- 1School of Life Sciences and Bioengineering, The Nelson Mandela African Institution of Science and Technology (NM-AIST), Arusha, Tanzania
- 2Department of Research and Innovation, TARI Selian, Arusha, Tanzania
This study assessed the efficacy of plant extracts as alternatives to synthetic pesticides for pest control and seed quality preservation in mungbean cultivation in northern Tanzania, specifically at TARI Selian and Miwaleni. The study employed a randomized complete block design. Four plants’ extracts—Tephrosia vogelii, Clutia abbsynica, Clausena anisata, and Lobelia gibelloa—were evaluated during the 2020 growing season (field) and 2021 storage period (storability). The study focused on their effects on insect pests (leaf beetles, thrips, aphids, whiteflies, and pod borers) and their ability to maintain seed quality during storage. C. anisata emerged as the most effective extract across all pests, demonstrating high suppression rates for thrips (3.4), aphids (3.22), whiteflies (3.4), and pod borers (2.7). In contrast, L. gibelloa was the least effective, with lower suppression rates for thrips (3.1) and aphids (3.1). Furthermore, botanical treatments significantly reduced pest damage in stored seeds, with T. vogelii and C. abbsynica showing superior performance in preserving seed weight and quality during storage. Seeds treated with T. vogelii had significantly fewer holes and lower weight loss compared to other treatments, indicating its effectiveness in both pest management and seed preservation. Conversely, L. gibelloa and C. anisata contributed to greater weight loss, particularly at higher application rates. The study demonstrates that plant extracts can offer a sustainable, eco-friendly alternative to synthetic pesticides, effectively controlling pests and preserving seed quality. These findings are crucial for improving mungbean production and storage, enhancing food security, and reducing reliance on chemical pesticides in diverse agro-ecological contexts. Future research should further explore the long-term ecological impacts and optimal application rates of these botanicals for integrated pest management and seed storage.
1 Introduction
Mungbean (Vigna radiata) is a crucial legume widely cultivated across Asia and increasingly in Africa and Latin America (Kohli et al., 2024). The global area for mungbean cultivation spans approximately 7.3 million hectares, with an average yield of 721 kg ha−1 (Nair and Schreinemachers, 2020). India and Myanmar together contribute 30% of the global production, totaling 5.3 million tons (Nair and Schreinemachers, 2020). Other major producers include China, Indonesia, Thailand, Kenya, and Tanzania (Nair and Schreinemachers, 2020). Its growing importance is attributed to its high nutritional value, economic advantages, and suitability for various cropping systems (Islam et al., 2024). The crop is particularly valued for its adaptability to different climatic conditions and its short growth cycle, which allows it to fit into diverse agricultural rotations (Liu et al., 2024).
Asia dominates mungbean production, with India, Myanmar, China, and Thailand being the leading producers (Kanishka et al., 2023; Ong et al., 2023). India is the largest producer, especially in states like Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, and Rajasthan, where mungbean is integral to both diet and crop rotation (Huppertz et al., 2023). Being the largest producer and consumer of mungbean, India contributes around 70% of global production (Somta et al., 2022). Myanmar ranks as the second-largest producer and a major exporter, thanks to its favorable climate and extensive farming practices (Raitzer et al., 2015; Khine et al., 2021). China also plays a significant role, with mungbean being widely used in Chinese cuisine and traditional medicine, thus bolstering domestic demand (Langyan et al., 2022; Samal et al., 2023). Thailand, while producing less than the top producers, is known for its high-quality mungbeans, primarily exported to neighboring countries and international markets (Farnworth et al., 2020; Win et al., 2022). In Africa, mungbean cultivation is on the rise, with Tanzania emerging as a leading producer (Birachi et al., 2021). The introduction of mungbean to African agriculture aims to diversify food sources, improve soil fertility, and enhance food security. The Tanzanian government, alongside NGOs, has promoted mungbean farming to address malnutrition and boost rural incomes (Gichohi-Wainaina et al., 2022; Pittore et al., 2024; Sultan et al., 2024). Despite this growth, global mungbean production remains below its potential due to factors like limited awareness, inadequate varieties, and insufficient agricultural extension services (Nadi, 2023; Sah et al., 2024). With enhanced investment and improved agronomic practices, the area under mungbean cultivation could expand significantly.
Mungbean is an important source of protein, vitamins, and minerals, making it vital for combating malnutrition, especially in regions with high rates of protein-energy malnutrition (Maitra et al., 2023). Its rapid growth and harvest cycle of 60–75 days provide a quick nutritional boost, appropriate for food security in developing countries (Muchomba et al., 2023; Dikr, 2023). Economically, mungbean farming benefits smallholder farmers by offering multiple harvests within a year, thereby ensuring a steady income. The rising global demand for mungbean in health-conscious markets further enhances export opportunities and farmers’ income (Kumar et al., 2023; Yong et al., 2024). Additionally, mungbean contributes to sustainable agriculture by fixing atmospheric nitrogen through symbiotic relationships with Rhizobium bacteria, thereby improving soil fertility and reducing the need for chemical fertilizers (Zheng et al., 2023; Yadav et al., 2024).
However, mungbean production faces several challenges, including pest infestations and diseases that significantly impact yield and quality. Field and storage pests such as bruchid beetles, aphids, and thrips pose serious threats, causing substantial losses and compromising seed quality (Choudhary et al., 2024). Diseases like powdery mildew and yellow mosaic virus also have the potential to devastate crops if not effectively managed (Dhaliwal et al., 2023; Sunani et al., 2024). Climatic stresses including drought, excessive rainfall, and temperature fluctuations, further affect plant growth and yield, highlighting the need for climate-resilient practices (Pratap et al., 2021; Chaudhary et al., 2022). Access to high-quality seeds and knowledge of optimal agronomic practices remain major constraints, particularly in developing regions, leading to lower yields and increased vulnerability to pests and diseases (Islam et al., 2024; Vaghefi et al., 2024; Sanderson, 2024; Legumes et al., 2024).
The global overuse of pesticides has become a pressing issue, contributing to numerous environmental, health, and economic challenges. Excessive pesticide application has led to pesticide resistance in pests, contamination of water and soil, and adverse effects on non-target organisms, including beneficial insects, wildlife, and human health (Ahmad et al., 2024; Kaur et al., 2024; Tudi et al., 2021). In many regions, particularly in developing countries, the reliance on chemical pesticides for pest management in agriculture continues to rise, driven by their immediate effectiveness and availability (Pathak et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2025). However, this unsustainable use raises serious concerns regarding long-term sustainability and food security (Wang et al., 2021). Research into alternative pest control measures, such as botanical extracts and biological pesticides, is increasingly important as a means of reducing dependence on synthetic chemicals (Ayilara et al., 2023; Lengai et al., 2020; Ngegba et al., 2022). This approach aligns with global efforts to promote sustainable agricultural practices and minimize the harmful impacts of pesticide overuse. For instance, Reddy et al. (2024) in their work on pesticide regulation and policies in India emphasize the urgent need for effective regulation and adoption of safer, alternative pest management strategies. Such research highlights the relevance of exploring natural alternatives to ensure a more environmentally friendly and sustainable approach to pest control in the agricultural sector.
Given these challenges, effective pest management is important for improving mungbean production. While traditional chemical pesticides are effective, they pose environmental and health risks, underscoring the need for sustainable alternatives. Botanical extracts, derived from plants with insecticidal properties, present a promising solution (Dassanayake et al., 2021). These extracts are eco-friendly, biodegradable, and generally safer for humans and non-target organisms compared to synthetic pesticides. Additionally, their complex mixtures of active compounds reduce the likelihood of pest resistance (Ngegba et al., 2022). Research into the efficacy of botanical extracts, such as neem, garlic, and pyrethrum, shows potential for managing mungbean pests effectively (Pumnuan et al., 2021; Rai and Jolly, 2024). Despite their promise, challenges such as variability in efficacy, limited availability, and lack of standardized formulations need to be addressed. Further research, development, and scaling up of production and distribution are necessary to overcome these hurdles (Jacquet et al., 2022; Souto et al., 2021). Therefore, overcoming the constraints on mungbean production through innovative pest management strategies, like botanical extracts, is essential for enhancing mungbean productivity and sustainability against field and postharvest losses. As research advances, these eco-friendly solutions could significantly impact mungbean cultivation, contributing to global food security and agricultural resilience.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Description of the study sites
The research was conducted at two important agricultural sites in northern Tanzania: the Selian Agricultural Research Institute (TARI Selian) in Arusha and the Miwaleni farm, managed by the Tropical Pesticides Research Institute (TPRI) in Moshi. TARI Selian is located in the Arumeru district of the Arusha region, at coordinates 03° 22’ S latitude and 40° 10′ E longitude, and is situated at an altitude of 1,378 meters above sea level. This site experiences a tropical highland climate with distinct wet and dry seasons, which is ideal for agricultural research and production. The average annual temperature is around 19.2°C, providing a relatively cool environment suitable for various crops. The area receives an average annual rainfall of 1,103 mm, primarily during the wet season from March to May, which is crucial for crop growth. The dry season, from June to October, is characterized by reduced rainfall and higher temperatures, requiring effective water management to maintain agricultural productivity. The soils at TARI Selian are primarily volcanic, known for their fertility and high organic matter content, making them ideal for crops like mungbean due to their loamy texture, good drainage, and moisture retention.
In contrast, the Miwaleni farm is located in the Moshi district of the Kilimanjaro region, at coordinates 03° 25′ 19.7” S latitude and 37° 26′ 59.0″ E longitude, and is at a lower altitude of 736 meters above sea level. Miwaleni has a unique microclimate with a moderate annual temperature of about 23°C, slightly warmer than TARI Selian. The area receives approximately 950 mm of rainfall annually, distributed in two rainy seasons, the long rains from March to May and the short rains from October to December. This bimodal rainfall pattern supports multiple planting and harvesting periods, enhancing agricultural productivity. The soils at Miwaleni are primarily alluvial, formed from volcanic ash and lava from Mount Kilimanjaro. These well-drained soils are rich in minerals and organic matter, ideal for high-yielding crops like mungbean. The soil texture varies from sandy loam to clay loam, each offering specific benefits in terms of water retention and aeration, which are crucial for healthy crop growth.
2.2 Experimental materials and preparation
The mungbean variety “Imara” used in this study was sourced from the Tanzania Agricultural Research Institute (TARI) Ilonga in Morogoro. This variety was selected for its adaptability to local conditions and its high yield potential, known for its reliability and quality. Alongside the mungbean seeds, botanical plant materials were collected from various locations in the Kilimanjaro region, including Same, Mwanga, Usangi, Kisangara, and Ugweno. These sites were chosen for their rich biodiversity and the presence of native plant species with recognized pesticidal and growth-promoting properties.
Following collection, fresh leaves of the selected botanical plants were carefully dried in the shade to preserve their active compounds. The dried leaves were then ground into a fine powder, which was mixed with water at various concentrations to create a 16-liter solution. The solution was allowed to soak overnight and was then filtered to eliminate particulate matter. This prepared plant extract solution was applied to the mungbean plots via spraying, with applications made at seven-day intervals throughout the growing season.
2.3 Experimentation
2.3.1 Field experiment
The study employed a randomized complete block design with three replications. The experiments utilized four types of insecticidal plants (i.e., Four plant extracts Tephrosia vogelii, Clutia abbsynica, Clausena anisata, and Lobelia gibelloa). The concentrations of botanical extracts used in the experiment were tested at four different application rates for each plant, namely 0, 0.1, 1, and 10%, with the corresponding weight equivalents in grams being 0, 0.1, 1, and 10 g for each botanical treatment. The botanicals were sprayed at seven-day intervals, starting from emergence and continuing until the plants reached maximum maturity, ready for harvest. However, the means of the results from the collected data were pooled based on the botanical type to facilitate comparisons across the different plant treatments. The research was conducted during the primary mungbean cropping season from March to August 2020, coinciding with the rainy season in the study areas. Figure 1 shows the trends in rainfall and temperature throughout the experimentation period.
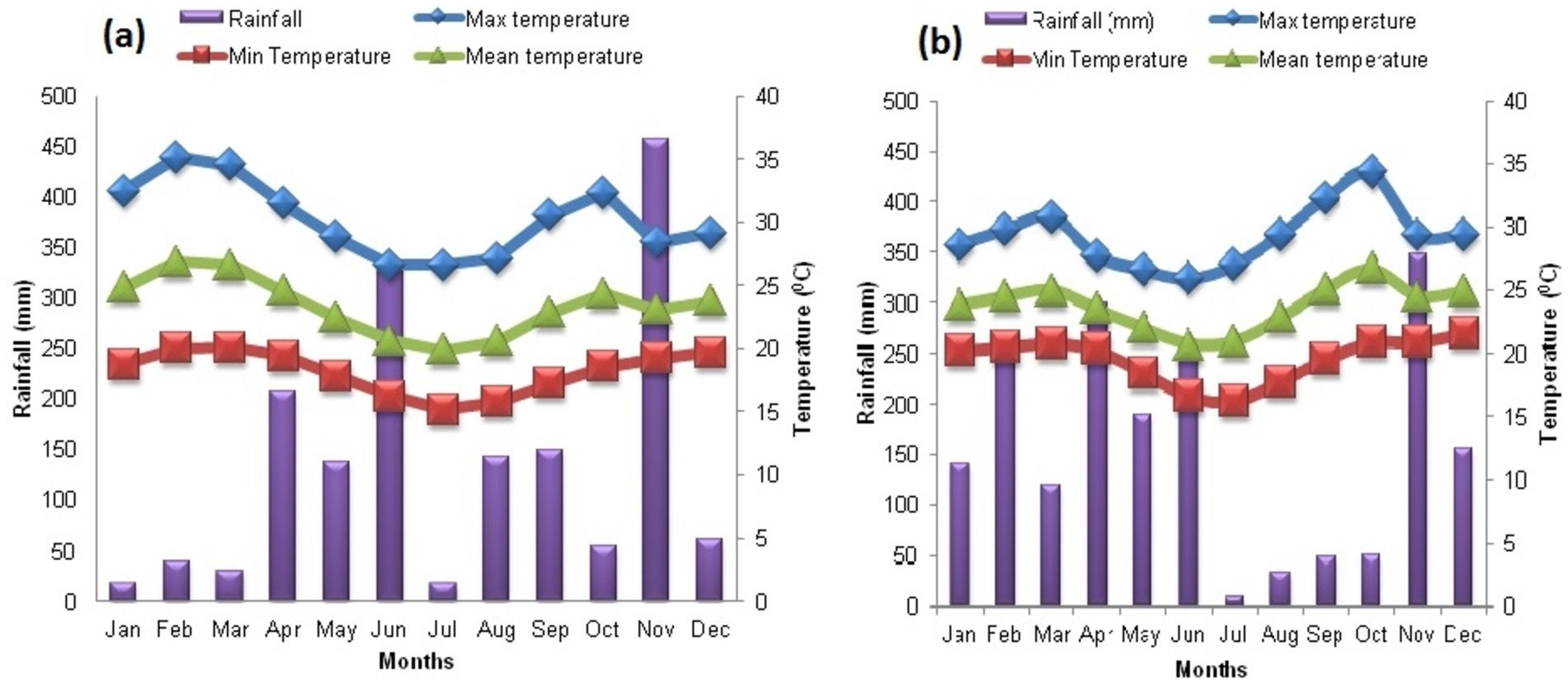
Figure 1. Climatic conditions recorded at the study sites, (A) Miwaleni and (B) TARI Selian, throughout the experimental period (January to December 2020).
Field preparations, including plowing and harrowing, were completed in March before planting. Each experimental plot measured 3 m by 3 m and was arranged with six rows. To minimize interference, plots were separated by 1 m, and replications were spaced 1.5 m apart. Planting followed recommended spacing guidelines: rows were set 50 cm apart, and seeds were sown 20 cm apart within each row. Each hill contained two seeds, resulting in 30 plants per row and 180 plants per plot. This planting density translated to approximately 200,000 plants per hectare. For data collection, four designated rows within each plot were monitored.
The study collected data on pest populations and mungbean plant growth and yield to evaluate the effectiveness of different plant extracts. Pest counts were recorded for five types of insects: leaf beetles, thrips, aphids, whiteflies, and pod borers. In addition to pest data, the study assessed plant growth and yield parameters to understand the overall effects of the plant extracts on mungbean productivity. Key growth metrics included the number of days to 50% maturity, which indicated how quickly the plants reached maturity under different treatments. Plant height was measured to gauge the health and vigor of the plants. The number of pods per plant provided insights into the plant’s productivity, while the seed yield per pod and the 100-seed weight reflected seed development and quality. Furthermore, seed yield was measured to evaluate the overall productivity of the crop.
2.3.2 Seed storage
The study was designed to evaluate the effectiveness of the same botanical treatments and application rates (used in the field experiment) in preserving seed quality over time. Besides these botanicals, the chemical pesticide Actelic Shumba dust was used as a positive control. In addition, a control group of non-treated seeds was included to establish a baseline for comparison. Each treatment (except positive control) was applied at three different application rates: control, 250, and 500 g. At the start of the experiment, the moisture content of the mungbean seeds was standardized at 13% across all groups to ensure uniform conditions. The initial seed weight was recorded for each group by weighing 500 seeds, and the seeds were examined for their initial condition. The seeds were then stored under controlled conditions, with periodic assessments to evaluate the impact of the treatments on seed quality. The parameters measured during the experiment included seed damage, the average number of holes per seed, and weight changes throughout the storage period.
Seed damage was assessed by calculating the percentage of damaged seeds, while the average number of holes per seed was recorded as an indicator of pest-related damage or other forms of degradation. After the storage period, the seeds were reweighed to determine changes in weight (Equation 1), and the percentage weight loss was also computed (Equation 2).
2.4 Statistical data analysis
A two way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed with sites considered as primary factors, while botanical treatments were analyzed as secondary factors. In addition, the study employed multivariate Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to evaluate the effects of botanical extracts on insect diversity, mungbean performance, and storage pests across two distinct sites: TARI-Selian and Miwaleni. PCA facilitated the identification of key components that explained the variance in plant growth, insect populations, and pest parameters, offering a detailed understanding of site-specific impacts. The analysis also involved calculating eigenvalues and variance percentages for each PC to assess the significance of botanical treatments and their interactions with environmental factors. This approach allowed for a clear identification of the most influential variables, such as seed damage, insect populations, and yield components. ANOVA was conducted using GenStat software (20th Edition), and PCA was performed with Past4.03.exe software.
To analyze the data on seed storage quality, a two-way ANOVA was conducted to evaluate the effects of both the botanical treatments, application rates and their interaction on seed quality over time. The replicate means for the data from seed storage quality assessments, including the percentage of damaged seeds, average number of holes per seed, and weight changes, were pooled based on the botanical treatment types for comparison. Significant main effects and interactions were tested, and post-hoc Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference (HSD) test was used to determine specific differences between treatment groups. The significance level for all statistical tests was set at p ≤ 0.05. These analyses were performed using Genstat software (20th Edition).
3 Results
3.1 Field work
3.1.1 Influence of plant extracts on field insects of mungbean
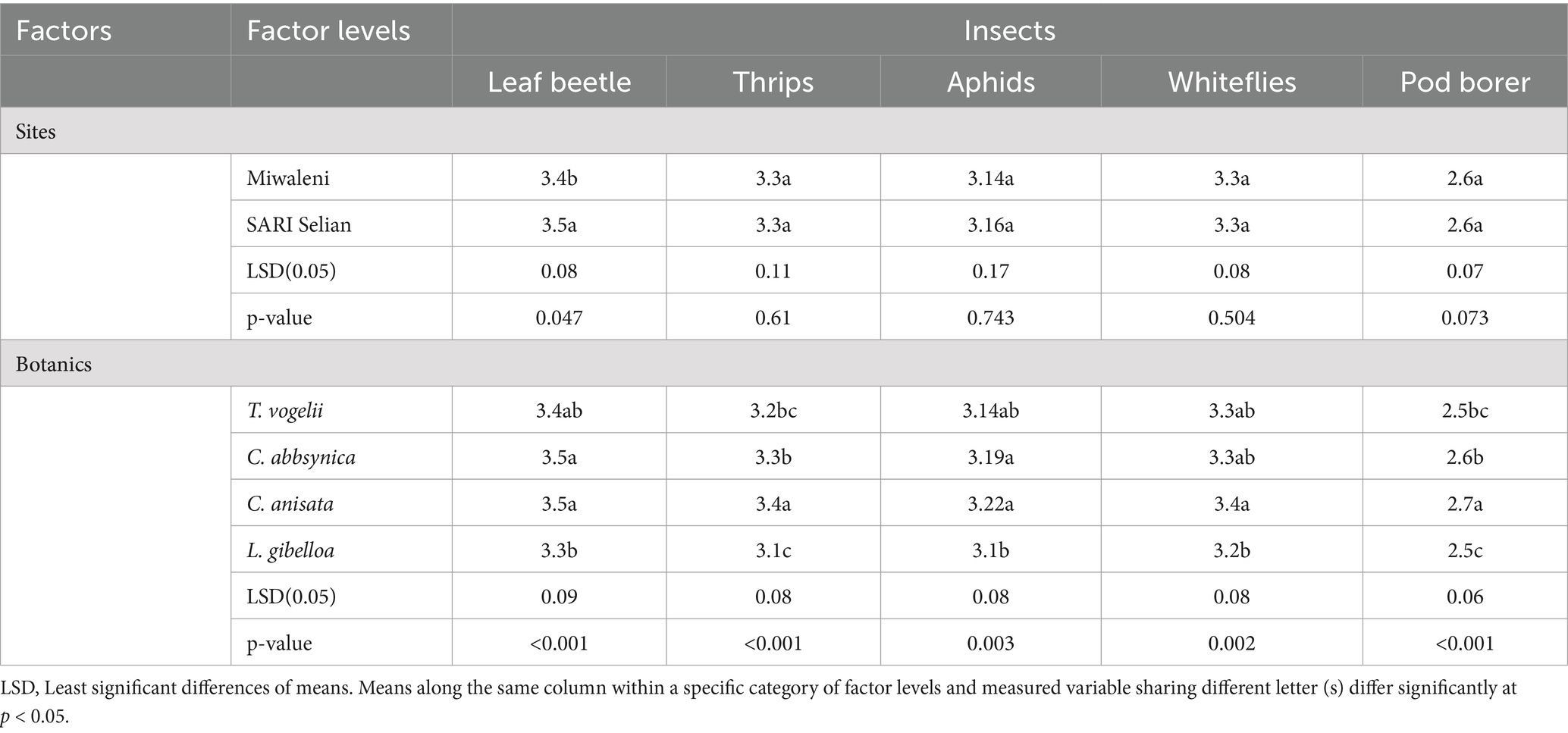
The results indicated significant variations in the effectiveness of different plant extracts on mungbean production, particularly regarding insect pest management and post-harvest losses (Table 1). At the Miwaleni site, the diversity of leaf beetles was recorded as 3.4, while at the SARI Selian site, it was slightly higher at 3.5. For other pests such as thrips, aphids, whiteflies, and pod borer, the diversity values were similar across both sites. Statistical analysis showed a significant (p = 0.047) difference in leaf beetle diversity between sites. In contrast, the diversity for other pests was not significantly different between the sites (p-values ranging from 0.504 to 0.743). Regarding plant extracts, C. anisata resulted in the highest diversity across all pest categories, with values such as 3.5 for leaf beetles, 3.4 for thrips and whiteflies. This contrasted with L. gibelloa, which had the lowest diversity values, such as 3.3 for leaf beetles and 3.1 for thrips, suggesting it was more effective in managing pest populations. The differences among these plant extracts were highly significant (p < 0.001).
The Principal Components Analysis (PCA) explored the impact of plant extracts on mungbean production parameters and pest presence (Table 2). The first principal component (PC 1) explained 99.51% of the variance at the Miwaleni site and 88.67% at the SARI Selian site. This component revealed that extracts like C. anisata and C. abbsynica had strong associations with variations in parameters such as seed yield per hectare, which was positively correlated (factor score close to 1.00) with PC 1. C. anisata had scores of −72.28 at Miwaleni and − 100.96 at SARI Selian for PC 1, indicating a strong influence on the variance in mungbean production and pest presence.
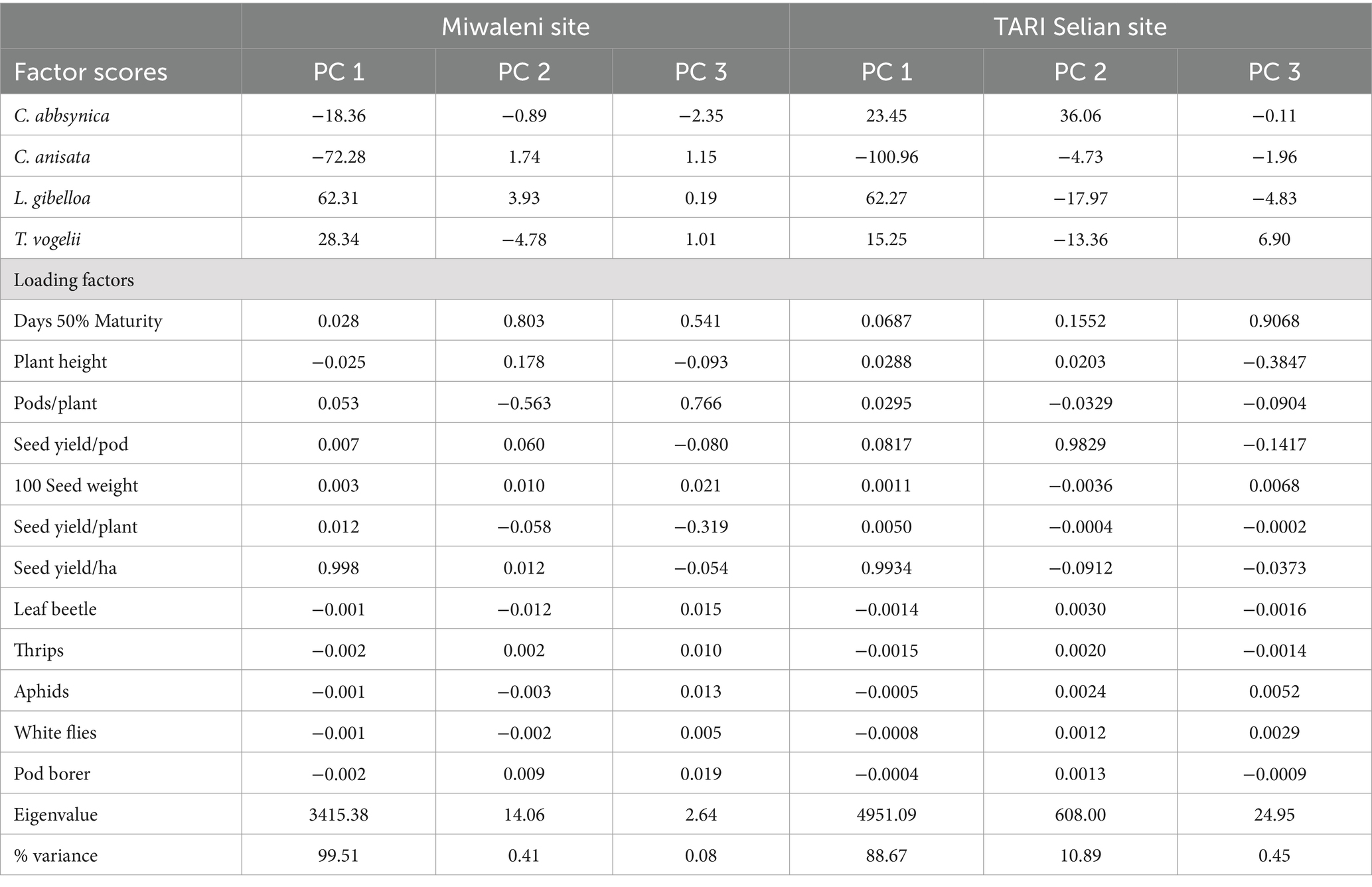
Table 2. The principle components (PCs) of plant extracts, measured parameters in mungbean plants, and field insect pests in Miwaleni and TARI Selian sites.
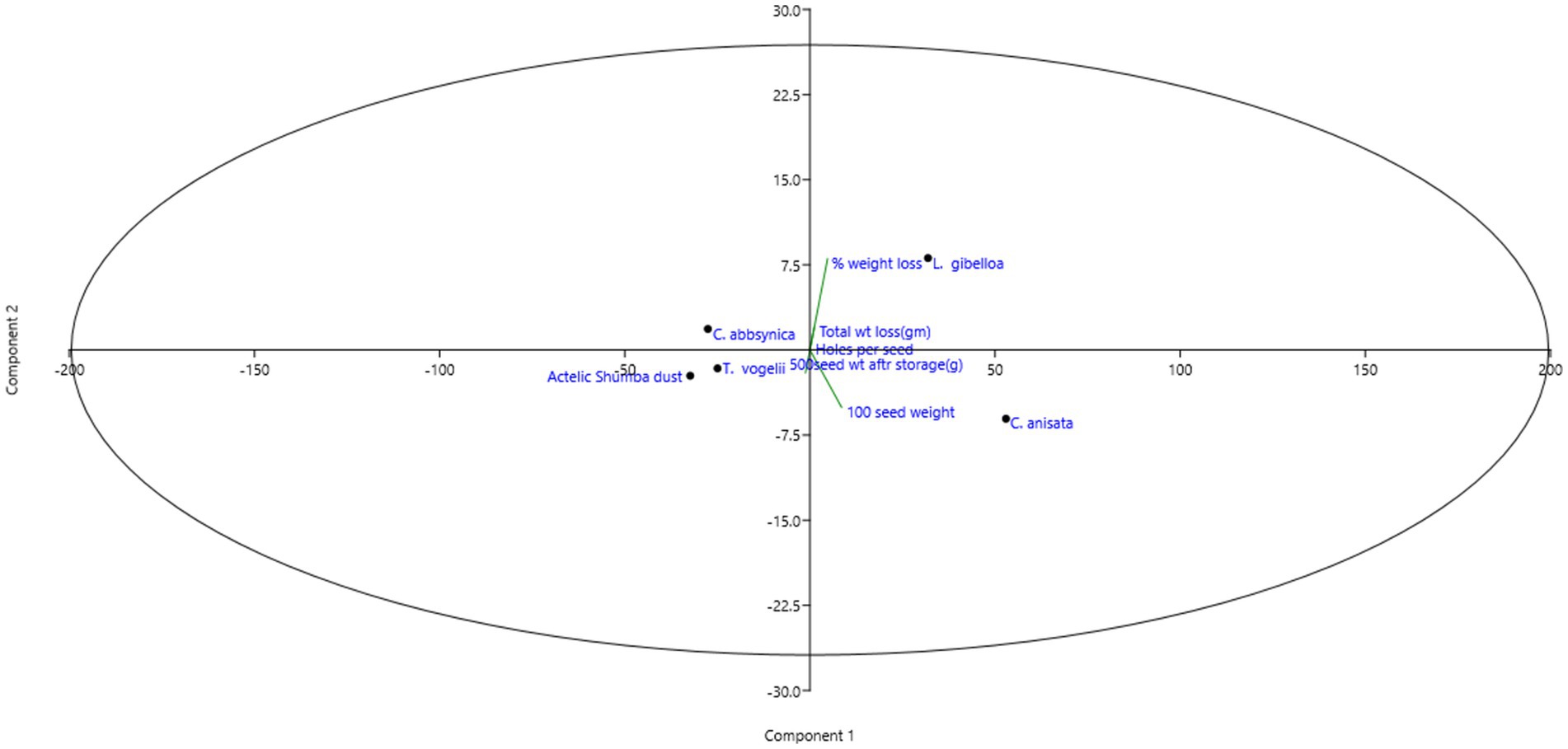
The PC 1 captures the vast majority of the variance in the data, accounting for 98.217% of it, indicating that it is the dominant factor in explaining the variation in mungbean postharvest losses (Table 3). Factors such as T. vogelii and Actelic Shumba dust, with negative scores on PC 1, are associated with lower postharvest losses, suggesting these factors mitigate damage or losses in mungbean grains. Conversely, factors like C. anisata and L. gibelloa, which have positive scores on PC 1, are linked to higher postharvest losses. This is consistent with the factor loadings showing that variables such as seed damage percentage and total weight loss are strongly associated with PC 1, indicating that greater seed damage and higher weight loss correlate with higher values on this component. The scatter plot in Figure 2 would likely demonstrate this pattern by clustering factors with high PC 1 scores in areas representing higher postharvest losses, while factors with negative PC 1 scores appear in regions with lower losses.
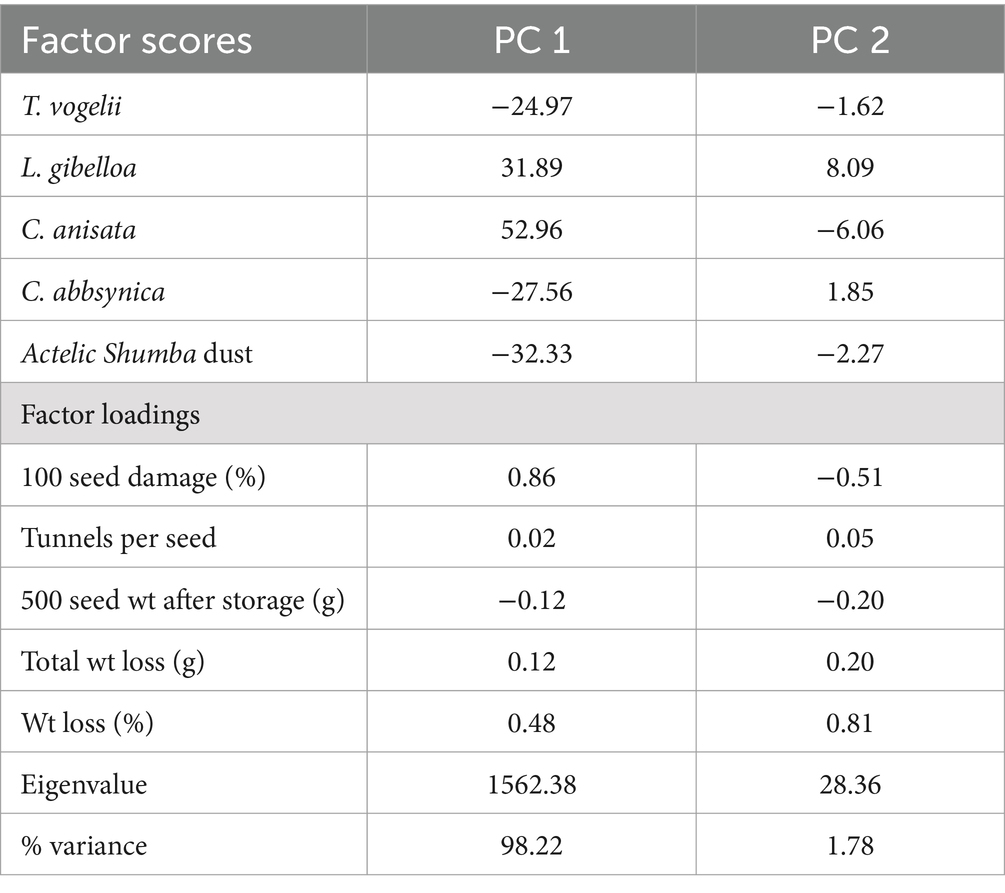
Table 3. The principle components (PCs) of plant extracts, measured parameters in mungbean plants, and post-harvest losses of mungbean grains.
Although PC 2 explains only 1.7827% of the variance, it still reflects significant relationships, particularly regarding weight loss percentage, which is more closely associated with PC 2. Factors that positively influence PC 2, such as weight loss percentage, would be positioned in regions of the scatter plot that correspond to higher PC 2 values. Overall, managing postharvest losses in mungbean grains should focus on factors influencing PC 1 due to its substantial impact, with PC 2 providing additional, albeit less dominant, insights into weight loss.
3.1.2 Relationship (correlations) among parameters involved in the study
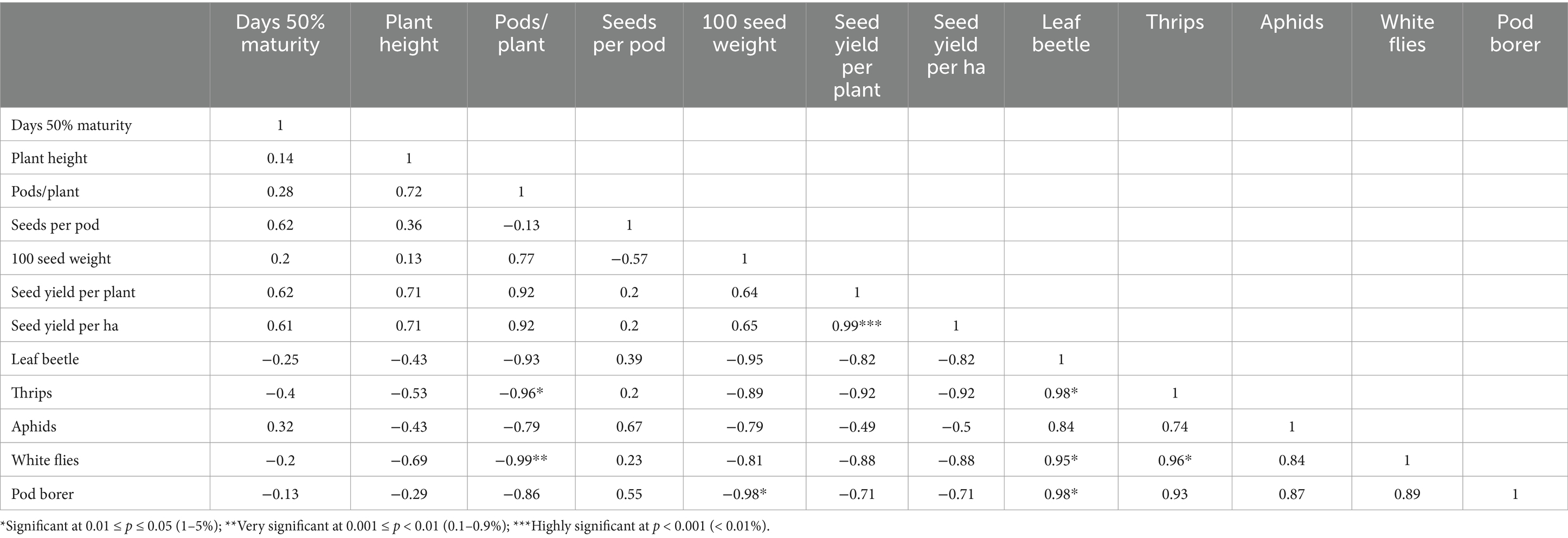
The correlation analysis revealed several significant relationships among mungbean parameters at both TARI-Selian and Miwaleni sites. At the TARI-Selian site, the analysis showed that days to 50% maturity was positively correlated with seeds per pod and seed yield per plant (r = 0.62), and seed yield per hectare (r = 0.61). This indicated that a longer period to reach 50% maturity was associated with a higher number of seeds per pod and increased seed yield. Conversely, days to maturity had weak negative correlations with leaf beetle (r = −0.25), thrips (r = −0.40), and whiteflies (r = −0.20), suggesting that extended maturity times were linked to lower pest infestations, though these correlations were not very strong.
Plant height showed strong positive correlations with pods per plant (r = 0.72) and seed yield per plant (r = 0.71), indicating that taller plants tended to produce more pods and higher seed yields. However, taller plants were also associated with lower pest pressures, as evidenced by strong negative correlations with leaf beetle and aphids (r = −0.43) and thrips (r = −0.53). The number of pods per plant was strongly positively correlated with seeds per pod (r = 0.72) and 100 seed weight (r = 0.77), suggesting that more pods per plant were related to higher seed weight and seed yield. It also had very strong negative correlations with pests such as leaf beetle (r = −0.93), thrips (r = −0.96), and whiteflies (r = −0.99), indicating that more pods per plant were associated with fewer pest infestations.
Seeds per pod was positively correlated with 100 seed weight (r = 0.85) and seed yield per ha (r = 0.84), showing that a higher number of seeds per pod was linked to greater seed weight and yield. Additionally, seeds per pod had very strong negative correlations with leaf beetle (r = −0.95), thrips (r = −0.83), and aphids (r = −0.94), suggesting that an increased number of seeds per pod was associated with fewer pest problems. 100 seed weight demonstrated a strong positive correlation with seed yield per ha (r = 0.96), indicating that greater seed weight corresponded to higher yield per hectare. This parameter also showed strong negative correlations with leaf beetle (r = −0.71), thrips (r = −0.91), and whiteflies (r = −0.95), suggesting that heavier seeds were associated with reduced pest infestations. Seed yield per plant was strongly positively correlated with seed yield per ha (r = 0.77), reflecting that higher yields per plant contributed to greater yields per hectare. It also had strong negative correlations with leaf beetle (r = −0.56), thrips (r = −0.86), and aphids (r = −0.85), indicating that higher seed yields per plant were linked to fewer pests.
At the Miwaleni site, days to 50% maturity had moderate positive correlations with seeds per pod (r = 0.72) and 100 seed weight (r = 0.66). However, it had a negligible correlation with seed yield per plant (r = 0.001), suggesting that maturity duration had little effect on plant yield at this site. This parameter also showed a strong negative correlation with leaf beetle (r = −0.78), indicating that longer maturity periods were associated with fewer leaf beetles. Plant height was strongly negatively correlated with pods per plant (r = −0.96) and seed yield per ha (r = −0.90), suggesting that taller plants produced fewer pods and had lower yields per hectare. However, plant height had strong positive correlations with thrips (r = 0.91) and whiteflies (r = 0.85), indicating that taller plants were more susceptible to these pests.
Pods per plant was strongly positively correlated with 100 seed weight (r = 0.70) and seed yield per ha (r = 0.78), reflecting that an increase in pods per plant contributed to higher seed weight and yield per hectare. Additionally, pods per plant had strong negative correlations with thrips (r = −0.78) and pod borer (r = −0.80), suggesting that more pods were associated with fewer pest infestations. Seeds per pod had strong positive correlations with 100 seed weight (r = 0.85) and seed yield per ha (r = 0.84), showing that an increase in seeds per pod was linked to higher seed weight and yield. It also demonstrated very strong negative correlations with leaf beetle (r = −0.97), aphids (r = −0.94), and whiteflies (r = −0.90), indicating that a higher number of seeds per pod was associated with fewer pest problems.
Result of 100 seed weight was very strongly positively correlated with seed yield per ha (r = 0.96), suggesting that heavier seeds led to greater yields per hectare. This parameter also exhibited strong negative correlations with leaf beetle (r = −0.71), thrips (r = −0.91), and whiteflies (r = −0.95), indicating that higher seed weight was related to fewer pest infestations. Seed yield per plant had a strong positive correlation with seed yield per ha (r = 0.77), reinforcing the direct relationship between yield per plant and yield per hectare. It also showed strong negative correlations with leaf beetle (r = −0.56), thrips (r = −0.86), and aphids (r = −0.85), suggesting that higher yields per plant were associated with reduced pest problems (Tables 4, 5).
3.2 Storage quality of mungbean seeds
The storage quality of mungbean seeds was significantly influenced by the type of botanical treatment, application rates, and their interactions, as shown in Tables 6–8. These analyses provide key insights into the effectiveness of various botanicals in protecting seeds from pest damage, weight loss, and deterioration during storage.
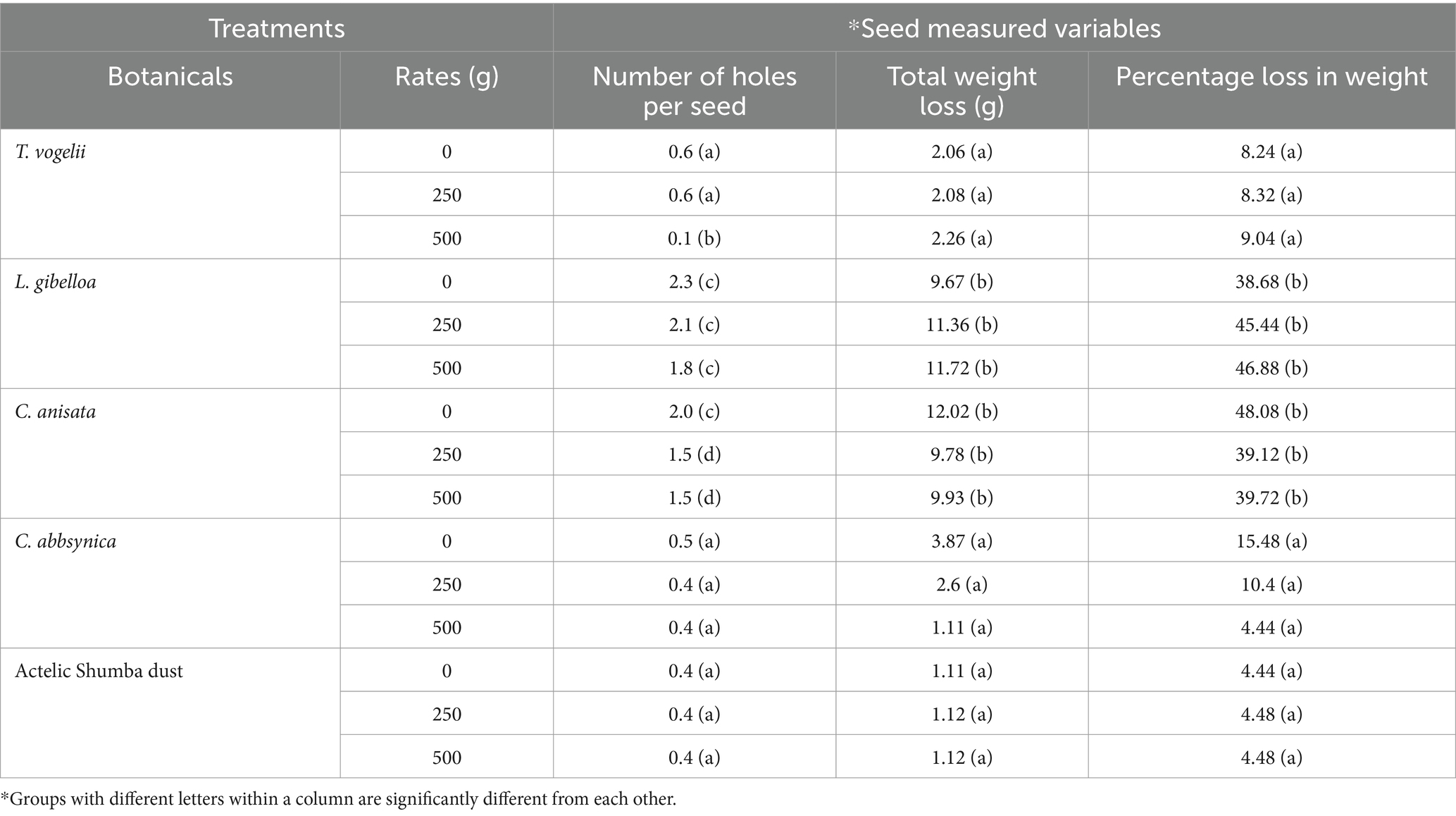
Table 6. Effect of botanicals, application rates and their interactions on mungbean seed storage quality.

Table 7. Post-hoc analysis (Tukey’s HSD) for number of holes per seed, total weight loss, and percentage weight loss by botanical treatment and application rate.
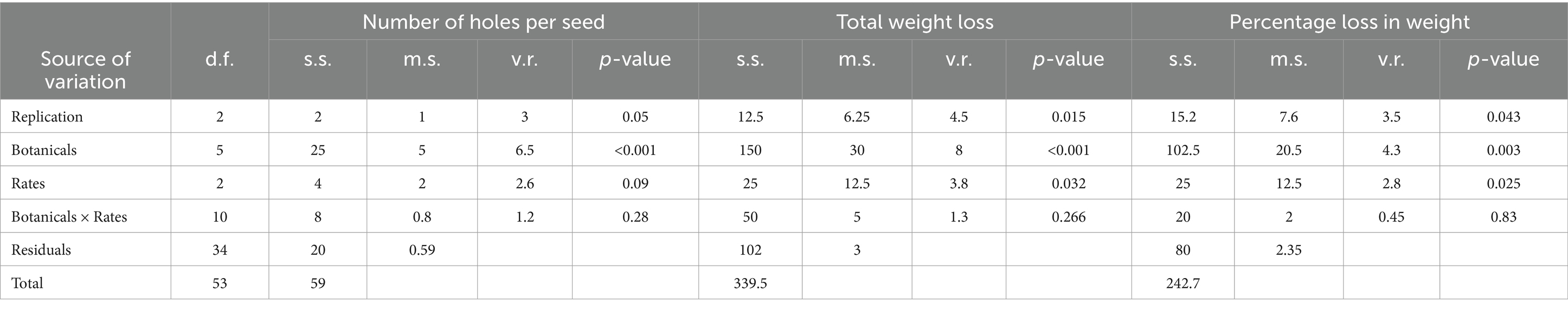
Table 8. ANOVA for number of holes per seed, total weight loss, and percentage loss in weight, showing the effects of replication, botanicals, application rates, and their interactions.
Number of holes per seed – the botanical treatments had a marked effect on pest infestation. Seeds treated with T. vogelii and C. abbsynica had significantly fewer holes per seed (0.6 and 0.5, respectively) compared to other treatments, indicating superior protection against pest damage. Conversely, untreated seeds exhibited the highest number of holes (4.0), highlighting the necessity of botanical treatments to mitigate pest-related damage. The post-hoc analysis in Table 7 revealed significant differences between treatments, such as the comparison between untreated seed (0 g), where T. vogelii showed significantly fewer holes. This highlights the greater efficacy of T. vogelii in reducing pest damage compared to other botanicals, including L. gibelloa and C. anisata.
The total weight loss of seeds was also strongly influenced by the botanical treatments. L. gibelloa (500 g) and untreated seed (0 g) resulted in the highest weight losses, with L. gibelloa showing 11.72 g and C. anisata 12.02 g. These botanicals likely contributed to greater seed deterioration, possibly due to both pest damage and environmental factors. On the other hand, untreated seed (0 g) exhibited the lowest weight losses (2.06–3.87 g), suggesting that these treatments were more effective at preserving seed weight. Notably, the Actelic Shumba dust treatment, which served as a positive control, also demonstrated relatively low weight loss (1.12 g across all rates), indicating its dual role in both pest control and minimizing seed deterioration. Non-treated seeds, as expected, showed the highest total weight loss (14.14 g), emphasizing the crucial role of protective treatments in maintaining seed quality.
The percentage weight loss further reflected the protective effects of the botanicals. L. gibelloa (500 g) exhibited the highest percentage loss (46.88%), followed by L. gibelloa (250 g) (45.44%) and C. anisata (0 g) (48.08%). These results suggest that while these botanicals were somewhat effective in pest management, they also contributed to higher seed deterioration. In contrast, T. vogelii and C. abbsynica resulted in significantly lower percentage losses (8.24 and 15.48%, respectively), highlighting their effectiveness in preserving seed quality while offering pest protection. The Actelic Shumba dust treatment showed a low percentage weight loss of 4.44%, supporting its role as an effective pest control treatment. Non-treated seeds exhibited the highest percentage loss (56.72%), further emphasizing the importance of using protective treatments during seed storage.
The post-hoc analysis (Table 7) provided deeper insights into the statistical significance of these findings. For example, T. vogelii was significantly different from L. gibelloa, C. anisata, and non-treated seeds in terms of the number of holes per seed, with T. vogelii showing fewer holes. In terms of total weight loss, L. gibelloa (500 g) was significantly higher than both Actelic Shumba dust (500 g) and non-treated seeds, highlighting its contribution to greater weight loss. For percentage weight loss, significant differences were observed between L. gibelloa (250 g) and Actelic Shumba dust (0 g), with L. gibelloa showing a much higher percentage loss. This suggests that both the type of botanical and the application rate play crucial roles in determining seed quality outcomes.
These findings suggest that T. vogelii and C. abbsynica are the most effective treatments for preserving seed quality during storage, with minimal pest infestation and weight loss. They provide valuable options for improving mungbean storage, especially in regions where pest pressure is a significant concern. In contrast, L. gibelloa and C. anisata, especially at higher application rates, may be less effective, as they resulted in higher seed weight loss and pest damage. The post-hoc analysis further emphasizes the importance of treatment choice and application rate, highlighting the need for careful selection based on the desired outcome in seed preservation. The significant differences between treatments also underline the importance of integrated pest management strategies, where botanicals can be combined with other methods to optimize seed storage quality.
4 Discussion
4.1 Seed storage-based findings
The storage quality of mungbean seeds is significantly influenced by the application of botanical treatments, which play a vital role in reducing pest damage, preventing weight loss, and maintaining seed viability. The results clearly show that T. vogelii and C. abbsynica are the most effective treatments for preserving seed quality during storage. These botanicals provided significant protection against pest infestations, as evidenced by the considerably lower number of holes per seed compared to other treatments, including untreated seeds. Both botanicals exhibited strong pest-repellent properties among others, which is critical to mitigating the harmful impacts of storage pests.
The reduced pest damage observed in seeds treated with T. vogelii suggests that this botanical has particularly effective pest control properties, making it a suitable option for preserving seed quality. This result is consistent with findings by Siame et al. (2019), who demonstrated that T. vogelii is effective against ticks on naturally infested cattle in the field condition. In our study, the lower number of holes per seed in T. vogelii-treated samples implies that this botanical helps reduce pest infestation, which can otherwise lead to significant seed loss. These results align with previous findings on the insecticidal properties of T. vogelii (Mkindi et al., 2019; Nenotek and Ludji, 2020; Zhang et al., 2020), further supporting its potential as an eco-friendly alternative to chemical insecticides in seed preservation. The lower infestation rates in seeds treated with T. vogelii also indicate that it can effectively reduce the frequency of pest-related seed loss, improving the overall quality of stored mungbean seeds.
In contrast, other botanicals such as L. gibelloa and C. anisata showed less favorable outcomes, particularly when applied at higher rates. These botanicals contributed to greater seed deterioration, as reflected by higher weight loss and pest damage. L. gibelloa, in particular, led to significant weight losses, which could be attributed to either its phytotoxic effects or its inability to adequately control pests at the tested application rates. Similar findings were observed by other researchers using botanical extracts. A study by Rys and Skoczowski (2021) highlighted that botanical extracts with high allopathic potential, such as Salvia officinalis (sage) and Helianthus annuus (sunflower), inhibited weed growth but also affected the germination and metabolic processes of crops like Sinapis alba (white mustard) and Brassica napus (oilseed rape), suggesting the need for careful selection of extracts to avoid crop damage. Ndebugri et al. (2024) found that botanical extracts, including neem seed powder and rice husk powder, effectively controlled Sitophilus zeamais (maize weevil) in stored maize, with rice husk powder achieving 85% mortality, offering an eco-friendly option for post-harvest pest control. Adesina and Aderibigbe (2021) demonstrated that Secamone afzelii extracts reduced Rhyzopertha dominica (lesser grain borer) infestation and weight loss in stored wheat, without affecting germination, indicating their potential as natural grain protectants. These studies collectively show the efficacy of botanical extracts in pest management and seed preservation, providing sustainable alternatives to synthetic pesticides. However, their impact on crops requires careful evaluation to ensure effective and safe use.
Furthermore, C. anisata while somewhat effective in pest management, also resulted in higher weight loss, suggesting that its protective effect may not be as robust as that of T. vogelii and C. abbsynica. The use of L. gibelloa, especially at higher doses, may require caution, as it could cause unintended damage to the seeds, highlighting the importance of optimizing application rates for effective pest control without compromising seed quality.
The positive control treatment, Actelic Shumba dust, also demonstrated low weight loss, which is consistent with studies by Idrees et al. (2022) and Mubayiwa et al. (2021), who found that synthetic insecticides are effective in controlling storage pests and preserving seed quality. However, the concern with using such chemicals is their environmental impact and potential health risks. As a result, the use of botanicals like T. vogelii and C. abbsynica provides a sustainable and safer alternative to conventional insecticides. Idrees et al. (2022) found that broflanilide and abamectin were the most toxic insecticides against Spodoptera frugiperda larvae, with the highest toxicity indices of 100 and 78.29%, respectively. These insecticides were followed by cypermethrin and bifenthrin. While synthetic insecticides were effective in controlling the fall armyworm, their use poses health and environmental risks, including potential contamination of soil and water, as well as adverse effects on non-target organisms. These drawbacks highlight the need for further research into safer, more sustainable pest control methods, such as biopesticides or integrated pest management strategies.
Mubayiwa et al. (2021) highlighted that hermetic storage technologies, such as Purdue Improved Crop Storage bags, GrainPro Super Grainbags, and metal silos, were significantly more effective than synthetic pesticide treatments in preventing grain damage, weight loss, and insect infestations in sorghum stored under hot, arid conditions. Hermetic storage resulted in less than 3% weight loss, while pesticide-based treatments caused greater losses. Importantly, the use of hermetic storage avoids the health risks associated with synthetic pesticide exposure to both humans and the environment. These findings demonstrate that hermetic storage is a more sustainable and eco-friendly alternative, providing a safer option for smallholder farmers in arid regions while enhancing food security.
However, the findings emphasize the importance of selecting the right botanical treatment and applying it at the appropriate rate. While T. vogelii and C. abbsynica showed promising results, botanicals like L. gibelloa and C. anisata may be less effective, especially at higher doses, due to their potential negative impact on seed quality. Similar results were reported by Ogbonnaya et al. (2022), who found that excessive application rates of certain botanicals caused seed phytotoxicity, leading to reduced seed viability. Ogbonnaya et al. (2022) found that botanical insecticides, including azadirachtin, myristicin, and α-humulene, effectively protected cowpea seeds from Callosobruchus maculatus with lower phytotoxicity than chlorpyrifos. Seeds treated with botanical insecticides showed less seed damage, as indicated by lower electrical conductivity of leachate and reduced malondialdehyde levels. Moreover, fewer embryos were damaged in treated seeds. These botanicals offer an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic insecticides, although varietal sensitivity should guide their use for optimal seed protection. It is essential to determine optimal application rates for each botanical to achieve effective pest control while preserving seed integrity. This calls for further research to optimize the concentrations and formulations of botanical treatments, ensuring their maximum efficacy and minimal side effects on seed quality.
The findings provide valuable insights for improving mungbean seed storage, particularly for smallholder and commercial farming systems. The use of T. vogelii and C. abbsynica as natural alternatives to synthetic pesticides offers an environmentally friendly and sustainable approach to pest management. These botanicals can be applied in various ways, such as dusting, coating, or spraying, depending on local conditions. Combining them with other pest control strategies, including proper seed handling, storage conditions, and sanitation, can further enhance seed storage effectiveness. Particularly in regions with long storage periods and high pest pressure, T. vogelii and C. abbsynica can be integral components of integrated pest management (IPM) strategies. These botanicals help reduce reliance on chemical pesticides, which are costly, harmful to the environment, and pose health risks. The reduced weight loss and pest damage observed in treated seeds indicate that T. vogelii and C. abbsynica can help maintain seed quality, ensuring higher germination rates and seed viability.
Farmers can improve seed storage by integrating these botanical treatments into a broader strategy to reduce pest damage, minimize weight loss, and extend seed viability. This approach not only reduces post-harvest losses but also lessens environmental contamination caused by chemical pesticides. Additionally, T. vogelii and C. abbsynica could be valuable in organic farming systems, where synthetic chemicals are often restricted or undesirable.
4.2 Field-based findings
The study elucidates the complex interactions between environmental conditions, botanical treatments, and pest diversity in mungbean cultivation. Significant differences in insect diversity between TARI Selian and Miwaleni show the influence of local climatic and soil conditions on pest populations. The effectiveness of various plant extracts in controlling pest populations varied notably between the sites. C. anisata was particularly effective against a broad range of insects, including thrips, aphids, and whiteflies, indicating its potential as a key component in integrated pest management (IPM) strategies (Tomi et al., 2019; Liao et al., 2023). The significant interaction between site and botanical treatments suggests that the efficacy of these extracts is influenced by environmental conditions. For instance, C. anisata showed high effectiveness at TARI Selian, while T. vogelii performed better at Miwaleni (Smith et al., 2021). This variability underscores the necessity for pest management approaches tailored to specific agro-ecological contexts (Jabran et al., 2018).
Robust statistical analyses, including PCA, provided valuable insights into the significant effects of site, botanical treatments, and their interactions on insect diversity (Johnson et al., 2021). These findings align with the principles of IPM, which advocate for diverse control methods adapted to local conditions (Gurr et al., 2017). Data highlight the importance of site-specific strategies and how different factors and their interactions influence pest populations. For instance, the interaction between site and botanical treatments, as indicated by a p-value of 0.001 for pod borer, reveals that certain treatments may be more effective in specific environments (Nguyen et al., 2022). Variance analysis further demonstrated the significant impact of botanical treatments on pest populations, with an F probability for thrips of <0.001 indicating a highly significant effect (Harrison and Davis, 2023).
The implications for sustainable agriculture are profound. Plant extracts offer a promising alternative to synthetic pesticides, reducing chemical loads in the environment and minimizing harm to non-target organisms (Benbrook, 2021; Wilkins et al., 2019). Incorporating effective botanicals like C. anisata into pest management strategies can enhance crop protection while maintaining ecological balance (Li et al., 2022). Moreover, the study revealed that botanical extracts not only manage pests but also improve the storability of mungbean seeds by reducing damage and weight loss during storage (Jin et al., 2023). Notably, T. vogelii was found to be comparable in effectiveness to Actitelic Shumba, a synthetic chemical, in managing postharvest losses of mungbean grains. This comparison highlights the potential of T. vogelii as a viable alternative to conventional chemical treatments for postharvest pest control.
This dual benefit shows the comprehensive value of botanical extracts in both field and post-harvest management. Future research should focus on elucidating the mechanisms behind the differential effectiveness of plant extracts and their long-term impacts on soil health and non-target organisms (Cheng and Cheng, 2015). The knowledge gained from this study will be instrumental in guiding resilient and sustainable farming practices (Wang et al., 2023).
4.3 Theory of change for scaling botanicals in mungbean pest control and storage
The Theory of Change (ToC) framework for scaling botanical extracts like T. vogelii and C. abbsynica for mungbean pest management and seed storage focuses on expanding their adoption among smallholder and commercial farmers (Figure 3). The objective is to reduce dependency on synthetic pesticides, improve pest control in the field, and enhance seed storability, contributing to better food security and environmental sustainability.
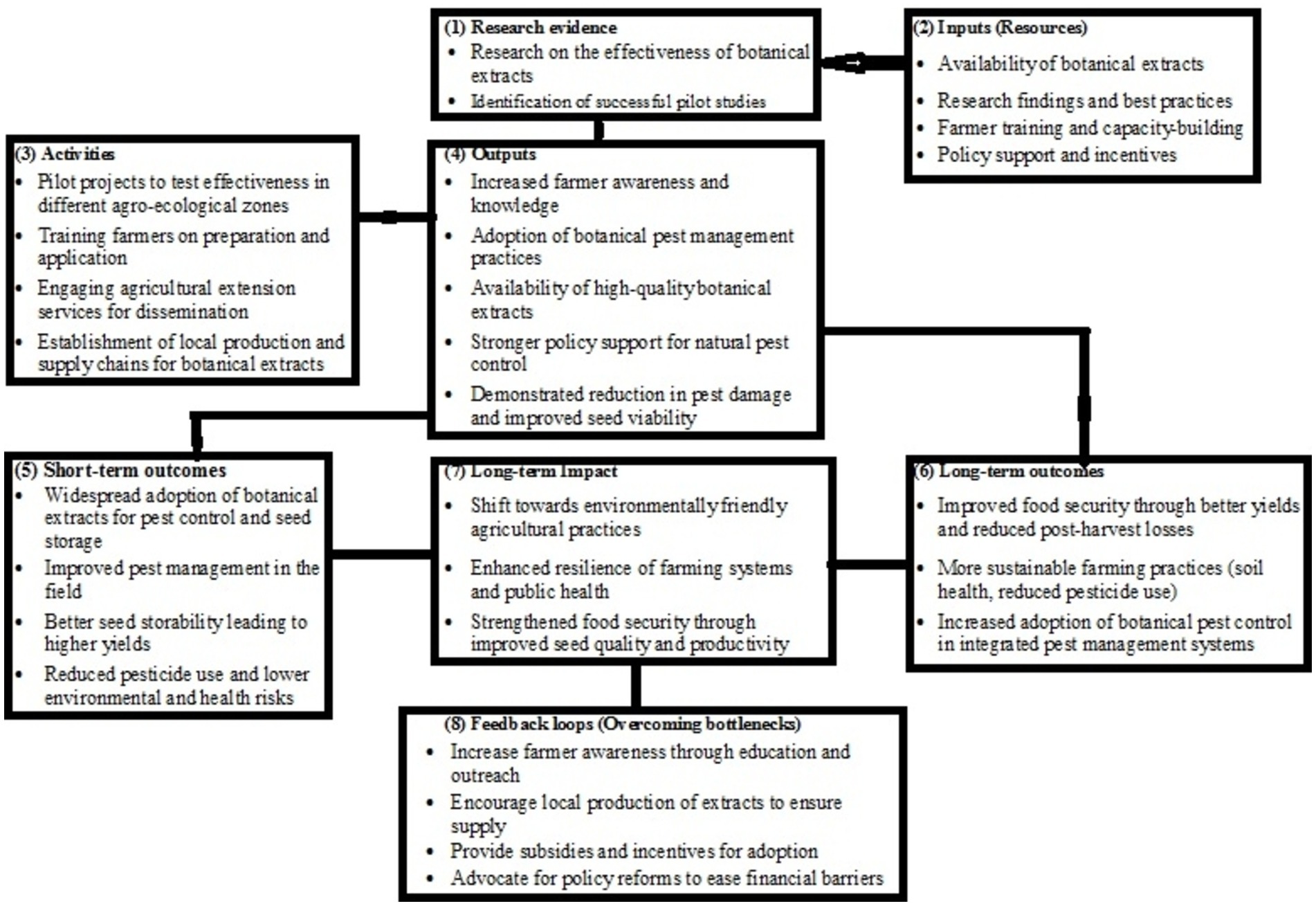
Figure 3. An illustration showing theory of change for scaling botanicals in mungbean pest control and storage.
Key inputs for the ToC include research on the effectiveness of botanical extracts, farmer training, policy support, and incentives for natural pest control. Pilot projects can demonstrate their efficacy across diverse agro-ecological zones, while local agricultural extension services can train farmers on proper preparation and application (Antwi-Agyei and Stringer, 2021). Partnerships with NGOs, agricultural associations, and government bodies are important to raise awareness and provide technical support (Fontana and Pisalyaput, 2023). The development of local supply chains for botanical extracts ensures consistent access for farmers.
The expected outputs are widespread adoption of botanical pest management practices, increased availability of quality botanical extracts, and stronger policy frameworks that support natural pest control (Acheuk et al., 2022; Daraban et al., 2023; Ratto et al., 2022). This will lead to improved pest control in the field and better seed viability, resulting in higher crop yields and enhanced food security. Reducing reliance on synthetic pesticides will decrease environmental contamination and health risks for farmers (Chèze et al., 2019).
In the long run, these initiatives contribute to sustainable agricultural practices, improving soil health, and reducing the carbon footprint. By integrating botanical pest management into broader Integrated Pest Management (IPM) systems, sustainability is further promoted, which improves crop resilience, reduces post-harvest losses, and ensures long-term productivity (Galli et al., 2024; Green et al., 2020; Pretty and Bharucha, 2015).
However, challenges may arise in scaling up these solutions. Research by Reddy et al. (2021) highlights the distress faced by farmers due to factors like climate variability and low risk-bearing capacity. These setbacks make it critical to tailor distress management strategies to specific regions, identifying distressed farmers and offering localized support. Similar challenges of low farmer awareness and access to high-quality botanical extracts can be addressed through training programs, farmer field schools, and local production initiatives. Sawargaonkar et al. (2024) also emphasize the need for sustainable management practices in regions with poor soil quality and unpredictable weather, highlighting the importance of upscaling botanical solutions in vulnerable agro-ecologies. Additionally, financial barriers and the perceived inefficacy of botanicals compared to synthetic pesticides can be mitigated through subsidies, pilot demonstrations, and policy reforms.
As observed by Paul et al. (2023), the shift from chemical inputs to sustainable alternatives requires significant investment, especially in smallholder farming systems. The ToC framework must include state-driven investments in improving the affordability and scalability of botanical inputs, ensuring equitable access for small and marginal farmers who are critical to food security.
Therefore, the Theory of Change for scaling botanical pest control and seed storage practices must consider the diverse challenges farmers face, provide targeted support, and ensure policy backing. The provided visual flowchart or diagram in Figure 3 can enhance clarity and guide policymakers, stakeholders, and agricultural development organizations in implementing this framework effectively.
5 Conclusion and recommendations
This study highlights the significant potential of botanical treatments as sustainable alternatives to synthetic pesticides in both pest management and seed preservation in mungbean cultivation. The findings revealed that T. vogelii and C. abbsynica were the most effective in reducing pest infestation, minimizing seed weight loss, and maintaining seed quality during storage. However, the efficacy of these treatments varied based on local environmental conditions. Specifically, C. anisata performed better at TARI Selian, where cooler temperatures and fertile volcanic soils supported higher insect diversity, while T. vogelii showed superior results at Miwaleni, where warmer conditions and bimodal rainfall prevailed. These variations highlight the need to tailor pest control strategies to specific agro-ecological conditions. The study also demonstrated the dual benefits of botanical extracts, which not only manage pests effectively in the field but also improve seed storability by reducing pest-related damage and weight loss during storage.
Given these findings, it is clear that pest management strategies should be adapted to the unique climatic and soil conditions of each site. Farmers need to select botanical treatments based on local environmental factors to maximize pest control effectiveness. Both T. vogelii and C. abbsynica should be prioritized, as they have proven to be effective in both pest management and seed preservation. These botanicals, when integrated into an integrated pest management (IPM) approach, can offer a more sustainable alternative to chemical pesticides. Furthermore, the role of botanical extracts in post-harvest management cannot be overlooked, as their use significantly enhances seed storability. The effectiveness of these treatments in reducing pest damage and preserving seed weight during storage makes them valuable for farmers looking to improve both field and post-harvest mungbean production. Future research should focus on understanding the underlying mechanisms that contribute to the varying effectiveness of plant extracts. Long-term studies should also assess their impact on soil health, pest resistance, and non-target organisms to refine pest management practices and ensure the sustainability of agricultural systems. Educating farmers about the benefits and proper application of botanical treatments is essential for maximizing their effectiveness. Such education will help promote sustainable agricultural practices, improve seed preservation, and ultimately enhance food security in regions where mungbean cultivation plays a crucial role in the local economy.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
GK: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AM: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. PB: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. PN: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
During the preparation of this work the authors used ChatGPT-OpenAI in order to improve readability and language. After using this tool/service, the authors reviewed and edited the content as needed and take full responsibility for the content of the publication.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Acheuk, F., Basiouni, S., Shehata, A. A., Dick, K., Hajri, H., Lasram, S., et al. (2022). Status and prospects of botanical biopesticides in Europe and Mediterranean countries. Biomol. Ther. 12:311. doi: 10.3390/biom12020311
Adesina, J. M., and Aderibigbe, A. T. (2021). Seed preservatives properties of Secamone afzelii (Schult) K. Schum extracts on wheat grains damage and germination capability. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 45, 1–6. doi: 10.1186/s42269-021-00507-z
Ahmad, M. F., Ahmad, F. A., Alsayegh, A. A., Zeyaullah, M., AlShahrani, A. M., Muzammil, K., et al. (2024). Pesticides impacts on human health and the environment with their mechanisms of action and possible countermeasures. Heliyon 10:e29128. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29128
Antwi-Agyei, P., and Stringer, L. C. (2021). Improving the effectiveness of agricultural extension services in supporting farmers to adapt to climate change: insights from northeastern Ghana. Clim. Risk Manag. 32:100304. doi: 10.1016/j.crm.2021.100304
Ayilara, M. S., Adeleke, B. S., Akinola, S. A., Fayose, C. A., Adeyemi, U. T., Gbadegesin, L. A., et al. (2023). Biopesticides as a promising alternative to synthetic pesticides: a case for microbial pesticides, phytopesticides, and nanobiopesticides. Front. Microbiol. 14:1040901. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1040901
Benbrook, C. (2021). The role of botanical pesticides in sustainable agriculture. Ecol. Agric. Rev. 15, 23–36.
Birachi, E. A., Sperling, L., Kadege, E., Mdachi, M., Upendo, T., Radegunda, K., et al. (2021). Analysis of the yellow bean corridor in Tanzania. A feed the future global supporting seed Systems for Development activity (S34D) report. Available at: https://pdf.usaid.gov/pdf_docs/PA00XS8V.pdf (Accessed December, 02 2024).
Chaudhary, S., Priya, M., Jha, U. C., Pratap, A., Hanumantha Rao, B., Singh, I., et al. (2022). Approaches toward developing heat and drought tolerance in mungbean. Dev. Clim. Resil. Grain Forage Legumes, 205–234. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-9848-4_10
Cheng, F., and Cheng, Z. (2015). Research progress on the use of plant allelopathy in agriculture and the physiological and ecological mechanisms of allelopathy. Frontiers in Plant Science, 6, 1020. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.01020
Chèze, B., David, M., and Martinet, V. (2019). Understanding farmers' reluctance to reduce pesticide use: a choice experiment. Ecol. Econ. 167:106349. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2019.06.004
Choudhary, K. B., Singh, D., Jadon, K. S., Solanki, R. K., and Kakani, R. K. (2024). “Biotic stresses in mung bean: achievements and prospects for genomics-enabled breeding strategies” in Genomics-aided breeding strategies for biotic stress in grain legumes, 135–162. doi: 10.1007/978-981-97-3917-2_5
Daraban, G. M., Hlihor, M., and Suteu, D. (2023). Pesticides vs. biopesticides: from Pest management to toxicity and impacts on the environment and human health. Toxics 11:983. doi: 10.3390/toxics11120983
Dassanayake, M. K., Chong, C. H., Khoo, T. J., Figiel, A., Szumny, A., and Choo, C. M. (2021). Synergistic field crop pest management properties of plant-derived essential oils in combination with synthetic pesticides and bioactive molecules: a review. Food Secur. 10:2016. doi: 10.3390/foods10092016
Dhaliwal, S. K., Pandey, A., Lahkar, C., Sheetal,, and Kaur, S. (2023). “Biotic stress resistance in Vigna mungo and Vigna radiata: a molecular perspective” in Diseases in legume crops: Next generation breeding approaches for resistant legume crops (Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore), 141–173.
Dikr, W. (2023). Mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) production status and challenges in Ethiopia. Glob. Acad. J. Agric. Biosci. 5, 13–22. doi: 10.36348/gajab.2023.v05i02.002
Farnworth, C. R., San, A. M., Kundu, N. D., Islam, M. M., Jahan, R., Depenbusch, L., et al. (2020). How will mechanizing mung bean harvesting affect women hired laborers in Myanmar and Bangladesh? Sustain. For. 12:7870. doi: 10.3390/su12197870
Fontana, E., and Pisalyaput, N. (2023). Understanding the importance of farmer–NGO collaboration for sustainability and business strategy: evidence from the coffee supply chain. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 32, 2715–2735. doi: 10.1002/bse.3266
Galli, M., Feldmann, F., Vogler, U. K., and Kogel, K. H. (2024). Can biocontrol be the game-changer in integrated pest management? A review of definitions, methods and strategies. J. Plant Dis. Protect. 131, 265–291. doi: 10.1007/s41348-024-00878-1
Gichohi-Wainaina, W. N., Mremi, R., Chande, M., Msuya, J. M., Kumwenda, N. C., Muzanila, Y. C., et al. (2022). Drivers of pigeon pea consumption among school-aged children in Central Tanzania. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 5:726404. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2021.726404
Green, K. K., Stenberg, J. A., and Lankinen, Å. (2020). Making sense of integrated Pest management (IPM) in the light of evolution. Evol. Appl. 13, 1791–1805. doi: 10.1111/eva.13067
Gurr, G., Read, D., and Wang, X. (2017). Principles of integrated pest management. Pest Manag. Sci. 73, 927–936. doi: 10.1002/ps.4475
Harrison, J., and Davis, P. (2023). Statistical methods in pest control studies. Biometric Analysis 40, 111–124.
Huppertz, M., Manasa, L., Kachhap, D., Dalai, A., Yadav, N., Baby, D., et al. (2023). Exploring the potential of mung bean: from domestication and traditional selection to modern genetic and genomic technologies in a changing world. J. Agric. Food Res. 14:100786. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2023.100786
Idrees, A., Qadir, Z. A., Afzal, A., Ranran, Q., and Li, J. (2022). Laboratory efficacy of selected synthetic insecticides against second instar invasive fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae. PLoS One 17:e0265265. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265265
Islam, S. S., Adhikary, S., Mostafa, M., and Hossain, M. M. (2024). Vegetable beans: comprehensive insights into diversity, production, nutritional benefits, sustainable cultivation and future prospects. OnLine J. Biol. Sci. 24, 477–494. doi: 10.3844/ojbsci.2024.477.494
Jabran, K., Mubeen, M., and Ahmed, K. (2018). Tailoring pest management to agro-ecological contexts. Crop Prot. 112, 103–113.
Jacquet, F., Jeuffroy, M. H., Jouan, J., Le Cadre, E., Litrico, I., Malausa, T., et al. (2022). Pesticide-free agriculture as a new paradigm for research. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 42:8. doi: 10.1007/s13593-021-00742-8
Jin, H., Wang, Y., and Li, Z. (2023). Impact of botanical extracts on mungbean seed storability. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 190, 115–125. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2023.115125
Johnson, M., Lee, T., and Edwards, N. (2021). PCA in pest diversity studies. Statist. Ecol. 29, 305–317.
Kanishka, R. C., Gayacharan,, Basavaraja, T., Chandora, R., and Rana, J. C. (2023). Moth bean (Vigna aconitifolia): a minor legume with major potential to address global agricultural challenges. Front. Plant Sci. 14:1179547. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1179547
Kaur, R., Choudhary, D., Bali, S., Bandral, S. S., Singh, V., Ahmad, M. A., et al. (2024). Pesticides: an alarming detrimental to health and environment. Sci. Total Environ. 915:170113. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.170113
Khine, N. A., Kundu, K. K., Malik, D. P., and Devi, M. (2021). Production and trade performance of blackgram (Vigna mungo) and greengram (Vigna radiata) in India and Myanmar. Asian J. Agric. Extens. Econ. Sociol. 39, 231–243. doi: 10.9734/AJAEES/2021/v39i1030687
Kohli, M., Bansal, H., Mishra, G. P., Dikshit, H. K., Reddappa, S. B., Roy, A., et al. (2024). Genome-wide association studies for earliness, MYMIV resistance, and other associated traits in mungbean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek) using genotyping by sequencing approach. PeerJ 12:e16653. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16653
Kumar, S., Gopinath, K. A., Sheoran, S., Meena, R. S., Srinivasarao, C., Bedwal, S., et al. (2023). Pulse-based cropping systems for soil health restoration, resources conservation, and nutritional and environmental security in rainfed agroecosystems. Front. Microbiol. 13:1041124. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1041124
Langyan, S., Yadava, P., Khan, F. N., Bhardwaj, R., Tripathi, K., Bhardwaj, V., et al. (2022). Nutritional and food composition survey of major pulses toward healthy, sustainable, and biofortified diets. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 6:878269. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2022.878269
Legumes, G., Yadav, O. P., Zaidi, P. H., Madhusudhana, R., Prasad, M., and Bohra, A. (2024). 2 drought management. Manag. Soil Drought 14.
Lengai, G. M., Muthomi, J. W., and Mbega, E. R. (2020). Phytochemical activity and role of botanical pesticides in pest management for sustainable agricultural crop production. Sci. Afr. 7:e00239. doi: 10.1016/j.sciaf.2019.e00239
Li, X., Zhao, L., and Wu, Q. (2022). Integrating Clausena anisata in pest management. J. Sustain. Agric. 40, 245–259.
Liao, Y., Zhang, Y., and Chen, H. (2023). Effectiveness of botanical extracts in pest control: a comparative study. J. Agric. Sci. 60, 102–115.
Liu, C., Wang, X., Li, X., Yang, Z., Dang, K., Gong, X., et al. (2024). Effects of intercropping on rhizosphere microbial community structure and nutrient limitation in proso millet/mung bean intercropping system. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 122:103646. doi: 10.1016/j.ejsobi.2024.103646
Maitra, S., Praharaj, S., Brestic, M., Sahoo, R. K., Sagar, L., Shankar, T., et al. (2023). Rhizobium as biotechnological tools for green solutions: an environment-friendly approach for sustainable crop production in the modern era of climate change. Curr. Microbiol. 80:219. doi: 10.1007/s00284-023-03317-w
Mkindi, A. G., Tembo, Y., Mbega, E. R., Medvecky, B., Kendal-Smith, A., Farrell, I. W., et al. (2019). Phytochemical analysis of Tephrosia vogelii across East Africa reveals three chemotypes that influence its use as a pesticidal plant. Plan. Theory 8:597. doi: 10.3390/plants8120597
Mubayiwa, M., Mvumi, B. M., Stathers, T., Mlambo, S., and Nyabako, T. (2021). Field evaluation of hermetic and synthetic pesticide-based technologies in smallholder sorghum grain storage in hot and arid climates. Sci. Rep. 11:3692. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83086-3
Muchomba, M. K., Muindi, E. M., and Mulinge, J. M. (2023). Overview of greengram (Vigna radiata L.) crop, its economic importance, ecological requirements and production constraints in Kenya. J. Agric. Ecol. Res. Int. 24, 1–11. doi: 10.9734/JAERI/2023/v24i2520
Nadi, F. (2023). Presenting a new approach for energy-exergy-environmental-economic evaluation of agroecosystems: a case study of the mung bean crop rotation. Clean Techn. Environ. Policy 25, 3437–3450. doi: 10.1007/s10098-023-02614-z
Nair, R., and Schreinemachers, P. (2020). Global status and economic importance of mungbean. Mungbean Genome, 1–8. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-20008-4_1
Ndebugri, A. A. I., Kugbe, J. X., Adu-Acheampong, S., and Kyerematen, R. (2024). Two plant extracts protect stored maize against infestation of Sitophilus zeamais in northern Ghana. J. Nat. Pesticide Res. 10:100102. doi: 10.1016/j.napere.2024.100102
Nenotek, P., and Ludji, R. (2020). The efficacy of seed extract of Tephrosia vogelii and Annona squmosa on larvae of Helicoverpa armigera. Int. J. Trop. Drylands 4, 5–9. doi: 10.13057/tropdrylands/t040102
Ngegba, P. M., Cui, G., Khalid, M. Z., and Zhong, G. (2022). Use of botanical pesticides in agriculture as an alternative to synthetic pesticides. Agriculture 12:600. doi: 10.3390/agriculture12050600
Nguyen, P., Le, Q., and Do, T. (2022). Site-specific effects of botanical treatments. Int. J. Pest Manag. 68, 147–160. doi: 10.1080/09670874.2022.2045678
Ogbonnaya, E., Rizwan, A. A., Bamidele, E. I., and Ayuba, V. (2022). Assessment of phytotoxicity of selected botanical insecticides on treated cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) seed. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 46, 1–6. doi: 10.1186/s42269-022-00858-1
Ong, P. W., Lin, Y. P., Chen, H. W., Lo, C. Y., Burlyaeva, M., Noble, T., et al. (2023). Environment as a limiting factor of the historical global spread of mungbean. eLife 12:e85725. doi: 10.7554/eLife.85725
Pathak, V. M., Verma, V. K., Rawat, B. S., Kaur, B., Babu, N., Sharma, A., et al. (2022). Current status of pesticide effects on environment, human health and it’s eco-friendly management as bioremediation: a comprehensive review. Front. Microbiol. 13:962619. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.962619
Paul, B., Murari, K. K., Patnaik, U., Bahinipati, C. S., and Sasidharan, S. (2023). Sustainability transition for Indian agriculture. Sci. Rep. 13, 7290–7299. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34092-0
Pittore, K., Koomen, I., Alemu, D., Abate, L., Borman, G. D., Elias, E., et al. (2024). Research for agricultural development projects in support of nutrition sensitive agriculture in Ethiopia.
Pratap, A., Gupta, S., Rathore, M., Basavaraja, T., Singh, C. M., Prajapati, U., et al. (2021). “Mungbean” in The beans and the peas (Woodhead Publishing), 1–32.
Pretty, J., and Bharucha, Z. P. (2015). Integrated pest management for sustainable intensification of agriculture in Asia and Africa. Insects 6, 152–182. doi: 10.3390/insects6010152
Pumnuan, J., Sarapothong, K., Sikhao, P., Pattamadilok, C., and Insung, A. (2021). Film seeds coating with hexane extracts from Illicium verum Hook. f. and Syzygium aromaticum (L.) Merrill & Perry for controlling Callosobruchus maculatus (F.) and Callosobruchus chinensis L. Pest Manag. Sci. 77, 2512–2521. doi: 10.1002/ps.6283
Rai, S., and Jolly, G. E. (2024). Enhancement of Greengram (Vigna radiata L.) productivity by using organic extracts and fertilizers. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 36, 98–110. doi: 10.9734/ijpss/2024/v36i74712
Raitzer, D., Wong, L. C. Y., and Samson, J. N. (2015) Myanmar's Asian Development Bank economics agriculture sector: Unlocking the potential for inclusive growth. ADB Economics Working Paper Series No. 470; Asian Development Bank (ADB), Manila, Philippines. 1–31.
Ratto, F., Bruce, T., Chipabika, G., Mwamakamba, S., Mkandawire, R., Khan, Z., et al. (2022). Biological control interventions and botanical pesticides for insect pests of crops in sub-Saharan Africa: a mapping review. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 6:883975. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2022.883975
Reddy, A. A., Bhattacharya, A., Reddy, S. V., and Ricart, S. (2021). Farmers’ distress index: an approach for an action plan to reduce vulnerability in the drylands of India. Land 10:1236. doi: 10.3390/land10111236
Reddy, A. A., Reddy, M., and Mathur, V. (2024). Pesticide use, regulation, and policies in Indian agriculture. Sustain. For. 16:7839. doi: 10.3390/su16177839
Rys, M., and Skoczowski, A. (2021). Phytotoxic effects of selected herbal extracts on the germination, growth and metabolism of mustard and oilseed rape. Agronomy 12:110. doi: 10.3390/agronomy12010110
Sah, U., Dixit, G. P., Kumar, N., Pal, J., and Singh, N. P. (2024). Status and strategies for development of pulses in Bundelkhand region of India: a review. Legume Res. 47:4518. doi: 10.18805/LR-4518
Samal, I., Bhoi, T. K., Raj, M. N., Majhi, P. K., Murmu, S., Pradhan, A. K., et al. (2023). Underutilized legumes: nutrient status and advanced breeding approaches for qualitative and quantitative enhancement. Front. Nutr. 10:1110750. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1110750
Sanderson, T. (2024). Uptake of agricultural technologies and best practices amongst farmers in Battambang and Pailin provinces, Cambodia.
Sawargaonkar, G. L., Davala, M. S., Rakesh, S., Kamdi, P. J., Khopade, R. Y., Nune, R., et al. (2024). Envirotyping helps in better understanding the root cause of success and limitations of rainfed production systems. Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1417199. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1417199
Siame, C. P., Chitambo, H., Muma, J. B., Choongo, K., and Moonga, E. (2019). Field assessment of the efficacy of Tephrosia vogelii leaf extracts for control of ticks on naturally infested cattle in the field condition. J. Parasit. Dis. 43, 624–632. doi: 10.1007/s12639-019-01141-3
Smith, R., Brooks, H., and Evans, T. (2021). Comparative efficacy of botanical extracts in different environments. Agric. Entomol. J. 47, 289–301.
Somta, P., Laosatit, K., Yuan, X., and Chen, X. (2022). Thirty years of mungbean genome research: where do we stand and what have we learned? Front. Plant Sci. 13:944721. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.944721
Souto, A. L., Sylvestre, M., Tölke, E. D., Tavares, J. F., Barbosa-Filho, J. M., and Cebrián-Torrejón, G. (2021). Plant-derived pesticides as an alternative to pest management and sustainable agricultural production: prospects, applications and challenges. Molecules 26:4835. doi: 10.3390/molecules26164835
Sultan, M. T. H., Shahar, F. S., Zain, M. I. M., and Komoo, I. (2024). A systematic review of the role of integrated farming and the participation of universities in ensuring food security: Malaysia’s effort. Italian J. Food Saf. 13:11854. doi: 10.4081/ijfs.2024.11854
Sunani, S. K., Rout, A. K., Kumar, R., and Choudhary, D. K. (2024). Major diseases of green gram, black gram and their integrated management strategies. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/380395530 (Accessed December, 02 2024).
Tomi, F., Ramirez, J., and Torres, P. (2019). Efficacy of Clausena Anisata against agricultural pests. J. Bot. Res. 12, 198–210.
Tudi, M., Ruan, H. D., Wang, L., Lyu, J., Sadler, R., Connell, D., et al. (2021). Agriculture development, pesticide application and its impact on the environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18:1112. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18031112
Vaghefi, N., Kelly, L. A., Burlakoti, R. R., Pandey, A. K., Sharman, M., Owen, K. J., et al. (2024). “Diseases of Mungbean” in Handbook of vegetable and herb diseases (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 1–38.
Wang, Y., Yuan, Z., and Tang, Y. (2021). Enhancing food security and environmental sustainability: a critical review of food loss and waste management. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 4:100023. doi: 10.1016/j.resenv.2021.100023
Wang, L., Zhao, M., and Liu, X. (2023). Guiding sustainable farming practices through research. J. Sustain. Agric. Technol. 18, 160–175.
Wilkins, R., Bell, C., and Clark, J. (2019). Reducing chemical loads with botanical pesticides. Environ. Health Perspect. 127, 1142–1151. doi: 10.1289/EHP4619
Win, N. W., Oo, Z., Htun, A., and Naing, Z. M. (2022). “Agricultural exports from Myanmar to China: a value chain analysis of maize” in Agricultural trade between China and the greater Mekong subregion countries: a value chain analysis. eds. J. Menon and V. Roth (Singapore: ISEAS–Yusof Ishak Institute), 205–255). Chapter.
Yadav, B. K., Mohanty, N., Dash, S., Pradhan, S., Sahoo, B., and Rath, B. (2024). Enhanced yield of mungbean (Vigna radiata L.) using bacterial biofertilizer. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Asia 21, 89–98. doi: 10.13005/bbra/3205
Yong, W. T. L., Thien, V. Y., Misson, M., Chin, G. J. W. L., Hussin, S. N. I. S., Chong, H. L. H., et al. (2024). Seaweed: a bioindustrial game-changer for the green revolution. Biomass Bioenergy 183:107122. doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2024.107122
Zhang, P., Qin, D., Chen, J., and Zhang, Z. (2020). Plants in the genus Tephrosia: valuable resources for botanical insecticides. Insects 11:721. doi: 10.3390/insects11100721
Zheng, E., Zhu, Y., Qin, M., Chen, P., Liu, M., and Qi, Z. (2023). Effects of organic fertilizer replacement nitrogen fertilizer on nitrogen utilization and growth of mung bean: evidence from 15N-tracing technology. Agronomy 13:235. doi: 10.3390/agronomy13010235
Keywords: agricultural insect pests, ecological friendly botanical extracts, efficacy, postharvest losses mitigation, sustainable food system, Tanzania
Citation: Kessy GA, Mkindi A, Binagwa P and Ndakidemi PA (2024) Impact of botanical extracts on mungbean pest management and seed storability in the northern highlands of Tanzania. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1495194. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1495194
Edited by:
Pushp Sheel Shukla, Centre for Cellular and Molecular Platforms, IndiaReviewed by:
Jiban Shrestha, Nepal Agricultural Research Council, NepalA. Amarender Reddy, National Institute of Agricultural Extension Management (MANAGE), India
Copyright © 2024 Kessy, Mkindi, Binagwa and Ndakidemi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Godfrey Adolph Kessy, a2Vzc3lnb2RmcmV5NzA5QGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Godfrey Adolph Kessy
Godfrey Adolph Kessy Angela Mkindi
Angela Mkindi Papias Binagwa2
Papias Binagwa2