- 1College of Economics and Management, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, China
- 2Department of Agricultural Economics, School of Business and Economics, Woliso Campus, Ambo University, Woliso, Ethiopia
Conventional agriculture harms the environment and threatens sustainability. To address these issues, sustainable agricultural practices (SAPs) have become imperative. This study utilizes a meta-analysis approach to comprehensively assess empirical studies, investigate the impact of SAPs on crop productivity, identify influencing factors, and examine their temporal evolution. The findings reveal that (1) SAP adoption significantly and positively influences crop productivity, with multiple practices exhibiting the most substantial impact, followed by sustainable agricultural technology. Individuals who adopted SAPs achieved crop productivity that was 980 kilograms per hectare higher than those who did not. (2) Factors such as age, farm size, family size, livestock units, credit access, off-farm income, market distance, and cooperative membership negatively affect crop productivity, whereas education and extension services have a positive impact. (3) The positive effects of education and extension services on crop productivity strengthen over time. The strengthening of these variables over time implies a gradual increase in farmer awareness, access to resources, and adoption of SAPs, highlighting their evolving role in driving them. Accordingly, none of the past researchers identified any patterns in the variables influencing crop productivity. Therefore, promoting SAP adoption and prioritizing education and extension services can offer farmers with experience and support, thereby enhancing crop productivity. Future initiatives should therefore combine interdisciplinary methods, technology, and community involvement for ensuring SAP’s sustainability and scalability.
1 Introduction
The second objective of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDG-2) aims to eradicate hunger and achieve global food security by the year 2030 (Kumar and Pant, 2023). However, the planet’s swiftly changing climate, marked by more severe and unpredictable weather patterns, poses a significant threat to crop yields (Singh et al., 2023; Kassa and Abdi, 2022; Mpanga et al., 2020). Agriculture, as the backbone of global food production, therefore faces a myriad of challenges in the 21st century. The need to feed a growing population, coupled with concerns about environmental sustainability, has spurred a shift toward re-evaluating traditional farming practices. Traditional methods, known for their intensive use of chemical inputs and monoculture, have faced scrutiny due to their potential implications for soil degradation, water pollution, and biodiversity loss (Mgomezulu et al., 2023a; Naik et al., 2024; Wolka et al., 2023). In light of these circumstances, the embracing of sustainable agricultural practices (SAPs) has gained momentum as a viable strategy to strike a balance between the necessities of food production, conservation of the environment, and economic sustainability (Javan and Darestani, 2024; Simutowe et al., 2024; De Corato et al., 2024).
Sustainable farming practices encompass a range of approaches designed to harmonize agricultural activities with ecological processes (Manson et al., 2024; Li et al., 2024; Han and Niles, 2023). Organic farming, one of the most recognized sustainable practices, eschews synthetic fertilizers and pesticides in favor of natural inputs, emphasizing soil health and biodiversity (Hough and Contarini, 2023; Naik et al., 2022). Agroecology, another prominent paradigm, integrates ecological principles into agricultural systems, considering farms as ecosystems and promoting biodiversity, resilience, and resource use efficiency (Zeng et al., 2023; Venn and Burbi, 2023; Roques et al., 2023). Precision agriculture, on the other hand, leverages tools to optimize inputs, reduce waste, and enhance the precision of farming operations (Avola et al., 2024; Sanaeifar et al., 2023; Karydas et al., 2023). Beyond environmental concerns, the economic sustainability of farming practices is a critical dimension. Sustainable agriculture is often posited to be economically viable in the long term, with potential benefits such as reduced input costs, improved resilience to environmental shocks, and enhanced market opportunities for sustainably produced goods (Sukayat et al., 2023). However, the economic implications of different sustainable farming practices need careful consideration, as they may vary across contexts and farming systems.
The necessity of embracing sustainable farming practices extends globally, despite their limited adoption rates (Chao et al., 2024; Benitez-Altuna et al., 2024; Oyetunde-Usman et al., 2021). With the projected global population surpassing 9 billion by 2050, there is a considerable increase in food demand (Wagner et al., 2023). Concurrently, the agricultural sector faces challenges associated with climate change, dwindling resources, and the imperative to diminish its environmental impact (Sinore and Wang, 2024). Sustainable agriculture is seen as a key strategy for managing these challenges, as it offers a pathway for improving resilience, mitigating environmental impacts, and fostering economic sustainability for farmers (Mgomezulu et al., 2023a). Nevertheless, the acceptance of sustainable agricultural methods is influenced by different factors, including socioeconomic circumstances, cultural conventions, and agroclimatic differences (Bojago and Abrham, 2023; Belay et al., 2023; Nigus et al., 2024; Adhikari and Thapa, 2023). While some regions have embraced organic farming as a means to enhance environmental and human health (Merot and Smits, 2024; Liu et al., 2024), others have invested in precision agriculture technologies to optimize resource use (Zain et al., 2024; Mossie, 2022; Xie and Huang, 2021). Agroecology, with its emphasis on local context and community involvement, has gained prominence in regions seeking to enhance resilience through diversified agricultural systems (Caicedo-Vargas et al., 2023; Bezner Kerr et al., 2023). Understanding these regional variations is crucial for tailoring sustainable agricultural interventions to specific needs and challenges.
In sub-Saharan Africa, SAPs are vital for addressing low productivity, poverty, and land degradation, yet adoption remains limited (Mutyasira et al., 2018; Liben et al., 2018; Corbeels et al., 2014; Teklewold et al., 2013). Ethiopia, endowed with a rich agricultural heritage, grapples with challenges related to food security and environmental sustainability. Ethiopian farmers face a range of environmental and socio-economic challenges that hinder agricultural productivity and sustainability. Environmental issues such as soil degradation, deforestation, and erratic rainfall patterns due to climate change have significantly reduced the quality and availability of arable land (Adgo et al., 2013; Dawid Mume et al., 2023). Socio-economically, limited access to credit, markets, and agricultural inputs, coupled with low levels of education and extension services, further constrain their ability to adopt improved practices (Ayele and Tarekegn, 2020; Ayenachew and Abebe, 2024; Yigezu Wendimu, 2021; Zerssa et al., 2021). These challenges underscore the need for sustainable agricultural practices (SAPs), yet historical adoption rates in Ethiopia remain relatively low (Kudama et al., 2021; Tariku and Kebede, 2024). Addressing these barriers is critical to enhancing resilience and productivity in the Ethiopian agricultural sector.
In recent years, the implementation of sustainable agricultural practices has emerged as a vital strategy for addressing these issues, with the Ethiopian government actively promoting SAP initiatives to enhance agricultural productivity (Alemu et al., 2023; Schmidt and Tadesse, 2019). This shift toward sustainable agriculture is motivated not only by the target of enhancing crop productivity but also by the necessity of alleviating the adverse effects of traditional farming on the environment (Kakiso, 2023). Research by Asfew et al. (2023) illustrates that sustainable farming practices contribute to enhanced soil structure, increased water retention, and improved nutrient availability, positively impacting crop yields. According to a different study (Erkossa et al., 2018), applying integrated soil and water conservation widely can help to improve productivity and revers negative trends. Additionally, as noted by Edwards (2020), applying agro-ecological concepts can lead to a more adaptive and resilient agricultural system that is better able to endure extreme weather events and climatic unpredictability. Soil and water conservation (SWC) was the most widely adopted practice, with an average adoption rate of 61.5%, followed by integrated soil fertility management (56.5%) and agroforestry (48.8%). Over 80% of these contributions originated from the Oromia, Amhara, and Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples’ regions, while other regions showed minimal significance (Abegaz et al., 2024). Therefore, the adoption of sustainable agriculture practices in Ethiopia holds great potential for improving crop output and resolving social and environmental issues at the same time (Etensa et al., 2024; Lejissa et al., 2023).
Several research endeavors have explored the effect of SAPs on crop productivity, particularly in the context of Ethiopia (Gebeyehu, 2023; Zegeye et al., 2023; Zeweld et al., 2020; Adego et al., 2019). While individual studies contribute valuable information, no comprehensive meta-analysis of SAPs, particularly with crop productivity, has been done in Ethiopia. These investigations, which were conducted across diverse geographical locations and agroclimatic zones, offer a wealth of data and insights. Amede et al. (2023), Abesha et al. (2022) and Yigezu Wendimu (2021) note a lack of consensus between researchers and between researchers and government policies in the country. Moreover, trends in the factors influencing the productivity of crops were overlooked. Therefore, this meta-analysis aims to address existing knowledge gaps by systematically reviewing and synthesizing studies conducted over the past decade in Ethiopia. Through this approach, we aim to provide a nuanced perspective on the relationship between SAPs and the productivity of crops, the determinants of crop productivity, and the trend of these effects over time.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Data sources
Our data originate from the findings presented in published journal articles that explore the effect of SAPs on crop productivity in Ethiopia. This study gathered data from diverse databases including Elsevier, Springer Link, Web of Science, the Wiley Online Library, Google Scholar, and the online library of Northwest Agricultural and Forestry University, among other sources. Throughout the search period, we employed the terms “sustainable agricultural practice/s” along with alternative terms such as agroforestry, crop rotation, cover crops, integrated pest management, soil enrichment, urban agriculture, permaculture, better water management, biodiversity, conservation tillage, organic farming, polycultures, renewable resources, water conservation, natural pest eliminators, better incomes for farmers, precision agriculture, soil structure and fertility, biological pest control, sustainable farming techniques, food forests, crop diversity, and others to identify the original studies. To ensure the quality of the selected studies, we selected peer-reviewed journals. The sampling period spans from 2005 to 2024, the time of manuscript preparation. We could not obtain relevant and suitable data from reputable journals before 2005.
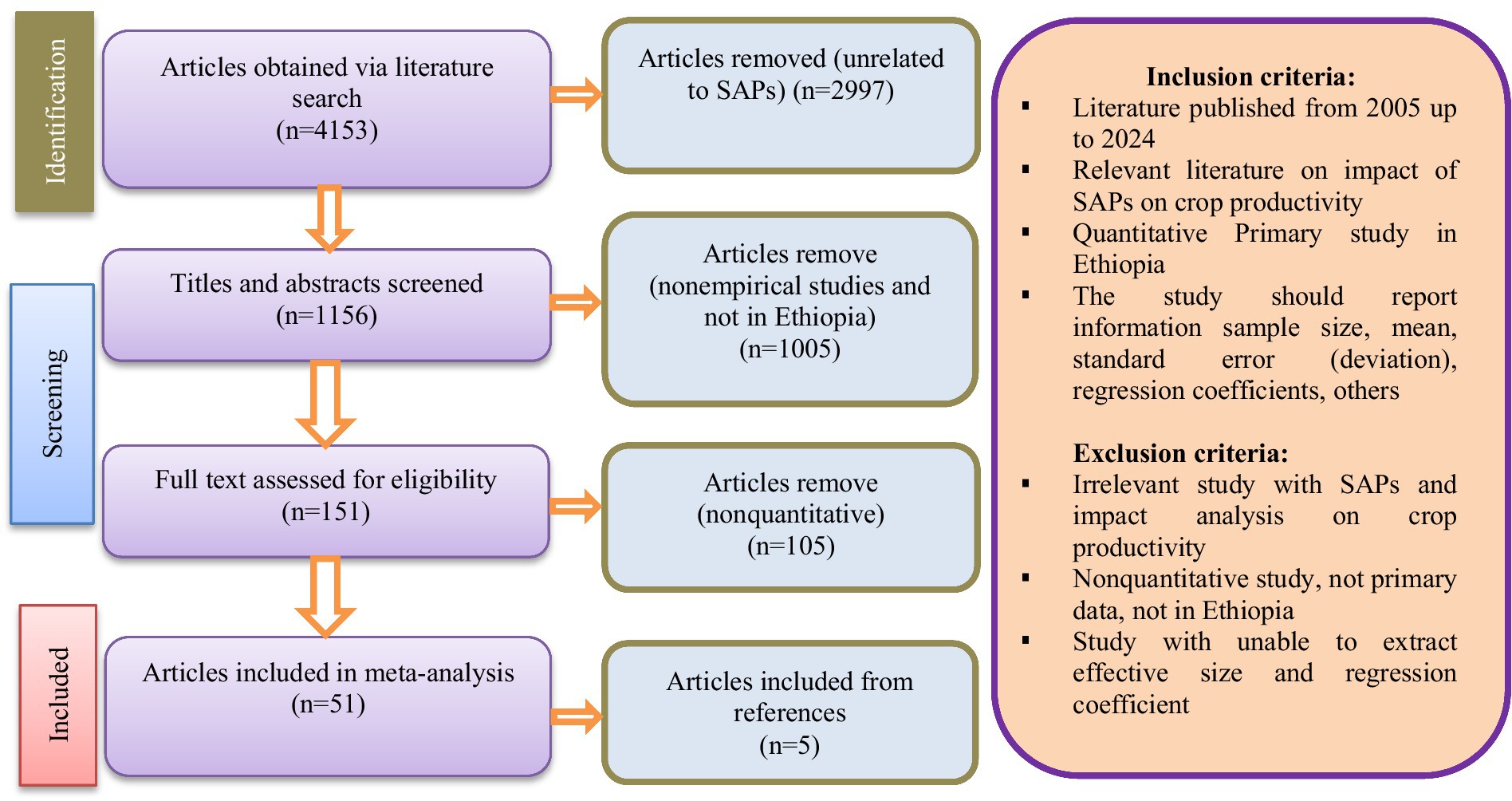
After applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria (Figure 1), we done a systematic review of pertinent studies identified during the literature search to perform the meta-analysis. Initially, a total of 4,153 original research articles were identified, but 2,997 were deemed irrelevant to SAPs and were excluded as potential data sources. Subsequently, after looking over the abstracts and titles of the remaining 1,156 articles, 1,005 nonempirical studies and studies conducted in other countries were eliminated. In the next step, 151 studies underwent a full-text suitability evaluation. Of these, 105 studies were excluded because they did not allow for the calculation of effect sizes for crucial variables. Furthermore, in the comprehensive examination of the full texts, five studies referenced in the original sources but not initially identified in the initial search were included. Ultimately, 51 studies were selected for inclusion in this meta-analysis based on their fulfillment of the predetermined inclusion and exclusion criteria. As a result, every study that is included is a quantitative primary study (observational studies) conducted in Ethiopia.
2.2 Coding of data and selection of variables
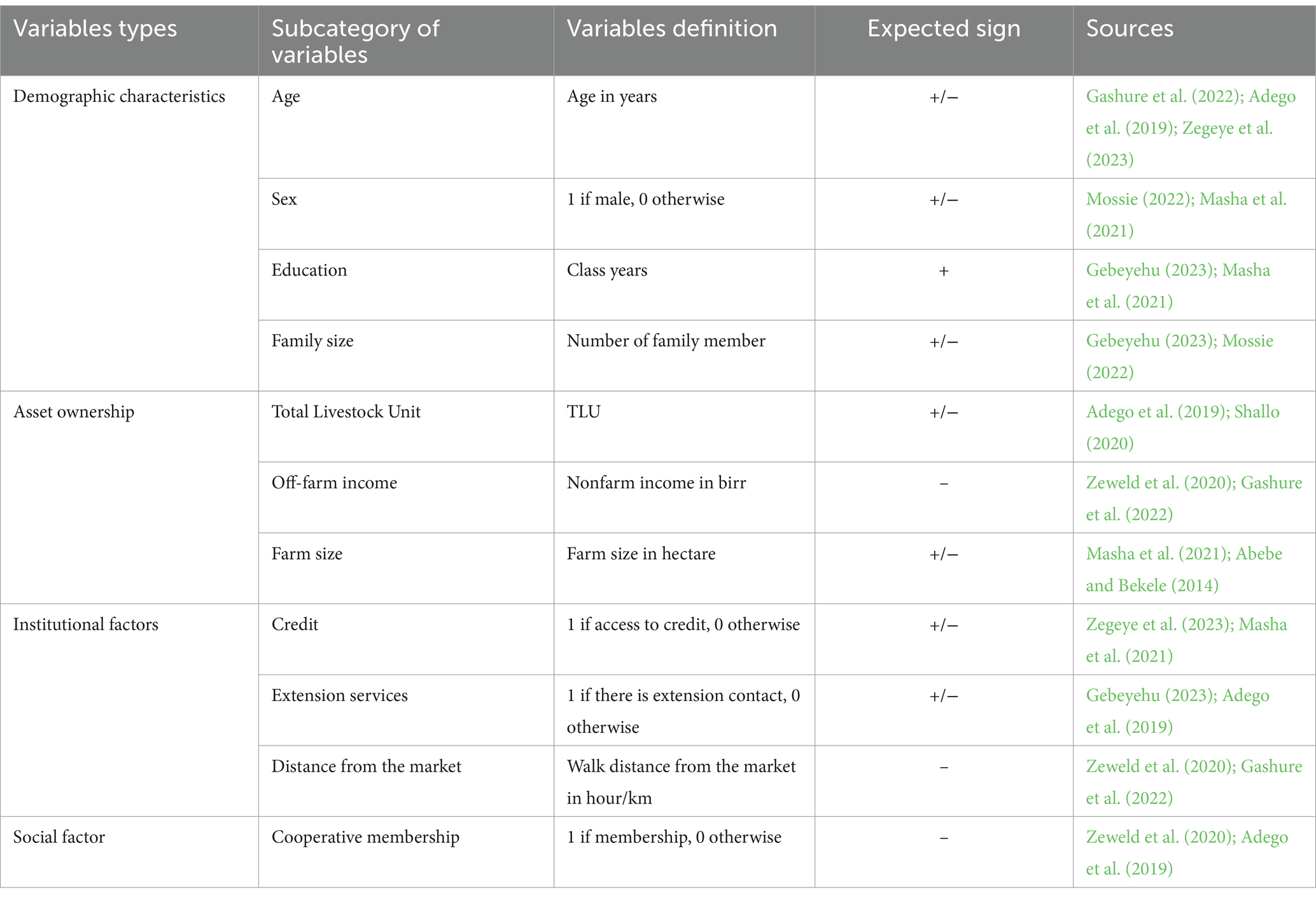
The data encoding process followed the procedure proposed by Xie and Huang (2021) and was based on the guidelines presented by Hansen et al. (2022). Initially, the study characteristics and effect sizes were identified. Individual study characteristics, such as authorship, publication year, journal, types of SAPs, sample size, research area, and research methods, were independently recorded. Similarly, effect size data included regression coefficients of relevant variables and standard errors/deviations. Following the rule of thumb, variables appearing in at least 5 out of the 51 selected papers’ regression analyses were chosen. This resulted in the selection of a total of 11 variables categorized into four groups for use in the meta-analysis (see Table 1). To ensure coding accuracy, a subset of documents from this study was randomly selected and re-encoded by other authors, and a consensus was reached through discussions.
2.3 Methods of data analysis
The meta-analysis commonly employs three models: the common-effect model, the random-effect model, and the fixed-effect model. In light of the observed substantial heterogeneity among the studies, this study chose to employ a random effects meta-analysis model. This approach is appropriate when heterogeneity is evident, assuming variations in study effect sizes, and the gathered studies signify a random sample from a broader population. A random-effects model yields results that are relevant to the whole set of related investigations, extending beyond those specifically chosen for the meta-analysis. Consistent with recommendations in the meta-analysis literature, the default approach for estimating between-study variance ( ) is the restricted maximum likelihood (REML) method. The restricted maximum likelihood is a statistical method used to estimate variance components in mixed models. Unlike ordinary maximum likelihood, REML accounts for the loss of degrees of freedom when estimating fixed effects, providing unbiased estimates of random effects and variances. It is widely used in fields like agriculture, genetics, and econometrics (Johnson and Thompson, 1995). This approach is widely used in real-world applications because it provides an objective, nonnegative estimate of between-study variance (Raudenbush, 2009). The meta-analysis procedure encompasses the determination of the mean effect, testing for heterogeneity, executing meta-regression analysis, and conducting cumulative meta-analysis. The detailed steps of the adopted analysis process are described below:
a Effect size determination
In accordance with Raudenbush (2009), the effect size (ES) can be computed by utilizing standard mean differences. The standard mean difference (SMD) is commonly used in meta-analyses to synthesize results from studies with different measurement scales, providing a dimensionless measure of effect size. The effect size (ES) and pooled standard deviation ( ) were calculated as follows in Equations 1, 2:
In the provided equations, represents the mean value of the treatment group, represents the mean value of the control group, signifies the variance of the treatment group, and signifies the variance of the control group.
The restricted maximum likelihood (REML) used for estimation is specified as follows in Equation 3:
b Heterogeneity test
When there is intrinsic variance in the effect size estimates from individual research, heterogeneity occurs. A heterogeneity test in meta-analysis assesses whether the variation in effect sizes across studies is greater than expected due to random chance alone. It determines if the observed differences in study results arise from true variability in effects (e.g., differences in study populations, interventions, or methodologies) rather than random sampling error. Two types of heterogeneity were identified: methodological heterogeneity, arising from differences in study design and conduct, and clinical heterogeneity, stemming from variations in participants, treatments, and exposures or outcomes. Statistical heterogeneity, as defined by the authors, exists when observed effects differ between studies, often resulting from clinical and methodological differences or a combination of both as explained in Equations 4, 5 (Deeks et al., 2019).
In this study, Galbraith plots were employed for a more visual assessment of heterogeneity, presenting an alternative to forest plots. Additionally, Q statistics, and were used to quantify heterogeneity following the approach of (Higgins and Thompson, 2002).
values of 25, 50, and 75%, in accordance with the criteria set forth by Higgins et al. (2003), indicate low, moderate, and high heterogeneity, respectively. In light of the significant value that we observed in our study, which is a significant amount of heterogeneity, we performed a thorough meta-regression analysis. In addition, we performed in-depth subgroup analyses on moderating variables (Table 2) to fully explore and address the sources of heterogeneity that were apparent in the meta-analysis results.
c Publication bias test and correction
When studies that are not involved in the meta-analysis consistently differ from those that are, this is known as reporting bias. One popular method for examining publication bias is funnel plots (Sterne et al., 2005). The asymmetry of the funnel plot can be more formally examined using statistical tests since the graphical interpretation of funnel plots can be subjective. Therefore, publication bias was also found using the trim-and-fill method, a nonparametric rank-based test (Begg and Mazumdar, 1994). The trim-and-fill method is a statistical technique used in meta-analysis to assess and adjust for publication bias. It identifies asymmetry in a funnel plot, which may indicate missing studies (often unpublished or with non-significant results), and “trims” the asymmetric studies to estimate the true effect size. Then, it “fills” the plot with imputed missing studies to create a more symmetric funnel plot, providing an adjusted overall estimate of the effect size. This method helps improve the robustness and reliability of meta-analytic conclusions (Duval, 2005; Mavridis and Salanti, 2014). Usually, this technique is applied as a sensitivity analysis to evaluate how possible publication bias affects meta-analysis findings.
d The meta-regression
The goal of meta-regression is to examine and clarify between-study heterogeneity by utilizing a study-specific random effect model as a representation of the moderators. With a variance of , which represents the remaining unexplained between-study heterogeneity, and a mean of zero, it is believed that these random effects are normally distributed. The influencing factors of crop productivity were analyzed through meta-regression, assuming the calculated mean effect and explanatory variables described in Table 1. The meta-regression function is specified as follows in Equation 6:
, where and
e Cumulative meta-analysis
To investigate how factors influencing the productivity of crops evolve over time and affect the effect size of individual studies, a cumulative meta-analysis was performed. A graph is created to show shifting research patterns, and the year of publication is utilized for cumulative purposes, taking into account the sample size and accuracy of the data gathering period.
3 Results
3.1 The impact of SAP adoption on the productivity of crop
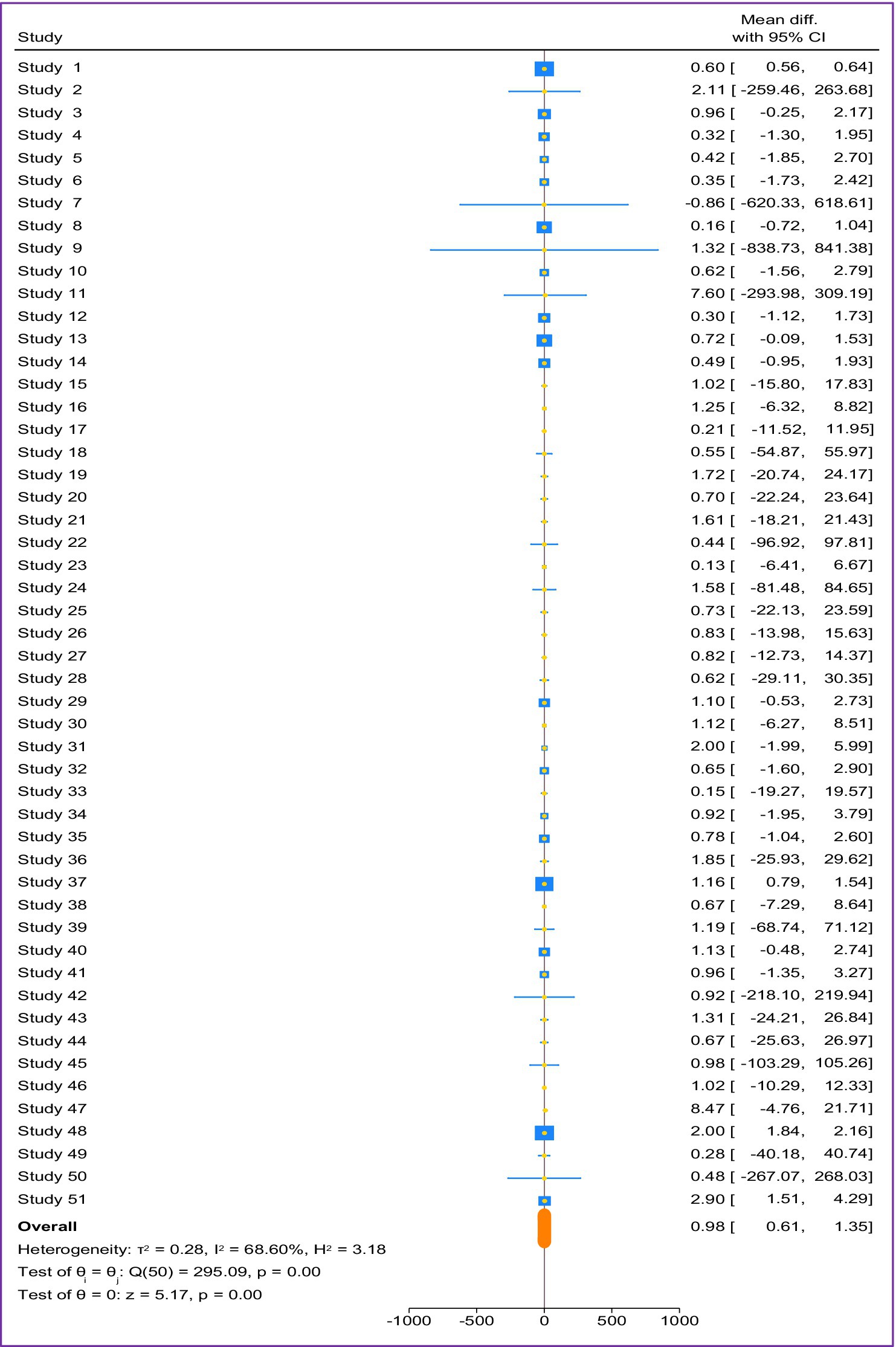
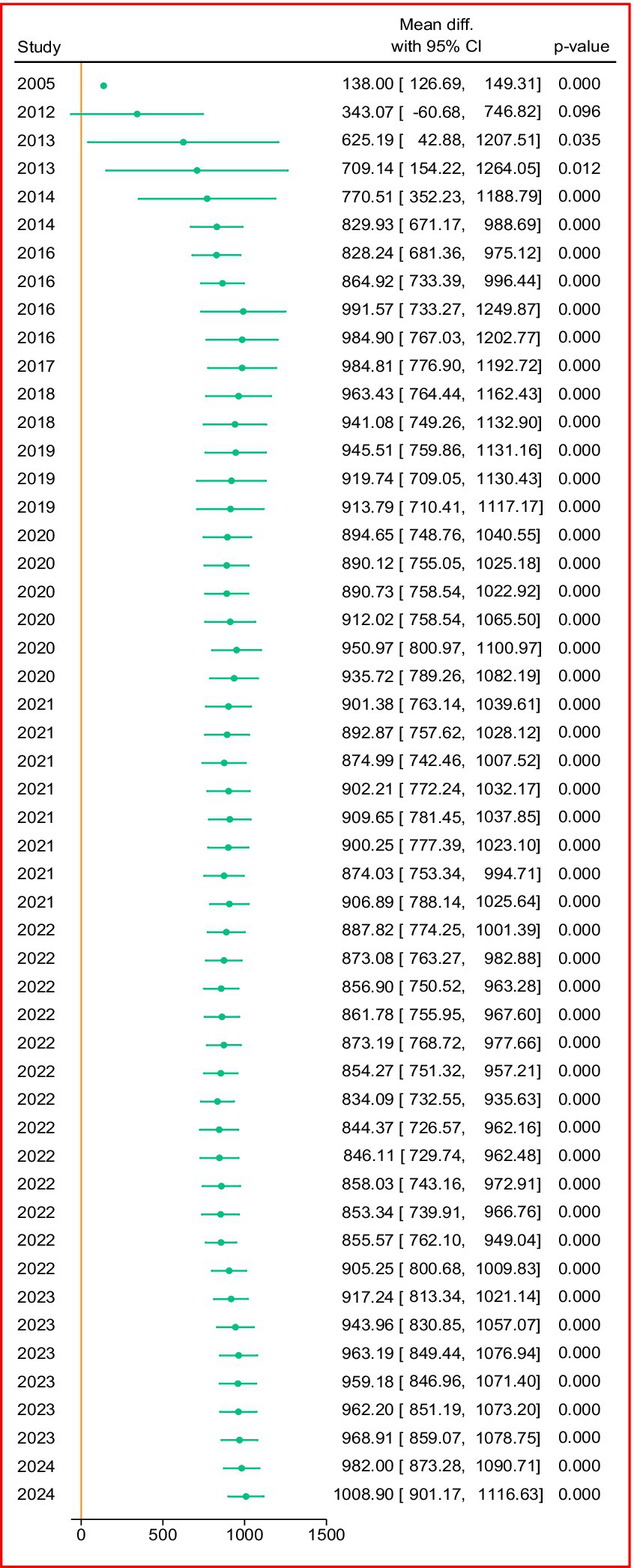
By applying a random effects model analysis, Figure 2 shows the effects of adopting SAPs on crop productivity in Ethiopia’s rural districts. According to the model’s findings, the pooled difference in means was 0.98, indicating that the crop productivity for individuals who adopted SAPs was 980 kilograms (0.98 tons) per hectare greater than that for people who did not use SAPs. The true mean difference in the universe of studies may be within the range indicated by the confidence interval for the mean difference, which spans from 0.61 to 1.35 tons. Crucially, the fact that a difference of zero is not included in this range suggests that the actual difference is probably not zero. With a p value of 0.00 and a z value of 5.17 for the summary effect, the null hypothesis which claims that there is no true mean difference, can be ruled out. This rejection implies that the mean crop productivity is not the same in both groups (adopters and nonadopters of SAPs), and it is greater in the adopter group.
The vertical line is the effect size line; the shapes on the line are the effect size of each study; and the pink color is the overall effect size. Effect size is measured in ton.
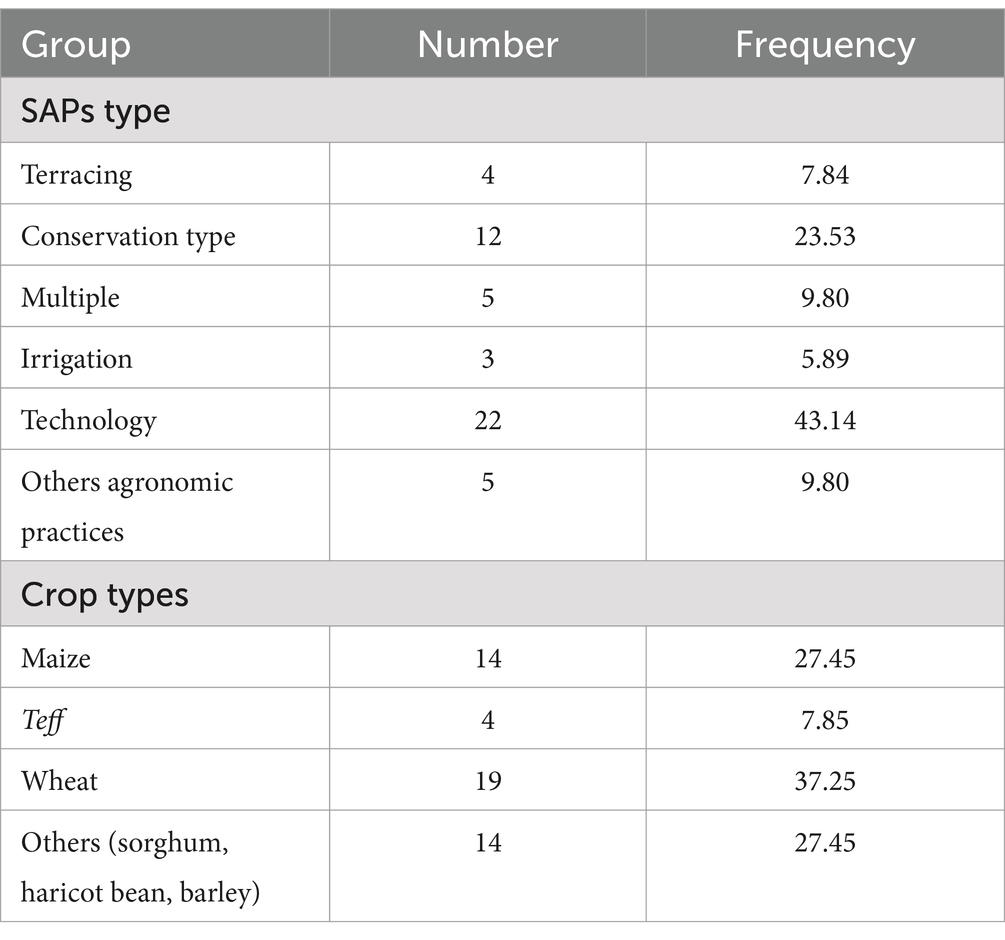
The findings presented in Table 3 indicate that adoption of sustainable agricultural technology accounts for 43% of SAPs in the nation, with conservational practices closely following 24%. The country also adopts a variety of SAPs, irrigation, and other agronomic practices. Wheat is the most highly cultivated crop (37%) under SAPS adoption in Ethiopia. Maize, other crop types, and teff, account for the next-greatest share of the country.
3.2 Heterogeneity test
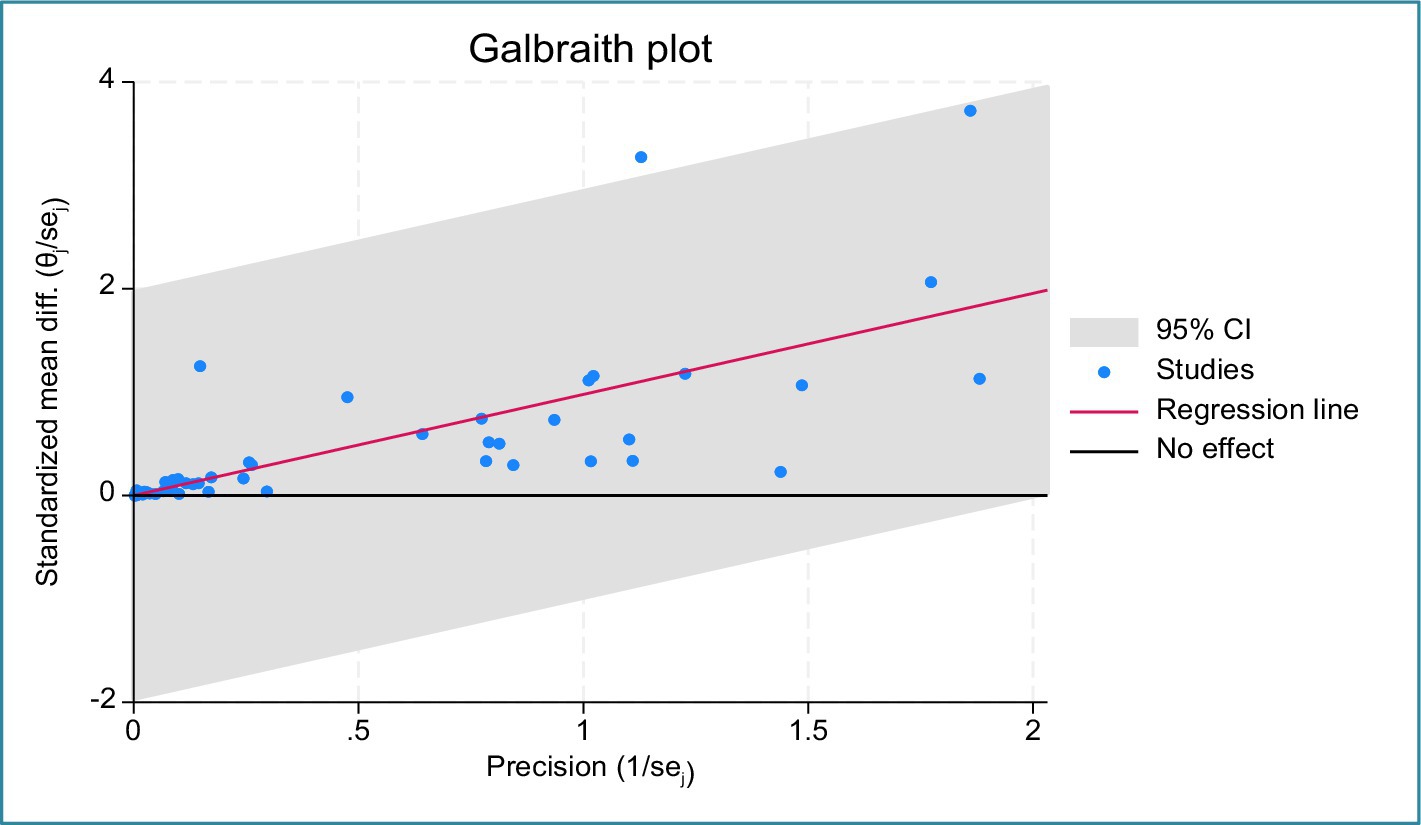
As shown in Figure 2, the heterogeneity statistic ( ) was approximately 69%. Only 31% of variability in effect sizes is due to sampling, while 69% stems from differences among studies. This score is consistent with significant heterogeneity according to Higgins et al. (2003) classification. Strong statistical evidence of substantial between-study heterogeneity is provided by the homogeneity test, which is shown by the 295 Q test statistic with a 0.00 p value. Furthermore, the Galbraith plot Galbraith (1988) serves as a valuable tool for evaluating the heterogeneity of studies and identifying potential outliers.
Figure 3 uses the reference black line (y = 0) as a benchmark to show the case where crop yield in adopters and nonadopters is the same or very similar, a “no-effect” line. A circle above the graph indicates that crop productivity is greater for SAP adopters than for nonadopters, and vice versa. As was covered in the section above, our research does show that crop productivity is greater in SAP adopters than in nonadopters.
Regression line across the origin, whose slope equals the estimate of the overall impact size, represents the overall mean of crop productivity. This line is colored red. Larger impact size estimates are seen in studies that are above the regression line than in those that lie below it. If there is no significant heterogeneity, we expect that approximately 95% of the studies will fall within the 95% confidence interval (CI) region, which is represented by the shaded area. In our analysis, 1 of the 51 trials did not fall inside the CI. As a result, the results of the random effects model should address probable causes of the discrepancy among studies. To determine the sources of heterogeneity, subgroup meta-analysis and meta-regression were then performed.
3.3 Subgroup meta-analysis
A subgroup meta-analysis was carried out according to several parameters, such as the kinds of SAPs and the crops and regions in Ethiopia that produce crops. After subgroup analysis, there was no significant variation among studies because of the absence of heterogeneity.
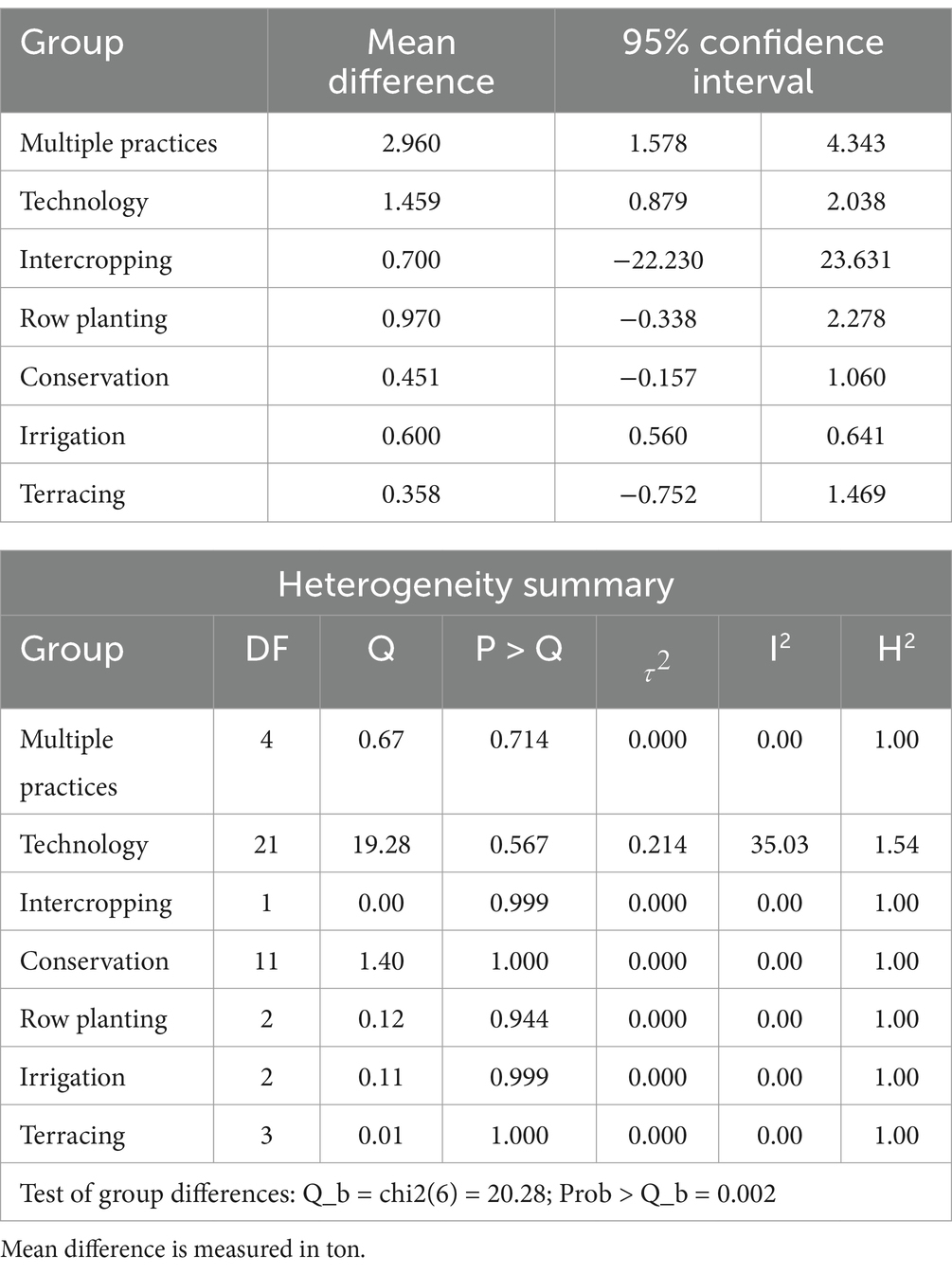
SAP types were the subject of one of the subgroup analyses. The test of group differences revealed statistical significance, as shown in Table 4, suggesting that the means of the differences between the subgroups (conservation, technology, terracing, irrigation, multiple practices, and other agronomic practices) were significantly different from one another. With a mean difference of 2,960 kilograms per hectare greater than that of nonadopters, multiple sustainable practices appear to have the greatest effects on agricultural productivity among Ethiopian adopters. Crop productivity increases by 1,459 kilograms and 600 kilograms, respectively, for adopters of sustainable agriculture technology and irrigation techniques. This beneficial effect demonstrates the important role that agricultural technology plays in producing food in a sustainable manner. The mean difference in crop productivity for conservational practices, terracing, and other agronomic techniques was positive but not statistically significant among crop producers. In this subgroup, low heterogeneity (I2 = 0.00%) suggested relatively low variability among studies, which is explained by improved crop production stability as a result of all these sustainable practices (Sun et al., 2024; Vitali et al., 2024).
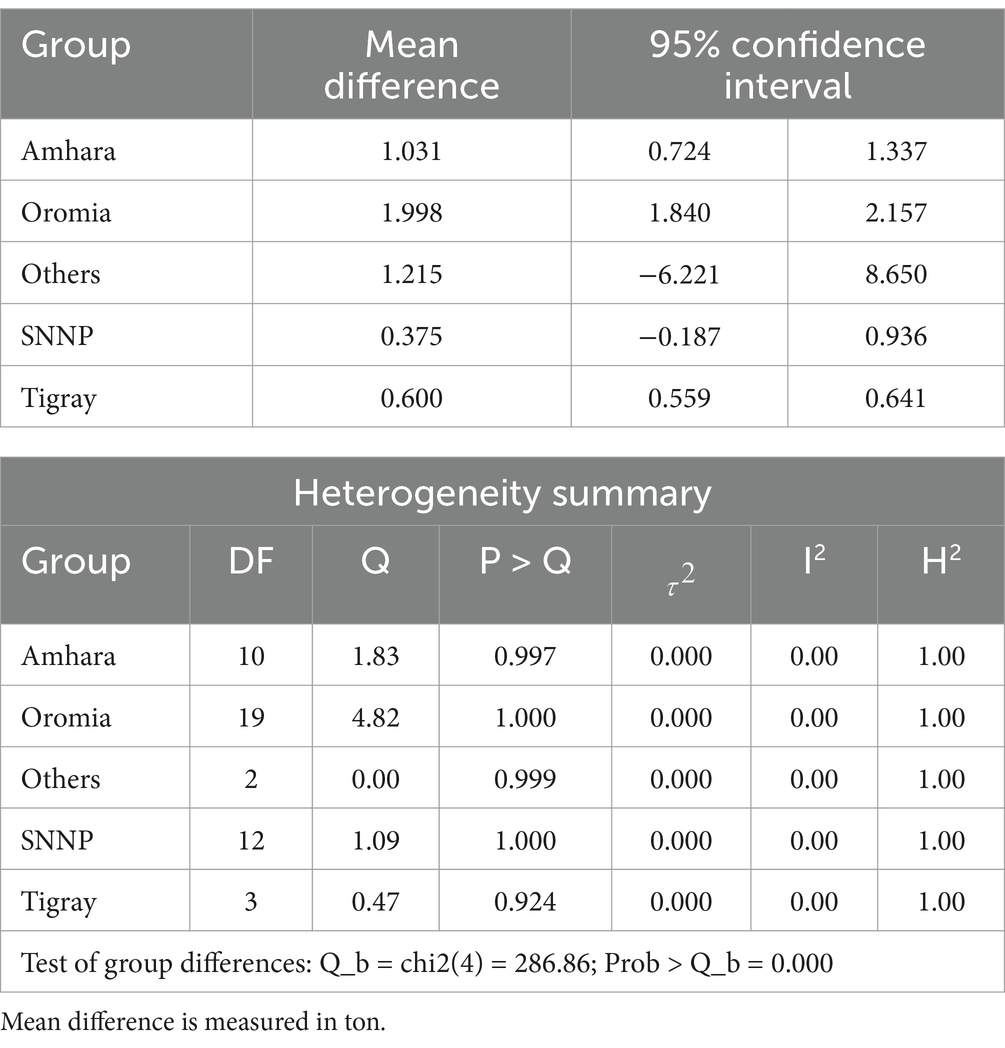
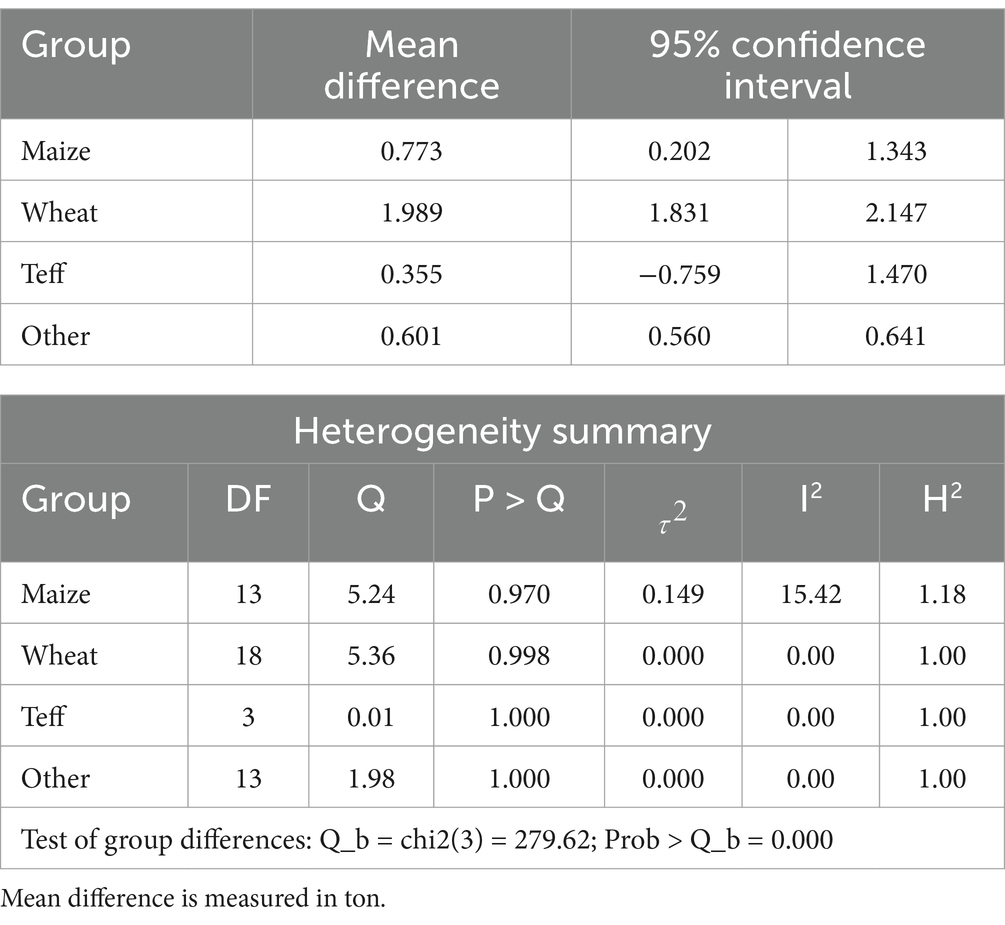
The subgroup analysis based on the region of crop production in Table 5 shows the absence of heterogeneity, suggesting greater consistency in the studies. Accordingly, crop productivity is high in the Oromia region, which is on average 1998 kilograms per hectare for the adopters of SAPs. SAP has also had a significant positive impact in the regions of Amhara and Tigray. In Southern Nation Nationality People (SNNP) and other regions of Ethiopia, the impact of SAP adoption has a positive impact with nonsignificant results. The crop type subgroup meta-analysis in Table 6 reveals a positive impact of SAPs on each crop, with the productivity of wheat showing the greatest impact, followed by that of maize.
The test of group differences for both region type and crop type in subgroup meta-analysis revealed significant differences, suggesting that the effect does significantly differ among regions and crop types. Subgroup analysis revealed diverse effects of various SAPs on crop productivity. Policymakers, in addition to practitioners, may consider tailoring interventions based on specific sustainable practices that exhibit positive impacts in the given context. Moreover, future research should delve into the reasons behind the observed heterogeneity, explore additional sustainable practices, and consider contextual factors influencing the effectiveness of these practices, providing valuable insights for further development.
3.4 Factors influencing crop productivity
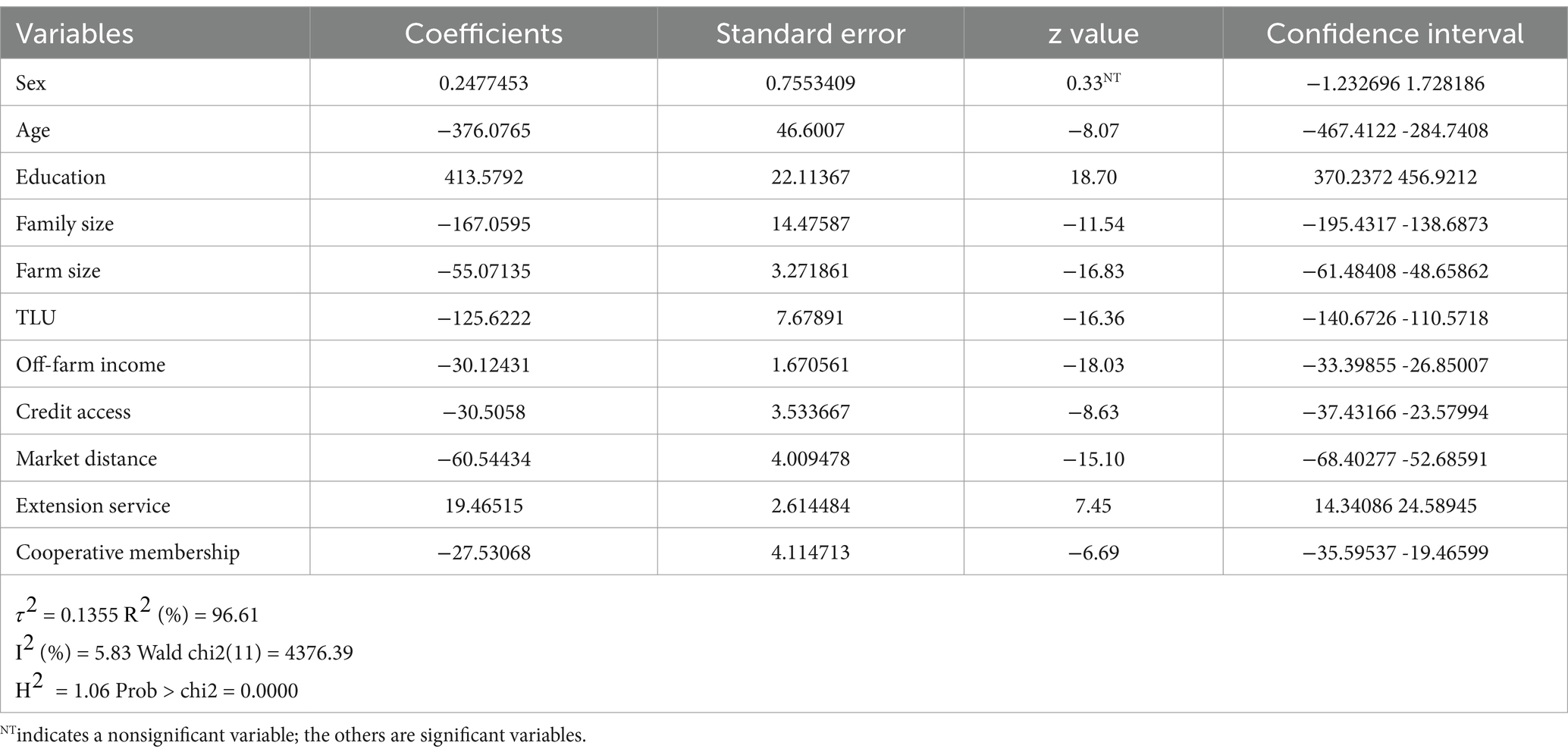
The primary objective of this meta-regression is to pinpoint the origins of heterogeneity and identify the determinants of crop productivity. The results underscore the diverse and interconnected nature of factors influencing crop productivity, encompassing demographic, resource ownership, institutional, and social aspects. Approximately 11 of the variables used in the original research were used consistently throughout the majority of the investigations. Tailoring agricultural interventions and policies to address these specific factors can significantly enhance productivity and contribute to promoting sustainable farming practices. A comprehensive approach considering the interplay of these variables is crucial for fostering agricultural development and ensuring food security.
Following the meta-regression analysis incorporating various characteristics, the level of heterogeneity was reduced to a low (5.83%) level. This suggests that real heterogeneity, as opposed to sampling error, accounts for a relatively tiny portion of the observed variability. Although this value suggests a low level of heterogeneity between studies, it also implies that the majority of the observed variability is influenced by factors other than heterogeneity. In a meta-regression context, the R-squared number indicates the percentage of the total variance that the model accounts for. With a high R-squared of 96.61%, the model may enlighten considerable portion of the variation in crop productivity reported in the included studies. Furthermore, the Wald chi-square test and its associated p value confirm the overall significance of the model. Table 7 presents the variables utilized in this meta-analysis, along with estimated mean effects and their respective significance levels.
3.5 Publication bias
When a study’s statistical significance affects whether or not to publish its findings, it is known as publication bias, and it is a serious risk in meta-analyses. We used the Begg and Mazumdar (1994) technique to address publication bias in this study. We employed the trim-and-fill approach for a formal test and a funnel plot for visual evaluation. Evaluating the possible influence of publication bias on the study outcomes is the main goal of this investigation.
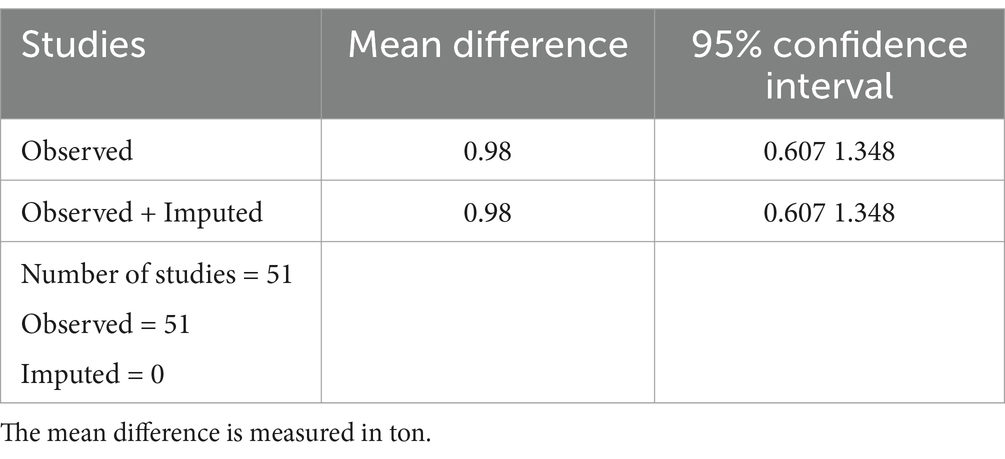
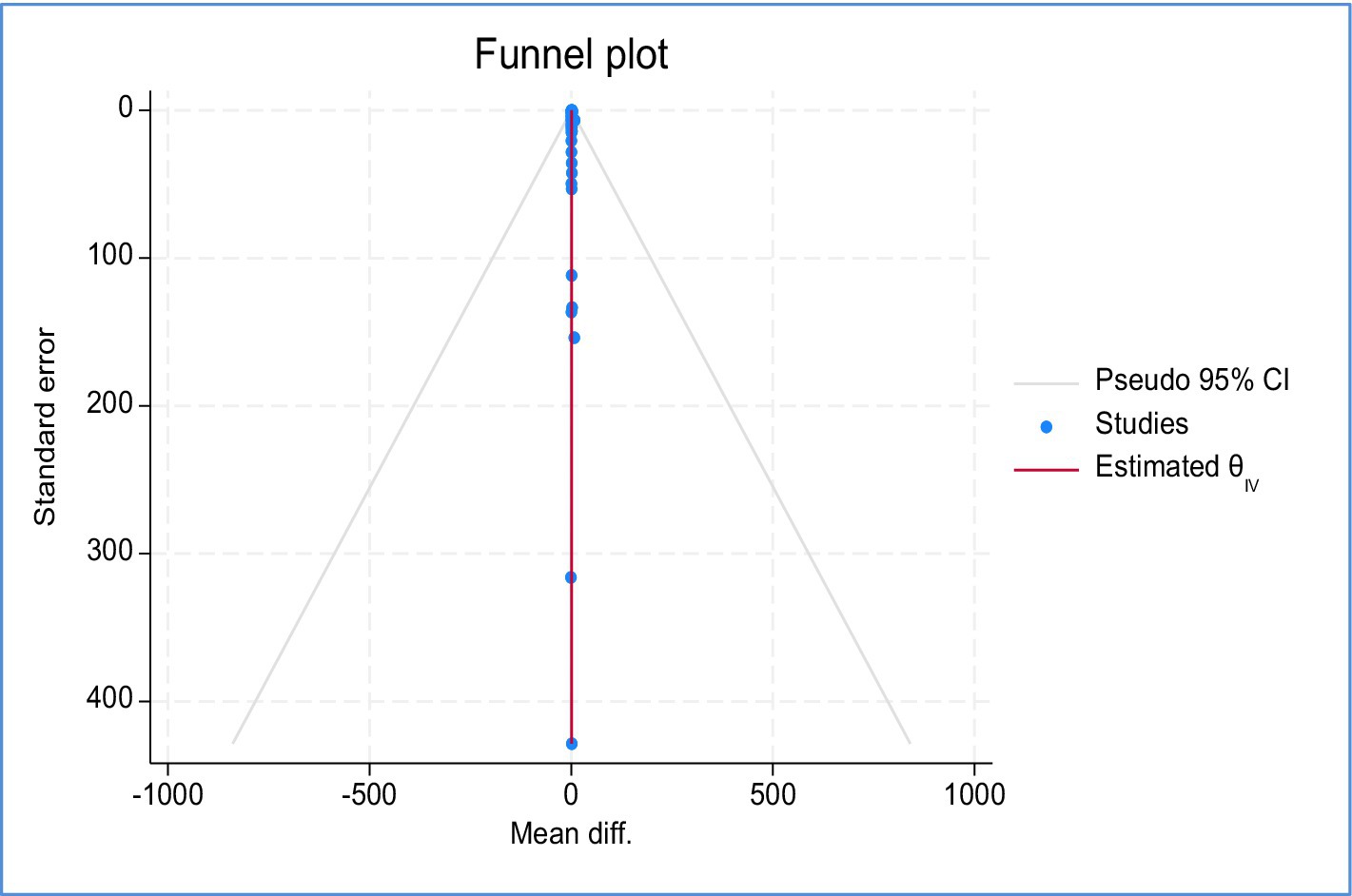
With a 95% confidence interval spanning from 0.61 to 1.35, the average effect size, based on the 51 studies taken into consideration, is 980 kilograms per hectare, as shown in Table 8. None of the hypothetical studies are anticipated to be missing, according to the results of the trim-and-fill technique model. This means that no more studies were included in the meta-analysis to address the asymmetry in the results, as indicated by the imputed value of zero. A symmetrical and inverted funnel shape is also shown in the funnel plot in Figure 4, which suggests that the studies are dispersed equally around the overall effect size.
3.6 Cumulative meta-analysis
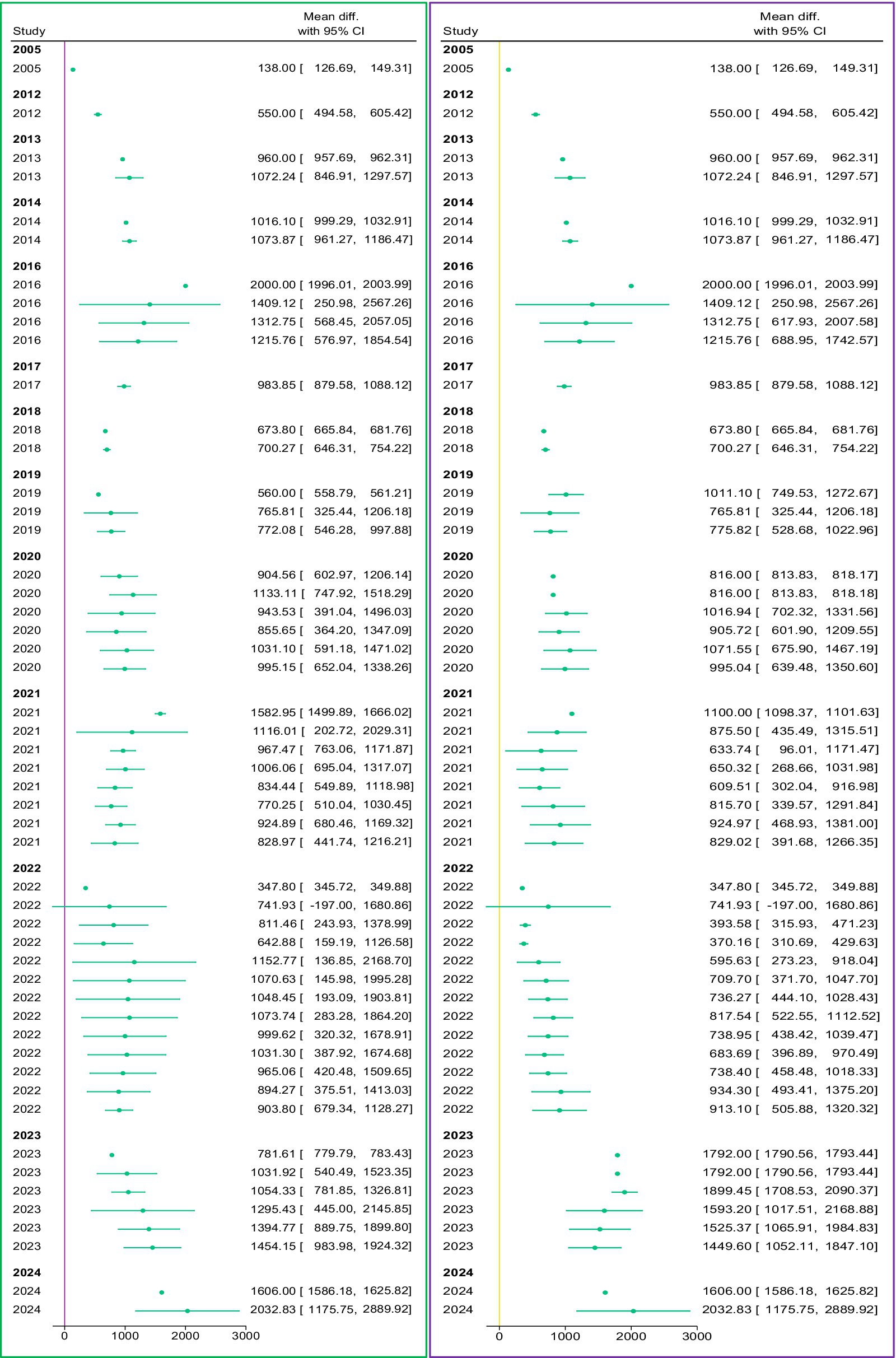
The cumulative meta-analysis proves valuable in monitoring the evolving trend in overall effect size estimates by incrementally adding studies over time. This method helps to find situations when time is the ordering variable and the effect size’s direction or magnitude may change (Daly and Soobiah, 2022). Initially, we performed a cumulative meta-analysis as part of our investigation to examine the changing patterns in how the adoption of SAPs affects crop yield. The results are illustrated in Figure 5, which depicts a cumulative meta-analysis plot spanning the years.
The positive and ascending trajectory in the cumulative effect size signifies an increasing source of evidence supporting the positive influence of implementing SAPs on the productivity of crops. This encouraging outcome suggests that with an increasing number of studies, there is a consensus favoring a beneficial relationship between sustainability measures and improved crop yields. Notably, in recent years, the effect size has demonstrated an upward trend with minor fluctuations, possibly attributed to uncertainties or methodological diversity in the studies. Education and extension services emerge as major contributors to this stabilization, as depicted in Figure 6. The pronounced effect of education and extension services on agricultural outcomes over time can be attributed to several key mechanisms. Education enhances farmers’ knowledge and awareness of sustainable agricultural practices (SAPs), empowering them to make informed decisions and adopt improved techniques. Extension services play a critical role in bridging the gap between research and practice by disseminating innovations, providing technical support, and improving access to critical resources such as seeds and fertilizers. Additionally, regular training and advisory programs build farmers’ skills and confidence, enabling the effective implementation of SAPs. Over time, these interventions also foster the development of social networks for knowledge sharing, further driving community-wide adoption and long-term productivity improvements (Obsi Gemeda et al., 2023; Nigus et al., 2024; Karim et al., 2024; Tega and Bojago, 2024; Zeweld et al., 2020). While the trends for other variables were deemed insignificant and are not presented here, they can be made available upon request.
A vertical line from above to zero is a ‘no effect’ line; small horizontal lines and dots represent the mean difference and effect size, respectively.
4 Discussion
Farmers stand to benefit from adopting any sustainable agricultural practice to enhance production per unit of input utilized. These results are consistent with studies by Chao et al. (2024), De Corato et al. (2024), and Mutyasira et al. (2018), which indicate that in addition to increasing productivity, SAPs are essential for increasing producer welfare and food security. As a result, it is essential to increase the amount of experience and information that is disseminated about SAPs using a variety of platforms, which include field demonstrations, extension visits, training courses, and media campaigns. By reducing dis-adoption and ensuring sustained acceptance, this strategy seeks to support the larger-scale sustainable development of agriculture (Mgomezulu et al., 2023b).
Subgroup meta-analysis has also confirmed that SAPs, including multiple practices, technology, conservation practices, irrigation, terracing, and other agronomic practices, are essential in enhancing crop productivity in Ethiopia. Among these SAPs, multiple sustainable practices, eco-friendly agricultural technologies, and irrigation techniques play a crucial role in enhancing crop production. Crop type variations indicate that the productivity of wheat and maize benefits significantly from SAP application. Additionally, regional differences in Ethiopia reveal that SAPs have a positive impact on crop productivity in Oromia, Amhara, Tigray, and the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples’ (SNNP) regions. The targeted government initiatives and projects promoting SAPs in these regions have amplified their impact, leading to improved productivity and resource management. These show that variations in crop types, SAP types, and regions of production limit the generalizability of the results. It emphasizes how implementing different sustainable agriculture methods can significantly increase crop output while considering Ethiopia’s varied agro-ecological zones and climate unpredictability. It addresses soil degradation and water scarcity and enhances smallholder resilience, aligning with traditional farming methods and government initiatives for sustainable agriculture. This result aligns with Zegeye et al. (2023), Gashure et al. (2022), and Zeweld et al. (2020). Consistent with our findings, studies in other areas also confirm that the application of different SAPs significantly enhances crop productivity, nutrient use efficiency, and soil health (Naik et al., 2022, 2024).
The negative coefficient for age suggests that as farmers’ age increases by 1 year, crop productivity tends to decrease by 376 kilograms per hectare, ceteris paribus. This decline may be attributed to older farmers facing physical limitations, reduced energy levels, or adherence to outdated farming practices, leading to reluctance to adopt new technologies and innovative agricultural methods. Due to their greater likelihood of education and longer planning horizons, younger farmers are more likely to apply SAPs, which boost their output. This finding aligns with the works of Zeweld et al. (2020) and Adego et al. (2019). Education increases crop productivity by 413.58 kilograms per hectare. Well-educated farmers are more prone to adopting modern agricultural techniques, efficient farming practices, and utilizing available resources effectively, leading to higher productivity. The application of SAPs is encouraged by education, which gives farmers the knowledge and skills they need to make informed decisions. This outcome agrees with Gebeyehu (2023). A negative relationship between family size and crop productivity suggests that smaller family sizes have greater crop productivity, with a difference of 167 kilograms per hectare compared to larger family sizes. Smaller families may benefit from more resources and time available per capita, enabling better farm management, attention to detail, timely decision-making, and effective resource utilization, resulting in higher productivity. This finding is supported by Shallo (2020).
Larger farm sizes are associated with lower crop productivity, with a decrease of 55 kilograms per hectare when the farm size increases by 1 hectare. Managing larger areas efficiently and potential issues with resource allocation could pose challenges, whereas small to medium-sized farms might benefit from more focused attention and resources per unit of land. This finding aligns with the findings of Abebe and Bekele (2014). The negative coefficient for TLU implies that an increase of one TLU is linked to a decrease in crop productivity of 125.62 kilograms per hectare. Livestock farming, which is resource intensive, may compete for land and resources that could otherwise be dedicated to crop cultivation. A reduction in TLU could free up resources for crop production, positively impacting productivity. This is consistent with the study conducted by Mossie (2022). Engagement in off-farm activities negatively correlates with crop productivity, with a decrease of 30 kilograms per hectare for every increase of one birr (0.018 dollars) in income from off-farm activities. Farmers who engage in nonfarm pursuits could find it difficult to dedicate their time and attention to agricultural duties, particularly those involving SAPs. Crop management may receive less attention when off-farm work and agricultural obligations are balanced, which can diminish output. This is in line with what Gashure et al. (2022) found.
Increased credit availability is associated with lower crop productivity, with a decrease of 30.51 kilograms per hectare, holding other factors constant. While credit can be a vital resource for farmers, excessive reliance without proper planning or utilization may lead to inefficient practices or overextension. Mismanagement of credit can result in lower productivity due to increased debt burdens. To pay back credit, farmers revealed that they frequently spent less time on SAPs and more time on nonfarm activities. The findings of Zegeye et al. (2023) and Adego et al. (2019) are in line with this outcome. An increase in the market distance of 1 kilometer or 1 h is associated with a decrease in crop productivity of 60.54 kilograms per hectare when other factors remain constant. Longer distances to markets can lead to higher transportation costs, delays in selling crops, and increased postharvest losses. Farmers closer to markets may have better access to buyers, infrastructure, and market information, which positively impacts crop productivity. Gashure et al. (2022) reported a similar finding. Access to extension services is positively associated with increased crop productivity, with an increase of 19.46 kilograms per hectare, holding other factors constant. Households with access to extension services receive valuable information, training, and support, leading to improved crop productivity. Farmers with access to extension services are more likely to adopt new technologies and best practices, which will boost output. A study by Adego et al. (2019) provided support for this finding.
Cooperative membership is negatively associated with crop productivity, with households that are cooperative members having lower crop productivity by 27.53 kilograms per hectare, holding other factors constant. Cooperative membership may involve resource sharing and collective decision making, particularly regarding the adoption of SAPs. However, challenges such as coordination issues, conflicts of interest, or uneven distribution of benefits within the cooperative can negatively impact individual farmers’ productivity. This result aligns with the studies conducted by Gashure et al. (2022).
The increasing trend in education (Figure 6) is evident over time, driven by various recent initiatives in the country. Factors contributing to this trend include individuals’ attitudes toward formal or informal learning, enhanced dietary diversity for children, a rapid overhaul of preprimary education, and nutrition education interventions (Adugna et al., 2024; Kim et al., 2023; Kim, 2022; Mengistie, 2022; Zikargae et al., 2022). This emphasis on education within the context of sustainable agriculture underscores the acknowledgment of the pivotal role played by knowledge and awareness in achieving positive outcomes in crop productivity. This trend can manifest in various forms, including formal education programs, workshops, training sessions, and educational materials targeting farmers, agricultural practitioners, and relevant stakeholders (Karim et al., 2024; Xie et al., 2023; Luh et al., 2023). Well-informed farmers are more likely to make decisions aligned with sustainable practices, understanding principles such as agro-ecology, soil and water management, organic farming, conservation tillage, integrated pest management, and other relevant approaches, ultimately contributing to enhanced crop productivity (Tega and Bojago, 2024; Zeweld et al., 2020; Ninh, 2021). Future educational efforts could benefit from tailoring programs to address specific regional needs and tackle emerging challenges in agriculture. The integration of technology and digital platforms may be explored to achieve wider dissemination of information. Sustainable agriculture education programs can be strengthened even further by cooperative efforts between academic institutions, authorities, and organizations that are not governmental.
The increasing trend in extension services (Figure 6) is indicative of a growing understanding of how critical it is to provide farmers with on-going help and direction. Extension services entail delivering science-based information, technical assistance, and practical advice to farmers, aiding them in adopting sustainable practices and enhancing overall farm management (Nigus et al., 2024; Obsi Gemeda et al., 2023; Ogola et al., 2023). Timely and pertinent advice on crop management, pest control, and sustainable practices can significantly contribute to increased crop productivity (Yitayew et al., 2023; Girma and Kuma, 2022; Yitayew et al., 2021). Ethiopia has experienced the positive impact of extension services (Gebresilasse, 2023). Therefore, the future of extension services may involve leveraging technology for more efficient and widespread information dissemination. Mobile apps, online platforms, and remote sensing technologies could enhance the reach of extension services, especially in remote or underserved areas. Collaborative endeavors between extension services and other institutions can ensure that the latest advancements in sustainable agriculture are effectively communicated to farmers (Cai et al., 2024; Cai et al., 2023; Abate et al., 2023; Demem, 2023; Kabir et al., 2023; Anang et al., 2020).
The findings of this study reveal that SAPs significantly improve crop productivity in Ethiopia, aligning closely with national agricultural policies like the Growth and Transformation Plans (GTPs), which emphasize sustainable intensification and land restoration (FDRE Planning and Development Commission, 2021). This underscores the effectiveness of policy-driven initiatives in promoting SAP adoption. Furthermore, while Ethiopia’s adoption rates are comparatively lower than regions such as Asia, where SAP integration is more advanced, the observed productivity gains mirror global trends, highlighting the transformative potential of SAPs in enhancing agricultural efficiency within resource-limited contexts.
5 Conclusion
This work employs a meta-analysis, in contrast to previous research on SAP adoption, to thoroughly examine the impact of SAP adoption on crop productivity, crop productivity-influencing factors, and patterns in the relative contributions of various factors over time. The following section presents the findings and their implications for policy. Higher mean crop productivity within the adopter group indicates that the use of sustainable agriculture practices (SAPs) increases crop productivity. To encourage farmers to embrace SAP, policies that offer incentives for using these practices should be developed and promoted.
Subgroup analyses have revealed nuanced insights into the impact of different types of SAPs on crop productivity. Notably, adopting many SAPs simultaneously results in even greater production levels. Fascinatingly, the subgroup analysis revealed statistically significant variations between regions and crop types, indicating that SAPs are differently applicable in a variety of agricultural scenarios. Meta-regression analysis identified key factors that significantly influence crop productivity, including age, farm size, off-farm income, family size, credit access, market distance, cooperative membership (negative), and education and extension services (positive). These variables also contributed to the observed heterogeneity in the study. Therefore, it is imperative to design interventions that address these identified factors during the implementation of SAPs. The cumulative effect size analysis underscores the sustained positive impact of SAPs, with education and extension services emerging as particularly influential factors. Consequently, it is recommended that the government invest in educational programs and extension services for farmers, aiming to maximize the positive impact of sustainable agricultural practices. Continuous monitoring of cumulative trends is essential to adapt strategies and ensure a long-term positive impact on crop productivity.
The implementation of SAPs in Ethiopia should focus on promoting multiple sustainable practices, eco-friendly agricultural technologies, and irrigation techniques to enhance crop production. Additionally, targeted initiatives should prioritize underrepresented regions beyond Oromia, Amhara, Tigray, and the Southern Nations Nationalities Peoples’ region to ensure equitable adoption and impact across the country.
As a meta-analysis focused exclusively on Ethiopia, this study is limited in generalizability beyond the country’s context. Expanding future meta-analyses to include comparative or regional studies could provide broader insights into SAP adoption and impacts. Therefore, future efforts should integrate technology, community engagement, and interdisciplinary approaches to ensure SAP scalability and sustainability.
Author contributions
TE: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XB: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by Ministry of Education of Humanities and Social Science Foundation (22YJA790001) and Shaanxi Soft Science (2024ZC-YBXM-002).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the Ministry of Education of Humanities and Social Science Foundation of China, Shaanxi Soft Science, and Ambo University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abate, G. T., Bernard, T., Makhija, S., and Spielman, D. J. (2023). Accelerating technical change through ICT: evidence from a video-mediated extension experiment in Ethiopia. World Dev. 161:106089. doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2022.106089
Abebe, Y., and Bekele, A. (2014). The impact of soil and water conservation program on the income and productivity of farm households in Adama District. Ethiopia. Sci Technol Arts Res J 3:198. doi: 10.4314/star.v3i3.32
Abegaz, A., Abera, W., Jaquet, S., and Tamene, L. (2024). Adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices (CSAPs) in Ethiopia. Clim. Risk Manag. 45:100628. doi: 10.1016/j.crm.2024.100628
Abesha, N., Assefa, E., and Petrova, M. A. (2022). Large-scale agricultural investment in Ethiopia: development, challenges and policy responses. Land Use Policy 117:106091. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2022.106091
Adego, T., Simane, B., and Woldie, G. A. (2019). The impact of adaptation practices on crop productivity in Northwest Ethiopia: an endogenous switching estimation. Dev Stud Res 6, 129–141. doi: 10.1080/21665095.2019.1678186
Adgo, E., Teshome, A., and Mati, B. (2013). Impacts of long-term soil and water conservation on agricultural productivity: the case of Anjenie watershed, Ethiopia. Agric. Water Manag. 117, 55–61. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2012.10.026
Adhikari, J., and Thapa, R. (2023). Determinants of the adoption of different good agricultural practices (GAP) in the command area of PMAMP apple zone in Nepal: the case of mustang district. Heliyon 9:e17822. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17822
Adugna, G., Egata, G., Fufa, D. A., and Desta, D. T. (2024). Effect of nutrition education on improving dietary diversity of children aged 6–23 months in Horo district, Oromia region. Ethiopia. Hum Nutr Metab 35:200244. doi: 10.1016/j.hnm.2024.200244
Alemu, T., Tolossa, D., Senbeta, F., and Zeleke, T. (2023). The effects of continuous sustainable land management practices on agricultural land productivity in Central Ethiopia. J Degrad Min Lands Manag 10, 4389–4403. doi: 10.15243/jdmlm.2023.103.4389
Amede, T., Konde, A. A., Muhinda, J. J., and Bigirwa, G. (2023). Sustainable farming in practice: building resilient and profitable smallholder agricultural Systems in sub-Saharan Africa. Sustain 15, 1–16. doi: 10.3390/su15075731
Anang, B. T., Bäckman, S., and Sipiläinen, T. (2020). Adoption and income effects of agricultural extension in northern Ghana. Sci African 7:e00219. doi: 10.1016/j.sciaf.2019.e00219
Asfew, M., Bakala, F., and Fite, Y. (2023). Adoption of soil and water conservation measures and smallholder farmers’ perception in the bench-Sheko zone of Southwest Ethiopia. J Agric Food Res 11:100512. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2023.100512
Avola, G., Distefano, M., Torrisi, A., and Riggi, E. (2024). Precision agriculture and patented innovation: state of the art and current trends. World Patent Inf. 76:102262. doi: 10.1016/j.wpi.2024.102262
Ayele, A., and Tarekegn, K. (2020). The impact of urbanization expansion on agricultural land in Ethiopia: a review. Environ Socio-Economic Stud 8, 73–80. doi: 10.2478/environ-2020-0024
Ayenachew, Y. A., and Abebe, B. G. (2024). Navigating urbanization implications: effects of land expropriation on farmers’ livelihoods in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Front Sustain Cities 6, 1–13. doi: 10.3389/frsc.2024.1385309
Begg, C. B., and Mazumdar, M. (1994). Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 50, 1088–1101. doi: 10.2307/2533446
Belay, A. D., Kebede, W. M., and Golla, S. Y. (2023). Determinants of climate-smart agricultural practices in smallholder plots: evidence from Wadla district, Northeast Ethiopia. Int J Clim Chang Strateg Manag 15, 619–637. doi: 10.1108/IJCCSM-06-2022-0071
Benitez-Altuna, F., Materia, V. C., Bijman, J., Gaitán-Cremaschi, D., and Trienekens, J. (2024). Farmer–buyer relationships and sustainable agricultural practices in the food supply chain: the case of vegetables in Chile. Agribusiness 40, 3–30. doi: 10.1002/agr.21829
Bezner Kerr, R., Postigo, J. C., Smith, P., Cowie, A., Singh, P. K., Rivera-Ferre, M., et al. (2023). Agroecology as a transformative approach to tackle climatic, food, and ecosystemic crises. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 62:101275. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2023.101275
Bojago, E., and Abrham, Y. (2023). Small-scale irrigation (SSI) farming as a climate-smart agriculture (CSA) practice and its influence on livelihood improvement in Offa District. Southern Ethiopia. J Agric Food Res 12:100534. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2023.100534
Cai, Y., Qi, W., and Yi, F. (2023). Does ICT-based agriculture extension service use promote litchi farmers’ involvement in diversification? Evidence from southern China. J Agric Food Res 14:100795. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2023.100795
Cai, Y., Qi, W., and Yi, F. (2024). Effects of ICT-based extension service use on fertilizer knowledge and use efficiency: evidence from litchi farmers in rural China. Environ Dev 49:100944. doi: 10.1016/j.envdev.2023.100944
Caicedo-Vargas, C., Pérez-Neira, D., Abad-González, J., and Gallar, D. (2023). Agroecology as a means to improve energy metabolism and economic management in smallholder cocoa farmers in the Ecuadorian Amazon. Sustain Prod Consum 41, 201–212. doi: 10.1016/j.spc.2023.08.005
Chao, J., Li, T., Yin, H., and Wang, Z. (2024). Adoption of multiple sustainable agricultural practices among farmers in northwest. China. Cogent Food Agric 10, 1–21. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2023.2300189
Corbeels, M., de Graaff, J., Ndah, T. H., Penot, E., Baudron, F., Naudin, K., et al. (2014). Understanding the impact and adoption of conservation agriculture in Africa: a multi-scale analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 187, 155–170. doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2013.10.011
Daly, C., and Soobiah, C. (2022). Software to conduct a meta-analysis and network meta-analysis. Meta-Res. Methods Protoc 2345, 223–244. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1566-9_14
Dawid Mume, I., Haji Mohammed, J., and Aman Ogeto, M. (2023). Impact of small-scale irrigation on the livelihood and resilience of smallholder farmers against climate change stresses: evidence from Kersa district, eastern Oromia. Ethiopia. Heliyon 9:e18976. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18976
De Corato, U., Viola, E., Keswani, C., and Minkina, T. (2024). Impact of the sustainable agricultural practices for governing soil health from the perspective of a rising Agri-based circular bioeconomy. Appl. Soil Ecol. 194:105199. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2023.105199
Deeks, J. J., JPT, H., and Altman, D. G.Group CSM (2019). Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. Cochrane Handb Syst Rev Interv, 241–284. doi: 10.1002/9781119536604.ch10
Demem, M. S. (2023). Impact and adaptation of climate variability and change on small-holders and agriculture in Ethiopia: a review. Heliyon 9:e18972. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18972
Duval, S. (2005). The trim and fill method. Pub. Bias in Meta-Analysis, 127–144. doi: 10.1002/0470870168.ch8
Edwards, S. (2020). Environment for development adoption of organic farming techniques. Environ Dev Initiat.
Erkossa, T., Williams, T. O., and Laekemariam, F. (2018). Integrated soil, water and agronomic management effects on crop productivity and selected soil properties in Western Ethiopia. Int Soil Water Conserv Res 6, 305–316. doi: 10.1016/j.iswcr.2018.06.001
Etensa, T., Alemu, T., and Yayo, M. (2024). Rethinking the measurements and predictors of environmental degradation in Ethiopia: predicting long-term impacts using a kernel-based machine learning approach. Environ Sustain Indic 25:100554. doi: 10.1016/j.indic.2024.100554
FDRE Planning and Development Commission (2021). Ten years development plan: a pathway to prosperity. Ten Years Dev Plan A Pathw to Prosper 2:86.
Galbraith, R. F. (1988). Graphical display of estimates having differing standard errors. Technometrics 30, 271–281. doi: 10.1080/00401706.1988.10488400
Gashure, S., Wana, D., and Samimi, C. (2022). Impacts of climate variability and climate-smart agricultural practices on crop production in UNESCO designated cultural landscapes of Konso, Ethiopia. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 150, 1495–1511. doi: 10.1007/s00704-022-04244-9
Gebeyehu, T. A. (2023). Adoption and impacts of conservation agriculture on smallholder farmers’ livelihoods in the case of Arba Minch Zuria district of southern Ethiopia. Cogent Soc Sci 9, 1–15. doi: 10.1080/23311886.2023.2235782
Gebresilasse, M. (2023). Rural roads, agricultural extension, and productivity. J. Dev. Econ. 162:103048. doi: 10.1016/j.jdeveco.2023.103048
Girma, Y., and Kuma, B. (2022). A meta analysis on the effect of agricultural extension on farmers’ market participation in Ethiopia. J Agric Food Res 7:100253. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2021.100253
Han, G., and Niles, M. T. (2023). An adoption spectrum for sustainable agriculture practices: a new framework applied to cover crop adoption. Agric. Syst. 212:103771. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2023.103771
Hansen, C., Steinmetz, H., and Block, J. (2022). How to conduct a meta-analysis in eight steps: a practical guide. Manag Rev Q 72, 1–19. doi: 10.1007/s11301-021-00247-4
Higgins, J. P. T., and Thompson, S. G. (2002). Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 21, 1539–1558. doi: 10.1002/sim.1186
Higgins, J. P. T., Thompson, S. G., Deeks, J. J., and Altman, D. G. (2003). Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. Br. Med. J. 327, 557–560. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Hough, G., and Contarini, A. (2023). Can low-income consumers choose food from sustainable production methods? Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 51:101035. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2023.101035
Javan, K., and Darestani, M. (2024). Assessing environmental sustainability of a vital crop in a critical region: investigating climate change impacts on agriculture using the SWAT model and HWA method. Heliyon 10:e25326. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25326
Johnson, D. L., and Thompson, R. (1995). Restricted maximum likelihood estimation of variance components for univariate animal models using sparse matrix techniques and average information. J. Dairy Sci. 78, 449–456. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(95)76654-1
Kabir, K. H., Rahman, S., Hasan, M. M., Chowdhury, A., and Gow, G. (2023). Facebook for digital agricultural extension services: the case of rooftop gardeners in Bangladesh. Smart Agric Technol 6:100338. doi: 10.1016/j.atech.2023.100338
Kakiso, T. (2023). Endangered indigenous knowledge: assessing locally adopted tree conservation practices in Aleta Wondo district, Sidama regional state. Ethiopia. Heliyon 9:e15401. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15401
Karim, A. R., Darsono, D., Harisudin, M., and Dharmawan, B. (2024). Uncovering hidden determinants of millennial farmers’ intentions in running conservation agriculture: an application of the norm activation model. Open Agric 9, 1–14. doi: 10.1515/opag-2022-0257
Karydas, C., Chatziantoniou, M., Stamkopoulos, K., Iatrou, M., Vassiliadis, V., and Mourelatos, S. (2023). Embedding a precision agriculture service into a farm management information system - ifarma/PreFer. Smart Agric Technol 4:100175. doi: 10.1016/j.atech.2023.100175
Kassa, B. A., and Abdi, A. T. (2022). Factors influencing the adoption of climate-smart agricultural practice by small-scale farming households in Wondo genet, Southern Ethiopia. SAGE Open 12, 1–13. doi: 10.1177/21582440221121604
Kim, J. H. (2022). Preschool participation and students’ learning outcomes in primary school: evidence from national reform of pre-primary education in Ethiopia. Int. J. Educ. Dev. 94:102659. doi: 10.1016/j.ijedudev.2022.102659
Kim, S. S., Sununtnasuk, C., Berhane, H. Y., Walissa, T. T., Oumer, A. A., Asrat, Y. T., et al. (2023). Feasibility and impact of school-based nutrition education interventions on the diets of adolescent girls in Ethiopia: a non-masked, cluster-randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Child Adolesc Heal 7, 686–696. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(23)00168-2
Kudama, G., Wana, H., and Dangia, M. (2021). The adoption of bundled sustainable farm and environmental practices by coffee farmers in Southwest Ethiopia. Sci. World J. 2021, 1–11. doi: 10.1155/2021/9954230
Kumar, A., and Pant, S. (2023). Analytical hierarchy process for sustainable agriculture: an overview. MethodsX 10:101954. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2022.101954
Lejissa, L. T., Wakjira, F. S., Tanga, A. A., and Etalemahu, T. Z. (2023). Smallholders’ conservation agriculture adoption decision in Arba Minch and Derashe districts of southwestern Ethiopia. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2023, 1–13. doi: 10.1155/2023/9418258
Li, X., Mao, N., Zhang, W., Wei, X., Liu, T., Cheng, J., et al. (2024). Appropriateness of introducing earthworms into sustainable agriculture from the perspective of soil carbon emissions. Soil Tillage Res. 237:105961. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2023.105961
Liben, F. M., Tadesse, B., Tola, Y. T., Wortmann, C. S., Kim, H. K., and Mupangwa, W. (2018). Conservation agriculture effects on crop productivity and soil properties in Ethiopia. Agron. J. 110, 758–767. doi: 10.2134/agronj2017.07.0384
Liu, W. Y., Chiang, C. Y., Yap, J. L., and Lin, C. C. (2024). Assessing the ecosystem service values of tea plantations using conventional and organic farming methods: is organic farming always better? Ecol. Indic. 158:111355. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.111355
Luh, Y. H., Chang, Y. C., and Hsieh, M. F. (2023). What determines how green crop farming can get? Spatial factors or green awareness spillovers. J. Environ. Manag. 326:116667. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116667
Manson, S., Nekaris, K. A. I., Nijman, V., and Campera, M. (2024). Effect of shade on biodiversity within coffee farms: a meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 914:169882. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.169882
Masha, M., Yirgu, T., and Debele, M. (2021). Impacts of soil and water management measures on crop production and farm income of rural households in the Damota area districts. Southern Ethiopia. Int J Agron 2021, 1–13. doi: 10.1155/2021/5526713
Mavridis, D., and Salanti, G. (2014). How to assess publication bias: funnel plot, trim-and-fill method and selection models. Evid Based Ment Heal 17:30. doi: 10.1136/eb-2013-101699
Mengistie, T. A. (2022). How do learners view adult education? Women learners’ perception on the Ethiopia’s adult education programme. Heliyon 8:e09272. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09272
Merot, A., and Smits, N. (2024). Explaining yield dynamics during vineyard conversion to organic farming. Eur. J. Agron. 153:127068. doi: 10.1016/j.eja.2023.127068
Mgomezulu, W. R., Edriss, A.-K., Machira, K., and Pangapanga-Phiri, I. (2023a). Towards sustainability in the adoption of sustainable agricultural practices: implications on household poverty, food and nutrition security. Innov Green Dev 2:100054. doi: 10.1016/j.igd.2023.100054
Mgomezulu, W. R., Machira, K., Edriss, A.-K., and Pangapanga-Phiri, I. (2023b). Modelling farmers’ adoption decisions of sustainable agricultural practices under varying agro-ecological conditions: a new perspective. Innov Green Dev 2:100036. doi: 10.1016/j.igd.2023.100036
Mossie, W. A. (2022). The impact of climate-smart agriculture technology on productivity: does row planting matter? Evidence from southern Ethiopia. Sci. World J. 2022, 1–11. doi: 10.1155/2022/3218287
Mpanga, I. K., Neumann, G., Schuch, U. K., and Schalau, J. (2020). Sustainable agriculture practices as a driver for increased harvested cropland among large-scale growers in Arizona: a paradox for small-scale growers. Adv Sustain Syst 4, 1–8. doi: 10.1002/adsu.201900143
Mutyasira, V., Hoag, D., and Pendell, D. (2018). The adoption of sustainable agricultural practices by smallholder farmers in Ethiopian highlands: an integrative approach. Cogent Food Agric 4, 1–17. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2018.1552439
Naik, B. S. S. S., Sharma, S. K., Pramanick, B., Chaudhary, R., Yadav, S. K., Tirunagari, R., et al. (2022). Silicon in combination with farmyard manure improves the productivity, quality and nitrogen use efficiency of sweet corn in an organic farming system. SILICON 14, 5733–5743. doi: 10.1007/s12633-022-01818-0
Naik, B. S. S. S., Sharma, S. K., Pramanick, B., Yadav, S. K., Reddy, G. K., Tirunagari, R., et al. (2024). Development of an improved Silicon application protocol for organic sweet corn cultivation ensuring higher productivity and better soil health. SILICON 16, 2547–2555. doi: 10.1007/s12633-024-02858-4
Nigus, G., Ketema, M., Haji, J., and Sileshi, M. (2024). Determinants of adoption of urban agricultural practices in eastern Haraghe zone of Oromia region and Dire Dawa City administration, eastern Ethiopia. Heliyon 10:e26758. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26758
Ninh, L. K. (2021). Economic role of education in agriculture: evidence from rural Vietnam. J. Econ. Dev. 23, 47–58. doi: 10.1108/jed-05-2020-0052
Obsi Gemeda, D., Korecha, D., and Garedew, W. (2023). Determinants of climate change adaptation strategies and existing barriers in southwestern parts of Ethiopia. Clim Serv 30:100376. doi: 10.1016/j.cliser.2023.100376
Ogola, P. A., Ngesa, F., and Makanji, D. L. (2023). Influence of access to extension services on milk productivity among smallholder dairy farmers in Njoro Sub-County, Nakuru County. Kenya. Heliyon 9:e20210. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20210
Oyetunde-Usman, Z., Olagunju, K. O., and Ogunpaimo, O. R. (2021). Determinants of adoption of multiple sustainable agricultural practices among smallholder farmers in Nigeria. Int Soil Water Conserv Res 9, 241–248. doi: 10.1016/j.iswcr.2020.10.007
Raudenbush, S. W. (2009). Analyzing effect sizes: random-effects models. Handb Res Synth meta-analysis 2, 295–316.
Roques, S., Koning, L., van Riel, J., Bossers, A., Schokker, D., Kar, S. K., et al. (2023). Influence of agroecology practices on rumen microbiota associated with methane emission in dairy cattle. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 303:115716. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2023.115716
Sanaeifar, A., Guindo, M. L., Bakhshipour, A., Fazayeli, H., Li, X., and Yang, C. (2023). Advancing precision agriculture: the potential of deep learning for cereal plant head detection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 209:107875. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2023.107875
Schmidt, E., and Tadesse, F. (2019). The impact of sustainable land management on household crop production in the Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. L Degrad Dev 30, 777–787. doi: 10.1002/ldr.3266
Shallo, L. (2020). Impact of soil and water conservation practice on crop productivity in Ethiopia. Int J Econ Manag Stud 7, 130–142. doi: 10.14445/23939125/ijems-v7i3p118
Simutowe, E., Ngoma, H., Manyanga, M., Silva, J. V., Baudron, F., Nyagumbo, I., et al. (2024). Risk aversion, impatience, and adoption of conservation agriculture practices among smallholders in Zambia. Heliyon 10:e26460. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26460
Singh, A., Rajput, V. D., Varshney, A., Ghazaryan, K., and Minkina, T. (2023). Small tech, big impact: Agri-nanotechnology journey to optimize crop protection and production for sustainable agriculture. Plant Stress 10:100253. doi: 10.1016/j.stress.2023.100253
Sinore, T., and Wang, F. (2024). Impact of climate change on agriculture and adaptation strategies in Ethiopia: a meta-analysis. Heliyon 10:e26103. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26103
Sterne, J. A. C., Becker, B. J., and Egger, M. (2005). The funnel plot. Publ bias meta-analysis Prev Assess Adjust John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 73–98.
Sukayat, Y., Setiawan, I., Suharfaputra, U., and Kurnia, G. (2023). Determining factors for farmers to engage in sustainable agricultural practices: a case from Indonesia. Sustain. For. 15, 1–14. doi: 10.3390/su151310548
Sun, J., Niu, W., Mu, F., Li, R., du, Y., Ma, L., et al. (2024). Optimized tillage can enhance crop tolerance to extreme weather events: evidence from field experiments and meta-analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 238:106003. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2024.106003
Tariku, G. D., and Kebede, S. A. (2024). Climate-smart agricultural practices and its implication in Ethiopia: a systematic review. Int J Clim Chang Strateg Manag. doi: 10.1108/IJCCSM-01-2024-0012
Tega, M., and Bojago, E. (2024). Determinants of smallholder farmers’ adoption of agroforestry practices: Sodo Zuriya District, southern Ethiopia. Agrofor. Syst. 98, 1–20. doi: 10.1007/s10457-023-00885-5
Teklewold, H., Kassie, M., and Shiferaw, B. (2013). Adoption of multiple sustainable agricultural practices in rural Ethiopia. J. Agric. Econ. 64, 597–623. doi: 10.1111/1477-9552.12011
Venn, R., and Burbi, S. (2023). Agroforestry policy development in England: a question of knowledge transference. Land Use Policy 134:106936. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2023.106936
Vitali, A., Moretti, B., Lerda, C., Said-Pullicino, D., Celi, L., Romani, M., et al. (2024). Conservation tillage in temperate rice cropping systems: crop production and soil fertility. F Crop Res 308:109276. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2024.109276
Wagner, M., Lask, J., Kiesel, A., Lewandowski, I., Weselek, A., Högy, P., et al. (2023). Agrivoltaics: the environmental impacts of combining food crop cultivation and solar energy generation. Agronomy 13, 1–14. doi: 10.3390/agronomy13020299
Wolka, K., Biazin, B., Getachew, F., Girma, F., and Desta, G. (2023). Towards sustainable watershed-based landscape restoration in degraded drylands: perceived benefits and innovative pathways learnt from project-based interventions in Ethiopia. J. Environ. Manag. 335:117499. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.117499
Xie, Y., Chen, Z., Tang, H., Boadu, F., and Yang, Y. (2023). Effects of executives’ pro-environmental education and knowledge sharing activities on eco-friendly agricultural production: evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 395:136469. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136469
Xie, H., and Huang, Y. (2021). Influencing factors of farmers’ adoption of pro-environmental agricultural technologies in China: Meta-analysis. Land Use Policy 109:105622. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2021.105622
Yigezu Wendimu, G. (2021). The challenges and prospects of Ethiopian agriculture. Cogent Food & Agriculture, 7, 1–26. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2021.1923619
Yitayew, A., Abdulai, A., and Yigezu, Y. A. (2023). The effects of advisory services and technology channeling on farm yields and technical efficiency of wheat farmers in Ethiopia. Food Policy 116:102436. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2023.102436
Yitayew, A., Abdulai, A., Yigezu, Y. A., Deneke, T. T., and Kassie, G. T. (2021). Impact of agricultural extension services on the adoption of improved wheat variety in Ethiopia: a cluster randomized controlled trial. World Dev. 146:105605. doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2021.105605
Zain, M., Ma, H., Ur Rahman, S., Nuruzzaman, M., Chaudhary, S., Azeem, I., et al. (2024). Nanotechnology in precision agriculture: advancing towards sustainable crop production. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 206:108244. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.108244
Zegeye, M. B., Asratie, T. M., Getahun, D. K., and Deredera, M. G. (2023). Impact of climate change adaptation practices on crop productivity: evidence from north Shewa zone, Amhara region. Ethiopia. Lett Spat Resour Sci 16, 1–24. doi: 10.1007/s12076-023-00349-5
Zeng, S., Li, J., and Wanger, T. C. (2023). Agroecology, technology, and stakeholder awareness: implementing the UN food systems summit call for action. iScience 26:107510. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107510
Zerssa, G., Feyssa, D., Kim, D. G., and Eichler-Löbermann, B. (2021). Challenges of smallholder farming in Ethiopia and opportunities by adopting climate-smart agriculture. Agriculture 11, 1–26. doi: 10.3390/agriculture11030192
Zeweld, W., Van Huylenbroeck, G., and Tesfay, G. (2020). Sustainable agricultural practices, environmental risk mitigation and livelihood improvements: empirical evidence from northern Ethiopia. Land Use Policy 95:103799. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2019.01.002
Keywords: crop productivity, sustainable agriculture practices, meta-analysis, Ethiopia, effect
Citation: Ejeta TT and Bai X (2025) The effect of sustainable agricultural practices on crop productivity in Ethiopia: insights from a meta-analysis. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1499412. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1499412
Edited by:
Biswajit Pramanick, Dr. Rajendra Prasad Central Agricultural University, IndiaReviewed by:
Sri Sai Siddartha Naik.B, Acharya N. G. Ranga Agricultural University, IndiaMohan Lal, G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology, India
Copyright © 2025 Ejeta and Bai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiuguang Bai, YmFpeGc5NjBAbndhZnUuZWR1LmNu
†ORCID: Tadesse Tolera Ejeta, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6377-0251
 Tadesse Tolera Ejeta
Tadesse Tolera Ejeta Xiuguang Bai
Xiuguang Bai