
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Sustain. Food Syst. , 18 December 2024
Sec. Climate-Smart Food Systems
Volume 8 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2024.1497599
This article is part of the Research Topic Transforming African Food Systems View all 15 articles
 Gcobisa Mbadlisa
Gcobisa Mbadlisa Osden Jokonya*
Osden Jokonya*With the rise in food insecurity, one of the United Nation’s Sustainable Development Goals is to end hunger, achieve food security, and promote sustainable agriculture. This can be achieved through the strengthening and development of existing food systems. Integrating emerging technologies such as blockchain technology can help develop sustainable food systems. Blockchain technology allows the tracking and tracing of food items as they move through the supply chain. Blockchain technology also allows for low transactional costs at almost instantaneous applications. There is however a low adoption rate of blockchain technology amongst organisations in the food supply chain. The objective of the study was to explore factors that affect the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The study adopted a quantitative research method that was guided by the technology, organisation, and environment Framework (TOE) to explore factors affecting blockchain technology adoption in the food supply chain. A systematic literature review was used for the study. Quantitative content analysis was used to analyse peer-reviewed articles. Results showed that TOE factors affect the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. Factors such as cost, scalability, firm size, and IT policy were noted as important factors affecting the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The study contributes to the body of knowledge on factors that affect the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain.
Food insecurity is a notable issue across the globe. It is defined as a lack of access to adequate amounts of nutritious and inexpensive foods at all times. One of the United Nation’s Sustainable Development Goals is to end hunger, achieve food security, and promotion of sustainable agriculture. When dealing with the topic of food, the process from farm to fork must be noted. This is the supply chain of food often called a food system. With the rise of technology, it is essential to find solutions to improve food systems (Goedde et al., 2020). The application of emerging technologies in food has been referred to as the digital food systems. In a food system, many stakeholders form part of the system as well as contribute to the system. There are several stakeholders in a food system with the main one being the farmer which is the backbone of a food system. The focus of the study is organisations within food systems in particular the small-scale farmers. Small-scale farmers can be identified as farms with a scale that is too small to engage with the level of provision needed to improve their productivity (Kirsten and van Zyl, 1998; Pienaar and Traub, 2015). The farmers are part of the food system where buying centres purchase produce (Rambhia et al., 2022). Retailers as stakeholders of the food systems purchase products from buying centre hubs. They then sell packaged and ready products to consumers. Customers are usually the end-users of the food and products produced by the food system (Rambhia et al., 2022).
Digital technologies such as blockchain technology may improve sustainable food systems by storing information in a digital format. Blockchain technology stores information in interlinked data sets grouped and linked in a chain of blocks (Shakhbulatov et al., 2019; Vern et al., 2024). The interlinked blockchain technology system allows digital food system stakeholders to define their roles in the supply chain. The stakeholders can provide information to the blockchain technology that allows tracking and tracing of foods as they move through the supply chain (Duan et al., 2020). The importance of this study is to explore factors that affect blockchain technology adoption in the food supply chain. The study adopted the Technology, Organisational, and Environmental framework to explore the factors that affect blockchain technology adoption in the food supply chain.
With the advent of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) have seen a growing need for digital transformation of the food systems like all other sectors (Knorr et al., 2011; Vern et al., 2024). With the rise of emerging technologies such as blockchain technology, it is important to adopt them into the food systems processes. There are however barriers to the adoption of blockchain technology such as high costs and lack of knowledge among others (Vu et al., 2023; Sri Vigna Hema and Manickavasagan, 2024; George and Al-Ansari, 2024). These barriers hinder the adoption of blockchain technology adoption in food systems. Considering the previous literature, the is a gap in the literature on factors affecting the adoption of emerging technologies, in particular, blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The study objective therefore is to explore the factors affecting the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain.
Sulaiman et al. (2021) highlighted the need for social, physical, and economic access to enough, safe and nutritious foods by people that always meet their dietary needs as well as food preferences for a healthy lifestyle. Food insecurity, therefore, occurs when access to safe and nutritious foods is limited or uncertain. There is a rising need to address food insecurity as part of the United Nations 2nd Sustainable Development Goal (Mollier et al., 2017). As part of the food systems, the issue of food must focus on a more holistic approach to food, not only on dietary and nutritional provisions but also on the production and distribution of food goods (Béné et al., 2019; Vern et al., 2024). The food supply chain includes the process of raw materials and how it becomes a product ultimately used by the consumer. Due to issues like urbanisation and globalisation, there is an increasing demand for food (Thornton et al., 2011; Vern et al., 2024). This increase in demand puts pressure on food systems to provide adequate provisions for growing populations. Food systems can benefit from adopting emerging technologies (Antonucci et al., 2019; George and Al-Ansari, 2024). Adopting emerging technologies in food systems can help improve productivity and address the pressures placed on food systems. The integration of various technologies into food systems, results in digital food systems.
The food supply chain involves the process of turning food from raw materials to consumable goods. The food systems consist of various processes that bring about food security. The activities include the processing of food, packaging, and distribution of food as well as the selling and consumption of food (Ingram, 2011; Vern et al., 2024). Food in its raw state and processing typically falls under the agricultural sector of the food system. Vern et al. (2024) note that the processing and packaging of food increase value rather than just the typical farming activities. The distribution of food has expanded into various markets, and the consumption of foods has both increased and changed throughout the years (Ericksen, 2008; Vern et al., 2024).
The Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) has ushered in the widespread adoption of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and blockchain, among others, within food systems (Prisecaru, 2016; Vern et al., 2024). The adoption of emerging digital technologies in food systems may help to address consumer needs (Knorr et al., 2011; Vern et al., 2024). The concept of Food 4.0, associated with the Fourth Industrial Revolution, focuses on incorporating these technologies into the food industry to enhance operations and stakeholder engagement. These technological advancements play a role in helping food systems adapt to the evolving landscape of the 4IR.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution brought many emerging technologies that have disrupted several industries. One of those technologies is blockchain technology which consists of interlinked datasets, each block represents several transactions that are then linked via a chain to relate transactions in other blocks (Nofer et al., 2017). The blockchain technology’s main characteristics are traceability, transparencyand security (Taherdoost, 2022; Vern et al., 2024). Blockchain technology has a distributed structure that allows all stakeholders to contribute to the data and have access to the ledger (Chen et al., 2021). Blockchain technology which is the foundation of cryptocurrency has also gained popularity across various sectors such as healthcare, logistics, and supply chain (Taherdoost, 2022; Vern et al., 2024). Blockchain technology is a distributed ledger that all stakeholders have access to as part of the system. Each block within the blockchain technology consists of three characteristics namely, its data, its hash as well the hash of the previous block. The hash serves as the unique identification of each transaction that takes place and it changes with every block and change (Batwa and Norrman, 2020). Figure 1 shows the simplification of the blockchain technology process.
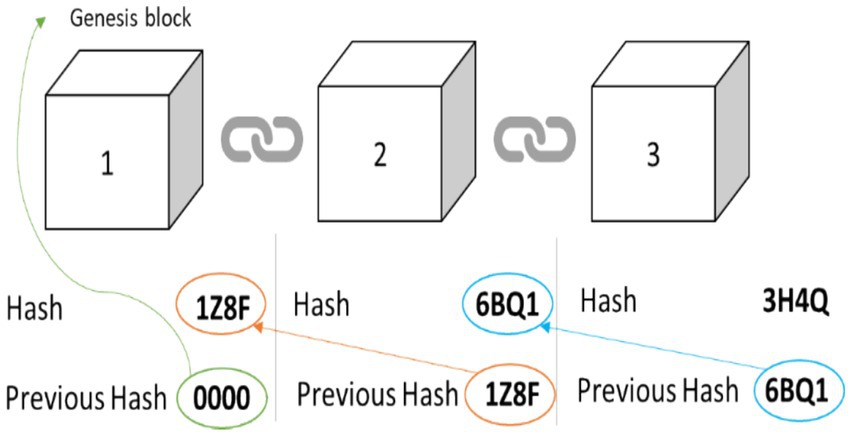
Figure 1. The simplified blockchain technology process (Source: Batwa and Norrman, 2020).
The adoption of blockchain technology in food systems may be beneficial for existing food systems and supply chains. Blockchain technology may provide food systems with transparency, low costs for transactions, and almost instantaneous applications (Antonucci et al., 2019; George and Al-Ansari, 2024). Antonucci et al. (2019) added that blockchain technology allows for the authenticity of data groups to be guaranteed as the stakeholders within the food system are working in collaboration rather than in competition Blockchain technology revolutionizes the supply chain through the application of security and reduction of redundancy to inventory meaning no inventory is allowed to exist in two different places at the same time (Brody, 2017; George and Al-Ansari, 2024). Blockchain technology eliminates supply chain partners and replaces them with banking nodes to form a newer approach to supply chain management.
One of the main concerns of a food system is the safety and quality of food. Feng et al. (2020), point out that improving durability, integrity, security, and traceability transparency within the food systems is the solution to food safety and quality concerns. Prashar et al. (2020), note that food traceability management allows for the tracking of food from farm to fork and helps to monitor food safety and quality. To improve the safety and security of food, a proper management system is required. Prashar et al. (2020), highlighted that the adoption of blockchain technology may strengthen existing food systems. They added that blockchain technology may provide accurate and transparent information regarding shipping information, origins of food, manufacturing, and the entire end-to-end process that improves tracking and control. Vu et al. (2023), note that although blockchain technology is still considered to be in its infancy, there have been some successful blockchain technology application cases that have seen improvement in food quality and safety (e.g., Walmart using blockchain technology to trace its supply of pork from China). The application of blockchain technology in food systems traceability may be ensured through tagging and sensing, communication and navigation, location, reading recognition technology, and a digital ledger assisting in upholding food safety and quality assurance systems (Prashar et al., 2020), as shown in Figure 2 in a poultry food system perspective.
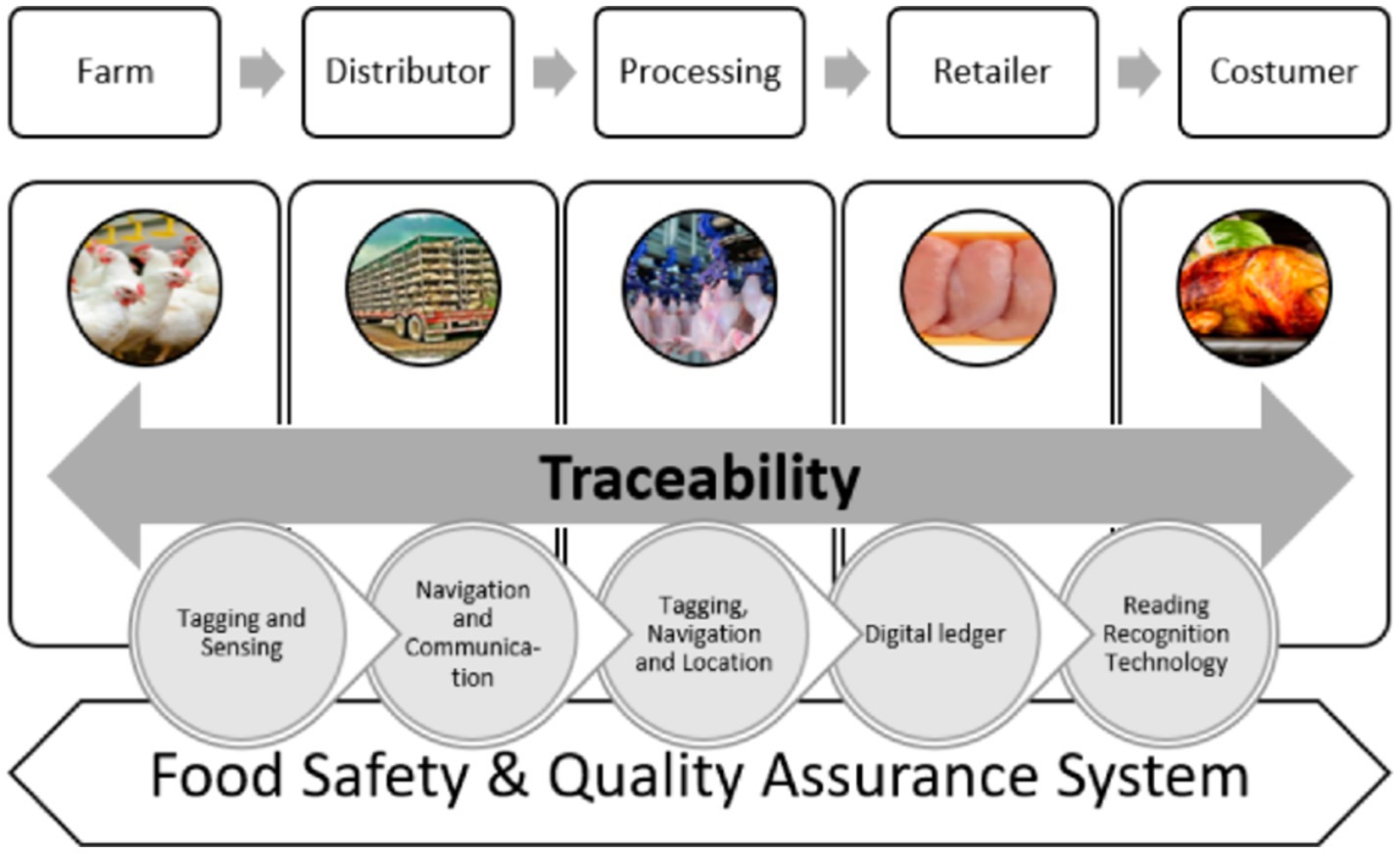
Figure 2. Food safety and quality assurance system with blockchain technology functions (Source: Prashar et al., 2020).
Several studies have been conducted on blockchain technology and its adoption in different areas of the food supply chain. Aldrighetti et al. (2021) study focused on blockchain technology adoption to increase food traceability. The study found that blockchain technology had potential and was an innovative solution for internal and external traceability management although factors such as lack of resources, regulations, and skills hindered blockchain technology adoption. Another study by Vu et al. (2023) on the adoption of blockchain technology in food supply chains through systematic literature found that organisations implement blockchain technology in phases before focusing on a mass-scale implementation. Chen et al. (2021) focused on blockchain technology adoption and used a thematic analysis that found that the benefits of blockchain technology adoption included improved food quality management and traceability. Some of the challenges were the complexity and immature application of blockchain technology. The literature review did not find a study-based quantitative content analysis investigating factors affecting blockchain technology adoption in the food supply chain.
The study adopted the Technology-Organisational-Environmental (TOE) Framework to explore factors affecting blockchain technology adoption technologies in the food supply chain. According to Rosario Oliveira Martins et al. (2011), the technology factors refer to both internal and external relevant technologies to an organisation. These can be related to the equipment owned by the firm or technologies not used by the organisation. The organisational aspect of the framework focuses on factors such as the size, structure of the organisation, and its scope among others. The environmental aspect focuses on the scope and area of organisation operations. The TOE Framework has been found to have influential factors that affect the adoption of IT Innovations in organisations (Clohessy et al., 2019). The framework is useful for assessing and validating technology adoption at an organisational level (Malik et al., 2021). With blockchain technology being an emerging technology, the TOE framework was found useful for understanding its adoption in the food supply chain.
The technological context of the TOE framework is defined by Malik et al. (2021) as the characteristics of technology that are influential in the adoption process. Guo and Liang (2016), mention the technological factors of cost, complexity, security, compatibility, and relative advantage as technological considerations that may influence the adoption of blockchain technology technologies in organisations. Khadivar et al. (2021), discussed the complexity of technology as an influencing factor, and how easy to use and integrate into business processes technology is important as those technologies which are easy to understand are adopted at a much faster rate as compared to more complex technologies.
The organisational context of the TOE framework alludes to the characteristics of an organisation, these characteristics include but are not limited to senior managerial support, firm size, infrastructure, innovation capacity, and human capital quality (Bryan and Zuva, 2021). Wang et al. (2016), notes factors such as organisational readiness, top managerial support, the size of the organisation, and the responding capability as organisational considerations to be taken note of that influence the adoption of blockchain technology. Malik et al. (2021), noted that top managerial support was integral to the adoption of new technologies in orgasiations. They added that lack of that support could lead to fewer resources being allocated to the adoption of new technologies and reduce the chances of technologies being adopted.
The environmental context of the TOE framework focuses on the operational area of the organisation, the organisation’s competitors and industry, and the government (Khadivar et al., 2021). Swan (2015), noted the regulatory environment, market dynamics, public perception, and government support as key environmental factors that affect the adoption of blockchain technology technologies. Regulators are key players in the adoption of blockchain technology, and their involvement in the technical and legal formulation of rules for blockchain technology is important (Guo and Liang, 2016; Sri Vigna Hema and Manickavasagan, 2024). Blockchain technology should not self-regulate due to its critical impact on existing systems and environments.
The research design used in the study helped to answer the research question and was based on a systematic literature review. A quantitative content analysis research design was used for the study. Content analysis is described by Babbie and Mouton, 2005 as a tool used in research that allows the emergence and showing of certain words or concepts to be determined within sources such as journal articles or texts. It allows the exploration of various viewpoints and the use of credible sources to support the study being proposed (Coners and Matthies, 2014). Gupta et al. (2018) added that a researcher is provided with a pre-defined literacy tool through a systematic literature review and is thus able to identify reliable evidence.
The unit of analysis type for the study is organisational. The chosen unit of analysis for the study was the organisation within the food supply chain and the study was based on secondary data. The study reviewed 50 peer-reviewed articles published on various databases. The primary research objective of the study was to explore factors affecting the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The literature search focused on published articles on adopting blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The literature search focused on peer-reviewed articles on the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain published between 2018 and 2022. The 50 journal articles on factors affecting the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain were selected for this study after the screening process.
The literature for the study was identified through different platforms such as Elsevier and Google Scholar among others. It was searched through keywords such as blockchain technology adoption and TOE Framework. The selected articles were read and reviewed and if they met the criteria they were stored. The relevant published articles on the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The study included all articles that dealt with the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain published between the years 2018 and 2022. The information from the selected articles was captured manually in a tabulated format in Microsoft Excel. This was used to make arguments for the findings. The themes from selected articles were categorised and coded manually according to the factors in Table 1.
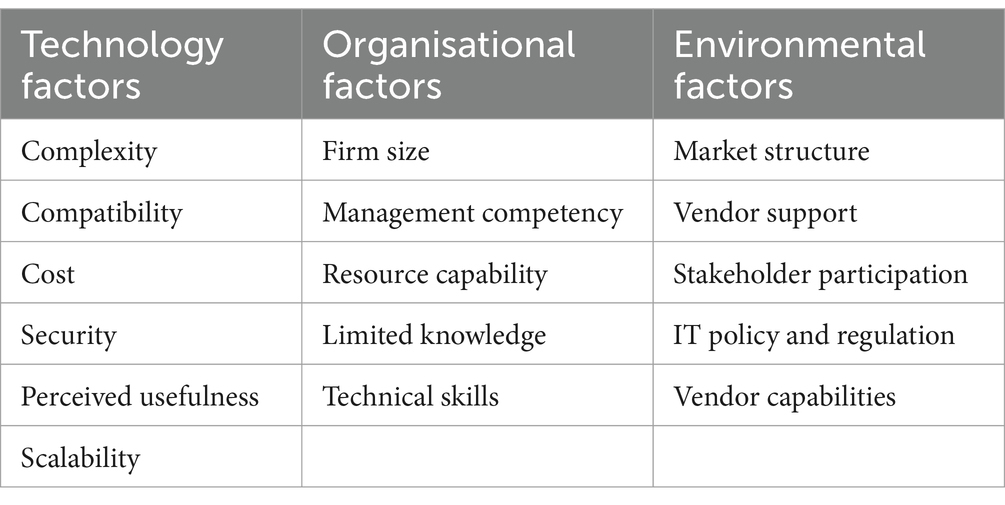
Table 1. Technical-organisational-environmental factors affecting the adoption of blockchain technology in food systems.
The study used convenience sampling which non-probability sampling strategy. Convenience sampling allows for articles to be chosen based on how easy they are to access (Etikan, 2016). All articles from different platforms had a chance of being selected for the study if they met the criteria. Searching credible databases using the chosen keywords such as “Blockchain technology adoption in food systems,” “TOE Framework,” “Blockchain technology adoption “and “digital food systems” was used as part of convenience sampling. The study selected were 50 peer-reviewed articles published between the years 2018 and 2022.
A quantitative content analysis method was used for the study to analyse journal articles on factors affecting blockchain technology adoption in the food supply chain. The TOE factors listed in the table format are used to identify a factor mentioned in an article to be entered in the table. The articles were coded and categorised according to different TOE factors.
The collected data was captured in the Excel spreadsheet which was categorised into demographic variables data and TOE framework factors. The data was categorised and coded according to TOE framework factors. The collected was analysed by the researcher through the interpretation of keywords from the framework. The identified data from the articles were categorised based on factors that affect the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The data in Excel format was imported into the SPSS PC statistical package for analysing quantitive data. Various types of statistics were conducted from the data which include frequencies, analysis of variance (ANOVA), and correlations.
This section presents the results of the analysed collected data of the study. The study focussed on exploring factors that affect the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The results from the analysed data are based on published articles between 2018 and 2022. The results in this section are structured as follows: section 4.1 demographic data frequencies, section 4.2 TOE framework factors frequency, section 4.3 the ANOVA of TOE framework factors, and lastly section 4.4 correlation of TOE framework factors.
Figure 3 presents the frequency of published articles between the years 2018 and 2022 on factors that affect the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The results show that 26% of articles relating to the factors that affect blockchain technology adoption in the food supply chain were published between the years 2018 and 2019 while 74% of related articles were later, between the years 2020 and 2022. The results suggest an increase in the research output from 2018 to 2022. The year 2018 had the lowest research output of 8% compared to other years.
Figure 4 presents the research methods used in the published articles relating to adopting blockchain technology in the food supply chain. It presents the research methods through the frequency of the chosen method in each article published between 2018 and 2022. The results show that 58% of the published articles used qualitative research methods. This was followed by 28% of the published articles that used quantitative research methods and 14 of those that used mixed-method research of all articles published between 2018 and 2022 related to factors affecting the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The results suggest that qualitative research was the most popular method used in published articles between 2018 and 2022 on factors that affect the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain.
Figure 5 presents frequencies of the research design types of published articles factors that affect the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain between the years 2018 and 2022. The results show that most articles published between 2018 and 2022 used a systematic literature review (SLR) research design at 48%. Further, 26% of articles published between 2018 and 2022 used a survey research design. Case study research design was used by 18% of the published articles and 8% of the published articles on factors that affect the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain did not have a research design.
Figure 6 presents the results for the frequency of research frameworks used in articles relating to factors affecting the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain published between the years 2018 and 2022. The results show that most articles (62%), did not use a research framework. The results further show that the most used framework was the TOE Framework at 18% of published articles. The other frameworks at 20% represented other insignificant percentages of frameworks used in published articles between the years 2018 and 2022 on factors affecting the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain.
Figure 7 presents the regional frequency of published articles between the years 2018 and 2022 on factors affecting the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The results indicate that 42% of articles were published in Europe, 38% in Asia, 6% in North America, 6% were transcontinental in both Asia and North America, and a further 4% in Asia and Europe. Tied for the lowest number of published articles were South America and Australia both with 2% of articles on factors affecting blockchain technology adoption in the food supply chain between 2018 and 2022. There are no articles published in Africa.
This section presents the technology, organisation, and environment factors frequency results of the factors affecting blockchain technology adoption in the food supply chain published between the years 2018 and 2022.
The study analysed six technological factors that affect the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. These factors include complexity, compatibility, cost, perceived usefulness, scalability, and security. The presented frequency results are drawn from peer-reviewed published articles between the years 2018 and 2022 on factors affecting blockchain technology adoption in the food supply chain. The results of the analysis of technology factors show that cost is considered the most important factor with 72% of the published articles on factors affecting the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain (Sri Vigna Hema and Manickavasagan, 2024). Furthermore, security and scalability had 46% of articles published between 2018 and 2022. Furthermore, 42% of the published articles mentioned the complexity of the technology as a factor, followed by compatibility at 28% and perceived usefulness at 22% as depicted in Figure 8. These results suggest that companies need to be aware of the financial costs of blockchain technology (Guo and Liang, 2016; Sri Vigna Hema and Manickavasagan, 2024). The results imply that financial resources, security, and scalability are important factors for the adoption of blockchain technologies adopting blockchain technology (Guo and Liang, 2016). Firms also need to consider the complexity of blockchain technology to be adopted.
The study analysed five organisational factors, that may affect the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The organisational factors include firm size, management competency, limited knowledge, technical skills, and resource capacity. Figure 9 presents the results of the organisational factors identified from published articles between the years 2018 and 2022. The results show that firm size with 40% of articles is considered the most important factor, followed by limited knowledge at 34% and management competency at 26%. The least mentioned organisational factors were technical skills and resource capacity both mentioned in 22% of articles relating to the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The study results suggest that firm size is an important factor in the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain (Bryan and Zuva, 2021). How large or small is an organisation is important in deciding to adopt blockchain technology. Firms with limited knowledge of blockchain technology may also have challenges in adopting blockchain technology (Vu et al., 2023). Management was also considered to be an important factor in the adoption of blockchain technology in organisations.
The study analysed five environmental factors that affect the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. These factors included market structure, vendor support, IT policy and regulations, stakeholder participation, and vendor capabilities. Figure 10 shows the frequency results of the environmental factors mentioned in published articles between the years 2018 and 2022. According to the results, the most mentioned environmental factor is IT policy and regulations at 58% of the published articles followed by stakeholder participation at 50% and vendor support at 14%. The least mentioned factors were market structure at 10% and vendor capabilities at 0% of the published articles. The results suggest that IT policy and regulations, stakeholder participation (Duan et al., 2020), and vendor support affect decisions regarding the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain (Guo and Liang, 2016; Sri Vigna Hema and Manickavasagan, 2024). This result suggests that the least factor to consider for organisations when adopting blockchain technology in the food supply chain should be vendor capabilities as it has no influence.
The study performed an analysis of variance (ANOVA) on demographic variables and TOE framework constructs. Table 2 shows the analysis of variance (ANOVA) of the region the organisational variables and environmental factors. The table shows significant differences below 0.05 on organisational factors at 0.012 and environmental factors at 0.048. These statistical analyses suggest that there were significant differences between organisational, and environmental variables and the regional demographic variable. The results indicate that organisational variables and environmental variables were the only factors that showed significant differences when measured against the region variable. The results suggest that different regions perceived differently the importance of organisational and environmental factors on the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain.
The study performed correlation on technological, organisational, environmental, and demographic year variables to find out the relationships between the variables. The correlation s was conducted to understand relationships between the TOE framework constructs and demographic year on the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. Table 3 shows the correlation between the technology, organisational, environmental (TOE) factors, and demographic year variable) of the published articles. The correlation for the study is deemed to be significant at below 0.05. The year variable did not have a significant correlation with the TOE constructs (technological, organisational, and environmental variables. Additionally, the results indicate a significant correlation between technology factor, and organisational at positive 0.009 and between technological and environmental factors at a positive 0.004 had a significant. Lastly, the organisational factors and environmental factors had a significant positive correlation of 0.007.
The study conducted a systematic literature review on factors affecting the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The systematic literature review focused on articles published between 2018 and 2022. Fifty peer-reviewed articles were selected and analysed to provide a view of factors affecting the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The study adopted the TOE framework to determine the factors that affect the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The study results showed that the main technological factors in the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain are cost, security, and scalability. The results are aligned with the findings literature that states that security is the biggest risk in ICT Adoption and the cost of technology is important (Lanzini et al., 2021). The results suggest that organisations and stakeholders within the food supply chain may consider adopting blockchain technology if it can ensure that security is maintained high in the food supply chain, the technology is cost-effective, and it can be scaled either up or down depending on the organisation’s needs.
The results further revealed that the organisational factors of firm size, limited knowledge, and management competency were important in the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The results suggest that larger firms are more likely to adopt blockchain technology than smaller firms and that knowledge of the technology is considered for the adoption of blockchain technology organisations. Furthermore, IT policy & regulation and stakeholder participation were considered important environmental factors for the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. These results imply that awareness of regulations of blockchain technology (Guo and Liang, 2016; Sri Vigna Hema and Manickavasagan, 2024) and stakeholders’ participation (Duan et al., 2020) are considered important factors in the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The results, therefore, suggest that technology factors (cost, security, and scalability), organisational factors (firm size, management competency, and limited knowledge), and environmental factors (IT policy& regulations and stakeholder participation) are important factors in the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain.
Further analysis conducted indicated that there is a significant difference between the regional environmental factors, and organisational factors affecting the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The results suggest that the effects of organisational and environmental factors on the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain differ in different regions. The additional correlation analysis between years of publication and the TOE factors (technological, organisational, and environmental factors) did not show a significant relationship. However, correlation analysis revealed a positive significant relationship between technology, organisational, and environmental factors on the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The results suggest that when one factor increases the other factors will also increase their effect on the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain.
In conclusion, the study suggests that technological factors (cost, security, and scalability), organisational factors (firm size, management competency, and limited knowledge), and environmental factors (IT policy & regulations and stakeholder participation) influence the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The study suggests that the bigger the size of the firms, the knowledge of blockchain technology, as well as access to all regulations and policies, are considered important for the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. For organisations to adopt blockchain technologies in the food supply chain should be aware of IT policies and regulations, knowledgeable of the technology, and competent management.
The study achieved its objective of exploring the factors that affect the consideration of adopting blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The study assists in understanding factors affecting the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The study contributed to the body of knowledge on factors that affect the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. Despite the study’s contribution, it had some limitations worth mentioning. The study was not based on empirical data but on secondary data from published articles on the adoption of blockchain technology in the food supply chain. The study was based on convenience sampling instead of random sampling meaning the results are not an accurate representation of the food supply chain industry. The limitations present an opportunity for future studies to be taken further by using empirical data as well as other research methods.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
GM: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. OJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Aldrighetti, A., Canavari, M., and Hingley, M. K. (2021). A Delphi study on blockchain application to food traceability. Int. J. Food Syst. Dyn. 12, 6–18. doi: 10.18461/ijfsd.v12i1.72
Antonucci, F., Figorilli, S., Costa, C., Pallottino, F., Raso, L., and Menesatti, P. (2019). A review on blockchain applications in the agri‐food sector. J. Sci. Food Agric. 99, 6129–6138. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.9912
Batwa, A., and Norrman, A. (2020). A framework for exploring blockchain technology in supply chain management. OSCM Int J 13, 294–306. doi: 10.31387/oscm0420271
Béné, C., Oosterveer, P., Lamotte, L., Brouwer, I. D., de Haan, S., Prager, S. D., et al. (2019). When food systems meet sustainability- current narratives and implications for actions. World Dev. 113, 116 (116-130)–130. doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2018.08.011
Brody, P. (2017). How blockchain is revolutionizing supply chain management. Digitalist Magazine. Available at: http://www.digitalistmag.com/tag/blockchain-and-supply-chain (Accessed May 18, 2022).
Bryan, J. D., and Zuva, T. (2021). A review on TAM and TOE framework progression and how these models integrate. Adv Sci Technol Eng Syst J 6, 137–145. doi: 10.25046/aj060316
Chen, S., Liu, X., Yan, J., Hu, G., and Shi, Y. (2021). Processes, benefits, and challenges for adoption of blockchain technologies in food supply chains: a thematic analysis. IseB 19, 909–935. doi: 10.1007/s10257-020-00467-3
Clohessy, T., Acton, T., and Rogers, N. (2019). “Blockchain adoption: technological, organisational and environmental considerations,” in Business transformation through blockchain. Vol. 1. eds. H. Treiblmaier and R. Beck (Cham, Switzerland: Palgrave Macmillan), 47–76.
Coners, A., and Matthies, B. (2014). “A content analysis of content analyses in research: purposes, data sources, and methodological characteristics,” in The Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems (PACIS). (Chengdu, China: PACIS 2014 Proceedings), 111.
Duan, J., Zhang, C., Gong, Y., Brown, S., and Li, Z. (2020). A content-analysis based literature review in blockchain adoption within food supply chain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17:1784. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17051784
Ericksen, P. J. (2008). Conceptualizing food systems for global environmental change research. Glob. Environ. Chang. 18, 234–245. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2007.09.002
Etikan, I. (2016). Comparison of convenience sampling and purposive sampling. Am. J. Theor. Appl. Stat. 5:1. doi: 10.11648/j.ajtas.20160501.11
Feng, H., Wang, X., Duan, Y., Zhang, J., and Zhang, X. (2020). Applying blockchain technology to improve agri-food traceability: a review of development methods, benefits, and challenges. J. Cleaner Prod. 260:121031. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121031
George, W., and Al-Ansari, T. (2024). Roadmap for national adoption of blockchain technology towards securing the food system of Qatar. Sustain. For. 16:2956. doi: 10.3390/su16072956
Goedde, L., Katz, J., Menard, A., and Revellat, J. (2020). Agriculture’s connected future: how technology can yield new growth. Available at: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/agriculture/our-insights/agricultures-connected-future-howtechnology-can-yield-new-growth
Guo, Y., and Liang, C. (2016). Blockchain application and outlook in the banking industry. Financ. Innov. 2:24. doi: 10.1186/s40854-016-0034-9
Gupta, S., Raijah, P., Middlebrooks, E. H., Baruah, D., Carter, B. W., Burton, K. R., et al. (2018). Systematic review of the literature: best practices. Acad. Radiol. 25, 1481–1490. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2018.04.025
Ingram, J. (2011). A food systems approach to researching food security and its interactions with global environmental change. Food Secur. 3, 417–431. doi: 10.1007/s12571-011-0149-9
Khadivar, A., Nazarian, H., and Salemi, S. (2021). Modeling the factors affecting the adoption of mobile supply chain management in the food distribution industry. Int J Logist Syst Manag 1:1. doi: 10.1504/ijlsm.2021.10040905
Kirsten, J. F., and van Zyl, J. (1998). Defining small-scale farmers in the South African context. Agrekon 37, 551–562. doi: 10.1080/03031853.1998.9523530
Knorr, D., Froehling, A., Jaeger, H., Reineke, K., Schlueter, O., and Schoessler, K. (2011). Emerging technologies in food processing. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2, 203–235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.food.102308.124129
Lanzini, F., Ubacht, J., and de Greeff, J. (2021). Blockchain adoption factors for SMEs in supply chain management. J Supply Chain Manag Sci 2, 1–2. doi: 10.18757/jscms.2021.5624
Malik, S., Chadhar, M., Vatanasakdakul, S., and Chetty, M. (2021). Factors affecting the organizational adoption of blockchain technology: extending the technology–organization– environment (TOE) framework in the Australian context. Sustain. For. 13:9404. doi: 10.3390/su13169404
Mollier, L., Seyler, F., Chotte, J.-L., and Ringler, C. (2017). “End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture,” in A guide to SDG interactions: from science to implementation. Part two: End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture. eds. D. J. Griggs, M. Nilsson, A. Stevance, and D. McCollum (Paris, France: International Council for Science (ICSU)).
Nofer, M., Gomber, P., Hinz, O., and Schiereck, D. (2017). Blockchain. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 59, 183–187. doi: 10.1007/s12599-017-0467-3
Pienaar, L., and Traub, L., (2015). "Understanding the smallholder farmer in South Africa: towards a sustainable livelihoods classification," 2015 Conference, August 9–14, 2015, Milan, Italy 212633, International Association of Agricultural Economists.
Prashar, D., Jha, N., Jha, S., Lee, Y., and Joshi, G. P. (2020). Blockchain-based traceability and visibility for agricultural products: a decentralized way of ensuring food safety in India. Sustain. For. 12:3497. doi: 10.3390/SU12083497
Rambhia, V., Mehta, R., Shah, R., Mehta, V., and Patel, D. (2022). Blockchain – ICBC 2021. Conference Paper India. Springer
Rosario Oliveira Martins, M., Oliveira, T., and Fraga Martins, M. (2011). Literature review of information technology adoption models at firm level. Electron J Inf Syst Eval 14:110.
Shakhbulatov, D., Arora, A., Dong, Z., and Rojas-Cessa, R. (2019). Blockchain implementation for analysis of carbon footprint across the food supply chain. In Proceedings - 2019 2nd IEEE international conference on blockchain, blockchain 2019. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc. 546–551.
Sri Vigna Hema, V., and Manickavasagan, A. (2024). Blockchain implementation for food safety in supply chain: a review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 23:e70002. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.70002
Sulaiman, N., Yeatman, H., Russell, J., and Law, L. S. (2021). A food insecurity systematic review: experience from Malaysia. Nutrients 13, 1–41. doi: 10.3390/nu13030945
Taherdoost, H. (2022). A critical review of blockchain acceptance models- blockchain technology adoption frameworks and applications. Computers 11:24. doi: 10.3390/computers11020024
Thornton, P. K., Jones, P. G., Ericksen, P. J., and Challinor, A. J. (2011). Agriculture and food systems in sub-Saharan Africa in a 4°C+ world. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci 369, 117–136. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2010.0246
Vern, P., Panghal, A., Mor, R. S., and Kamble, S. S. (2024). Blockchain technology in the agri-food supply chain: a systematic literature review of opportunities and challenges. Manag Rev Quart. 74, 1–33. doi: 10.1007/s11301-023-00390-0
Vu, N., Ghadge, A., and Bourlakis, M. (2023). Blockchain adoption in food supply chains: a review and implementation framework. Prod. Plan. Control 34, 506–523. doi: 10.1080/09537287.2021.1939902
Keywords: food systems, digital food systems, food supply chain, blockchain technology, TOE framework, blockchain adoption, food insecurity
Citation: Mbadlisa G and Jokonya O (2024) Factors affecting the adoption of blockchain technologies in the food supply chain. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1497599. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1497599
Received: 17 September 2024; Accepted: 29 November 2024;
Published: 18 December 2024.
Edited by:
Andrew John Dougill, University of York, United KingdomReviewed by:
Larry C. Bates, Independent Researcher, Detroit, MI, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Mbadlisa and Jokonya. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Osden Jokonya, b2pva29ueWFAdXdjLmFjLnph
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.