2019, the gross domestic product (GDP) of Qufu was 35.506 billion yuan, the resident population at the end of the year was 649,900 people, and the per capita GDP was 54,654 yuan; moreover, the agricultural output value of Qufu was 2.61 billion yuan, the grain cultivation area was 63,900 hectares, and the grain output was 436,300 tons.
In 1978, China launched the reform and opening-up. Afterward, urbanization in Qufu City, Shandong Province, also accelerated significantly, and many rural laborers began to enter the cities and towns in search of jobs. At the beginning of the 21st century, a large area of arable land in Qufu began to be transferred under the guidance of a series of national and local policies on land transfer and agricultural support with the accelerated development of urbanization and industrialization. Correspondingly, the livelihood strategies of rural households began to differentiate at an accelerated pace and started to develop in the direction of nonfarm work, part-time employment, and agricultural specialization. The surveyed rural area’s arable land accounts for 81% of the total land area. In 2020, the per capita net income was approximately 12,800 yuan, and the agricultural labor force constituted 50% of the total population. The level of agricultural mechanization in the villages has continuously increased. Agricultural organizations such as family farms, agricultural cooperatives, and leading agricultural enterprises have been fully developed, and the agricultural economy has gradually diversified. As a pilot area for agricultural reform in China, Qufu city’s agricultural production and operations involve a higher degree of industrialization and standardization. The phenomena and problems that have arisen in the process of livelihood transition will have significant implications for similar areas that are starting or have already experienced livelihood transitions.
3.2 Data sources
The data used in this study were obtained from a field survey on livelihoods and land use status of rural households in Qufu City, Shandong Province, conducted in December 2023. The survey was carried out by researchers and 20 university students over 3 days, following training sessions on the project’s context, questionnaire completion rules, and interviewing techniques.
To ensure sufficient representativeness, it was first necessary to determine the minimum sample size required for the survey. In statistics, the minimum sample size depends on factors such as population size, desired confidence level, confidence interval width, and population variability. The following formula is typically used to estimate sample size (Equation 1):
Where N is the required sample size, Z represents the z-score for the desired confidence level (e.g., 1.96 for a 95% confidence level), ppp is the estimated population proportion (for large samples, p can be set to 0.5 to maximize the sample size), and E is the margin of error. For this study, with a 90% confidence level, a 5% margin of error, and an estimated population proportion of 0.5, the minimum sample size N was determined to be 269.
A multi-stage sampling method was usded to be surveyed. First, three towns were selected as the sampling points in the north and south wings of Qufu based on the representative sampling point principle: the north wing represented Wangzhuang, Wucun and Shimenshan Towns, and the west wing represented Xiaoxue, Nishan and Xizou Towns. Next, three villages were randomly selected within each town, and finally, 25 households were randomly selected in each village. As some households could not be reached, a total of 387 questionnaires were distributed. These questionnaires mainly included basic information on rural households, their livelihood capital ownership, existing land assets and their utilization, and future livelihood intentions. The participatory survey method was used in the survey process. Face-to-face interviews with farmers and consultation with relevant experts from local agricultural technology centers were also conducted to ensure the reliability of the data. A total of 379 valid questionnaires were recovered, with a recovery rate of 97.9%.
4 Methods
4.1 Classification of rural households’ livelihood strategy types
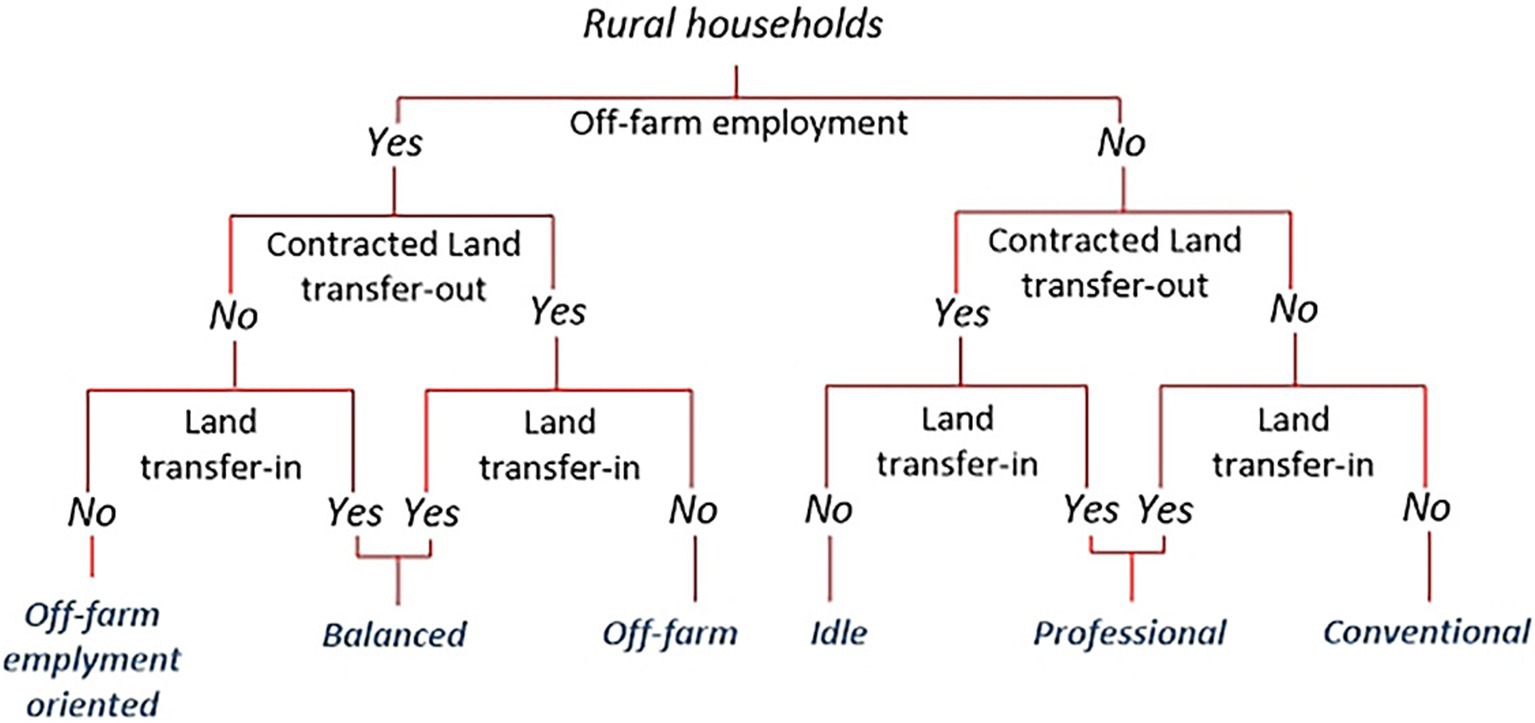
The criteria for classifying the types of rural households’ livelihood strategies from the existing studies vary according to the study area, period, and purpose (Su et al., 2009a; Xu and Yue, 2012). On the basis of the studies examining livelihood diversification and farmer typology, we selected three livelihood choice-related variables, namely, off-farm employment, land transfer-out, and land transfer-in, to identify rural household types. Off-farm employment was defined by whether households engaged in off-farm employment, land transfer-out was defined by whether households rented farmland to others, and land transfer-in was defined by whether households rented farmland from others.
Focusing on household off-farm employment decisions and land transfer decisions, we used a classification tree to construct the typology (Figure 2). We also classified the households’ livelihood strategies into six types (OFO, BA, OF, IDL, PRO, and CON) based on the households’ engagement in each of the three dominant livelihood choices of the region.
4.2 Constructing a comprehensive evaluation index system of rural households’ LCS and LUE
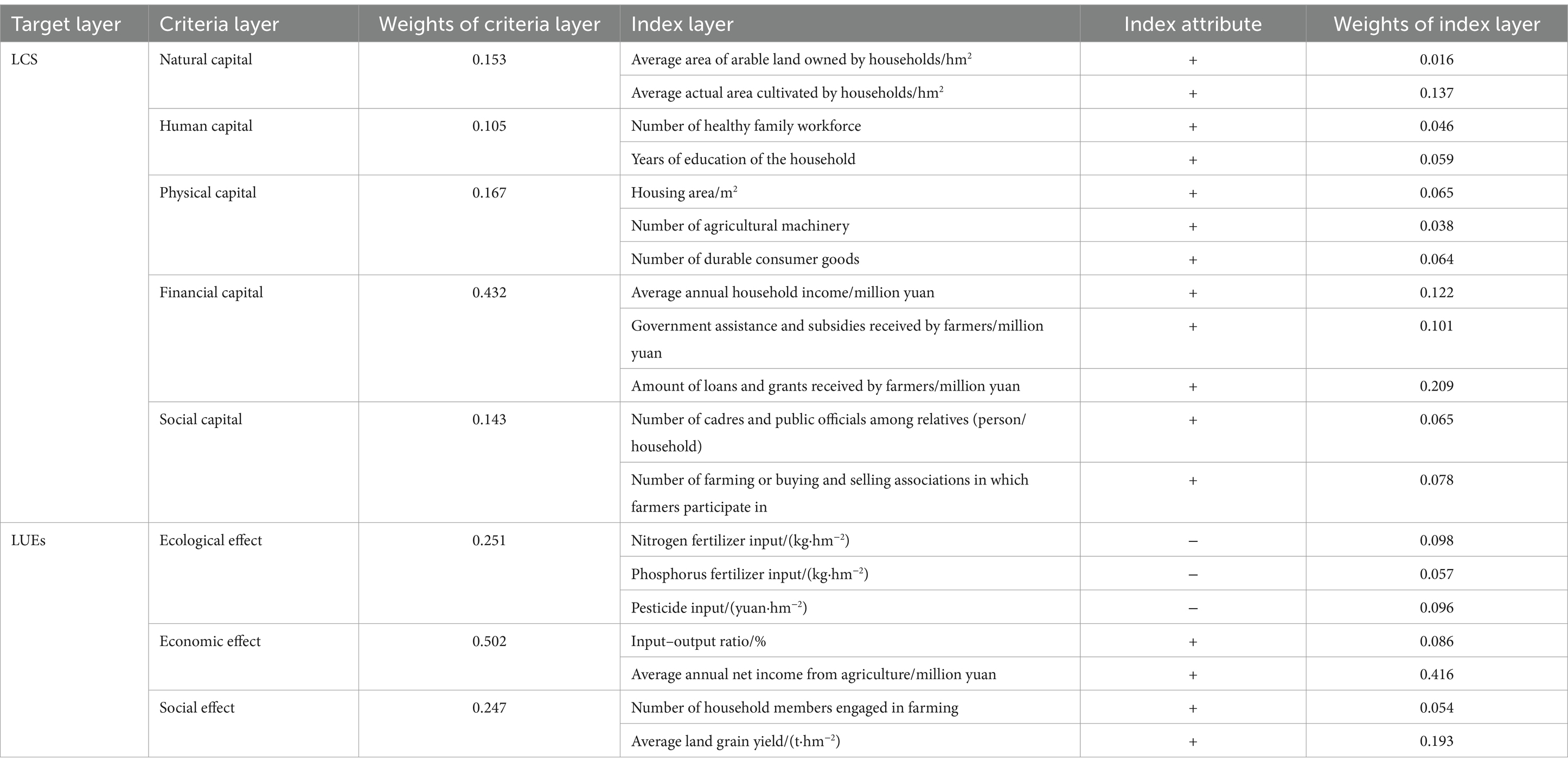
As two subsystems of the human−land system, rural households’ livelihood system and land use system interact and influence each other. According to the sustainable livelihood framework proposed by the UK Department for International Development (DFID, 1999), rural households’ livelihood strategy, which refers to how livelihood capital is combined and used, is determined by the external livelihood environment and the status of the livelihood capital inherently possessed by households (Su et al., 2009b). Livelihood capital is at the core of the framework and is the basis for the options available to rural households, the livelihood strategies they employ, and their resilience to livelihood risks; it is also a necessary condition for positive livelihood outcomes (Guo et al., 2013). Significant differences exist in the livelihood capitals of rural households with different livelihood strategy types; thus, LCS can be used as a proxy for rural households’ livelihood status (Guo and Zhang, 2013; Xu and Yue, 2012). Significant differences can be found in the land use behaviors of farmers with different livelihood strategy types (Wang and Yang, 2012). As a result, different ecological–economic–social effects are produced (Yang et al., 2019), i.e., integrated LUE. Therefore, rural households’ land use status can be characterized by LUE. In summary, this study takes LCS and LUE as the target layers of the comprehensive evaluation index system of rural households’ livelihood–land use system. Moreover, five-criteria layer indicators, including natural capital, human capital, physical capital, financial capital, and social capital, are selected from the livelihood capital perspective to reflect rural households’ livelihood status; from the LUE perspective, three criteria-level indicators, including ecological effect, economic effect, and social effect, are selected to characterize different LUEs of rural households. According to scientific principles and the representation of the selected indicators, 19 evaluation indicators are selected based on the actual situation of the study area and the availability of data (Table 1).
4.3 Data standardization and determination of index weights
First, this study adopts the polarization method to standardize the original data and eliminate the influence of the different magnitudes on the quantification results (Equations 2, 3).
where xij and rij are the original and standardized values of the i-th index of the j-th quantified object, respectively, and ximin and ximax are the minimum and maximum values of the i-th index, respectively.
This study adopts a combination of subjective and objective methods to determine the index weights and make them highly scientific and reasonable. First, we apply the Analytic Hierarchy Process and the entropy weight method to calculate the index weights (Al-Aomar, 2010). Then, we apply the multiplicative normalization formula to calculate the combination weights of each index (Equation 4).
where wi1 and wi2 are the weight values of the i-th indicator calculated by applying the hierarchical analysis and the entropy weight method, respectively, and m is the number of indicators.
The combined weight values of the indicator layer to the target layer can be obtained by the above steps, and the weights of the criterion layer to the target layer are obtained by summing the weights of the indicator layer (Table 2).
Based on the standardization and weighting of each indicator, the comprehensive evaluation formulas for the two subsystems of rural households’ livelihood capital and LUE are
In Equations 5, 6, xi and yj denote the standardized values of each evaluation index of the subsystem, ai and bj are the weights of each index, m and n are the number of evaluation indices of the two subsystems.
4.4 CD model
Coupling is a concept in physics used to describe the degree of interaction and the influence between elements of a system or within a system. Based on the CD function, the CD model of rural households’ LCS and LUE is constructed as
In Equation 7, C represents the CD, and its value is between 0 and 1. When C = 0, no coupling relationship exists between rural households’ LCS and LUE; when C = 1, the CD value is maximum, indicating that the two subsystems have reached a high coupling state. Based on relevant studies, the CD value is divided into four levels: when 0 < C ≤ 0.3, the two subsystems of rural households’ livelihood strategy and land use behavior are in the low-level coupling stage; when 0.3 < C ≤ 0.5, the two subsystems are in the antagonistic stage; when 0.5 < C ≤ 0.8, the two subsystems are in the grinding stage; when 0.8 < C ≤ l, the two subsystems are in the high-level coupling stage.
4.5 CCD model
The CD model can only quantify the strength of the degree of interaction between systems or between elements within a system but not the degree of coordination of the interactions and the magnitude of benign coupling. From the perspective of synergy, the higher the degree of coupling and coordination is between the two subsystems and the stronger the synergy is between them in the development process, the more orderly the system tends to be and the higher the degree of sustainable development is. CCD can be used to measure the degree of coordination between systems or between elements within a system in the development process. Therefore, a CCD model is introduced to reflect the level of coordinated development of the two subsystems of farmers’ livelihoods and land use and accurately judge the interaction between them. The model form is
In Equation 8, D denotes CCD, C denotes CD, T denotes the comprehensive evaluation index of rural households’ livelihood strategy–land use behavior system, α and β are coefficients to be determined, and the values of the two usually depend on the importance of each subsystem in the system. The two subsystems of human and land are considered equally important in the study of the human–land relationship, i.e., the contributions of both to the sustainable development of the human–land system are the same. Similarly, the value of coupling coordination can be divided into four levels: when 0 < D ≤ 0.3, the two subsystems of rural households’ livelihood strategy and land use behavior are in the low-level coupling coordination stage; when 0.3 < D ≤ 0.5, the two subsystems are in the medium-level coupling coordination stage; when 0.5 < D ≤ 0.8, the two subsystems are in the high-level coupling coordination stage; when 0.8 < D ≤ 1 the two subsystems are in the extreme-level coupling coordination stage.
4.6 Application of Skinner’s reinforcement theory in analyzing the impact of rural household land use behavior on livelihood strategies
Reinforcement theory, also called behavior modification theory, is proposed by Burrhus Frederic Skinner, an American psychologist and behavioral scientist. In this theory, reinforcement refers to an affirmative or negative consequence (reward or punishment) for a behavior that determines, at least in part, whether the behavior will be repeated in the future. Depending on the nature and purpose of reinforcement, reinforcement can be divided into positive and negative reinforcement. Positive reinforcement means that when people take a certain behavior, they can obtain some kind of result that makes them feel happy. This result can become the force that propels people to tend to or repeat this behavior. As a stimulus, the result is called positive reinforcement, which enhances the probability of occurrence of a certain behavior. Negative reinforcement means that when people adopt a behavior, they obtain an unpleasant result that reduces the probability of continuing the behavior. This unpleasant result is called negative reinforcers.
According to human–land relationship theory, rural households’ livelihood strategies and land use behaviors interact and influence one another. LUEs and their coupling coordination with LCS as a result of rural households’ land use behavior can have a certain degree of influence on their livelihood strategies. Therefore, based on Skinner’s reinforcement theory, LUEs and their coupling coordination with LCS are used as some kind of stimuli as a way of exploring the feedback mechanism of rural households’ land use behavior on livelihood strategies.
5 Results and analysis
5.1 Basic characteristics of rural households with different types of livelihood strategies
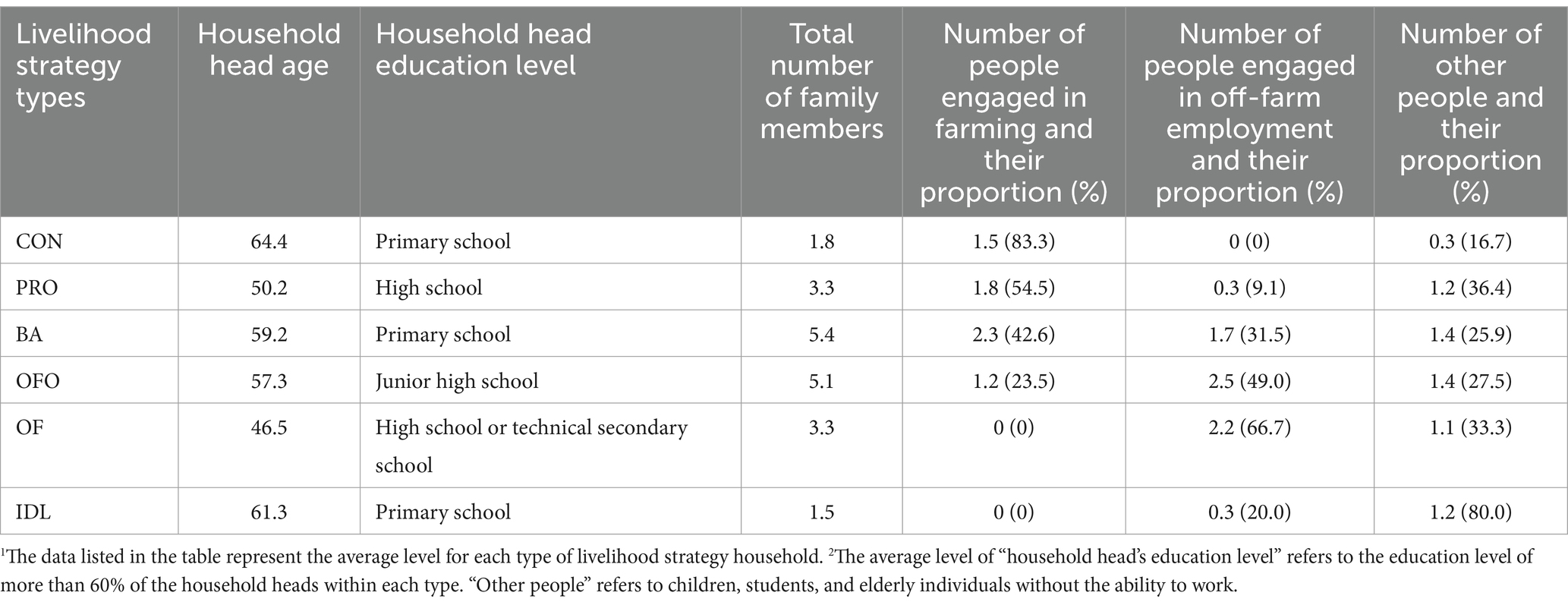
Table 2 summarizes the socio-demographic characteristics and labor allocation of different types of households. We aimed to survey the household heads, who were generally older, and most of the respondents were male.
CON does not involve nonfarm work and land transfer. The average age of the household heads in this type is 64.5 years old, and most of them have an elementary school education level. This type has the smallest number of family members who live separately from their children. In this type of household livelihood strategy, agricultural production is used as the main source of household income, and the land cultivation area is generally <10 hm2.
PRO does not involve nonfarm work, and the household members in this type devote all their labor to agricultural production. Moreover, large-scale operation is realized through land transfer. Thus, this type is generally characterized by large-scale agricultural production and a single source of agricultural income. The heads of this type of farming household are young and have a high education level, mostly at the high school level. Moreover, the scale of their land operation is large, generally higher than 20 hm2 and reaching up to 133 hm2.
BA involves nonfarm work and land transfer to increase the scale of cultivation. In addition to nonfarm work, agricultural production is still an important source of income for these households.
OFO involves nonfarm labor but not land transfer. The heads of this type of farming household have a slightly higher education level than those of BA. The number of household laborers is large, and they allocate part of the labor force to nonfarm work while keeping the contracted land for agricultural production. When certain conditions are met, this type of farming household tends to diversify into other livelihood types.
In OF, all household labor is allocated to nonfarm work, and all contracted lands are rented out to other farmers. Thus, the household with this strategy no longer engages in farming activities. Among other types of rural households, this type of household has the youngest and most educated household heads, who are least dependent on farmland; they are independent of the agricultural economy, leaving only their land and household registration in the countryside.
In IDL, the household members of this type rent out all their contracted land to other rural households and are not involved in agricultural production or off-farm employment. The heads of this type of household, which have the smallest number of family workers, are the oldest and have the lowest level of education. In general, idle rural households are characterized by old age and lack of labor force or poverty. Their main sources of income are land rent, government subsidies, or pension insurance.
OF and IDL households have transferred all their contracted lands and have no further land use behavior. Therefore, the analysis of LUE and coupling coordination of rural households does not involve these two types of farmers.
5.2 Analysis of the coupling relationship between LCS and LUE for rural households with different types of livelihood strategies
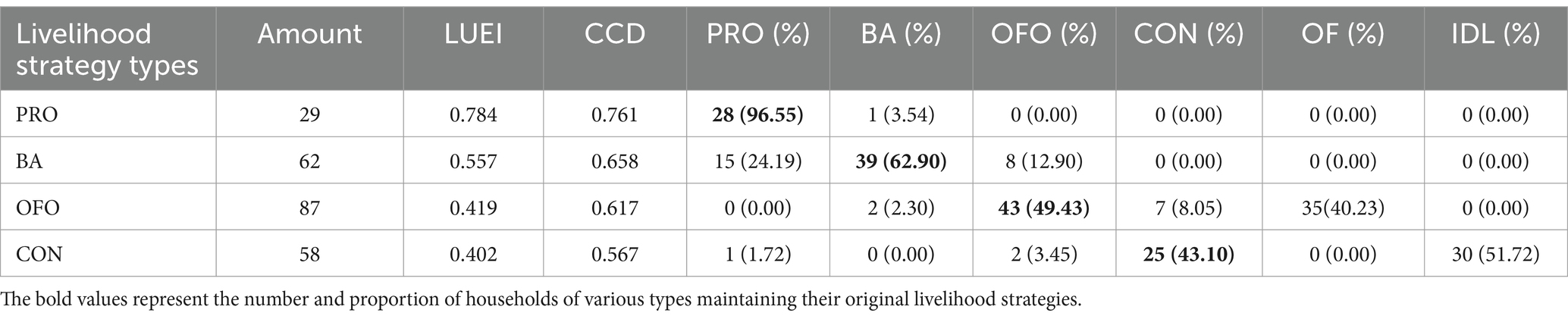
We used the LCS index (LCSI) and LUE index (LUEI) to represent the livelihood status and land use status of rural households, respectively. LCSI represents the holdings of each livelihood capital of rural households and their ability to use livelihood capital to cope with livelihood risks; LUEI reflects the combined ecological, economic, and social effects of rural households’ land use behavior (Table 3). In terms of livelihood status, the livelihood capital indices of different types of rural households are, in descending order, 0.428 for PRO, 0.347 for OFO, 0.336 for BA, and 0.258 for CON. In terms of land use status, the LUE indices of different types of rural households are, from high to low, 0.784 for PRO, 0.557 for BA, 0.419 for OFO, and 0.402 for CON.
On this basis, the CD between rural households’ LCS and LUE reflects the interrelationship between them (Table 3). The CDs of different types of households are, from high to low, 0.996 (OFO), 0.976 (CON), 0.969 (BA), and 0.956 (PRO). The CD between different types of households is not very different. However, it reflects the actual situation. In particular, the LCSI and LUEI for OFO are both in the middle; however, the difference between LCSI and LUEI is the smallest, and their CD is the highest. The LCSI and LUEI for CON are both the lowest; however, the difference between the two is also small, resulting in their CD ranking second. The LCSI and LUEI for BA are also in the middle state; however, the gap between the two is large, and their CD ranks third. The LCSI and LUEI for PRO are both the highest; however, the gap between the two is large, resulting in their lowest CD.
Based on the CD classification scale, the CD values of all four types of farmers range from 0.9 to 1, which belong to the high-level coupling stage. This finding indicates that a strong dependence and correlation can be found between the households’ LCS and LUE.
5.3 Analysis of the coupling coordination relationship between LCS and LUE for households with different livelihood strategies
In terms of coupling coordination relationship, the CCD between LCSI and LUEI differs significantly among different types of farmers, which are PRO (0.761), BA (0.658), OFO (0.617), and CON (0.567) in descending order (Table 4).
PRO has the highest coupling coordination. Given that PRO cultivates large areas, relevant personnel from Qufu Agricultural Technology Center regularly provides agricultural training or technical guidance to farmers with large-scale operations to make their farming highly scientific and help them obtain maximum returns with reasonable inputs, use highly advanced agricultural machinery (e.g., drip irrigation equipment and pesticide machines), and realize modern agricultural operations. Thus, the ecological and economic effects of land use by such farmers are high. In addition, the two land social effect indicators of PRO, including the number of household members engaged in farming and the average land grain yield, are both at a high level. Thus, the LUE of PRO is the highest among the four types of rural households at 0.784. Due to the scale effect, PRO households possess significant advantages in natural capital, physical capital, and financial capital. Moreover, the household heads in PRO generally have a high education level, are mostly between 35 and 55 years old, and have advantages in human capital. Thus, PRO’s total value of LCS is the highest, with a comprehensive evaluation index T value of 0.606, which is much higher than that of the three other types of rural households. The CCD of PRO is 0.761, indicating that LCS and LUE are at a high level of coupling coordination. Moreover, the two promote each other and develop harmoniously.
In BA, the household members are involved in off-farm employment while renting farmland from others and engaging in agricultural production to obtain profits. The labor forces from this type are relatively plentiful enough to engage in off-farm employment and comparatively small-scale farm management simultaneously. Moreover, they are limited by the conditions of technology and the scale of operation because of the need to combine on-farm and off-farm employment as their sources of income. Thus, the LUE of BA is lower than that of PRO. Given that the improvements in the LCS of BA are highly correlated with their agricultural land use, the CCD between LCS and LUE of BA is higher than that of CON and OFO but lower than that of PRO at 0.658, which is in the moderate stage.
Although OFO has a relatively high LCSI, the lack of land transfers and the relatively small arable land area, combined with the primary purpose of agricultural production meeting personal needs, result in a low LUE of 0.419. The improvement of the LCS of OFO is marginally correlated with agricultural land use. Thus, the degree of coordination between households’ LCS and LUE is 0.617, which is also in the moderate stage.
In CON, traditional farming methods are used, and the agricultural production techniques are outdated. Therefore, they use too much pesticide and chemical fertilizer, resulting in low ecological effect and economic effects of land use. In addition, CON is influenced by traditional concepts and does not use much agricultural machinery. Thus, the social effect is not high either. Among the four types of households, CON exhibits the lowest LUE at 0.402. The total value of livelihood capital is 0.258, which is also at the lowest level. This finding indicates that engaging in agricultural production does not have a significant effect on improving the LCS of farmers, and the two do not develop in their respective favorable directions. The lowest value of coupling coordination between LCS and LUE is 0.567, which is at the moderate stage.
According to the CCD classification level, the CCD between the LCS and LUE of PRO is the highest, which is at the high coupling coordination stage, and the two are in a benign and coordinated development state. The CCD of the three remaining types of households is at the medium stage, among which, the CCD of CON is the lowest.
5.4 Analysis of the feedback mechanism of rural households’ land use behavior on livelihood strategies
Table 4 shows that among the four types of households, the proportion of households maintaining their original livelihood strategies increased and the proportion of households changing their original livelihood strategies decreased as the value of LUE and their coupling coordination with LCS increased.
On the basis of the classification of stimuli in Skinner’s reinforcement theory and the statistical results of rural households’ livelihood intentions, we attempted to classify positive and negative reinforcers based on the threshold of 50% of households maintaining their livelihood strategies. For PRO and BA, the combined effect of land use and the value of coupling coordination are high, and they act as positive reinforcers to promote households to maintain their original livelihood strategies. For OFO and CON, the combined effect of land use and the value of coupling coordination are relatively low. They also act as negative reinforcers for households, inhibiting them from maintaining their original livelihood strategies and reducing the incidence of the original behavior based on the original one.
The reasons for this phenomenon are closely related to the rural households’ conditions and their goals of agricultural production. In PRO, the proportion of those who are willing to maintain their original livelihood strategy is high, accounting for 96.55%. The heads of PRO had a high education level, were younger than those of other types of households, pursued economic profits from large-scale farming operations as the goal of agricultural production, and received regular training from the local agricultural technology center. Thus, the combined effect of land use was the highest among the four types of households at 0.784. The coupling coordination between LCS and LUE was good, with a CCD of 0.761. Given the promotion of various farmland subsidy policies implemented in Qufu, PRO was willing to continue to keep its original livelihood strategy.
BA is similar to PRO in that its agricultural production goal is for economic profits. Given that its farming scale and agricultural technology level are lower than those of PRO, the combined effect of land use and coupling coordination values are slightly lower at 0.557 and 0.658, respectively. Both of which act as positive reinforcers resulting in a high proportion of households who maintain their original livelihood strategies. In BA, a high percentage of farmers, 62.90%, were willing to maintain their original livelihood strategy. In addition, 24.19% of household members in BA plan to stop working in nonfarm jobs and change to PRO. Thus, the tendency of this type of household to change into PRO is evident, indicating that strengthening further the specialization of agricultural production is attractive for a significant proportion of BA households.
The trend of the division of OFO is evident. In particular, 49.43% of OFO households are willing to maintain the original livelihood strategy, and 40.23% have the will to transfer out of contracted land and transform to OF. In addition, 2.30% plan to transform to BA, and 8.05% plan to transform to PRO. In OFO, household members use their farmland loosely, and the combined effect of land use is not high, at 0.419. However, they are engaged in agricultural production mainly to meet the needs of their families. Moreover, they do not need to change their original livelihood strategy. Thus, the proportion of farmers in OFO who maintain their original livelihood strategy is higher than that of farmers in CON.
The proportion of household members in CON who maintain their original livelihood strategy is the lowest at 43.10%. In CON, the households are generally headed by older people who live separately from their children and are limited by capital, age, and literacy level. The combined effect of land use is not high at 0.402, and the coupling coordination of LCS and LUE is poor. Given the objective conditions, the willingness of household members in CON to expand the farmland area or increase the arable land input is not strong. The proportion of household members in CON who maintain their original livelihood strategy is lower than that of household members in other types of households. However, the trend of converting into IDL is evident, with 51.72% of household members in CON planning to transfer their contracted lands out. Under the policy of moderate scale management, the rent of land transfer has been increasing and is equal to or more than the net income obtained by farmers from their farming jobs. Thus, many household members in CON tend to transfer their contracted land.
6 Conclusion and discussion
This study quantifies the interaction between rural households’ LCS and LUE in terms of coupling and coupling coordination by taking Qufu in Shandong Province, a developed region in eastern China, as an example. As a result, the limitation of existing studies that mainly explore the one-way influence between the two is addressed. Supported by Skinner’s reinforcement theory, this study attempts to classify coupling coordination and LUE into positive and negative reinforcers by using 50% of the proportion of farmers maintaining their livelihood strategies as the threshold. This study also elucidates the mechanism of the influence of rural households’ land use behavior on the choice of livelihood strategies.
From the human–land system perspective, this study treats rural households’ livelihoods and land uses as two subsystems and draws on the capacity CCD model in physics. Moreover, it takes Qufu, Shandong Province, as an example and constructs a CCD model of rural households’ LCS and LUE to explore the interaction relationship between them and their coordinated development level. On this basis, the feedback mechanism of rural households’ LUE and their coupling coordination with LCS on livelihood strategy is analyzed by introducing Skinner’s reinforcement theory. The main research findings are as follows:
1. Different types of households differ in the coupling relationship and the coupling coordination relationship between LCS and LUE. In terms of coupling relationship, the CD for different types of households ranges from 0.9 to 1, denoting a high-level coupling stage, with OFO registering the highest degree of 0.996. This finding indicates that the strongest correlation is between the LCS and LUE for this type of household. The CCD of the remaining three types of households is in the range of 0.4–0.5, which is in the moderate coupling coordination stage.
2. LUEs and their coupling coordination with LCS have significant effects on rural households’ livelihood strategies. According to Skinner’s reinforcement theory, for PRO and BA, the LUE and the degree of coupling coordination are high. They also act as positive reinforcers for the households, prompting more than 50% of the households to tend to maintain their original livelihood strategy in future agricultural production. For OFO and CON, the LUE and coupling coordination are relatively low and act as negative reinforcers for households, thereby inhibiting more than 50% of households from maintaining their original livelihood strategy. The reasons for this phenomenon are closely related to rural households’ conditions and household livelihood goals.
3. PRO outperforms other types of households in terms of LCS, LUE, and the coupling coordination between LCS and LUE. This finding indicates that the livelihood strategies of PRO are conducive to improving rural households’ livelihood levels and promoting the rational use of farmland resources. The survey results show that 96.55% of household members in PRO intend to maintain their original livelihood strategy in future agricultural production. Additionally, 24.19% of household members in BA intend to adopt the livelihood strategy of PRO. This finding indicates that the livelihood strategy of PRO is highly attractive to farmers.
An important aspect of future research on human–land systems is to explore the coupling mechanisms of human–land interactions at different scales (such as individual, regional, and global) at a deeper level. The coupling coordination of human–land systems is influenced by numerous factors. In this study, we analyzed farmers’ livelihoods and land use under different strategies of land and labor allocation and found that adopting large-scale, specialized planting strategies can effectively improve the level of coupling coordination between farmers’ livelihoods and land use. This finding aligns with field observations by Li et al. (2024). However, our study does not analyze the structure of planting or breeding; research by Su et al. (2022) suggests that when farmers increase the proportion of cash crops and livestock, their livelihood efficiency and land use levels may be enhanced. Pensuk and Shrestha (2008) also found that households engaged in long-term rubber cultivation tend to have relatively better livelihood conditions. Therefore, livelihood strategies involving the cultivation of cash crops or livestock rearing are crucial factors to consider when discussing farmers’ livelihoods and land use.
Furthermore, the coupling coordination between farmers’ livelihood and land use is influenced not only by their livelihood strategies, planting, and breeding but also by various factors, such as regional development levels, resource endowments, geographical location, infrastructure quality, and agricultural policies (Bradstock, 2005; McCusker and Carr, 2006; Peng et al., 2022). To genuinely achieve coordinated development of human–land systems, it is essential to optimize livelihood and land use strategies in the future, such as by expanding non-agricultural activities and optimizing the structure and types of planting and breeding. Additionally, it is necessary to explore the interaction between livelihood and land use at multiple scales, such as at the levels of farmers, villages, and counties. By establishing an integrated, cross-scale livelihood efficiency and land-use composite system, we aim to provide a multi-dimensional and multi-level optimization framework for various entities, including farmers, villages, and counties.
The study of the interaction between rural households’ livelihoods and land use can provide a reference for improving rural households’ livelihoods and rationalizing the use of arable land resources. It can also provide a reference for government departments to introduce agricultural policies. Promoting the coordinated and sustainable development of rural households’ livelihood status and LUE should be given high priority by local governments. The greater the degree of the coupling coordination between LCS and LUE is, the stronger the synergy of this human–land system is and the higher the degree of sustainable development is. In this study, we found that CCD significantly differs among different livelihood types of rural households. Therefore, the rational allocation of arable land resources among farmers of different livelihood types is crucial. For OFO, the heads of the households are highly educated and have many options for nonfarm livelihood activities. Relevant government departments should adopt policies to encourage household heads in OFO to advance toward the direction of nonfarm activities, transfer excess farmland, and promote the flow of such farmland to PRO. CON is limited by the age and number of laborers. Moreover, the overall labor capacity in this type is not high enough to engage in large-scale agricultural production activities. Thus, CON household members can be encouraged to transfer their farmland to PRO through agricultural subsidies. Moreover, relevant government departments should focus on improving the pension and medical insurance systems, expanding the care service system for the elderly left behind in rural areas, and implementing effective services around the basic livelihood security, health, and ideological and emotional aspects of the left-behind people to ensure the livelihood security of household members in CON after transferring their farmland. BA uses agricultural income as an important source of household economy. It also has a high overall family labor capacity. Thus, BA household members can be guided to transfer large arable land or merge arable land appropriately, expand the scale of cultivation, and advance toward the direction of agricultural specialization. Guiding the rational allocation of arable land resources and promoting the development of PRO can advance the rational allocation of arable land resources, improve the efficiency of arable land utilization, and realize the transformation of farmers’ livelihoods and sustainable agricultural development, thereby ensuring regional food security and social stability.
This study has two main shortcomings. First, given the limitation of space, this study takes only the developed regions as examples. In these regions, the types of rural households’ livelihood strategies are fast differentiated. Moreover, this study does not compare the regions with middle development levels with those with low development levels. Expanding the study area will be the focus and direction of the next study to obtain a comprehensive understanding of the overall situation in China. Second, the ranking of coupling and coupling coordination is mainly based on existing studies. However, the calculation results show that the ranking span is slightly large, and the differences between different livelihood types of farmers are not well differentiated. In future studies, the ranking of coupling and coupling coordination must be refined to increase the accuracy of research results.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ZL: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft. JS: Conceptualization, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing. YL: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. HW: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. ZZ: Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the National Social Science Fund of China (no. 22BGL189).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all interview participants for generously giving their time.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Al-Aomar, R. (2010). A combined ahp-entropy method for deriving subjective and objective criteria weights. Int. J. Ind. Eng.-Theory Appl. Pract 17, 12–24. doi: 10.23055/ijietap.2010.17.1.330
Ashley, C., and Carney, D. (1999). Sustainable livelihoods: Lessons from early experience. London: Department for International Development.
Bradstock, A. (2005). Changing livelihoods and land reform: evidence from the Northern Cape Province of South Africa. World Dev. 33, 1979–1992. doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2005.07.005
Carr, E. R., and McCusker, B. (2009). The co-production of land use and livelihoods change: implications for development interventions. Geoforum 40, 568–579. doi: 10.1016/j.geoforum.2009.04.010
Chen, X., Li, J., Zhang, G. L., Meng, L. J., Pan, Z. H., and An, P. L. (2021). Green-depressing cropping system: a referential land use practice for fallow to ensure a harmonious human-land relationship in the farming-pastoral ecotone of northern China. Land Use Policy 100:104917. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104917
DFID (1999). Sustainable livelihoods guidance sheets. London: Department for International Development.
Djanibekov, U., Djanibekov, N., Khamzina, A., and Bhaduri, A. (2013). Impacts of innovative forestry land use on rural livelihood in a bimodal agricultural system in irrigated drylands. Land Use Policy 35, 95–106. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2013.05.003
Guo, R. W., Liu, S. Q., Chen, G. J., Xie, F. T., Yang, X. J., and Liang, L. (2013). Research progress and tendency of sustainable livelihoods for peasant households in China. Prog. Geogr. 32, 657–670. doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2013.04.018
Guo, S. Q., and Zhang, J. W. (2013). Analysis on rural households’ livelihood capital vulnerability. Econ. Surv. 116, 756–759. doi: 10.1115/1.2910933
Kamwi, J. M., Chirwa, P. W. C., Manda, S. O. M., Graz, P. F., and Kätsch, C. (2015). Livelihoods, land use and land cover change in the Zambezi region, Namibia. Popul. Environ. 37, 207–230. doi: 10.1007/s11111-015-0239-2
Li, M., Feng, X., Tian, C., Li, Y., Zhao, W., Guo, B., et al. (2024). Do large-scale agricultural entities achieve higher livelihood levels and better environmental outcomes than small households? Evidence from rural China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 31, 21341–21355. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-32245-w
Li, X. Y., Yang, Y., Liu, Y., Chen, Y. Y., and Xia, S. Y. (2021). The systematic structure and trend simulation of China’s man-land relationship until 2050. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 41, 187–197. doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.02.001
Lyu, X., Peng, W. L., Niu, S. D., Qi, Y., and Xin, Z. F. (2022). Evaluation of sustainable intensification of cultivated land use according to farming households’ livelihood types. Ecol. Indic. 138:108848. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108848
McCusker, B., and Carr, E. R. (2006). The co-production of livelihoods and land use change: case studies from South Africa and Ghana. Geoforum 37, 790–804. doi: 10.1016/j.geoforum.2005.09.007
Nielsen, J. Ø., De Bremond, A., Roy Chowdhury, R., Friis, C., Metternicht, G., Meyfroidt, P., et al. (2019). Toward a normative land systems science. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 38, 1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2019.02.003
Peng, J. Q., Chen, L. L., Yu, B. W., Zhang, X. H., and Huo, Z. H. (2022). Effects of multiple cropping of farmland on the welfare level of farmers: based on the perspective of poverty vulnerability. Front. Ecol. Evol. 10:988757. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2022.988757
Pensuk, A., and Shrestha, R. P. (2008). Changes in land use and rural livelihoods: a study of Phatthalung watershed in southern Thailand. Asia-Pac. J. Rural Dev. 18, 143–164. doi: 10.1177/1018529120080209
Rounsevell, M. D. A., Pedroli, B., Erb, K. H., Gramberger, M., and Wolfslehner, B. (2012). Challenges for land system science. Land Use Policy 29, 899–910. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2012.01.007
Scoones, I., Marongwe, N., Mavedzenge, B., Murimbarimba, F., Mahenehene, J., and Sukume, C. (2012). Livelihoods after land reform in Zimbabwe: understanding processes of rural differentiation. J. Agrar. Change 12, 503–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0366.2012.00358.x
Su, F., Chang, J., Shang, H., and Fahad, S. (2022). A simulation-based study on the coupling coordination of farmers’ livelihood efficiency and land use: a pathway towards promoting and implementing the rural development and rural revitalization strategy. Land 12, 1–25. doi: 10.3390/land12010124
Su, B. Z., Li, Y. H., Li, L. Q., and Wang, Y. (2018). How does nonfarm employment stability influence farmers' farmland transfer decisions? Implications for China’s land use policy. Land Use Policy 74, 66–72. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.09.053
Su, F., Pu, X. D., Xu, Z. M., and Wang, L. A. (2009a). Analysis about the relationship between livelihood capital and livelihood strategies: take Ganzhou in Zhangye City as an example. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 19, 119–125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2009.06.022
Su, F., Xu, Z. M., and Shang, H. Y. (2009b). An overview of sustainable livelihoods approach. Adv. Earth Sci. 26, 61–69. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-00205-2_9
Tittonell, P. A., Muriuki, A., Shepherd, K. D., Mugendi, D., Kaizzi, K. C., Okeyo, J., et al. (2010). The diversity of rural livelihoods and their influence on soil fertility in agricultural systems of East Africa–a typology of smallholder farms. Agric. Syst. 103, 83–97. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2009.10.001
Verburg, P. H., Erb, K. H., Mertz, O., and Espindola, G. (2013). Land system science: between global challenges and local realities. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 5, 433–437. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2013.08.001
Vista, B. M., Nel, E., and Binns, T. (2012). Land, landlords and sustainable livelihoods: the impact of agrarian reform on a coconut hacienda in the Philippines. Land Use Policy 29, 154–164. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2011.06.002
Wang, C. C., and Yang, Y. S. (2012). An overview of rural households’ livelihood strategy change and its effect on land use/cover change in developing countries. Prog. Geogr. 31, 792–798. doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2012.06.016
Wu, C. J. (2008). Theoretical research and regulation of the regional system of human-land relationship. J. Yunan Norm. Univ. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Ed. 211, 1–3.
Wu, J., Li, R. Z., and Cheng, S. H. (2008). From disorder to order—nonlinearity is the power for the order of system’s structure. J. Syst. Sci. 22, 13–18.
Xu, H. S., and Yue, Z. (2012). Livelihood strategies of livelihood capital, livelihood risks and farmers. Probl. Agric. Econ. 33, 100–105.
Yang, L., Liu, M. C., Yan, Q. W., He, S. Y., and Jiao, W. J. (2019). Review of eco-environmental effect of rural households’ livelihood strategy transformation. Acta Ecol. Sin. 39, 8172–8182. doi: 10.5846/stxb201809121960
Zhao, L. J., Kang, X. H., and Shi, J. H. (2017). The empirical analysis on the effects of the farmland transfer on households’ livelihood transformation. Chin. J. Agric. Res. Reg. Plann. 38, 158–162.
Zhen, N. H., Fu, B. J., Lü, Y. H., and Zheng, Z. M. (2014). Changes of livelihood due to land use shifts: a case study of Yanchang County in the loess plateau of China. Land Use Policy 40, 28–35. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2013.05.004
Keywords: livelihood capital status, land use effect, coupling coordination analysis, livelihood strategy, Skinner’s reinforcement theory
Citation: Liu Z, Sun J, Li Y, Wang H and Zhang Z (2024) Exploring the sustainability of farmers’ livelihood–land use systems from a coupled coordination perspective. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1511505. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1511505
Edited by:
Arnab Majumdar, Imperial College London, United KingdomReviewed by:
Peng Jiquan, Jiangxi University of Finance and Economics, ChinaJózef Ober, Silesian University of Technology, Poland
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Sun, Li, Wang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jinghua Sun, amhzdW4yMDE2QDEyNi5jb20=
 Zhaoxu Liu
Zhaoxu Liu Jinghua Sun
Jinghua Sun Yu Li1
Yu Li1 Ziyu Zhang
Ziyu Zhang