- 1Ankang Branch of Shaanxi Provincial Land Engineering Construction Group Co., Ltd., Xi’an, China
- 2Shaanxi Provincial Land Engineering Construction Group Co., Ltd., Xi’an, China
Aims: This study aimed to evaluate the impact of subsurface drip fertigation (SDF) on soil moisture content, potato growth, and tuber yield in loam soils, and compare these results with conventional surface drip fertigation (CF). The focus was on determining whether SDF could improve water use efficiency and yield quality, particularly in water-scarce regions.
Methods: The experiment was conducted during the 2022 spring growing season in Xunyang, Ankang, Shaanxi Province, China. A randomized complete block design (RCBD) was used with three treatments: subsurface drip fertigation (SDF), conventional surface drip fertigation (CF), and a no-fertilization control (NF), with four replications per treatment. Soil moisture content at a 20 cm depth was monitored, and plant growth parameters such as plant height, stem diameter, leaf color index, and chlorophyll fluorescence index were measured during the flowering and harvest stages. Tuber yield characteristics, including tuber diameter, number of tubers per plant, total yield, and marketable yield, were also assessed.
Important findings: The results indicated that subsurface drip fertigation significantly improved soil moisture content, with up to 45.5% higher moisture retention compared to conventional fertigation, particularly in the early stages of fertilization. This improved moisture availability led to enhanced plant growth and tuber development. Tuber diameter increased by 6.9 mm, and the number of tubers per plant increased by 18.1% under SDF. Marketable tuber yield was approximately 10% higher in the SDF treatment compared to CF. However, the study found that soil texture plays a critical role in the effectiveness of SDF, and further research is needed to explore its application in other soil types.
1 Introduction
Potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.) are among the most critical staple crops worldwide, contributing significantly to global food security, particularly in regions such as Europe, Asia, and the Americas. Given its shallow root system and high water demand, potato production is highly sensitive to water availability, especially during tuber initiation and development stages. In regions with limited water resources, optimizing water use through efficient irrigation systems is essential to maintain productivity and meet increasing food demand (Anderson et al., 2020). Traditional surface irrigation methods, while effective, often result in water losses due to evaporation and surface runoff, leading to inefficient use of water resources (Abioye et al., 2020).
Drip irrigation, particularly subsurface drip irrigation (SDI), has been promoted as a water-efficient alternative to traditional surface irrigation methods (Patel and Rajput, 2008). SDI systems deliver water directly to the root zone, minimizing surface evaporation and reducing water wastage (Plauborg et al., 2022). When combined with fertigation—delivering nutrients through the irrigation system—subsurface drip irrigation further enhances nutrient-use efficiency by ensuring that nutrients are supplied directly to the root zone, reducing nutrient leaching and improving plant uptake (Li et al., 2021). Recent studies have shown that SDI can significantly improve water-use efficiency in a variety of crops, including maize and tomatoes, where water savings of up to 40% have been reported (Soliman et al., 2020; Tahoun et al., 2022).
Although subsurface drip irrigation (SDI) is recognized for its water efficiency in various crops, its specific application in potato cultivation—a crop with distinct physiological requirements—has been insufficiently explored. Potatoes have a shallow root system and are highly sensitive to soil moisture variations, particularly during key stages like tuber initiation and enlargement. Consequently, precise irrigation strategies are critical for optimizing yield and water-use efficiency in regions facing water scarcity (Abioye et al., 2020). Current research does not adequately address SDI’s potential for potato production, thus presenting a significant gap that this study seeks to fill. Studies on crops such as tomatoes and maize have demonstrated the benefits of SDI, but similar research in potatoes is lacking (Wang et al., 2022). Given the crop’s economic and nutritional importance, it is crucial to evaluate the effectiveness of SDI and fertigation for potatoes, particularly in terms of soil moisture dynamics, yield improvement, and overall resource-use efficiency (Table 1).
The research gap identified in this context is the limited understanding of how subsurface drip fertigation (SDF) affects potato growth, yield, and soil moisture retention in comparison to surface drip irrigation (SDI) and conventional fertigation methods. While some studies have explored the use of SDF in other high-water-demand crops, few have directly assessed its impact on potatoes. Given the distinct physiological requirements of potatoes, the extrapolation of findings from other crops may not be applicable. Specifically, potatoes have a different root architecture and tuber formation process, which may respond differently to subsurface irrigation compared to crops like maize and tomatoes. Therefore, targeted research is necessary to determine whether SDF can provide similar or superior benefits in potato cultivation, particularly in water-scarce regions (Table 2).
This study aims to address this research gap by evaluating the effects of subsurface and surface drip fertigation on soil moisture dynamics, potato growth, and tuber yield in loam soils. By assessing soil moisture retention, plant growth parameters, and tuber yield characteristics, the study seeks to determine the potential of SDF to optimize water and nutrient use in potato production under conditions of limited water availability. Additionally, this research will explore the economic viability of implementing SDF systems, considering the trade-off between installation costs and long-term gains in productivity and resource efficiency (Figure 1). The findings of this study will provide critical insights into the potential of SDF to enhance sustainable potato production, contributing to the broader body of research on precision irrigation and fertigation in agriculture (Table 3).
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Experimentation year and location
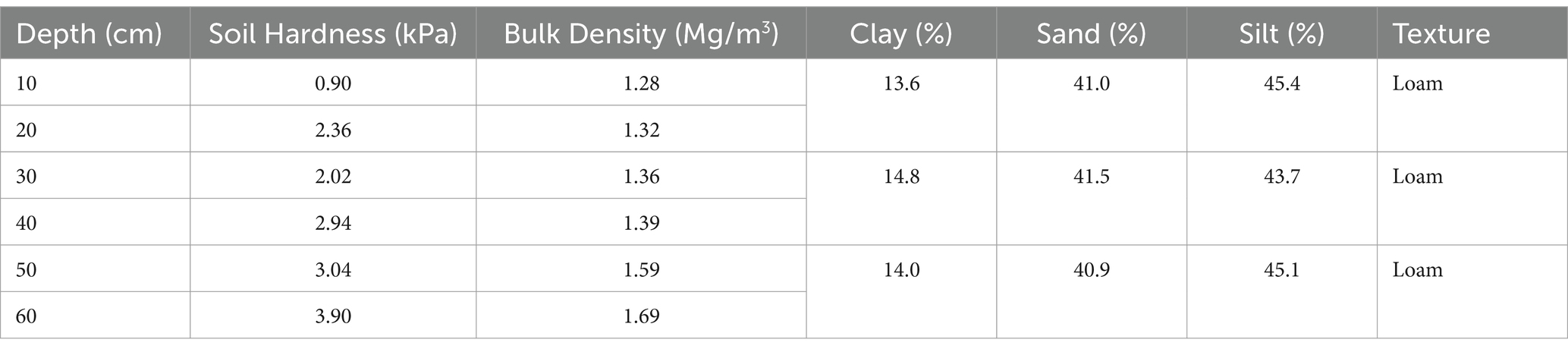
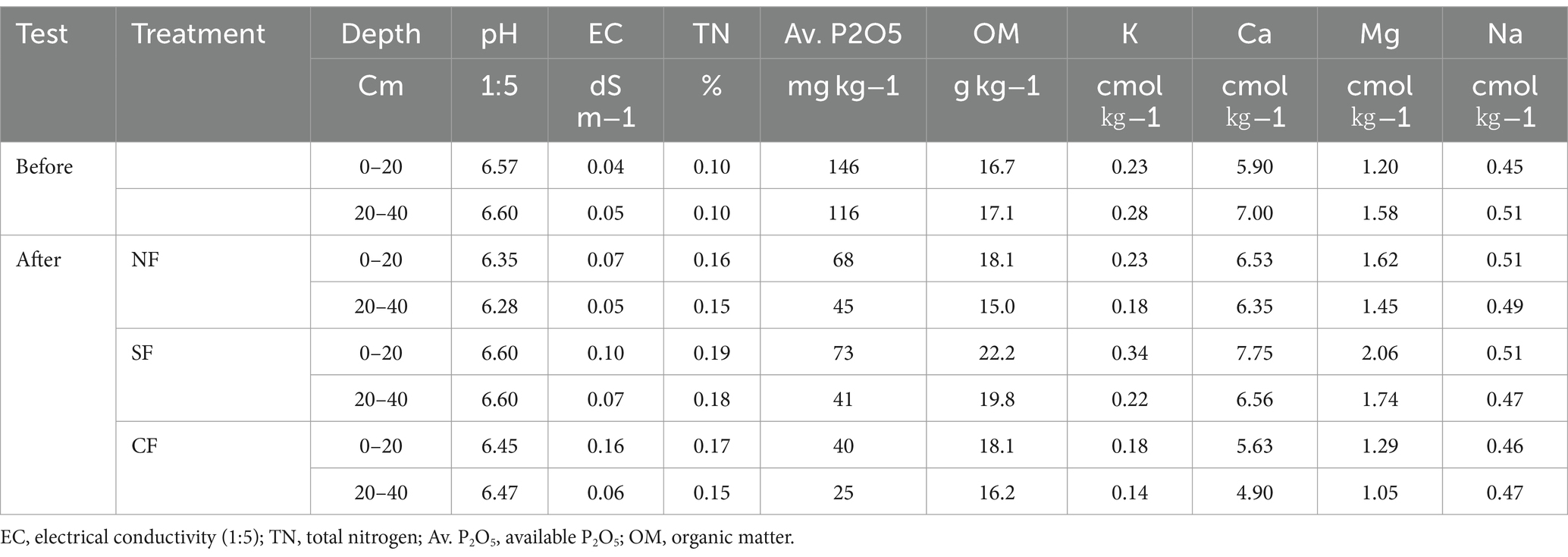
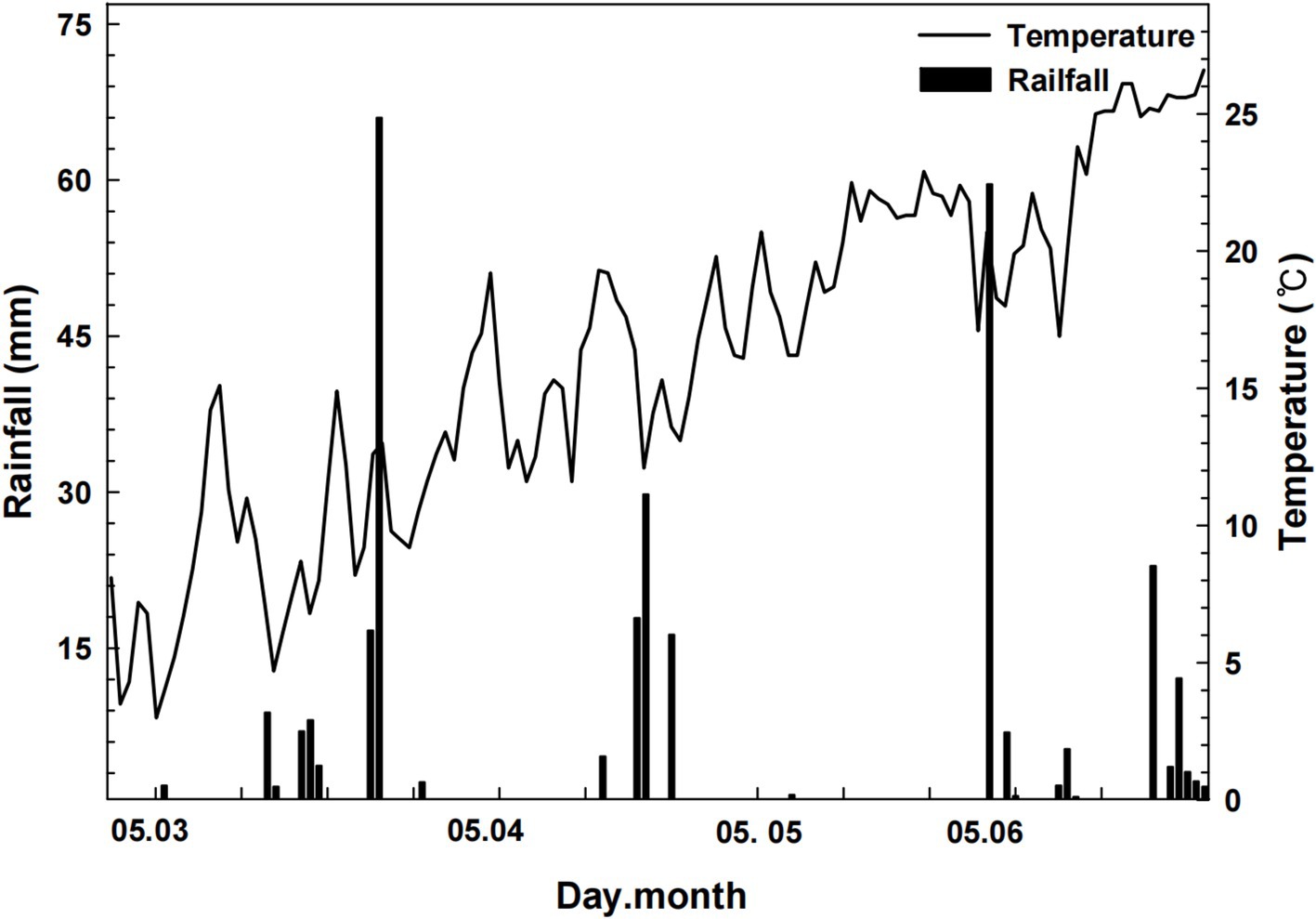
This study was conducted during the spring growing season of 2022 (March to June) at an experimental farm located in Xunyang, Ankang, Shaanxi Province, China (32°51′N, 109°23′E), covering a total area of 600 m2. The region experiences a temperate climate, with an average temperature of 14.5°C and total accumulated rainfall of 246 mm during the study period, conditions typical for spring potato cultivation. The soil at the study site is classified within the loam textural class, characterized by a balanced mixture of sand, silt, and clay, which provides favorable conditions for both water retention and drainage. Prior to planting, the physical and chemical properties of the soil were assessed. The bulk density ranged from 1.28 to 1.69 Mg/m3 across different depths (10 to 60 cm). According to Patel and Rajput (2008), bulk densities between 1.2 and 1.6 Mg/m3 are considered optimal for root growth and water infiltration, categorizing the soil’s bulk density as medium, which facilitates root penetration and minimizes compaction, thus supporting potato cultivation. The soil pH values ranged from 6.57 to 6.60 at depths of 0–40 cm, categorized as neutral to slightly acidic, which, according to Wang et al. (2022), is ideal for nutrient uptake in potatoes, which generally thrive in soils with a pH range of 5.0 to 6.5. The electrical conductivity (EC) values were low, ranging from 0.04 to 0.05 dS/m, indicating minimal soil salinity. As reported by Li et al. (2021), low EC values are beneficial for potato cultivation as they reduce the risk of salt stress, which can negatively impact plant growth and tuber formation (Table 4).
The total nitrogen (TN) content was measured at 0.10%, which is classified as medium according to soil fertility standards for loam soils (Plauborg et al., 2022). This nitrogen level is adequate to support healthy crop growth, especially when supplemented with fertigation, which delivers nutrients directly to the root zone. The organic matter (OM) content ranged from 16.7 to 17.1 g/kg, categorized as medium based on soil fertility standards (Soliman et al., 2020), providing a balance of nutrient availability and water retention, both essential for optimal potato growth. The available phosphorus (P2O5) levels were high, with 146 mg/kg in the upper 20 cm and 116 mg/kg at a depth of 20–40 cm. High phosphorus levels are crucial for promoting root development and tuber formation, as confirmed by Patel and Rajput (2008).
In April of the same year, they were buried in the soil of the plot according to Figure 1. In summary, the soil properties at the experimental site, categorized as medium for bulk density, nitrogen, and organic matter, and high for phosphorus, indicate that the field was well-suited for potato cultivation. The neutral pH and low EC provided favorable conditions for nutrient uptake and reduced salinity stress, aligning with the optimal growth conditions for potatoes (Wang et al., 2022). The medium levels of nitrogen and organic matter suggest moderate soil fertility, with the fertigation system playing a critical role in enhancing crop performance. Additionally, the high phosphorus levels supported strong root development, contributing to the observed yield improvements under subsurface drip fertigation. These findings align with existing literature on the benefits of optimizing soil conditions for increased yield and efficiency in drip fertigation systems (Li et al., 2021; Plauborg et al., 2022).
2.2 Experimental design
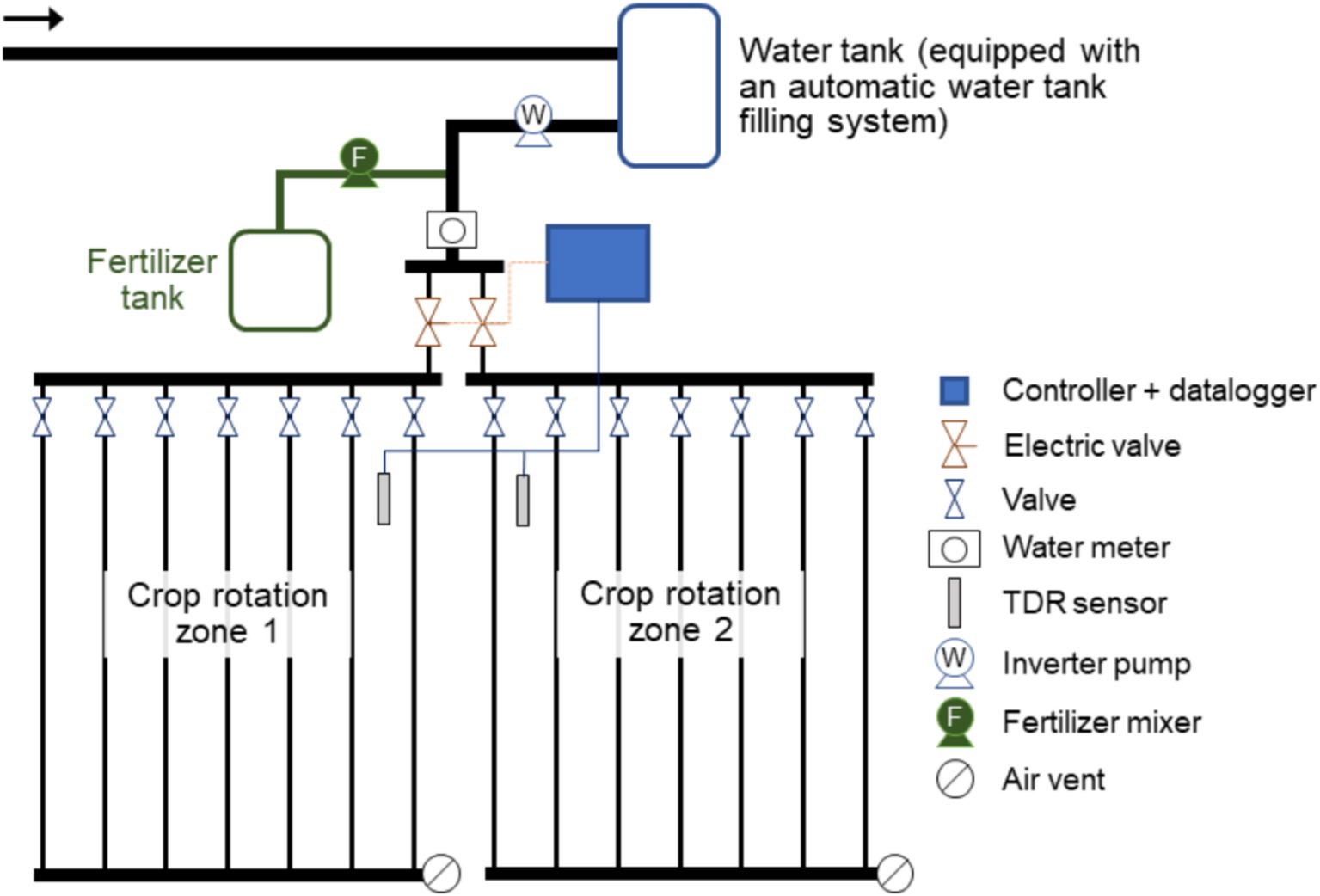
The study was conducted over one growing season (March to June 2022) using a randomized complete block design (RCBD) with three irrigation treatments: no fertilization (NF), subsurface drip fertigation (SF), and surface drip fertigation (CF). Each treatment was replicated four times to meet the statistical requirements for valid inference. Plots measuring 10 m2 were used, with a 1-meter buffer zone between treatments to prevent cross-contamination of water and nutrients (Figure 2). This design ensured a comprehensive evaluation of soil moisture dynamics, potato growth parameters, and yield outcomes under varying irrigation regimes. The treatments included:
No Fertilization (NF) – Control group with no irrigation or fertilization.
Subsurface Drip Irrigation/Fertigation (SF) – Drip pipes buried at 40 cm depth.
Surface Drip Irrigation/Fertigation (CF) – Drip pipes placed on the soil surface.
Each plot measured 10 m2 (2 m x 5 m), and a 1-meter buffer zone was maintained between each plot to avoid water and nutrient contamination. The degree of freedom for the statistical analysis was calculated based on the number of treatments and replications, ensuring the validity of the results (Table 5).
2.3 Soil sampling method
Soil sampling was conducted at three depths: 0–20 cm, 20–40 cm, and 40–60 cm, to assess soil physical and chemical properties and monitor soil moisture dynamics. Soil samples were collected using a soil auger at five randomly selected points within each plot to ensure representative sampling. The samples were then composited, air-dried, and sieved through a 2 mm sieve for further analysis. A total of three sampling events were conducted: before planting, mid-season, and after harvest (Figure 3).
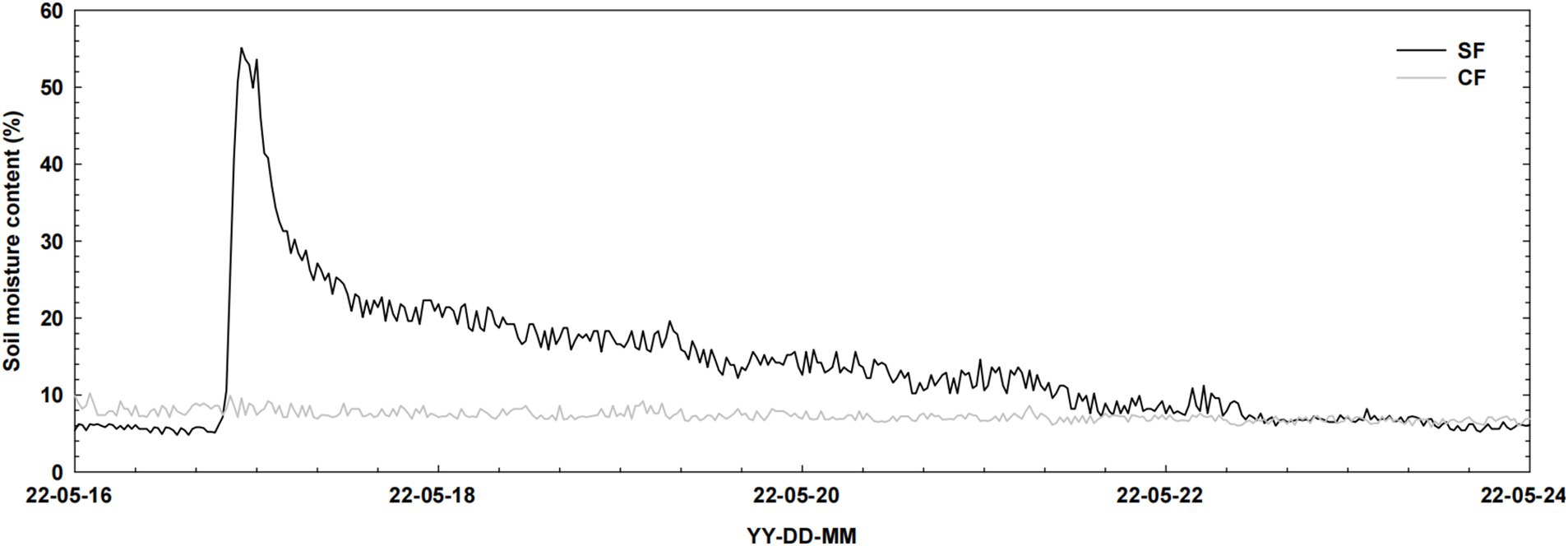
Figure 3. Change of soil water content after subsurface drip irrigation/fertigation at soil depth 20 cm.
2.4 Soil parameters and measurements
The following soil parameters were analyzed:
Soil moisture content was measured using a Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) probe at three depths (10 cm, 20 cm, and 30 cm). Data were logged at regular intervals to track moisture fluctuations throughout the season.
Bulk density was determined using the core method, with undisturbed soil samples collected at 10 cm depth increments.
Soil pH and electrical conductivity (EC) were measured using a pH/conductivity meter after diluting soil samples in a 1:5 soil-water suspension.
Total nitrogen (TN), organic matter (OM), and available phosphorus (P2O5) were analyzed following standard soil analysis protocols.
2.5 Fertilization and irrigation management
The fertilization regimen consisted of two stages: 50% of the recommended N-P-K (100–88-130 kg/ha) applied as basal fertilizer, and the remaining 50% applied via fertigation during the tuber formation (April 29) and tuber enlargement stages (May 17). Irrigation was based on soil moisture data from the TDR sensors, with the goal of maintaining soil moisture levels at field capacity (13%). Irrigation was applied through pressure-compensated emitters with a flow rate of 2 L/h for both subsurface and surface systems (Figure 4).
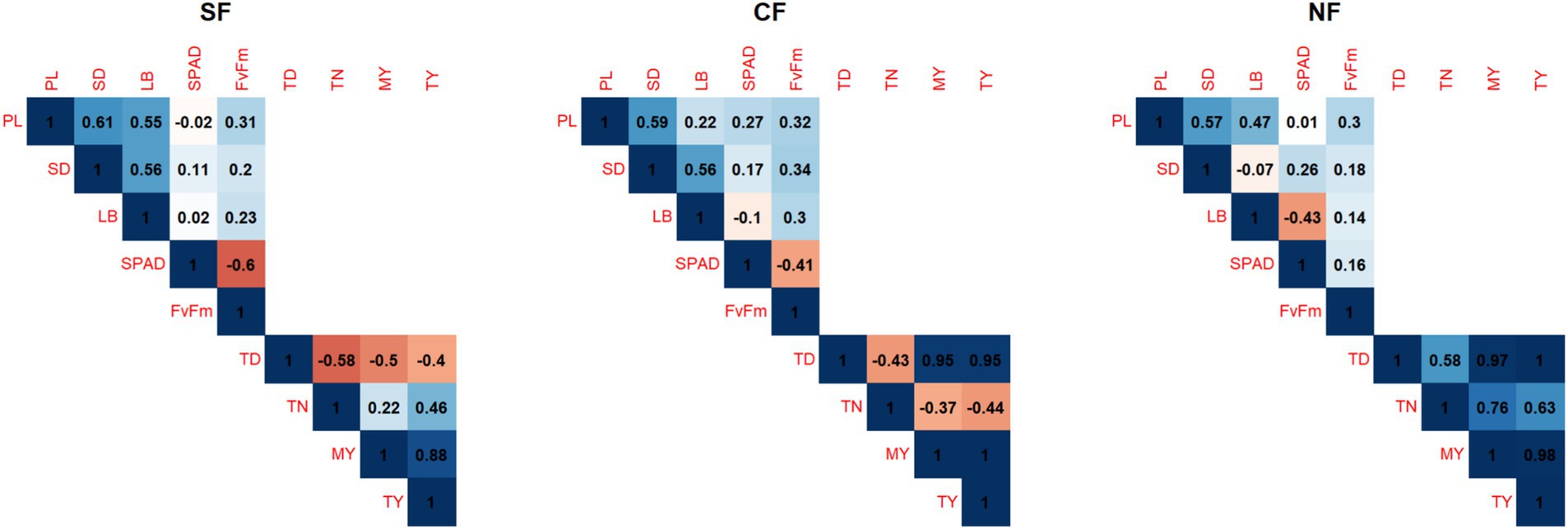
Figure 4. Correlation coefficients of potato growth and yield characteristics. NF, non irrigation/fertigation; SF, subsurface drip irrigation/fertigation; CF, conventional irrigation/fertigation; PL, plant length; SD, stem diameter; LB, lateral branch; SPAD, leaf color index; Fv/Fm, chlorophyll fluorescence; TD, tuber diameter; TN, tuber number; MY, marketable yield; TY, total yield.
2.6 Plant growth and yield measurements
Potato growth characteristics, including plant height, stem diameter, and leaf color index (SPAD), were measured at flowering (May 13) and before harvest (June 4). Yield parameters, including tuber diameter, number of tubers per plant, total yield, and marketable yield, were assessed after harvesting.
2.7 Data analysis
The collected data were analyzed using Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) to determine the statistical significance of treatment effects on soil moisture content, plant growth, and yield parameters. A Student–Newman–Keuls (SNK) test was used for post-hoc comparisons among treatments. All statistical analyses were performed using R software (version 4.0), and significance was assessed at a p-value of 0.05. Pearson correlation analysis was conducted to explore relationships between growth characteristics, soil moisture content, and yield.
2.8 Discussion of soil parameters
Soil moisture content at different depths was monitored continuously throughout the growing season. Subsurface drip fertigation led to significantly higher soil moisture retention compared to surface drip irrigation, particularly at the 20 cm depth, where moisture content was 45.5% higher. The results demonstrate a substantial increase in soil moisture retention at the 20 cm depth under subsurface drip fertigation (SF) compared to surface drip fertigation (CF), particularly during critical growth periods. Soil moisture content in the SF treatment was 45.5% higher than in the CF treatment on the day following irrigation, which likely contributed to improved root development and tuber formation. Additionally, subsurface drip irrigation positively influenced soil bulk density and porosity by enhancing water distribution and reducing compaction in deeper soil layers. This consistent availability of moisture at the root zone is a key driver of the observed 10% increase in marketable tuber yield in the SF treatment compared to CF. These findings align with previous studies, such as Soliman et al. (2020), which reported similar benefits in other water-intensive crops. pH and EC remained relatively stable across treatments, though slight variations were observed following fertigation, likely due to the movement of salts within the soil profile. Available phosphorus and total nitrogen levels were notably higher in the subsurface treatment plots, indicating more efficient nutrient uptake facilitated by precise water and nutrient delivery directly to the root zone.
3 Results
3.1 Soil environment changes
Soil moisture content at a depth of 20 cm was measured to evaluate the effectiveness of the subsurface drip fertigation system. On May 17, following fertilization, soil moisture in the subsurface drip treatment area was significantly higher than in the control (surface drip irrigation) area. Specifically, the control area had a moisture content of 9.6%, while the subsurface drip treatment area showed 55.1%, representing a 45.5% increase. By May 18, the subsurface drip treatment area recorded a moisture content of 21.8%, which was 13.2% higher than the control area (8.6%). Over the subsequent days, the moisture content in the subsurface drip area gradually decreased, reaching 9.2% after approximately four days, showing a similar or lower trend compared to the control area.
3.2 Plant growth and yield
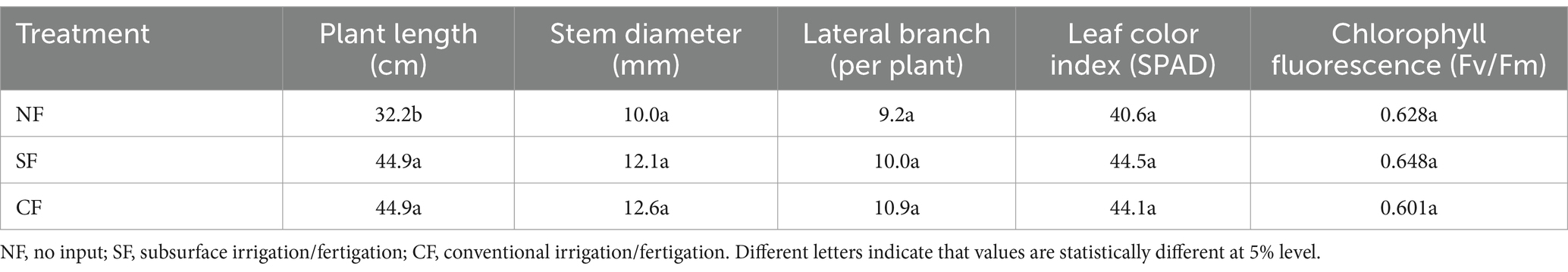
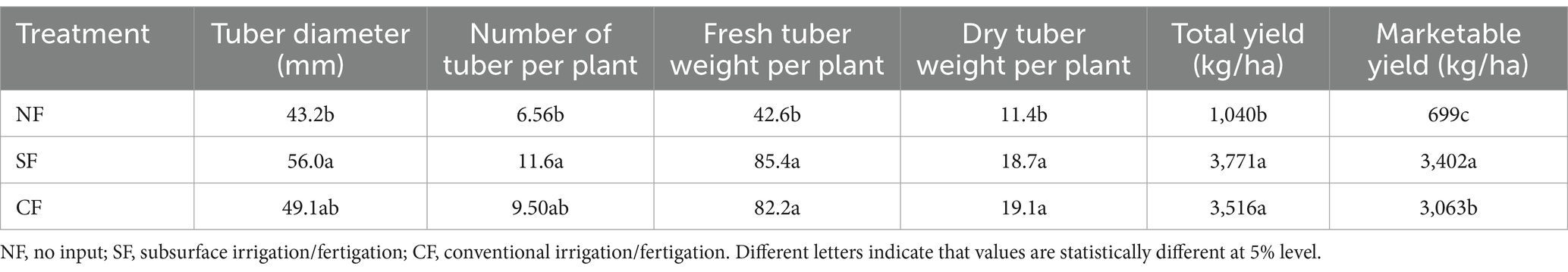
Growth parameters of the potato plants were measured across the different treatment areas. During the flowering stage, the plant height in the subsurface drip treatment area and the control area were 66.2 cm and 67.9 cm, respectively, both significantly higher than the no-fertilization area at 36.5 cm. The stem diameter in the subsurface drip treatment area and the control area were 14.9 mm and 14.5 mm, respectively, again significantly thicker than the no-fertilization area at 10.1 mm.
Yield assessment at harvest showed that the average tuber diameter in the subsurface drip treatment area was 56.0 mm, 6.9 mm larger than the control area (49.1 mm). The subsurface drip treatment also produced more tubers per plant, with an average of 11.6 tubers compared to 9.5 tubers in the control area, an increase of 18.1%. Additionally, marketable tuber yield in the subsurface drip treatment area reached 34.02 tons per hectare, approximately 10% higher than the 30.63 tons per hectare recorded in the control area.
3.3 Soil physical and chemical properties
Changes in soil physical and chemical properties were observed after fertilization. The organic matter content and total nitrogen levels were significantly higher in the subsurface drip treatment area compared to the no-fertilization area. In the subsurface drip area, organic matter content at 0–20 cm and 20–40 cm depths were 22.2 g/kg and 19.8 g/kg, respectively, whereas the control area recorded 18.1 g/kg and 16.2 g/kg at the same depths. Additionally, the pH and cation exchange capacity were also higher in the subsurface drip treatment area, indicating a positive impact of subsurface drip fertigation on soil quality.
4 Discussion
4.1 Impact on soil environment
The findings of this study demonstrate that subsurface drip fertigation significantly improved soil moisture retention at a depth of 20 cm, particularly during the critical stages of crop development. This aligns with the broader body of research indicating that subsurface drip irrigation systems can enhance water-use efficiency by delivering water directly to the root zone, thereby minimizing surface evaporation and runoff losses (Soliman et al., 2020; Plauborg et al., 2022). By maintaining higher soil moisture levels over an extended period, subsurface drip systems not only provide more stable moisture conditions but also mitigate the risks of waterlogging and nutrient leaching, which are common in conventional irrigation systems (Patel and Rajput, 2008). These results fill a critical research gap in understanding the behavior of soil moisture dynamics under subsurface drip fertigation, particularly in loam soils, where capillary action and vertical water movement may differ from sandy or clay soils. This trend was consistent across the three decomposition environments (Figure 2A). Similarly, after 6 months, mixed straw and potato straw still showed significantly higher decomposition rates compared to maize straw, with both monoculture environments reflecting comparable patterns (Figure 2B). Further, this study provides empirical evidence to support the theoretical framework of precision irrigation, where optimizing water delivery to match crop demands improves both soil health and plant growth (Reyes-Cabrera et al., 2016). Future research could extend these findings by exploring soil-specific responses to subsurface drip systems in other soil textures and climatic conditions, contributing to the refinement of irrigation models (Du et al., 2023).
4.2 Impact on plant growth and yield
The results also demonstrate that subsurface drip fertigation led to significant improvements in plant growth and yield, notably with a 10% increase in marketable yield compared to conventional surface drip irrigation. This increase is largely due to the precise control of both water and nutrients, which supports the balanced development of both the vegetative and reproductive structures of the potato plant (Tahoun et al., 2022). Enhanced nutrient uptake and reduced nutrient losses, thanks to the fertigation process, likely contributed to the increase in tuber size and number. From a theoretical standpoint, these results align with the principles of nutrient-use efficiency and sustainable intensification in agriculture. Precision fertigation, where nutrients are delivered in sync with plant growth demands, not only enhances nutrient-use efficiency but also reduces environmental impacts, such as nitrate leaching and greenhouse gas emissions (Li et al., 2021). The present study thus contributes to the growing body of research advocating for integrated water and nutrient management as a key component of sustainable agricultural systems (Rana et al., 2023). In practice, the use of subsurface drip fertigation could serve as a critical tool for addressing global food security concerns, particularly as climate change exacerbates water scarcity in many regions (Anderson et al., 2020). By improving both water and nutrient-use efficiencies, this system can potentially enable farmers to maintain or even increase yields under conditions of limited water availability, which is crucial for ensuring food production in water-scarce environments.
4.3 Economic benefits of subsurface drip fertigation
Beyond the agronomic benefits, subsurface drip fertigation offers substantial economic advantages, particularly in high-value crops like potatoes. While the initial installation cost of subsurface drip systems is higher than traditional irrigation methods, the long-term economic benefits outweigh these upfront costs, making it a sound investment for farmers. These benefits include:
Water Savings: Subsurface drip systems have been shown to reduce water usage by up to 40%, compared to conventional surface drip irrigation (Soliman et al., 2020). In regions where water is a limited or costly resource, the ability to significantly reduce water consumption translates directly into lower operational costs. This is particularly relevant in arid and semi-arid regions, where water conservation is essential for economic sustainability. Throughout the decomposition period, all straw-decomposing microorganisms were capable of utilizing carbon substrates, with a primary focus on the utilization of carbohydrates and carboxylic acids (Figure 3).
Fertilizer Efficiency: Fertigation allows for precise nutrient delivery directly to the root zone, reducing fertilizer wastage and enhancing nutrient uptake efficiency. This results in a reduction of fertilizer use by up to 20–30%, as demonstrated in recent studies on potato cultivation (Akkamis and Caliskan, 2023). This not only lowers input costs but also contributes to environmental sustainability by minimizing nutrient runoff and soil degradation. It was found that after 6 months of decomposition, compared to single straw types, mixed straw significantly enhanced microbial utilization of carbohydrate and carboxylic acid carbon substrates (Figure 4B). However, at the 3-month decomposition stage, the microorganisms from mixed straw did not show a significant advantage in the utilization of carbon substrates (Figure 4A).
Increased Yield and Revenue: The 10% increase in marketable tuber yield observed in this study is particularly significant from an economic perspective. Higher-quality tubers, which meet market standards for size and appearance, typically command higher prices, resulting in increased revenue for farmers. For instance, a 10% yield increase in a farm producing 30 tons per hectare could lead to an additional 3 tons of marketable potatoes per hectare. With potato prices ranging from $300 to $500 per ton, this could result in an additional revenue of $900 to $1,500 per hectare, improving the profitability of potato farming.
Labor and Operational Cost Reductions: Subsurface drip systems are highly automated, requiring less manual labor for irrigation management. Automated systems can be controlled remotely using soil moisture sensors, significantly reducing labor costs associated with manual irrigation (Cheng et al., 2023). Furthermore, the reduction in soil-borne diseases—due to the drier soil surface in subsurface irrigation systems—decreases the need for chemical inputs, providing further cost savings.
From an economic theory perspective, these savings align with the principles of capital investment and operational efficiency in agriculture. While the capital costs of installing subsurface drip systems are higher, the reduction in variable costs (water, fertilizer, and labor) and the increase in revenue due to higher yields and better-quality produce make the investment economically viable within 3–5 years, as evidenced in similar studies (Mattar et al., 2021; Du et al., 2023).
4.4 Theoretical and practical contributions
This study makes several theoretical contributions by advancing the understanding of subsurface drip fertigation’s impact on soil moisture dynamics, nutrient-use efficiency, and crop yield in potato cultivation. It fills a gap in the existing literature by providing empirical data on the performance of subsurface drip systems in loam soils, where water retention and movement differ from other soil types. Moreover, the findings contribute to the broader discourse on precision agriculture, particularly in optimizing resource use under varying environmental conditions. From a practical perspective, the economic benefits outlined in this study provide a compelling argument for the wider adoption of subsurface drip fertigation, especially in regions where water scarcity and rising input costs are significant challenges. By offering a sustainable solution that improves both resource use and economic returns, this study highlights the potential of subsurface drip fertigation to contribute to more resilient and profitable agricultural systems.
5 Conclusion
This study demonstrated that subsurface drip fertigation (SDF) significantly enhances potato growth, yield, and water-use efficiency compared to surface drip irrigation (SDI). Specifically, the SDF system resulted in a 10% increase in marketable tuber yield, improved plant growth parameters, and better soil moisture retention, particularly at the root zone. The consistent moisture and nutrient delivery provided by the SDF system supported more stable plant growth and reduced periods of water stress, which are crucial for optimizing potato production, particularly during critical growth stages such as tuber formation.
The economic analysis of the study suggests that, while SDF involves higher initial installation costs, these can be offset by long-term benefits, including water savings of approximately 40%, reduced fertilizer wastage, and increased revenue from higher marketable yields. The partial budget analysis indicates that the SDF system is cost-effective, with net positive returns within 3–5 years of implementation.
However, the study also acknowledges certain limitations, including its focus on a single growing season and its application in loam soils. Future research should investigate the long-term effects of SDF on soil health and crop productivity across multiple seasons and in different soil types. Additionally, exploring the optimal combination of irrigation and fertigation schedules to maximize yield while minimizing environmental impacts is essential for the wider adoption of this technology.
Overall, the findings of this study highlight the potential of subsurface drip fertigation as a sustainable and economically viable irrigation technology for potato cultivation, particularly in regions facing water scarcity. By improving both water and nutrient-use efficiency, SDF can contribute to more resilient agricultural systems and support the growing need for sustainable food production.
5.1 Research limitations and future directions
While this research provides valuable insights into the benefits of subsurface drip irrigation in potato cultivation, it is not without limitations. First, the study was conducted in a specific soil type—loam—which may limit the generalizability of the findings to other soil types, such as sandy or clay soils. Future research should explore the effectiveness of subsurface drip systems across a wider range of soil textures and environmental conditions to better understand their adaptability and performance.
Additionally, the study focused on a single crop cycle under controlled conditions. Long-term studies across multiple growing seasons and different climatic regions are necessary to assess the durability and long-term benefits of subsurface drip systems. Future research should also investigate the economic feasibility of widespread adoption of this technology, considering installation costs and maintenance requirements.
Lastly, the study observed variations in tuber yield and quality based on different fertilization regimes. Further exploration into the optimal combination of fertilizers and irrigation schedules is needed to maximize the benefits of subsurface drip irrigation. This includes studying the effects of different nutrient management strategies on both above-ground and below-ground growth to achieve a more balanced and sustainable crop production system.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
GZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. GS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Internal Projects of Shaanxi Land Engineering Construction Group (DJNY2024-58).
Conflict of interest
GZ, XL, ZW, GS, WL, and YW were employed by the Ankang Branch of Shaanxi Provincial Land Engineering Construction Group Co., Ltd. GZ, XL, ZW, GS, WL, and YW were employed by the Shaanxi Provincial Land Engineering Construction Group Co., Ltd.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abioye, E. A., Abidin, M. S. Z., Mahmud, M. S. A., Buyamin, S., Ishak, M. H. I., Rahman, M. K. I. A., et al. (2020). A review on monitoring and advanced control strategies for precision irrigation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 173:105441. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2020.105441
Akkamis, M., and Caliskan, S. (2023). Responses of yield, quality and water use efficiency of potato grown under different drip irrigation and nitrogen levels. Sci. Rep. 13:9911. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36934-3
Anderson, R., Bayer, P. E., and Edwards, D. (2020). Climate change and the need for agricultural adaptation. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 56, 197–202. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2019.12.006
Cheng, M., Wang, H., Zhang, F., Wang, X., Liao, Z., Zhang, S., et al. (2023). Effects of irrigation and fertilization regimes on tuber yield, water-nutrient uptake and productivity of potato under drip fertigation in sandy regions of northern China. Agric. Water Manag. 287:108459. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2023.108459
Du, Y., Liu, X., Zhang, L., and Zhou, W. (2023). Drip irrigation in agricultural saline-alkali land controls soil salinity and improves crop yield: evidence from a global meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 880:163226. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.163226
Li, H., Mei, X., Wang, J., Huang, F., Hao, W., and Li, B. (2021). Drip fertigation significantly increased crop yield, water productivity and nitrogen use efficiency with respect to traditional irrigation and fertilization practices: a meta-analysis in China. Agric. Water Manag. 244:106534. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106534
Mattar, M. A., Zin El-Abedin, T. K., Al-Ghobari, H. M., Alazba, A. A., and Elansary, H. O. (2021). Effects of different surface and subsurface drip irrigation levels on growth traits, tuber yield, and irrigation water use efficiency of potato crop. Irrig. Sci. 39, 517–533. doi: 10.1007/s00271-020-00715-x
Patel, N., and Rajput, T. B. S. (2008). Dynamics and modeling of soil water under subsurface drip irrigated onion. Agric. Water Manag. 95, 1335–1349. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2008.06.002
Plauborg, F., Motarjemi, S. K., Nagy, D., and Zhou, Z. (2022). Analysing potato response to subsurface drip irrigation and nitrogen fertigation regimes in a temperate environment using the daisy model. Field Crop Res. 276:108367. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2021.108367
Rana, B., Parihar, C. M., Jat, M. L., Patra, K., Nayak, H. S., Reddy, K. S., et al. (2023). Combining sub-surface fertigation with conservation agriculture in intensively irrigated rice under rice-wheat system can be an option for sustainably improving water and nitrogen use-efficiency. Field Crop Res. 302:109074. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2023.109074
Reyes-Cabrera, J., Zotarelli, L., Dukes, M. D., Rowland, D. L., and Sargent, S. A. (2016). Soil moisture distribution under drip irrigation and seepage for potato production. Agric. Water Manag. 169, 183–192. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2016.03.001
Soliman, A. I. E., Morad, M. M., Wasfy, K. I., and Moursy, M. A. M. (2020). Utilization of aquaculture drainage for enhancing onion crop yield under surface and subsurface drip irrigation systems. Agric. Water Manag. 239:106244. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106244
Tahoun, A. M. M. A., El-Enin, M. M. A., Mancy, A. G., Sheta, M. H., and Shaaban, A. (2022). Integrative soil application of humic acid and foliar plant growth stimulants improves soil properties and wheat yield and quality in nutrient-poor Sandy soil of a semiarid region. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 22, 2857–2871. doi: 10.1007/s42729-022-00851-7
Keywords: subsurface drip irrigation, potato cultivation, soil moisture content, tuber yield, loam soil, fertigation, agricultural water management
Citation: Zhao G, Luo X, Wang Z, Sheng G, Liu W and Wang Y (2024) Effects of subsurface drip fertigation on potato growth, yield, and soil moisture dynamics. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1485377. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1485377
Edited by:
Matteo Balderacchi, Independent Researcher, Piacenza, ItalyReviewed by:
Poonam Biswal, Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, IndiaWorkat Sebnie, Sekota Dryland Agricultural Research Center, Ethiopia
Copyright © 2024 Zhao, Luo, Wang, Sheng, Liu and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Gang Sheng, Mjg0NDY3NzkwQHFxLmNvbQ==
 Guoqiang Zhao
Guoqiang Zhao Xianxin Luo1,2
Xianxin Luo1,2