- 1School of Agricultural Engineering, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, China
- 2School of Physics and Electronic Engineering, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, China
- 3College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Shihezi University, Shihezi, China
Phthalic acid esters (PAEs) are often added to plastics to enhance elasticity, transparency, durability and prolong service life as a kind of plasticizer. However, they are not chemically bonded to polymers and are difficult to degrade, which makes it easy for them to release into the environment and enter the human body from various potential sources. This results in environmental pollution and poses health risks. In order to protect ecosystem, ensure food safety and prevent disease, there is an urgent need for sensors that can achieve point-of-care detection of PAEs. Optical sensors have advantages of simplicity, portability and low cost, and have been widely applied to the detection of PAEs. In this review, we focus on introducing the recent advancements and trends in optical sensors for detection of PAEs represented by colorimetric (CL) sensors, fluorescence (FL) sensors and surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) platform. Based on recognition strategies (e.g., label-free, aptamer, molecularly imprinted polymer, antibody and enzyme), the significant achievements of these optical sensors in the past 5 years are systematically classified and described in detail. Researchers can quickly know the development status of optical sensors for detection of PAEs in the past 5 years. This review highlights the strengths of each sensor type while also identifying their application limitations, providing researchers with valuable insights into future directions for optical sensor research.
1 Introduction
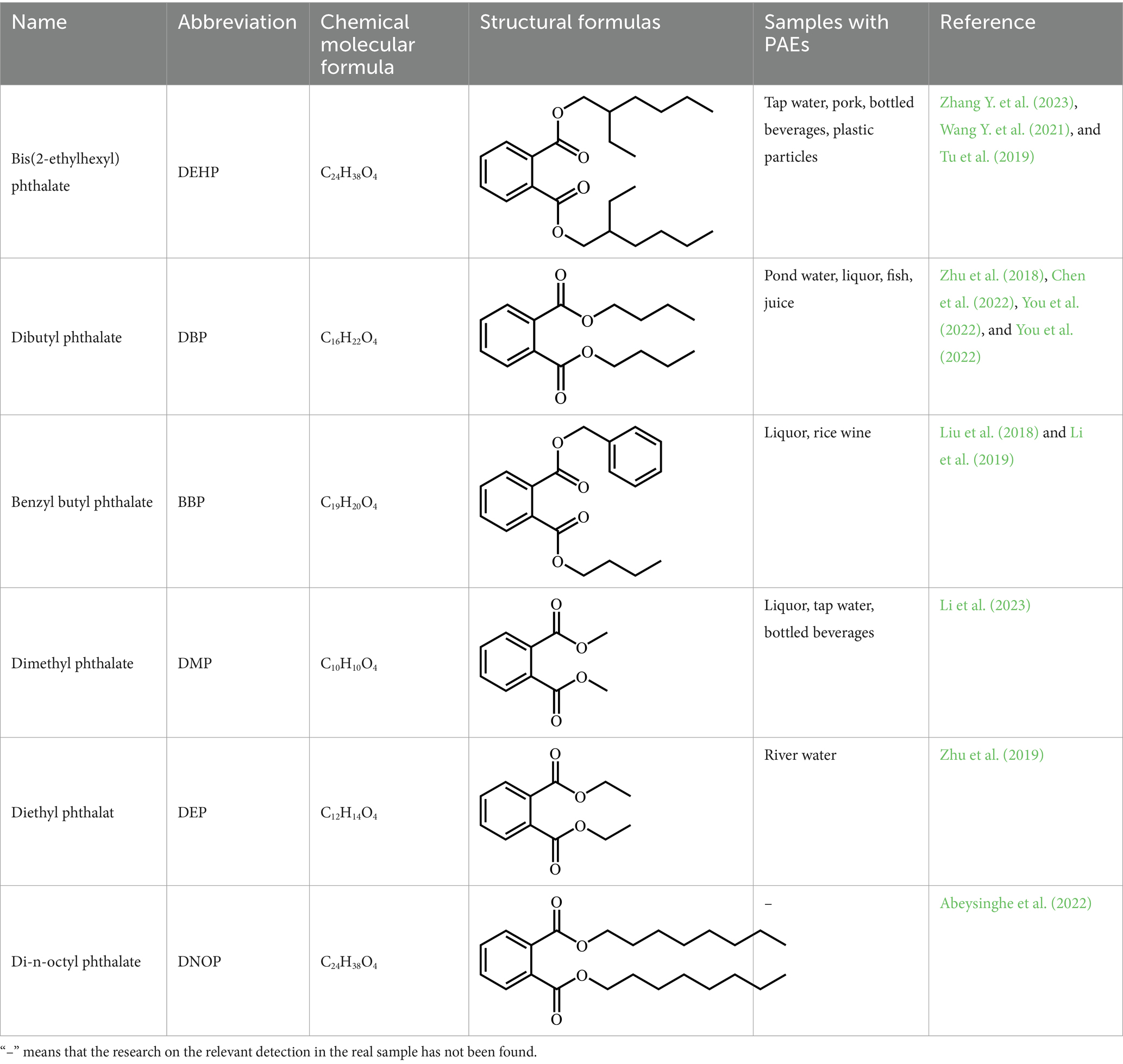
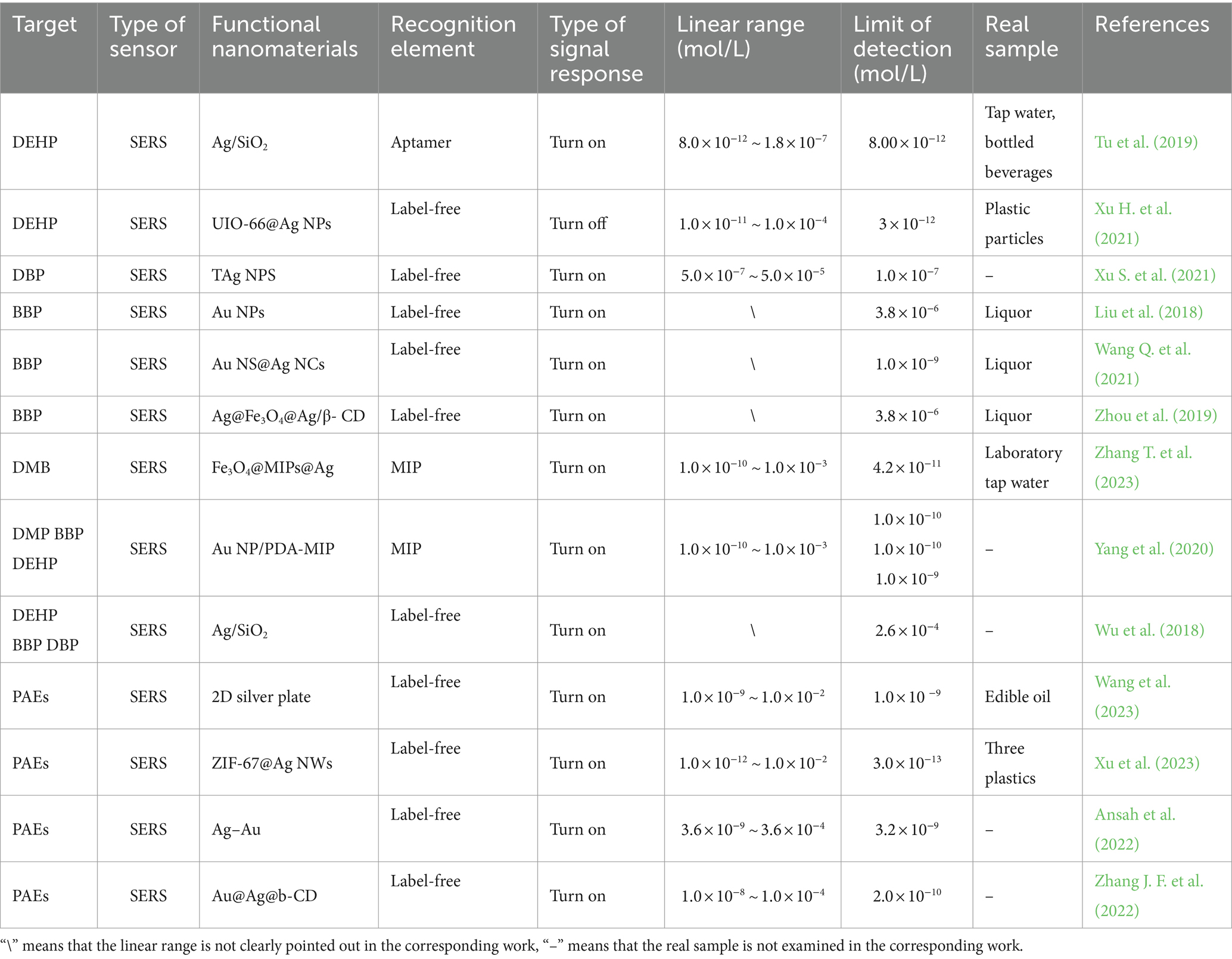
Phthalic acid esters (PAEs) are a series of ester compounds containing benzene ring, which are composed of dialkyl or alkylaryl esters of 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid (Lee et al., 2019). PAEs as plasticizers are extensively added to personal care products (e.g., nail polish and shampoo), drugs, solvent adhesives, food packaging, medical equipment, building materials and agricultural films (Wang Y. et al., 2019; Abeysinghe et al., 2022). PAEs are not chemically bound to the polymer, so they can easily release into environment and finally enter human body from various potential sources, which will cause environmental pollution and health threatening (Zhang et al., 2021). With the development of industrialization, a large number of PAEs are used in plastic products. Studies have shown that PAEs can be detected in the air, soil, water of the Yangtze River and the ocean (Chen, 2019; Hidalgo-Serrano et al., 2022; Mi et al., 2019; Wang W. et al., 2018). PAEs in the environment will be absorbed during plant growth, and will also enter and accumulate in the organism. That could cause significant toxic and side effects such as plant growth retardation, yield decline and quality degradation and will also have a huge negative impact on the biota (Cao et al., 2022; Wang F. et al., 2022; Sun et al., 2023; Zhang D. et al., 2023). PAEs have also been detected in agricultural products, most fermented food products and foods containing plastic packaging bags (Dong et al., 2019; Tan et al., 2018). These PAEs can cause harm to health after entering the human body through the food chain (Reyes and Price, 2018; Fu et al., 2023). Long-term intake of PAEs can affect neurotransmitter activity, lead to neurobehavioral disorders, and increase the risk of asthma in children (Kang et al., 2023; Garí et al., 2019; Huang P. C. et al., 2022; Zhao Y. et al., 2022). Up to now, there are more than 30 kinds of PAEs (Dong et al., 2024). Six kinds of PAEs including DEHP, DBP, butyl benzyl phthalate (BBP), dimethyl phthalate (DMP), diethyl phthalate (DEP) and di-n-octyl phthalate (DNOP) are listed as priority pollutants by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA), the European Union (EU) and China (Gong et al., 2024). The basic information about the above six PAEs is shown in Table 1.
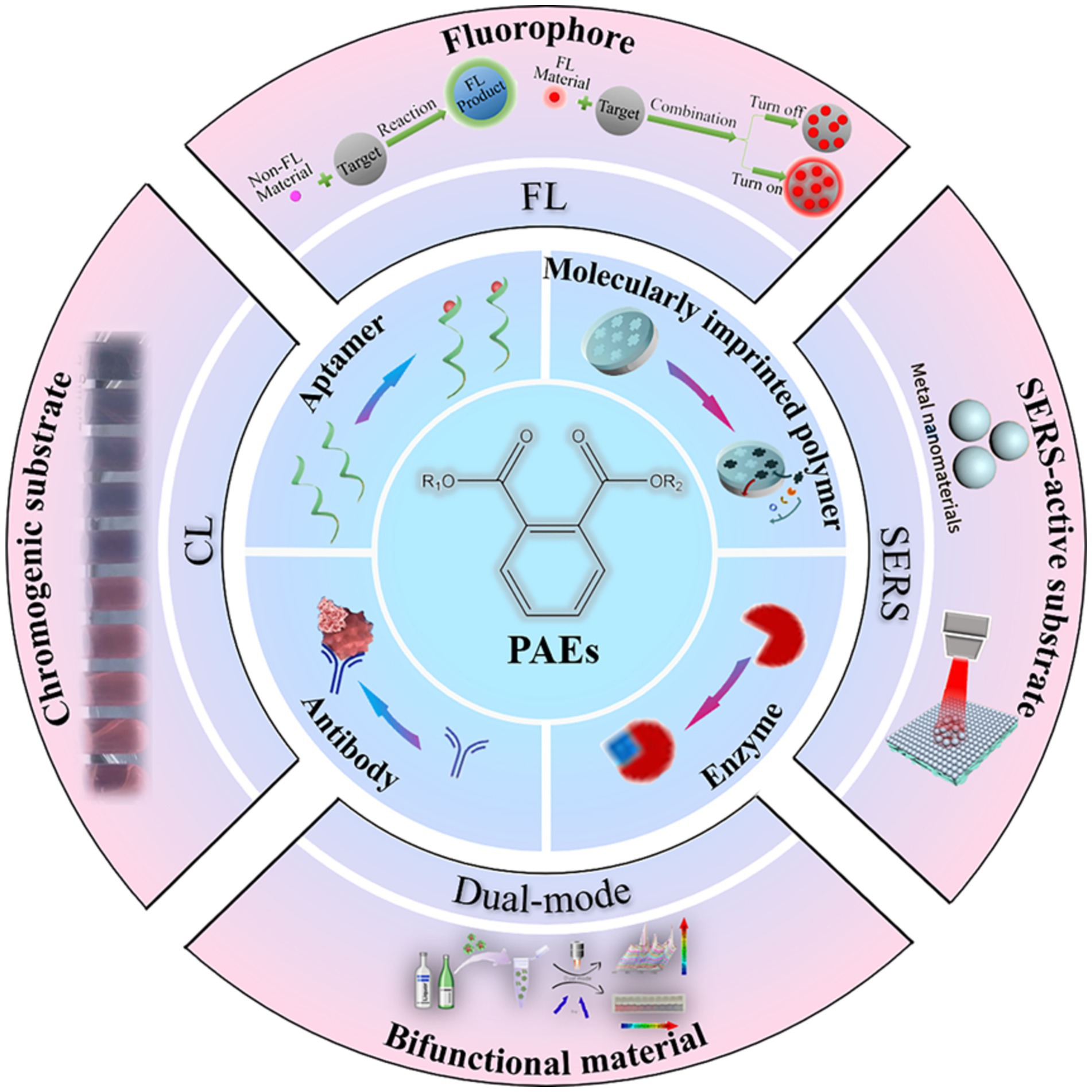
The concentration of DEHP in drinking water should be lower than 8 μg/L (2.05 × 10−8 mol/L), which is one of the lowest molarity limits of pollutants including heavy metal ions, pesticides and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons recommended by the WHO (Net et al., 2015). China, the United States, Japan and other countries have regulated the content of these six PAEs in all toys and products of children to no more than 0.1% [Commission Regulation (EU), 2018]. China has put forward relevant suggestions on the maximum residue of PAEs in food. For example, the content of DEHP and DBP in liquor and other distilled liquor should not be higher than 5 and 1 mg/kg (Sate Administration for Market Regulation, 2019). About 600 million people around the world suffer from diseases after ingesting contaminated food every year, and about 10% of them die from diseases (World Health Organization, 2021). In recent years, food safety awareness has been widely spread among consumers, and food safety analysis methods have been continuously improved. However, issues related to food safety incidents are still the focus of attention in many developing countries (Soon et al., 2020; Selva Sharma et al., 2024; Ding et al., 2022). Therefore, the development of sensors that can achieve point-of-care detection of PAEs is of great significance for the prevention and control of PAEs. Optical sensors have the advantages of simplicity, non-destructiveness and portability, which are expected to realize the point-of-care detection of PAEs. A series of optical sensors for quantitative detection of PAEs have been developed (Zhang C. et al., 2023; Pablo et al., 2023; Ly et al., 2021). However, there is a lack of systematic summary for the current research on colorimetric (CL) sensors, fluorescence (FL) sensors, surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) platform and dual-mode optical sensors for detection of PAEs. Therefore, this review aims to summarize the recent advancements of optical sensors including CL, FL, SERS and dual-mode sensors for detection of PAEs, from the aspects of detection mechanism and application. As shown in Figure 1, CL, FL, SERS and dual-mode sensors for detection of PAEs are discussed as follows: (i) The CL sensors for detection of PAEs are divided into direct detection and indirect detection. (ii) The FL sensors for detection of PAEs are classified to direct detection and labeled with FL probe. (iii) The different metal materials (e.g., Ag, Au, and Au-Ag) are used to construct the Raman substrate in SERS sensing platform. (iv) The bifunctional materials in the dual-mode sensor are discussed. In addition, it is quick to understand the development status of optical sensors for detection of PAEs in the past 5 years and the future research directions of optical sensors by this review. In conclusion, this review provides guidance for the rapid, real-time and sensitive detection of PAEs by optical sensors.
2 Application of optical sensors for the detection of PAEs
Optical sensors detect small entities based on the interaction between light and matter with the strength of the principles of absorption, emission, and FL (Qin et al., 2022). When light interacts with objects, there are three forms of energy transfer: absorption, transmission and reflection. Owing to the differences in the internal biochemical components, texture and apparent morphology of the target compound, the optical signal is attenuated at different intensities. The optical sensors can collect the generated signal and visualize it into a spectral line through computers (Liu F. et al., 2023; Lu et al., 2020). Based on this, the type and concentration of the target can be determined. Optical sensors usually include a transducer component and a recognition unit that can interact selectively with targets. Various optical sensors currently have been developed for quantitative analysis include CL, FL, SERS. In these methods, color changes, FL generation and quenching, as well as changes in spectral patterns and peak shifts, are related to the concentration of the target. Moreover, the optical sensing system has immunity to electromagnetic interference, and can exhibit stable performance and high signal-to-noise ratio even in complex environments (Ma et al., 2023). Recently, optical sensors have also been widely used in the detection of PAEs. Next, the optical sensors for detection of PAEs will be described based on CL, FL, SERS, and dual-mode methods.
2.1 CL sensor for detection of PAEs
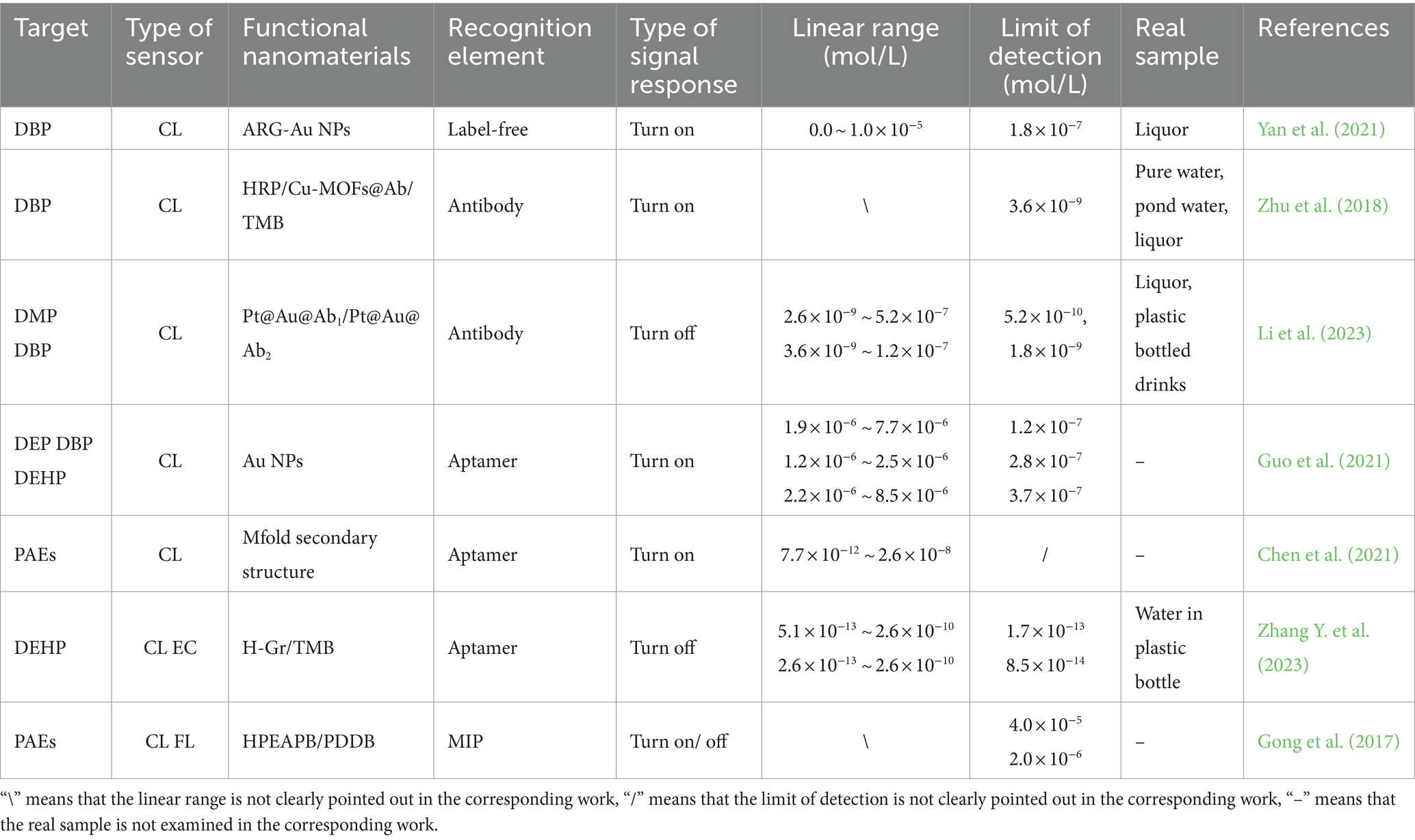
The CL methods can determine the content of the target by measuring or comparing the color depth of the colored substance solution. This method utilizes the absorption characteristics to the specific wavelength light of the colored substance to qualitatively analyze. The principle is that the color of the colored solution generated after the addition of the chromogenic agent or the color depth of the measured substance solution is proportional to the content of the substance (Wang Y. et al., 2022). The CL methods have many advantages: Firstly, CL methods allow in situ visual detection founded on color change without complex instruments (Jiang et al., 2022). Secondly CL sensor arrays provide an approach with simplicity and efficiency for the rapid detection and recognition of chemical substrates by utilizing digital imaging (Lin et al., 2023). Thirdly, CL sensors are easy to miniaturize and allow multiple analyses using a single control instrument at the central site. Fourthly, it can be used for the detection of explosive, flammable and toxic substances. In addition, it also has the advantages of high selectivity, non-destructiveness, fast response and low limit of detection (LOD) (Huang et al., 2018). In recent years, CL methods have made some progress in the detection of PAEs. The characteristics of CL sensors constructed in these works are shown in Table 2.
After converting PAEs into dyes, the total amount of PAEs at sub-micromolar levels can be easily determined by CL method. The CL method without recognition elements is known as direct detection. For example, the PAEs are hydrolyzed in sodium hydroxide solution, and then dehydrated to form phthalic anhydride. The product can be converted into a marker by reacting with resorcinol. The presence of PAEs can be determined by absorbance spectrophotometry (Yanagisawa and Fujimaki, 2019). This CL method provides a simple screening method for the detection of PAEs, but it cannot identify individual PAEs. Au nanomaterials display different colors according to their aggregation state, shape and size, which provide good platforms for the development of CL sensors in biological field. The development of Au nanomaterials has promoted the progress of CL detection (Yu et al., 2020). PAEs can cause the aggregation of functionalized Au nanoparticles (Au NPs), resulting in a change in the color of the solution, which provides a research idea for the detection of PAEs by CL sensors. Yan et al. (2021) proposed a simple and innovative CL method based on DBP-induced aggregation of arginine functionalized Au NPs (ARG-Au NPs). There is a strong non-covalent interaction between DBP and ARG-Au NPs (electrostatic, van der Waals force and hydrogen bonding), which leads to the decrease of electrostatic repulsion between the nanoparticles and aggregation. Therefore, the color of ARG-Au NPs changes from red to blue. When the concentration of DBP in the solution is more than 1.0 mg/L (3.59 × 10−6 mol/L), the color change of the solution can be obviously observed by the naked eye. In this system, DBP can be rapidly and semi-quantitatively detected without sample pretreatment technology and tedious operation. Recently, M13 bacteriophage-based sensors have also been widely studied for their flexible responses to changes in the target substance (Lee et al., 2023). The intermolecular interactions (or binding affinities) between the M13 bacteriophage and target chemicals can be regulated by genetic engineering techniques. When the external gas is exposed, the distance between the self-assembled M13 bacteriophage bundles will change, resulting in a change in the scattering color. The self-assembled structure has the characteristics of easy tunability and multi-functionality, so we have advantages in using M13 bacteriophage as sensor applications and biomaterials (Kim et al., 2023). Seol et al. (2019) studied the potential of CL sensors based on M13 bacteriophage for the analysis and detection of four PAEs (DEHP, DBP, DEP, and BBP) with similar molecular structures. The magnitude and pattern of the RGB color change vary due to the functional groups present in the PAEs structures. DEHP with a long alkyl chain causes a slight color change. BBP with an additional benzene ring has a large color change when measured. Because the tryptophan-histidine-tryptophan residues on the self-assembled phages contain imidazole and indole, the surface of the sensor constructed by the self-assembled phages can interact with the benzene ring in BBP by π-π interaction, resulting in a large color change. The CL sensor constructed in this study is multifunctional and can be applied to on-site screening. Although direct detection mode is simple, the selectivity of the CL sensors is limited.
By introducing recognition elements such as aptamers and antibodies into the CL method, the selectivity of the sensor can be improved. Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) is a natural enzyme with high selectivity and excellent catalytic efficiency, which is often used in the study of CL sensors (Zhao T. et al., 2022; Wang D. N. et al., 2019). Zhu et al. (2018) constructed an ingenious HRP-based CL immunosensor for detection of trace DBP in Figure 2A. In the presence of HNO3, a large amount of Cu (II) is released after Cu-MOFs@Ab2 is captured by the antigen-primary Ab1 complex. After the addition of sodium ascorbate, Cu (II) is further reduced to Cu (I), resulting in the inhibition of HRP-catalyzed colorless 3,3 ′, 5,5 ′ -tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) to blue oxidation product (oxTMB). The method shows good accuracy and reproducibility and the proposed immunosensor indicates great potential for trace DBP determination from environmental and food samples. However, nanozymes have a wide range of applications in many fields such as the detection of biomedicine, biosensing, pollutant and antibacterial products because of their advantages of economy, stability and large-scale preparation, compared with natural enzymes. As a kind of nanomaterial with a variety of enzyme-like activities and enzymatic catalytic properties, nanozymes have become a new strategy for design of CL sensors. Single-atom nanozymes have received extensive attention due to their unique structures and high enzyme-like activities of atomically dispersed metal sites, among the multitudinous nanozyme materials. They have displayed tremendous potential to replace natural enzymes in the field of disease treatment, environmental control, biochemical analysis and other fields (Zhang T. et al., 2022; Wang M. et al., 2020; Cai et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023; Niu et al., 2019). At the same time, the aptamer can quickly and conveniently detect the target, and it can be introduced into the CL sensors to detect PAEs, which can simultaneously identify a variety of PAEs with similar structures (Chen et al., 2021). Zhang Y. et al. (2023) realized the detection of DEHP by using the aptamer of hemin-graphene chloride (H-Gr) hybrid and DEHP. The H-Gr nanocomposites have intrinsic peroxidase-like activity that can catalyze the colorless TMB to generate blue oxTMB. The constructed sensor has the potential to be an efficient tool for the detection of DEHP in water samples. Au NPs can also be combined with recognition elements to achieve selective detection of PAEs. Based on DNA-modified Au NPs, a simple and rapid method for the detection of DEP, DBP and DEHP was proposed by Guo et al. (2021). After DNA modification (aptamer-B, aptamer-E and aptamer-H), Au NPs can form aggregates in the presence of PAEs. Therefore, it can be observed that as the concentration of PAEs increases, the absorption ratio increases, and the solution shows an obvious color change from red to blue. Li et al. (2023) used a new strategy to combine Pt@Au nanozymes with high catalytic performance to create two catalytic signal probes: Pt@Au@Ab1 and Pt@Au@Ab2, which were specifically used to detect DMP and DBP, as shown in Figure 2B. These catalytic signal probes realize the simultaneous detection of DMP and DBP, which lay a foundation for the development of CL immunoassay. Although this CL sensor with indirect detection mode provides a powerful tool for simultaneous quantification of DMP and DBP in real samples, its linear ranges are relatively narrow. It is necessary to design novel materials with high activity and high stability to increase the sensitivity of sensors for detection of PAEs in real samples.
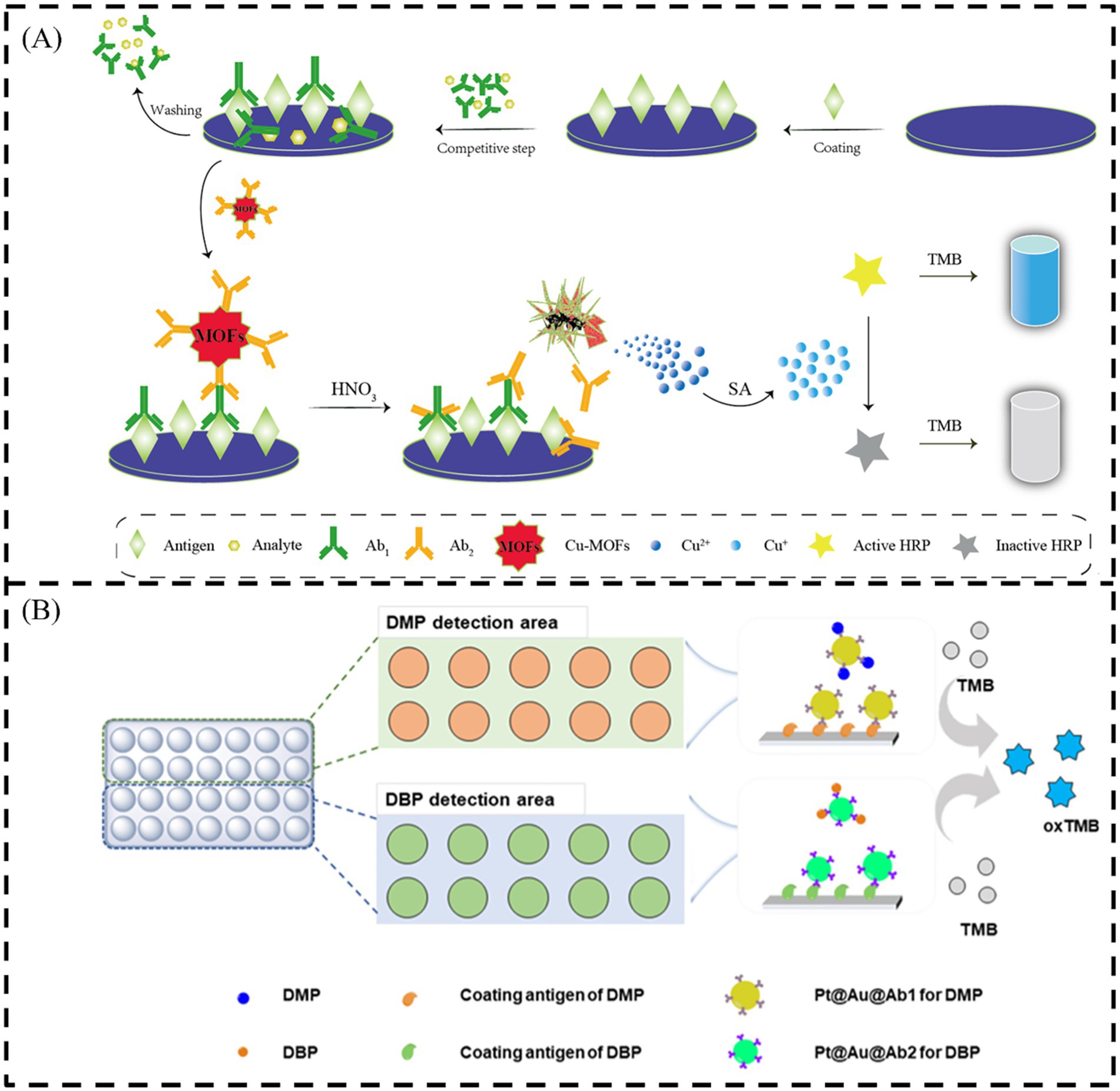
Figure 2. Scheme illustration of (A) the principle of the constructed CL immunosensor (Zhu et al., 2018) and (B) detection principle of the developed CL immunoassay (Li et al., 2023). Sodium ascorbate (SA).
2.2 FL sensor for detection of PAEs
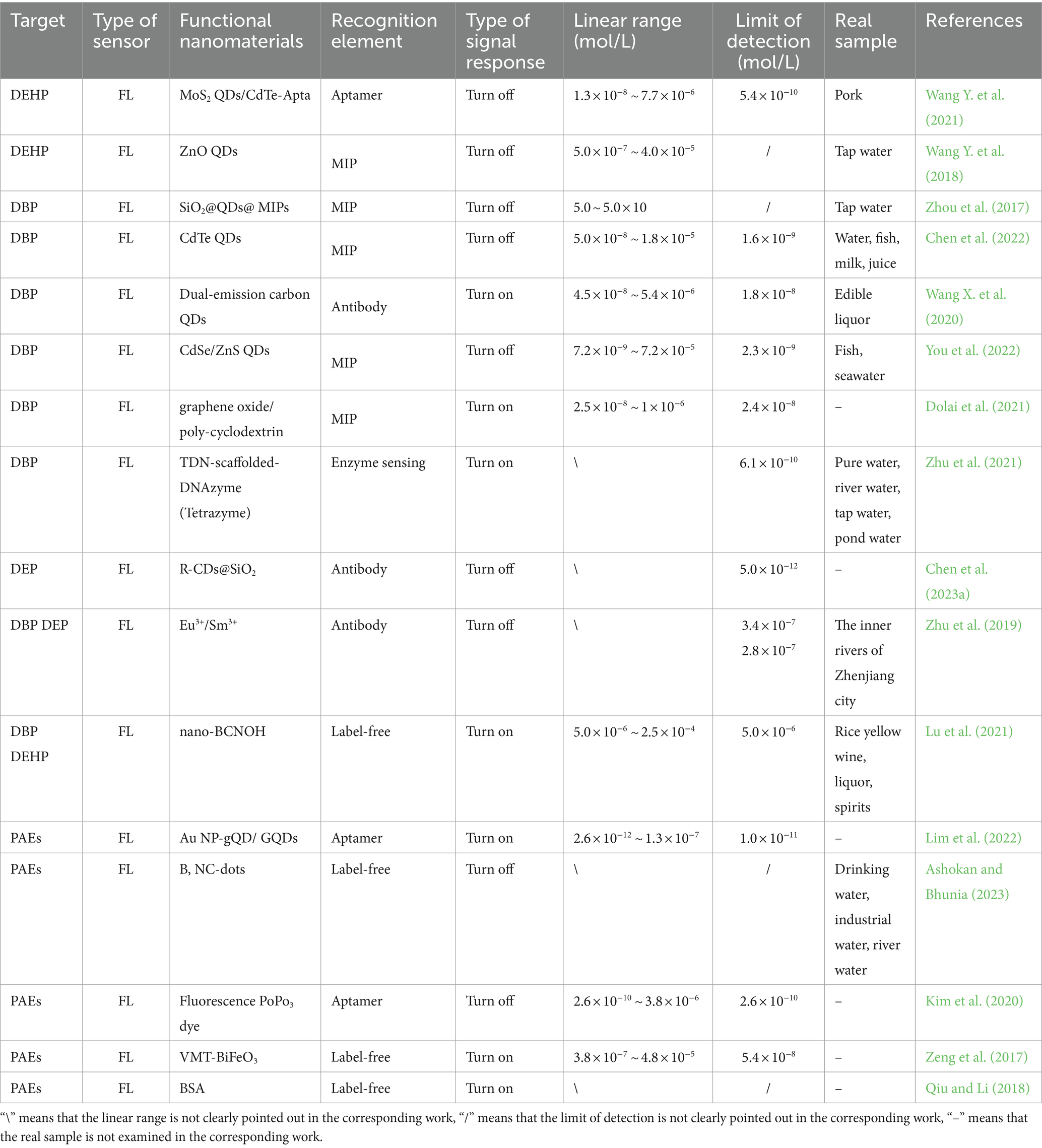
The generation of FL is that the material can emit light when it returns to the ground state after absorbing short-wave energy (Jablonski, 1933). The condition for the FL of organic molecules is that the energy level difference between the highest occupied molecular orbital and the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital is small. The presence of fluorophore is a necessary condition for the generation of fluorescence. The FL sensors include two elements: recognition group and fluorophore, which are commonly used methods for detection of substances. These two elements can be connected in a conjugate system to achieve the detection of the target. The FL of the fluorophore will be affected, when the analyte is identified, giving rise to changes in FL signals such as FL lifetime and FL intensity. The fluorophore can convert the information of the analyte into a FL signal, so as to achieve simple and highly selective detection (Liu et al., 2020). Due to the increasing requirements for the detection ability and stability of FL sensors, more and more emerging nanomaterials (e.g., Au NPs, MoS2 nanosheets, graphene oxide, and carbon nanotubes) have been applied to FL sensors to improve sensor performance. Nanomaterials have efficient FL quenching characteristics, which promote the development of FL sensors (Liu et al., 2020; Lan et al., 2018; Guo et al., 2011). The research on the detection of PAEs by FL method in recent years is summarized in Table 3.
It is well known that PAEs themselves do not emit light, but they can be converted into luminescent products. For example, PAEs are hydrolyzed into FL-free PAEs in a strong alkaline solution, which then react with hydroxyl free radicals generated during photo-Fenton process catalyzed by vermiculite-loaded BiFeO3 to produce a fluorescent product. The FL intensity is proportional to the concentration of PAEs, based on which the sensitive detection of PAEs can be realized (Zeng et al., 2017). In order to improve the FL intensity of PAEs derivatives, Qiu and Li (2018) proposed a simple method for detection of PAE derivatives by FL spectroscopy founded on a double-substitution modification. This method does not affect the function (stability and insulation) of the sensor. The detection of PAEs derivatives is more environmentally friendly, because the toxicity, mobility, and persistence of PAE derivatives are reduced to varying degrees compared with PAEs, and their amounts of bioaccumulation are not changed obviously. In order to realize the detection of PAEs, Lu et al. (2021) proposed a BODIPY fluorescent dye (3-(4-(5,5-difluoro-2-(4-(hydroxymethyl) phenyl))-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl5H-5 l4,6 l4-Bispyrrole [1,2-c:2′,1′-f] (Lee et al., 2019; Abeysinghe et al., 2022; Wang Y. et al., 2019) borothiaserine-10-yl) phenyl)-2-(4-nitro) phenylnier (BCNOH) modified with p-nitrodiphenyl acrylonitrile and hydroxymethyl phenyl group, as shown in Figure 3A. BCNOH is turned on by PAEs to form a non-emission water caged BCNOH. The combination of water caged BCNOH and PAEs can generate nano FL dyes (nano-BCNOH). Hydroxymethyl phenyl group of BCNOH could bind more DBP. The trigger that turned on the FL emission is the interaction between p-nitrodiphenyl acrylonitrile and DBP. The results show that weakening the isomerization of water caged BODIPY dyes provides a potential method for turn-on FL sensors. Although the method is simple, it is not sensitive.
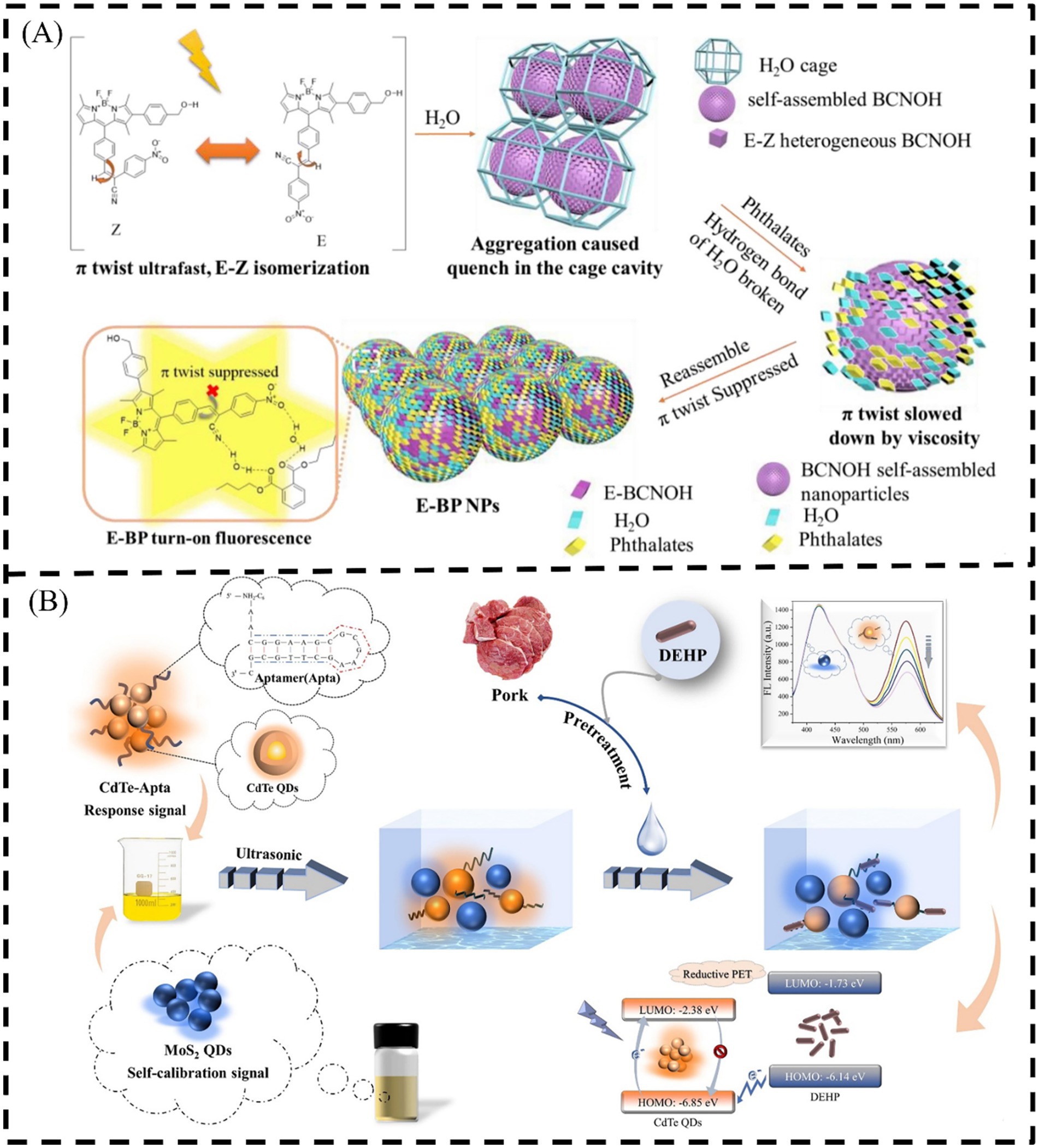
Figure 3. Schematic illustration of (A) BCNOH and phthalates and water assembled nanoparticles to turn on the FL emission (Lu et al., 2021) and (B) MoS2 QDs/CdTe-Apta for the DEHP detection assay (Wang Y. et al., 2021). Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital (LOMO), Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital (HOMO).
Fluorophores or fluorescent dyes have been used widely as mediums to gain readout signals in various assays or bioimaging due to their versatilities such as biocompatibility (Huang X. et al., 2022). Those fluorescent dyes-based techniques manipulate glycan-lectin interaction, base complementation, Ab-protein interaction, etc., for the selectivity analysis of molecular interactions of biomacromolecules (Luan et al., 2016). Although PAEs themselves do not emit light, they can be labeled with fluorescent labels for detection through emission (Savicheva et al., 2020) In recent years, quantum dots (QDs), as an emerging nanomaterial, have been widely used in the study of fluorescent sensors because of their ability to enhance FL signals. CdTe QDs can also be combined with MoS2 QDs (Figure 3B) that provide self-calibration signals to construct a proportional FL sensor system for the detection of DEHP (Wang Y. et al., 2021). Zhou et al. (2017) synthesized a novel fluorescent molecularly imprinted polymer (SiO2@QDs@MIP) based on Mn-doped ZnS QDs and SiO2 nanoparticles. The composites exhibit outstanding molecular recognition ability of MIP and optical properties. It can recognize the template molecule DBP with high selectivity. The QDs of metal oxides [such as ZnO (Wang Y. et al., 2018)] or metal compounds [such as CdTe (Chen et al., 2022)] as optical materials can be combined with MIP to achieve selective detection of DEHP and DBP in Figure 4A. Graphene QDs (GQDs) can be quenched by Au NPs. Based on this, an aptasensor can be developed for detection of 11 PAEs (Lim et al., 2022). Carbon dots (CDs) have the characteristics of real-time and non-destructive detection. CDs have been widely applied in rapid detection. Some studies have used CDs to detect PAEs, such as Chen et al. (2023a) reported an ultrasensitive FL immunoassay using red CDs@SiO2 (R-CDs@SiO2) as tags for trace detection of DEP. SiO2 as a nanocarrier can effectually enhance the utilization rate and bio-functionalization of CDs. In addition, R-CDs embedded in SiO2 nanospheres (NS) can enhance sensitivity and amplify the FL signal. The FL immunosensor constructed by R-CDs@SiO2 coupled with anti-DEP Ab can realize the selective recognition of DEP. Ashokan and Bhunia (2023) synthesized nitrogen and boron co-doped yellow FL CDs (B, N-C-dots). These B, N-C-dots selectively detect PAEs in aqueous solution, and the FL quenching rate is as high as 95% after PAEs treatment. The method for labeling amino-modified nucleic acid aptamers using double-emission CQDs provides more precise results and has a stronger anti interference ability compared with the single wavelength emission method. Therefore, the sensor can be used for detection of DBP in soybean oil and edible liquor (Wang X. et al., 2020). The tricolor ratiometric FL sensors have a wider range of color variations in the visual detection of DBP compared with single-emission or dual-emission sensors. It provides an ideal choice for intuitive and rapid detection of DBP in the aquatic products and environment (You et al., 2022). Other nanomaterials with efficient FL quenching properties have also been used in the study of FL sensors. Zhu et al. (2019) established a dual-label time-resolved FL immunoassay using europium (Eu3+) and samarium (Sm3+) as fluorescent markers to detect DEP and DBP in aquatic environment. In order to shorten the detection time, Kim et al. (2020) proposed a non-equilibrium rapid replacement aptamer (NERRA) assay, which could perform ultra-fast (in 30 s) quantitative detection of PAEs without waiting for the reaction to reach equilibrium. The PoPo3 dye is embedded into the aptamer of ssDNA by NERRA assay. When the intercalated dye is replaced by PAEs, it will quench in water. The change rate of FL is proportional to the concentration of PAEs. Based on this, PAEs in water can be selectively detected and quantified. As shown in Figure 4B, Dolai et al. (2021). combined the nanocomposites composed of poly-cyclodextrin and graphene oxide with the molecular imprinting of DBP. The molecular imprint inside the nanocomposite can achieve selective capture of DBP. After that, the “turn on” detection of the constructed FL sensor is realized by the competitive binding of graphene oxide and fluorescein. The combination of nanocomposites and paper strips can be used for rapid and simple read out detection of DBP in polluted water. In order to improve the impact of the inherent interior correction calibration on the environment and improve the accuracy and precision, Meng et al. (2022) combined the dual-output ratiometric FL assays with the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to construct a ratiometric FL immunoassay based on Ag NPs for the detection of DBP. Ag NPs are labeled on the Ag NPs@Ab2 for signal amplification to regulate the concentration of H2O2. The addition of H2O2 can effectively quench the blue fluorescence of scopoletin and produce the red fluorescence of Amplex Red, when Ag NPs-Ab2 and antigen–primary Ab1 are linked by selective recognition. Founded on a new tetrahedral DNA nanostructure (TDN) -scaffold-DNAzyme (Tetrazyme), Zhu et al. (2021) established a high-throughput proportional FL amplification ELISA for the detection of DBP in aquatic systems. Among them, the HRP-mimicking enzyme is derived from the Tetrazyme formed by the precise folding of the G-quadruplex sequence on the three apexes of hemin and TDN. The rigid TDN can avoid the local crowding effect, thus providing a reasonable spatial spacing for the G-quadruplex sequence on the interface. In addition, it can also enhance the catalytic ability of the DNAzyme, thereby increasing the chance of collision between the substrate and the DNAzyme. In summary, the sensor provides a potential strategy for rapid detection of DBP in environmental water. However, the sensor suffers from various interferences such as non-selective binding and cross-fluorescence reactions in the actual environmental. In addition, the direct detection mode of FL methods is currently unable to achieve selective recognition of single PAE. To obtain the FL sensors with simplicity and portability, the composite materials combine function of recognition and signal amplification should be carried out.
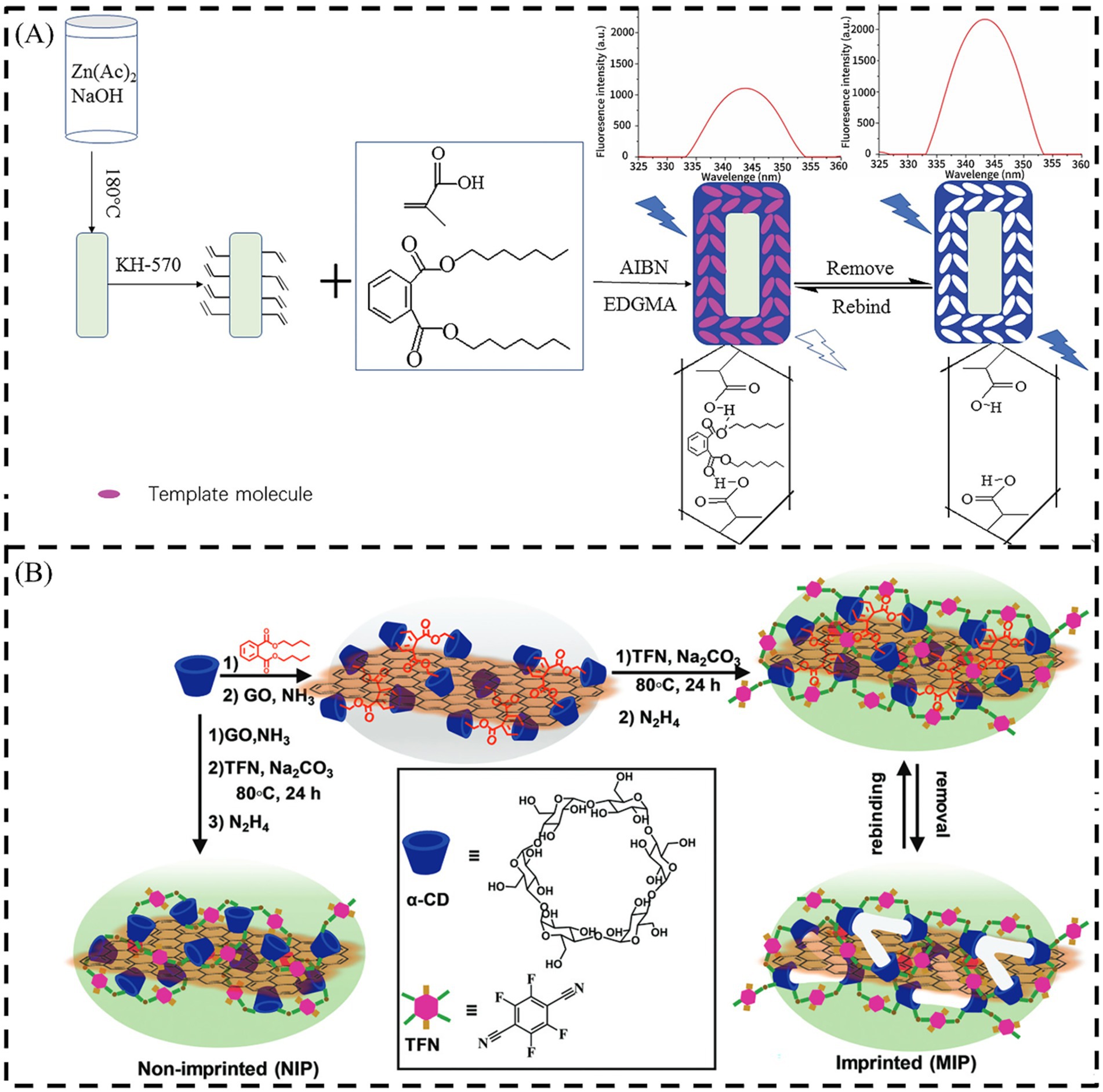
Figure 4. Schematic illustration of (A) MIP@QDs for preparation (Wang Y. et al., 2018) and (B) the preparation of the poly-cyclodextrin–graphene oxide nanocomposite with DBP molecular imprinting. The a-CDs are spatially aligned in the imprinted polymer according to their interaction with DBP (Dolai et al., 2021). 2,2′-azobis(2-methylpropionitrile) (AIBN), Ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EDGMA), 3-(Methacryloyloxy)propyltrimethoxysilane (KH-570), Tetrafluoroterephthalonitrile (TFN), Graphene oxide (GO).
2.3 SERS platform for detection of PAEs
SERS is an ultrasensitive vibrational spectroscopy technique for analyte characterization and determination. It has remarkable characteristics such as high resolution, fingerprint recognition, nondestructive and strong anti-interference ability to samples (Guo et al., 2020). Raman scattering is that when light interacts with matter, photons will exchange energy with molecules in matter, resulting in a slight change in the frequency and intensity of light. The signal intensity of SERS is vastly affected by the modification of Raman dyes in plasmonic hot spots and the compositional details and structural of the plasmonic nanostructures (Xue and Jiang, 2023). Therefore, the key to obtaining strong, controllable and quantifiable SERS signals is a strategy for high-yield and accurate synthesis of plasmonic nanostructures with strong enhanced electromagnetic fields and the controllable modification of the number and position of Raman dyes in plasmonic hotspots (Nam et al., 2016). The Raman activity of PAEs is poor, and the affinity of metal surface is very low, which greatly hinders the realization of direct and effective detection of PAEs by SERS. The equivalent charge oscillation on the metal surface can produce an electric field enhancement effect, which makes the Raman scattering signal of the material greatly enhanced. Therefore, the SERS platform for detection of PAEs are based on metal nanomaterials. The SERS platform characteristics currently used for detection of PAEs are shown in Table 4.
SERS is an ultra-sensitive analytical tool that usually measures single molecules by an obviously enhanced Raman scattering signal of molecules located near the surface of metals such as Au, Ag, and Cu (Zhang T. et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024). As the first material to appear Raman signal, Ag has been studied a lot in recent years because of its strong Raman signal (Fleischmann et al., 1974; Li et al., 2016; Li et al., 2021). A high-density ordered SERS substrate based on triangular Ag NP (T Ag NP) array self-assembly is developed for detection of DBP (Xu S. et al., 2021). The sharp edges and ordered arrangement of T Ag NPs can offer uniform and sufficient hotspots for highly active and reproducible SERS effects. Wang et al. (2023) developed a two-dimensional (2D) Ag plate synergizing with a Ag sol as a SERS substrate for the detection of potassium hydrogen phthalate (PHP), a hydrolysate of a PAE in Figure 5A. The results show that the detection of PHP by SERS platform is hopeful to offer a way for the detection of PAEs in fats and oils, and has prospect application prospects in food safety. By combining Ag with other metal nanomaterials, such as Fe3O4@MIP@Ag, the detection of DMP can be realized by SERS characterization. Ag@Fe3O4@Ag/β- cyclodextrin (CD) NPs as a SERS active substrate is shown in Figure 5B (Zhou et al., 2019). When malachite green is used as a probe molecule, the substrate is proved to have good repeatability and sensitivity. Recently, MOFs have received extensive attention in the research of SERS platforms due to their excellent absorption capacity to capture target molecules entering the electromagnetic field. In the detection of sensors, Ag nanowires (NWs) are embedded in functionalized metal–organic frameworks ZIF-67 (ZIF-67@Ag NWs) composite as substrate to construct a platform for highly sensitive detection of six kinds of PAEs (Xu et al., 2023). In addition, Ag NPs can also be grown on the surface of MOFs octahedron UIO-66 (UIO-66@Ag NPs) with large specific surface area and high porosity to form a composite SERS substrate for detection of DEHP. The prepared UIO-66 @ Ag NPs substrate has good adsorption performance for DEHP, and it can reduce the aggregation of Ag NPs, thereby increasing the “hot spots” formed by local surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) of Ag NPs. This work preliminarily discusses the SERS enhancement mechanism of UIO-66@Ag NPs substrate, and the SERS signal enhancement factor of the platform is calculated to be about 1.1 × 107. The results show that this method provides a suitable way for the monitoring of DEHP in plastics by studying advanced SERS sensing materials (Xu H. et al., 2021). Ag can also be combined with non-metallic materials to prepare high-performance SERS substrates. The most common is to combine with SiO2 to prepare composite materials such as self-assembly of monodisperse SiO2 colloidal spheres on silicon wafers, and then coating Ag layer on them to prepare SERS substrates. Ag NPs can also be gathered together and coated with silica. The obtained Ag/SiO2 SERS substrates can achieve rapid and sensitive detection of PAEs (Tu et al., 2019; Wu et al., 2018).
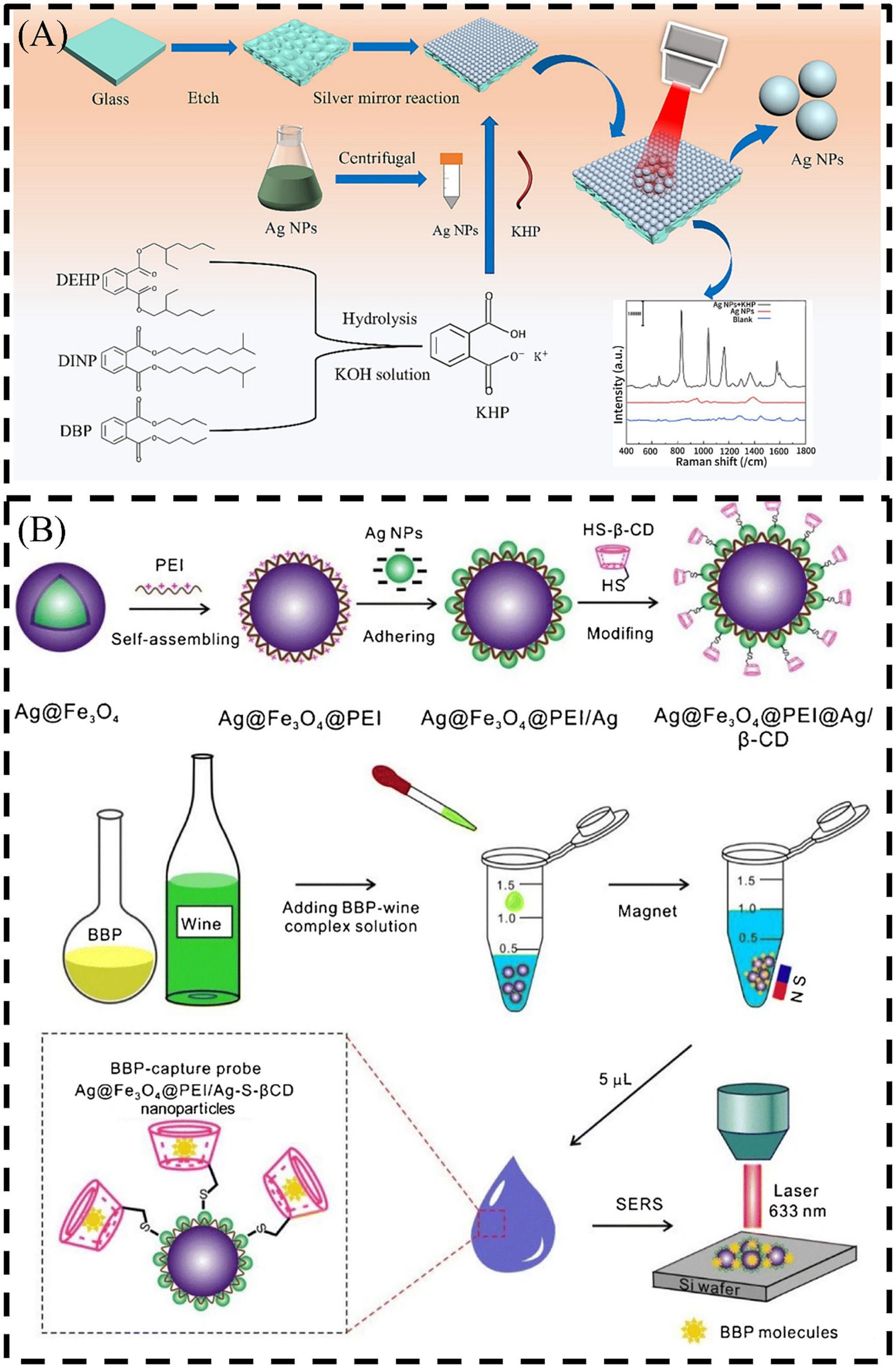
Figure 5. Schematic illustration of (A) SERS detection of PAEs in oil (Wang et al., 2023) and (B) the SERS detection of BBP and Ag@Fe3O4@Ag/β-CD NPs (Zhou et al., 2019). Polyethylenimine (PEI).
Although the Raman signal of Ag is very good, Ag NPs are easily oxidized in the air, giving rise to the weakening of the surface plasmon resonance effect and affecting the Raman enhancement effect. Therefore, it is also a research direction to explore other metal materials with better performance to replace Ag NPs. Au NPs, with antibacterial activity, unique surface plasmon resonance effect and biocompatibility, are intermediates between metal blocks and atoms. Spherical Au NPs have potential applications in optics due to their low toxicity, good photoelectric properties, excellent biocompatibility and high surface-to-volume ratio. Au NPs can increase surface compatibility by surface modification with different substances. Therefore, a SERS detection platform based on Au NPs can be constructed for the analysis of PAEs (Liu L. et al., 2023). Simply, the analyte BBP molecules can be loaded into the nanogaps with SERS activity in the Au array by inducing the self-assembly of Au NPs at the organic/water interface, thereby achieving sensitive detection of BBP (Liu et al., 2018). Au NPs are easily anchored and growth on bio-inspired polydopamine MIP (PDA-MIP) coating to form a three-dimensional (3D) architecture, as shown in Figure 6A. The distribution and particle size of PDA and Au NPs can be well controlled through adjusting the reaction conditions. The Au NP/PDA-MIP nanocomposite can be used to construct an excellent SERS sensing platform for selective recognition of PAEs (Yang et al., 2020).
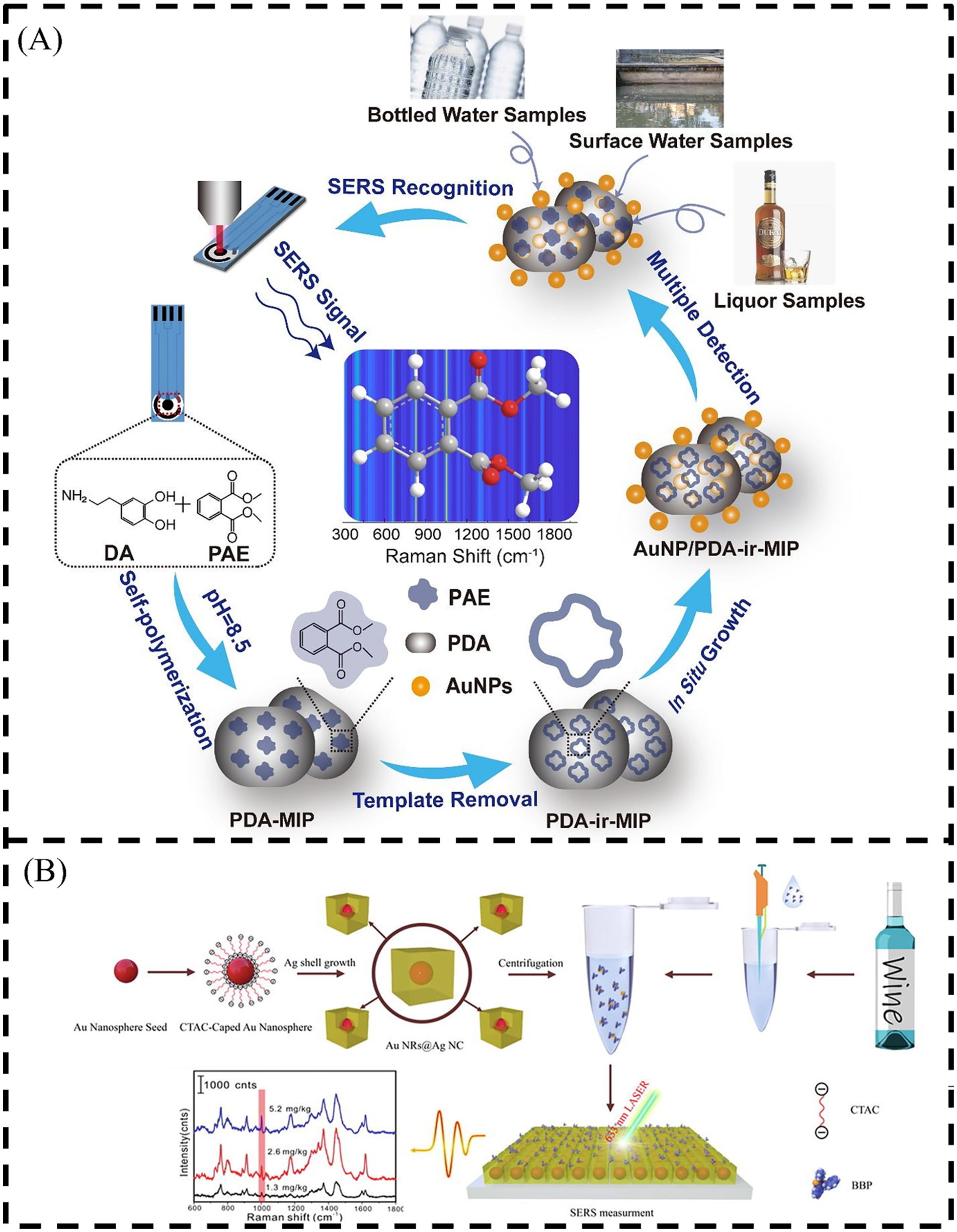
Figure 6. Scheme illustration of (A) the preparation of Au NP/PDA-MIP/SPE and the constructed SERS-active platform for PAEs selective recognition in different real samples (Yang et al., 2020) and (B) the Au NS@Ag NCs and it use as a SERS active platform for the detection of BBP (Wang Q. et al., 2021). Dopamine (DA), Hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride (CTAC).
The anisotropic growth of bimetallic nanostructures can not only skillfully integrate the two properties into one nanoarchitecture, but also highly improve the original properties. Therefore, people are committed to synthesize anisotropic bimetallic nanostructures by selectively growing a second material on the template nanostructures (Yang et al., 2023). Among them, anisotropic Au-Ag bimetallic nanostructures are prominent SERS platforms (Zhang et al., 2018). Wang Q. et al. (2021) combined the SERS strategy with plasmonic core–shell Au NS@Ag nanocubes (Au NCs) with abundant LSPR as substrates and successfully used it for sensitive and rapid detection of BBP in liquor. As shown in the Figure 6B, the synthesized Au@Ag NCs composed of Ag cuboid shells and Au nanorod (NR) cores can produce broader and richer plasmon resonance modes than Au NRs (Wang Q. et al., 2021). In this system, the unique core-shell Au@Ag NCs are used as SERS active substrates. The SERS sensing platform based on this SERS substrate realizes the detection of BBP content in liquor samples, and the LOD is as low as 1.3 mg/kg. Therefore, the unique bimetallic material provides an effective tool for the sensitive and rapid detection of PAEs in liquor samples. Ansah et al. (2022) proposed an Ag-Au bimetallic nanocomposite (SGBMNC) with internal hot spots to construct a SERS sensing platform for PAEs detection. Compared with the traditional SERS platform without internal hotspots, Au significantly enhances the plasmonic activity by replacing Ag NPs to provide the hotspots area for SGBMNC by galvanic replacement reaction (GRR). During the GRR process, the analyte diffuses to the proposed interior hotspots, and sensitive detection can be achieved within 10 s. Zhang J. F. et al. (2022) synthesized Au@Ag@b-CD NPs with a particle size about 13 nm, and successfully modified b-CD on its surface. An efficient synthetic method for the preparation of a SERS substrate is proposed, that is, Au@Ag@b-CDNPs and analytes are self-assembled into a coffee ring pattern through the coffee ring effect. This effect can make Au@Ag@b-CD NPs and PAEs gather to the edge together to achieve concentration enrichment. In addition, the b-CD modified on the surface of Au@Ag@b-CD with core-shell structure has a cavity structure, which can adsorb the analyte into the hydrophobic cavity through host-guest recognition, so as to achieve the purpose of enriching the analyte concentration. In the process of enrichment, the concentration of the analyte surface is improved. In addition, the analyte and other substances in the analyte solution can be effectively separated in this process. SERS seems to be a promising technique to fabricate a simple and universal biosensor, but it depends on Ag, Au and Ag-Au materials. To popularize the application of SERS method in practical detection, more low-cost and high-stability materials should be designed.
2.4 Dual-mode sensor for detection of PAEs
The above-mentioned individual methods for detection of PAEs still have some challenges in ensuring the accuracy of their results. The results obtained by the dual-mode measurement method can be mutually confirmed, and the accuracy of the detection results can be effectively improved by self-correction. The bifunctional materials are required for construction of dual-mode sensors. For example, Li et al. (2019) provided an effective and selective dual-mode sensor for the detection of trace BBP by constructing β-CD stabilized Au NPs (Au NPs@β-CD) colloids in Figure 7A. As switchable Raman reporters and macromolecular binder, BBP could assemble Au NPs@β-CD into photonic clusters with various shapes. The Au NPs@β-CD cluster triggered by BBP has rich hot spots in SERS mode, so it can amplify the corresponding SERS signal, and the LOD is 1.0 × 10−8 mol/L. In CL mode, the Au NPs@β-CD cluster is used as the chromogenic substrate, and the distinguishable response of CL can be accurately quantified by UV–Vis spectroscopy. The LOD of BBP can reach 1.49 × 10−8 mol/L. In addition, the combination of FL and CL to construct a multifunctional chemical sensor is expected to be used for low-cost, accurate and simple detection of trace PAEs (Gong et al., 2017). Chen et al. (2023b) constructed a dual-mode immunoassay based on blue CDs@SiO2@MnO2 (B-CDs@SiO2@MnO2), which could simultaneously detect DEP by FL method and CL method, as show in Figure 7B. In this system, MnO2 nanosheets have oxidase-like activity. Under acidic conditions, colorless TMB can be oxidized to yellow TMB2+ and the color of the solution also changes. Moreover, the FL of B-CDs@SiO2 is quenched by MnO2 nanosheets. After the addition of ascorbic acid, MnO2 nanosheets are reduced to Mn2+, and the fluorescence of B-CDs@SiO2 is restored. The experimental results show that the results of the constructed dual-mode immunosensor have good consistency, and it can be considered that the dual-mode immunosensor is reliable for the detection of DEP. Figure 7C shows that a simple preparation method of dual-mode nanocomposites for sensitive detection of PAEs by coupling SERS and up conversion FL as signal can be proposed (Rong et al., 2021). In the sensing system based on Au NPs modified up conversion NPs (UCNPs), UCNPs are used as signal molecules, Au NPs are applied as SERS substrates, and aptamer is used as recognition tags for PAEs. The method has been successfully applied to food packaging and spiked food samples. At the same time, the EC-CL dual-mode sensor can be constructed by combining the H-Gr complex with the aptamers of DEHP for detection of DEHP (Zhang Y. et al., 2023). The principle is that the H-Gr nanocomposite has peroxidase-like activity, which can catalyze the chromogenic substrate TMB to produce a blue oxTMB in CL mode. Moreover, H-Gr can be used as an in situ probe in EC mode, and the formed DEHP-aptamer complex will reduce the EC signal of H-Gr. The strategy of dual-mode detection of DEHP proposed in this study has a wide linear range and has the potential to be applied to the detection of DEHP in water samples. Compared with the EC sensors, the PEC sensors with higher sensitivity have been used to construct a PEC-CL dual-mode sensors. For example, the MXene/In2S3/In2O3 composite material can be used to construct a PEC-CL dual-mode aptasensor for the ultra-sensitive detection of DEHP (Zhang et al., 2024). The linear range of the constructed sensor is 1.0 × 10−13 ~ 2.0 × 10−10 mol/L, and the LOD is 2.0 × 10−14 mol/L. This research provides a good prospect for the detection of PAEs by dual-mode sensors. In view of the high accuracy of dual-mode sensor, more dual-mode sensors are worth designing and developing.
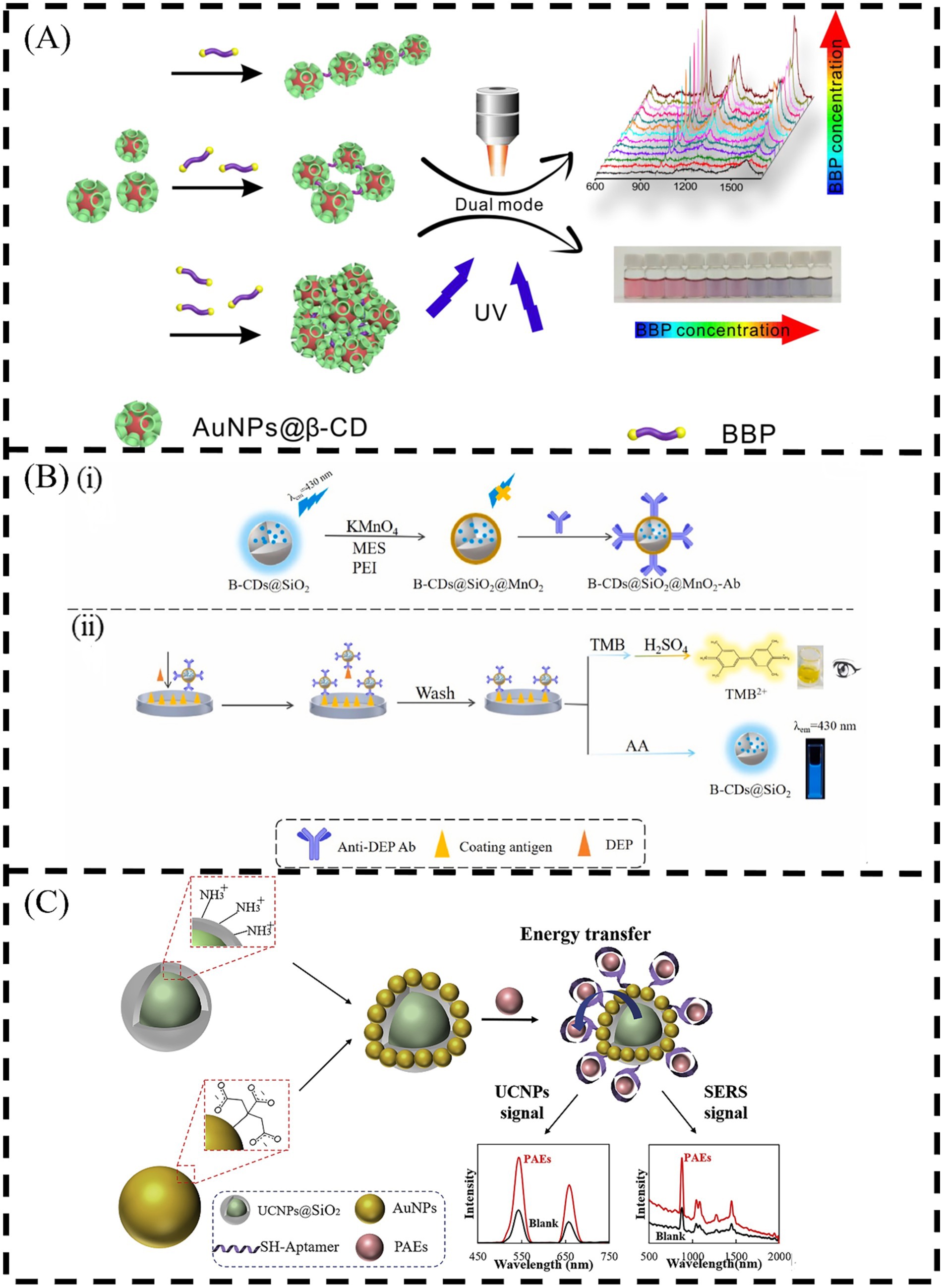
Figure 7. Schematic illustration of (A) the BBP-mediated AuNPs@β-CD assembly and its dual-modal sensing of BBP (Li et al., 2019); (B) antibody labeled B-CDs@SiO2@MnO2 nanocomposite (i), dual-modal immunosensor for detection of DEP (ii) (Chen et al., 2023b) and (C) FL and SERS dual-mode sensors for detection of PAEs. Inset: upconversion emission and Raman spectral changes in spectra and photographs (Rong et al., 2021). Ultraviolet (UV), 2-morpholineethanesulfonic acid (MES), Polyethylenimine (PEI), Ascorbic acid (AA).
3 Summary and perspectives
High toxicity, wide distribution and harmfulness are the characteristics of PAEs. PAEs in the environment not only affect the growth of plants, but also accumulate in organisms and eventually enter the human body. Long-term intake of PAEs can lead to obvious depressive behavior and neurobehavioral disorders, and can increase the risk of asthma in children. In order to prevent and control the pollution of PAEs, several countries have introduced relevant limit standards in water, toys and food. The relevant limit standards of PAEs and their actual limitation of low concentration in the environment determine that it is very important to realize the sensitive detection of trace PAEs. Optical sensors have the advantages of simplicity, high selectivity, simple operation, portability and low cost, which have been applied to the detection of PAEs. Among them, CL sensors, FL sensors and SERS sensing platforms have been focused on due to their excellent detection performance, and have achieved encouraging results in the detection of PAEs. This review mainly discusses (i) the CL methods without recognition elements and the CL methods combined with aptamers and antibodies with high selectivity; (ii) the FL methods with fluorescent products or fluorescent tag; (iii) the SERS methods using Ag and Au for signal amplification, and (iv) the dual-mode methods with high accuracy. The latest research above shows that optical sensors are moving toward a broader prospect. However, due to some limitations of the optical sensor, its application in practice has not been greatly expanded. The sensitivity of CL sensors still needs to be improved. And the range of sample that detected by optical sensors has certain limitations. There is also lots of space for improvement in the portability of the detection device. The types of substances that applied by the FL sensor are very limited. The enhancement of SERS signal requires the introduction of precious metals Ag and Au, and it is necessary to find materials that can replace precious metals to reduce costs.
In the future research, the practical application of optical sensors can be expanded from the following aspects. The range of samples that detected by optical sensors should be expanded to obtain a wider range of application. More types of receptors need to be designed and explored. We can try to combine optical sensors with other transmission or storage technologies (e.g., smart phones, shared networks) to achieve real-time detection of PAEs on online platforms. It is more portable and cheaper to combine the optimized design of the optical sensors with the paper sensing system. And it can also realize the separation and simultaneous detection of multiple targets. Through programming and other technical means, the data collected by the optical sensors is processed to achieve a more convenient, fast and intuitive purpose. The optimization and development of optical sensors from the above aspects will help them consolidate their own advantages, expand their application scope, and facilitate the development of their hot fields.
Author contributions
LZ: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. MC: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Conceptualization. HD: Investigation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. QB: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Funding acquisition. XD: Writing – original draft, Supervision, Project administration, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62201230 and 32171713), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20220546), Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (No. 2021M691314), Fund of Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Food Quality and Safety, China (No. 2021KF001), Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps Key Laboratory of Modern Agricultural Machinery, China (No. XDNJ2022-001), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (No. PAPD-2023-87).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abeysinghe, H., Wickramasinghe, G., Perera, S., and Etampawala, T. (2022). MWCNT buckypaper as electrochemical sensing platform: a rapid detection technology for phthalic acid esters in solutions. Chem. Select 7:e202201900. doi: 10.1002/slct.202201900
Ansah, I. B., Lee, S. H., Mun, C., Kim, D. H., and Park, S. G. (2022). Interior hotspot engineering in ag–au bimetallic nanocomposites by in situ galvanic replacement reaction for rapid and sensitive surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy detection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:11741. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911741
Ashokan, I., and Bhunia, S. K. (2023). Boron and nitrogen co-doped bright yellow fluorescent carbon dots as real-time selective detection of phthalic acid plasticizer in aqueous medium. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 437:114489. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2022.114489
Cai, Y., Liu, C., Wang, J., Liu, X., Zhang, Y., Yang, S., et al. (2021). CuxO nanorods with excellent regenerable NADH peroxidase mimics and its application for selective and sensitive fluorimetric ethanol sensing. Anal. Chim. Acta 1186:339126. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2021.339126
Cao, Y. R., Li, J., Wu, R. B., et al. (2022). Phthalate esters in seawater and sediment of the northern South China Sea: occurrence, distribution, and ecological risks. Sci. Total Environ. 811:151412. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151412
Chen, H. (2019). Distribution, source, and environmental risk assessment of phthalate esters (PAEs) in water, suspended particulate matter, and sediment of a typical Yangtze River Delta City, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 26, 24609–24619. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05259-y
Chen, S., Fu, J., Zhou, S., Zhao, P., Wu, X., Tang, S., et al. (2022). Rapid recognition of di-n-butyl phthalate in food samples with a near infrared fluorescence imprinted sensor based on zeolite imidazolate framework-67. Food Chem. 367:130505. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130505
Chen, B., Li, L., Yang, Q., Liu, B., Hu, Y., Zhang, M., et al. (2023a). Fluorescence signal amplification: red carbon dots@SiO2-induced ultra-sensitive immunoassay for diethyl phthalate. J. Fluoresc. 33, 487–495. doi: 10.1007/s10895-022-03100-3
Chen, B., Li, L., Yang, Q., and Zhang, M. (2023b). Self-corrected dual-optical immunosensors using carbon dots@SiO2@MnO2 improving diethyl phthalate detection accuracy. Talanta 261:124652. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2023.124652
Chen, Y. Q., Wang, Z. M., and Liu, S. Y. (2021). A highly sensitive and group-targeting aptasensor for total phthalate determination in the environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 412:125174. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125174
Commission Regulation (EU) . (2018). Amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) no 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council Concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as Regards Certain Substances Classified as Carcinogenic, Mutagenic or Toxic for Reproduction (CMR), Category 1A or 1B [S/OL]. Available at: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A32018R1513#ntr2-L_2018256EN.01000101-E0002 (Accessed October 10, 2018).
Ding, X., Ahmad, W., Zareef, M., Rong, Y., Zhang, Y., Wu, J., et al. (2022). MIL-101(Cr)-induced nano-optical sensor for ultra-sensitive detection of enrofloxacin in aquatic products using a fluorescence turn-on mechanism via upconversion nanoparticles. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 365:131915. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2022.131915
Dolai, J., Ali, H., and Jana, N. R. (2021). Selective capturing and fluorescence “turn on” detection of dibutyl phthalate using a molecular imprinted nanocomposite. New J. Chem. 45, 19088–19096. doi: 10.1039/D1NJ04169J
Dong, W., Guo, R., Sun, X., Li, H., Zhao, M., Zheng, F., et al. (2019). Assessment of phthalate ester residues and distribution patterns in baijiu raw materials and baijiu. Food Chem. 283, 508–516. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.069
Dong, X., Zhang, L., Ge, M., Wu, M., Niu, Q., et al. (2024). Recent advances of sensitive electrochemical sensing platforms for rapid detection of phthalate acid esters. Instrumentation 11, 1–15. doi: 10.15878/j.instr.202400185
Fleischmann, M., Hendra, P. J., and McQuillan, A. J. (1974). Raman spectra of pyridzne adsorbed at a sliver electrode. Chem. Phys. Lett. 26, 163–166. doi: 10.1016/0009-2614(74)85388-1
Fu, L., Song, S., Luo, X., Luo, Y., Guo, C., Liu, Y., et al. (2023). Unraveling the contribution of dietary intake to human phthalate internal exposure. Environ. Pollut. 337:122580. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2023.122580
Garí, M., Koch, H. M., Pälmke, C., Jankowska, A., Wesołowska, E., Hanke, W., et al. (2019). Determinants of phthalate exposure and risk assessment in children from Poland. Environ. Int. 127, 742–753. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.04.011
Gong, C. B., Ou, X. X., Liu, S., Jin, Y. L., Huang, H. R., Tang, Q., et al. (2017). A molecular imprinting-based multifunctional chemosensor for phthalate esters. Dyes Pigments 137, 499–506. doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2016.10.047
Gong, X., Xiong, L., Xing, J., Deng, Y., Qihui, S., Sun, J., et al. (2024). Implications on freshwater lake-river ecosystem protection suggested by organic micropollutant (OMP) priority list. J. Hazard. Mater. 461:132580. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.132580
Guo, X., Li, J., Arabi, M., Wang, X., Wang, Y., Chen, L., et al. (2020). Molecular-imprinting-based surface-enhanced Raman scattering sensors. ACS Sensors 5, 601–619. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.9b02039
Guo, Z., Ren, J., Wang, J., and Wang, E. (2011). Single-walled carbon nanotubes based quenching of free FAM-aptamer for selective determination of ochratoxin A. Talanta 85, 2517–2521. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2011.08.015
Guo, R. H., Shu, C. C., Chuang, K. J., and Hong, G. B. (2021). Rapid colorimetric detection of phthalates using DNA-modified gold nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 293:129756. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2021.129756
Hidalgo-Serrano, M., Borrull, F., Marcé, R. M., and Pocurull, E. (2022). Phthalate esters in marine ecosystems: analytical methods, occurrence and distribution. Trends Anal. Chem. 151:116598. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2022.116598
Huang, P. C., Cheng, P. K., Chen, H. C., Shiue, I., Chang, W. T., Huang, H. I., et al. (2022). Are phthalate exposure related to oxidative stress in children and adolescents with asthma? A cumulative risk assessment approach. Antioxidants 11:1315. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071315
Huang, X., Sun, W., Li, Z., Shi, J., Zhang, N., Zhang, Y., et al. (2022). Hydrogen sulfide gas sensing toward on-site monitoring of chilled meat spoilage based on ratio-type fluorescent probe. Food Chem. 396:133654. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133654
Huang, X. W., Zou, X. B., Shi, J. Y., Zhi-hua, L., and Jie-wen, Z. (2018). Colorimetric sensor arrays based on chemo-responsive dyes for food odor visualization. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 81, 90–107. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2018.09.001
Jablonski, A. (1933). Efficiency of anti-stokes fluorescence in dyes. Nature 131, 839–840. doi: 10.1038/131839b0
Jiang, H., Lin, H., Lin, J., Adade, S. Y. S. S., Chen, Q., Xue, Z., et al. (2022). Non-destructive detection of multi-component heavy metals in corn oil using nano-modified colorimetric sensor combined with near-infrared spectroscopy. Food Control 133:108640. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108640
Kang, J. S., Baek, J. H., Yeong, S. M., et al. (2023). Long-term exposure changes the environmentally relevant bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate to be a neuro-hazardous substance disrupting neural homeostasis in emotional and cognitive functions. Environ. Pollut. 324:121387. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121387
Kim, S. J., Lee, Y., Choi, E. J., Lee, J. M., Kim, K. H., Oh, J. W., et al. (2023). The development progress of multi-array colourimetric sensors based on the M13 bacteriophage. Nano Conv. 10, 1–12. doi: 10.1186/s40580-022-00351-5
Kim, D., Lim, H. J., Ahn, Y. G., Chua, B., and Son, A. (2020). Development of non-equilibrium rapid replacement aptamer assay for ultra-fast detection of phthalic acid esters. Talanta 219:121216. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121216
Lan, L., Chen, D., Yao, Y., Peng, X., Wu, J., Li, Y., et al. (2018). Phase-dependent fluorescence quenching efficiency of MoS2 nanosheets and their applications in multiplex target biosensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 42009–42017. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b15677
Lee, Y., Kim, S. J., Kim, Y. J., Kim, Y. H., Yoon, J. Y., Shin, J., et al. (2023). Sensor development for multiple simultaneous classifications using genetically engineered M13 bacteriophages. Biosens. Bioelectron. 241:115642. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2023.115642
Lee, Y. M., Lee, J. E., Choe, W., Kim, T., Lee, J. Y., Kho, Y., et al. (2019). Distribution of phthalate esters in air, water, sediments, and fish in the Asan Lake of Korea. Environ. Int. 126, 635–643. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.02.059
Li, J., Dong, S., Tong, J., Zhu, P., Diao, G., Yang, Z., et al. (2016). 3D ordered silver nanoshells silica photonic crystal beads for multiplex encoded SERS bioassay. Chem. Commun. 52, 284–287. doi: 10.1039/C5CC08332J
Li, J., Hu, X., Zhou, Y., Zhang, L., Ge, Z., Wang, X., et al. (2019). β-Cyclodextrin-stabilized au nanoparticles for the detection of butyl benzyl phthalate. ACS Appl. Nano Mat. 2, 2743–2751. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.9b00258
Li, J., Li, W., Rao, Y., Shi, F., Yu, S., Yang, H., et al. (2021). Synthesis of highly ordered AgNPs-coated silica photonic crystal beads for sensitive and reproducible 3D SERS substrates. Chin. Chem. Lett. 32, 150–153. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2020.10.043
Li, W., Zhang, X., Zhang, H., Zhang, C., Chen, Y., Li, C., et al. (2023). A nanozymatic-mediated smartphone colorimetric sensing platform for the detection of dimethyl phthalate (DMP) and dibutyl phthalate (DBP). Biosensors 13:919. doi: 10.3390/bios13100919
Lim, H. J., Jin, H., Chua, B., and Son, A. (2022). Clustered detection of eleven phthalic acid esters by fluorescence of graphene quantum dots displaced from gold nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14, 4186–4196. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c21756
Lin, H., Wang, F., Lin, J., Yang, W., Kang, W., Jiang, H., et al. (2023). Detection of wheat toxigenic aspergillus flavus based on nano-composite colorimetric sensing technology. Food Chem. 405:134803. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134803
Liu, Z., Ge, D., Zhao, C., Shi, J., Zeng, Z., Fang, Z., et al. (2024). A porous silicon composite with irregular silver nano-dendritic particles: a rapid optical sensor for trace detection of malachite green in freshwater fish. Anal. Methods 16, 608–614. doi: 10.1039/D3AY02044D
Liu, J., Li, J., Li, F., Zhou, Y., Hu, X., Xu, T., et al. (2018). Liquid–liquid interfacial self-assembled au NP arrays for the rapid and sensitive detection of butyl benzyl phthalate (BBP) by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 410, 5277–5285. doi: 10.1007/s00216-018-1184-6
Liu, M., Mou, J., Xu, X., Zhang, F., Xia, J., Wang, Z., et al. (2020). High-efficiency artificial enzyme cascade bio-platform based on MOF-derived bimetal nanocomposite for biosensing. Talanta 220:121374. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121374
Liu, F., Yang, R., Chen, R., Guindo, M. L., He, Y., Zhou, J., et al. (2023). Digital techniques and trends for seed phenotyping using optical sensors. J. Adv. Res. 63, 1–16. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.11.010
Liu, X. X., Ying, Y. B., and Ping, J. F. (2020). Structure, synthesis, and sensing applications of single-walled carbon nanohorns. Biosens. Bioelectron. 167:112495. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112495
Liu, L., Zhang, T., Wu, Z., Zhang, F., Wang, Y., Wang, X., et al. (2023). Universal method for label-free detection of pathogens and biomolecules by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy based on gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 95, 4050–4058. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c04525
Lu, R., Van Beers, R., Saeys, W., Li, C., Cen, H., et al. (2020). Measurement of optical properties of fruits and vegetables: a review. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 159:111003. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2019.111003
Lu, J. Y., Wang, J. X., Li, Y., Chen, Q. Y., Qu, L. L., Meng, S. C., et al. (2021). A water caged BODIPY as fluorescence sensor of phthalates. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 331:129396. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2020.129396
Luan, C., Yang, Z. X., and Chen, B. A. (2016). Signal improvement strategies for fluorescence detection of biomacromolecules. J. Fluoresc. 26, 1131–1139. doi: 10.1007/s10895-016-1806-3
Ly, N. H., Son, S. J., Jang, S., Lee, C., Lee, J. I., and Joo, S. W. (2021). Surface-enhanced Raman sensing of semi-volatile organic compounds by plasmonic nanostructures. Nano 11:2619. doi: 10.3390/nano11102619
Ma, C., Jiang, N., Sun, X., Kong, L., Liang, T., Wei, X., et al. (2023). Progress in optical sensors-based uric acid detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 237:115495. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2023.115495
Meng, H., Yao, N., Zeng, K., Zhu, N., Wang, Y., Zhao, B., et al. (2022). A novel enzymefree ratiometric fluorescence immunoassay based on silver nanoparticles for the detection of dibutyl phthalate from environmental waters. Biosensors 12:125. doi: 10.3390/bios12020125
Mi, L. J., Xie, Z., Zhao, Z., et al. (2019). Occurrence and spatial distribution of phthalate esters in sediments of the Bohai and yellow seas. Sci. Total Environ. 653, 792–800. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.438
Nam, J. M., Oh, J. W., Lee, H., and Suh, Y. D. (2016). Plasmonic nanogap-enhanced raman scattering with nanoparticles. Acc. Chem. Res. 49, 2746–2755. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00409
Net, S., Sempéré, R., Delmont, A., Paluselli, A., and Ouddane, B. (2015). Occurrence, fate, behavior and ecotoxicological state of phthalates in different environmental matrices. Environ. Sci. Technol. 49, 4019–4035. doi: 10.1021/es505233b
Niu, X., Shi, Q., Zhu, W., Liu, D., Tian, H., Fu, S., et al. (2019). Unprecedented peroxidase-mimicking activity of single-atom nanozyme with atomically dispersed Fe–Nx moieties hosted by MOF derived porous carbon. Biosens. Bioelectron. 142:111495. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2019.111495
Pablo, L. V., Marie, G., Guillaume, R., and Menu, M. J. (2023). A review on solution-and vapor-responsive sensors for the detection of phthalates. Anal. Chim. Acta 1282:341828. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2023.341828
Qin, J., Jiang, S., Wang, Z., Cheng, X., Li, B., Shi, Y., et al. (2022). Metasurface micro/mano-optical sensors: principles and applications. ACS Nano 16, 11598–11618. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c03310
Qiu, Y. L., and Li, Y. (2018). A theoretical method for the high-sensitivity fluorescence detection of PAEs through double-substitution modification. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 25, 34684–34692. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3432-x
Reyes, J. M., and Price, P. S. (2018). Temporal trends in exposures to six phthalates from biomonitoring data: implications for cumulative risk. Environ. Sci. Technol. 52, 12475–12483. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b03338
Rong, Y., Ali, S., Ouyang, Q., Wang, L., Li, H., Chen, Q., et al. (2021). Development of a bimodal sensor based on upconversion nanoparticles and surface-enhanced Raman for the sensitive determination of dibutyl phthalate in food. J. Food Compos. Anal. 100:103929. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2021.103929
Sate Administration for Market Regulation . (2019). The Guidance of the General Administration of Market Supervision on the Prevention and Control of 'plasticizer' Pollution Risk in Food[S/OL]. Available at: https://www.samr.gov.cn/zw/zfxxgk/fdzdgknr/spscs/art/2023/art_904e69afd8ea41c69e55509556db15f0.html (Accessed November 3, 2019).
Savicheva, E. A., Mitronova, G. Y., Thomas, L., Böhm, M. J., Seikowski, J., Belov, V. N., et al. (2020). Negatively charged yellow-emitting 1-aminopyrene dyes for reductive amination and fluorescence detection of glycans. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 5505–5509. doi: 10.1002/anie.201908063
Selva Sharma, A., Marimuthu, M., Varghese, A. W., Wu, J., Xu, J., Xiaofeng, L., et al. (2024). A review of biomolecules conjugated lanthanide up-conversion nanoparticles-based fluorescence probes in food safety and quality monitoring applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 64, 6129–6159. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2163975
Seol, D., Jang, D., Oh, J. W., Cha, K., and Chung, H. (2019). Discrimination of phthalate species using a simple phage-based colorimetric sensor in conjunction with hierarchical support vector machine. Environ. Res. 170, 238–242. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2018.12.030
Soon, J. M., Brazier, A. K. M., and Wallace, C. A. (2020). Determining common contributory factors in food safety incidents - a review of global outbreaks and recalls 2008-2018. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 97, 76–87. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2019.12.030
Sun, Q., Zhang, X., Liu, C., Nier, A., Ying, S., Zhang, J., et al. (2023). The content of PAEs in field soils caused by the residual film has a periodical peak. Sci. Total Environ. 864:161078. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.161078
Tan, W., Yu, H., Huang, C., Li, D., Zhang, H., Zhao, X., et al. (2018). Intercropping wheat and maize increases the uptake of phthalic acid esters by plant roots from soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 359, 9–18. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.07.026
Tu, D., Garza, J. T., and Coté, G. L. (2019). A SERS aptasensor for sensitive and selective detection of bis (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate. RSC Adv. 9, 2618–2625. doi: 10.1039/C8RA09230C
Wang, M., Chang, M., Chen, Q., Wang, D., Li, C., and Hou, Z. (2020). Au2Pt-PEG-Ce6 nanoformulation with dual nanozyme activities for synergistic chemodynamic therapy/phototherapy. Biomaterials 252:120093. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120093
Wang, X., Chen, C., Chen, Y., Kong, F., Xu, Z., et al. (2020). Detection of dibutyl phthalate in food samples by fluorescence ratio immunosensor based on dual-emission carbon quantum dot labelled aptamers. Food Agric. Immunol. 31, 813–826. doi: 10.1080/09540105.2020.1774746
Wang, W., Leung, A. O. W., Chu, L. H., and Wong, M. H. (2018). Phthalates contamination in China: status, trends and human exposure-with an emphasis on oral intake. Environ. Pollut. 238, 771–782. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.02.088
Wang, Y., Li, W., Hu, X., Zhang, X., Huang, X., Li, Z., et al. (2021). Efficient preparation of dual-emission ratiometric fluorescence sensor system based on aptamer-composite and detection of bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in pork. Food Chem. 352:129352. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129352
Wang, M., Shi, F., Li, J., Min, L., Yang, Z., Li, J., et al. (2024). An au bipyramids@CuZn MOF core-shell nanozyme enables universal SERS and a colorimetric dual-model bioassay. Chem. Commun. 60, 6019–6022. doi: 10.1039/D4CC01602E
Wang, H., Wang, C., Huang, J., Liu, Y., Wu, Y., You, R., et al. (2023). Preparation of SERS substrate with 2D silver plate and nano silver sol for plasticizer detection in edible oil. Food Chem. 409:135363. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135363
Wang, Q., Wang, J., Li, M., Ge, Z., Zhang, X., Luan, L., et al. (2021). Size-dependent surface enhanced Raman scattering activity of plasmonic AuNS@AgNCs for rapid and sensitive detection of butyl benzyl phthalate. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 248:119131. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2020.119131
Wang, F., Wang, Y., Xiang, L., Redmile-Gordon, M., Gu, C., Yang, X., et al. (2022). Perspectives on ecological risks of microplastics and phthalate acid esters in crop production systems. Soil Ecol. Lett. 4, 97–108. doi: 10.1007/s42832-021-0092-4
Wang, H., Wu, F., Wu, L., Guan, J., and Niu, X. (2023). Nanozyme colorimetric sensor array based on monatomic cobalt for the discrimination of sulfur-containing metal salts. J. Hazard. Mater. 456:131643. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131643
Wang, Y., Zhang, K. W., and Du, Y. K. (2022). Recent progress of carbon dot fluorescent probes for tetracycline detection. New J. Chem. 46, 20554–20560. doi: 10.1039/D2NJ04064F
Wang, D. N., Zhang, Y. Z., Zhao, X. Y., and Xu, Z. (2019). Plasmonic colorimetric biosensor for visual detection of telomerase activity based on horseradish peroxidase-encapsulated liposomes and etching of au nanobipyramids. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 296:126646. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2019.126646
Wang, Y., Zhou, Z., Xu, W., Luan, Y., Lu, Y., Yang, Y., et al. (2018). Surface molecularly imprinted polymers based ZnO quantum dots as fluorescence sensors for detection of diethylhexyl phthalate with high sensitivity and selectivity. Polym. Int. 67, 1003–1010. doi: 10.1002/pi.5596
Wang, Y., Zhu, H. K., and Kannan, K. (2019). A review of biomonitoring of phthalate exposures. Toxics 7:21. doi: 10.3390/toxics7020021
World Health Organization . (2021). Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/food-safety (Accessed March 15, 2021).
Wu, M. C., Lin, M. P., Lin, T. H., and Su, W. F. (2018). Ag/SiO2 surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate for plasticizer detection. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 57:04FM07. doi: 10.7567/JJAP.57.04FM07
Wu, J., Lv, W., Yang, Q., Li, H., and Li, F. (2021). Label-free homogeneous electrochemical detection of MicroRNA based on target-induced anti-shielding against the catalytic activity of two-dimension nanozyme. Biosens. Bioelectron. 171:112707. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112707
Xu, S., Li, H., Guo, M., Wang, L., Li, X., Xue, Q., et al. (2021). Liquid–liquid interfacial self-assembled triangular ag nanoplate-based high-density and ordered SERS-active arrays for the sensitive detection of dibutyl phthalate (DBP) in edible oils. Analyst 146, 4858–4864. doi: 10.1039/D1AN00713K
Xu, H., Zhu, J. H., and Cheng, Y. X. (2021). Functionalized UIO-66@ag nanoparticles substrate for rapid and ultrasensitive SERS detection of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in plastics. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 349:130793. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2021.130793
Xu, H., Zhu, J., Wu, X., Cheng, Y., Wang, D., Cai, D., et al. (2023). Recognition and quantitative analysis for six phthalate esters (PAEs) through functionalized ZIF-67@ag nanowires as surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 284:121735. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2022.121735
Xue, Y. C., and Jiang, H. (2023). Monitoring of chlorpyrifos residues in corn oil based on Raman spectral deep-learning model. Foods. 12:2402. doi: 10.3390/foods12122402
Yan, Y., Qu, Y., Du, R., Zhou, W., Gao, H., Lu, R., et al. (2021). Colorimetric assay based on argininefunctionalized gold nanoparticles for the detection of dibutyl phthalate in baijiu samples. Anal. Methods 13, 5179–5186. doi: 10.1039/D1AY01464A
Yanagisawa, H., and Fujimaki, S. (2019). Simple colorimetric determination of phthalates in polymers by dye formation. Anal. Sci. 35, 1215–1219. doi: 10.2116/analsci.19P165
Yang, Y. Y., Li, Y. T., Li, X. J., Zhang, L., Kouadio Fodjo, E., and Han, S. (2020). Controllable in situ fabrication of portable AuNP/mussel-inspired polydopamine molecularly imprinted SERS substrate for selective enrichment and recognition of phthalate plasticizers. Chem. Eng. J. 402:125179. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.125179
Yang, H., Li, J., Rao, Y., Yang, L., Xue, Y., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). Ultrasensitive multiplex SERS immunoassay based on porous au-ag alloy nanoparticle–amplified Raman signal probe and encoded photonic crystal beads. Microchim. Acta 190:13. doi: 10.1007/s00604-022-05539-4
You, J. J., Liu, H., Zhang, R. R., Pan, Q. F., Sun, A. L., Zhang, Z. M., et al. (2022). Development and application of tricolor ratiometric fluorescence sensor based on molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for visual detection of dibutyl phthalate in seawater and fish samples. Sci. Total Environ. 848:157675. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157675
Yu, L. L., Song, Z. R., Peng, J., Yang, M., Zhi, H., He, H., et al. (2020). Progress of gold nanomaterials for colorimetric sensing based on different strategies. Trends Anal. Chem. 127:115880. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2020.115880
Zeng, H. H., Li, X. Q., Hao, W. L., Zhang, L. Z., Wei, T., Zhao, X. F., et al. (2017). Determination of phthalate esters in airborne particulates by heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyzed aromatic hydroxylation fluorimetry. J. Hazard. Mater. 324, 250–257. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.10.055
Zhang, T., Guan, A., Wang, G., Huang, X., Li, W., Liu, C., et al. (2023). Magnetic molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for rapid and selective detection of dimethyl phthalate in water using SERS. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 11, 11149–11160. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.3c01847
Zhang, Y. J., Guo, J. L., Xue, J. C., Bai, C. L., and Guo, Y. (2021). Phthalate metabolites: characterization, toxicities, global distribution, and exposure assessment. Environ. Pollut. 291:118106. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118106
Zhang, Y., Han, Y., Liu, Z., Fan, L., Guo, Y., et al. (2023). Colorimetric and electrochemical assay for dual-mode detection of di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate based on hemin-graphene nanocomposites. Microchem. J. 191:108788. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2023.108788
Zhang, W., Liu, J., Niu, W., Yan, H., Lu, X., Liu, B., et al. (2018). Tip-selective growth of silver on gold nanostars for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 14850–14856. doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b19328
Zhang, T., Liu, Y., Pi, J., Lu, N., Zhang, R., Chen, W., et al. (2022). A novel artificial peroxisome candidate based on nanozyme with excellent catalytic performance for biosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 196:113686. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113686
Zhang, J. F., Zhang, Y., and Shi, G. Y. (2022). Interface engineering with self-assembling au@ag@β-cyclodextrin bimetal nanoparticles to fabricate a ring-like arrayed SERS substrate for sensitive recognition of phthalate esters based on a host–guest interaction and the coffee ring effect. Anal. Methods 14, 259–268. doi: 10.1039/D1AY01636A
Zhang, H., Zhang, M., Zhou, Y., Qiao, Z., Gao, L., Cao, L., et al. (2024). Organic photoelectrochemical transistor aptasensor for dual-mode detection of DEHP with CRISPR-Cas13a assisted signal amplification. J. Hazard. Mater. 470:134175. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.134175
Zhang, D., Zhou, K., Liu, C., Li, X., Pan, S., Zhong, L., et al. (2023). Dissipation, uptake, translocation and accumulation of five phthalic acid esters in sediment-Zizania latifolia system. Chemosphere 315:137651. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137651
Zhang, C., Zhou, J., Ma, T., Guo, W., Wei, D., Tan, Y., et al. (2023). Advances in application of sensors for determination of phthalate esters. Chin. Chem. Lett. 34:107670. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2022.07.013
Zhao, T., Chen, Q., Wen, Y., Bian, X., Tao, Q., Liu, G., et al. (2022). A competitive colorimetric aptasensor for simple and sensitive detection of kanamycin based on terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated signal amplification strategy. Food Chem. 377:132072. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132072
Zhao, Y., Sun, Y., Zhu, C., Zhang, Y., Hou, J., Zhang, Q., et al. (2022). Phthalate metabolites in urine of Chinese children and their association with asthma and allergic symptoms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19:14083. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192114083
Zhou, Z., Li, T., Xu, W., Huang, W., Wang, N., Yang, W., et al. (2017). Synthesis and characterization of fluorescence molecularly imprinted polymers as sensor for highly sensitive detection of dibutyl phthalate from tap water samples. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 240, 1114–1122. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.09.092
Zhou, Y., Li, J., Zhang, L., Ge, Z., Wang, X., Hu, X., et al. (2019). HS-β-cyclodextrin-functionalized ag@Fe3O4@ag nanoparticles as a surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy substrate for the sensitive detection of butyl benzyl phthalate. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 411, 5691–5701. doi: 10.1007/s00216-019-01947-3
Zhu, N., Li, X., Liu, Y., Liu, J., Wang, Y., Wu, X., et al. (2021). Dual amplified ratiometric fluorescence ELISA based on G-quadruplex/hemin DNAzyme using tetrahedral DNA nanostructure as scaffold for ultrasensitive detection of dibutyl phthalate in aquatic system. Sci. Total Environ. 784:147212. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147212
Zhu, F., Zhang, H., Qiu, M., Wu, N., Zeng, K., Du, D., et al. (2019). Dual-label time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay as an advantageous approach for investigation of diethyl phthalate & dibutyl phthalate in surface water. Sci. Total Environ. 695:133793. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133793
Zhu, N. F., Zou, Y. M., Huang, M. L., Dong, S., Wu, X., Liang, G., et al. (2018). A sensitive, colorimetric immunosensor based on cu-MOFs and HRP for detection of dibutyl phthalate in environmental and food samples. Talanta 186, 104–109. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2018.04.023
Glossary
Keywords: phthalic acid esters, fluorescence, colorimetric, surface-enhanced Raman, detection
Citation: Zhang L, Chen M, Duan H, Bu Q and Dong X (2024) Recent advances of optical sensors for point-of-care detection of phthalic acid esters. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1474831. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1474831
Edited by:
Zhanjun Yang, Yangzhou University, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Zhang, Chen, Duan, Bu and Dong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiuxiu Dong, ZG9uZ3h4QHVqcy5lZHUuY24=
 Lili Zhang
Lili Zhang Mingming Chen2
Mingming Chen2 Quan Bu
Quan Bu Xiuxiu Dong
Xiuxiu Dong