- 1Department of Public Health, College of Health Sciences, Salale University, Fiche, Ethiopia
- 2Department of Postharvest Management, Jimma University College of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine, Jimma, Ethiopia
Introduction: Foodborne infections caused by a variety of variables pose serious public health risks, resulting in significant morbidity and mortality in poor nations like Ethiopia. However, the study contains a deficit in information about food safety practices and associated factors. Thus, this study assessed food safety practices and influencing factors among food handlers in public food establishments in Adama town, Central Ethiopia.
Methods: An institution-based cross-sectional design was used for this study. A total of 319 food handlers were selected through systematic random sampling, with data collected through face-to-face interviews using the Kobo tool. The data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, binary and multivariate logistic regressions using SPSS V-27. Significant factors associated with food safety practices were determined based on Adjusted Odds Ratios (AOR), 95% Confidence Intervals (CI), and a significance level set at p < 0.05.
Results and discussion: The findings revealed that 64.79% of food handlers exhibited commendable food safety practices. Factors significantly associated with the food safety practices included knowledge (AOR = 2.106, 95% CI: 1.23–3.606), attitude (AOR = 2.0, 95% CI: 1.169–3.334), ownership status of the establishment (AOR = 2.65, 95% CI: 1.48–4.98), and monthly salary (AOR = 0.516, 95% CI: 0.293–0.906). Food safety practices among food handlers in public food establishments rank as medium compared to other studies conducted in the country. These findings indicates the vital role of education, awareness campaigns, and training programs in promoting safe food handling practices. Therefore, to ensure safe and healthy food, there is a need for targeted interventions, mainly focusing on improving food handler knowledge and attitudes, to enhance food safety standards in public food establishments. It is recommended that authorities and organizations prioritize significant factors identified in this study to reduce foodborne illnesses, ensure public health, and foster a culture of responsible food-handling practices.
Introduction
Food safety practices are crucial for protecting people from illnesses caused by contaminated food. This includes a set of procedures that should be followed in food establishments to ensure safe food consumption (Abegaz, 2022; Hassauer and Roosen, 2020). A key aspect of food safety is proper food handling, which includes all steps in preparing, storing, serving food and also from its arrival at an establishment to when it is consumed. Every stage, from production to consumption, requires careful attention to ensure the food is free from harmful contaminants (Holban and Grumezescu, 2018).
World Health Organization emphasized food safety as a critical global concern and has identified five key practices: maintaining cleanliness, separating raw and ready-to-eat food, thorough cooking, proper temperature control, and rigorous raw materials inspection (Haddad et al., 2020). However, foodborne illnesses remain a significant threat, often stemming from inadequate food handling practices within the food supply chain and establishments. These outbreaks can impact large populations simultaneously, posing a major public health challenge (Islam et al., 2023; Grace, 2015). The impact of foodborne diseases is particularly acute in low-and middle-income countries, especially those in Africa and sub-Saharan regions. Beyond the immediate health risks, poor food safety practices obstruct progress toward sustainable development goals focused on ending hunger and poverty, while also promoting overall health and wellbeing (Hoffmann et al., 2019; Morse et al., 2018).
Annually, 420,000 deaths, 600 million illnesses, and 33 million lost years of healthy life are attributed to foodborne diseases, affecting one in 10 people worldwide (World Health Organization, 2022; Faour-Klingbeil and Todd, 2020; Lee and Yoon, 2021). In the United States alone, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report approximately 48 million annual cases of illness, with 128,000 hospitalizations and 3,000 deaths attributed to foodborne diseases (Mattia and Manikonda, 2018; Kim, 2023). In Africa, microbiological and chemical food contamination results in 91 million acute illnesses and 137,000 deaths annually, contributing to 1,200 Disability Life Years (DALYs) per 100,000 people in Eastern and Southern Africa (World Health Organization, 2016). Ethiopia also faces a similar challenge as a foodborne bacterial illnesses account for a significant proportion of reported illnesses and drug resistance. These diseases result in a substantial economic loss of at least 723 million USD annually and cause an estimated 1,570 deaths and 3.1 million illnesses per year (Ayana et al., 2015; Tesfaye, 2023).
Although food safety practices and associated factors in public food establishments are a global concern, implementation of these practices varies significantly across countries. In California, a meta-analysis reported an 80.0% implementation rate of general food safety practices in public food establishments (Insfran-Rivarola et al., 2020). Similar findings emerged from Brazil, with self-reported and observational methods revealing rates of 80.71 and 75.40%, respectively (Souza et al., 2018). In South Asia, food safety practices among food handlers in Lahore, Pakistan, were reported at 65.34% (Ahmed et al., 2021). A meta-analysis of Asian low-and middle-income countries revealed an average food safety practice rate of 59.8% in public food establishments (Kwoba et al., 2023). African countries show diverse rates, ranging from 71% in South Africa to 56% in Malaysia, 62.9% in Ghana, and 59% in Egypt (Nyawo et al., 2021; Tuglo et al., 2021; Abd Lataf Dora-Liyana et al., 2018; Allam et al., 2016).
Similarly, Ethiopian government has established regulations and guidelines for food handling in public food establishments, including licensing requirements and health inspections. However, implementing food safety standards effectively in the country faces challenges. These include a lack of training, financial resources, and limited knowledge about food safety among food handlers and consumers. Additionally, some traditional food preparation practices may not align with modern food safety standards. Previous research in Ethiopia has emphasized the significant variability in food safety practices across different regions. For instance, two meta-analyses reported prevalence rates of food safety issues in public food establishments at 50.72 and 47.14%, respectively (Tamene et al., 2022; Tadele et al., 2022). Furthermore, regional studies demonstrate this variability, with rates ranging from 53.1% in Makelle Town, Tigray, to 49.5–72.4% in various areas of the Amhara region (Azanaw et al., 2019; Chekol et al., 2019; Adane et al., 2018; Lalit et al., 2015). Towns like Adama, Addis Ababa Bole Subsite, Fitche, and Bishoftu also show diverse levels of implementation of food safety practices (Girmay et al., 2022; Abdi et al., 2020; Teferi, 2020).
Foodborne illnesses are a significant public health problem in Ethiopia, mainly due to widespread unsafe food handling practices and different factors. These practices, which occur at every stage of the food chain from farm to table, lead to contamination by harmful bacteria (Chen and Alali, 2018). For or example, a study conducted in Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, found that mothers’ lack of awareness of microbes was substantially connected with foodborne infections (Saeed et al., 2021). In Kenya, being female, possessing a valid medical examination certificate, and not boiling or sanitizing water before delivering it to consumers were all risk factors for foodborne pathogen infections (Kimemia et al., 2023). In Indonesia, the risk factors for foodborne disease were nail hygiene, knowledge level, nail trimming activity, and hand-washing behavior (Lubis et al., 2019). Therefore, placing greater emphasis on safe food handling practices can significantly reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses, thereby protecting consumer health.
Food establishments that adhere to safe handling practices build trust with customers, encouraging repeat business and contributes to economic growth by ensuring the safety and quality of food products, promoting tourism, and supporting the local food industry. While previous studies in Ethiopia, identified multiple factors influencing food safety practices including food handler knowledge, manager supervision, and sanitation facilities, training, attitude, education, income, and work experience (Tamene et al., 2022; Teferi, 2020), these studies have primarily relied on quantitative and cross-sectional approaches, A significant gap remains in understanding these factors comprehensively through a mixed-methods approaches. Thus, this study aims to address this gap by offering a comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing food safety practices in Adama town. It seeks to fill important information gaps and provide valuable insights to improve food safety measures in Ethiopia.
This finding will contribute to developing practical solutions to enhance food safety practices and protect consumers’ health. Beyond identifying factors contributing to food safety risks, the study uses its findings to inform practical interventions to improve food safety practices. This finding analyzed the interplay of various factors and identified specific areas where food handlers require additional training, support, and resources to improve their practices. The result of this study will also inform food establishments and relevant authorities about developing effective policies and strategies that promote better food safety practices within food establishments. Ultimately, this contributes to public health by protecting consumers’ health and reducing the incidence of foodborne illnesses.
Methods
Study setting and design
The study employed an institution-based cross-sectional design. The study was conducted in Adama town from July 15, 2023, to October 23, 2023, aimed to gather information through both primary and secondary data sources. Primary data was collected through surveys, interviews with key informants, and site visits/field observations. Secondary data sources included a review of existing literature and archived data from the district health offices. Adama was established in 1916 to support the Addis Ababa-Djibouti railway line. Adama town was chosen for this study because of its strategic location and economic significance. It is located in the East Shewa Zone, 99 kilometers southeast of Addis Ababa’s capital. According to the town’s Tourism and Culture office, the town is home to a thriving food service industry, with 1,110 establishments, including hotels, restaurants, and cafeterias. The town also serves as a key agricultural hub and a significant industrial center, which makes the town a strong representation of the challenges and opportunities many towns face in Ethiopia’s development trajectory.
Population and eligibility
The source population included all public food establishments recognized in Adama town at the time of the survey. The survey considered 319 respondents from from three categories of food establishments (hotels, restaurants, and cafeterias) in Adama town. Food handlers, irrespective of sex and employment status, who were at least 18 years old and had been actively engaged in the preparation, butcher shops, and food service areas within food establishments during the study period were included. Food handlers who faced hearing, speaking, or overall communication challenges were excluded from the study inorder to get more details and valid data.
Sample size determination and procedures
The single population proportion formula was used to determine the sample size needed to assess the level of food safety practices among food handlers in public food establishments. Based on a prevalence of food safety practices observed in a study in Bishoftu town (51.0%), with a 95% confidence level and a 5% margin of error, the initial calculation yielded a sample size (n) of 384 (Kim, 2023).
Where:
• N is the minimum possible sample size
• Z α/2 is the standard score value for 95% confidence level
• P is the population proportion (prevalence)
• d is the margin of error (5%)
As the total population is less than 10,000, a correction was applied using the formula:
The sample size was calculated using the double population proportion to identify factors associated with food safety practices among public food establishments. The calculation considered a confidence level of 95%, a power of 80%, and a ratio of 1 (unexposed: exposed). In the unexposed group (those with training), the proportion of good food safety practices was 0.18, while in the exposed group (those without training), it was 0.33. The calculation yielded a sample size of 290. By considering a 10% non-response rate, the total sample size for the second objective was 319, with the following assumptions.
The Adama Town Tourism and Culture Office provided 1,110 public food establishments, categorized as 210 hotels, 354 restaurants (including butcher shops), and 546 cafeterias (including juice houses and Shiro houses). Sample proportional allocation and a systematic random sampling technique were employed to select representatives: 60 hotels, 102 restaurants, and 157 cafeterias. The lottery method determined the starting point, and the interval (K) was set at 4 K were added to the starting point to identify the selected establishments until the required sample size was reached. If more than two food handlers were present, the lottery method was applied to select one kitchen worker, waiter, or butcher.
Methods of data collection and quality assurance
The survey employed questionnaires developed through literature review and standard guidelines, translated into local languages (Afaan Oromo and Amharic) and back-translated to ensure consistency. After questionnaire development, four trained health professionals, including two nurses, one clinical nurse, and one environmental health professional, were recruited as enumerators. Enumerators underwent twodays training session emphasizing impartiality, responsibilities, and respondent rights, ensuring standardized and unbiased data collection.
Data cleaning procedures were developed to detect and correct outliers or anomalies in the collected data, ensuring accuracy and reliability. The reliability of knowledge, attitude, and food safety practice questionnaires was assessed using a Cronbach-alpha test, and consistency scores of 0.722, 0.846, and 0.79, respectively. Since the value of Cronbach alpha is greater than 0.7, the reliability in the collected data was good.
Similarly, for the food hygienic practices data, 23 questions were used to categorize their practices into good and poor depending on their answer. Therefore, for every correct answer, the score is one (Abegaz, 2022) point and for every wrong answer, the score zero (0) point. Then, an individual could score a minimum of zero and a maximum of 23 points. Thus, the respondents who scored less than mean out of 23 questions had poor food safety practices and those who scored greater than or equal to mean had good food practices.
Study variables
The dependent variable for this study was food safety practice. Independent variables included sociodemographic factors like sex, monthly income, service years, age, marital status, educational status, Job description, food safety training medical certificate and other factors like level of food establishment, ownership of food establishments, knowledge status, attitude status, environmental factors like liquid waste disposal, functional latrine, dishwashing system, work clothes, pip water in a cooking area, pip water for customers, shower room, refrigerator and legal license.
Statistical analysis
In the quantitative analysis, data from the Kobo tool were transferred to Microsoft Excel and imported into SPSS version 27. Cleaning procedures were implemented to ensure accuracy and consistency and address missing values, utilizing descriptive statistics like frequencies and proportions. Variables related to food safety knowledge, attitudes, and practices were dichotomized, employing coding such as “yes = 1” and “no = 0” for some and a five-scale measurement of attitudes. Collinearity effects were examined using tolerance values and variance inflation factor (VIF), excluding violating variables. Non-collinear covariates were incorporated into a binary logistic regression model. Simple binary logistic regression identified significant variables (p < 0.2) included in the multivariate binary logistic regression. The model’s fitness was evaluated using the Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test. Inferential statistics, including binary logistic regression analysis, determine variables related to the dependent variable. Significance was reported based on the adjusted odds ratio (AOR), 95% confidence interval (CI), and a p-value less than 0.05.
Results
Sociodemographic characteristics
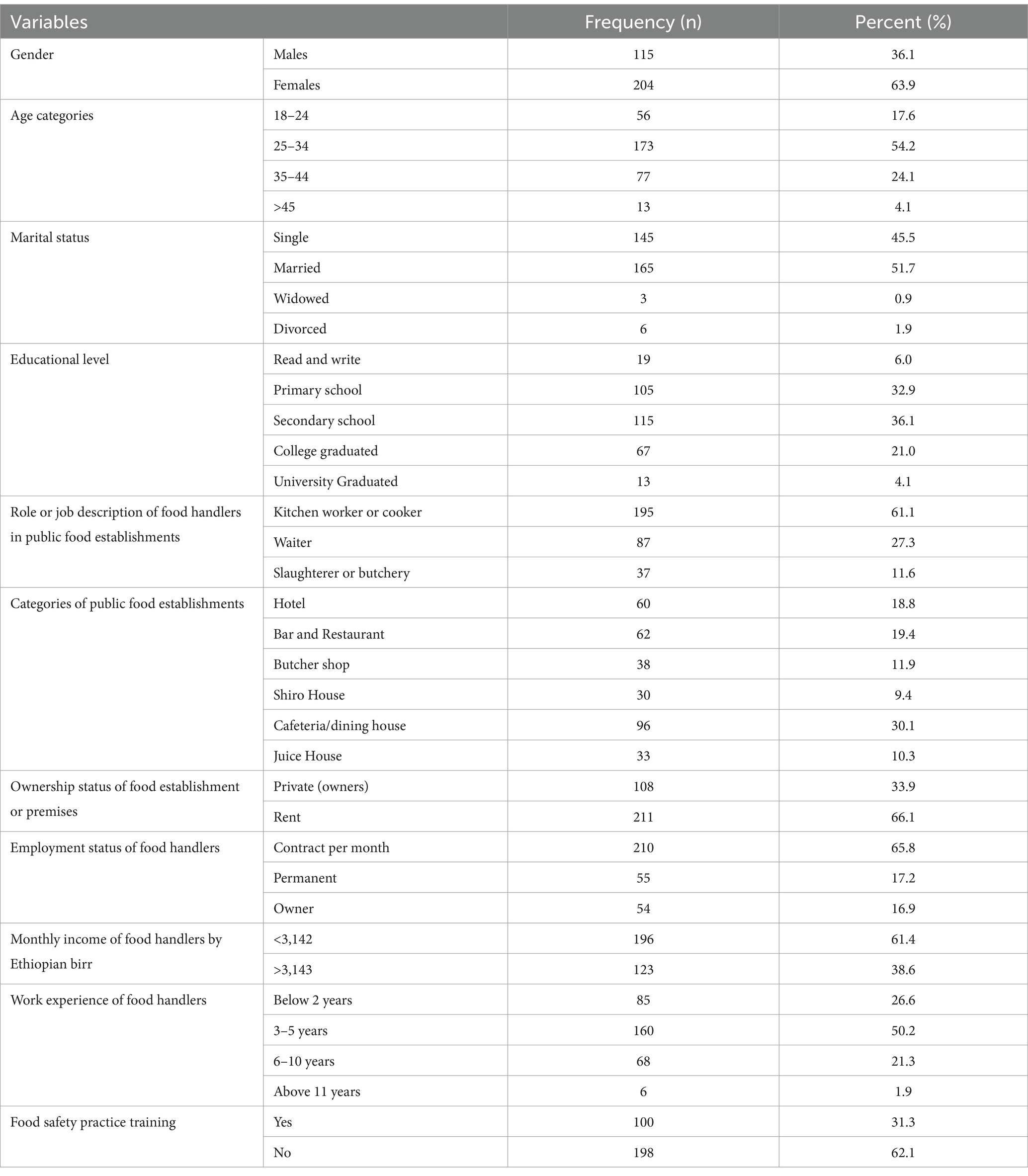
In this study involving 319 respondents with a 100% response rate, a diverse demographic profile of food handlers in public food establishments was observed. The demographic snapshot of individuals in this study reveals a predominantly female presence, accounting for 63% of the participants, underscoring the substantial contribution of women. The mean age of the participants was 30.17 ± 6.36, with the highest frequency observed among those aged 25 years. Employment-wise, the majority were on monthly contracts (65.8%), and the mean monthly salary stood at 4,018.50 ± 3561.50 birr, with 61.4% earning less than 3,142 Ethiopian birr. Regarding work experience, 50.2% had 3–5 years of experience, and 31.3% had received food safety practice training. Additionally, a significant percentage of establishments were rented (66.1%) (Table 1).
Food handlers’ knowledge toward food safety practices
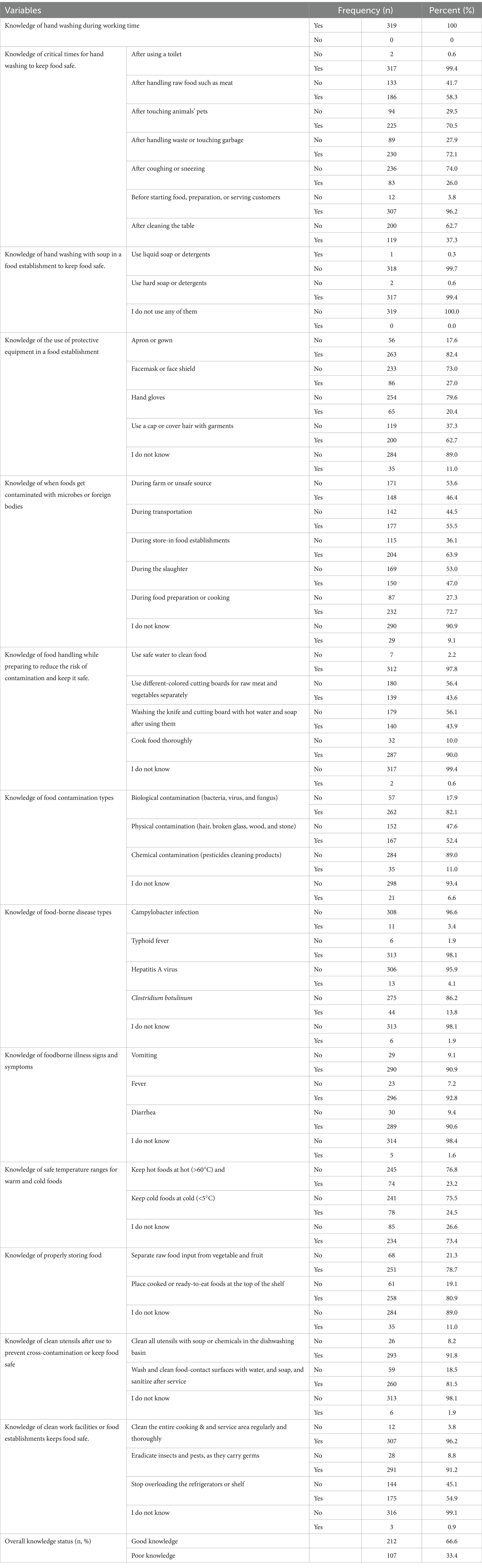
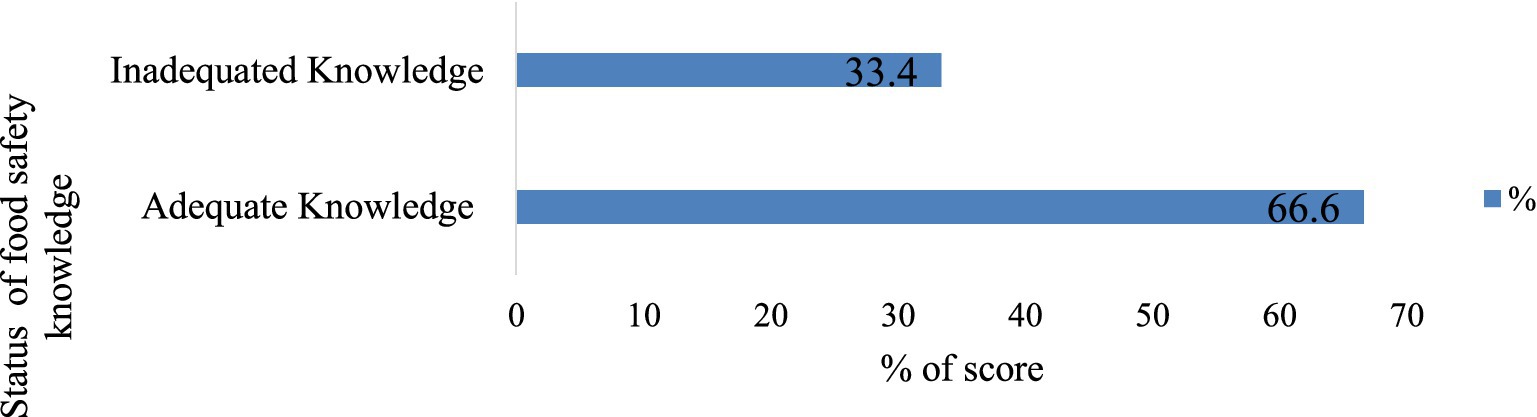
The mean knowledge score of respondents to the food safety knowledge questionnaire was 25.7981 ± 4.014. Handwashing knowledge was universally high (100%), with 75.2% recognizing critical times, especially after using the toilet. Knowledge of protective equipment usage was observed by 58.5%, while understanding food contamination sources and safe handling practices was reported by 65.4 and 74%, respectively. Recognition of different types of food contamination (51.2%) and foodborne diseases (29.8%) varied (Table 2). The poor knowledge and good knowledge toward food safety practices among food handlers were 33.45 and 66.6%, respectively (Figure 1). While all food establishments provided soap and other personal protective materials, a significant number of food handlers demonstrated inadequate knowledge about their proper use, posing a potential risk to food safety.
Food handlers’ attitude toward food safety practices
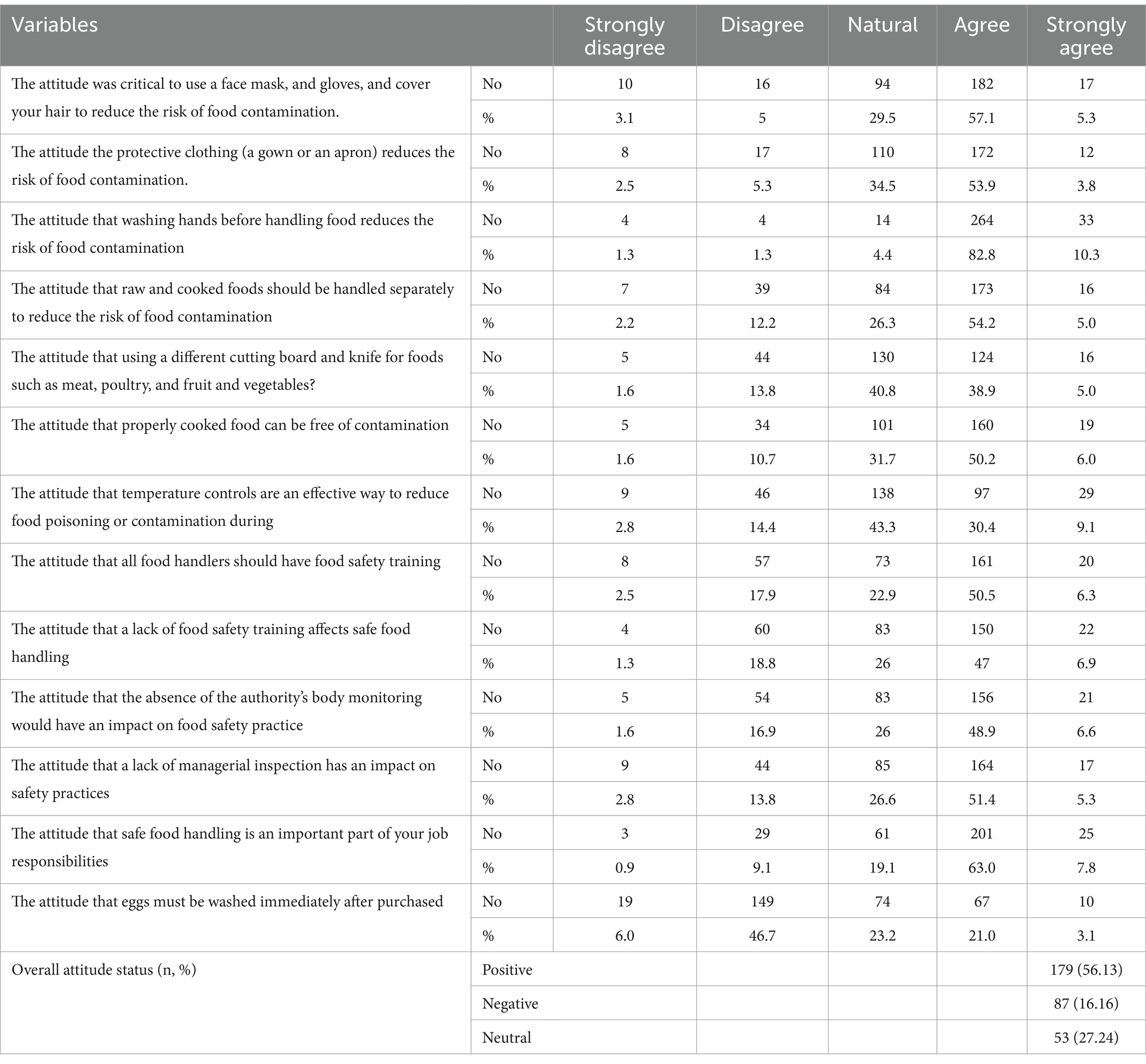
The mean attitude score of participants was 41.30 ± 4.99, indicating that 66.1% held favorable attitudes toward food safety practices. Regarding food handling, 70.5% supported separate handling to decrease contamination, and 62.4% endorsed using different cutting boards for meat and vegetables. Awareness of adequately cooked food was high (70.8%), and 54.5% believed in temperature controls to reduce contamination (Table 3).
Food handlers’ food safety practice status
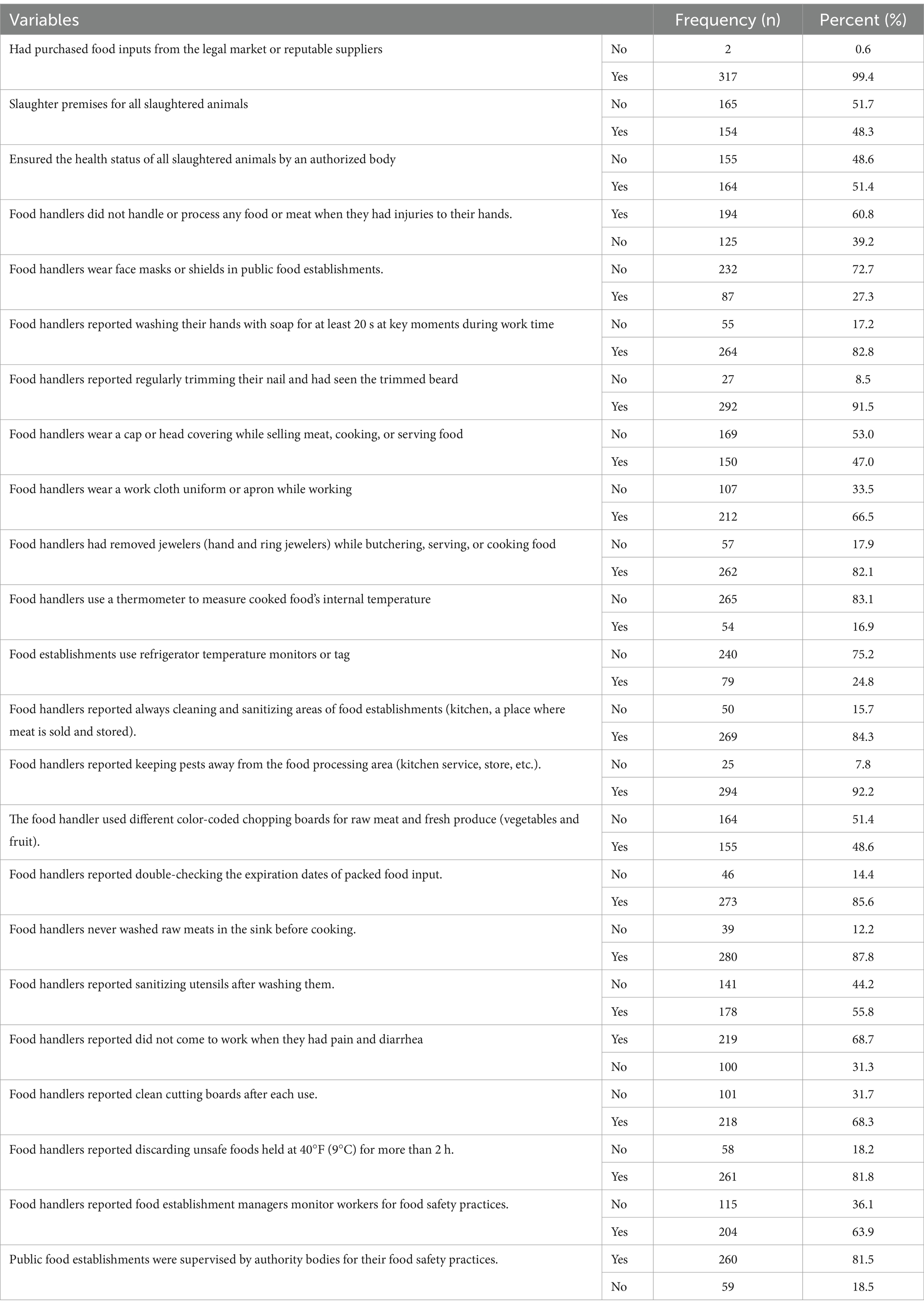
An analysis of food safety practices revealed a mean score of 11.21 ± 1.49, with 64.97% demonstrating commendable practices. Notably, 99.4% of establishments sourced food legally, and 94% of handlers maintained proper personal hygiene. However, only 19.1% used thermometers for cooked food, and 35.7% monitored refrigerator temperatures. Effective pest control (94.7%) and color-coded chopping boards (71.8%) were positive aspects, while 89% discarded unsafe foods, and 69% reported managerial oversight (Table 4).
The finding of this study reveals that good and poor practices among food handlers were 65 and 35%, respectively (Figure 2).
Inspection of resources or infrastructure status of food establishments
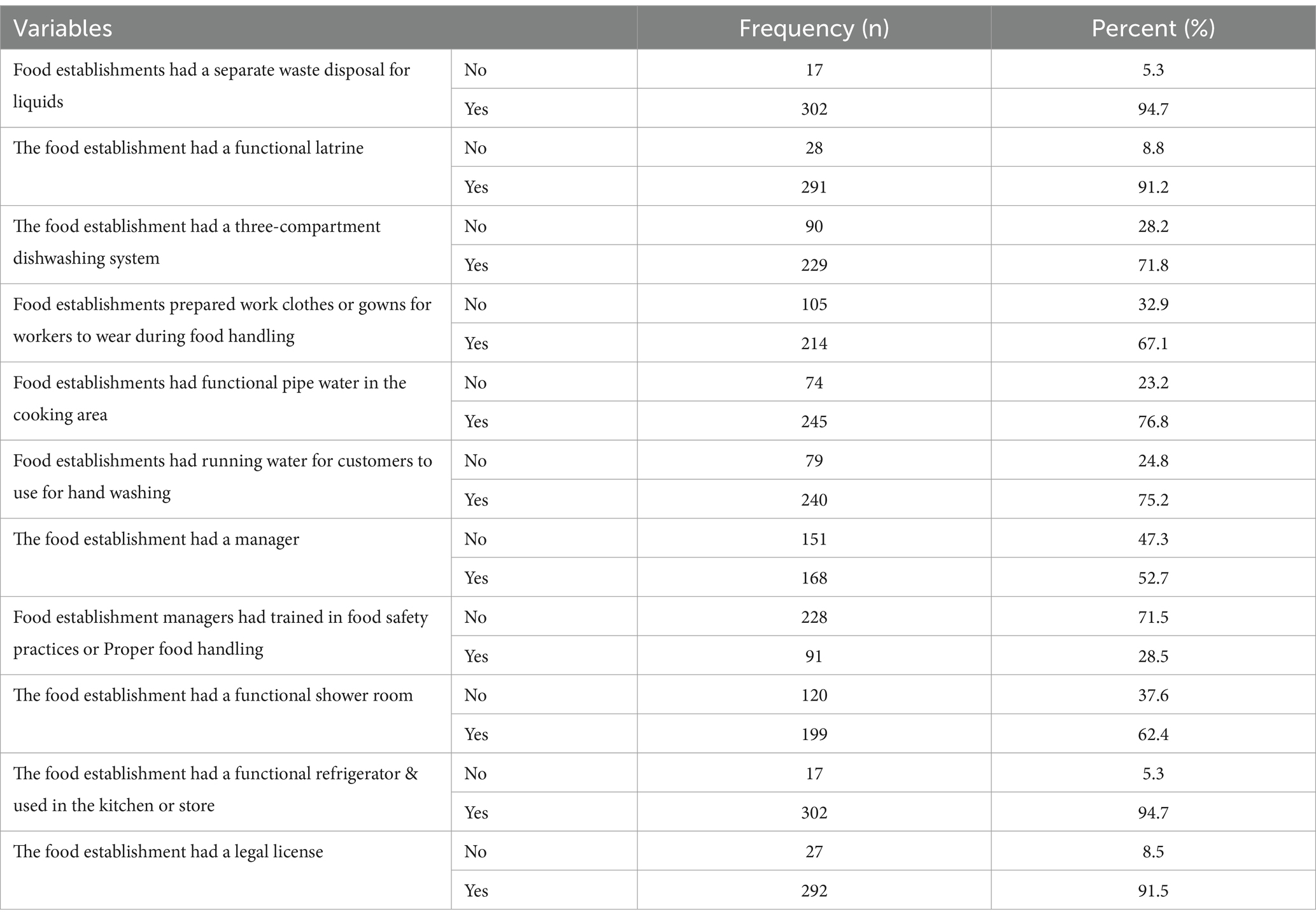
The inspection checklist analysis revealed robust infrastructure in public food establishments. Notably, 94.7% had functional refrigerators, and 91.5% possessed legal trading licenses. Facilities demonstrated commitment to waste management (94.7%) and sanitation with functional latrines (91.2%). Access to piped water for cooking (76.8%) and customer handwashing facilities (75.2%) contributed to overall hygiene. However, only 28.5% of establishments reported managerial training in food safety, suggesting a potential area for improvement (Table 5).
Factors associated with food safety practice
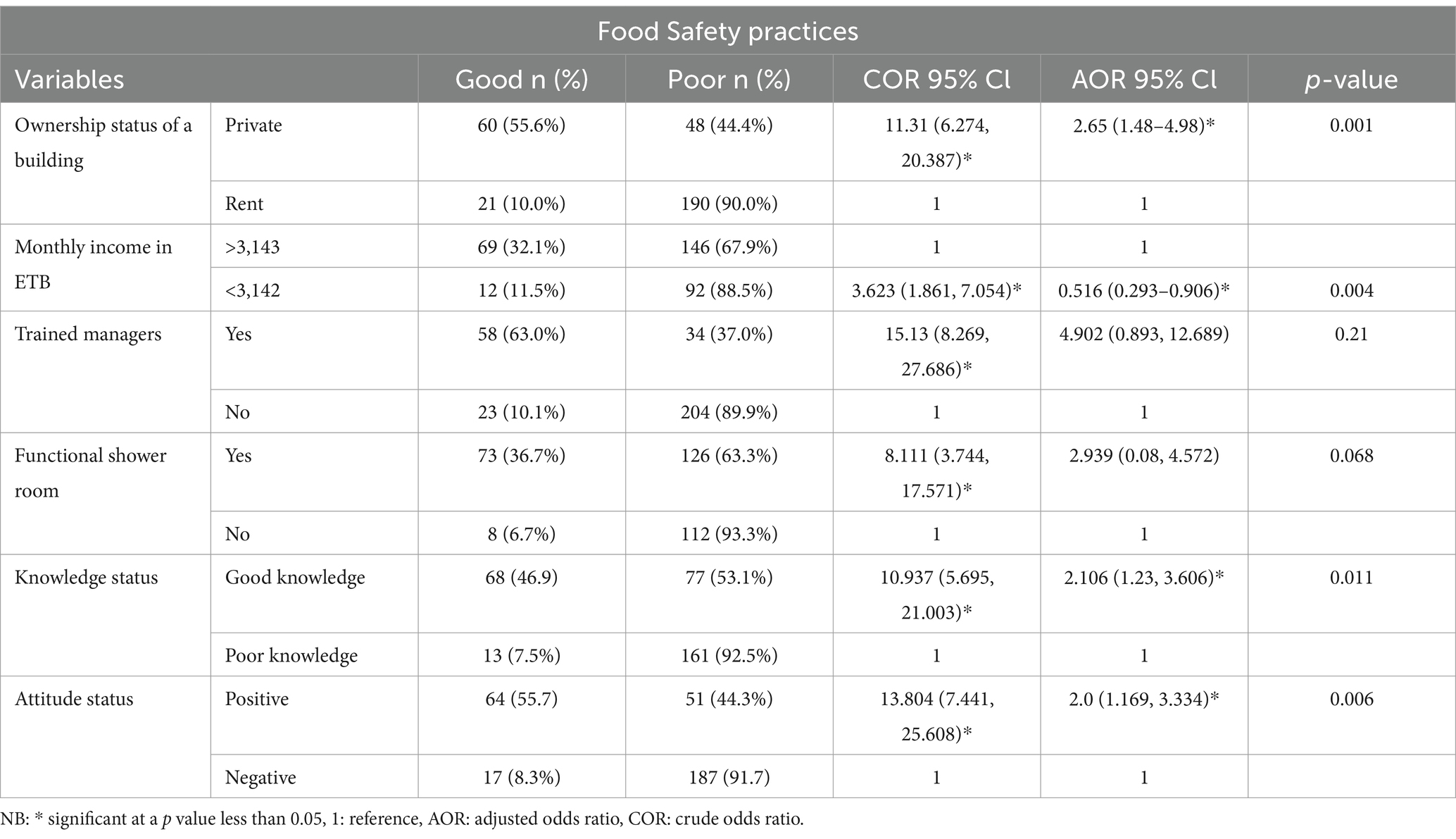
The multivariable logistic regression analysis, knowledge (AOR = 2.106, 95% CI: 1.23–3.606), attitude (AOR = 2.0, 95% CI: 1.169–3.334), ownership status of the establishment (AOR = 2.65, 95% CI: 1.48–4.98), and monthly salary (AOR = 0.516, 95% CI: 0.293–0.906) were identified as the key factors significantly associated with food safety practices among food handlers in public establishments (Table 6).
Discussion
The study revealed that 64.79% of food handlers in public food establishments in Adama town exhibit medium food safety practices. The study’s results align with findings from similar studies conducted in Bahir Dar, 67.6% (Chen and Alali, 2018) and Asosa, 67.8% (Saeed et al., 2021). This similarity may be attributed to shared sociodemographic characteristics, including comparable educational levels among respondents and adherence to national regulatory guidelines for food safety in towns of a similar nature. However, the observed percentages in this study are lower than those reported in studies from Dassie town of Ethiopia, 72.4% (Adane et al., 2018), South Africa, 71% (Teffo, 2017) and Indonesia, 82% (Putri and Susanna, 2021). The variance in results could be attributed to differences in environmental factors influencing food safety practices, the effectiveness of food safety training programs, the level of regulatory activities by governing bodies, and the concerted efforts of the respondents. Sociodemographic disparities, particularly the higher educational levels of food handlers in studies abroad, may contribute to variations in food safety practices.
In the study, food handlers with adequate food safety knowledge were 2.1 times more likely to practice good food safety than those with poor knowledge. The study findings are in line with studies conducted in Addis Ababa Bole sub-city (Abdi et al., 2020), Fitche town of Ethiopia (Teferi et al., 2021), and Namibia (Hakwenye, 2019). The similarity in results may stem from shared sociodemographic characteristics such as educational status, monthly income, and cultural factors among the respondents. Additionally, the comparable national economic status could impact the food safety knowledge of food handlers domestically and abroad. However, it is dissimilar to studies done in Debre Markos town (Alemayehu et al., 2021), Mettu and Bedelle towns (Tamiru et al., 2022), and Gondar town of northern Ethiopia (Yenealem et al., 2020). These disparities may arise from variations in the study settings, the developmental status of the researched sites, and differences in the sociodemographic profiles of respondents, including work experience and exposure to food safety training. These results reinforce the evidence that adequate knowledge of food safety plays a crucial role in encouraging and supporting food handlers to practice good food safety in public food establishments.
The study identified a significant association between the attitudes of food handlers toward food safety practices. The research revealed that having a positive attitude toward food safety practices increases the likelihood of food handlers practicing good food safety, making them twice as likely as those with negative attitudes. This finding is in line with studies conducted the Addis Ababa Bole sub-city (Abdi et al., 2020), Batu town (Abe and Arero, 2021) and Walkite town of the southern Ethiopia (Oumer, 2019). The similarity of study findings could be due to the culture of food safety practices among respondents and data management methods. However, it is dissimilar to study findings from Northwest Ethiopia, Deblek town (Chekol et al., 2019) and western parts of Ethiopia, Mettu and Bedelle towns (Tamiru et al., 2022). The variation may be attributed to social desirability bias, study setting differences, and measurement tool variations. This might also be the level of food safety practices increases if food handlers have positive attitudes toward food safety practices.
Moreover, the study revealed that food handlers working in private premises were 2.65 times more likely to exhibit good food safety practices than those in rental premises. This finding contradicts with a study conducted in Mekelle town (Lalit et al., 2015). The variability in results across studies may stem from differences in study settings, interviewer bias, and data management methods. This could be due to the fact that ensuring well-maintained private facilities could create a more conducive environment for implementing and sustaining food safety protocols.
Furthermore, those food handlers who had a lower monthly salary were 48.4% less likely to practice food safety than those with higher earnings. The study findings align with research conducted in Woldia town (Bantie et al., 2023) and Bahir Dar City of Ethiopia (Reta et al., 2021). However, it differs from a study in Ghana (Tuglo et al., 2021) and Dessie town of Ethiopia (Adane et al., 2018). This disparity could be due to differences in sociodemographic characteristics and sample size related to the country’s economics.
Conclusion
The research findings indicated that the food safety practices of food handlers in public food establishments are at a moderate level when compared to similar studies conducted nationwide. Key factors influencing food safety practices include knowledge, attitude, ownership of food establishments, and monthly income. It is imperative for all relevant authorities to prioritize providing food safety training to both owners and employees to enhance their understanding and approach toward food safety practices, ultimately safeguarding the wellbeing of the public.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The Institutional Ethics Review Board of Salale University (SLU Protocol Approval 2023/242) granted ethical approval for this study and written consent to participate were obtained before inclusion.
Author contributions
NG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MM: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Writing – original draft. CK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their sincere gratitude to Salale University and Oromia Health Bureau.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abd Lataf Dora-Liyana, N. A., Mahyudin, M. R., Ismail-Fitry, A. A., and Rasiyuddin, H. (2018). Food safety and hygiene knowledge, attitude and practices among food handlers at boarding schools in the northern region of Malaysia. Soc. Sci. 8, 238–266. doi: 10.6007/IJARBSS/v8-i17/5228
Abdi, A. M., Amano, A., Abrahim, A., Getahun, M., Ababor, S., and Kumie, A. (2020). Food hygiene practices and associated factors among food handlers working in food establishments in the bole Sub City, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Risk Manage. Healthc. Policy 13, 1861–1868. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S266342
Abe, S., and Arero, G. (2021). Food handlers safety practices and related factors in the public food establishments in Batu town, Central Oromia, Ethiopia. Health 2, 1–8.
Abegaz, S. B. (2022). Food safety practices and associated factors in food operators: a cross-sectional survey in the students’ cafeteria of Woldia University, North Eastern Ethiopia. Int. J. Food Sci. 2022, 1–12. doi: 10.1155/2022/7400089
Adane, M., Teka, B., Gismu, Y., Halefom, G., and Ademe, M. (2018). Food hygiene and safety measures among food handlers in street food shops and food establishments of Dessie town, Ethiopia: a community-based cross-sectional study. PLoS One 13:e0196919. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196919
Ahmed, M. H., Akbar, A., and Sadiq, M. B. (2021). Cross sectional study on food safety knowledge, attitudes, and practices of food handlers in Lahore district, Pakistan. Heliyon 7:e08420. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08420
Alemayehu, T., Aderaw, Z., Giza, M., and Diress, G. (2021). Food safety knowledge, handling practices and associated factors among food handlers working in food establishments in Debre Markos Town, Northwest Ethiopia, 2020: institution-based cross-sectional study. Risk Manage. Healthc. Policy 14, 1155–1163. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S295974
Allam, H. K., Al-Batanony, M. A., Seif, A. S., and Awad, E. T. (2016). Hand contamination among food handlers. Brit. Microbiol. Res. J. 13, 1–8. doi: 10.9734/BMRJ/2016/24845
Ayana, Z., Yohannis, M., and Abera, Z. (2015). Food-borne bacterial diseases in Ethiopia. Acad. J. Nutr. 4, 62–76.
Azanaw, J., Gebrehiwot, M., and Dagne, H. (2019). Factors associated with food safety practices among food handlers: facility-based cross-sectional study. BMC. Res. Notes 12, 1–6. doi: 10.1186/s13104-019-4702-5
Bantie, G. M., Woya, A. A., Ayalew, C. A., Mitiku, K. W., Wubetu, G. A., Aynalem, Z. B., et al. (2023). Food safety and hygiene practices and the determinants among street vendors during the chain of food production in Northwest Ethiopia. Heliyon 9:e22965. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22965
Chekol, F. A., Melak, M. F., Belew, A. K., and Zeleke, E. G. (2019). Food handling practice and associated factors among food handlers in public food establishments, Northwest Ethiopia. BMC Res. Notes 12, 1–7. doi: 10.1186/s13104-019-4047-0
Chen, L., and Alali, W. (2018). Editorial: recent discoveries in human serious foodborne pathogenic Bacteria: resurgence, pathogenesis, and control strategies. Front. Microbiol. 9:2412. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02412
Faour-Klingbeil, D., and Todd, E. C. D. (2020). Prevention and control of foodborne diseases in Middle-East North African countries: review of national control systems. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17:70. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17010070
Girmay, A. M., Mengesha, S. D., Weldetinsae, A., Alemu, Z. A., Dinssa, D. A., Wagari, B., et al. (2022). Factors associated with food safety practice and drinking-water quality of food establishments in Bishoftu town, Ethiopia. Discov. Food 2:35. doi: 10.1007/s44187-022-00037-1
Haddad, F., Yahfoufi, N., Abou Haidar, M., and Hoteit, M. (2020). Knowledge, attitude and practices of Lebanese married women towards food safety. Atena J. Public Health 2:6.
Hakwenye, H. L. (2019). Knowledge, attitudes and practices on food safety among food handlers in Opuwo district, Kunene region, Namibia (Doctoral dissertation): University of Namibia.
Hassauer, C., and Roosen, J. (2020). Toward a conceptual framework for food safety criteria: analyzing evidence practices using the case of plant protection products. Saf. Sci. 127:104683. doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2020.104683
Hoffmann, V., Moser, C., and Saak, A. (2019). Food safety in low and middle-income countries: the evidence through an economic lens. World Dev. 123:104611. doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2019.104611
Holban, A. M., and Grumezescu, A. M. (2018). Food safety and preservation: modern biological approaches to improving consumer health : Elsevier.
Insfran-Rivarola, A., Tlapa, D., Limon-Romero, J., Baez-Lopez, Y., Miranda-Ackerman, M., Arredondo-Soto, K., et al. (2020). A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of food safety and hygiene training on food handlers. Food Secur. 9:1169. doi: 10.3390/foods9091169
Islam, S., Thangadurai, D., Sangeetha, J., and Cruz-Martins, N. (Eds.) (2023). Global food safety: microbial interventions and molecular advancements. Routledge: CRC Press.
Kim, T. N. (2023). Evaluating environmental health agency-level interventions for foodborne illness outbreak prevention and surveillance (Doctoral dissertation): University of Minnesota.
Kimemia, J. M., John, G. K., Alfred, O. O., and Murima, P. N. A. (2023). Factors associated with foodborne pathogens among food handlers: a case study of Thika, Kiambu County, Kenya. Adv. Public Health 2023, 1–12. doi: 10.1155/2023/9918421
Kwoba, E., Oduori, D. O., Lambertini, E., Thomas, L. F., Grace, D., and Mutua, F. (2023). Food safety interventions in low-and middle-income countries in Asia: a systematic review. Zoonoses Public Health 70, 187–200. doi: 10.1111/zph.13028
Lalit, I., Brkti, G., and Dejen, Y. (2015). Magnitude of hygienic practices and its associated factors of food handlers working in selected food and drinking establishments in Mekelle town, northern Ethiopia. Int. Food Res. J. 22.
Lee, H., and Yoon, Y. (2021). Etiological agents implicated in foodborne illness world wide. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 41, 1–7. doi: 10.5851/kosfa.2020.e75
Lubis, N. D., Sri, A., Nurfida, K. A., and Muhammad, F. R. (2019). Modelling of risk factors associated with foodborne disease among school-aged children in Medan, Indonesia. Open Access Macedonian J. Med. Sci. 7, 3302–3306. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2019.721
Mattia, D. D., and Manikonda, K. (2018). Morbidity and mortality weekly report surveillance for foodborne disease outbreaks—United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention MMWR editorial and production staff MMWR editorial board. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 6262:1.
Morse, T. D., Masuku, H., Rippon, S., and Kubwalo, H. (2018). Achieving an integrated approach to food safety and hygiene—meeting the sustainable development goals in sub-saharan Africa. Sustain. For. 10:2394. doi: 10.3390/su10072394
Nyawo, T., Kesa, H., and Onyenweaku, E. (2021). Food safety and hygiene: knowledge, attitude and practices among food handlers. African J. Hosp. Tour. Leis. 10, 547–558. doi: 10.46222/ajhtl.19770720.117
Oumer, A. (2019). Determinants of food safety practices among food handlers in selected food establishments. Int. J. Public Health Sci. 8, 229–237. doi: 10.11591/ijphs.v8i2.18364
Putri, M. S., and Susanna, D. (2021). Food safety knowledge, attitudes, and practices of food handlers at kitchen premises in the port ‘X’area, North Jakarta, Indonesia 2018. Italian. J. Food Saf. 10. doi: 10.4081/ijfs.2021.9215
Reta, M. A., Lemma, M. T., Gemeda, A. A., and Lemlem, G. A. (2021). Food handling practices and associated factors among food handlers working in public food and drink service establishments in Woldia town, Northeast Ethiopia. Pan Afr. Med. J. 40:128. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2021.40.128.19757
Saeed, B. Q., Tareq, M. O., and Sadi, T. (2021). Foodborne diseases risk factors associated with food safety knowledge and practices of women in Sharjah-united Arab emirate. Food Control 125:108024. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108024
Souza, C. V., Azevedo, P. R., and Seabra, L. M. (2018). Food safety in Brazilian popular public restaurants: food handlers’ knowledge and practices. J. Food Saf. 38:e12512. doi: 10.1111/jfs.12512
Tadele, M. M., Dagnaw, A., and Alamirew, D. (2022). Food handling practice and associated factors among food handlers in public food establishments of Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 12:e051310. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-051310
Tamene, A., Habte, A., Woldeyohannes, D., Afework, A., Endale, F., Gizachew, A., et al. (2022). Food safety practice and associated factors in public food establishments of Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 17:e0268918. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268918
Tamiru, S., Bidira, K., Moges, T., Dugasa, M., Amsalu, B., and Gezimu, W. (2022). Food safety practice and its associated factors among food handlers in food establishments of Mettu and Bedelle towns, Southwest Ethiopia, 2022. BMC Nutr. 8:151. doi: 10.1186/s40795-022-00651-3
Teferi, S. C. (2020). A review on food hygiene knowledge, practice and food safety in Ethiopia. Sci. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 5, 023–029. doi: 10.7176/FSQM/105-04
Teferi, S. C., Sebsibe, I., and Adibaru, B. (2021). Food safety practices and associated factors among food handlers of fiche town, north Shewa zone, Ethiopia. J. Environ. Public Health 2021, 1–7. doi: 10.1155/2021/6158769
Teffo, LA . Food safety knowledge and attitudes of food handlers in hospitals in the Capricorn District municipality in Limpopo Province, South Africa (Doctoral dissertation). (2017).
Tesfaye, H. Foodborne diseases cost Ethiopia USD 723 million annually, study the reporter latest Ethiopian news today. Ethiopian Reporter (2023), p 1–4. Available at: https://www.thereporterethiopia.com/37135/ (Accessed October 28, 2023).
Tuglo, L. S., Agordoh, P. D., Tekpor, D., Pan, Z., Agbanyo, G., and Chu, M. (2021). Food safety knowledge, attitude, and hygiene practices of street-cooked food handlers in north Dayi District, Ghana. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 26:54. doi: 10.1186/s12199-021-00975-9
World Health Organization . (2022). World food safety day 2022 in pictures and numbers (no. WHO/HEP/NFS/AFS/2022.8). World Health Organization. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/food-safety (Accessed 10 October 2022).
World Health Organization . (2016). Department of maternal, newborn, child and adolescent health (MCA): progress report 2014–15.
Keywords: food handling, food safety, practices, public food establishment, Ethiopia
Citation: Gemeda N, Yazew T, Moroda M and Kuyu CG (2025) Food safety practices and associated factors among food handlers in food establishments in Adama town, Central Ethiopia. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1471429. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1471429
Edited by:
Shoukui He, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, ChinaReviewed by:
Kalmia Kniel, University of Delaware, United StatesAgnes Kilonzo-Nthenge, Tennessee State University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Gemeda, Yazew, Moroda and Kuyu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tamiru Yazew, dGFtaXJ1eWF6ZXcyMDEyQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Nimona Gemeda
Nimona Gemeda Tamiru Yazew
Tamiru Yazew Meseret Moroda
Meseret Moroda Chala G. Kuyu2
Chala G. Kuyu2