- 1Bremen International Graduate School of Social Sciences, University of Bremen, Bremen, Germany
- 2Department of Agricultural Engineering and Environmental Technology, University of Ruhuna, Matara, Sri Lanka
- 3Department of Sociology, University of Ruhuna, Matara, Sri Lanka
The excessive use of pesticides has been identified as a main barrier to sustainable agriculture in the developing countries, that can lead to several negative consequences, posing a significant threat to the total environment. Therefore, the present study investigated the informedness of smallholder vegetable farmers on responsible use of pesticides, exploring how their knowledge, attitudes and protective practices (KAP) are associated with the safe use of pesticides. A questionnaire survey was conducted with 206 smallholder farmers in the central highlands of Sri Lanka to identify how KAP are associated with responsible use of pesticides. Secondly, two focus group discussion were conducted to gain insights into the farmers’ awareness of the responsible use of pesticides. The analysis reveals an overall deficiency in informedness about responsible pesticide use, primarily stemming from moderate level of knowledge and perceptions related to protective practices. Furthermore, farmers tend to face constraints due to limited access to information on responsible use of pesticides and a heavy reliance on pesticides, believing pesticides to be a primary means of increasing crops. Results also indicate a significant association between knowledge, practice, and informedness, whereas attitudes did not significantly contribute to informedness. Significant disparities in informedness were identified among different demographic groups, with men and younger farmers exhibiting higher levels of awareness. Thus, we suggest that farmers’ informedness can be improved by targeted efforts to enhance their knowledge and correct misconceptions on the use of pesticides.
Highlights
• The level of informedness on the responsible use of pesticides is significantly low among smallholder crop cultivators.
• The degree of knowledge and perceptions of protective practices affect informedness, but attitudes do not have a significant impact.
• Despite possessing positive attitudes, farmers often engage in irresponsible pesticide use.
• The degree of informedness varies across different demographic characteristics, such as sex, education, age, land area owned, and monthly income.
• Farmer networks, a lack of reliable information, retailer influence, and a conviction in the necessity of pesticides are some factors that contribute to the overuse of pesticides.
1 Introduction
Sustainable agriculture has garnered heightened attention as a means of achieving more environmentally friendly food production concerning the health risks and adverse environmental impacts that have a detrimental impact on the overall wellbeing of people (Pimbert, 2009). Sustainable agriculture is a system that generates nutritious food, ensures its accessibility to all, and manages natural resources in a manner that maintains the functionality of ecosystems to satisfy the current and future needs of humanity (Velten et al., 2015). The responsible use of pesticides has become a crucial aspect of sustainable agriculture, as the overuse or misuse of these chemicals can lead to far-reaching problems (European Commission, 2022). While completely avoiding pesticides with toxic properties is often impractical—given their role in meeting the food demands of a growing population—their responsible and informed use is strongly advocated (Ali et al., 2020; Rather et al., 2017). Responsible pesticide use involves applying them judiciously to maximize benefits while minimizing harmful effects. This approach requires a strong understanding at the user level, as farmers are the ones directly handling and applying pesticides. This is particularly critical for smallholder farmers, who frequently rely on pesticides but often lack the necessary knowledge and training to use them effectively and safely.
The present study aims to explore smallholder vegetable farmers’ informedness, or their ability to understand the responsible use of pesticides. In order to do so, we explored the association between knowledge, attitudes and practice perspectives on the use of pesticides and the informedness among selected smallholder farmers in Sri Lanka. Responsible use of pesticides is strongly determined by individual knowledge, attitudes and practice perspectives (Vlaiculescu and Varrone, 2022). We thus show how knowledge, attitudes, and perceptions of protective practices related to pesticide use among smallholder vegetable farmers are associated with their informedness. Informedness is considered a prerequisite for the responsible use of pesticides, that involves understanding of the several aspects of pesticide use such as health risks associated with the applicator, selection of suitable pesticides, crop profitability and economic implications, and critical issues associated with incorrect application (European Commission, 2022). Even though there are several studies on pesticide use behavior and its impact on the total environment across countries (Jayasiri et al., 2022b; Maggi et al., 2023; Okonya et al., 2013), there is a lack of initial understanding of how pesticide use behavior among farmers is associated with informedness on responsible use. Studies often show that misuse of pesticides can constrain establishing sustainable agriculture (Datta et al., 2016; European Commission, 2022), but it is still widely recognized that pesticide use has contributed to preventing the impact of undesirable organisms in cultivation and ensuring food security, mainly in the global south (Popp et al., 2013).
Even though irresponsible use of pesticides is harmful to the total environment and human health, studies suggest that crop failures are apparent without pesticide use, especially in a climate change situation (Delcour et al., 2015; Ma et al., 2021). The European Union has thus introduced a framework for the sustainable use of pesticides, which aims to reduce the risks and impacts of pesticide use and promote integrated pest management (IPM) and alternative approaches to pesticides (European Commission, 2022). This particularly highlights the individual level interventions for responsible use of pesticides. Even though sustainable agriculture is promoted, there is a severe gap in knowledge regarding the extent to which farmers in developing countries are ready for responsible pesticide use.
Responsible pesticide use is an essential component of sustainable agriculture, which aims to produce adequate amounts of high-quality food while preserving the environment and resources for future generations (European Commission, 2021). The responsible pesticide use entails applying pesticides in a manner that minimizes environmental contamination, protects users from hazards, and safeguards the health of consumers. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a cornerstone of responsible pesticide use, providing an environmentally friendly approach to pest management at the community level. FAO, 2022 defines it as careful consideration of all available pest control techniques and subsequent integration of appropriate measures, and ultimately reduce the risk for total environment. However, there is a significant lack of knowledge on IPM and responsible pesticide practices in Sri Lanka, particularly among smallholder farmers in the highlands where commercial crop cultivation is heavily promoted.
The responsible use of pesticides encompasses multiple dimensions, including knowledge and training on safe usage, informed selection of required pesticides, safe application procedures, environmental considerations, proper storage and disposal, legal and ethical compliance, as well as community and ecosystem awareness (Mohamed et al., 2024). These dimensions align closely with knowledge, attitudes, and practice (KAP) perspectives. In the present study, we strived to understand how these aspects are reflected in the knowledge, attitudes, and practices of smallholder farmers and how they contribute to informed decision-making with regard to the use of pesticides.
Given the importance of farmers’ knowledge, attitudes, and perspectives on the responsible use of pesticides, several studies have emphasized the need to enhance farmers’ understanding and educate them on the judicious use of pesticides. For example, Sharifzadeh and Abdollahzadeh (2021) demonstrate that although some farmers have limited knowledge about the safe use of pesticides, certain interventions aimed at improving their knowledge and moderating their attitudes can promote safer pesticide practices. They suggest that educational interventions can yield positive outcomes by increasing awareness and knowledge regarding the safe use of pesticides. Furthermore, Maddah et al. (2020) also support this, highlighting that even one-time educational interventions can successfully enhance farmers’ knowledge, attitudes, and practices concerning pesticide use. Therefore, research is essential to understand the extent to which knowledge, attitudes, and practice (KAP) perspectives influence awareness of the responsible use of pesticides. Ssekkadde et al. (2024) similarly recognize this need, emphasizing that educational interventions designed to encourage behavioral change can deliver significant benefits for farmers, who often use pesticides to increase crop yields.
Moreover, when examining the informed use of pesticides, research highlights the critical role of labeling, particularly in developing countries (Abou Ibrahim et al., 2023; Rother, 2018). For farmers who lack knowledge or access to reliable information, labels serve as a crucial tool for promoting responsible pesticide use. Farmers in developing countries are often blamed for pesticide poisoning and environmental contamination, primarily due to misuse (Abou Ibrahim et al., 2023). To address this issue, appropriate labeling has been proposed as a viable solution. Effective labeling should be accessible and use simple, comprehensible language tailored to the literacy levels of the target audience. Studies indicate that pesticide misuse often arises from inadequate communication about their responsible use. As Rother (2018) suggests, what is often labeled as “misuse” is better understood as “unintended use” stemming from a lack of awareness. To mitigate this, the use of pictograms is recommended to convey information clearly, especially for farmers who are illiterate. This challenge is particularly evident in Sri Lanka, where many smallholder farmers are unable to read English instructions, and small printed texts often go unnoticed, as we show in this paper.
Sri Lanka is country with more than 80% of the population living in rural areas and engaged in agricultural work (Central Bank of Sri Lanka, 2023). Rice cultivation is primarily prevalent in the dry zones of the country, whereas commercial vegetable farming is more prominent in the highland regions (Haque et al., 2021; Kadupitiya et al., 2022). Research indicates that profits generated from paddy cultivation are low relative to those from commercial crop cultivation in the highlands (Burchfield et al., 2018; Haque et al., 2021; The World Bank, 2009). Pesticides are often used in both rice and commercial vegetable crops, yet there is evidently heavier pesticide usage in the highlands, as crops growing in wet-highland areas are more frequently subjected to pest damage (Dissanayake et al., 2022; Sumudumali et al., 2021; The World Bank, 2013). These farmers continue to use substantial amount of pesticides, fungicides, insecticides, and fertilizers, despite the associated high cost.
Several studies demonstrate that pesticides have become an indispensable ingredient in agriculture for farmers working in central highlands of Sri Lanka (FAO, 2021; Nishantha et al., 2016; The World Bank, 2013). For example, some studies found that the banning of certain herbicides in 2014 has severely affected the crop production of the country (Marambe and Herath, 2020). While the indiscriminate application of pesticides is acknowledged to have propagated severe health consequences, highland commercial crop cultivation is estimated to be a high-volume consumer of both pesticides and fertilizers, largely owing to the short durations of cultivated crops (The World Bank, 2013). Nuwara Eliya and Badulla represent two critical districts amidst the country’s central highlands, where World Bank and FAO reporting suggests smallholder vegetable farmers tend to apply pesticides in excess of prescribed levels (FAO, 2021; The World Bank, 2009).
Research indicates pesticide usage in highland vegetable cultivations often constitutes either unpermitted WHO class I or class II formulations (Padmajani et al., 2014). Studies have also identified pesticide application as a usual practice (without necessity), with farmers prone to spraying even in the absence of pest symptoms (Nishantha et al., 2016; Padmajani et al., 2014). They show that farmers often tend to mix various pesticides without any justification, operating under the belief that such combinations minimize labor inputs. Moreover, studies evidence a lack of preparatory measures for pesticide usage, including the absence of protective boots, masks, gloves, or attire, consequently increasing pesticide exposure and posing severe health risks (Jayasooriya and Aheeyar, 2016; Padmajani et al., 2014). As they suggest the intensive cultivation of hybrid crop varieties further necessitates heavy use of pesticides.
The causes of the irresponsible use of pesticides mainly include a lack of awareness and knowledge, and weaknesses in government regulations (Jayasooriya and Aheeyar, 2015, 2016). Insufficient technical expertise in pesticide application and integrated pest management, as well as an overreliance on pesticides as a preventative measure in cultivation, are some other causes of irresponsible application of pesticides. Sumudumali et al. (2021) also demonstrated that there is a strong influence of pesticide retailers. As a result of pesticide misuse, disruptions can occur in agroecosystems and the broader environment, causing several unintended consequences, such as chronic kidney disease of unknown origin (CKDu) (Jayasumana et al., 2014; Valcke et al., 2017). Furthermore, in Sri Lanka, many suicide cases in agricultural communities involve pesticide poisoning (Bagheri et al., 2019; Buckley et al., 2021; Weerasinghe et al., 2020). Pesticide poisoning among the country’s farmers has thus been recognized as a major health issue, though Buckley et al. (2021) observed that government bans on selected pesticides have decreased suicide incidences. Recent assessments by Jayasiri et al. (2022a) and Shipley et al. (2022) found significant temporal variability in water quality, with pesticide and agrochemical residues highest in localized communities neighboring slow-moving reservoirs. Jayasiri et al. (2022a) also demonstrated that common pesticide misuse malpractices can impart severe ecological impacts in Sri Lanka. Some research into the adoption of integrated pest management (IPM) among Sri Lankan vegetable growers discovered that insufficient knowledge and information can limit farmers’ decision-making process regarding pesticide use (Jayasooriya and Aheeyar, 2015).
Despite ongoing efforts to promote sustainable agriculture and research on farmers’ preparedness for adopting sustainable practices, empirical studies in this area remain limited. Existing studies primarily focus on pesticide use, while the association between sustainable agriculture and farmers’ informedness and responsible pesticide use has not been adequately explored. This lack of comprehensive research hinders policymakers, particularly in developing countries, from formulating effective and community-relevant sustainable agricultural policies. Moreover, in our study, resonating with the theories and empirical studies, a responsible use of pesticides is recognized as a response associated with informedness resulting from the level of knowledge, attitudes and perspectives on protective practices.
Considering the widespread and often improper use of pesticides in the highlands of Sri Lanka, a thorough understanding of the knowledge, attitudes, and practices driving these practices among smallholder farmers is crucial. This understanding is essential for designing sustainable interventions that effectively prepare farmers for adopting sustainable agriculture practices. Therefore, our study aims to investigate the knowledge, attitudes, and perceptions on protective practices of smallholder highland farmers in Sri Lanka regarding responsible pesticide use. The insights gained from this study will be discussed in the context of promoting responsible pesticide use practices associated with IPM, particularly among commercial smallholder crop cultivators in the highlands of Sri Lanka.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Theoretical framework and research design
Our study employed the Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices (KAP) framework, a prevalent approach used by researchers to inquire into the behavioral and cognitive aspects of pesticide usage (Dunn et al., 2023; Liao et al., 2022). While the operationalization of this framework varies across studies, it can be generally adapted to assess smallholder farmers’ readiness for adopting responsible pesticide practices. The KAP framework recognizes that behavioral changes stem from a combination of knowledge and attitudes (Ali et al., 2020; Dunn et al., 2023). Considering the validation of the KAP framework in multiple studies related to pesticide exposure, we adopted this framework for designing survey questions and focus group guidelines.
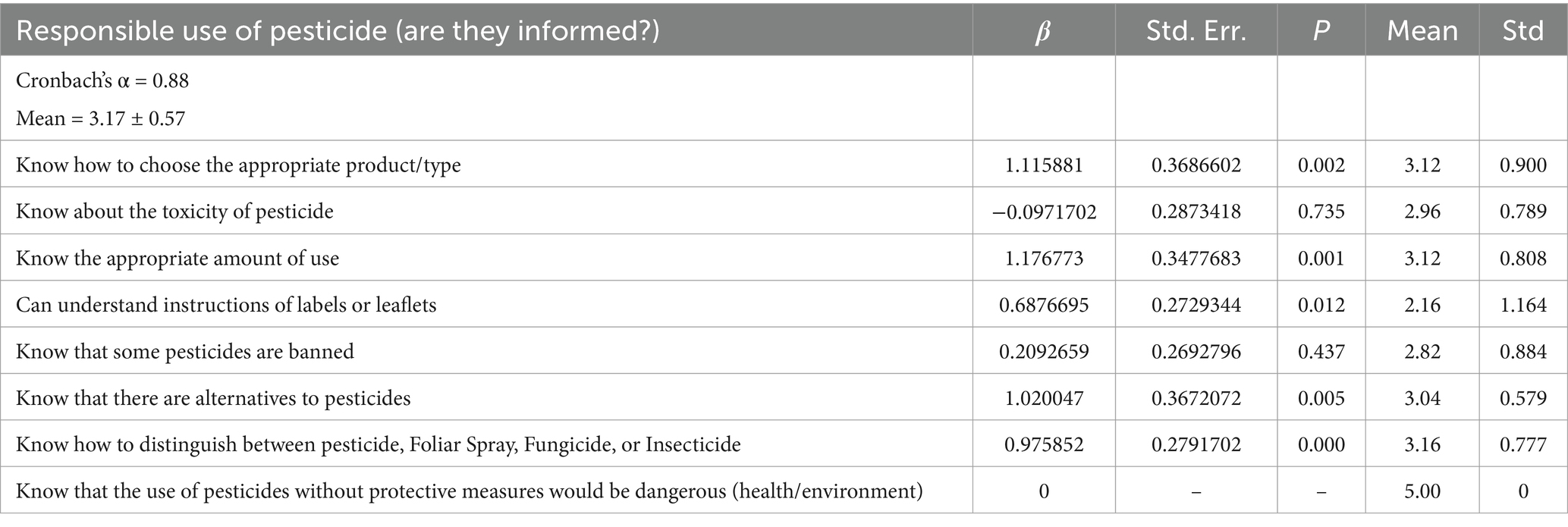
All those questionnaire items were generated in line with the theoretical guidelines as suggested by Ali et al. (2020) and Dunn et al. (2023). In the context of this study, knowledge refers to farmers’ overall understanding of pesticides, their usage, and the potential consequences associated with their application. The administered survey incorporated a collection of questions devised to gage smallholder farmers’ knowledge levels and responsible pesticide usage. Eight inquiry areas were included, encompassing the knowledge on the selection of pesticides employed, perceived toxicity and appropriateness, label readability and comprehension, banned chemical awareness, ability to distinguish different products, and use of protective countermeasures.
Attitudes encompass farmers’ beliefs about the effects of pesticides, including environmental and health impacts, and any potential misconceptions they may hold. To assess the attitudes of farmers, 10 questionnaire statements were included. These statements addressed topics such as the perceived effects of pesticides, access to pesticide purchases, and the perceived necessity of pesticides in farming practices.
Practices include farmers’ protective behaviors regarding pesticide use, including the use of safety measures, decision-making processes, and pesticide purchase. This study focused specifically on perceptions of protective practices. Ten survey statements measured perceptions of protective behaviors associated with pesticide use. Overall responsible pesticide use is determined by the cumulative effect of the knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors adopted by farmers. Applying this framework to smallholder farmers is important because, unlike large-scale farmers, community-level factors can readily shape the knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors of smallholder farmers. (The operationalisation procedure and questionnaire items are detailed in Section 1 of the Supplementary materials).
A mixed method approach, that encompassed both qualitative and quantitative techniques were used as the research design of the present study. Mixed method approach refers to a study design that encompasses both quantitative and qualitative methods (Bryman, 2008). Some aspects of human behavior are difficult to grasp through quantitative approaches, and where qualitative inquiries are needed. Considering this we initially conducted a survey to gather preliminary insights into the factors contributing to smallholder farmers’ informedness of pesticide use. Thereafter, these initial findings were used to guide two focus group discussions. Seven participants were included in the first focus group discussion, and the second one included 8. On average 120 min were taken to complete a focus discussion. Both men and women took part in these focus group interviews.
2.2 Study area, sample, and data collection
Nuwara Eliya district in Sri Lanka, located in the central highlands, is renowned for smallholder commercial vegetable farming. In 2022, total rainfall in Nuwara Eliya measured 2,250 millimeters (89 inches). The wettest month was August, with 375 millimeters (15 inches) of precipitation, while the driest was January, receiving just 30 millimeters (1.2 inches). Per district records, 21,684 individual farmers were recorded in the Nuwara Eliya divisional secretariat division, with 20,393 involved in contemporary short-term vegetable cultivation. Of those, 18,253 farmers work land areas under one acre (Department of Census and Statistics, 2015). Figure 1 shows the map of the Nuwara Eliya divisional secretariat division.
Compared to other regions of Sri Lanka, these smallholder farmers with less than one cultivated acre contribute most substantially to national vegetable demand. Research also indicates heavy pesticide reliance among these producers (Nishantha et al., 2016). Therefore, the present study focused specifically on the Nuwara Eliya district divisional secretariat division. Applying an 85% confidence level, a 5% acceptable margin of error, and a population estimate of 50%, 206 survey respondents were recruited, encompassing both men and women farmers owning less than one acre.
Considering the research focus, we recruited farmers who own less than one acre of land. These farmers are categorized as smallholders, with their primary purpose being to support their household economy. A total number of 206 such smallholder farmers were selected for the study. For on-site data collection, we initially approached the selected smallholder farmers and gathered data directly from them. We then asked these farmers to identify other smallholder farmers within their community to participate in the study. This snowball sampling approach ensured representation across a wide range of demographic variations, including different age groups, genders, and communities within the same divisional secretariat division. Applying the principle of information power—where the sample size is determined by the richness of data provided by participants—we set an 85% confidence level (Palinkas et al., 2015). This decision was justified by the homogeneity of participants in terms of their farming background, despite demographic differences. As a result, we were able to recruit 206 participants for the questionnaire survey from the Nuwara Eliya District divisional secretariat division. Increasing the number of participants in this context would not have altered the study outcomes due to the similarity of participants in their farming practices.
Data were collected from a structured questionnaire from those respondents, and the questions associated with knowledge, attitudes, and practices were measured on a Likert scale from 1 to 5, which included very unlikely/strongly disagree, somewhat unlikely/disagree, unsure/uncertain, somewhat likely/agree, and very likely/strongly agree. After analysis of the survey data, we conducted two focus groups with framers (each focus group included five participants). Before we asked questions, the purpose of the survey was communicated to participants, and we ensured their participation was voluntary and they could withdraw at any time. Participants provided consent to participate in the study. Notes were taken during the focus group with the participants’ consent (more details in the Supplementary materials).
2.3 Data analysis
The survey data were analysed using STATA 17. First, respondents’ demographic profiles were analysed, and the relationship between those variables and self-reported pesticide use informedness was explored. Mann–Whitney U tests and Kruskal-Wallis H tests were then used to identify differences in self-reported informedness. Mann-Whiteney U test is important for analysing data with ordinal nature, and it compares two independent groups. Kruskal-Wallis H extends this to identify any differences between the distribution of three or more groups. These tests are thus used accordingly to identify the difference of informedness between respective groups of people. Pearson’s correlation analysis used to examine associations between demographics and informedness.
Respondent characteristics were compared against informedness using an ordinal logistic regression model (Proportional Odds Model) (details are provided in Table 1). Considering the ordinal nature of the dependent variable (informedness), the ordinal logistic regression was employed. Thereafter, knowledge, attitudes, and practice perspective levels were measured, with internal item consistency analysed via Cronbach’s alpha tests. An alpha value above 0.7 suggests strong internal consistency (Tavakol and Dennick, 2011). Additional ordinal logistic regression models compared each item to self-reported informedness or readiness for responsible pesticide use. For each dimension—knowledge, attitudes, and practice perspectives—several questionnaire items were included. The values of these items were averaged into three distinct categories: knowledge, attitudes, and practice perspectives. These averaged values were then used in the Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) analysis. We used SEM in order to reveal the impact of knowledge, attitudes, and practices on overall informedness toward responsible pesticide use among highland farmers. Tables 2–5 shows both β values and mean scores for each self-assessed statements.
Qualitative focus group data were transcribed and analysed by hand coding. A thematic analysis approach was employed (Braun and Clarke, 2019), with descriptive narrative excerpts presented as evidence. Detailed description on survey questionnaire and data analysis is provided in Supplementary material.
3 Results
3.1 Demographic profile of respondents
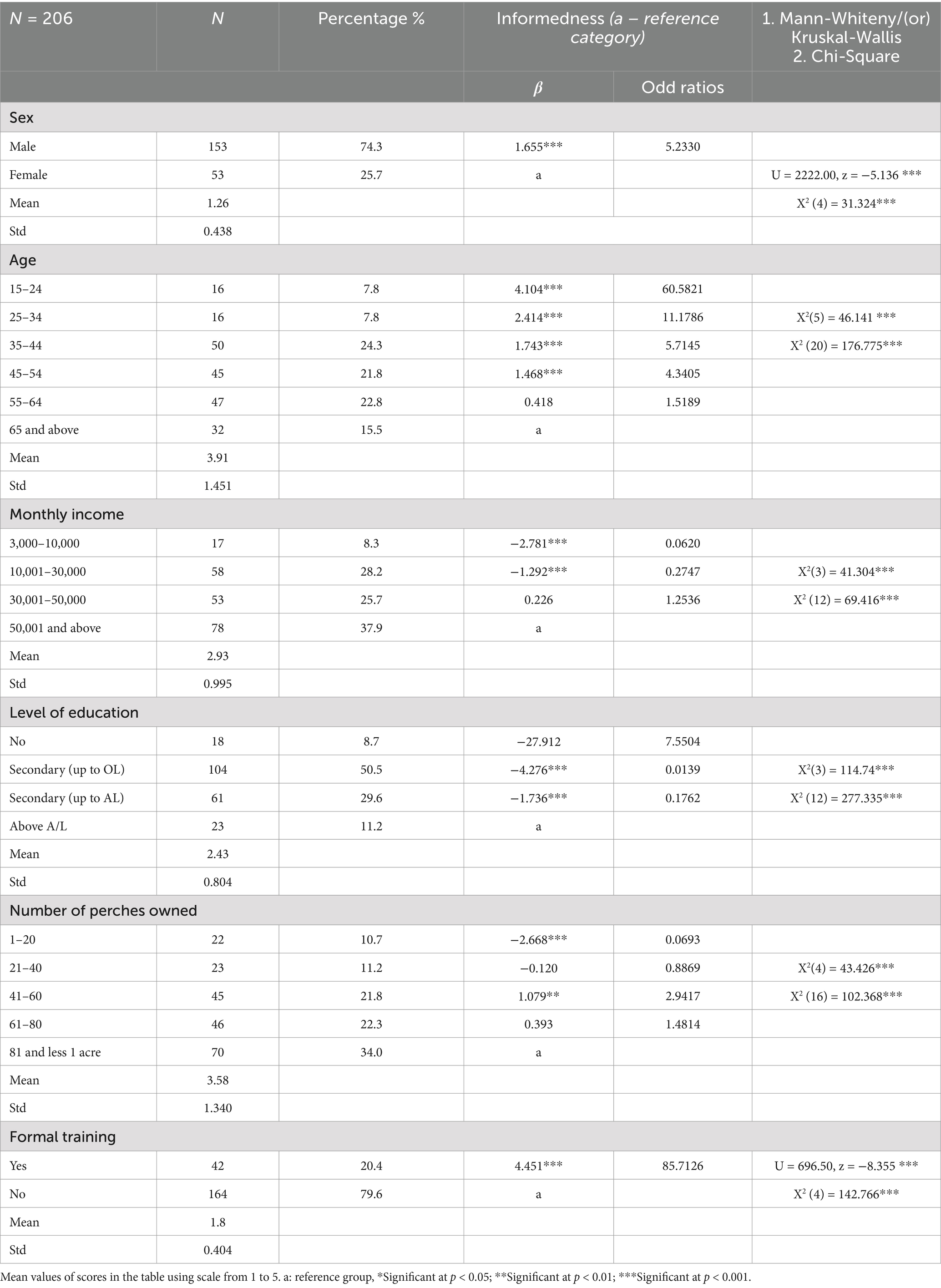
The Nuwara Eliya district has a long history of commercial crop cultivation, dating back to the British colonial era. These crops include non-traditional vegetables for Sri Lanka, such as carrots, leeks, radishes, cabbage, and potatoes. Many smallholder farmers engage in commercial crop cultivation, which is often seasonal and profitable. Among the 206 participants in the present study, 74.3% are men, while women constitute 25.7%. Female farmers often work alongside their husbands but are not typically sole owners of vegetable gardens. Highland commercial agriculture is predominantly male-dominant, with women being supporters of male farmers (husbands). Qualitative data reveal that women heavily rely on husbands or male farmers when selecting pesticides, season-appropriate seeds, and fertilizers. Gender norms thus shape the practices of sustainable agriculture.
Among the participants, over 50% are aged 45 and above, while only a small percentage falls within the 15–34 age range. Findings from focus groups reveal that young individuals are less inclined to engage in agriculture, often opting to migrate to urban areas in pursuit of alternative job opportunities. As a result, only a limited number of young members participate in commercial agriculture, despite the potential profits associated with commercial crop cultivation. Furthermore, we observed that some individuals enter into commercial crop cultivation in their mid-twenties. Notably, 15.5% of farmers are aged 65 or older.
Furthermore, the results indicate that commercial crop cultivation among smallholder farmers is reasonably profitable, with over 37.9% earning more than 50,001 LKR (approximately $150 in 2023) per month. Only 8.3% indicated that they earn <10,000 LKR per month. While commercial crop cultivation is expensive, our results show that a reasonably high income can be obtained.
In terms of education among smallholder farmers, 50.5% have at least a secondary level education (up to the ordinary level), while only 8.7% have no formal education. The results show that 34% of farmers own 81 perches or more, 22.3% own 61 to 80 perches, and 41% own 41–60 perches. Only 10.7% own <20 perches. Focus group discussions revealed that a perch is priced relatively high due to its agricultural value. Land prices are increasing daily, and even owning a small number of perches can be used for agriculture to generate a reasonably high monthly income. Generally, these farmers do not receive a monthly income, but they earn a substantial amount seasonally, which they distribute throughout the months. For instance, one farmer stated, “I have 60 perches, and if I can sell leeks at a good price, I can earn nearly 1 million LKR. After factoring in the costs, I still make a profit of at least 600,000 LKR.”
Only 20.4% of farmers have formal training in pesticide use (mainly with young farmers who learned them in schools), while the rest have not received any training. The data also suggests that those who have received formal training do not necessarily exhibit more informed pesticide use practices, indicating that these trainings have not been effective in reaching farmers. Table 1 presents demographic information about the respondents along with statistical analyses conducted to examine the relationship between demographic characteristics and informedness of pesticide use.
3.2 Association between demographic characteristics and informedness on pesticide use
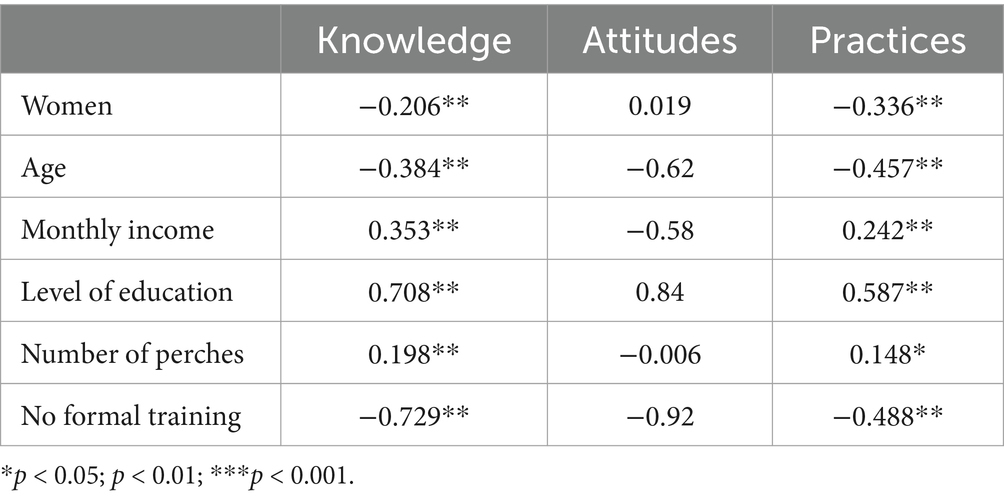
Supplementary Table A1 illustrates the correlation between demographic characteristics and participants’ overall levels of informedness regarding pesticide use. The last two columns of Table 1 present ordinal logistic regression coefficients and Mann–Whitney U test and Kruskal-Walli’s test values, along with chi-square values. All chi-square values are significant implying that there is a strong relationship between demographic characteristics and overall informedness, yet there are within group differences. Among the demographic characteristics, the number of perches owned exhibits a strong correlation with monthly income, and the level of education also shows a fair correlation with monthly income. This suggests that the level of education among farmers can positively influence their profits. This is corroborated by the ordinal logistic regression analysis, which will be discussed later. Formal training on pesticide use demonstrates a fair correlation with gender and age. Male farmers with a younger age are more likely to have received formal training compared to farmers in the age range above 45.
The findings also reveal that formal training in pesticide use is not significantly correlated with the level of education. Descriptive statistics show that while some farmers with education qualifications above A/L have received formal training and some with secondary level education (A/L) have also received training, the correlation between these factors is not statistically significant. In terms of self-reported informedness, monthly income, level of education, and the number of perches owned are significantly correlated. Our results indicate that the level of education is a primary determinant of informedness. Notably, formal training did not contribute to the overall level of informedness among farmers. Qualitative data suggests that this lack of impact from formal training is primarily due to the neglect of instructions obtained from the trainings and the perceived ineffectiveness of these trainings. Farmers believe that these trainings do not directly contribute to increasing their profits. Moreover, most of the training received by younger farmers was from schools or other formal training institutions rather than task-specific awareness programmes.
Gender is significantly associated with age and formal training on pesticide use. Young women are less likely to be involved in farming compared to women in their late forties or fifties. Middle-aged men are heavily involved in commercial crop cultivation in the studied area and tend to use pesticides more frequently. Furthermore, compared to women, men are more informed about pesticide use. The Mann–Whitney U tests confirm a significant difference between men and women, and the β coefficient shows that women are less informed about pesticide use. This is likely because men are heavily involved in agriculture and have greater access to information through informal farmer networks (this will be discussed in later sections).
Furthermore, there is a significant difference in the informedness of pesticide use among different age categories. As shown in Table 1, the β coefficients indicate that younger individuals generally exhibit higher levels of informedness. Those in the age group of 15 to 34 years show high odd ratios, suggesting a higher degree of informedness regarding pesticide use. In terms of monthly income, individuals with lower earnings are less likely to possess higher levels of informedness compared to those engaged in commercial crop cultivation, who can attain more than 30,001 LKR per month. Since pesticides involve significant costs, those with higher incomes tend to purchase pesticides more frequently compared to those with a monthly income below 30,000 LKR.
The level of education also plays a crucial role in being informed. Individuals with at least a secondary level education (A/L) are generally more informed compared to those with education below A/L. Within each group of education levels, there is also a significant difference in informedness about pesticide use. Among farmers belonging to different land categories, those in the 41–60 perch group exhibit a higher level of informedness with 2.9 odd ratios. Additionally, individuals with formal training on pesticide use generally show a higher level of informedness, which imply that task-tailored awareness programmes would increase the level of informedness.
3.3 Overall informedness among farmers on responsible pesticide use
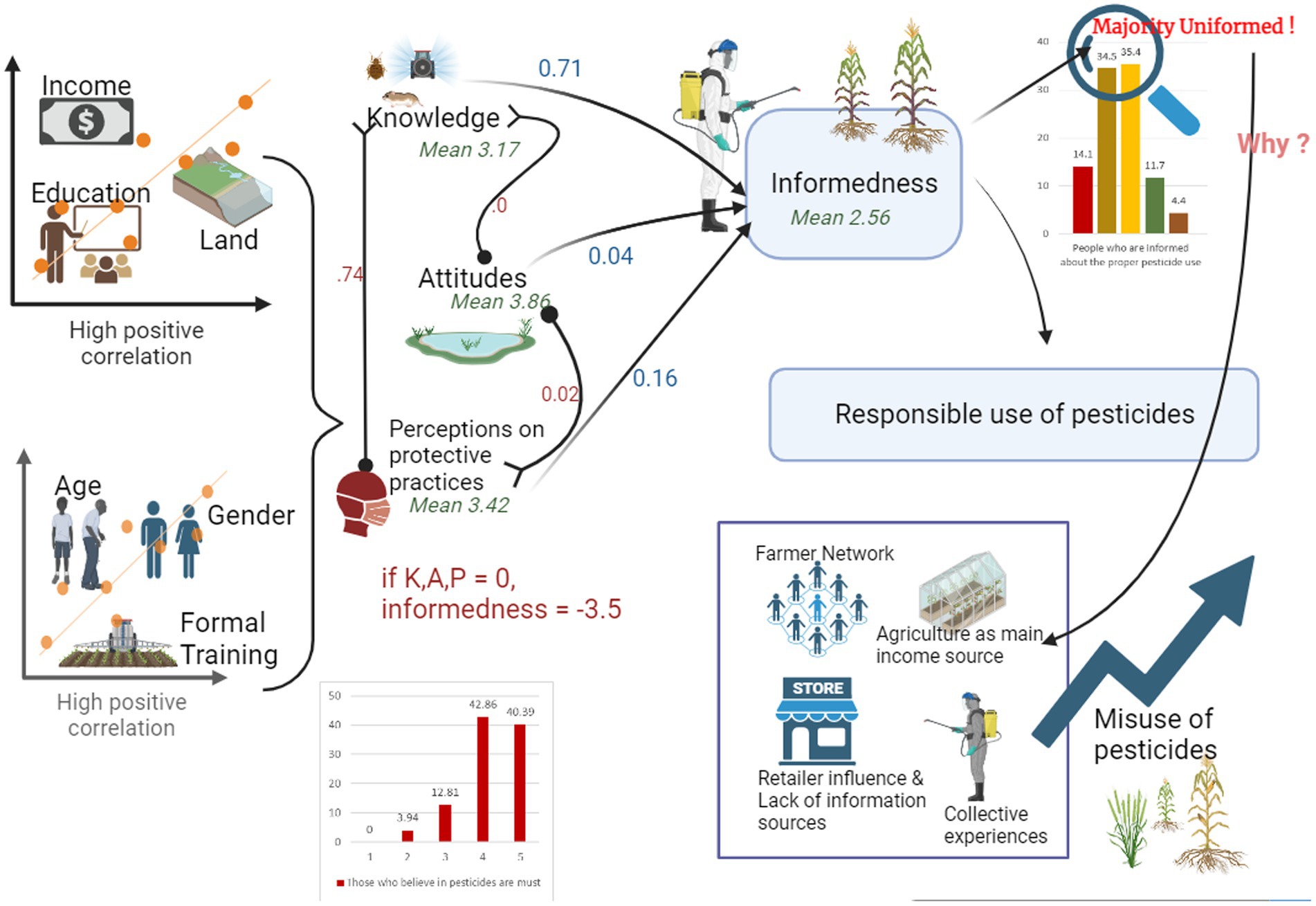
Figure 2 present descriptive statistics related to overall awareness of pesticide use, the ability to distinguish pesticides from other products, the adherence to prescribed pesticide use, and the readiness to seek instructions. The results reveal that 35.4% of participants express uncertainty regarding their awareness regarding the responsible use of pesticides. This suggests a general lack of awareness among farmers about responsible pesticide use (mean: 2.57 ± 0.07), posing a challenge for sustainable agriculture. These scores vary from 1 to 5, and hence 2.57 means lack awareness. A considerable proportion of farmers (34.5%) indicate a reluctance to provide a definitive answer regarding their awareness. Only 11.7% claim to be somewhat informed about pesticide use, and a mere 4.4% assert having a strong level of awareness.
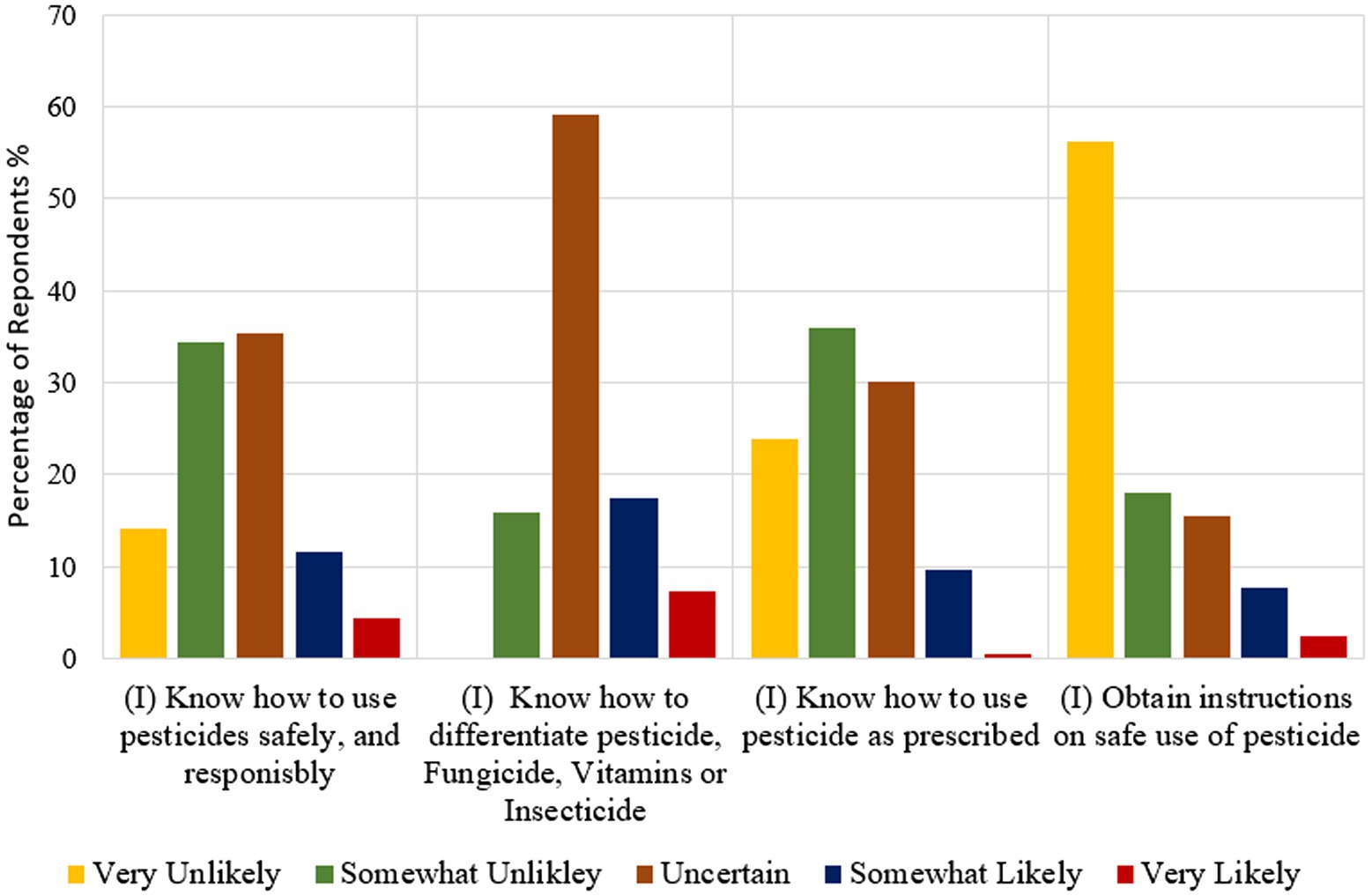
Figure 2. Descriptive statistics on five main statements related to the use of pesticide. This bar chart includes four questionnaire items, each measuring the main knowledge areas (according to Ali et al., 2020; Dunn et al., 2023). “Very unlikely” indicates an extreme lack of understanding of the statement; “Very Likely” indicates a very good level of understanding. In terms of the fourth column, very unlikely indicates the extreme lack of tendency to obtain instruction, and very likely represents the very good tendency to obtain instructions.
A significant proportion (59.2%) of farmers are uncertain about distinguishing between pesticides, fungicides, foliar sprays, and insecticides. Qualitative data reveal that farmers often use pesticides, insecticides, fungicides, or foliar sprays under the common term “wasa” (=chemical) without understanding the specific purpose of each item. One participant remarked, “When we see a problem in the cultivation, we purchase a kind of pesticide and spray it. Often vitamins (foliar spray) are applied to cultivations, seeking high profits.” The data indicate that farmers unnecessarily apply pesticides even without observing symptoms.
Overall, the level of understanding among farmers regarding the distinction between these products is extremely low. Only 7.3% of farmers with a higher education level can accurately distinguish between pesticides, fungicides, foliar sprays, and insecticides. This lack of understanding poses a significant barrier to increase informedness on pesticide use.
Only 10.2% of farmers are aware of the proper use of pesticides, and a significant proportion lacks adequate knowledge about prescribed pesticide application practices. This lack of awareness stems primarily from the scarcity of information sources for obtaining instructions. Nearly 24% of farmers are unable to use pesticides as prescribed, and 30.1% are unsure about the correct application procedures.
Moreover, it is evident that only 2.4% of farmers seek instructions before applying pesticides, while a large majority of 56.3% do not obtain any guidance. This lack of instruction is primarily due to the absence of readily available, responsible personnel. Qualitative data reveal that government-appointed agricultural officers do not provide adequate support to farmers. Furthermore, over 83% of participants believe that pesticides are essential for successful commercial crop cultivation, with only 3.88% expressing the opinion that pesticide use is not mandatory. However, no participant unequivocally stated that pesticide use is entirely unnecessary in commercial crop cultivation.
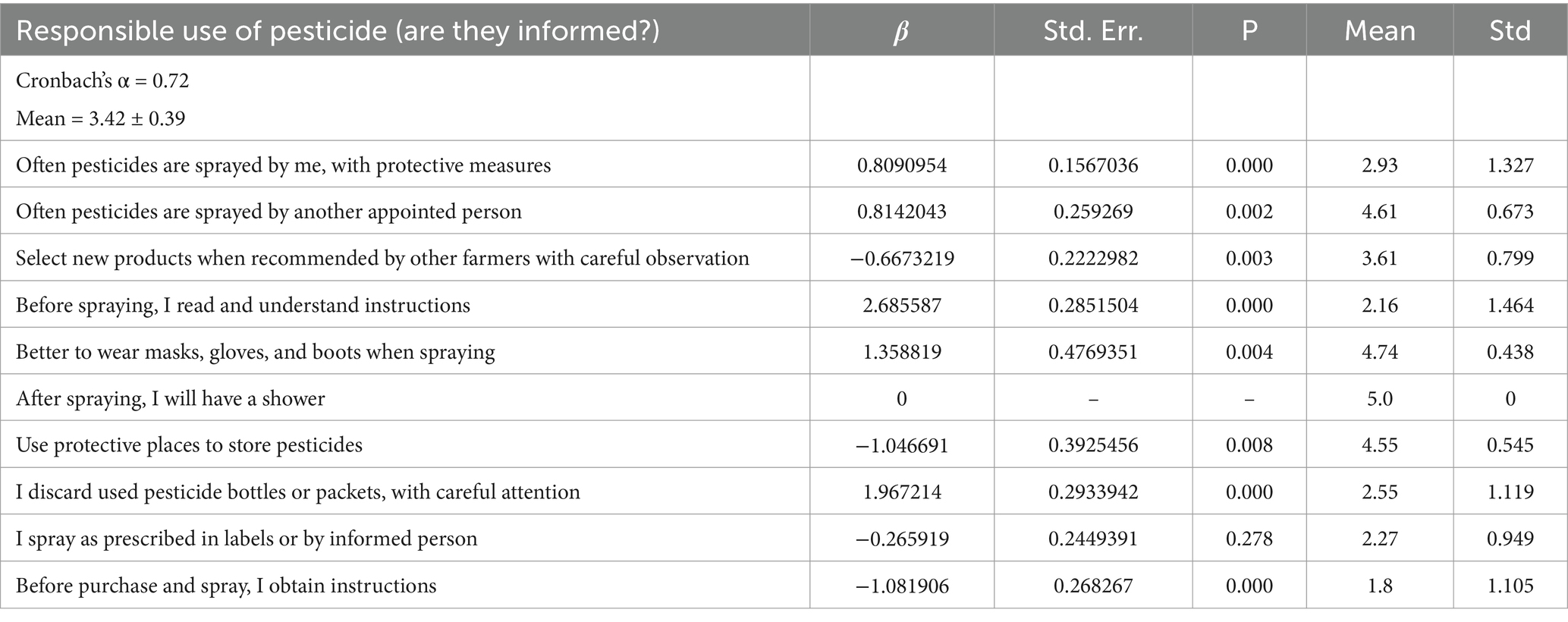
3.4 Knowledge, attitudes, and perceptions on protective practices
Following a clear explanation of the responsibilities associated with pesticide use, farmers’ self-reported informedness or overall mindset on pesticide use behavior was recorded. The knowledge of highland commercial crop cultivators regarding pesticide use was measured using eight self-assessment statements (Table 5). The mean total score for knowledge is 3.17 ± 0.57, suggesting a slightly moderate level of understanding of pesticides. All these mean scores may range from 1 to 5, and middle point is considered as moderate level, and deviation leftwards signify lack of knowledge and rightward drift signify higher level of mean score for the selected item.
Table 5 also displays the mean scores and β values of the ordinal regression model for each self-assessment statement, along with their overall self-reported informedness on pesticide use. All farmers were aware that using pesticides without protective measures would pose a danger to their health and the environment. However, it is worth noting that many farmers are unable to read the instructions on pesticide packets or bottles due to language barriers. Some farmers are aware that certain pesticides are banned, but the majority are unaware (mean score of 2.82 ± 0.88). There are uncertainties even with the appropriate amount of pesticide use, alternatives for pesticides, and the toxicity of pesticides. While some farmers are aware of the toxicity of pesticides, a significant number are unsure. Notably, only 21.36% are aware of the toxicity of pesticides.
The results also demonstrate that farmers are unable to distinguish between pesticides, insecticides, fungicides, or foliar sprays. This implies that respondents have a severe lack of knowledge on pesticide use, which can hinder the success informedness toward responsible use of pesticides (Table 5).
The ordinal logistic regression analysis results indicate that among the eight knowledge-related factors, knowledge of choosing the appropriate product or type, the amount of use, the ability to understand instructions, and knowledge of alternatives to pesticides influence the overall informedness of farmers compared to other elements. In contrast, knowledge of toxicity and awareness of banned products are not significant.
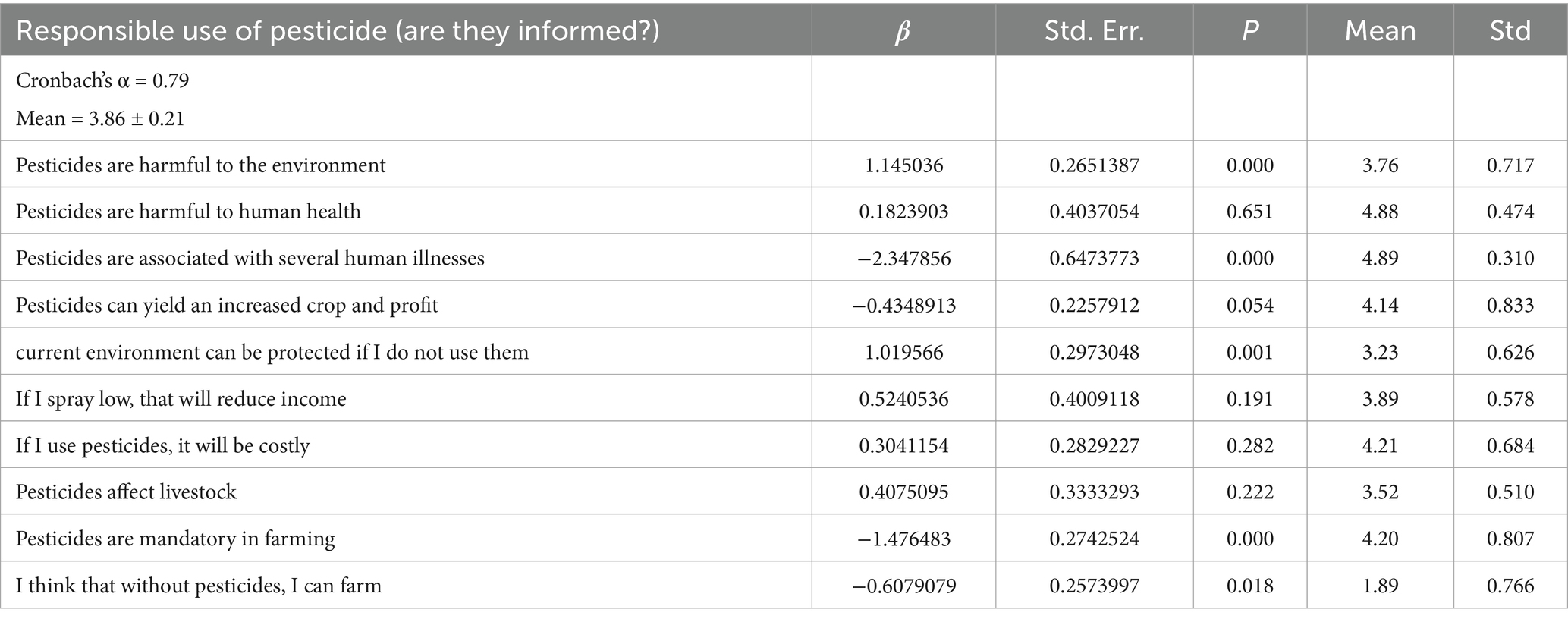
Table 2 presents farmers’ attitudes toward pesticide use. We measured these attitudes using 10 items scale, and the total mean score is 3.86 ± 0.21. Overall, farmers’ attitude scores are moderate and leaning toward good level, suggesting a fair positive trend toward responsible pesticide use. However, regression results indicate that many statements do not influence the level of informedness toward the use of pesticides.
A significant majority of farmers believe that cultivation is impossible without pesticides. None of the respondents indicated even a moderate (4) or high (5) level of confidence in their ability to cultivate without pesticides. Notably, 42.72% believe that pesticides are mandatory, and 40.78% strongly agree that pesticides are necessary. No respondent indicated that pesticides are unimportant. This suggests that promoting organic agriculture in the hill country could face challenges. The mean scores for the influence of pesticides on human health and the environment are higher, indicating that farmers perceive pesticides to be harmful to both the environment and human health. Additionally, the majority of farmers believe that pesticides can lead to higher profits (mean score: 4.14). At the same time, they recognize that decreasing pesticide use would protect the current environment (mean score: 3.23). Overall, the average mean scores for pesticide use as a mandatory practice suggest that hill country farmers are heavily reliant on pesticides, even with a clear understanding of the consequences of heavy use.
Regression results also demonstrate that, compared to other factors, attitudes toward the environment and the perceived influence of pesticides significantly contribute to informedness on pesticide use. When farmers perceive pesticides as mandatory, this belief negatively influences informedness, indicating a decreased level of knowledge regarding pesticide use. A significant majority of farmers (89.32%) believe that pesticides can harm human health. The remaining elements in the attitude section do not significantly influence the overall informedness on pesticide use among farmers, as indicated in Table 3.
Table 3 presents the scores for perceptions of protective behaviors related to pesticide use. It was measured using 10 items scale, and the total mean value is 3.42 ± 0.39, indicating that a majority of respondents demonstrate a moderate level of perception of protective behaviors associated with pesticide use. Oftentimes, farmers prefer to have someone else spray pesticides instead of doing it themselves. Approximately 30.1% of farmers rarely spray pesticides themselves, and only 14.56% solely handle pesticide application. This practice of employing others for pesticide spraying significantly contributes to overall informedness regarding pesticide use, as regression coefficients demonstrate. A large majority of respondents tend to hire someone else to spray pesticides as a protective measure. However, qualitative data reveal that poor daily laborers are employed for spraying pesticides, and they lack adequate protective measures. Due to their fear of pesticides and their potential aftereffects, farmers often prefer to have someone else handle this task. Nevertheless, regression analysis indicates that employing a trained individual for pesticide spraying positively influences informedness about pesticide use.
Farmers often rely on recommendations from other farmers when purchasing pesticides, but this practice does not positively contribute to their informedness. In fact, the tendency to consider recommendations from other farmers can have a negative impact on informedness. A lack of English language proficiency hinders farmers’ ability to read pesticide instructions, which are often printed in English. This lack of readiness to read instructions also negatively affects informedness. Increasing the level of perception regarding the importance of reading instructions before spraying could positively influence the level of informedness.
On a positive note, a significant number of farmers adopt protective measures by wearing masks, gloves, and boots when spraying pesticides. This practice positively correlates with overall informedness regarding pesticide use. Additionally, all respondents indicated that they shower after spraying, making it a generally integrated part of their pesticide use behavior.
The majority of respondents (mean score of 4.74) store pesticides in a protective place, indicating that this practice is well-established in their behavior. However, this practice does not significantly impact informedness. Conversely, the perception of discarding pesticide packets or bottles after use positively contributes to informedness, with a mean value of 2.55 ± 1.11. A major concern identified through perception analysis is that farmers lack adequate interventions to spray pesticides as prescribed. This is primarily due to a lack of information sources and the unreadability of instructions.
Table 4 summarizes the correlation coefficients between knowledge, attitudes, and practice perspectives, along with demographic characteristics. Overall, demographic characteristics are not significantly correlated with attitudes. When compared to the level of knowledge and perspectives on protective practices, attitudes remain uncorrelated. Knowledge and practices exhibit a negative relationship with gender, indicating that men tend to be more knowledgeable about pesticide use and have more positive perceptions of protective behaviors. Similar observations are evident for age, with younger individuals demonstrating a more positive trend compared to older adults. Moreover, farmers with higher incomes tend to exhibit a higher level of knowledge and practice perspectives. Higher levels of education are also correlated with knowledge and protective practice perspectives, suggesting that more educated individuals possess greater knowledge and more positive perspectives on protective practices. The same trend applies to the land area owned by farmers. In addition, having formal training positively contributes to the level of knowledge and practice perspectives to a greater extent.
Supplementary Table A2 illustrates the correlations between self-reported informedness, level of knowledge, attitudes, and perspectives on protective practices. The table reveals a strong correlation between knowledge and practice, indicating that higher levels of knowledge lead to more positive practice perspectives. Despite exhibiting a moderate level of attitudes, farmers demonstrate that attitudes are not significantly related to knowledge, practices, or self-reported informedness. This observation suggests that even though farmers acknowledge the potential risks posed by pesticides to human health and the environment, they continue to overuse pesticides. Qualitative data confirms this finding. For instance, one farmer remarked, “I believe that the current environment can be protected if I do not spray pesticides consecutively. However, in order to increase profits, I spray them.” Another farmer commented, “Organic farming is good. But I do not think that without pesticides, hybrid crops are possible to grow here.” These statements highlight that despite having positive attitudes toward responsible pesticide use, individuals may prioritize short-term economic gains over long-term environmental and health concerns. Overall, our analysis implies that implementing IPM strategies will be difficult for the highland vegetable growers in Sri Lanka, as they are locked-in to pesticide use.
Furthermore, overall informedness, or the propensity for responsible pesticide use, is strongly associated with knowledge and practice perspectives. Attitudes do not exhibit significant correlations with other primary factors. All this implies that even with fairly positive attitudes, informedness on the responsible use of pesticides can be minimum due to several other background factors we discovered through qualitative data analysis.
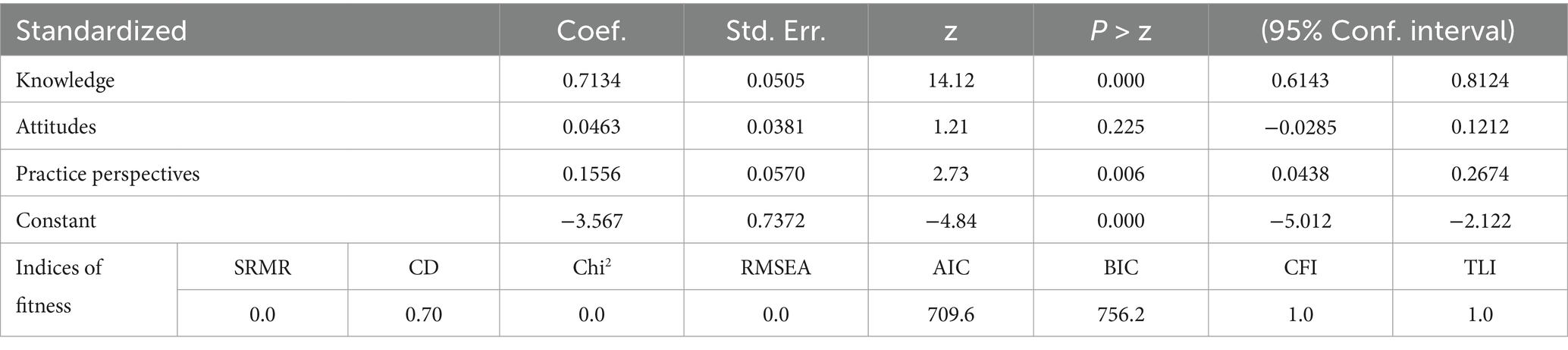
The SEM results presented in Table 6 support this observation. Indices of fitness of the SEM confirms the appropriateness of the model. Path diagram is depicted in Supplementary Figure A1. The level of knowledge positively contributes to self-reported informedness (0.713, p < 0.05). Conversely, attitudes do not exert a statistically significant effect on informedness. For every 0.156 standard deviation increase in perceptions of protective practices, there is a corresponding increase in informedness. When knowledge, attitudes, and practice perceptions are zero, informedness is expected to be −3.567 standard deviations.
In summary, the SEM results demonstrate significant relationships between knowledge, practice, and informedness, while attitudes do not make a significant contribution. Indices of fitness for the structural model are also shown in Table 6, and overall, all reported indices indicate a good fit to the data.
3.5 Factors affecting the informedness for pesticide use
Statistical analysis revealed that the level of knowledge and perceptions of protective behaviors are closely associated with the overall informedness on responsible pesticide use among smallholder crop cultivators in the highland areas of Sri Lanka. However, the impact of attitudes on informedness was found to be insignificant. Qualitative data obtained from focus group discussions revealed four main reasons that may contribute to this disconnect.
3.5.1 Theme 1: obtaining information from farmer-networks
Despite the absence of formal training in pesticide use, a large number of farmers demonstrate a relatively good level of knowledge regarding responsible pesticide practices. This knowledge primarily stems from their extensive experience in commercial crop cultivation over prolonged periods of time. With involvement in agriculture spanning over two decades, older farmers often rely on information obtained through informal social networks within their villages. These networks, typically formed based on shared interests, provide farmers with insights into pesticide use, but the credibility of these information is often questionable.
“Often, when we meet, we discuss matters related to our farming. My friends recommend certain solutions for crop diseases, and pesticides are often recommended by them.”
Another farmer stated, “I do not understand and know the toxicity of those pesticides or their real use. However, since my friends have experienced the use of those new products, I also tend to use them.”
Farmers’ reliance on informal social networks stems primarily from a lack of reliable information sources. As indicated by participants, government-appointed agricultural officers often lack sufficient knowledge about pesticide use, particularly in hilly areas. As a result, farmers refrain from seeking guidance from these officials.
“Agriculture officers do not know much about commercial crop cultivation. They just came to visit us and inform about farmer insurance or collecting taxes. They do not know anything about farming.”
Furthermore, many middle-aged and older farmers lack the ability to access information through the internet, primarily due to illiteracy in internet usage. As a result, they heavily rely on pesticide retailers for information. These factors collectively contribute to a shortage of authentic knowledge regarding pesticide use among farmers.
Despite understanding the detrimental consequences of pesticide overuse, farmers continue to engage in excessive usage. This behavior is largely attributed to the lack of reliable information and genuine knowledge they have received. As a result, benefits that they can obtain from responsible use of pesticides have been neglected.
3.5.2 Theme 2: dependence on commercial crop cultivation
Highland commercial crop cultivators involved in this study heavily rely on agriculture as their primary source of income. Even though some farmers or family members may engage in off-farm employment, farming remains the cornerstone of their income generation. The scarcity of alternative income sources compels farmers to place a heavy reliance on agriculture. This reliance often drives profit-seeking behavior, leading to the overuse of pesticides.
“Since we depend solely on agriculture, we have to protect our crops. And we think of using pesticides and other chemicals, including fertilizers, as much as possible.”
Hill country areas are frequently characterized by high rainfall, making crops susceptible to frequent pest attacks. As a result, even in the absence of visible symptoms, farmers tend to adopt a continuous approach to pesticide usage. In addition, farmers strive to apply multiple foliar sprays or pesticides until they meet a favorable price for their harvested crops.
A farmer commented, “Even after 6 months, I had to spray pesticides mixed with foliar spray to keep my Leaks cultivation for about 2 weeks or more to meet a good market price.”
The financial struggles faced by farmers, characterized by the stark contrast between high expenditures and fluctuating crop income, often lead to the indiscriminate use of pesticides. Over time, this practice has developed a mindset indicating that pesticides are an indispensable element of agriculture.
3.5.3 Theme 3: dependence on collective experiences rather than formal information or attitudes
Among the studied farmers, the level of informedness regarding responsible pesticide use was low to moderate. This limited knowledge can be attributed to their reliance on past experiences and the collective knowledge of farmer networks. Over an extended period, farmers have heavily utilized pesticides, and the positive experiences of increased profits have reinforced their existing pesticide use practices. This reliance on past experiences hinders the adoption of integrated pest management (IPM) practices at the individual level. For instance, the practice of spraying pesticides even in the absence of symptoms in cultivations has been perpetuated by past experiences and the experiences of other farmers.
“Heavy use of pesticides is bad for health and the environment. But we experienced that during past years, without spraying such an amount of pesticides, we cannot increase profits.”
These experiences associated with heavy pesticide use inhibit farmers’ understanding of responsible pesticide use. However, these experiences have also promoted protective behaviors related to pesticide use. Despite this, some farmers still fail to adhere to precautionary measures during pesticide application.
Another farmer commented, “Several farmers died during the past few years due to cancer. I think this is because of heavy pesticide use without any protective measures.”
Although past experiences have contributed to an increase in protective behaviors and knowledge levels, responsible pesticide use practices have not been widely adopted. This is primarily due to the neglect of formal information compared to the weight given to past experiences.
3.5.4 Theme 4: belief on mandatory association between pesticides and hybrid seeds
Farmers perceive pesticides as an obligatory component of cultivating hybrid seeds, particularly since the introduction of hybrid seeds in the Nuwara Eliya region. Due to the climatic conditions, cultivating local vegetables is challenging, leading farmers to believe that pesticides and associated chemical products are essential for the success of hybrid crops.
“We think that these hybrid seeds cannot be grown without related fertilizers and pesticides. Once, I tried to do so but failed.”
Farmers also expressed the belief that pest infestations cannot be effectively controlled without pesticide use.
“If we do not use pesticides, pest attacks cannot be resolved. It is constant. Therefore, from time to time, as a practice, we tend to spray them.”
Over time, pesticide use has become ingrained in the agricultural practices of farmers in the region. They firmly believe that, even in the absence of visible symptoms, preventive pesticide spraying is necessary to mitigate future pest attacks and plant diseases.
This deep-rooted belief in the mandatory association between pesticides and hybrid seeds contributes to the excessive use of pesticides, hindering the adoption of responsible pesticide use practices.
The mandatory use of pesticides has been advocated by pesticide retailers, and data indicate that they exert significant influence over pesticide selection, usage, and the introduction of new pesticides. Nevertheless, the authenticity and trustworthiness of their intervention are questionable, given their lack of formal training.
“We often obtain instructions from pesticide shops. They introduce us the relevant pesticides.”
In summary, the four factors discussed above explain why farmers in the hilly areas of Sri Lanka continue to employ pesticides indiscriminately, despite their generally positive attitudes and knowledge toward responsible use of pesticide.
4 Discussion
Responsible use of pesticides is widely recognized as a cornerstone of sustainable agriculture, promoting total environmental health. However, research at the individual level on the preparedness of smallholder farmers for responsible use of pesticides is relatively limited. Our study aimed to fill this gap exploring how knowledge, attitudes, and practice perspectives regarding protective behaviors influence the overall informedness of responsible pesticide use among smallholder farmers in the Sri Lankan highlands. Our approach entailed measuring correlations between demographic characteristics and the level of informedness, examining differences between demographic groups, and analysing how knowledge, attitudes, and perspectives on protective practices contribute to the overall informedness of responsible pesticide use.
Our study looked into the unique characteristics of highland commercial vegetable cultivation in Sri Lanka, where a significant portion of smallholder farmers are heavily engaged in seasonal vegetable production and hold strong beliefs in the necessity of extensive pesticide use. Farmers’ deep-rooted dependence on pesticides can be attributed to their limited understanding and lack of confidence in alternative pest management strategies. Our findings resonate with those of Dunn et al. (2023), who identified a high likelihood of pesticide overuse among rice farmers in Cambodia. However, our findings deviate from the conclusions of Dissanayake et al. (2022) by indicating that knowledge levels and practice perspectives play a more significant role in influencing pesticide use patterns than do farmers’ attitudes.
Although a lack of knowledge, awareness, and positive attitudes toward IPM have often been cited as impediments to the implementation of IPM policies in Sri Lanka (Jayasooriya and Aheeyar, 2016), our study highlights that even with relatively positive attitudes, the level of informedness regarding responsible pesticide use can be diminished by various sociocultural factors. One such factor is the influence of farmer networks, where individuals may be pressured to conform to prevailing practices, including the heavy use of pesticides. Somewhat similar observation was done by Mohankumar et al. (2024) in India, where pesticide misuse occur as a result of non-authentic information received from informal farmer networks. Moreover, the heavy reliance on agriculture as a primary source of income may drive farmers to continue using excessive pesticides, even when they possess a good understanding of alternative approaches. This is due to the perceived need to maximize yields and secure their livelihoods. Vlaiculescu and Varrone (2022) notes that due to the same reason, even within EU, alternative approaches to pesticides are not being fully attended.
A significant majority of smallholder farmers in the Sri Lankan highlands hold the firm belief that pesticide application is an essential component of agricultural practices. This mindset often leads to the misuse or irresponsible use of pesticides, resulting in adverse environmental and health consequences. This finding aligns with observations made by Flor et al. (2019) in Cambodia, where a similar pattern of pesticide overuse was prevalent. This is comparable to some regions on Africa where smallholder cultivators predominantly work in agriculture sector (Srinivasan et al., 2022). However, it is noteworthy that the level of heavy reliance on pesticides observed among Sri Lankan farmers is not as pronounced as that seen among rice farmers in Cambodia (Horgan and Kudavidanage, 2020).
While no studies specifically informed us about gender norms and pesticide use in Sri Lanka, evidence from various studies conducted across different countries indicates that women generally have lower exposure to pesticides (Asmare et al., 2022). Findings of the present study align with this trend, confirming that women’s exposure to pesticides is minimal, primarily due to the male dominance in highland vegetable cultivation. Women are less likely to make informed decisions regarding pesticide use, relying heavily on instructions from men. Owing to their limited involvement in farming activities, women also lack awareness about the responsible use of pesticides. As highlighted by Wang et al. (2017), male farmers tend to possess better knowledge and awareness of pesticide use. Our study reaffirms these findings, demonstrating that women exhibit a lack of awareness regarding the responsible use of pesticides. However, we also found that highland vegetable cultivation is closely linked to gender norms, with men being more openly welcomed into agriculture than women. This gender disparity contributes to a higher level of informedness among men, and the farmer network among male farmers further amplifies this informedness.
The overall informedness among farmers regarding the responsible use of pesticides is significantly undermined by four main factors: the inability to distinguish pesticides and related chemicals, the inability to use them as prescribed, a belief in the mandatory use of pesticides, and a lack of motivation to seek instructions. Previous research has highlighted the impact of misconception on the mandatory use of pesticides and the tendency to avoid seeking instructions (Jayasooriya and Aheeyar, 2016; Weerasinghe et al., 2020). However, our study reveals an additional influential factor—the inability to distinguish among different products. Building on the work of Bagheri et al. (2019), who emphasized the importance of attitudes, knowledge, and perceptions in shaping safety behaviors, our findings support the notion that knowledge and perceptions play a crucial role in influencing informedness regarding the responsible use of pesticides.
Smallholder farmers in developing countries often come from impoverished communities and consider agriculture as their main source of income (Ali et al., 2020; Otchia, 2014). Research reveals that the agricultural sector employs many impoverished people because it does not require profound subject expertise (Horgan and Kudavidanage, 2020; Sumudumali et al., 2021). This is particularly common among highland crop cultivators in Sri Lanka, most of whom have lower levels of education and experience relative poverty. As a result, these farmers tend to focus on maximizing profits using pesticides and related products and heavily rely on any available source of information, often without verifying their authenticity. Therefore, research has suggested that product labeling can serve as an effective communication channel for promoting the responsible use of pesticides (Abou Ibrahim et al., 2023). However, our study found that respondents demonstrated only a moderate level of awareness regarding pesticide labels. Many found the instructions difficult to read or simply ignored the printed messages. Therefore, to effectively communicate safe pesticide usage, labels should use user-friendly language and include pictograms. The importance of labeling has been widely recognized in other parts of the world where smallholder farmers play a significant role in agriculture.
Moreover, several studies have examined pesticide poisoning incidents in Sri Lanka, particularly in the dry zone, where suicide by pesticide poisoning is prevalent (Mohamed et al., 2009; Weerasinghe et al., 2020). Our findings indicate a favorable attitude among farmers, likely contributing to the relatively low incidence of pesticide-related suicides. However, a concerning practice is the employment of untrained laborers for pesticide application instead of adequately trained individuals. To address this issue, we recommend providing farmers with comprehensive training on protective pesticide use practices, which extend beyond the mere use of personal protective equipment such as masks, gloves, and showering after application.
Overall, the findings imply that the highland crop cultivators in Sri Lanka are not readily on track toward sustainable agriculture through the conscious use of pesticides. However, it appears that there is a way to integrate these farmers with practices related to the responsible use of pesticides. One of the main entries focuses on raising awareness among participants about the importance of reading labels and advocating for government institutions to implement necessary policy provisions to make labeling more user-friendly and comprehensible. Furthermore, the lack of a robust information-receiving mechanism necessitates the revision of existing bureaucratic systems at the ground level and the training of trainers to incorporate knowledge about sustainable agriculture and responsible pesticide use. Given that fewer women work in agriculture, they have significantly less knowledge about responsible pesticide use. However, as studies suggested, in order to empower women through sustainable agriculture, they must be made aware of the responsible use of pesticides. Moreover, alternative methodologies for pesticides can be employed (Srinivasan et al., 2022; Vlaiculescu and Varrone, 2022). Overall, our findings are analytically generalisable to agricultural communities in the developing world, where the behaviors of farmers seem similar.
We acknowledge certain limitations of the present study. While our participants were smallholder crop cultivators in the highlands of Sri Lanka, the knowledge, attitudes, and practices of farmers with landholdings exceeding one acre may differ substantially. These larger landholders are likely to use large quantities of pesticides and related products, and number of these farmers are steadily increasing. Future studies should focus on these farmers, as they have the potential to evolve into large-scale commercial vegetable cultivators. We limited our study to highland vegetable growers in Sri Lanka, including both men and women. However, we did not deeply explore the gender dimension. Investigating gender-specific perspectives on the responsible use of pesticides could provide nuanced insights, particularly for the development of targeted policies. In addition, while farmer networks at the community level play a crucial role, they were not a primary focus of this study. Instead, we concentrated on understanding KAP dynamics at the individual level. Future research should consider examining collective decision-making among farmers, as it may yield important insights for promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
5 Conclusion
This study investigated the factors influencing informedness about the responsible use of pesticides among smallholder commercial vegetable farmers in the central highlands of Sri Lanka, particularly focusing on their level of knowledge, attitudes and practice perspectives. Overall, our findings indicated a deficiency in informedness on responsible pesticide use, primarily stemming from a moderate level of knowledge and perceptions regarding protective practices. Importantly, it was possible to moderate the level of knowledge and perceptions about practices to improve informedness among smallholder farmers. Farmers often find themselves dependent on pesticide use due to unreliable information sources and an economic imperative to maximize profits. Significant differences in informedness were identified among various demographic groups, with men exhibiting higher levels of informedness compared to women and younger farmers demonstrating a higher level of informedness. Proving customized awareness programmes to pesticide use at the individual level was found to enhance informedness among farmers, as formal training on pesticide use significantly influenced the tendency toward responsible pesticide use. Implementing Integrated Pest Management (IPM) interventions in this community posed challenges, as farmers could easily deviate from such practices. The lack of confidence in alternatives to pesticides primarily results in the irresponsible use of these chemicals. Therefore, authorities are required to introduce pragmatic solutions that promote both alternatives to pesticides and responsible mechanisms for pesticide use.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences, University of Ruhuna, Sri Lanka. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
SU: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BB: Writing – review & editing. HD: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The APC has been granted by the University of Bremen.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at:
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fsufs.2024.1490110/full#supplementary-material
References
Abou Ibrahim, S., Naji, R., Zeineldeen, H., and Ghach, W. (2023). Effectiveness of pesticide labels (pictograms and color codes): a cross-sectional study of farmers’ understanding and practices in Lebanon. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 29, 1336–1351. doi: 10.1080/10807039.2023.2266036
Ali, M. P., Kabir, M. M. M., Haque, S. S., Qin, X., Nasrin, S., Landis, D., et al. (2020). Farmer’s behavior in pesticide use: insights study from smallholder and intensive agricultural farms in Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 747:141160. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141160
Asmare, B., Freyer, B., and Bingen, J. (2022). Women in agriculture: pathways of pesticide exposure, potential health risks and vulnerability in sub-Saharan Africa. Environ. Sci. Eur. 34, 1–14. doi: 10.1186/s12302-022-00638-8
Bagheri, A., Emami, N., Damalas, C. A., and Allahyari, M. S. (2019). Farmers’ knowledge, attitudes, and perceptions of pesticide use in apple farms of northern Iran: impact on safety behavior. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 26, 9343–9351. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04330-y
Braun, V., and Clarke, V. (2019). Reflecting on reflexive thematic analysis. Q. Res. Sport Exercise Health 11, 589–597. doi: 10.1080/2159676X.2019.1628806
Buckley, N. A., Fahim, M., Raubenheimer, J., Gawarammana, I. B., Eddleston, M., Roberts, M. S., et al. (2021). Case fatality of agricultural pesticides after self-poisoning in Sri Lanka: a prospective cohort study. Lancet Glob. Health 9, e854–e862. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00086-3
Burchfield, E. K., Poterie, A., and de la, T. (2018). Determinants of crop diversification in rice-dominated Sri Lankan agricultural systems. J. Rural. Stud. 61, 206–215. doi: 10.1016/j.jrurstud.2018.05.010
Central Bank of Sri Lanka (2023). Economic and social statistics of Sri Lanka 2022. Colombo: Central Bank of Sri Lanka.
Datta, S., Singh, J., Singh, S., and Singh, J. (2016). Earthworms, pesticides and sustainable agriculture: a review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 23, 8227–8243. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6375-0
Delcour, I., Spanoghe, P., and Uyttendaele, M. (2015). Literature review: impact of climate change on pesticide use. Food Res. Int. 68, 7–15. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2014.09.030
Department of Census and Statistics. (2015). Agriculture related statistics - Nuwara Eliya District. Available at: http://www.statistics.gov.lk/Agriculture/StaticalInformation/new/EconomicCensus2013-14-AgricuturalEnumeration-BasicReports-NuwaraEliyaDistrict (Accessed April 30, 2024).
Dissanayake, D. M. P. N. K., Silva, S., De, N. T., Pathmarajah, S., Kodagoda, K. A. D. A., Chandimal, T. M. R., et al. (2022). Pesticides used in Rice cultivation: application pattern by farmers in Trincomalee District. Trop. Agric. Res. 33, 173–182. doi: 10.4038/tar.v33i2.8474
Dunn, L., Latty, T., Van Ogtrop, F. F., and Tan, D. K. Y. (2023). Cambodian rice farmers’ knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAPs) regarding insect pest management and pesticide use. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 21, 1–17. doi: 10.1080/14735903.2023.2178804
European Commission. (2021). The use of pesticides in developing countries and their impact on health and the right to food. Available at: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/cmsdata/219887/ (Accessed April 20, 2024).
European Commission. (2022). The sustainable use of plant protection products and amending regulation. Available at: https://food.ec.europa.eu/system/files/2022-06/pesticides_sud_eval_2022_reg_2022-305_en.pdf (Accessed May 24, 2024).
FAO. (2021). Ecosystem services assessment in selected agricultural lands in Kandy, Badulla and Nuwara Eliya districts of Sri Lanka. Available at: https://www.fao.org/3/cb4567en/cb4567en.pdf (Accessed May 15, 2024).
FAO. (2022). Pest and Pesticide Management. Integrated Pest Management. Available at: https://www.fao.org/pest-and-pesticide-management/ipm/integrated-pest-management/en/ (Accessed May 24, 2024).
Flor, R. J., Maat, H., Hadi, B. A. R., Kumar, V., and Castilla, N. (2019). Do field-level practices of Cambodian farmers prompt a pesticide lock-in? Field Crop Res. 235, 68–78. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2019.02.019
Haque, A. K. E., Mukhopadhyay, P., Nepal, M., and Shammin, R. (2021). Climate change and community resilience: Insights from South Asia. Singapore: Springer.
Horgan, F. G., and Kudavidanage, E. P. (2020). Use and avoidance of pesticides as responses by farmers to change impacts in Rice ecosystems of southern Sri Lanka. Environ. Manag. 65, 787–803. doi: 10.1007/s00267-020-01272-x
Jayasiri, M. M. J. G. C. N., Yadav, S., Dayawansa, N. D. K., Propper, C. R., Kumar, V., and Singleton, G. R. (2022a). Spatio-temporal analysis of water quality for pesticides and other agricultural pollutants in Deduru Oya river basin of Sri Lanka. J. Clean. Prod. 330, 129897–129811. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129897
Jayasiri, M. M. J. G. C. N., Yadav, S., Propper, C. R., Kumar, V., Dayawansa, N. D. K., and Singleton, G. R. (2022b). Assessing potential environmental impacts of pesticide usage in Paddy ecosystems: a case study in the Deduru Oya River basin, Sri Lanka. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 41, 343–355. doi: 10.1002/etc.5261
Jayasooriya, H. J. C., and Aheeyar, M. M. M. (2015). Application of integrated Pest management (IPM) in vegetable cultivation: past experiences and suggestions for promotion. Available at: http://www.harti.gov.lk/images/download/reasearch_report/new1/175.pdf (Accessed April 21, 2024).
Jayasooriya, H. J. C., and Aheeyar, M. M. M. (2016). Adoption and factors affecting on adoption of integrated Pest management among vegetable farmers in Sri Lanka. Procedia Food Sci 6, 208–212. doi: 10.1016/j.profoo.2016.02.052
Jayasumana, C., Gajanayake, R., and Siribaddana, S. (2014). Importance of arsenic and pesticides in epidemic chronic kidney disease in Sri Lanka. BMC Nephrol. 15, 1–5. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-15-124
Kadupitiya, H. K., Madushan, R. N. D., Gunawardhane, D., Sirisena, D., Rathnayake, U., Dissanayaka, D., et al. (2022). Mapping productivity-related spatial characteristics in Rice-based cropping Systems in Sri Lanka. J. Geovis. Spat. Anal. 6, 1–10. doi: 10.1007/s41651-022-00122-0
Liao, X., Nguyen, T. P. L., and Sasaki, N. (2022). Use of the knowledge, attitude, and practice (KAP) model to examine sustainable agriculture in Thailand. Reg Sust 3, 41–52. doi: 10.1016/j.regsus.2022.03.005
Ma, C. S., Zhang, W., Peng, Y., Zhao, F., Chang, X. Q., Xing, K., et al. (2021). Climate warming promotes pesticide resistance through expanding overwintering range of a global pest. Nat. Commun. 12, 5351–5310. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25505-7
Maddah, D., Ghach, W., Abi Farraj, N., Yehya, M., Al Khatib, J., and Alami, N. H. (2020). The first community-based intervention to promote safe pesticide use by developing knowledge, attitudes, and practices among Lebanese farmers. Hum. Ecol. Risk. Assess. 26, 2824–2835. doi: 10.1080/10807039.2019.1688639
Maggi, F., Tang, F. H. M., and Tubiello, F. N. (2023). Agricultural pesticide land budget and river discharge to oceans. Nature 620, 1013–1017. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06296-x
Marambe, B., and Herath, S. (2020). Banning of herbicides and the impact on agriculture: the case of glyphosate in Sri Lanka. Weed Sci. 68, 246–252. doi: 10.1017/wsc.2019.71
Mohamed, E., Jarboui, A., Garoui, N., Ibrahim, S., Alsalman, A. M., and Abbassi, W. (2024). The determinants of the responsible use of pesticides among date farmers in Qassim region, Saudi Arabia. Cogent Food Agric 10:14238. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2024.2314238
Mohamed, F., Manuweera, G., Gunnell, D., Azher, S., Eddleston, M., Dawson, A., et al. (2009). Pattern of pesticide storage before pesticide self-poisoning in rural Sri Lanka. BMC Public Health 9, 1–5. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-9-405
Mohankumar, L., Thiyaharajan, M., and Venkidusamy, K. S. (2024). Understanding the communication network of farmers to ensure the sustainable use of pesticides. J. Environ. Stud. Sci. 14, 12–23. doi: 10.1007/s13412-023-00861-6
Nishantha, K. M. D. W. P., Sandika, A. L., Babu, A. G. C., Hettiarachchi, H. A. S. N., Pushpanjali, K., Abeytilakeratna, P. D., et al. (2016). Farmers’ knowledge and attitudes on pesticide usage in vegetable cultivation in Sri Lanka. Trop. Agric. Res. Ext. 19:244. doi: 10.4038/tare.v19i2.5350
Okonya, J. S., Syndikus, K., and Kroschel, J. (2013). Farmers’ perception of and coping strategies to climate change: evidence from six agro-ecological zones of Uganda. J. Agric. Sci. 5:252. doi: 10.5539/jas.v5n8p252
Otchia, C. S. (2014). Agricultural modernization, structural change and pro-poor growth: policy options for the Democratic Republic of Congo. J. Econ. Struct. 3, 1–43. doi: 10.1186/s40008-014-0008-x
Padmajani, M. T., Aheeyar, M. M. M., and Bandara, M. A. C. S. (2014). Assessment of pesticide usage in up-country vegetable farming in Sri Lanka. Available at: http://www.harti.gov.lk/images/download/reasearch_report/new1/164.pdf (Accessed May 02, 2024).
Palinkas, L. A., Horwitz, S. M., Green, C. A., Wisdom, J. P., Duan, N., and Hoagwood, K. (2015). Purposeful sampling for qualitative data collection and analysis in mixed method implementation research. Adm. Policy Ment. Health Ment. Health Serv. Res. 42, 533–544. doi: 10.1007/s10488-013-0528-y
Pimbert, M. (2009). Key highlights in sustainable agriculture and natural resource management towards food sovereignty : London, Routledge.
Popp, J., Pető, K., and Nagy, J. (2013). Pesticide productivity and food security. A review. Agronomie 33, 243–255. doi: 10.1007/s13593-012-0105-x
Rather, I. A., Koh, W. Y., Paek, W. K., and Lim, J. (2017). The sources of chemical contaminants in food and their health implications. Front Pharmacol 8:830. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00830
Rother, H. A. (2018). Pesticide labels: protecting liability or health? – unpacking “misuse” of pesticides. Curr Opin Environ Sci Health 4, 10–15. doi: 10.1016/J.COESH.2018.02.004
Sharifzadeh, M. S., and Abdollahzadeh, G. (2021). The impact of different education strategies on rice farmers’ knowledge, attitude and practice (KAP) about pesticide use. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 20, 312–323. doi: 10.1016/j.jssas.2021.03.003
Shipley, E. R., Vlahos, P., Chandrajith, R., and Wijerathna, P. (2022). Agrochemical exposure in Sri Lankan inland water systems. Environ Adv 7:100150. doi: 10.1016/j.envadv.2021.100150
Srinivasan, R., Tamò, M., and Subramanian, S. (2022). The case for integrated pest management in Africa: transition from a pesticide-based approach. Curr Opin Insect Sci 54:100970. doi: 10.1016/j.cois.2022.100970
Ssekkadde, P., Tomberge, V. M. J., Brugger, C., Atuhaire, A., Dalvie, M. A., Rother, H. A., et al. (2024). Evaluating and enhancing an educational intervention to reduce smallholder farmers’ exposure to pesticides in Uganda through a digital, systematic approach to behavior change: protocol for a cluster-randomized controlled trial. JMIR Res Protocols 13:e55238. doi: 10.2196/55238
Sumudumali, R. G. I., Jayawardana, J. M. C. K., Piyathilake, I. D. U. H., Randika, J. L. P. C., Udayakumara, E. P. N., Gunatilake, S. K., et al. (2021). What drives the pesticide user practices among farmers in tropical regions? A case study in Sri Lanka. Environ. Monit. Assess. 193, 860–825. doi: 10.1007/s10661-021-09611-z
Tavakol, M., and Dennick, R. (2011). Making sense of Cronbach’s alpha. Int J Med Educ 2, 53–55. doi: 10.5116/ijme.4dfb.8dfd
The World Bank. (2009). Sri Lanka Agricultural Commercialization. Available at: https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/965241468308383472/pdf/489680ESW0LK0P1C0disclosed071281091.pdf (Accessed May 16, 2024).
The World Bank. (2013). Pest Management Plan. Available at: https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/416161468303014589/pdf/E21470v20EA0P00C0disclosed040160130.pdf (Accessed May 20, 2024).
Valcke, M., Levasseur, M. E., Soares Da Silva, A., and Wesseling, C. (2017). Pesticide exposures and chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology: an epidemiologic review. Environ Health Global Access Sci Source 16, 49–20. doi: 10.1186/s12940-017-0254-0
Velten, S., Leventon, J., Jager, N., and Newig, J. (2015). What is sustainable agriculture? A systematic review. Sustainability 7, 7833–7865. doi: 10.3390/su7067833
Vlaiculescu, A., and Varrone, C. (2022). “Sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives to reduce the use of pesticides” in Pesticides in the natural environment. ed. C. A. Edwards (Amsterdam: Elsevier), 329–364.
Wang, W., Jin, J., He, R., and Gong, H. (2017). Gender differences in pesticide use knowledge, risk awareness and practices in Chinese farmers. Sci. Total Environ. 590-591, 22–28. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.053
Keywords: informedness, integrated pest management, responsible use of pesticides, smallholder farmers, sociocultural reasons
Citation: Udayanga S, Bellanthudawa BKA and De Zoysa HLS (2024) Sustainable agriculture and responsible use of pesticides: commercial crop cultivators’ knowledge, attitudes, and practice perspectives regarding pesticide use. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1490110. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1490110
Edited by:
Gilles Guillot, CSL Behring AG, SwitzerlandReviewed by:
Wissam Ghach, Canadian University of Dubai, United Arab EmiratesVaibhavkumar Mehta, Navsari Agricultural University, India
Maria Clara Melo, The University of Queensland, Australia
Copyright © 2024 Udayanga, Bellanthudawa and De Zoysa. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Samitha Udayanga, c2VuaXRoc3Jpc2FtaUBnbWFpbC5jb20=
 Samitha Udayanga
Samitha Udayanga B. K. A. Bellanthudawa
B. K. A. Bellanthudawa H. L. S. De Zoysa
H. L. S. De Zoysa