- 1School of Management Science and Engineering, Shandong University of Finance and Economics, Jinan, China
- 2School of Economics, Shandong University of Finance and Economics, Jinan, China
- 3School of Computer Science and Technology, Shandong University of Finance and Economics, Jinan, China
- 4School of Health Management, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China
Background: Agricultural activities are the second largest source of its greenhouse gas emissions in China, making it imperative to prioritize the reduction of carbon emissions in agriculture to achieve carbon neutrality. Agricultural modernization is recognized as a key strategy for achieving this reduction. In response, China has introduced a smart agriculture policy to catalyze the progress of agricultural modernization. However, it is not clear that the policy will achieve agriculture carbon reductions.
Purpose: To examine the impact and mechanism of smart agriculture policy on agricultural carbon emissions, thereby facilitating the transition toward low-carbon practices in agriculture.
Methods: Using panel data across China’s 31 provinces from 2001 to 2020, this paper applies a multi-period differences-in-differences (DID) method to assess the impact and mechanisms of the smart agriculture policy on carbon reduction.
Results: ① The smart agriculture policy exerts a significant positive influence on reducing agricultural carbon emission. ② The policy’s effectiveness is particularly notable in China’s central and western regions and non-grain producing areas, in contrast to the limited impact observed in the eastern provinces and grain-producing areas. ③ Smart agriculture policies have greatly reduced agricultural carbon emissions by promoting the agricultural-scale operation and the advancement of agricultural technology.
Conclusion: The paper reveals that smart agriculture policy has a positive effect on carbon emission reduction and provides relevant policy recommendations for the government. This has considerable implications for promoting sustainable agriculture.
1 Introduction
Global warming and increasing extreme weather events profoundly affect human productivity and livelihood. This gives rise to a common human goal to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. In the field of agricultural production, subject to traditional production, the greenhouse gases generated in the process of agricultural production remain high, and it is one of the main sources of global greenhouse gas emissions (Bennetzen et al., 2016).
China, a leading agricultural nation globally, also grapples with significant agricultural carbon emissions. Since the turn of the millennium, the yield per unit area for grain has surged by 26.38%. Concurrently, there has been a substantial increase in the application of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and agricultural films, with respective increases of 45.25, 41.23, and 93.21% (Tian and Wu, 2020). Practices such as frequent land-use changes, excessive resource exploitation, and inadequate waste management further aggravate the issue of carbon emissions (Zhu and Xing, 2017). Studies indicate that traditional agricultural production techniques account for 17% of the nation’s total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions (Xu and Lin, 2017). By analyzing the data of agricultural carbon emission over the years, it is found that the total agricultural carbon emission in China shows a fluctuating upward trend from 2000 to 2021, with an annual growth rate of 0.23% (Chen et al., 2024). But in recent years, there has been a downward trend, approaching a peak. Since China’s agricultural technology level and agricultural scale still need to be improved, the emissions caused by them may become the biggest uncertainty factor causing agricultural carbon peak (Chi et al., 2020).
Reducing agricultural carbon emissions requires a shift away from traditional production and the integration of advanced technologies into modern agricultural practices. Consequently, the emergence of smart agriculture, underpinned by digital technologies such as robotics, the Internet of Things (IoT), and remote sensing, has become pivotal for advancing sustainable agricultural practices and safeguarding grain production amidst climate variability (Adamides, 2020). In this vein, the Chinese government launched the “Internet Plus” strategy in 2015, which includes integrating the Internet and the Internet of Things into agricultural development. The policy aims to foster a mature agricultural iot system, improve agricultural technology, guarantee the quality of agricultural products, and ultimately establish a networked and intelligent agricultural ecosystem.
To implement “Internet Plus” strategy and foster advancement in smart agriculture, the Chinese government has promulgated several key directives and policies to assist farmers. For instance, the Document No. 1 in 2012 initially proposed to promote the information development of rural agriculture. In 2015, the Document No. 1 prioritized the acceleration of smart agriculture as the inaugural policy of the year, marking the first time agricultural modernization was highlighted in this manner. In 2018, the connection between smart agriculture and rural revitalization was further strengthened, underscoring the importance of agricultural development. Additionally, pilot projects were initiated in nine provinces in 2015 and 2018 to demonstrate the integration of smart agriculture with rural revitalization strategies. Yet, questions remain: Can the implementation of smart agriculture policy effectively reduce agricultural carbon emissions? Are there regional disparities in the policy’s carbon emission reduction efficacy? What are the underlying mechanisms through which these policies achieve carbon emission reduction?
Currently, scholarly work pertinent to this paper predominantly centers on the impact of agricultural policies on carbon emissions and the environmental impact of smart agriculture. Regarding the impact of agricultural policies, Lu (2013) demonstrated that policies aimed at agricultural carbon emission reduction (ACER) successfully bolstered the low-carbon production intentions of agricultural firms, thereby encouraging their engagement in low-carbon practices. Solazzo et al. (2016) observed that green agricultural development policies are efficacious in reducing agricultural carbon emissions. Shi et al. (2021) dissected the impacts and mechanisms of government regulatory policies on ACER, specifically addressing measures such as emissions trading and targeted subsidies, thereby enriching the theoretical underpinnings of ACER effects. Du et al. (2023) evaluated the influence of China’s National Experimental Demonstration Zones of Sustainable Agricultural Development policy on ACER, concluding that the policy significantly contributed to carbon emission reductions. These studies offer substantial insights for the present paper, yet they do not delve into the specific carbon emission reduction effects and mechanisms of smart agriculture policy. Turning to the environmental impact of smart agriculture, Yuzhen (2021) developed a theoretical framework, positing that the adoption of smart agriculture technologies modulates the usage of agrochemical inputs, leading to environmental benefits. Wang et al. (2020) investigated the nexus between the agricultural producers’ inclination toward smart agriculture and their low-carbon production behaviors, suggesting that producers may be averse to the risks inherent in low-carbon practices, and that government policies promoting smart agriculture could mitigate such risks. Santiteerakul et al. (2020) discovered that the adoption of smart agriculture by agricultural operators leads to a diminished utilization of chemicals, including fertilizers and pesticides. Although these works have explored the environmental effect of smart agriculture, they have primarily concentrated on the technology itself, and have not yet thoroughly investigated the policy-driven carbon reduction effects from a smart agriculture policy perspective.
Therefore, taking China as an example, we study the relationship between smart agriculture policy and agricultural carbon emissions with the help of multi-period difference in differences (DID) to explore the answers to the above questions. DID is a prevalent analytical tool for evaluating policy impacts, positing policy changes and new implementations as “quasi-natural experiments” that are exogenous to the economic system. This methodology offers several distinct advantages: (1) It mitigates time-invariant heterogeneity and partially addresses endogeneity stemming from omitted variables; (2) The DID method provides a more rigorous scientific approach, enhancing the precision of policy effect estimations; and (3) It reduces the likelihood of reverse causality issues by rendering policies exogenous in relation to micro-level subjects.
The implementation of smart agriculture policies has been indicated by our study to have led to a significant decrease in total agricultural carbon emissions. The efficacy of these policies in carbon emission reduction exhibits notable regional heterogeneity. In provinces that are economically less developed, particularly in central and western China, as well as in those not classified as major grain producing areas, the policies have demonstrated a substantial inhibitory effect on carbon emissions. Conversely, in the economically vibrant eastern regions and the major grain producing areas, the impact of smart agriculture policy on reducing carbon emissions is not significant enough. The mechanism by which these policies reduce emissions primarily involves the expansion of the agricultural-scale operation and the advancement of agricultural technology.
The paper’s contributions as follows: (1) It empirically examines the influence of smart agricultural policies on the reduction of agricultural emissions, thereby enriched existing lit research. (2) We explored the mechanisms through which smart agricultural policies affect carbon emissions, delineating a clear pathway for emission reduction. It also offers policy recommendations aimed at national and local governments to foster emission reduction and agricultural sustainability. (3) By verifying the carbon emission reduction effects of smart agriculture policy in China, the paper provides valuable insights and policy implications for other countries and regions striving to achieve agricultural carbon reduction and sustainable development.
The structure of the ensuing paper is outlined as follows: Section 1 offers a comprehensive literature review coupled with an exposition of the implementation of smart agriculture policy within China. Section 2 articulates the theoretical framework and posits the research hypotheses. Section 3 details the data sources and the econometric modeling approach. Empirical analysis, encompassing robustness checks, heterogeneity examination, and mechanism inquiry, is conducted in Section 4. Section 5 extends the analysis further. Finally, Section 6 encapsulates the conclusions drawn from the paper and presents pertinent policy recommendations.
2 Theoretical analysis and research hypothesis
2.1 Smart agriculture policy and agricultural carbon emission reduction
Since the advent of the 21st century, China has placed significant emphasis on advancing the domain of agricultural informatization and intelligence, issuing a succession of pivotal policy documents from the central government and initiating pilot projects across nine provinces in 2015 and 2018. The smart agriculture policy is primarily anchored in three strategic thrusts: Firstly, it aims to expedite the development of agricultural informatization by constructing a digital agricultural production framework, integrating modern information technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and big data, and advancing initiatives for the modernization and enhancement of smart agriculture. Secondly, it seeks to establish and disseminate the agricultural and rural big data systems, fostering data resource integration and sharing, facilitating real-time access to resource information for agricultural producers, and offering decision support for agricultural operations. Thirdly, it leverages smart agricultural technologies to augment the efficiency of agricultural resource utilization, encourages the judicious use of pesticides and fertilizers, and steers the agriculture toward sustainability, environmental friendliness, and green development.
Addressing the absence of modern technology in China’s agricultural production, along with the ecological degradation wrought by extensive farming practices and the excessive use of chemical inputs, the smart agriculture policy is formulated with a dual focus. Firstly, it is designed to catalyze the transition toward agricultural modernization, enhance production efficiency, and ensure the sustainable progression of the agricultural industry, thereby implicitly aiming to reduce agricultural carbon emissions. Secondly, the policy strives to integrate information technology to bring agricultural practices up to standard and ecological requirements, thereby directly reducing the carbon footprint of farming operations. In sum, Hypothesis H1 is introduced.
H1: The implementation of smart agricultural policy is conducive to reducing agricultural carbon emissions.
2.2 Smart agricultural policy, agricultural-scale operation, and agricultural carbon emission reduction
The implementation of smart agriculture policy not only promotes the development of smart agriculture, but also provides impetus for the large-scale agricultural production and operation by improving the level of agricultural management and reducing the dependence on manpower. Specifically, smart agriculture policies introduce advanced information technology and automation equipment. It not only optimizes the agricultural production process and improves efficiency, but also enables agricultural operators to manage a larger land area more effectively, which promotes the expansion of production scale (Li et al., 2016). At the same time, the development of smart agriculture has also given rise to integrated agricultural service companies, which provide whole-process managed services, such as land management, planting planning, pest control and harvesting, greatly reducing the burden of agricultural operators. Agricultural operators are able to devote more energy and resources to expanding the scale of production. However, some bottlenecks may also be encountered in this process, such as low farmers’ acceptance of technology and policy (Reddy, 2019), insufficient capital investment (Yin et al., 2023). To overcome these challenges, relevant actors have adopted a series of strategies, including strengthening famer’s education and training, providing financial subsidies, to ensure the smooth implementation of smart agriculture policies and ultimately achieve effective expansion of agricultural production scale. Through the application of change theory, we can have a clearer understanding of how smart agriculture programs can promote the scale up of agricultural production by addressing potential bottlenecks.
Agricultural-scale operation can significantly reduce carbon emissions within the agricultural sector. By scaling up agricultural operation and refining management practices, the efficiency of pesticides can be optimized, thereby reducing the chemical inputs required per unit area of crops (Schlesinger, 2000). Additionally, employing intensive management practices can improve the operational efficiency of agricultural machinery and irrigation systems, as documented (Su et al., 2022), which in turn can lead to a decrease in carbon emissions throughout the farming process. Scaled management is pivotal for the conservation of soil nutrients and the protection of arable land. This approach effectively mitigates the loss of organic carbon during production.
In conclusion, the implementation of smart agriculture policy is pivotal for expanding the agricultural-scale operations. An expanded scale can significantly reduce chemical inputs, machinery usage and associated fuel consumption, irrigation energy expenditure, and soil organic carbon depletion, thereby diminishing the overall emission of carbon within agriculture. Consequently, Hypothesis H2 is introduced.
H2: Agricultural-scale operation plays an intermediary role in the impact of smart agriculture policy on agricultural carbon emissions.
2.3 Smart agriculture policy, agricultural technology advancement, and agricultural carbon emission reduction
The advent of smart agriculture policy has catalyzed a comprehensive advancement in agricultural technology. These policies serve as a potent signal, galvanizing collaboration among universities, research institutions, corporations, private investors, and financial entities, while also spurring enterprises to augment their research and development (R&D) expenditures. This concerted effort propels the evolution of agricultural technology (Luo et al., 2023). Furthermore, smart agriculture policy drives a shift in agricultural practices, speeding up the adoption and spread of innovative agricultural technologies. This shift not only meets the burgeoning demand for innovative agricultural solutions but also stimulates further advancement and refinement of these technologies (Huang and Zhu, 2022).
Advancements in agricultural technology are pivotal for reducing carbon emissions within the agricultural sector. These Advancements enhance agricultural management practices, leading to a diminished utilization of pesticides and chemical fertilizers, and bolstering the sequestration of soil organic carbon (Li et al., 2022). Consequently, this optimization results in a reduction of carbon emissions associated with agriculture. Moreover, agricultural technology advancement increases production efficiency and yield per unit area, reducing the land needed for agriculture and lowering the carbon emission intensity of agricultural production (Li et al., 2022). Given this analysis, Hypothesis H3 is introduced.
H3: Agricultural technology advancement plays a mediating role in the impact of smart agriculture policy on agricultural carbon emissions.
3 Variable selection and data description
3.1 Data source
The paper utilizes a panel dataset encompassing 31 Chinese provinces from 2001 to 2020, excluding Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan due to limitations in data availability. Agricultural carbon emission data are sourced from the China Rural Statistical Yearbook, while Supplementary data are derived from the China Statistical Yearbook, China Regional Economic Statistical Yearbook, additional issues of the China Rural Statistical Yearbook, and various provincial statistical yearbooks. To mitigate the impact of non-stationary macroeconomic data on the empirical findings, a logarithmic transformation is applied to all variables with absolute values.
3.2 Variable description
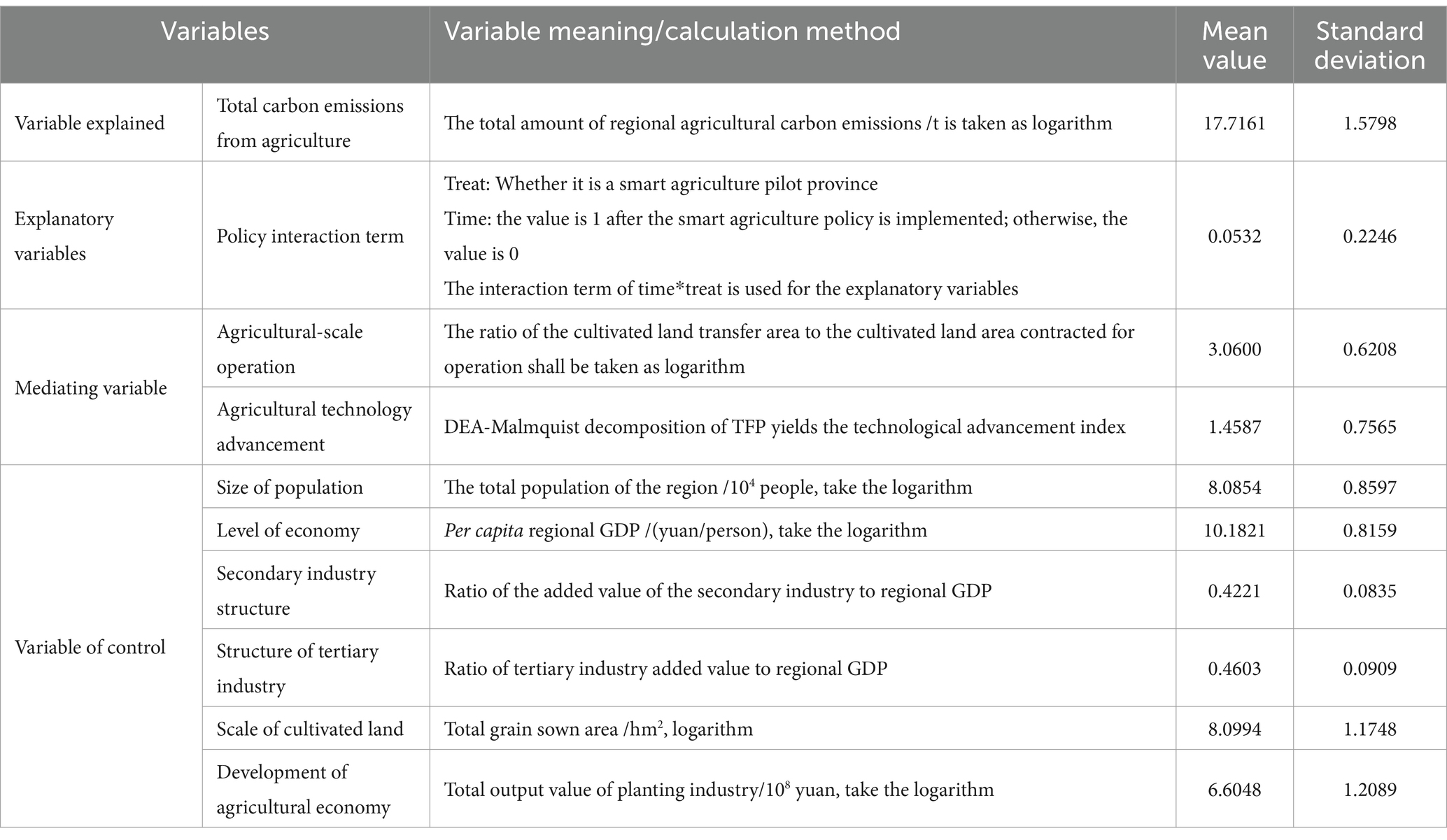
3.2.1 Dependent variable
The dependent variable in this paper is total agricultural carbon emissions. Total agricultural carbon emissions are mainly studied in the narrow sense of agriculture (planting), and the estimation formula is as follows:
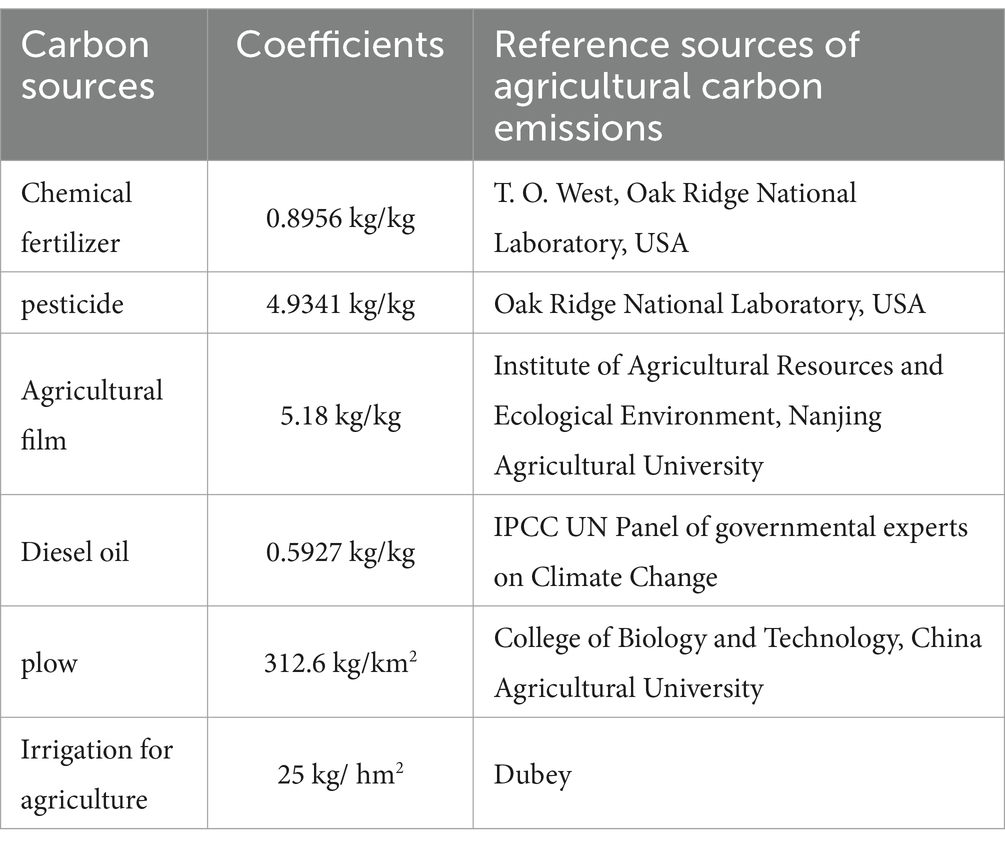
is the total amount of agricultural carbon emissions. is the carbon emission of the jth carbon source in province i at year t, is the quantity of the jth carbon source in province i at year t, and is the carbon emission coefficient of the jth carbon source. Where: carbon sources include fertilizer, pesticide, agricultural film, diesel fuel, tilling and agricultural irrigation, and the agricultural carbon emission coefficients refer to Li et al. (2016), as shown in Table 1.
3.2.2 Independent variable
To foster the development of smart agriculture, the Chinese government has strategically established high-tech agricultural industrial demonstration zones in select provinces. Initially, in 2015, the inaugural zones were established in Shaanxi and Shandong. Subsequently, an expanded initiative in 2018 led to the creation of seven additional zones in Shanxi, Jiangsu, Henan, Jilin, Heilongjiang, Inner Mongolia, and Xinjiang. In light of this phased rollout of the smart agriculture pilot policy, this paper delineates 2015 and 2018 as temporal breakpoints and employs a multi-period Differences-in-Differences (DID) methodology. The provinces that have not yet embraced the smart agriculture policy serve as the control group, while those that have are designated as the treatment group. The binary variable, post-policy implementation, is denoted by 1 for the treatment group at the time of adoption and 0 for all other instances. The independent variable is the interaction term between treat and time.
3.2.3 Control variables
Several factors exhibit significant correlations with the development of smart agriculture, necessitating the control of these variables to ensure accurate analysis and policy formulation.
(1) Population size: The demographic transition profoundly influences the agricultural cultivation structure, thereby affecting the predominance of grain-oriented cultivation practices (Luo and Chou, 2018).
(2) Level of economy: The level of economic development in different regions is different, and the scale of moderate agricultural operation in different regions is different. The economic level will also have an impact on the planting structure (Pang et al., 2021).
(3) Industrial structure: The composition of industry exhibits a significant correlation with the volume of carbon emissions from agriculture. This relationship varies with the proportionate representation of different industrial sectors (Dong et al., 2020).
(4) Agricultural economic development: The development of the agricultural economy can significantly affect the ecological environment, potentially leading to an escalation in agricultural carbon emissions (Li et al., 2016).
(5) Cultivated land size: The expanse of cultivated land influences the adoption of low-carbon farming practices among farmers, with larger areas often associated with the implementation of more sustainable production methods.
To address potential bias stemming from unobservable variables, this paper employs several methodological refinements. Initially, fixed effects for each province are incorporated to account for province-specific characteristics, such as geographic and cultural factors, that may influence the estimation outcomes. Subsequently, time fixed effects are introduced to mitigate the impact of policy shifts unrelated to smart agriculture on the results.
See Table 2 for the specific definitions of the variables used and descriptive statistical analysis.
3.2.4 Mediating variables
The theoretical analysis has identified two key mediating variables: agricultural-scale operation and agricultural technology advancement. Agricultural-scale operation is operationalized by referencing the work of Liu and Xiao (2020), who utilized the ratio of transferred arable land to contracted land, subjecting it to logarithmic transformation. Meanwhile, we refer to the method of Zhong et al. (2022) to measure agricultural technology advancement. This involves calculating the total factor productivity (TFP) across China’s 31 provinces from 2001 to 2020 using the DEA-Malmquist index. The TFP is subsequently decomposed into the technical efficiency change index (EFF) and the technological advancement index (TECH), with the latter serving as a proxy for agricultural technology advancement.
3.3 Model setting
The implementation of China’s smart agriculture policy is hypothesized to induce several effects. Firstly, it may result in variations in carbon emissions within the pilot provinces, comparing periods before and after the policy’s enactment. Furthermore, the policy is also expected to generate disparities in the aforementioned indicators between pilot and non-pilot provinces when assessed concurrently. The model’s regression estimates, grounded in a double-difference approach, adeptly control for extraneous cointegrating policies and pre-existing disparities between pilot and non-pilot provinces. This methodological rigor allows for the precise identification of the policy’s net impact on provincial carbon emissions and employment levels. Given that the policy was rolled out in two phases, the paper employs an asymptotic DID model to assess its long-term effects. However, considering that the traditional DID required to meet the homogeneity hypothesis of processing effects, and in reality, different groups may have different responses to the same policy, we introduced heterogeneous processing effects to solve this problem and divided China into three regions, namely middle, east and west, to ensure the robustness of the results.
3.3.1 Model specification
This paper employs a model to quantify the emission reduction impact of the smart agriculture policy. Based on the above discussion, the paper assesses the efficacy of the policy in reducing carbon emissions among pilot provinces at a provincial level. The DID is utilized to conduct this evaluation, formulated as follows.
In this analysis, is the dependent variable, denoting the total agricultural carbon emissions of a province for a given year. is the independent variable, defined as the interaction between the treated (indicating whether the province is a pilot or not) and the time (marking the year of policy implementation), which signifies whether the province is affected by the smart agriculture policy in that year. To facilitate the explanation of the fluctuations of the data and facilitate the calculation, we take the logarithm of the explained variables above.
3.3.2 Mediating effects model
Exploring the role mechanism model of the emission reduction effect of smart agriculture policy. To empirically ascertain the mechanisms by which these policies effect change, a mediation effect model is formulated, expanding upon Equation (1), as delineated below:
Let represent the kth mediating variable, encompassing both the agricultural-scale operation as well as advancements in agricultural technology. Equation (2) is employed to assess the total impact of smart agricultural policies on agricultural carbon emissions. Equation (3) evaluates the direct effect of these policies on the mediating variables. Provided that the core explanatory variables in Equation (2) yield significant coefficients, Equation (4) is then utilized to examine the mediating effect of the policy shock on carbon emissions.
4 Empirical analysis
4.1 Baseline regression
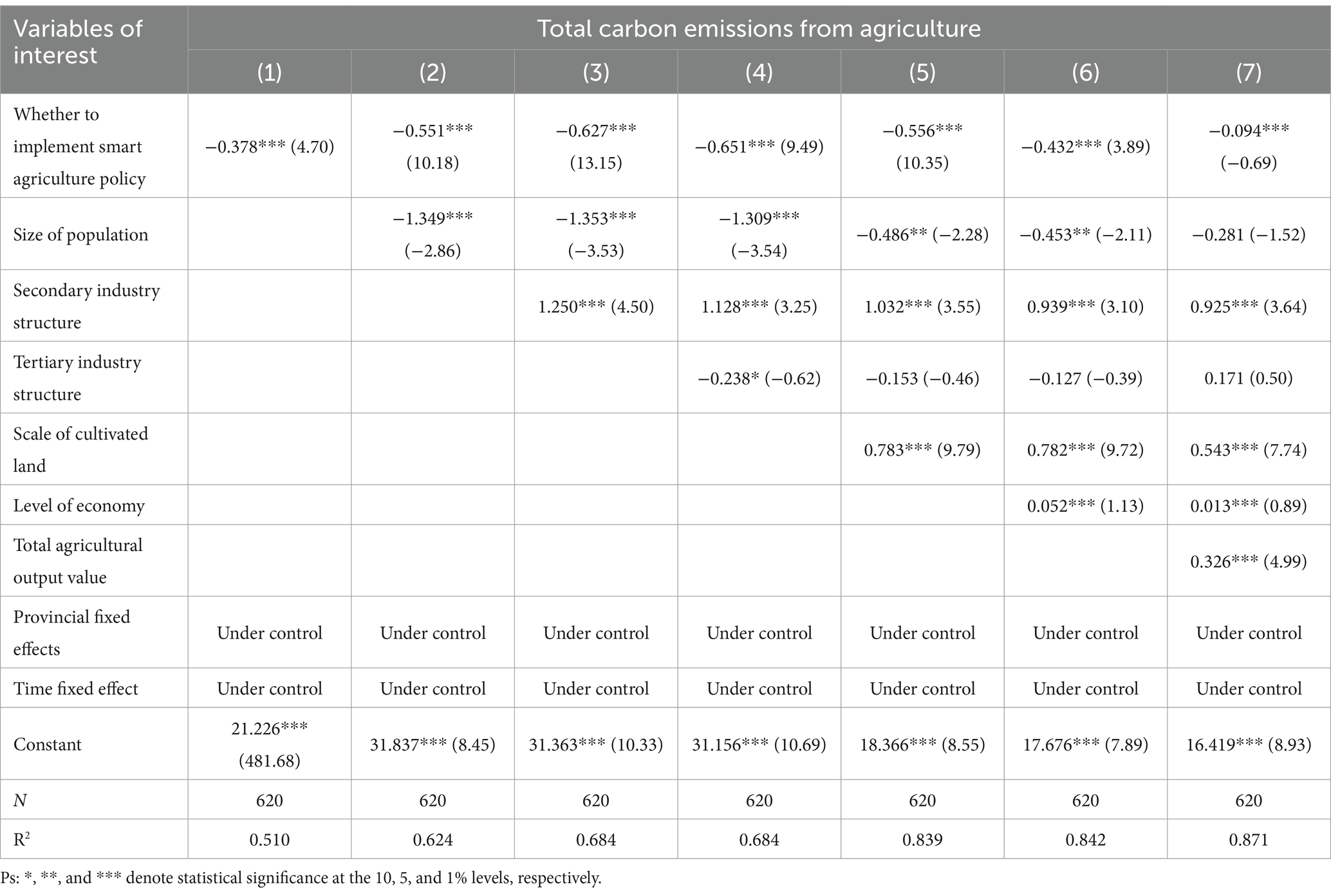
The paper introduces control variables incrementally into the baseline regression model (2) to assess the impact of smart agricultural policies on agricultural carbon emissions, with the results presented in Table 3. The coefficients associated with smart agricultural policies are uniformly negative and significant at the 1% level. Initially, column (1) reveals a significantly negative regression coefficient for total agricultural carbon emissions under the smart agriculture policy without the inclusion of control variables, suggesting a reduction in carbon emissions in pilot provinces. Subsequent columns (2) to (7) incorporate control variables stepwise, building upon the foundation of column (1). Specifically, column (7) demonstrates that after introducing control variables and two-way fixed effects for provinces, the regression coefficient for the smart agriculture policy is −0.094, significant at the 1% level. This indicates that, on average, the policy leads to a 9.4% increase in total agricultural carbon emissions in the subsequent year. In essence, the smart agriculture policy significantly curbs agricultural carbon emissions. Consequently, the findings confirm the policy’s positive contribution to agricultural carbon emission reduction in China, thereby validating research hypothesis H1.
Among the remaining control variables, the coefficients for population size and the tertiary industry structure are significantly negative, suggesting that a larger population and greater development of the tertiary sector may contribute to the suppression of agricultural carbon emissions. Conversely, the coefficients for the scale of secondary industry and economic development are significantly positive, implying that increased energy consumption could be a driving factor behind the rise in agricultural carbon emissions. Additionally, the expansion of arable land and the growth in the gross value of agricultural output might result in heightened use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, consequently boosting carbon emissions.
Column (1) is reduced by 1% for the variable explained. The results of the robustness test of the reduced sample show that there is no substantial change in the hypotheses of this paper and the results of the validation.
Column (2) presents the findings from a test that excludes the impact of municipalities on carbon emission efficiency. Given the initiation of the smart agriculture policy post-2017, the sample period was chosen to closely align with this policy’s implementation, enriching the data set with a substantial number of observations. The empirical analysis confirms that, aside from minor adjustments in the elevation coefficient, the validation conclusions remain consistent with those of the original study.
Column (3) details the results of a robustness test employing a one-period lag. The analysis and comparison of the regression outcomes confirm the consistency of these results with those of the initial examination, thereby validating the robustness of the findings.
Column (4) presents results that account for the exclusion of other agricultural policies, utilizing the trio of policies on agriculture, rural areas and farmers enacted in 2018 (referred to as Policy1) for the robustness test. Upon rigorous analysis and comparison of the regression outcomes, it is evident that the findings are positively significant, corroborating the baseline estimation’s conclusions.
4.2 Parallel trend test
The baseline regression analysis demonstrates that smart agricultural policies significantly reduce agricultural carbon emissions. However, the effectiveness of DID in identifying effects depends on the realization of the parallel trend assumption. To substantiate the validity of Hypothesis 1, a parallel trends test has been conducted on the data, the procedure of which is delineated as follows:
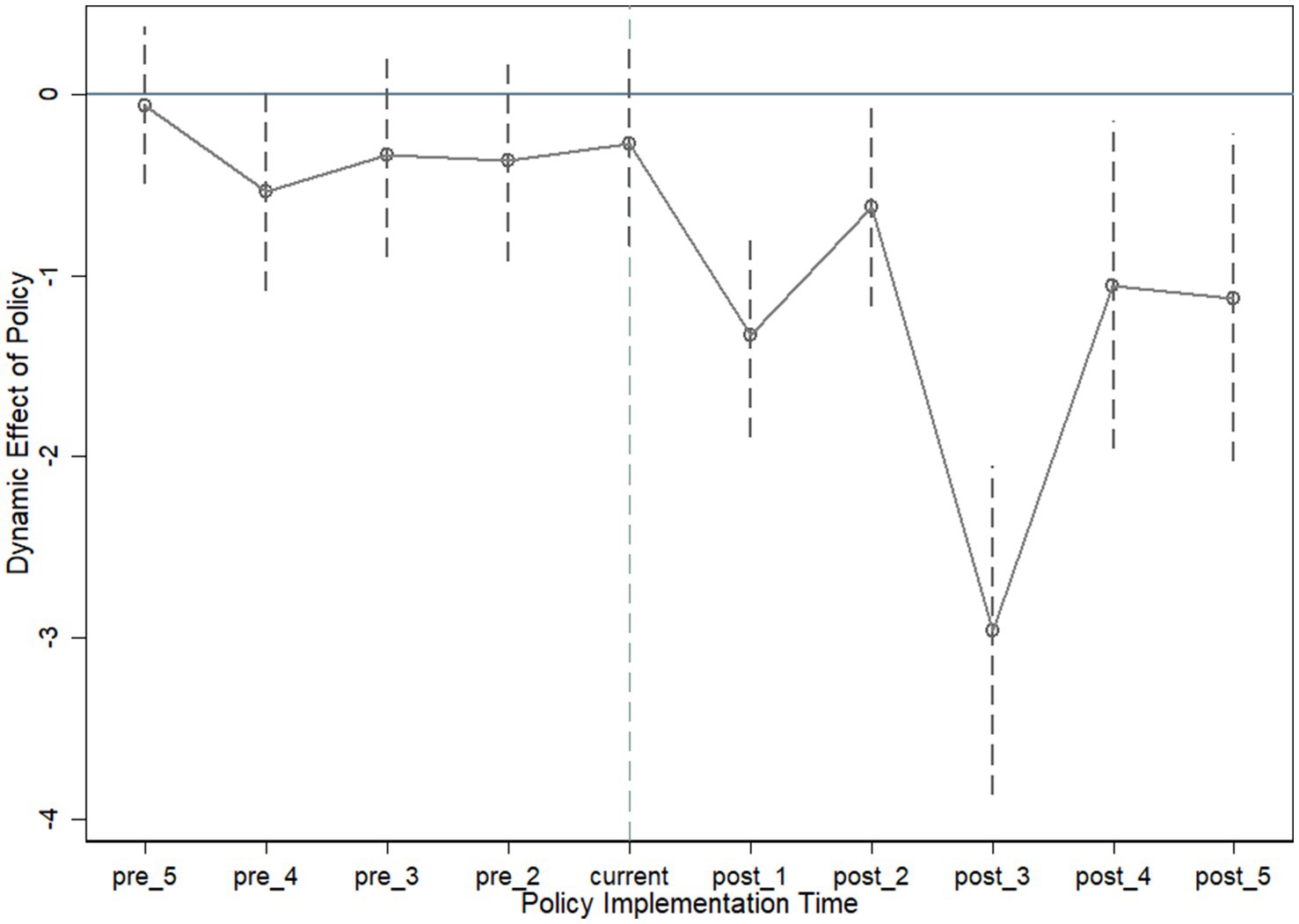
Among them, is a set of dummy variables that take the value of 1 if province i has implemented the pilot low-carbon city policy in year t, and vice versa 0. The sign meanings of the remaining variables are the same as those in Equation (5). On this basis, we take the 6th period before the implementation of the smart agriculture policy as the base period, and the running results are shown in Figure 1.
Examination of Figure 1 reveals that prior to the introduction of the smart agriculture policy, no significant disparities existed in agricultural carbon emissions, thereby fulfilling the parallel trends assumption. In contrast, post-implementation, a noticeable reduction in agricultural carbon emissions is observed in the treatment groups relative to the control group. This reduction underscores the enduring impact of the smart agriculture policy in fostering a decrease in agricultural carbon emissions. Consequently, the findings within this paper have successfully withstood the parallel trends test, substantiating the robustness of the conclusions drawn.
4.3 Placebo test
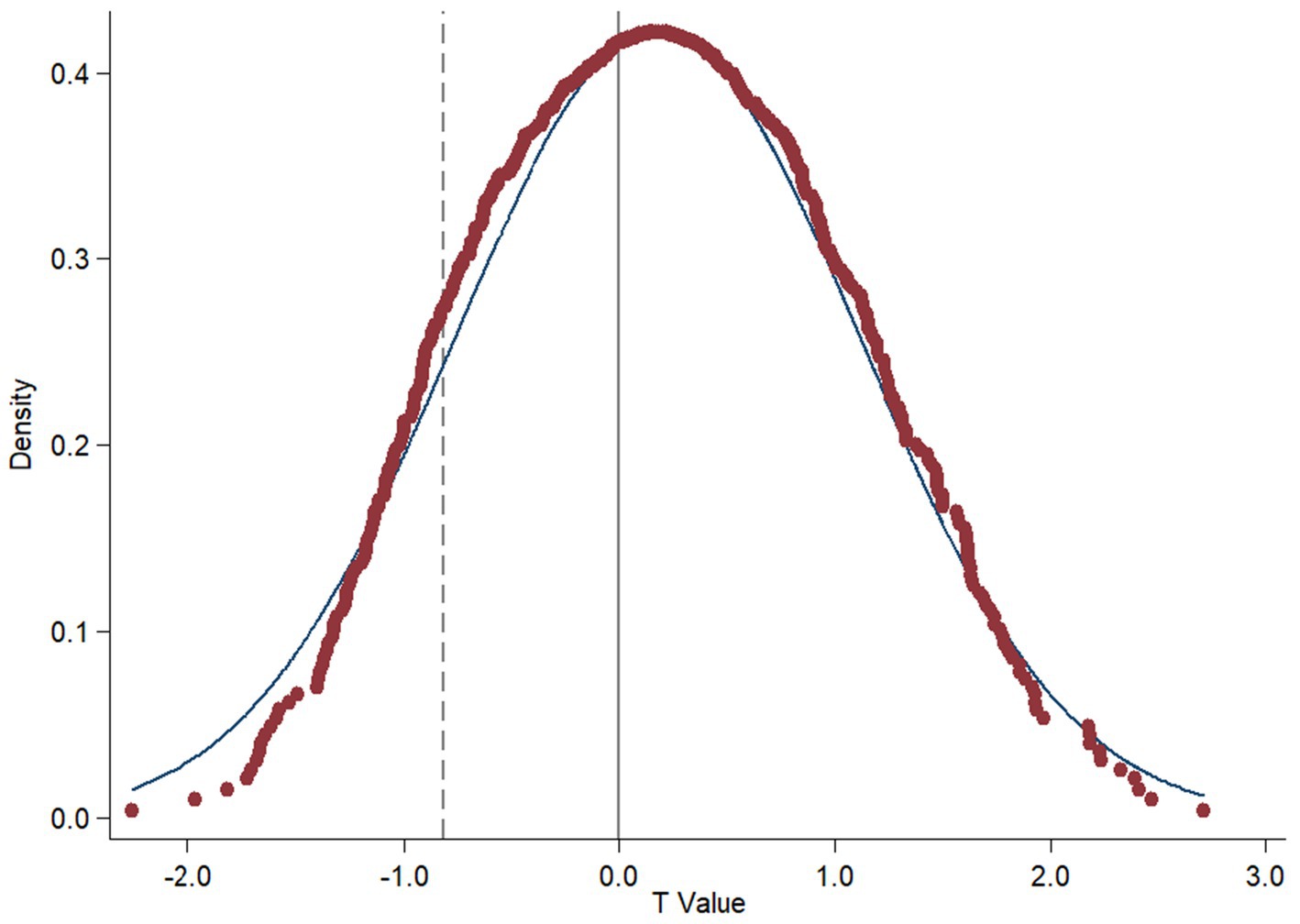
To mitigate the potential influence of unobservable omitted variables on the baseline regression, this paper employs a placebo test to ascertain the effects of smart agricultural policies. Following the methodology of Cai et al. (2016), “pseudo-policy dummy variables” are generated through a random sampling process, repeated 500 times, based on the distribution of provinces where smart agriculture policy has been implemented. Model (2) is then regressed to yield an ensemble of 500 estimated coefficients alongside their respective p-values.
The findings are presented in Figure 2, illustrating that the regression coefficients are predominantly centered around zero and conform to a normal distribution, with the majority exhibiting statistical insignificance. The baseline regression’s coefficient estimates are situated in the extreme upper tail of the distribution for spurious regression coefficients, which are characterized as low-probability outcomes in the provincial placebo tests. Consequently, the benchmark estimation results presented in this paper are unlikely to be attributed to unobservable factors.
4.4 Robustness test
To ensure that the paper’s findings are not confounded by extraneous variables, a battery of robustness checks has been performed, as detailed in Table 4.
Column (1) is reduced by 1% for the variable explained. The results of the robustness test of the reduced sample show that there is no substantial change in the hypotheses of this paper and the results of the validation.
Column (2) presents the findings from a test that excludes the impact of municipalities on carbon emission efficiency. Given the initiation of the smart agriculture policy post-2017, the sample period was chosen to closely align with this policy’s implementation, enriching the dataset with a substantial number of observations. The empirical analysis confirms that, aside from minor adjustments in the elevation coefficient, the validation conclusions remain consistent with those of the original paper.
Column (3) details the results of a robustness test employing a one-period lag. The analysis and comparison of the regression outcomes confirm the consistency of these results with those of the initial examination, thereby validating the robustness of the findings.
Column (4) presents results that account for the exclusion of other agricultural policies, utilizing the trio of policies on agriculture, rural areas and farmers enacted in 2018 (referred to as Policy1) for the robustness test. Upon rigorous analysis and comparison of the regression outcomes, it is evident that the findings are positively significant, corroborating the baseline estimation’s conclusions.
4.5 Heterogeneity analysis
Due to variations in agricultural resource endowments and levels of digital economic development across China’s regions, a regionally differentiated analysis of the carbon emission reduction effects of smart agricultural policies is warranted. The regional classification is based on economic development and grain production status, followed by sequential regression analyses on the categorized areas.
(1) Heterogeneity between the eastern region and the central and western regions.
Geographical constraints contribute to the uneven economic development across China, with the eastern region demonstrating robust development compared to the relatively underdeveloped central and western regions. This disparity is largely attributed to the eastern provinces’ coastal location, which affords them flat terrain, dense populations, and convenient transportation infrastructure. In contrast, the central and western provinces, situated inland and characterized by plateaus and deserts, have lower population densities and face transportation challenges. Consequently, this study categorizes the 31 provinces into eastern, central, and western regions to investigate the heterogeneity in the impact of smart agricultural policies on agricultural carbon emission reductions across these diverse geographical areas.
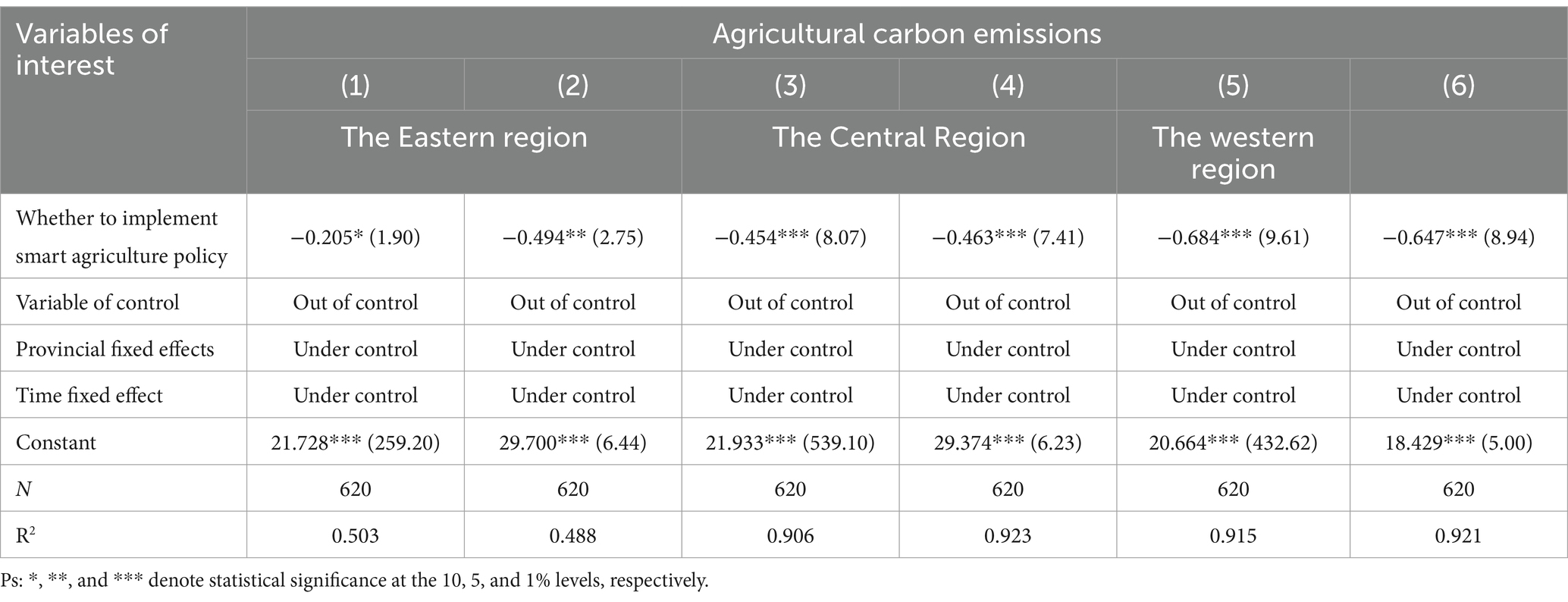
The disparities in regional outcomes are presented in Table 5, illustrating that the impact of smart agriculture policy on agricultural carbon emissions varies across regions. Specifically, columns (1) and (2) indicate that the influence of these policies in the eastern region is comparatively mild. In contrast, columns (3) to (6) reveal that the policies have a significantly negative effect on the total volume of agricultural carbon emissions in the central and western regions. This suggests that the primary findings of this study are predominantly attributed to the central and western regions.
The primary factors contributing to the evident disparity between the eastern region and the central and western regions are as follows: Firstly, the eastern region of China, being a more economically developed area, has already achieved a high level of modernization in its agricultural production. Its agricultural technology, equipment, and management are relatively advanced, leaving limited room for further improvement at the current technological level. Additionally, due to its superior resources and economic conditions, the region may have embraced the concept of low carbon and environmental protection earlier. As a result, related policies and market mechanisms have become more mature, leaving less opportunity for further exploration of carbon emission reduction within the existing framework. Furthermore, as a result of their superior resources and economic conditions, they may have embraced the idea of low carbon and environmental protection at an earlier stage. Consequently, the corresponding policies and market mechanisms are also more developed, leaving less opportunity for further exploration of the potential for reducing carbon emissions within the current framework. The central and western regions, in comparison to the eastern region, possess a greater abundance of conventional agricultural production techniques, untapped agricultural resources, and significant potential for reducing carbon emissions. Consequently, they are more receptive to the policy subsidies and technological advancements introduced through the implementation of the smart agriculture policy. By implementing contemporary agricultural technology, such as intelligent irrigation and accurate fertilization, the local community may minimize the inefficiency of chemical fertilizers and water resources, thereby attaining a reduction in carbon emissions in agriculture.
Based on the findings previously discussed, it is clear that the central and western regions have a significant potential for reducing carbon emissions. Moreover, the implementation of smart agriculture policy in these areas has led to notably more effective results. Consequently, the government should consider expanding the adoption of smart agriculture policy in the central and western regions. In the eastern region, the government should consider the specific agricultural and low-carbon development contexts and launch a well-planned pilot program to promote the harmonious and sustainable development of agriculture and the economy.
(2) Heterogeneity between major and non-grain producing areas.
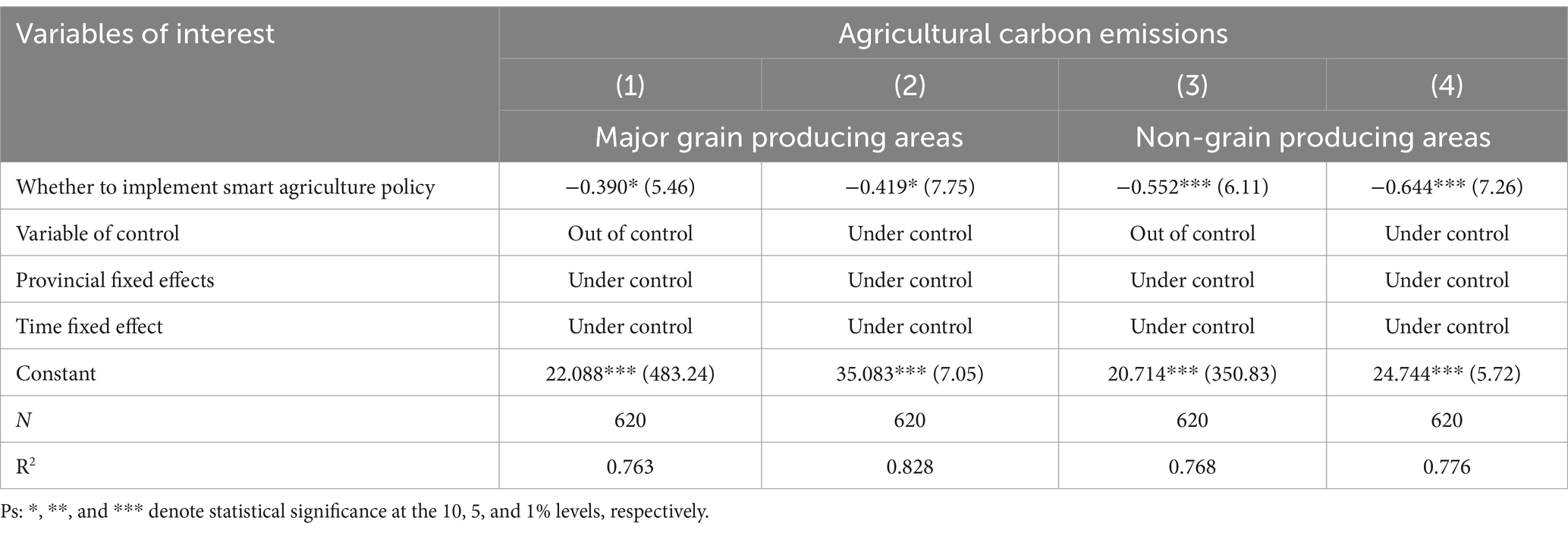
Separate regressions are conducted for major grain producing areas and non-grain producing areas, with the designation of major grain producing areas based on the ‘Opinions on Reform and Improvement of Certain Policies and Measures for Comprehensive Agricultural Development, as issued by China’s Ministry of Finance in 2003. The regression outcomes are detailed in Table 6. Specifically, columns 1 and 2 represent the 13 provinces categorized as major grain producing areas, while columns 3 and 4 correspond to the 18 provinces in non-grain producing areas.
Table 6 demonstrates that in the samples collected from the major grain producing areas, the smart agriculture policy does not contribute to a decrease in total agricultural carbon emissions. However, in the samples from the non-grain producing areas, the smart agriculture policy effectively reduces total agricultural carbon emissions. This indicates that the non-grain producing areas have greater potential for reducing carbon emissions.
The primary regions for grain production are limited by the “red line of arable land” policy, resulting in a significant portion of grain crops being cultivated. As a result, the planting patterns and management processes are more consistent, agricultural production is highly standardized, and there is limited potential for reducing carbon emissions in agriculture. In regions where grain production is not the primary focus, the cultivation of grains exhibits greater diversity and agricultural production is less standardized. Consequently, these locations provide greater potential for reducing carbon emissions in agriculture.
According to the analysis provided, it is evident that places that non-grain producing areas have a higher potential for reducing carbon emissions in agriculture. The government should enhance the execution of smart agriculture policy in these regions, reinforce standardized agricultural output, and broaden the utilization of contemporary agricultural technology. In addition, for major grain producing areas, the government should promote the optimization of agricultural planting structure, especially increasing the proportion of carbon sink grains planted to improve soil carbon sequestration and storage capacity. Furthermore, by implementing technology advancements and refining management practices, it is possible to enhance the productivity per unit of land, so facilitating the transition of agriculture toward a more efficient and environmentally sustainable production model.
4.6 Test for endogeneity
Endogeneity is an inherent issue in panel data analyses. Addressing endogeneity is crucial for establishing the presence of a causal link between variables. In this paper, we employ the two-stage least squares instrumental variable (IV-2SLS) method for regression, with the findings detailed in Table 7.
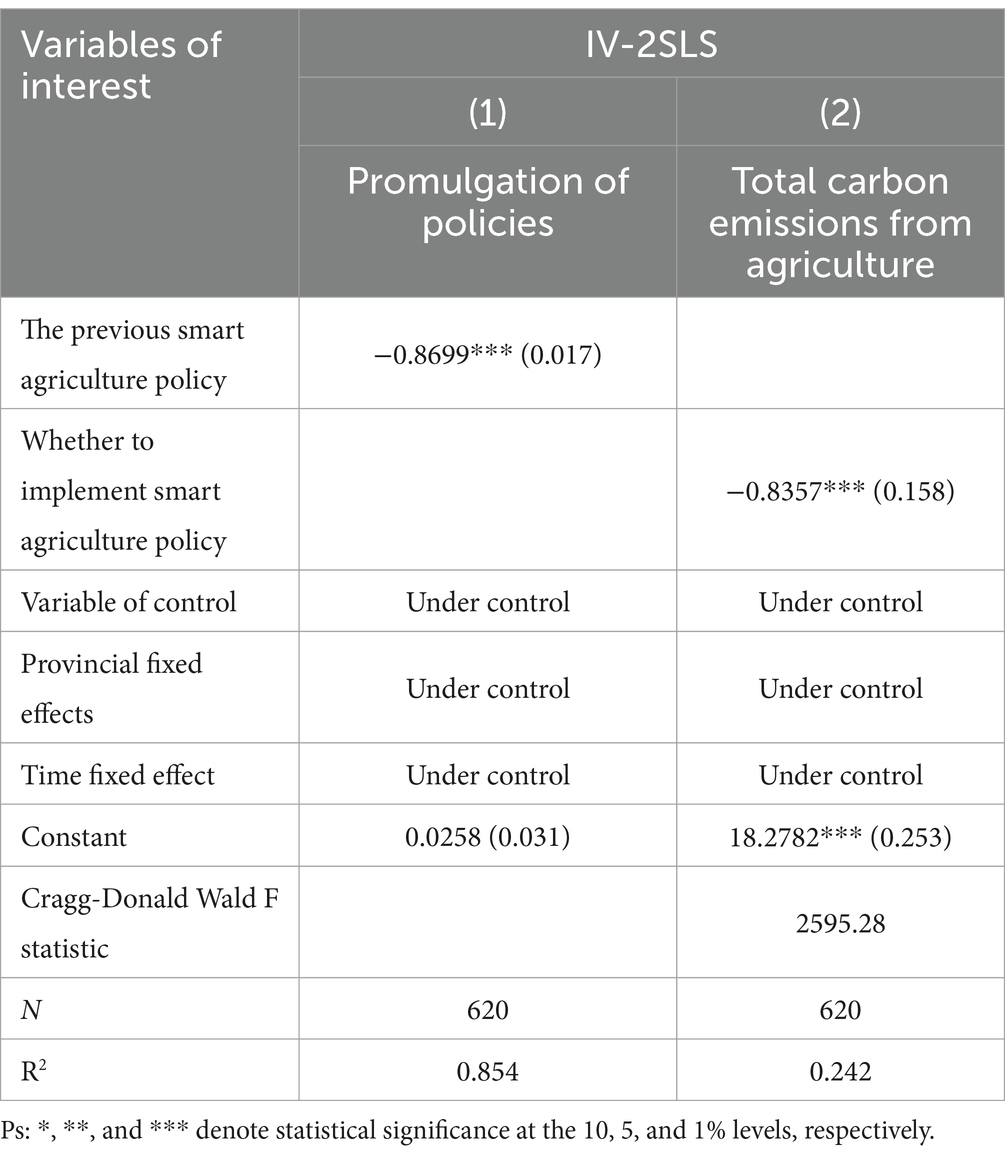
Table 7. IV-2SLS results of the impact of smart agriculture policy on total agricultural carbon emissions.
Table 7 demonstrates that the coefficients for the implementation of smart agricultural policies are significantly negative. A modest enhancement in both the magnitude and statistical significance of these coefficients. This suggests that, when accounting for endogeneity due to reverse causality, the impact of these policies on reducing agricultural carbon emissions is more pronounced. Furthermore, the Cragg-Donald Wald F statistic, at 2595.28, exceeds the critical value of 16.38, indicating that the IV-2SLS regression is robust against the issue of weak instruments. The findings from the IV-2SLS regression confirm that the introduction of smart agricultural policies has significantly contributed to the reduction of overall agricultural carbon emissions, addressing the endogeneity concern.
4.7 Mechanism analysis
In order to further explore the path of smart agriculture policy affecting agricultural carbon emissions, based on theoretical analysis, this paper empirically analyzes the action mechanism of smart agriculture policy on agricultural carbon emissions from two perspectives of operation scale and technology advancement.
The agricultural-scale operation is quantified by the ratio of transferred cultivated land to the total contracted cultivated land area. Technology advancement in agriculture is assessed through the decomposition of Total Factor Productivity (TFP) to derive the TECH variable. Utilizing a sequential testing approach for mediating effects, this paper conducts regression analyses for Equations (3, 4) in an orderly fashion, with the intermediary effect test outcomes presented in Table 8.
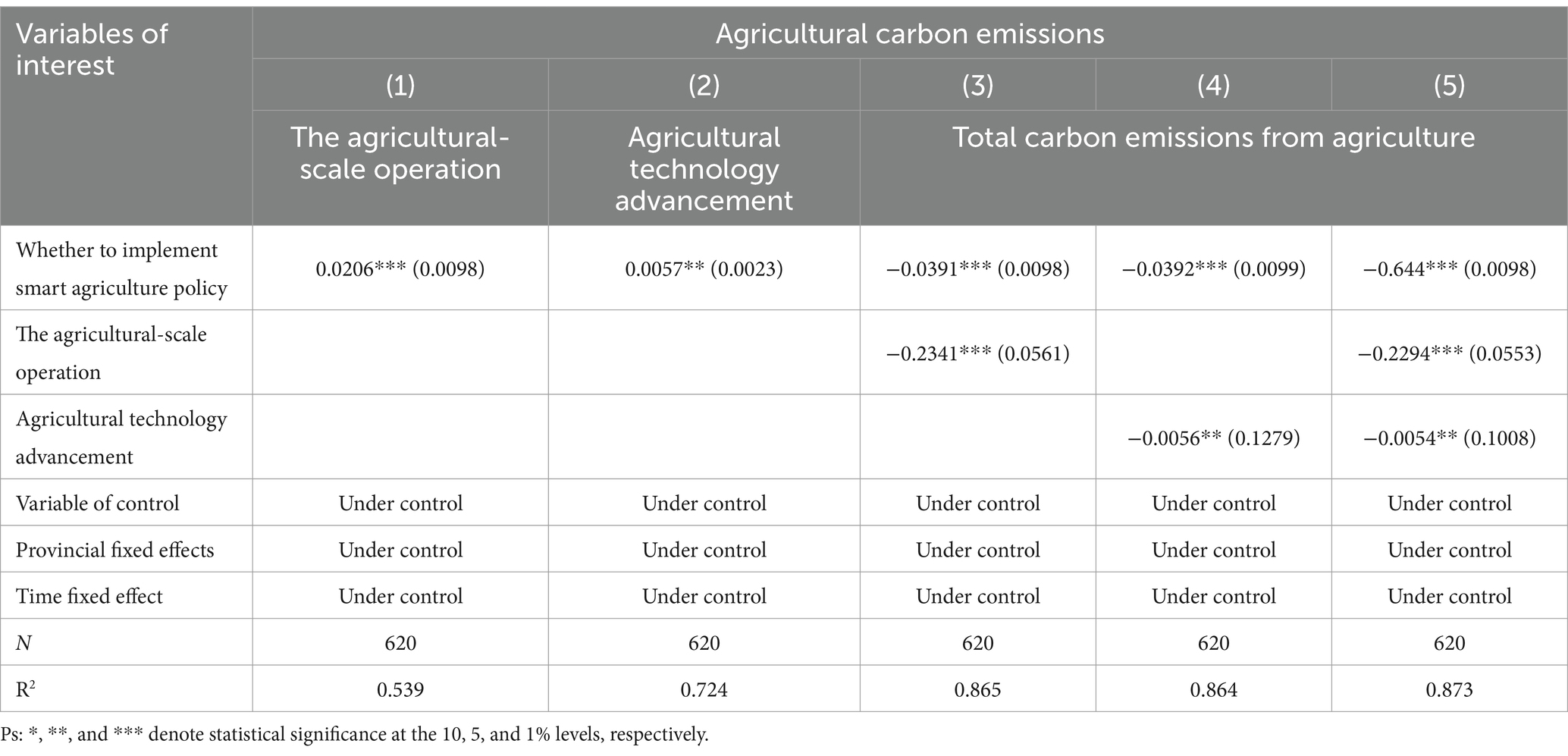
Table 8. Mediating mechanism test of the impact of smart agriculture policy on total agricultural carbon emissions.
Columns (1)–(2) of Table 8 examines to determine if the smart agriculture policy has a significant impact on the agricultural-scale operation and agricultural technology advancement. The findings indicate that the core explanatory variables exert a positive and significant influence on these mediating variables at the 1% confidence level, suggesting that the implementation of such policies significantly amplifies the agricultural-scale operation and fosters technology advancement. Column (3) presents the impact of the agricultural-scale operation on agricultural carbon emissions. The estimated coefficient for the agricultural-scale operation is significantly negative, suggesting that the implementation of smart agriculture policy, through the expansion of the agricultural-scale operation. It can lead to a reduction in total agricultural carbon emissions. Column (4) reveals that the coefficient attributed to agricultural technology advancement is significantly positive at the 1% confidence level, underscoring the role of technological advancements as a pivotal conduit in the smart agriculture policy to mitigate carbon emissions. This paper employed Sobel’s test to assess the significance of the mediating effects, yielding Z-values of −2.0431 and − 2.2378 for the respective mediating variables. Both values surpass the 5% significance level threshold, confirming the statistical significance of both the scale of operations and technology advancement as mediators. The results of the joint test after adding all mediating variables are reported in Column (5) of Table 8. Upon analysis of Table, the direction and significance of the two mediating variables are consistent with those presented in columns (3) and (4) of Table 8. This correspondence supports the proposition that the agricultural-scale operation, along with advancements in agricultural technology, constitute legitimate mediating mechanisms. As a result, Hypothesis H2 is corroborated.
This indicates that the agricultural-scale operation and agricultural technology advancement play a crucial role in attaining the goal of reducing carbon emissions in agriculture, as outlined in the smart agriculture strategy. Hence, in pilot zones where smart agriculture policy is being implemented, governments should additionally enhance the scope of agricultural scale management and stimulate agricultural technology advancement through diverse policy instruments and financial mechanisms.
5 Further analysis
In order to further verify the comprehensive impact of smart agriculture policy on carbon emissions, we use agricultural carbon emission intensity and density different from the above to measure agricultural carbon emissions, and explore the specific role of smart agriculture policy on agricultural carbon emission reduction.
Agricultural carbon emission intensity is the agricultural carbon emission per unit of agricultural output value, reflecting the relationship between agricultural carbon emission and agricultural economy; Agricultural carbon emission density is the total amount of agricultural carbon emissions per unit of land area, reflecting the efficiency of carbon emissions in agricultural production activities. Among them, the agricultural carbon emission intensity (kg/104 yuan) is equal to the ratio of the total agricultural carbon emission to the total agricultural output value, and the agricultural carbon emission density (kg/667 m2) is equal to the ratio of the total agricultural carbon emission to the grain sown area. Both variables are taken in logarithms. Processed. Overall, the exploration of the impact of smart agriculture policy implementation on the intensity and density of agricultural carbon emissions is deemed to possess significant research value.
The differences in differences regression is conducted on the intensity and density of agricultural carbon emissions by the enactment of smart agriculture policy, and the regression results are shown in Table 9. The regression analysis detailed in Table 9 indicates that Smart agricultural policy is instrumental in lowering the Agricultural carbon emission density, indicating a reduction in the average carbon emissions generated per unit of land area. The impact of smart agriculture policy on agricultural carbon emission intensity is also negative and significant, which indicates that smart agriculture policy also has a reduction effect on carbon emission per unit of agricultural output value.
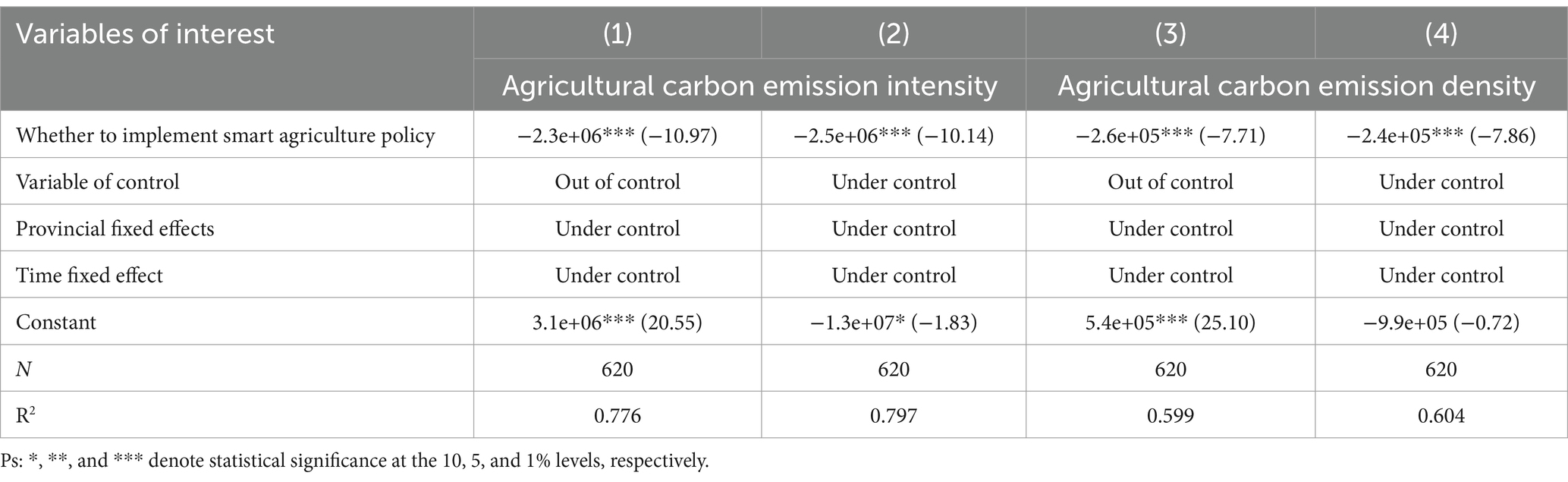
Table 9. Impact estimates of the impact of smart agriculture policy on agricultural carbon emission intensity and density.
The findings of the mechanism analysis test are displayed in Table 10. The effects of the two mediating variables on the intensity of agricultural carbon emissions are reported in columns (1) ~ (2) of Table 10. Two regression coefficients are found to be significantly negative and pass the Sobel test. The (3) ~ (4) column shows the effect of two mediation variables on the agricultural carbon emission density, and the regression results are similar to the (1) ~ (2) column, which also passed the Sobel test. The estimation results demonstrate that the implementation of smart agriculture policy enhances both the agricultural-scale operation and the technology advancement. Consequently, this leads to a simultaneous reduction in both the density and intensity of carbon emissions in agriculture.
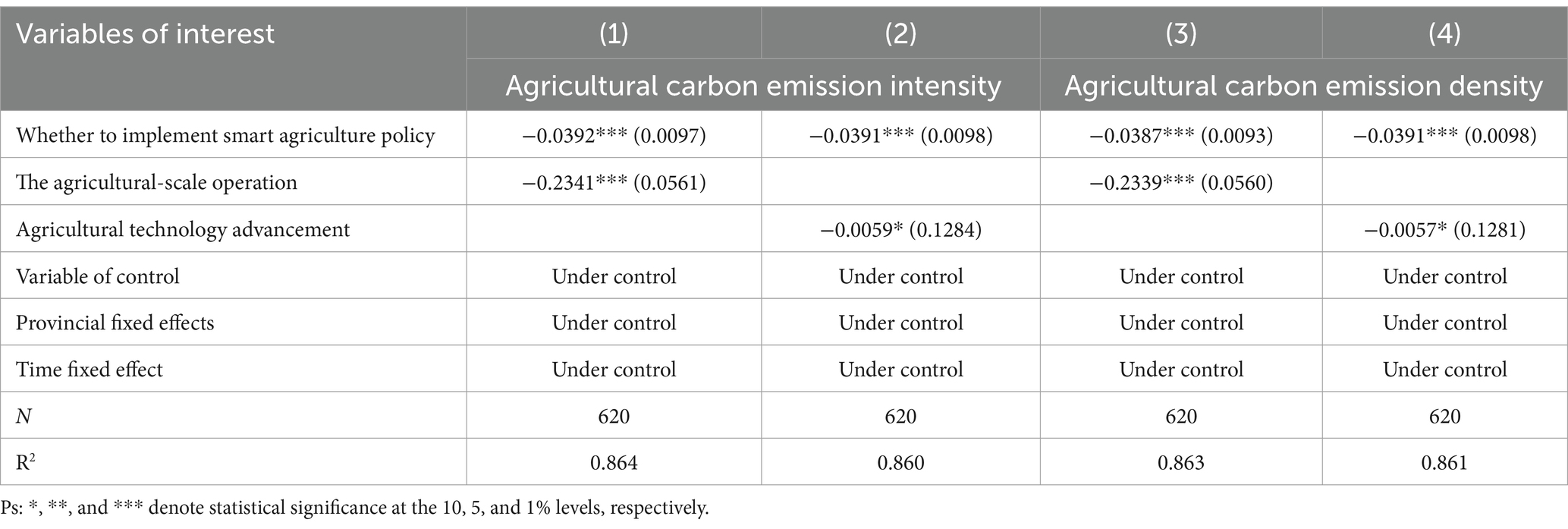
Table 10. Mediating mechanism test of the impact of smart agriculture policy on agricultural carbon emission intensity and density.
6 Conclusion and policy recommendations
This paper employs a multi-period difference-in-differences (DID) approach, delving into the policy’s role and the underlying mechanisms influencing agricultural carbon emissions. Rigorous tests are performed on the findings to substantiate the robustness of the regression outcomes. The principal findings of this research are summarized as follows: (1) Overall, smart agriculture policy significantly reduces the total amount of agricultural carbon emissions. Compared to non-pilot provinces, the pilot provinces reduced their agricultural carbon emissions by 9.4% on average. (2) From the perspective of heterogeneity, smart agriculture policy has a significant effect on carbon emission reduction in the economically underdeveloped areas and non-grain producing areas in central and western China. However, for the economically developed regions and major grain producing areas in eastern China, the carbon reduction effect of smart agriculture policy is limited. (3) Upon analyzing the underlying mechanisms, it is evident that the smart agriculture policy can significantly influence the reduction of agricultural carbon emissions by promoting the agricultural-scale operation and the advancement of agricultural technology.
Building on the empirical evidence presented, this paper offers the following targeted policy recommendations: (1) The government should enhance and refine the smart agriculture policy framework based on pilot experiences, progressively extend the pilot areas, and strive to elevate the level of agricultural intelligence, thereby promoting high-quality and sustainable agricultural development. (2) Advancing smart agriculture requires considering regional characteristics and implementing targeted measures accordingly. In less developed areas of central and western regions and non-grain production areas, smart agriculture should be prioritized to mitigate environmental impacts and reduce agricultural carbon emissions through intelligent production. For other regions, it is necessary to balance smart agriculture with low-carbon goals according to the needs of low-carbon development, achieving coordinated progress between the two. (3) Promoting the development of smart agriculture requires actively nurturing new agricultural operation entities and reasonably expanding agricultural-scale operations. In the pilot areas for smart agriculture policy, there should be an effort to foster the growth of new agricultural operation entities, such as family farms and rural cooperatives. Concurrently, agricultural-scale operations should be moderately increased to achieve economies of scale in farming, reduce environmental impacts, and foster a harmonious coexistence between agriculture and the ecological environment. (4) The government should intensify fiscal support for agriculture, encouraging technological innovation, particularly in the application of technologies such as the Internet of Things, big data, and artificial intelligence in the agricultural sector. Additionally, enterprises should be motivated to increase R&D investment to incubate and expand innovative agricultural businesses, accelerating the transformation and application of technological achievements. These can help overcome limitations in resources and technology, facilitating the intelligent upgrade of agricultural production methods. Furthermore, the government should enhance farmers’ acceptance and application of smart agricultural technologies through education and training, thereby improving the efficiency of agricultural production and management, and propelling the development of agriculture toward modernization and sustainability.
During the empirical analysis phase, several limitations were encountered in this paper: First, constrained by data availability, a detailed municipal-level analysis was precluded, necessitating the use of broader provincial-level data. Second, while the paper centers on environmental impact, the potential socio-economic ramifications of smart agriculture policy, including effects on farmers’ income and employment, warrant further investigation. Addressing these issues will be the focus of subsequent research endeavors.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary material.
Author contributions
ZZ: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SJ: Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. BS: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. YM: Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. XZ: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (Grant No.ZR2024QG141).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fsufs.2024.1482834/full#supplementary-material
References
Adamides, G. (2020). A review of climate-smart agriculture applications in Cyprus. Atmos. 11:898. doi: 10.3390/atmos11090898
Bennetzen, E. H., Smith, P., and Porter, J. R. (2016). Agricultural production and greenhouse gas emissions from world regions—the major trends over 40 years. Glob. Environ. Chang. 37, 43–55. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2015.12.004
Cai, X., Lu, Y., Wu, M., and Yu, L. (2016). Does environmental regulation drive away inbound foreign direct investment? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. J. Dev. Econ. 123, 73–85. doi: 10.1016/j.jdeveco.2016.08.003
Chen, P., Jia, J, and Yu, Q. (2024). Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Agricultural Carbon Emission in China. Res. Environ. Sci. 37, 1181–1192. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2024.04.18
Chi, L., Jiang, R., and Ren, T. (2020). Empirical decomposition and peak prediction of agricultural carbon emissions in China: from the perspective of dynamic policy scenarios. J. China Agric. Univ. 25, 187–201. doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2020.10.19
Dong, B., Ma, X., Zhang, Z., Zhang, H., Chen, R., Song, Y., et al. (2020). Carbon emissions, the industrial structure and economic growth: evidence from heterogeneous industries in China. Environ. Pollut. 262:114322. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114322
Du, Y., Liu, H., Huang, H., and Li, X. (2023). The carbon emission reduction effect of agricultural policy——evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 406:137005. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.137005
Huang, H. F., and Zhu, N. (2022). Rural financial efficiency, agricultural technological progress and agricultural carbon emissions: evidence from China. Nature Environ. Pollut. Technol. 21, 61–69. doi: 10.46488/NEPT.2022.v21i01.007
Li, D., Nanseki, T., Matsue, Y., Chomei, Y., and Yokota, S. (2016). Determinants of paddy yield of individual fields measured by IT combine: empirical analysis from the perspective of large-scale farm management in Japan. Agric. Inform. Res. 25, 39–46. doi: 10.3173/air.25.39
Li, J., Wang, W., Li, M., Li, Q., Liu, Z., Chen, W., et al. (2022). Impact of land management scale on the carbon emissions of the planting industry in China. Land 11:816. doi: 10.3390/land11060816
Liu, Q., and Xiao, H. (2020). The impact of farmland management scale and fiscal policy for supporting agriculture on agricultural carbon emission. Resour. Sci. 42, 1063–1073. doi: 10.18402/resci.2020.06.05
Luo, B., and Chou, T. (2018). China's agricultural planting structure adjustment: "non-grain" or "toward grain". Soc. Sci. Front. :13.
Luo, J., Hu, M., Huang, M., and Bai, Y. (2023). How does innovation consortium promote low-carbon agricultural technology innovation: an evolutionary game analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 384:135564. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135564
Lu, Z. (2013). The influence from the progress of agricultural science and technology to agricultural carbon emissionbased on provincial point. Stud. Sci. Sci. 5, 674–683. doi: 10.16192/j.cnki.1003-2053.2013.05.006
Pang, J., Wang, N., Li, X., Li, X., Wang, H., and Chen, X. (2021). Impact of economic development level and agricultural water use on agricultural production scale in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18:9085. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18179085
Reddy, A. A. (2019). The soil health card scheme in India: lessons learned and challenges for replication in other developing countries. J. Natural Resour. Policy Res. 9, 124–156. doi: 10.5325/naturesopolirese.9.2.0124
Santiteerakul, S., Sopadang, A., Yaibuathet Tippayawong, K., and Tamvimol, K. (2020). The role of smart technology in sustainable agriculture: a case study of wangree plant factory. Sustain. For. 12:4640. doi: 10.3390/su12114640
Schlesinger, W. H. (2000). Carbon sequestration in soils: some cautions amidst optimism. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 82, 121–127. doi: 10.1016/S0167-8809(00)00221-8
Shi, S., Jing, Y., and Zhai, T. (2021). Research on the role of market incentive environmental regulation on the development of low-carbon agriculture and its implementation path. Administrative forum, 28, 139–144. doi: 10.16637/j.cnki.23-1360/d.2021.01.018
Solazzo, R., Donati, M., Tomasi, L., and Arfini, F. (2016). How effective is greening policy in reducing GHG emissions from agriculture? Evidence from Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 573, 1115–1124. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.08.066
Su, M., Heerink, N., Oosterveer, P., and Feng, S. (2022). Upscaling farming operations, agricultural mechanization and chemical pesticide usage: a macro-analysis of Jiangsu Province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 380:135120. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135120
Tian, Y., and Wu, H. T. (2020). Research on fairness of agricultural carbon emissions in China’s major grain producing areas from the perspective of industrial structure. J. Agrotechnical Econ. 1, 45–55. doi: 10.13246/j.cnki.jae.2020.01.003
Wang, G., Liao, M., and Jiang, J. (2020). Research on agricultural carbon emissions and regional carbon emissions reduction strategies in China. Sustain. For. 12:2627. doi: 10.3390/su12072627
Xu, B., and Lin, B. (2017). Factors affecting CO2 emissions in China’s agriculture sector: evidence from geographically weighted regression model. Energy Policy 104, 404–414. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2017.02.011
Yin, Y. L., Zhong, C., He, K., and Li, Y. Y. (2023). Agricultural green development to achieve food security and carbon reduction in the context of CHINA'S dual carbon goals. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 0:01. doi: 10.15302/J-FASE-2023496
Yuzhen, S. (2021). RETRACTED ARTICLE: research on smart agricultural waste discharge supervision and prevention based on big data technology. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section B. Soil Plant Sci. 71, 683–695. doi: 10.1080/09064710.2021.1939409
Zhong, R., He, Q., and Qi, Y. (2022). Digital economy, agricultural technology progress, and agricultural carbon intensity: evidence from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19:6488. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19116488
Keywords: smart agriculture, carbon emission reduction, sustainable agriculture, agriculture policy, difference in differences
Citation: Zhang Z, Jiang S, Shen B, Mei YY and Zhang XR (2024) The carbon emission reduction effect of smart agricultural policy—evidence from China. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1482834. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1482834
Edited by:
Farirai Rusere, University of the Witwatersrand, South AfricaReviewed by:
Mbarouk Ali, State University of Zanzibar, TanzaniaJiansheng Qu, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Jiang, Shen, Mei and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xia Ran Zhang, emhhbmd4aWFyYW5AMTI2LmNvbQ==
 Zheng Zhang
Zheng Zhang Shu Jiang
Shu Jiang Bing Shen2
Bing Shen2 Xia Ran Zhang
Xia Ran Zhang