- 1National Research and Innovation Agency of Indonesia (BRIN), Bogor, Indonesia
- 2Department of Biology, Faculty of Military Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Kawasan IPSC, The Republic of Indonesia Defense University, Kampus Universitas Pertahanan Sentul, Bogor, West Java, Indonesia
- 3Department of Biology, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Universitas Indonesia, Depok, Indonesia
- 4Department of Agricultural Science and Technology, Faculty of Agriculture, Universitas Trunojoyo Madura, Bangkalan, Indonesia
- 5Department of Agronomy, Faculty of Agriculture, Hasanuddin University, Makassar, Indonesia
- 6Plant Production Department, College of Food and Agriculture Sciences, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- 7Department of Biosystems and Agricultural Engineering (BAE), College of Agriculture and Natural 19 Resources, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, United States
Mukia javanica is a close relative of the cucumber (Cucumis sativus) used to treat hypertension in the Leuwiliang community. Cucumis sativus contains calcium, magnesium, potassium, and phosphorus, which help lower blood pressure. In contrast, the content of metabolite compounds that are useful for lowering blood pressure in M. javanica has not been previously reported. Therefore, this research aimed to identify and determine the secondary metabolite content contained in several M. javanica organs and determine potential compounds that function in treating hypertension. The method used is the gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GCMS) method. The samples analyzed included several organs of M. javanica, such as roots, stems, leaves, and fruit. Several organs are tested to determine the part of the plant with the most potential secondary metabolite compound content. Data analysis used the R version 3.5.2 program and the Metaboanalyst program. Based on the test results, 98 secondary metabolite compounds were identified and divided into several compound classes, and the most significant number of compounds identified was the terpenoid compound group. The 13-Tetradecen-1-acetate (root), Oleic acid (fruit), Phytol (stem), and 4-hydroxy-3-nitrocoumarin (root) content in Mukia javanica has the potential to be antihypertensive. Based on correlation analysis, the metabolites Hexadecanoic Acid Methyl Ester, Squalene, Vitamin E, and Stigmasta-7,16-Dien-3 show high correlation values. The compound Hexadecanoic Acid Methyl Ester is found in all parts, and it is reported to be associated with antihypertension and antioxidants. In the future, this compound has the potential to be used as a raw material for antihypertensive drugs.
1 Introduction
Hypertension is a cardiovascular disease that is widely suffered and has a significant risk of developing other diseases such as endothelial dysfunction, metabolic syndrome, diabetes, kidney dysfunction, congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease, and stroke (Ogihara et al., 2006). Hypertension is a disease that affects many people throughout the world, namely 1.13 billion, and the majority (2/3) live in low and middle-income countries (WHO, 2019). In Indonesia, hypertension sufferers range from 6 to 15%. This is because hypertension sufferers usually do not have any symptoms or mild symptoms. Hypertension in the Leuwiliang community is the second most common disease after diabetes (Pratami et al., 2024). Hypertension is often found in old age due to several factors, such as unhealthy lifestyles and environmental factors. The risk of hypertension increases with age. Older people have a higher risk of developing hypertension (Dai et al., 2022).
Hypertension treatment is carried out using various methods, namely pharmacological and herbal. Pharmacologically, it is carried out using modern chemical medicines, while herbal treatment is carried out, one of which is using concoctions derived from plants. The use of plants as medicine is one of the alternative treatments that people choose because they have minimum side effects and are easy to obtain. According to Wang et al. (2013), Medicinal plants also have advantages in treating hypertension because, generally, medicinal plants have the function of treating hypertension and complications resulting from high blood pressure and have few side effects. Over 400.000 plant species contain primary and secondary metabolites (Van Wyk, 2020). Some plants that have the potential to treat hypertension, namely Phragmanthera incana leaf ethanol extract, possess antihypertensive, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties, suggesting a protective role in cardiovascular diseases (Adedapo et al., 2020) and Brassica rapa containing Methanol extract showed the highest antihypertensive potential by inhibiting ACE (79.39%) among all extracts. Methanol extract via GC–MS analysis revealed potent phytoconstituents and a molecular docking study confirmed that Oleic acid is the main antihypertensive metabolite (Abid et al., 2022). Sanrang and Faradiba (2024), reported plants used for the treatment of hypertension in Galung Village, including Andrographis paniculate, Averrhoa bilimbi, Annona muricata, Alium sativum, Cocos nucifera, Cymbopogon citratus, Muntingia calabura, Apium graveolens, Cucumis sativus, Sechium edule, Zingiber officinale; Cinnamomum verum, and Coriandrum sativum. The results of research related to hypertension show that flavonoid compounds play a role in hypertension therapy. Flavonoids are one of the chemical compounds of plants that have many properties, including as an antihypertensive. In hypertension therapy, flavonoid compounds act as ACE Inhibitors or inhibitors of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) where angiotensin I is not converted to angiotensin II so that aldosterone secretion will be inhibited. When aldosterone is inhibited, more water will be excreted by the body, the more water the lower the blood pressure (Sanrang and Faradiba, 2024).
According to (Pratami et al., 2024), the Leuwiliang community carries out modern and traditional treatment. Traditional medicine uses plants because medicinal plants contain metabolite compounds that have medicinal properties. Some of the plants used to treat hypertension in Leuwiliang include celery (Apium graveolens), insulin (Smallanthus sonchifolia), black cumin (Nigella sativa), shallots (Allium cepa), periwinkle (Catharanthus roseus), cherry (Muntingia Calabura), soursop (Annona muricata) and the most widely used is Mukia javanica (Pratami et al., 2024). M. javanica is closely related to the same family as Cucumis sativus and Sechium edule which are often used in the treatment of hypertension because they contain potassium. Potassium in Cucumis sativus can reduce renin secretion, causing inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system, and resulting in reduced reabsorption of water and sodium in the kidneys. Because of this working mechanism, diuresis increases which results in reduced blood volume, thereby lowering blood pressure. High levels of potassium can increase sodium excretion, thereby reducing blood pressure and blood volume (Lovindy and Tatik, 2014) and has the potential to lower systolic and diastolic blood pressure (Tukan, 2018). Sechium edule is also commonly used by the public in the treatment of hypertension because it contains potassium, which is a good mineral for lowering or controlling blood pressure (Septiana and Juwariyah, 2021).
Recently, research regarding the identification of compounds that have potential as medicines in Mukia javanica has never been carried out, even though there have been many reports regarding the use of traditional medicines made from M. javanica (Lemmens and Bunyapraphatsara, 2003). Based on ethnobotanical studies of M. javanica, many people use the leaves of M. javanica as an antihypertensive drug (Pratami et al., 2024). However, research on metabolite studies needs to be studied in more depth to obtain the desired metabolites.
One way to identify the active compound content in Mukia javanica is to analyze its metabolite profile. Metabolomics profiling is a metabolomic analysis to determine the diversity of metabolite compounds (metabolome) in cells and tissues (Van Dam and Bouwmeester, 2016; Wuolikainen et al., 2016). Information on the content of metabolite compounds can be determined using untargeted metabolomics analysis as a first step to collect as much in-depth and detailed information as possible on various metabolite compounds contained in M. javanica. This study aims to determine the secondary metabolite content in several M. javanica organs and determine potential compounds that treat hypertension.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental design
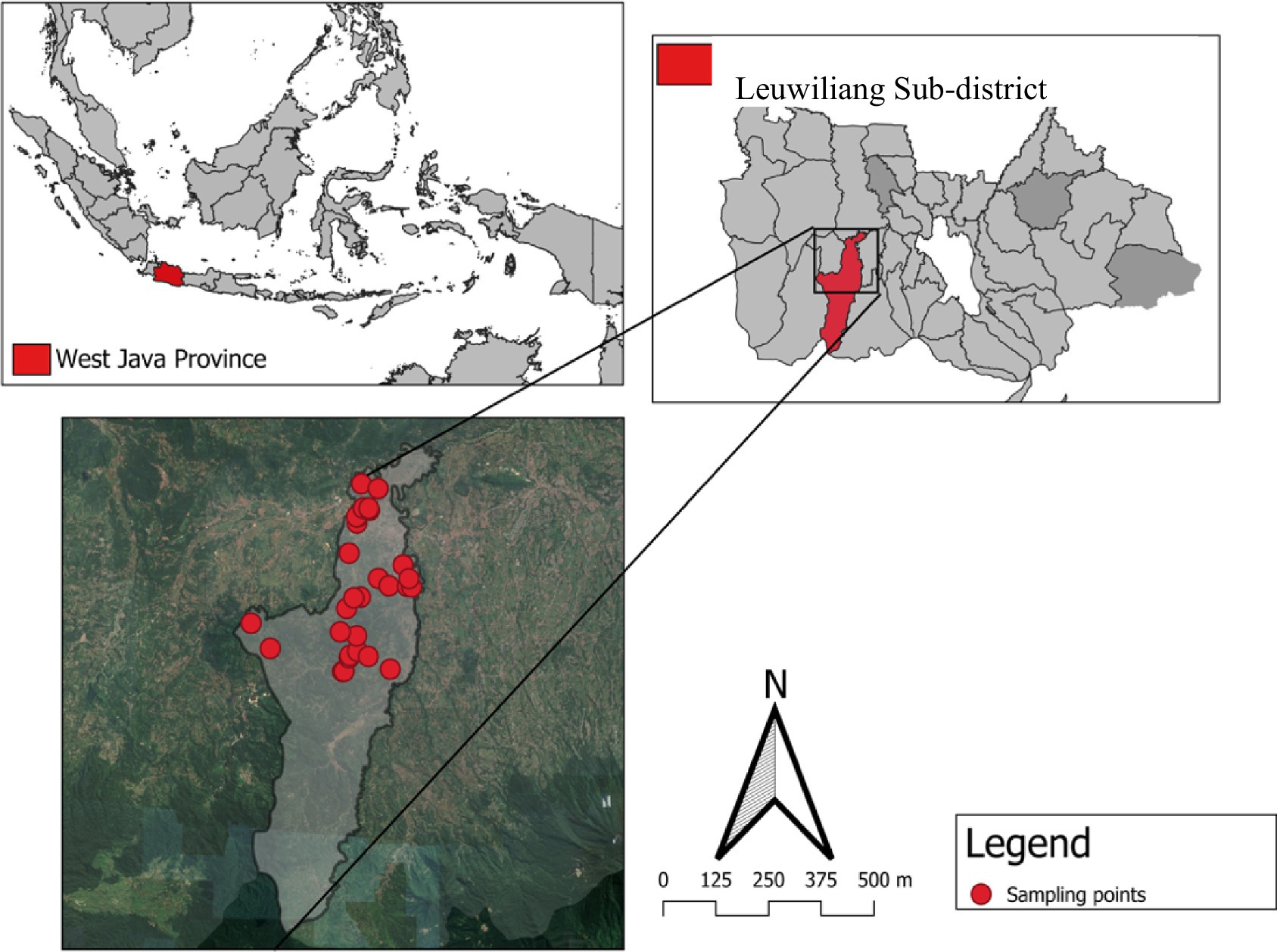
The Mukia javanica samples (roots, stems, leaves, and fruit) which were analyzed to grow wild in fields and hills in the Leuwiliang Sub-district, Bogor Regency, Indonesia (Figure 1). The selection of plant organs was carried out to compare the content of metabolite compounds that have the highest potential as antihypertensives in these organs.
2.2 Research procedure
Samples of healthy roots, stems, leaves, and fruits were prepared by cutting them into smaller sizes and then drying them at 140°C until the samples were dry. The dried samples were macerated in a bottle containing absolute ethanol for 5–7 days. After that, 10 mL of sample extract was taken and put into a tube to be evaporated using gas for 60 min at a temperature of 60°C. The dried sample was then dissolved with the remaining 200 μL of extract and ready to be inserted into the Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS) instrument. One way to identify metabolite profiles is by Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS) analysis. GC–MS analysis is often used to reveal metabolite profiles and their high resolution and provide good reproducibility. Another advantage of the GC–MS technique is that it has high sensitivity, which allows it to separate mixed compounds and analyze various compounds even in low concentrations (Gandjar and Rohman, 2012). Metabolomic analysis using GC–MS was carried out following the methods of Fendiyanto et al. (2020) and Fendiyanto et al. (2021). Root, stem, leaf, and fruit samples were analyzed in three replications for each species of M. javanica. Metabolite analysis was carried out at the Regional Health Laboratory of Jakarta Province.
2.3 Observation parameters and data analysis
Data from GC–MS metabolomics analysis were analyzed by creating a heatmap using the R version 3.5.2 program and the Metaboanalyst. R program following Fendiyanto et al. (2021). Graphs were analyzed using Microsoft Excel. The metabolomic data from the analysis results were then displayed in descriptive form. Correlation analysis and statistical testing of metabolite profiles were carried out using the Metaboanalyst application (Fendiyanto et al., 2020). For statistical analysis, this study used univariate and multivariate analysis including biomarker analysis using R in agricolae packages (Fendiyanto et al., 2020).
3 Results
3.1 Diversity of metabolite compounds in Mukia javanica
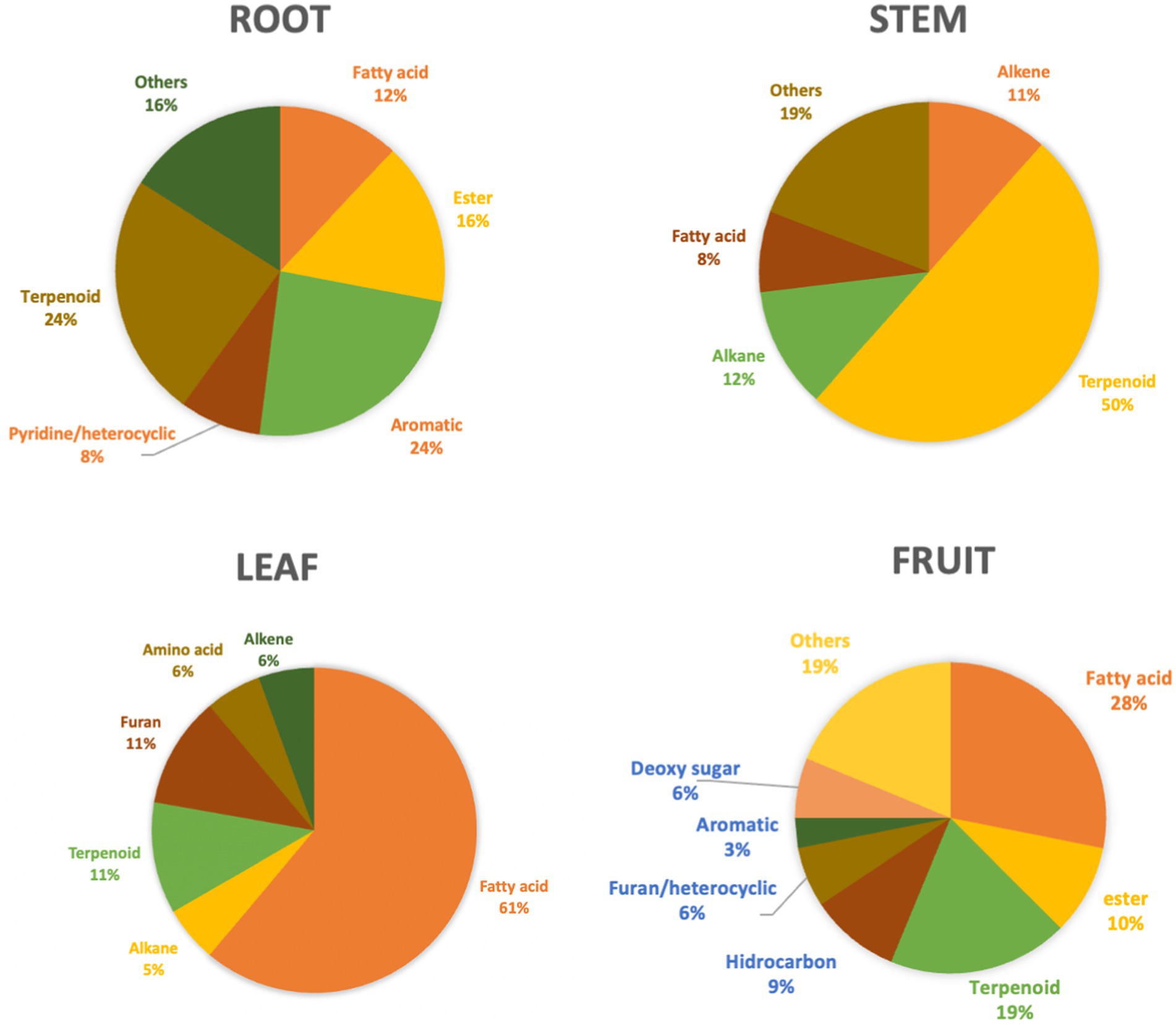
The Mukia genus is a taxon that has potential as a medicinal plant. Previous research reported that several Mukia genera have potential as medicinal plants because they contain secondary metabolites (Veeramani et al., 2012). Based on the results of metabolomics analysis, the classes of metabolite compounds in M. javanica roots, stems, leaves, and fruits consists of terpenoids, esters, fatty acids, amino acids, pyridines, aromatics, furans, alkanes, alkenes, deoxy sugars, and other compound classes (Figure 2). The largest number of compounds identified was the terpenoid group of compounds from the total identified metabolite compounds. Based on the results of GC–MS analysis of roots, stems, leaves, and fruit, M. javanica contains 98 compounds (Table 1). There were 23 metabolite compounds identified in the roots, 22 stem metabolite compounds, 24 leaf metabolite compounds, and 29 fruit metabolite compounds.
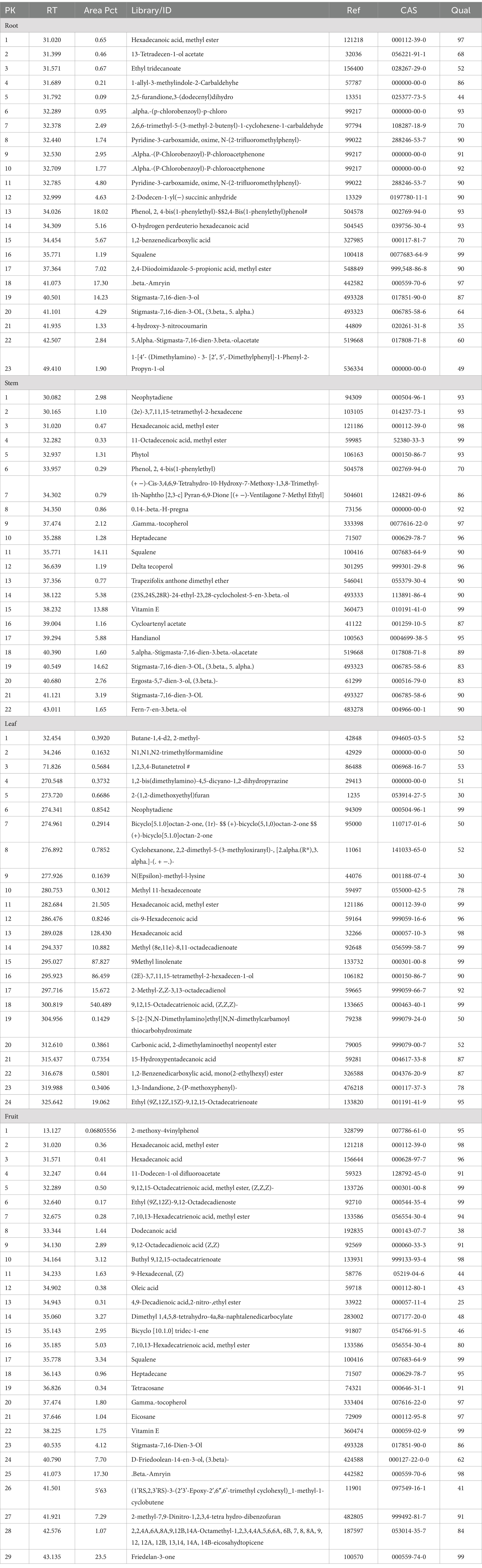
Table 1. Metabolite compounds resulting from metabolomics analysis using GC–MS on Mukia javanica roots, stems, leaves and fruits.
The group of terpenoids, flavonoids, alkaloids, steroids, and phenols is a group of compounds commonly found in plants, fruits, and vegetables that function as medicinal plants (Saeed et al., 2012). Flavonoid and terpenoid compounds are secondary metabolites in plants with high antioxidant activity (Azalia et al., 2023). Flavonoids and terpenoids belong to a group of very strong antioxidants (Graßmann, 2005). Terpenoids have a role as anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, anti-fungal, and anti-dementia drugs are used as perfume ingredients, insect repellent, and skin care raw materials (Cox-Georgian et al., 2019). The highest group of terpenoid compounds was found in the stem at 50%. The terpenoid compound group has antidiabetic, anticancer, and antibacterial functions (Bhargava et al., 2013).
3.2 Grouping of metabolites in the root, stem, leaf, and fruit organs
Metabolites detected in M. javanica were divided into four main groups according to organ type: root, stem, leaf, and fruit with a PC1 diversity value of 26.1% and PC2 of 44.8% (Figure 2). The root organ shows a relatively small grouping compared to other organs with the main compounds being 13-Tetradecen-1-acetate, Ethyl Tridecanoate, and Alpha.-(P-Chlorobenzoyl)-P-Chloroacetphenone, and others.
3.3 Correlation analysis
Metabolites detected in roots, stems, leaves, and fruits had relatively high correlation values. This metabolite profile is interconnected with other metabolites in all important organs of M. javanica. The highest positive correlation value is shown by groups of metabolites colored solid red and the number of metabolites with a high positive correlation shows a distribution of around 25%. Negative correlation values were also shown for metabolites in M. javanica, reaching a metabolite distribution value of 1% (Figure 3).
3.4 Metabolite profiles in various organs
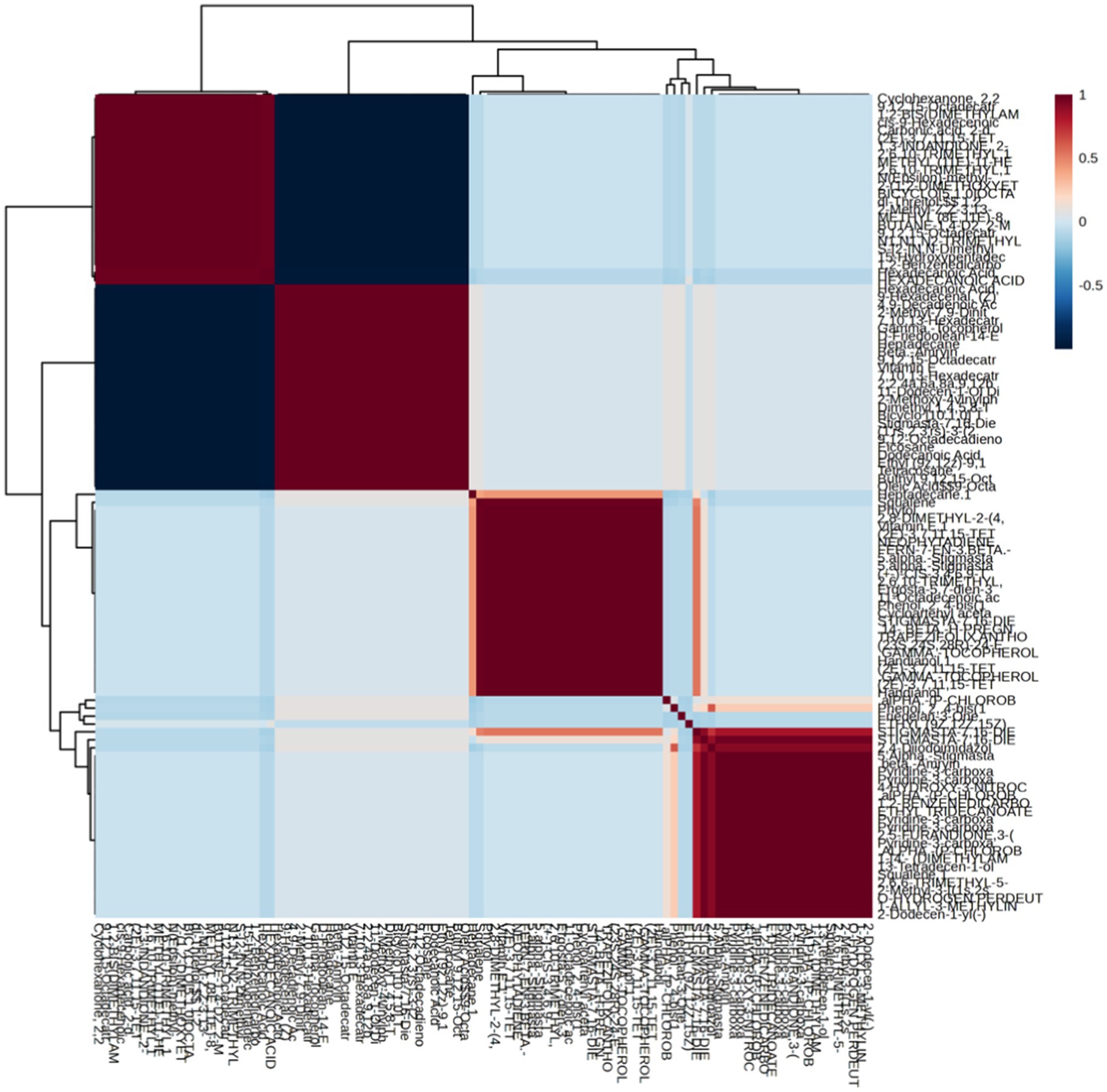
Metabolite profiles in various organs of M. javanica show differences (Figure 4). Ethnobotany shows differences in the use of plant parts as medicine. Several tribes in Maluku tend to use M. javanica leaves as a cornea cleansing medicine (Lemmens and Bunyapraphatsara, 2003), while Sundanese tribes, especially in Leuwiliang, use all parts of the plant as a medicine for hypertension (Pratami et al., 2024). Environmental conditions are one of the factors that influence the production of secondary metabolites (Wardani et al., 2021).
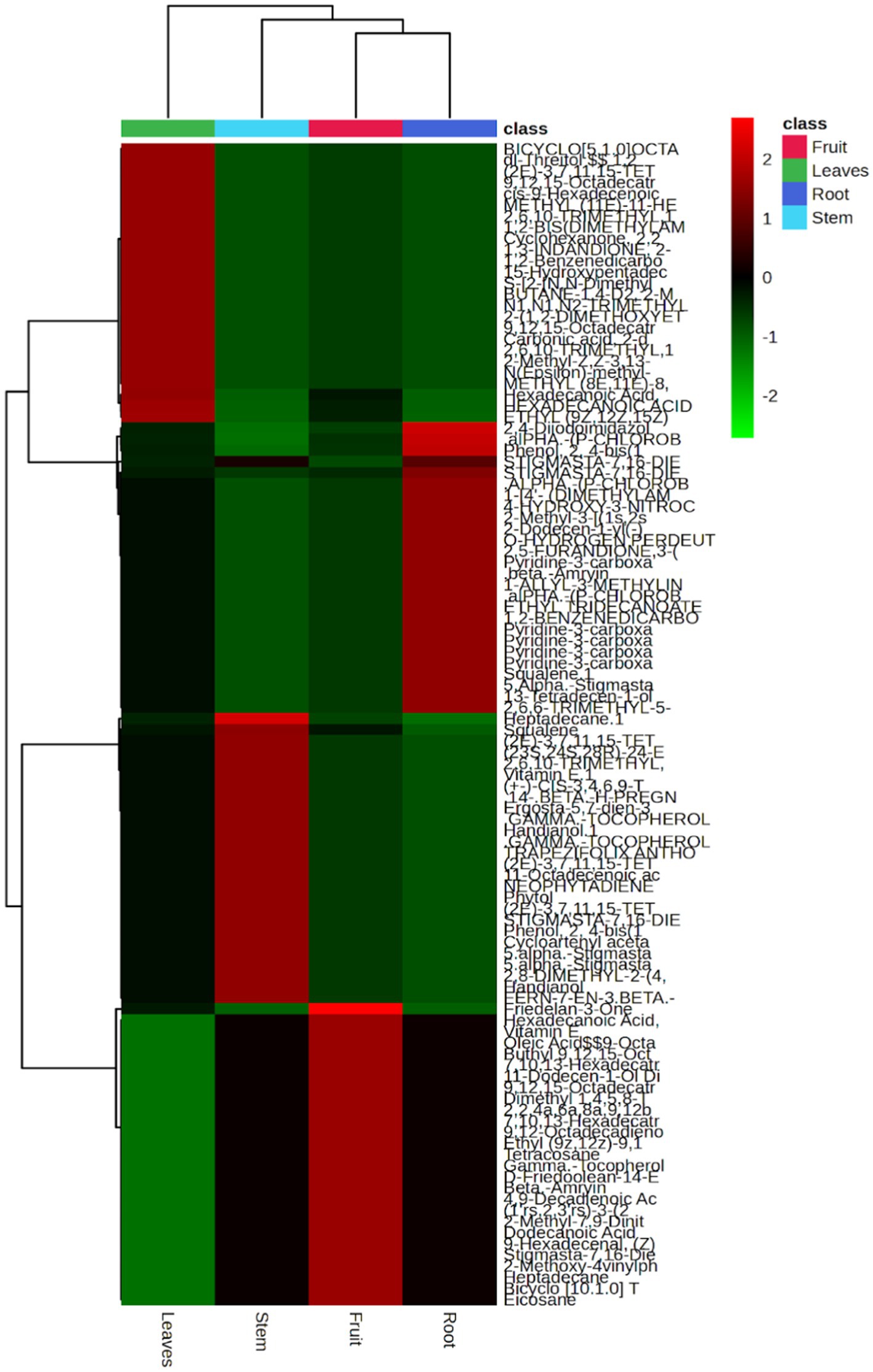
Figure 4. Metabolite profile in the root, stem, leaf, and fruit organs of Mukia javanica using heatmap.
3.5 Important compounds in Mukia javanica
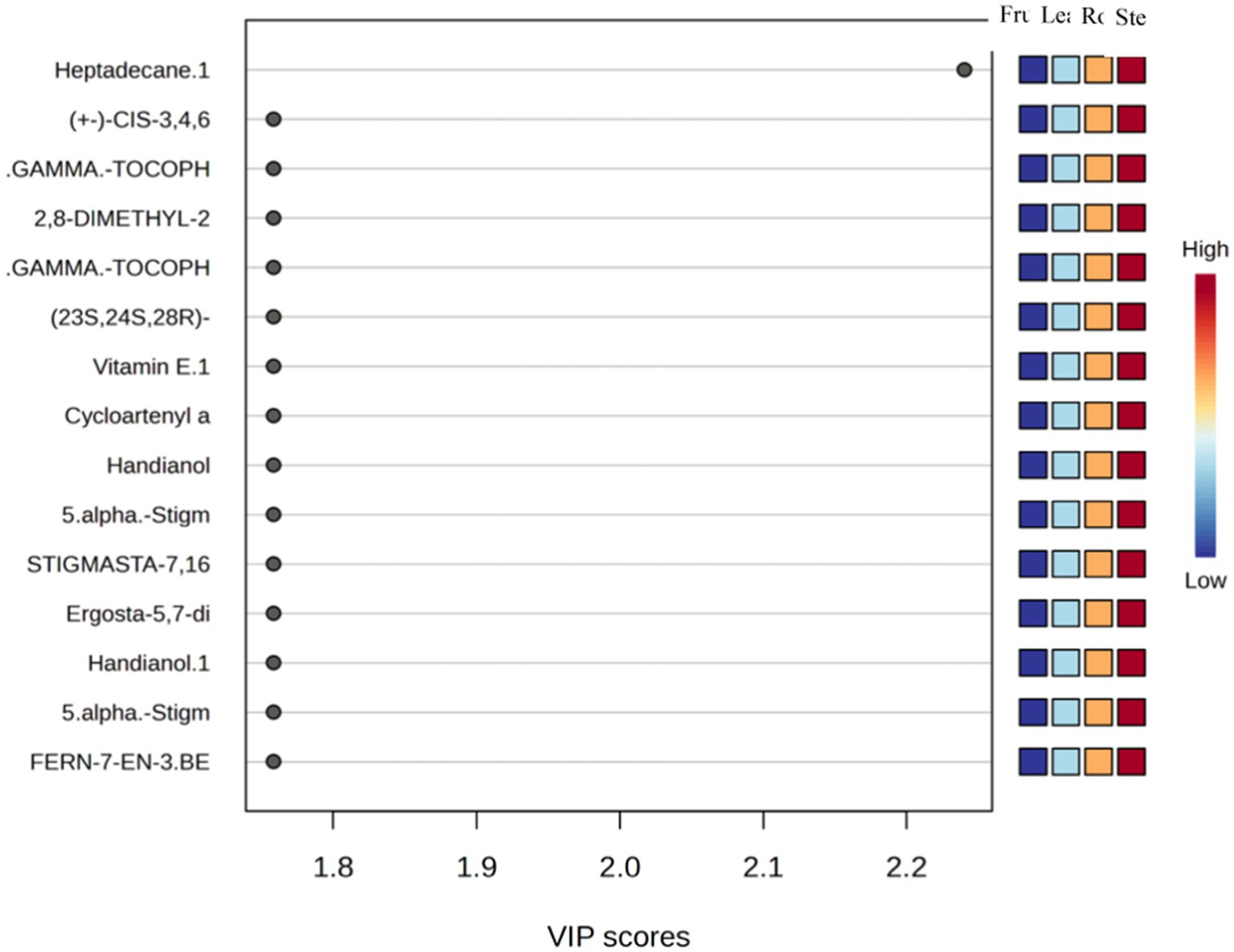
Based on the analysis of Variable of Importance (VIP) scores, the main metabolites in M. javanica organs show the presence of 15 important compounds related to antioxidant and antihypertensive metabolism, mainly Heptadecane; (+ −)-Cis-3,4,6,9-Tetrahydro-10-Hydroxy-7-Methoxy-1,3,8-Trimethyl-1 h-Naphtho; Gamma-Tocopherol; 2,8-Dimethyl-2-(4,8,12-Trimethyltridecyl)-6-Chromanol or Delta Tecoperol; Vitamin E; Stigmasta-7,16-dien-3-ol (3. beta., 5. alpha.); Handianol; Ergosta-5,7-dien-3beta-ol; and Fern-7-En-3.Beta (Figure 5).
4 Discussion
Hypertension is one of the risk factors for atherosclerosis and causes of cardiovascular disease. Hypertension may be caused by stroke or coronary heart disease in the subjects. One of the plants that can potentially be antihypertensive is Mukia maderaspatana which is a close relative of Mukia javanica. Veeramani et al. (2012) reported that ethanol in M. maderaspatana leaf extract can reduce systolic and diastolic pressure. M. maderaspatana leaf tea extract can reduce systolic and diastolic pressure (Raja et al., 2007). Furthermore the leaves of M. maderaspatana contain mainly Dichloroacetic acid, 4-methylpentyl ester, 2-Butyn-1-ol, 4-methoxy and also show the presence of other constituents such as flavonoids, saponins, carbohydrates, steroids, tannins, and phenolic compounds (Gomathy et al., 2012). Based on metabolite profile analysis, compounds were detected in all parts of Mukia javanica organs, namely the Hexadecanoate group such as Hexadecanoic Acid Methyl Ester. This compound in the Wilckia maritima is reported to be related to antihypertension and antioxidants and is reported to be used as a therapeutic agent (Jabeen et al., 2014). Antioxidants are useful in preventing various diseases and are used in treatment (Krishnaiah et al., 2011; Wulandari et al., 2013). Phytochemical studies using GC–MS carried out by Badejo et al. (2022) found the three most abundant compounds from the leaves of Persea americana, one of which was 11-Tetradecyn-1ol acetate which has antihypertensive activity. The results of this research support the existence of the main compound 13-Tetradecen-1-acetate which is the main compound in the root organs of M. javanica. Fruit organs have metabolites with a relatively concentrated PCA grouping (red in color) with the main compounds being Friedelan, Beta-Amryin, and D-Friedoolean-14-En-3-Ol, (3.Beta). Friedelin shows anti-proliferative ability against cultures of various cancer cells (Yessoufou et al., 2015). In their review, Singh et al. (2023) wrote that Friedelin had been studied because of its potential in the health sector and its biological activity, which can inhibit the growth of microorganisms. Friedelin extracted from Azima tetracantha, Calophyllum brasiliense, Calophyllum inophyllum, Cola lateritia, Garcinia smeathmannii, Jatropha tanjorensis, Maytenus undata, and Pterocarpus erinaceous is reported to have the ability to fight pathogenic bacteria and fungi. In addition, M. javanica fruit contains oleic acid which has the potential to be antihypertensive. A molecular docking study confirmed that Oleic acid is the main antihypertensive metabolite (Abid et al., 2022). Terés et al. (2008), reported in the study we demonstrate that the hypotensive effect of olive oil is caused by its high oleic acid (OA) content (≈70–80%). M. javanica roots contain 4-hydroxy-3-nitrocoumarin compounds. The coumarin content in Mukia maderaspatana leaf extract also has hypotensive activity (Petrus, 2012). According to Veeramani et al. (2012), M. maderaspatana leaves contain coumarin, valineic acid, p-coumaric acid, gallic acid, caffeic acid, and ferulic acid identified in EAFM (ethyl acetate). EAFM controls blood pressure in DOCA salt hypertensive rats and reverses changes in magnesium, copper, and zinc metabolism (Veeramani et al., 2012). In addition, M. javanica stems contain methanol compounds in the form of Phytol. Methanol extract in Brassica rapa showed the highest antihypertensive potential by inhibiting ACE (79.39%) among all extracts (Abid et al., 2022).
The class of terpenoid compounds found in stems consists of 2,6,10-trimethyl, neophytadiene, gamma-tocopherol or vitamin e, squalene, 2,8-dimethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-6-chromanol, (23 s,24 s,28r)-24-ethyl-23,28-cyclocholest-5-en-3.beta.-ol, cycloartenyl acetate, 5.alpha-stigmasta-7,16-dien-3.beta-ol, acetate, stigmasta-7,16-dien-3-ol, (3.beta., 5.alpha.) (Figure 2; Table 1). Neophytadiene is a group of terpenoid compounds that have the potential to be antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and have antifungal and antioxidant activity (Venkata et al., 2012). Pratama et al. (2019), reported the results of HPLC analysis of Cucumis melo leaf extract showing the presence of neophytadiene compounds in both healthy plants and those infected with the fungus Pseudoperonospora cubensis. This shows that the same compounds are produced by plants from the Cucurbitaceae family as M. javanica.
A study has proven that beta amyrin extracted from the resin of the woody stems of the Protium heptaphyllum (Burseraceae) has the potential to fight acute pancreatitis by acting as an anti-inflammatory and antioxidant (Melo et al., 2010). The leaf metabolite group shows relatively diverse coordinate values (green color) with the main metabolite compound being 9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic acid, 9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic acid, methyl ester, and 3,7,11,15-Tetramethyl-2-hexadecene. These results are similar to the results found by Rahman et al. (2014) from the methanol extract of Andrographis paniculata leaves via GC–MS chromatogram where the three main compounds have antimicrobial potential, namely 24.64% hexadecenoic acid methyl ester, 13.65% 9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid methyl ester (Z,Z,Z)-, and 12.18% 9,12-octadecadienoic acid, methyl ester. The bar metabolite group shows various metabolite coordinates at points − 15 to 25 (blue), with key metabolite characteristics in the form of Stigmasta-7,16-Dien-3-Ol, (3.Beta., 5.Alpha.), vitamin E, and Handianol. However, several metabolites are also found in various organs in roots, stems, leaves, and fruit, such as Hexadecanoic acid methyl ester, Stigmasta-7,16-dien-3-ol This is indicated by the centered and overlapping metabolite coordinate points in the PCA analysis (Figure 6).
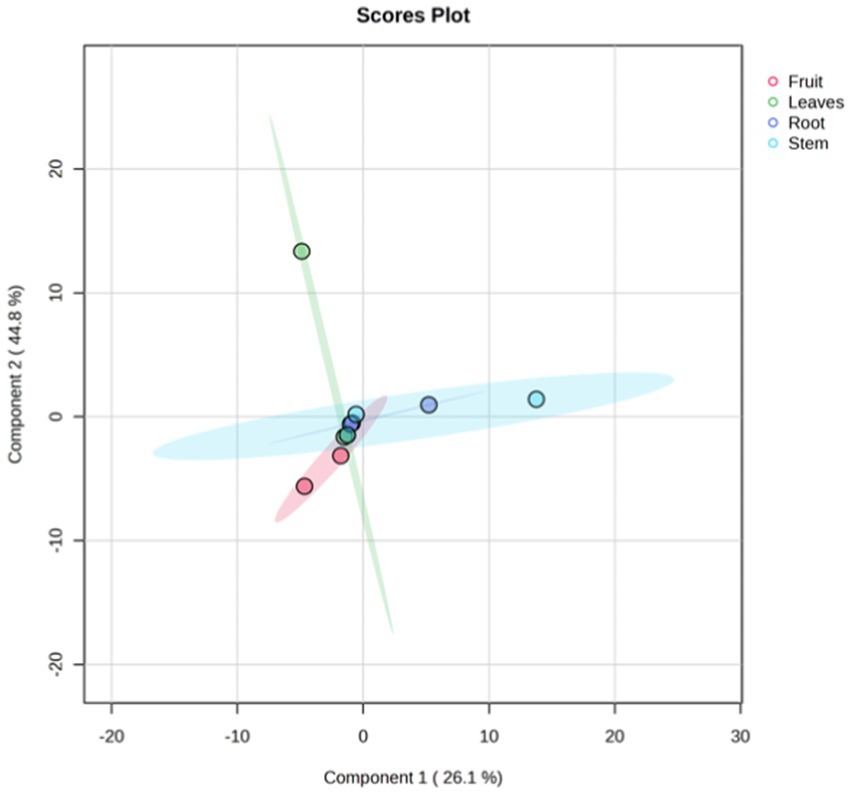
Figure 6. Grouping of metabolites in the root, stem, leaf, and fruit organs of Mukia javanica using principle component analysis (PCA).
The correlation value indicates a relationship between metabolites in certain organs and other organs in M. javanica. Based on correlation analysis, the metabolites Hexadecanoic Acid Methyl Ester, Squalene, Vitamin E, and Stigmasta-7,16-Dien-3 show high correlation values. These metabolites primarily act as antioxidants and are thought to reduce hypertension. The Mukia maderspatana leaf is reported to exhibit potent antioxidant capacity in vitro and in vivo and to possess antihypertensive, vasodialatory, antiulcer, anxiolytic, antimicrobial, and antiplatelet aggregation activities (Petrus, 2012). Rajeswari et al. (2013) also explained that the n-hexadecanoic acid compound has antioxidant activity, hypocholesterolemic, natural pesticide, lubricant, antiandrogenic, and 5-alpha hemolytic reductase enzyme inhibitor. Squalene is often used clinically in daily doses as an antioxidant, bactericidal, fungicide agent, antistatic agent, and moisturizer in cosmetic and pharmaceutical preparations (Norhidayah et al., 2012). Rajeswari et al. (2013), also explained that the squalene compound has antibacterial, antioxidant, antitumor, cancer prevention, lipoxygenase, pesticide, and diuretic activity. Vitamin E, also known as tocopherol, is included in the terpenoid class which also functions as a source of antioxidants (Ali et al., 2015). Mohan et al. (2014) also explained that Vitamin E has anti-bronchitis, anti-cancer, anti-coronary functions, and functions as a hepatic protector. Sitosterol and stigmasterol compounds are a group of phytosterol compounds that have a role in helping plants adapt to various environmental temperatures. Stigmasterol also has anticancer activity (Sianipar et al., 2023). Stigmasterol also has antioxidant activity and reduces the number of Ehrich Ascites Carcinoma (EAC) (Ghosh et al., 2011). The active compounds in Sechium edule fruit which function as antihypertensives are flavonoids that can inhibit angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) and act as a diuretic. Sechium edule fruit extract can be used as an alternative treatment for hypertension (Nadila, 2014). However, the results of the metabolite profile from previous ethnobotanical study (Pratami et al., 2024) need to be studied comprehensively to determine the role of the active substances from M. javanica in future research. The results of research by Solfaine et al. (2021), found that the active compound content in starfruit extract qualitatively consists of alkaloid, phenolic, flavonoid, saponin, tannin and terpene compounds. The flavonoid content in the extract and its proven antioxidant activity supports the antihypertensive activity of the methanol extract of Imperata cylindrica roots from Kendari, Indonesia (Dhianawaty et al., 2018). Flavonoids have a mechanism of action as antihypertensives by inhibiting ACE activity. ACE inhibitors cause relaxation of the blood vessel endothelium so that blood flows to the heart and blood pressure decreases (Fransiska and Fajar, 2019). Flavonoid compounds can reduce blood pressure and endothelial dysfunction in experimental animals induced by hypertension.
Some compounds have relatively high correlation values with Hexadecanoic Acid Methyl Ester. The Hexadecanoic Acid Methyl Ester compound is an antioxidant (Jabeen et al., 2014). Thus, M. javanica can be used to treat several diseases because it contains several important compounds such as Hexadecanoic acid methyl ester; Squalene, Vitamin E; Heptadecane; (+ −)-Cis-3,4,6,9-Tetrahydro-10-Hydroxy-7-Methoxy-1,3,8-Trimethyl-1 h-Naphtho; Gamma-Tocopherol; 2,8-Dimethyl-2-(4,8,12-Trimethyltridecyl)-6-Chromanol or Delta Tecoperol; Vitamin E; Stigmasta-7,16-dien-3-ol (3. beta., 5. alpha.); Handianol; Ergosta-5,7-dien-3beta-ol (3.beta.); and Fern-7-En-3.Beta. The compounds from the results of this metabolomic analysis show that M. javanica has a high compound content, one of them antioxidants that play a role in cardiovascular disease because they can neutralize or absorb free radicals. Several natural antioxidants in the M. javanica plant, including amino acids, vitamins, and others, have shown benefits for preventing hypertension. The important key compound in M. javanica, which is found in various organs in the roots, stems, leaves, and fruits, is Hexadecanoic Acid Methyl Ester. This research can strengthen the role of M. javanica, which has been used by people in various tribes, for example, in West Java, Indonesia, as an antihypertensive drug.
5 Conclusion
Mukia javanica has the potential to be used as a therapeutic agent in the treatment of hypertension because it contains various important compounds such as Hexadecanoic acid methyl ester; 13-Tetradecen-1-acetate, Oleic acid, Phytol, and 4-hydroxy-3-nitrocoumarin. This study provides scientific support for the traditional use of M. javanica as an antihypertensive drug in various communities, especially in Lewiliang, West Java, Indonesia.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
MP: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft. WS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. MF: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. RY: Data curation, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. IK: Validation, Writing – review & editing. NW: Funding acquisition, Validation, Writing – review & editing. MS: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. NA: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MFA: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Researchers supporting project number (RSPD2025R751), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. The National Research and Innovation Agency (Indonesian: Badan Riset dan Inovasi Nasional or BRIN) through the Postdoctoral Program Batch 2 to the MP.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the dedication of all the respondents who shared their knowledge in this study, and the support of King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia is acknowledged: Researchers supporting project number (RSPD2025R751).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abid, R., Islam, M., Saeed, A., Ahmad, I. F., Yasmeen, A., and Hassam, R. A. (2022). Antihypertensive potential of Brassica rapa leaves: an in vitro and in silico approach. Front. Pharmacol. 13:996755. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.996755
Adedapo, A. D. A., Ajayia, A. M., Ekwunifea, N. L., Falayib, O. O., Oyagbemic, A., Omobowaled, T. O., et al. (2020). Antihypertensive effect of Phragmanthera incana (Schum) Balle on NG-nitro- T L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) induced hypertensive rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 257:112888. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112888
Ali, H. A. M., Imad, H. H., and Salah, A. I. (2015). Analysis of bioactive chemical components of two medicinal plants (Coriandrum sativum and Melia azedarach) leaves using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 14, 2812–2830. doi: 10.5897/ajb2015.14956
Azalia, D., Rachmawati, I., Zahira, S., Andriyani, F., Melia Sanini, T., and Aulya, R. (2023). Uji Kualitatif Senyawa Aktif Flavonoid Dan Terpenoid Pada Beberapa Jenis Tumbuhan Fabaceae Dan Apocynaceae Di Kawasan Tngpp Bodogol. Bioma J. Biol. Makassar 8, 32–43.
Badejo, J. A., Michael, O. S., Odebiyi, O., Adetona, M. O., Abdulmalik, O., Agbebi, E., et al. (2022). Blood pressure-lowering activity of extract and fractions of Persea americana leaf. Arch. Bas. App. Med. 10, 25–32.
Bhargava, V. V., Patel, S. C., and Desa, K. S. (2013). Importance of terpenoids and essential oils in chemotaxonomic approach. Intl. J. Herb. Med. 1, 14–21.
Cox-Georgian, D., Ramadoss, N., Dona, C., and Basu, C. (2019). Therapeutic and medicinal uses of terpenes. Med. Plants Farm Pharm. 22, 333–359. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-31269-5_15
Dai, B., Addai-Dansoh, S., NutakorJA, O.-K. J., Larnyo, E., Oppong, S., Boahemaa, P. Y., et al. (2022). The prevalence of hypertension and its associated risk factors among older adults in Ghana. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 9:990616. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.990616
Dhianawaty, D., Ruslin, R., Syamsunarno, M. R. A. A., and Hamimah, H. (2018). Kandungan total flavonoid dari ekstrak metanol akar Imperata cylindrica (L) Beauv. (Alang-alang). Trop. Med. Conf. Series. 1, 25–28. doi: 10.32734/tm.v1i3.256
Fendiyanto, M. H., Satrio, R. D., and Darmadi, D. (2020). Metabolic profiling and pathway analysis in red arillus of salacca sumatrana demonstrate significant pyruvate, sulfur, and fatty acid metabolisms. Biodiversitas 21, 4361–4368. doi: 10.13057/biodiv/d210955
Fendiyanto, M. H., Satrio, R. D., Widana, I. D. K. K., Pratami, M. P., Nikmah, I. A., and Darmadi, D. (2021). Differential hierarchical metabolites expression of red/white Salacca Sumatrana arillus and its molecular docking studies. Biodiversitas 22, 1014–1024. doi: 10.13057/biodiv/d220258
Fransiska, M. F. J., and Fajar, P. (2019). Potensi Madu sebagai Penurun Tekanan Darah dan Kolestrol. Proc. Mulawarman Pharm. Conf. 10, 1–5. doi: 10.25026/mpc.v10i1.350
Gandjar, I. G., and Rohman, A. (2012). Analisis Obat Secara Spektrofotometri dan Kromatografi. Yogyakarta: Pustaka Pelajar.
Ghosh, T., Maity, T. K., and Singh, J. (2011). Evaluation of antitumor activity of stigmasterol, a constituent isolated from Bacopa monnieri Linn aerial parts against Ehrlich ascites carcinoma in mice. Orient Pharm Exp Med 11, 41–49. doi: 10.1007/s13596-011-0001-y
Gomathy, G., Vijay, T., Sarumathy, K., Gunasekaran, S., and Palani, S. (2012). Phytochemical screening and GC-MS analysis of Mukia maderaspatana (L.) leaves. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2, 104–106. doi: 10.7324/JAPS.2012.21220
Graßmann, J. (2005). Terpenoids as plant antioxidants. Vitam. Horm. 72, 505–535. doi: 10.1016/S0083-6729(05)72015-X
Jabeen, S., Hanifa, M. S., Khan, M. M., and Qadri, R. W. K. (2014). Natural products sources and their active compounds on disease prevention: a review. Int. J. Chem. Biochem. Sci. 6, 76–83.
Krishnaiah, D., Sarbatly, R., and Nithyanandam, R. (2011). A review of the antioxidant potential of medicinal plant species. Food Bioprod. Process. 89, 217–233. doi: 10.1016/j.fbp.2010.04.008
Lemmens, R. H. M. J., and Bunyapraphatsara, N. (2003). Plant resources of South-East Asia 12 (3). Medical and poisonous plants 3. Bogor: Prosea Foundation.
Lovindy, P. L., and Tatik, M. (2014). Pengaruh Pemberian Jus Mentimun (Cucumis Sativus L.) Terhadap Tekanan Darah Sistolik Dan Diastolik Pada Penderita Hipertensi. Semarang: Universitas Dipenogoro.
Melo, C. M., Carvalho, K. M. M. B., de Sousa Neves, J. C., Morais, T. C., Rao, V. S., Santos, F. A., et al. (2010). α,β-amyrin, a natural triterpenoid ameliorates L-arginine-induced acute pancreatitis in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 16, 4272–4280. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i34.4272
Mohan, D., Sarswat, A., Ok, Y. S., and Pittman, C. U. (2014). Organic and inorganic contaminants removal from water with biochar, a renewable, low cost and sustainable adsorbent - a critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 160, 191–202. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.120
Nadila, F. (2014). Review artikel: antihypertensive potential of chayote fruit extract for hypertension treatment. J. Major. 3, 34–38.
Norhidayah, S., Baharin, B. S., Hamed, M., and Zaidul, I. S. M. (2012). Squalene recovery from palm fatty acid distillate using supercritical fluid extraction. Int. Food Res. J. 19, 1661–1667.
Ogihara, T., Matsuzaki, M., Matsuoka, H., Shimamoto, K., Shimada, K., Rakugi, H., et al. (2006). Erratum: the combination of hypertension to prevent cardiovascular events (COPE) trial: rationale and design (hypertension research (2005) vol. 28 (331-338)). Hypertens. Res. 29:639. doi: 10.1291/hypres.28.331
Petrus, A. J. A. (2012). Mukia maderaspatana (L.) M. Roemer-a review of its global distribution, phytochemical profile and antioxidant capacity. Asian J. Chem. 24, 2361–2368.
Pratama, O. A., Tunjung, W., Sutikno, A. S., and Daryono, B. S. (2019). Bioactive compound profile of melon leaf extract (Cucumis melo l. ‘Hikapel’) infected by downy mildew. Biodiversitas 20, 3448–3453. doi: 10.13057/biodiv/d201143
Pratami, M. P., Anggraeni, A., and Sujarwo, W. (2024). Ethnobotany of medicinal plants in Leuwiliang (Bogor), Indonesia. Ethnobot. Res. Appl. 27:40. doi: 10.32859/era.27.1.1-40
Rahman, M. M., Ahmad, S. H., Mohamed, M. T. M., and Ab Rahman, M. Z. (2014). Antimicrobial compounds from leaf extracts of Jatropha curcas, Psidium guajava, and Andrographis paniculata. Sci. World J. 2014:240. doi: 10.1155/2014/635240
Raja, B., Kaviarasan, K., Arunan, M. M., and Pugalendi, K. V. (2007). Effect of Melothria maderaspatana (Linn.) leaf extract on blood pressure, lipid profile, anthropometry, fibrinogen, bilirubin and albumin levels in hypertensive patients. J. Alter Comp. Med. 13, 349–354. doi: 10.1089/acm.2006.5373
Rajeswari, G., Murugan, M., and Mohan, V. R. (2013). GC-MS analysis of bioactive components of Hugonia mystax L. (Linaceae). Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 3, 301–308.
Saeed, N., Khan, M. R., and Shabbir, M. (2012). Antioxidant activity, total phenolic and total flavonoid contents of whole plant extracts Torilis leptophylla L. BMC Complement Altern Med. 12:221. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-12-221
Sanrang, B. M., and Faradiba, S. I. (2024). Studi etnofarmasi tumbuhan obat yang berkhasiat sebagai antihipertensi di Kelurahan Galung, Kecamatan Liliriaja, Kabupaten Soppeng. Makassar Nat. Prod. J. 2, 153–163.
Septiana and Juwariyah (2021). Pemberian Jus Labu Siam Terhadap Penurunan Tekanan Darah pada Lansia Hipertensi. J. Manajemen Asuhan Keperawatan 22, 34–40.
Sianipar, N. F., Assidqi, K., Hadisaputri, Y. E., Salam, S., Purnamaningsih, R., and So, I. G. (2023). Mutant plant Tipobio variety of rodent tuber (Typhonium Flagelliforme): fatty acids compounds and in vitro anticancer activity. E3S Web Conf. 388, 4–8. doi: 10.1051/e3sconf/202338801032
Singh, S. K., Shrivastava, S., Mishra, A. K., Kumar, D., Pandey, V. K., Srivastava, P., et al. (2023). Friedelin: structure, biosynthesis, extraction, and its potential health impact. Molecules 28, 1–22. doi: 10.3390/molecules28237760
Solfaine, R., Sari, D. A. K., and Wati, A. N. (2021). Jurnal Vitek Bidang Kedokteran Hewan Mei 2021 Terhadap Gambaran Histopatologi Pankreas Pada Tikus Yang kurangnya latihan (terutama pada kucing rumah), dan umur terutama pada kucing yang lebih tua (Fitriani dkk, 2016). Pankreas tikus. J. Vitek Bid. Kedokt. Hewan 11, 15–24.
Terés, S., Barcelo-Coblijn, G., Benet, M., Alvarez, R., Bressani, R., Halver, J. E., et al. (2008). Oleic acid content is responsible for the reduction in blood pressure induced by olive oil. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 105, 13811–13816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0807500105
Tukan, R. A. (2018). Efektifitas Jus Mentimun dalam Menurunkan Tekanan Darah pada Pasien Hipertensi. J. Borneo Holistic Health 1, 45–49. doi: 10.35334/borticalth.v1i1.398
Van Dam, N. M., and Bouwmeester, H. J. (2016). Metabolomics in the rhizosphere: tapping into belowground chemical communication. Trends Plant Sci. 21, 256–265. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2016.01.008
Van Wyk, B. E. (2020). A family-level floristic inventory and analysis of medicinal plants used in traditional African medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 249:112351. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112351
Veeramani, C., Al-Numair, K. S., Chandramohan, K., Alsaif, M. A., Alhamdan, A. A., and Pugalendi, K. V. (2012). Antihypertensive effect of Melothria maderaspatana leaf fractions on DOCA-salt-induced hypertensive rats and identification of compounds by GC–MS analysis. J. Nat. Med. 66, 302–310. doi: 10.1007/s11418-011-0590-2
Venkata, R. B., Samuel, L. A., Pardha, S. M., Narashima, R. B., Naga, V. K. A., Sudhakar, M., et al. (2012). Antibacterial, antioxidant activity and GC-MS analysis of Eupatorium odoratum. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 5, 99–106.
Wang, J., Xingjiang, X., and Wei, L. (2013). Acupunture for essential hypertension. Int. J. Cardiol. 169, 317–326. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.09.001
Wardani, Y. K., Elok, K. E. B., and Sucahyo, S. (2021). Korelasi antara aktivitas antioksidan dengan kandungan senyawa fenolik dan lokasi tumbuh tanaman Celosia argentea Linn. Bioma: Berkala Ilmiah Biologi. 22, 136–142. doi: 10.14710/bioma.22.2.136-142
WHO (2019). A Global Brief on Hypertension: Silent Killer, global Public Health Crisis. Geneva: WHO.
Wulandari, R. C., Linda, R., and Mukarlina, L. (2013). Pertumbuhan Stek Melati Putih (Jasminum sambac (L) W. Ait.) dengan Pemberian Air Kelapa dan IBA (Indole Butyric Acid). J. Protobiont. 2, 39–43. doi: 10.26418/protobiont.v2i2.2737
Wuolikainen, A., Jonsson, P., Ahnlund, M., Antti, H., Marklund, S. L., and Moritz, T. (2016). Multi-platform mass spectrometry analysis of the CSF and plasma metabolomes of rigorously matched amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and control subjects. Mol. Syst. Biol. 12, 1287–1298. doi: 10.1039/C5MB00711A
Keywords: antihypertensive, antioxidant, correlation analysis, GCMS, Mukia javanica
Citation: Pratami MP, Sujarwo W, Fendiyanto MH, Yuniati R, Kurniyanto IR, Widiayani N, Seleiman MF, Ali N and Anshori MF (2025) Metabolite profiling of some organs and the potential of Mukia javanica as an antihypertension. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1487446. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1487446
Edited by:
Marcello Iriti, University of Milan, ItalyReviewed by:
Mukesh Meena, Mohanlal Sukhadia University, IndiaFırat Baran, Batman University, Türkiye
Copyright © 2025 Pratami, Sujarwo, Fendiyanto, Yuniati, Kurniyanto, Widiayani, Seleiman, Ali and Anshori. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Muhammad Fuad Anshori, ZnVhZC5hbnNob3JpQHVuaGFzLmFjLmlk
 Mentari Putri Pratami1,2
Mentari Putri Pratami1,2 Wawan Sujarwo
Wawan Sujarwo Mahmoud F. Seleiman
Mahmoud F. Seleiman Muhammad Fuad Anshori
Muhammad Fuad Anshori