- 1School of Land Science and Spatial Planning, Hebei GEO University, Shijiazhuang, China
- 2International Science and Technology Cooperation Base of Hebei Province, Hebei International Joint Research Center for Remote Sensing of Agricultural Drought Monitoring, Hebei GEO University, Shijiazhuang, China
- 3Regional Institutions Research Center, Hebei GEO University, Shijiazhuang, China
- 4Natural Resources Big Data Application Center, Hebei Geographic Information Group Co., Ltd., Shijiazhuang, China
- 5School of Big Data Application and Economics, Guizhou University of Finance and Economics, Guiyang, China
- 6School of Foreign Languages, Guizhou University of Finance and Economics, Guiyang, China
Improving the eco-efficiency of cultivated land use (ECLU) is important for ensuring food security, promoting social and economic development, and reducing carbon emissions. However, dynamic inter-period comparisons of the ECLU and clarifications of its influencing factors are limited. We calculated the ECLU at the county level in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, China, based on the super-efficiency slacks-based measure and global Malmquist–Luenberger index and analyzed its influencing factors utilizing a geographically and temporally weighted regression model. From 2000 to 2020, the number of higher counties decreased and that of medium counties increased. Geographically, the ECLU values in the north are higher than those in other districts and counties; counties in Beijing and Tianjin maintained moderate ECLU values, whereas Zhangjiakou and Chengde maintained high ECLU values. The ECLU value in the study area showed a trend of rapid decline–slow rise–continuous rise, with the upward trend of the ECLU value in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region being significantly less pronounced than those in most counties of Hebei Province. Resource allocation and scale expansion where initially dominant; however, technological progress and investment eventually prevailed. The ECLU is mainly affected by the multiple cropping index, industrial structure, irrigation index, mechanized farming level, and per capita cultivated land. This study assesses the ECLU in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, providing a scientific basis for the formulation and implementation of relevant policies for its improvement. Furthermore, this study enriches the theory and methods of research on the ECLU and has practical value and theoretical significance. Overall, the results have important social value as they contribute to ensuring national food security, reducing carbon emissions, promoting regional coordinated and sustainable development.
1 Introduction
Food security is a fundamental requirement for human survival and development, constituting a major concern worldwide (Rosegrant and Cline, 2003). According to the definition of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations (UN), food security refers to ensuring that all humans can afford and have access to their basic food requirements at any time. Ensuring the production of sufficient food, maximizing the stability of the food supply, and ensuring that all humans in need can obtain food are connotations of food security as a concept. According to the FAO publication The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2023, in 2022, between 691 and 783 million people worldwide suffered from hunger. Owing to population growth, changes in dietary structure, and increased bioenergy applications, food production will need to increase by an estimated 100–110% to meet the demand in 2050 (Tilman et al., 2011; Smith, 2013). In particular, the necessary increase of grain production requires increased grain yield and/or further expansion of the cultivated land area, which is limited by the need to protect the ecological environment and the decline of cultivated land quality (Foley et al., 2011; Smith, 2013; Liu Q. et al., 2023; Ye et al., 2024; Ye et al., 2023).
China and India are the most populous countries in the world, harboring over 1.4 billion people each. Among them, China is characterized by trends of increasing population and reduced available land; therefore, its policies are prioritizing national food security. By ensuring national food security, China is a major contributor to world food security. Having experienced a period of rapid economic growth, China is still in the stage of rapid urbanization, which has led to the expansion of the construction land area, allowing only limited potential for expansion of the cultivated land area (Liu et al., 2014; Ye et al., 2020). In this context, improving the cultivated land use (CLU) efficiency has become a key factor affecting the regional sustainable development and food security (Fei et al., 2021). The essence of the CLU efficiency is that in a certain cultivated land area, producers pursue social and economic benefits by investing in various production factors to obtain the expected output ratio (Kuang et al., 2020). Moreover, with the ongoing deterioration of the ecological environment, which is a direct consequence of global warming, CLU has acquired further connotations. For example, the ecological benefits stemming from CLU have been incorporated into the evaluation of CLU, thereby leading to the concept of the eco-efficiency of cultivated land use (ECLU) (Ma et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2023). Specifically, the ECLU is the degree to which social and economic outputs can be maximized and environmental pollution can be minimized through certain inputs of cultivated land production factors, while pursuing the broader objective of tandem social, economic, and ecological benefits (Cui et al., 2021; Ke et al., 2022; Xiao et al., 2022). Studying the spatial–temporal differentiation of the ECLU and its influencing factors can not only clarify the current situation and evolution process of CLU intensity, but also reveal its mechanism of action, which is of considerable practical significance for optimally allocating cultivated land resources, ensuring food security, and promoting regional sustainable development (Liu and Zhang, 2023).
Recently, the ECLU has garnered considerable research attention worldwide, with efficiency measurements, spatial–temporal analyses, causal mechanisms, and research scales attracting particular interest. Numerous methods have been used for calculating the ECLU regionally, such as the stochastic frontier approach (Ma et al., 2023), data envelopment analysis (DEA) (Tone, 2002, 2004, 2010; Fukuyama and Weber, 2010; Xiang et al., 2020; Ma et al., 2023), slacks-based measure (SBM) (Chen and Xie, 2019; Chen et al., 2020; Luo et al., 2020; Yang et al., 2021; Yin et al., 2022), super-efficiency SBM (Super-SBM) (Zhou et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2020; Lu et al., 2020; Cao et al., 2022; Ke et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2023), super epsilon-based measure (Super-EBM) (Li M. et al., 2023) and SBM–DEA (Cecchini et al., 2018; Kuang et al., 2020) models, the Malmquist–Luenberger (ML) (Chung et al., 1997; Han and Zhang, 2020a) and global Malmquist–Luenberger (GML) (Oh, 2010; Li and Wenbo, 2017) indices, and the non-radial directional distance function (NDDF) (Xie et al., 2018). In turn, methods such as spatial auto-correlation, kernel density, Markov chain, Thiel index, and Dagum Gini coefficient have been used to analyze the spatial pattern and evolution of the CLU efficiency (Fan et al., 2021; Tan et al., 2021; Zhou et al., 2022; Ke et al., 2023). To elucidate causal mechanisms, indicators affecting the ECLU selected on the basis of measuring the CLU efficiency have been employed to highlight potential influencing factors through the use of tobit models, panels, and geographically and temporally weighted regressions (GTWRs) along with geographical detectors (Zhou et al., 2018; Chen and Xie, 2019; Xiao et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2022; Feng et al., 2023; Ma et al., 2024). Scholars have also explored the impacts of single factors, such as agricultural productive services, rural labor transfer, landscape pattern change, and environmental regulation, on the ECLU (Huang et al., 2024; Zou et al., 2022; Liu C. et al., 2023; Li M. et al., 2023). Furthermore, ECLU research has ranged from macro-scale, e.g., national (Oh, 2010; Han and Zhang, 2020b; Liu et al., 2020; Yang et al., 2023), provincial (Zhou et al., 2018; Chen and Xie, 2019; Kuang et al., 2020; Xiao et al., 2022), and municipal (Lu et al., 2020; Ke et al., 2023), to micro-scale, e.g., villages (Xiang et al., 2020), farms (Gómez-Limón et al., 2012; Bonfiglio et al., 2017; Lin and Hülsbergen, 2017; Cecchini et al., 2018), farm households (Qu et al., 2021), landscapes (Hou et al., 2021), and specific geographical areas (Kühling et al., 2016; Chen et al., 2020; Fan et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2021; Zhou et al., 2022; Feng et al., 2023). However, most studies have used single modeling methods, such as Super-SBM, to measure the ECLU. Such methods are limited with regard to incorporating undesired outputs and making dynamic inter-period comparisons (Ma et al., 2023). Although the GML index addresses these shortcomings (Xie et al., 2018; Luo et al., 2020), few studies have combined the two methods to measure the ECLU (Oh, 2010; Han and Zhang, 2020a; Ma et al., 2023). Moreover, existing research has predominantly focused on certain macro-scales or individual micro-scales, and relatively few studies have adopted meso-scales, e.g., county, as evaluation units. Notably, the county is a basic unit of national governance in China. Therefore, considering county as the evaluation unit can more accurately reflect the spatial–temporal evolution patterns of ECLU and reveal influencing factors, thereby laying a foundation for the precise formulation and effective implementation of regulatory policies in China.
The Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region is an important agricultural production area in China. However, rapid economic development and urbanization have led to encroachment on high-quality cultivated land and a decline in land quality, posing challenges to regional food production security and sustainable CLU. Additionally, water and air pollution, declining groundwater levels, desertification, and other ecological and environmental issues are prominent in this region. Coupled with pronounced fertilizer use and over-exploitation of cultivated land, these phenomena have resulted in increased carbon emissions and agricultural non-point-source pollution. A more comprehensive understanding of the spatial–temporal patterns of the ECLU and influencing factors in this region can clarify the evolution of the ECLU and facilitate optimization of the management modes of cultivated land resources. Furthermore, this information is critical regarding effectively promoting coordinated and sustainable development of land use, cultivated land, and ecological environment, ultimately ensuring food security in China as well as other countries worldwide.
To address these issues, we posed the following questions, taking the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region as the study area and county as the evaluation unit:
1. What are the spatial–temporal differentiation characteristics of the ECLU?
2. What are the dynamic evolution patterns of the ECLU?
3. What are the influencing factors of the ECLU evolution?
To this end, we incorporated undesired outputs, such as non-point-source pollution and carbon emission produced during the CLU process, into the evaluation index system, combined Super-SBM with the GML index to calculate the ECLU in the study region at the county scale, analyzed its spatial–temporal differentiation and dynamic changes, and conducted efficiency decomposition. By directly incorporating undesirable outputs, considering slack variables, allowing super-efficiency scores, and having non-radial and non-angular characteristics, the Super-SBM model constitutes a more powerful and flexible tool for conducting efficiency evaluation of decision making units. We also utilized the GTWR method to reveal the factors influencing the evolution of the ECLU in specific counties in the study region. Overall, our findings serve as a reference for conducting generalized studies of regional ECLU as well as generating relevant data in the underinvestigated Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, providing a scientific basis for the precise formulation and implementation of policies on regional ECLU.
2 Data and methods
2.1 Study area
The Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region is among the most socioeconomically developed regions in China. Considered as a world-class city cluster with the capital as its core, the coordinated development of Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei has been incorporated into China’s national strategy. The region includes the two municipalities of Beijing and Tianjin, and eleven prefecture-level cities in Hebei Province, namely Shijiazhuang, Baoding, Tangshan, Langfang, Qinhuangdao, Zhangjiakou, Chengde, Cangzhou, Hengshui, Xingtai, and Handan. As of 2020, the regional population has exceeded 107 million people, accounting for approximately 7.6% of the total population in China. The region comprises 120,000 km2, representing 2.35% of the national land area, containing a vast plain area with a terrain that slopes from high in the northwest to low in the southeast. The region is located in a warm, temperate, semi-humid monsoon climate zone. Due to its favorable physical geography, the region has become a major agricultural production area in China. An overview of the study area is shown in Figure 1.
2.2 Research methodology
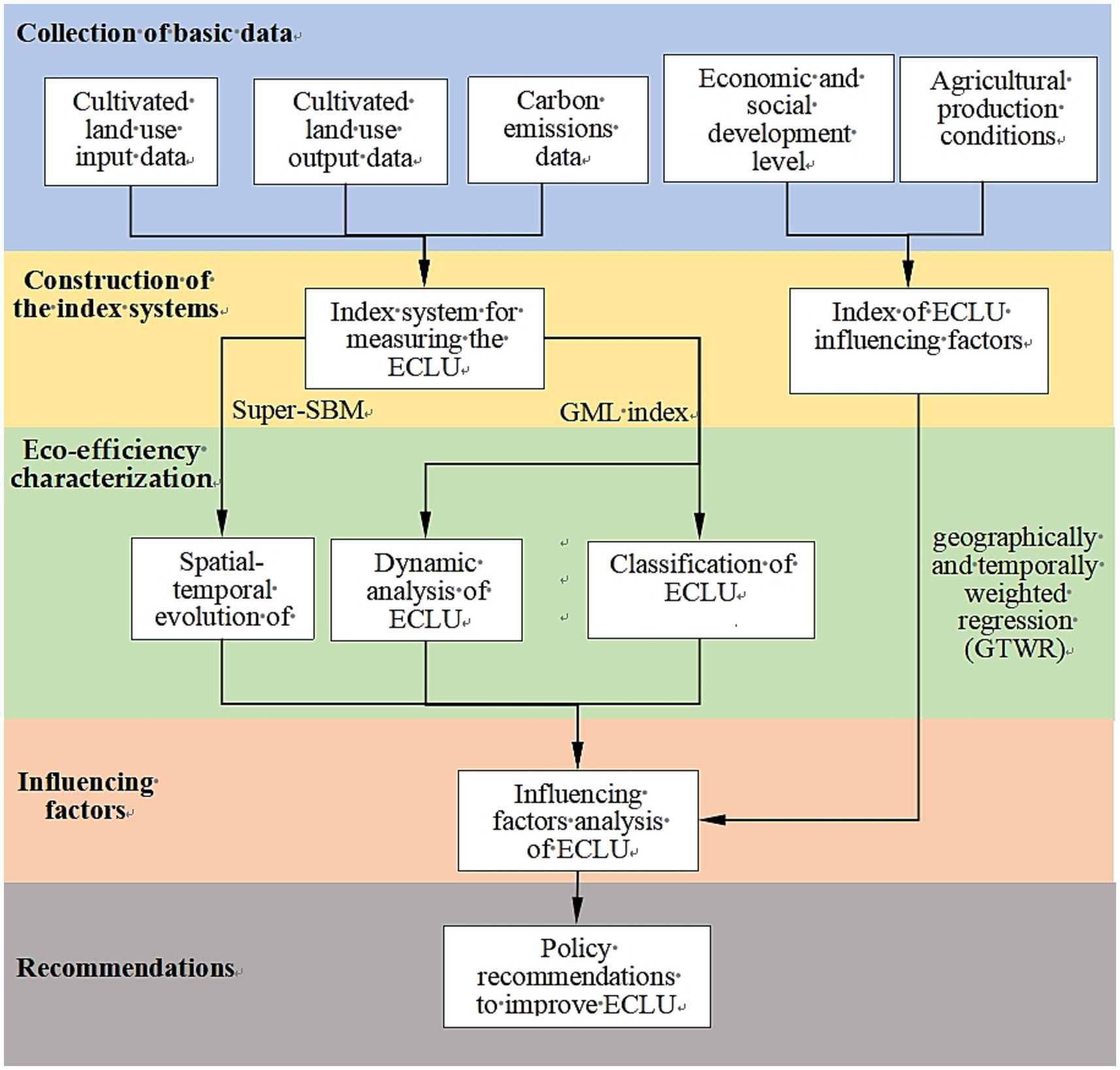
The main methodological framework of this study is shown in Figure 2. Our objectives were to (1) adjust the county-level administrative divisions in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region over 2000–2020 for consistency, and collect data related to the inputs, outputs, and carbon emissions of CLU and the social and economic development level and agricultural production conditions; (2) construct an evaluation system for the ECLU and an index system for its influencing factors based on published literature; (3) apply the Super-SBM model and GML index to measure the ECLU in various counties in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region; (4) use the GTWR model to measure the differences among the impacts of the indicators on the ECLU; and (5) recommend policy aspects for improving the ECLU based on the research findings.
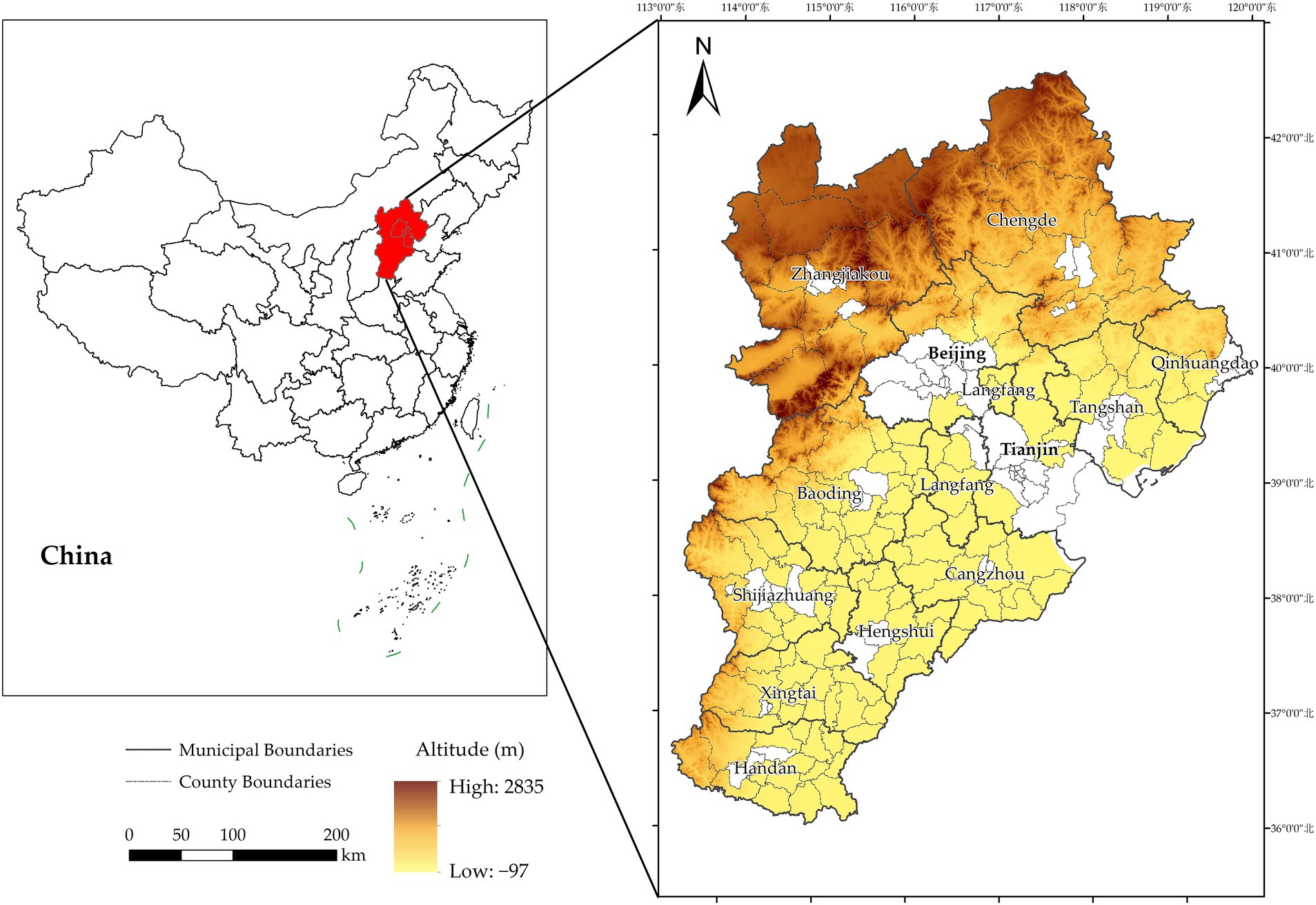
Figure 2. Research framework. SBM, slacks-based measure; ECLU, eco-efficiency of cultivated land use; GML, global Malmquist–Luenberger.
2.2.1 Super-SBM model
When the inputs or outputs contain non-zero slack variables, the radial DEA overestimates the value efficiency of decision-making units. Conversely, Super-SBM—a non-radial and non-angular DEA model based on slack variables—addresses the inability to compare among effective decision-making units in traditional DEA models. Accordingly, the Super-SBM model was applied in this study to handle the variables of undesired outputs (Han and Zhang, 2020a; Fan et al., 2021). As shown in Formulas (1,2):
where xi, yk, and zl denote the input, desired output, and undesired output indicators, respectively, and sx, sy, and sz are their corresponding slack variables. 𝜌 (>1) is the value of ecological efficiency; the greater the 𝜌, the higher the ECLU representation. Because the Super-SBM–DEA model can only evaluate and rank effective decision-making units, the undesired SBM model was first used to determine whether the decision-making unit reached the effective production frontier. For example, 𝜌 < 1 indicates that the decision-making unit does not reach the effective production frontier, whereas ρ = 1 indicates that it is effective.
2.2.2 Global Malmquist–Luenberger index
The Super-SBM model can only measure the relative efficiency of decision-making units and cannot describe the trend of efficiency changes. Therefore, we employed a GML index analysis model that can measure the total factor productivity, including undesired outputs, and also overcome the linear insolubility and non-transferability limitations of the ML index (Xie et al., 2018; Chen et al., 2020). As shown in Formula (3):
The GML index can be decomposed into the global technical efficiency change index ECC and the global technical progress index TCC. GML index = 1 indicates no change in the ECLU of the region over time; GML index >1 indicates an improvement in the ECLU of the region compared to that in the previous year; GML index <1 indicates a decline of the ECLU of the region.
2.2.3 GTWR
GTWR is commonly used for studying the spatial heterogeneity of land use; it explores the spatial variations and related driving factors of the study object at a certain scale by establishing local regression equations at each point within a spatial range. In this study, GTWR was used to introduce the time dimension and reveal the spatial heterogeneity differences in that dimension by constructing a spatially and temporally dependent local model for the spatial–temporal non-stationary relationship (Feng et al., 2023). As shown in Formulas (4–6):
where xi and yi are the spatial coordinates of sample point i (i.e., longitude and latitude), and ti is its temporal coordinate. P0 is the regression constant for point (xi, yi, ti). Xit represents the value of the kth independent variable at point i. ei is the residual value. Pk(xi, yi, ti) is the 𝑘th regression parameter for sample point i, estimated as follows:
where (xi, yi, ti) denotes the estimated value of sample point Pk(xi, yi, ti). X is the matrix of independent variables, and XT is the transpose of X. Y is the sample matrix and W(xi, yi, ti) is the spatial–temporal weight matrix. In this study, Gaussian distance and the bi-square spatial weight function were used to obtain W(xi, yi, ti), with the spatial–temporal distance dij between sample point i and sample point j being defined as follows:
The bandwidth of the GTWR model in this study was selected using the most widely used second order Akaike information criterion (AICc).
2.3 Data sources and index system construction
2.3.1 Data sources and processing
Natural condition data were sourced from the Hebei Rural Statistical Yearbook, Hebei Statistical Yearbook, Beijing Statistical Yearbook, and Tianjin Statistical Yearbook. Social and economic development metrics were sourced from the China Statistical Yearbook (county level) and Statistical Communiqué of National Economic and Social Development of Hebei Province. Agricultural production data were sourced from the Beijing Regional Statistical Yearbook, Tianjin Survey Yearbook, and Statistical Bulletin of National Economic and Social Development of Hebei Province. Resource and environmental data for China were accessed through the cloud platform at http://www.resdc.cn/, which includes land use remote sensing monitoring data, as well as information and data provided by the Hebei Provincial Department of Natural Resources. Some missing data were processed using interpolation or the average values of two adjacent years; all data were standardized. Considering the small amount of cultivated land and its relatively discrete distribution, we excluded the municipal districts in the main urban areas of the cities within each district. Owing to administrative adjustments or county-to-district changes in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region since 2000, we took the 2000 administrative divisions as the benchmark and reorganized spatially the districts and counties for 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020, resulting in 147 districts and counties.
2.3.2 ECLU evaluation index system
The production input variables of the ECLU comprised the cultivated land, labor, and capital inputs in each district and county. Specifically, the total sown area of crops represented the cultivated land input, the number of employees engaged in agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery represented the labor input, and the amount of pesticide use, pure amount of fertilizer application, and mulch use represented the capital input (Xiao et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2022). In addition, energy is both an essential consumable for agriculture and a major source of carbon emissions, and energy consumption is inextricably linked to the ECLU. Therefore, we chose the total power of agricultural machinery and effective irrigated area to represent energy inputs for agricultural development. Regarding output indicators, we divided outputs into desired and undesired outputs, in line with a previous theoretical analysis (Wang et al., 2023). Specifically, desired outputs were divided into social benefit outputs, including the total grain output, and economic benefit outputs, including the total agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery outputs. Undesirable output comprises mainly carbon emissions and non-point source pollution. Carbon emissions comprise mainly carbon dioxide emissions, and non-point source pollution of cultivated land stems mainly from the loss of nitrogen and phosphorus in chemical fertilizers, pesticide losses, and agricultural film residues. Therefore, carbon dioxide emissions and non-point source pollution were used as undesirable output indicators (Zhou et al., 2018; Chen and Xie, 2019; Xiao et al., 2022). The ECLU evaluation index system is presented in Table 1.
2.3.3 ECLU influencing factor indices
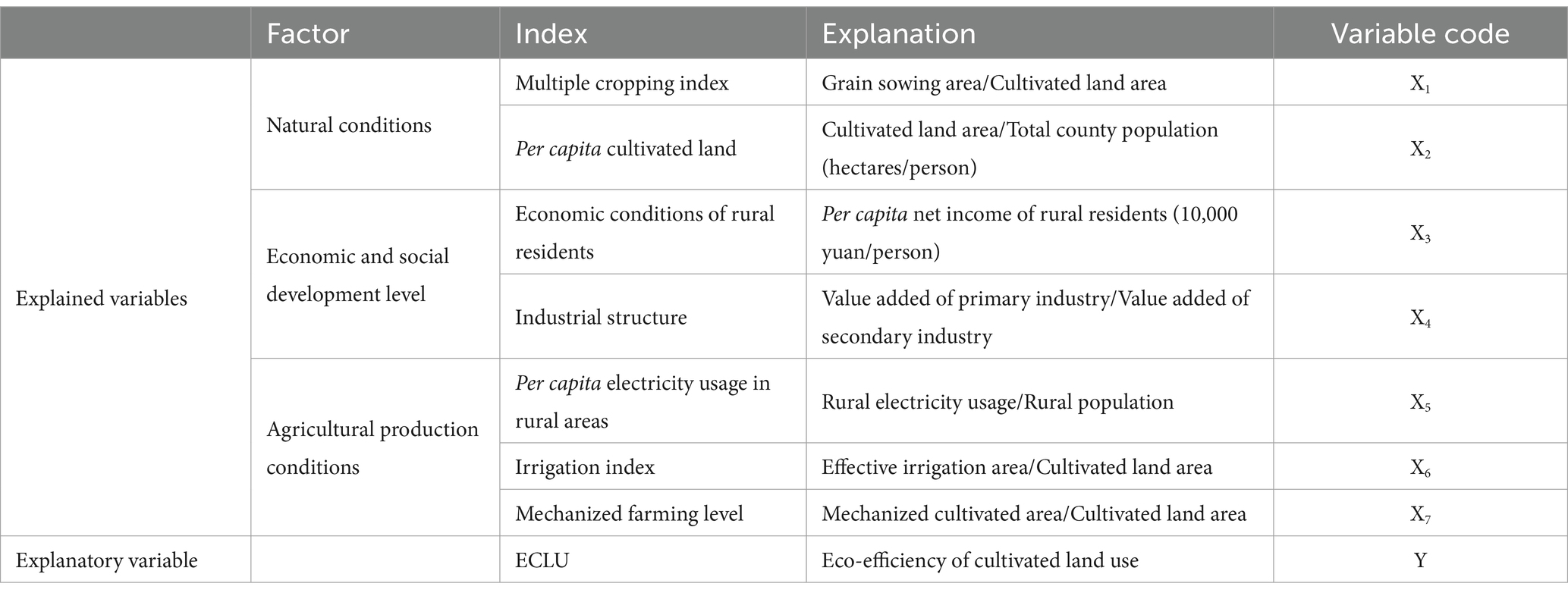
Based on existing studies (Zhou et al., 2018; Chen and Xie, 2019; Xiao et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2022), we selected several factors influencing the ECLU from the perspectives of natural conditions, social and economic development, and agricultural production conditions, as presented in Table 2. Natural conditions involve topography, climate, and other factors, with the cropping structure differing across regions. Therefore, the multiple cropping index and per capita cultivated land were used to represent the differences in natural conditions among districts and counties. Specifically, the multiple cropping index was calculated as the ratio of grain sowing area to cultivated land area, and per capita cultivated land was calculated as the ratio of cultivated land area to the total county population.
The social and economic development level was represented by the per capita net income of rural residents. The ratio of the value added of the primary industry to the value added of the secondary industry represented the agricultural and industrial development levels. In turn, as improvements in agricultural production conditions are directly manifested as increased mechanization and automation, the total power of agricultural machinery per unit area of cultivated land and per capita electricity usage in rural areas were used to represent the intensity of mechanized cultivation input, and the irrigation index was used to represent the proportions of land with different water conditions.
3 Results
3.1 Spatial–temporal differentiation of the ECLU at the county scale
3.1.1 Spatial–temporal evolution of the ECLU
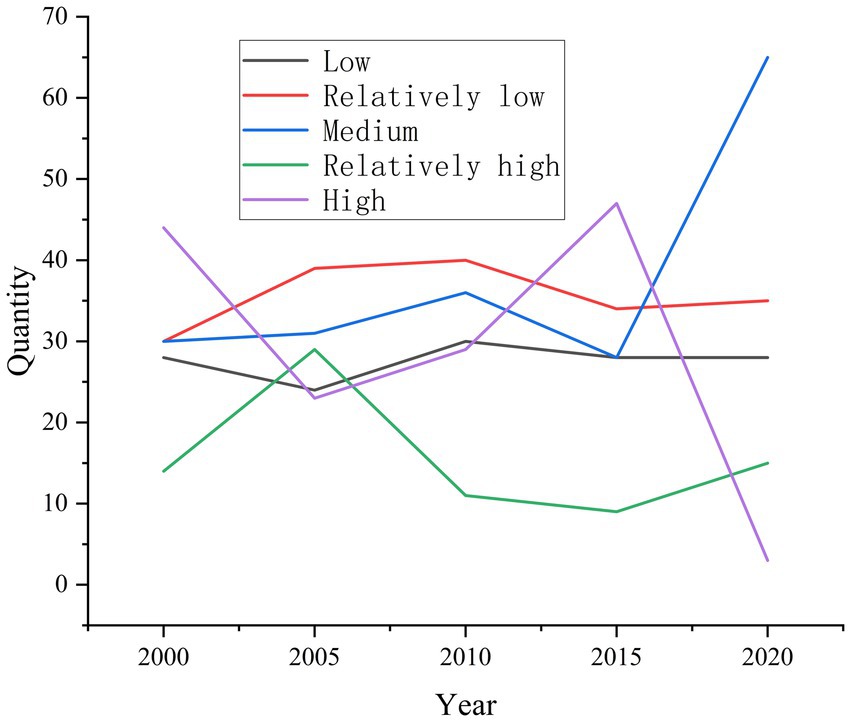
Based on the Super-SBM model, the Matlab software was used to calculate the ECLU in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region at the district and county scales. We then used natural breaks classification to classify the ECLU into low, relatively low, medium, relatively high, and high. The distribution of counties in each ECLU interval is shown in Figure 3. In 2000, there were 28 low-ECLU counties, 30 relatively low-ECLU counties, 30 medium-ECLU counties, 14 relatively high-ECLU counties, and 44 high-ECLU counties. In 2005, the numbers of relatively high- and relatively low-ECLU counties increased, the number of high-ECLU counties decreased, and the numbers of medium- and low-ECLU counties remained stable. In 2010, the number of relatively high-ECLU counties decreased to the same level as that in 2000, whereas the numbers of counties in all other ECLU intervals increased slightly. In 2015, the number of high-ECLU districts and counties increased significantly, whereas the numbers of districts and counties in all other ECLU intervals decreased slightly. In 2020, the numbers of medium- and high-ECLU districts and counties increased significantly, the number of high-ECLU districts and counties decreased significantly, and the number of districts and counties in all other ECLU intervals remained stable.
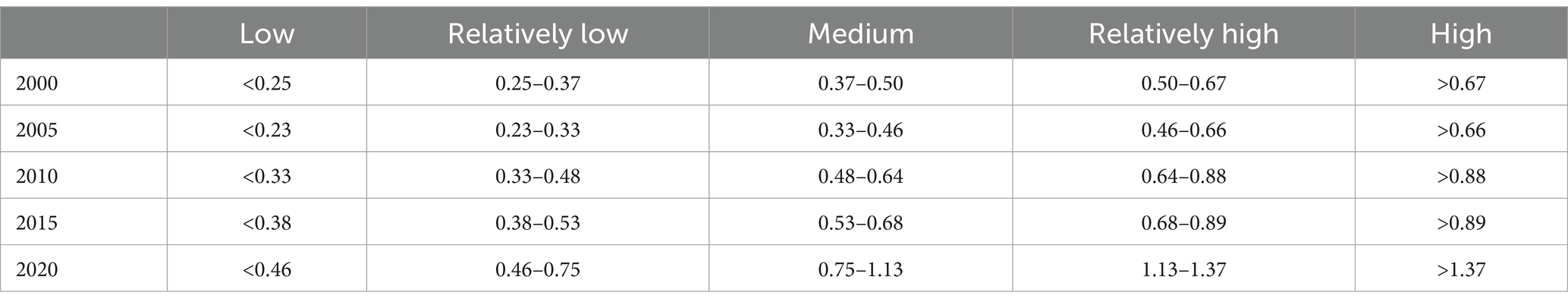
The ECLU interval distribution is shown in Table 3. In 2000, the low-ECLU value range increased from <0.25 in 2000 to <0.46 in 2020. The relatively low-ECLU value range increased from 0.25–0.37 in 2000 to 0.46–0.75 in 2020. The medium-ECLU value range increased from 0.37–0.50 in 2000 to 0.75–1.13 in 2020. The relatively high-ECLU value range increased from 0.50–0.67 in 2000 to 1.13–1.37 in 2020. The high-ECLU value range increased from >0.67 to >1.37. Due to the change of the ECLU value range in each interval, the transformation of high efficiency into low efficiency does not necessarily lead to an ecological efficiency decrease. On the one hand, the numbers of districts and counties in the low- and relatively low-ECLU ranges remained overall constant, whereas the number of districts and counties in the medium-ECLU range increased significantly; on the other hand, the ECLU value range in each interval overall increased.
The spatial–temporal evolution of the ECLU in the districts and counties of Hebei Province is shown in Figure 4. From the perspective of spatial–temporal distribution, in 2000, the medium- and high-ECLU counties were mainly distributed in Beijing, Tianjin, the central and southern plains of Hebei Province, Zhangjiakou, Chengde and a few mountainous counties in the west of Baoding. Low-ECLU counties were many and mainly distributed in the coastal areas of Cangzhou and the Taihang Mountains in the southwest. In 2005, the middle- and high-ECLU counties were mainly distributed in Zhangjiakou and Chengde in the north, Beijing and Tianjin, as well as the western mountainous areas of Baoding, whereas the other counties comprised mostly low-ECLU counties. In 2010, the middle- and high-ECLU counties were mainly distributed in Beijing, Tianjin, Zhangjiakou, Chengde, Shijiazhuang, Handan, and Xingtai, and the low-ECLU counties were mainly distributed in Cangzhou, Hengshui, and Qinhuangdao. In 2015, the middle- and high-ECLU values were distributed in some districts and counties of Beijing, Tianjin, Zhangjiakou, Chengde, Tangshan, Cangzhou, Baoding, Shijiazhuang, Xingtai, and Handan, whereas the low-ECLU values were mainly distributed in some districts and counties of Hengshui and Langfang. In 2020, except for some districts and counties in Zhangjiakou, Baoding, Shijiazhuang, Xingtai, Handan, and other places, most districts and counties had middle- and high-ECLU values, and their numbers were significantly increased. Overall, the ecological efficiency of the northern and western districts and counties in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region is higher than that of the central, southern, and eastern districts and counties. The ECLU values in Beijing and Tianjin counties fall mostly within the middle and high intervals in each year. The ECLU values in Zhangjiakou and Chengde are generally high. Overall, the ECLU in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region has improved.
3.1.2 Dynamic analysis of the ECLU
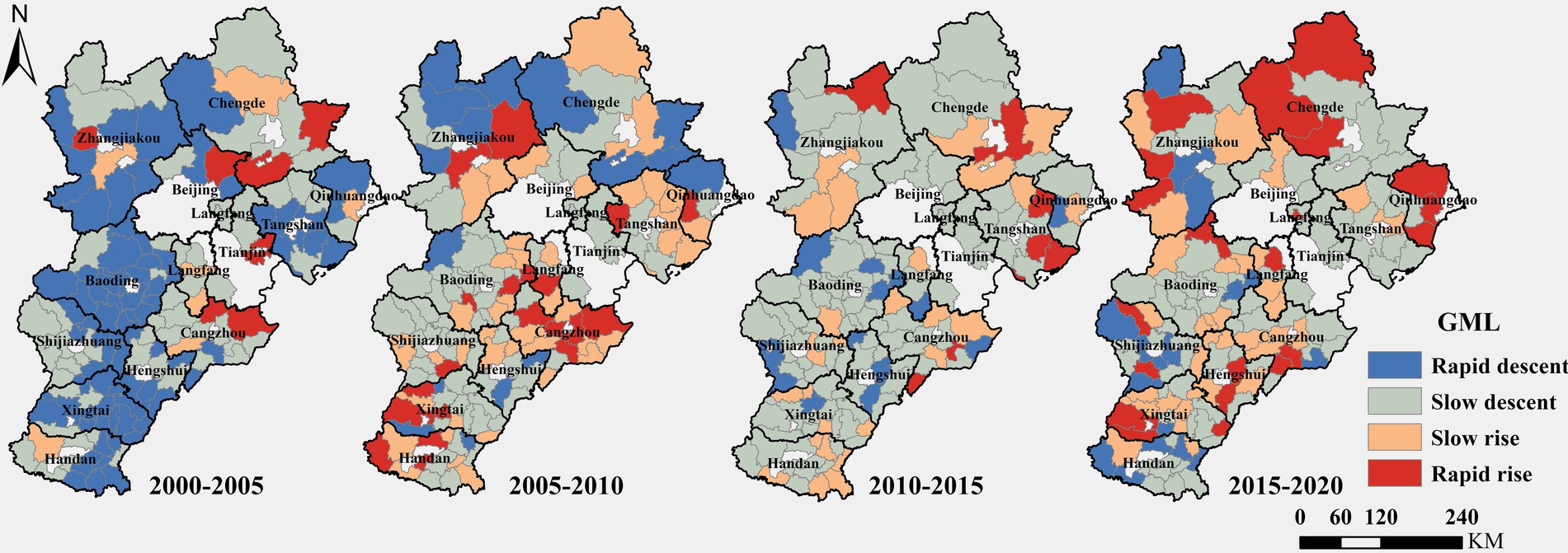
To further investigate the dynamic changes of the ECLU in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region in each year and explore the differences and potential causes of the ECLU changes in each region, we applied the GML index to measure the differences of the ECLU in the region and visualized them using ArcGIS. Taking GML = 1 as a threshold, the GML index was classified into several intervals through natural breaks classification. GML index values in the range of 0.00–0.67 signified rapid decline of the ECLU, those in the range of 0.67–1.00 signified a slow decline, those in the range of 1.00–1.69 signified a slow increase, and those >1.69 signified a rapid increase. The dynamic changes of the ECLU in Hebei Province are shown in Figure 5. During 2000–2005, the GML index was low in most regions, with only a few counties in the coastal and northern mountainous areas being characterized by high GML index values, indicating a high rate of decline of the ECLU. During 2005–2010, the areas around Beijing and Tianjin, the eastern coastal areas, and the southern plains were mostly characterized by GML index values >1.00, with the ECLU following an increasing trend. The number of GML1 in the western mountainous areas decreased significantly, and the increase of ECLU decelerated. During 2015–2020, most of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region was characterized by middle and high GML index values, with the number of counties experiencing decline of the ECLU being significantly reduced, and the ECLU across the entire region rising rapidly. Overall, the ECLU in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region showed a trend of rapid decline first and then slow and continuous rise. In the later period, there were fewer districts and counties in the rapid ECLU decline interval. The ECLU upward trend in districts and counties in Beijing and Tianjin was significantly weaker than that in most districts and counties in Hebei Province.
3.1.3 ECLU classification
As mentioned earlier, the GML index can be decomposed into the ECC and TCC indices, which together construct a four-quadrant scatter plot based on the origin “0.” The classification maps of the ECLU in Hebei Province over four periods are shown in Figure 6. Evidently, during 2000–2005, the distributions of the ECC and TCC indices of the districts and counties were more uniform in the four quadrants compared to the cases in the other three periods. Furthermore, they were slightly concentrated in the first and second quadrants, indicating that the number of districts and counties with increased TCC index was higher than that with decreased TCC index, reflecting that districts and counties during 2000–2005 had begun to introduce new technologies for green production of cultivated land. During 2005–2010, the ECC and TCC indices began to rise; however, there were still some districts and counties whose ECC and TCC indices were following downward trends, indicating that the scale of agricultural production in some districts and counties was expanded, with the internal organization being optimized. During 2010–2015, most districts and counties were concentrated in the first and second quadrants, indicating that the TCC index had been greatly improved, and the ECC index tended to decline. During 2015–2020, most districts and counties were concentrated in the first and second quadrants, with the TCC index having been improved at a high level. The number of districts and counties with decreased ECC index was higher than that of districts and counties with increased ECC index.
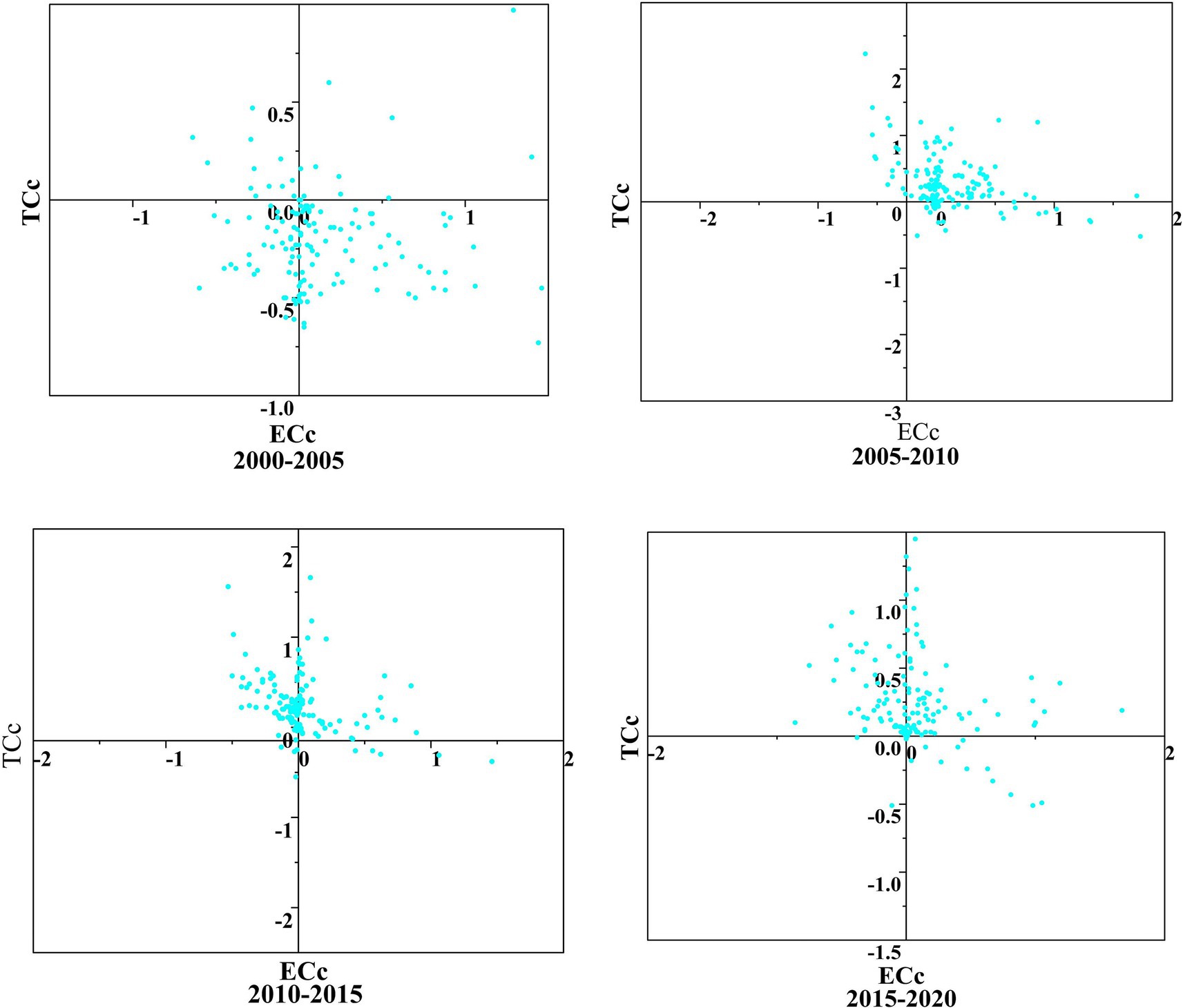
Figure 6. Classification map of the ECLU in Hebei Province during the four periods. TC, technical progress index; EC, technical efficiency index.
3.2 Analysis of factors influencing the ECLU
Before analyzing the factors influencing the ECLU using the GTWR model, we conducted a collinearity test on the independent variables. A variance inflation factor (VIF) <10 indicates no multicollinearity. In this study, all VIF values for the independent variables were < 5, indicating the absence of multicollinearity. We then compared the performance of the GTWR model with that of other commonly used regression models, such as temporally weighted, geographically weighted, and ordinary least squares. The comparative fitting results of the different models are presented in Table 4. The GTWR model had a higher R2 value and lower AICc value compared to those of the other three models, proving that its accuracy was superior and that incorporating spatial–temporal non-stationarity was necessary.
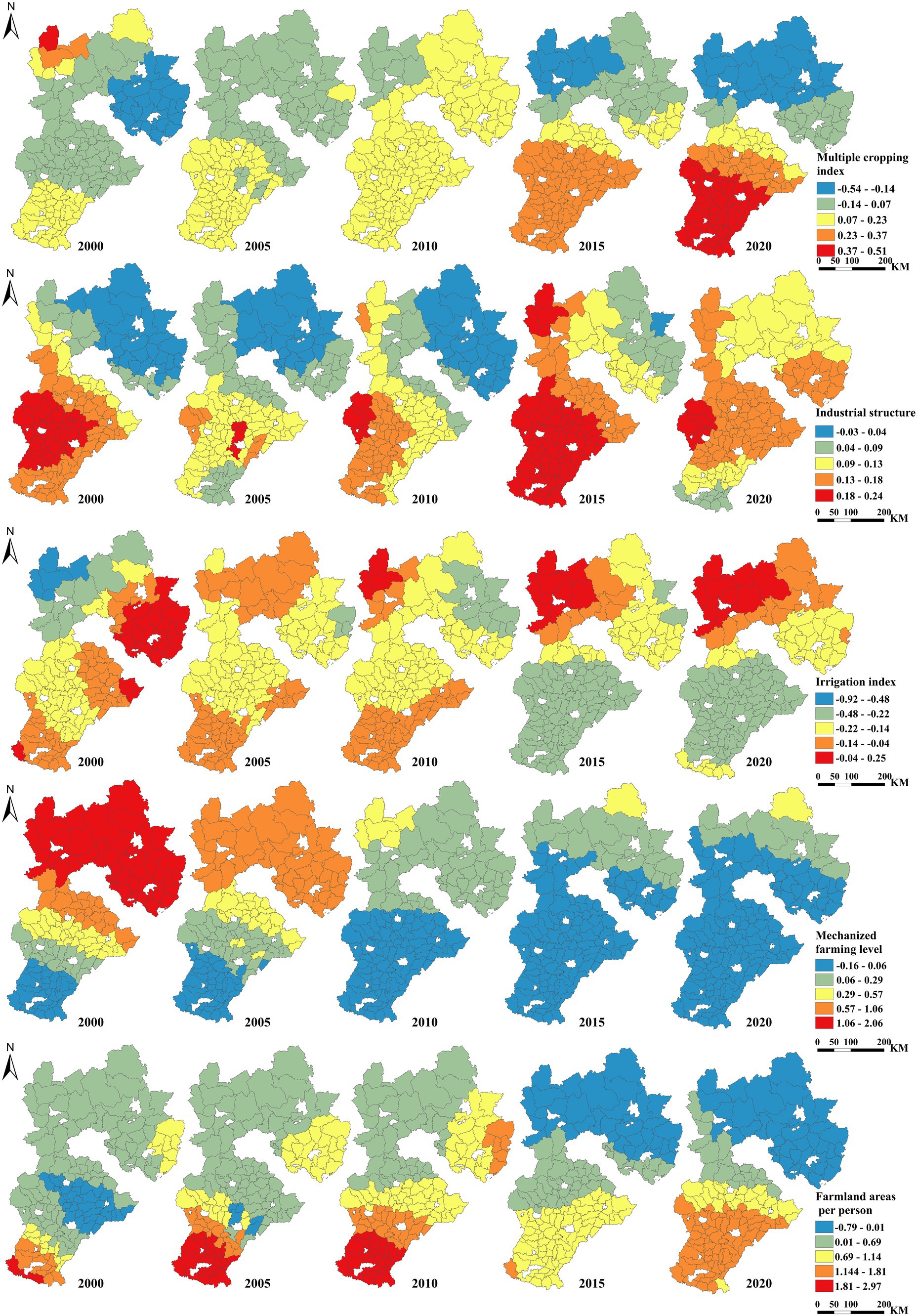
The results obtained using the GTWR model regarding the factors influencing the ECLU in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region at the county scale are presented in Table 5. The impacts of per capita cultivated land, rural economic conditions, and rural per capita electricity consumption on the ECLU are low. The remaining four indicators with greater impacts, namely multiple cropping index, industrial structure, irrigation index, and mechanized farming level, were visualized using ArcGIS. The calculation results of the indicators with greater impacts on the ECLU are shown in Figure 7.
Evidently, five indicators exhibit obvious spatial–temporal characteristics:
1. The GTWR results of the multiple cropping index gradually decreased from south to north. In most periods, the ECLU in the south was positively correlated with the multiple cropping index, with the GTWR values gradually increasing with time. The north was negatively correlated, rising first and then decreasing with time. The multiple cropping index is obviously affected by both climatic and land conditions, and the natural conditions in the northern mountainous areas are poor. Therefore, the GTWR results of the multiple cropping index in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region show certain latitude zone differentiation characteristics in multiple periods.
2. The GTWR results of the industrial structure gradually decreased from southwest to northeast, exhibiting a positive correlation in their entirety. The correlation of plain counties was significantly higher than that of mountain counties, with the high-value areas being mainly located in the provincial capital areas. The industrial structure in this study mainly considers the primary and secondary industries. The processes of agriculture and industry in the county economy show that when the proportion of agricultural output value is high, the positive impact on the ECLU increases.
3. The GTWR results of the irrigation index gradually increased from south to north except for a few areas. The ECLU in the central plain area showed a significant negative correlation with the irrigation index over the entire study period, and the negative correlation in the northern Zhangjiakou and Chengde mountainous areas was low for many years. The increase of the irrigation index also shows the improvement of cultivated land consolidation level and water conservancy facilities in a region. Generally speaking, with the increase of the irrigation index, the production efficiency of cultivated land should be improved accordingly, with the negative correlation in the southern plain area having unique characteristics. On the one hand, the rapid social and economic development in the southern districts and counties has led to serious groundwater exploitation in the region, forming multiple world-class groundwater ‘funnels’. The water infiltration of cultivated land irrigation is replenished to groundwater and cannot be fully absorbed by crops. On the other hand, the irrigation index itself has been high, and the other cultivated land is not suitable for irrigation. Therefore, the improvement of the irrigation index cannot result in the improvement of the ECLU. The irrigation index of the northern districts and counties was not high, and water was an important condition limiting agricultural production. With the increase of the irrigation index, the ECLU increased significantly.
4. The GTWR results of mechanized farming level gradually changed from positive to negative with time, especially in the southern plain area, which was negatively correlated for a long time. The level of mechanized farming reflects the degree of agricultural mechanization coverage in a certain area. However, from the perspective of CLU efficiency, excessive investment in agricultural machinery may not necessarily result in improvements. On the one hand, the input of agricultural machinery mainly improves the efficiency of farming by reducing labor input and reducing time cost, with the potential of the ECLU constrained by climatic conditions likely not being fully realized; on the other hand, although the level of green technology in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region continues to progress, there may be deficiencies in green machinery, resulting in higher mechanical carbon emissions and reduced ecological efficiency. The pollution of agricultural and forestry machinery cannot be ignored.
5. The GTWR results of per capita cultivated land are mainly positive except for a few areas, showing a significant positive correlation, with the high value areas being mainly concentrated in the southern plains. This positive correlation in the southern region may be related to the better climatic conditions, higher agricultural technology level, and more concentrated agricultural production activities. Cultivated land in the northern mountainous area is relatively scattered, and the scattered use of resources leads to a low positive correlation or even a negative correlation.
In particular, the GTWR results of the multiple cropping index indicate polarization. In the south, the ECLU correlated positively with the multiple cropping index, whereas in the north, it correlated negatively. No substantial topographic differences were observed. Overall, latitudinal zone differentiation characteristics are evident across the entire study region. The distribution pattern of GTWR results regarding industrial structure remained basically stable over the entire study period, generally showing a gradually increasing positive correlation, with lower correlation in plain counties compared to that in mountainous counties. In comparison, the GTWR results of the irrigation index gradually increased from south to north, except in a few areas. The ECLU was negatively correlated with the irrigation index in the central plains, whereas it was mainly positively correlated with that in the eastern coastal strip and areas surrounding Beijing and Tianjin. Conversely, the GTWR results of the mechanized farming level were primarily negative, with the ECLU being negatively correlated with the mechanized farming level and gradually decreasing from 2000 to 2020.
4 Discussion
Scholars have conducted extensive research on the ECLU across various regions, including the Yangtze River Economic Belt, Yellow River Basin, the black soil region in Northeast China, and Southern Germany (Feng et al., 2023; Ke et al., 2023; Zhou et al., 2022; Yin et al., 2022; Yang et al., 2021; Luo et al., 2020; Hou et al., 2019; Lin and Hülsbergen, 2017). In this study, we calculated the ECLU in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region and revealed its spatial–temporal evolution characteristics in the context of food security. The region, with its extensive plains and favorable climate conditions, is an important contributor to the total grain production of China. Under the background of current “dual carbon” goals, conducting research on the ECLU in this region is crucial for ensuring national food security and promoting regional social and economic development. In this study, both the Super-SBM model and the GML index were used to measure the ECLU, with the undesired outputs of cultivated land use being included in the index system, enabling the dynamic comparison of the ECLU and offering a more detailed depiction of the spatial–temporal evolution of the ECLU compared to those in previous studies (Li et al., 2017; Chen et al., 2020; Luo et al., 2020; Yang et al., 2021; Ke et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2022). Additionally, we considered county as the evaluation unit, which reflected the spatial–temporal evolution and differentiation of the ECLU in a more magnified and detailed manner, laying a foundation for the formulation and implementation of related policies (Tone, 2004; Fukuyama and Weber, 2010; Xiao et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2022; Liu and Zhang, 2023). Most of the existing studies use a single model method, such as Super-SBM, to measure the ECLU. These methods have limitations, such as not including undesired output and dynamic inter-temporal comparisons. The GML index compensates for this defect, and the combination of the two methods is more beneficial regarding measuring the ECLU.
4.1 Spatial–temporal evolution characteristics of the ECLU
During 2000–2020, the ECLU in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region showed an overall fluctuating upward trend, comparable to that reported by Li M. et al. (2023). 2000–2010 was characterized by rapid economic growth and modification of the planting structure. With insufficient technological support for agriculture, especially through the first half of this period as suggested by evaluation of the decomposed GML index, the abandonment of cultivated land and its occupation by construction land became more common. These factors, combined with the lack of attention to carbon emissions from cultivated land, resulted in obvious fluctuation in the ECLU during this time period. From 2010 onward, the ECLU increased substantially, indicating that considerable progress had been made regarding the protection of cultivated land and that carbon emissions had been effectively controlled. The ECLU in Beijing and Tianjin was markedly higher than that in most parts of Hebei Province. The counties in Hebei Province, located in the west and south of Beijing and Tianjin, had overall lower ECLU values than those of other counties, likely because these municipalities attract human resources, capital, and other factors from surrounding counties at the expense of sufficient input of agricultural factors. In addition, the counties in northern Hebei Province had higher ECLU values, likely deriving in part from their location upwind from Beijing, with higher requirements for ecological protection and policy support. The local agriculture also probably still occupies a large proportion of the area, with secondary and tertiary industries lagging.
The ECLU in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region generally presented a dynamic trend of rapid decline–slow rising–continuous rising, which is also in general agreement with the results of Wang et al. (2022). According to the GML index, the ECLU in this region transitioned from disorderly evolution to a large-scale production-driven efficiency increase; then, it further transitioned to technological progress-driven efficiency gains. Technological progress can provide long-term positive support for an ECLU increase, whereas large-scale production can markedly improve the ECLU in the short term. Owing to the law of diminishing returns to scale, continued improvements to the ECLU are difficult once the peak of production scale is reached. As the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region exhibits a high level of large-scale production, increasing the technological inputs represents currently the preferred way of improving the ECLU. Notably, Li X. et al. (2023) did not include a GML index analysis in their study; however, Gu et al. (2022) reported that the government in the region invests scientific and technological inputs to drive industrial transformation to curb carbon emissions, which further supports the conclusions of this study.
4.2 Driving mechanisms of the ECLU
The ECLU was mainly affected by the multiple cropping index, industrial structure, irrigation index,per capita cultivated land and mechanized farming level, in accordance with previous literature (Ke et al., 2022; Xiao et al., 2022). The relationship between per capita cultivated land area and ecological efficiency shows obvious regional differences. On the whole, there is a significant positive correlation between per capita arable land area and ecological efficiency, especially in the southern plains. The high-value areas in the southern plains are mainly due to the relatively superior natural conditions in the region, including climate and topography. These factors help to improve the productivity and ecological efficiency of cultivated land. In contrast, the distribution of cultivated land in the northern mountainous area is relatively scattered and the terrain is complex. The intensive utilization of cultivated land is low, and the expansion of cultivated land scale has not caused a significant improvement in the ecological efficiency of cultivated land. In contrast, the main influencing factors of the ECLU in Hebei Province include the multiple cropping index, proportion of agricultural output value, elevation, slope, proportion of agricultural population, and proportion of non-grain crops, with the proportion of agricultural output value and proportion of non-grain crops having more significant impacts (Wang et al., 2022). The reasons for these differences may be attributed to variations in regional scope, selection of indicators, and methodological approaches. The multiple cropping index, which is an important indicator reflecting the degree of CLU, is substantially constrained by the climate, land, technology, and labor, resulting in the GTWR results showing obvious climatic zoning. Specifically, the ECLU was positively and negatively correlated with the multiple cropping index in the southern and northern regions, respectively. In comparison, the distribution pattern of the GTWR results of industrial structure remained basically stable over the entire study period, exhibiting a gradually increasing positive correlation. This suggested that as the agricultural production capacity increases, the production capacity of green science and agricultural technology improves synchronously. The level of mechanized farming is negatively correlated with the ECLU, with the absolute value having gradually decreased during 2000–2020. This may be due to the large-scale use of agricultural machinery leading to an increase in carbon emissions, which in turn reduces the ECLU. The reduction in this impact may be attributed to the continuous improvement in the efficiency of agricultural machinery.
The ECLU was negatively correlated with the irrigation index in the central plains; however, it was positively correlated with the irrigation index in the eastern coastal strip and areas around Beijing and Tianjin. Notably, the rise in the irrigation index reflects not only the water application but also the enhancement of land improvement levels and water conservancy facilities in a region. Generally speaking, the production efficiency of cultivated land will improve with the increase of the irrigation index. The negative correlation in the southern plains has several unique characteristics. In the southern counties, the rapid social and economic development has led to serious groundwater extraction, creating several world-class groundwater “funnels” through which irrigation water seeps into the groundwater instead of being fully absorbed by crops. However, because the irrigation index itself was already high and most of the other land is unsuitable for irrigation, an increase of the irrigation index does not lead to a coordinate increase of the ECLU in this region. Conversely, in the northern counties with a lower irrigation index, water is an important limiting factor for agricultural production. Therefore, in these counties, the ECLU increases substantially with the increase of the irrigation index.
The mechanized farming level, which reflects the coverage of agricultural mechanization in a certain region, was mainly negatively correlated with the ECLU. However, from the perspective of the ECLU, excessive investment in agricultural machinery may not necessarily improve the efficiency. In particular, agricultural machinery inputs are mainly used to reduce labor inputs and time costs to improve the cultivation efficiency; thus, the potential for the ECLU constrained by climatic conditions may not be fully realized. Moreover, although green technology in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region continues to progress, lingering green machinery deficiencies may lead to high carbon emissions and reduction of the ecological efficiency. Additionally, the pollution from agricultural and forestry machinery constitutes a persistent concern.
4.3 Policy recommendations for enhancing the ECLU to promote food security
1. Promoting structural adjustment and optimization of the agricultural industry. Green and technology-driven agriculture should be encouraged. Through policy support and technological innovation, the production methods of agriculture can be transformed from traditional means into a modern and highly efficient process with low-consumption, thereby promoting the sustainable development of agricultural production and enhancing the ECLU.
2. Strengthening the protection of cultivated land and its quality improvement. Strict policies regarding the protection of cultivated land should be formulated and implemented to limit the development of land for non-agricultural purposes and ensure the sustainable use of cultivated land resources. Additionally, the investment in improving the quality of cultivated land should be increased to enhance the productivity and ecological service functions of the land, such as improving irrigation systems, promoting the use of organic fertilizers, and implementing soil restoration projects.
3. Promoting the development of agricultural mechanization and knowledge. Advanced agricultural machinery and technologies should be adopted, and subsidies, technical support, and maintenance services should be acquired to promote the popularization and upgrading of agricultural mechanization. This not only reduces the labor input and increases the production efficiency but also helps to reduce carbon emissions during agricultural production.
4. Enhancing water resource management and improve irrigation efficiency. Considering the impact of the irrigation index on the ECLU, the management and rational use of water resources should be strengthened and water-saving irrigation techniques, such as drip irrigation and sprinkler irrigation, should be promoted. Moreover, a water recycling system should be established to reduce water wastage and improve irrigation efficiency. In addition, for areas where groundwater levels are critically low, the protection and rational development of groundwater resources should be enhanced to prevent excessive groundwater extraction.
4.4 Study limitations
This study has several limitations. First, the selection of input and output indicators was not comprehensive. The input indicators did not include new factors, such as the internet and big data, leading to insufficient consideration of the contributions of emerging technologies to agricultural production. Moreover, due to the varying roles of different crops in ensuring food security, the output indicators adopted the total grain production, and the production of different food crops was neglected, likely leading to a deviation of the ECLU, especially in the context of cropping structure adjustments. In addition, agricultural production generates carbon emissions as well as carbon sinks, which should be included among the desired outputs. Second, the selection of influencing factor indicators was also limited. Insufficient consideration was given to technological development and the geographical location of transportation, considering that provinces in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region and areas among cities within Hebei Province markedly differ with regard to these aspects. Beijing, Tianjin, and surrounding areas exhibit better technological and transport conditions than those of other regions, which may affect the results of the influencing factor analysis. The current indicators substantially interfere with the input indicators, and the calculation of the multiple cropping index and industrial structure overlaps somewhat with that of several input indicators; therefore, adjusting the input–output model in future studies will be necessary. Furthermore, less consideration was given to indicators characterizing agricultural production in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, such as groundwater conditions and the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Finally, although this study concluded that the ECLU in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region was alternately affected by the technical progress and technical efficiency, as revealed using the GML index, and also analyzed the distribution of the two efficiency values, it did not conduct an in-depth investigation regarding the causes of these changes. Therefore, additional research is required to update the methods for calculating scale- or technological efficiency, clarify their quantitative differences, and select corresponding influencing factor indicators to analyze the substantive factors affecting their changes. In subsequent research, the selection of input–output indicators can be optimized and improved based on the above analysis. In addition to the GTWR model, other methods, such as geographical detectors, can also be used to analyze the influencing factors. Although the situation in other regions is not completely the same as that in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, the selection of indicators and the use of methods can still be referenced.
5 Conclusion
In this study, we selected county-level data from the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, covering 2000–2020, and employed the Super-SBM model and GML index to calculate the ECLU in the region. Furthermore, the GTWR model was applied to assess the differences of factors influencing the ECLU and, ultimately, food security. The primary findings are as follows:
1. From the perspective of temporal changes, during 2000–2020, the number of medium-ECLU districts and counties in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region gradually increased, the number of high-ECLU districts and counties decreased in its entirety, and the number of districts and counties in all other ECLU intervals did not change significantly. However, the ECLU value range in each interval migrated toward higher values, with the ECLU in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region improving in its entirety. From the perspective of spatial distribution, the ECLU values of the northern districts and counties in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region are higher than those in other regions. Counties in Beijing and Tianjin have mostly middle- and relatively high-ECLU values in each year, whereas counties in Zhangjiakou and Chengde have generally high-ECLU values. Overall, the ECLU in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region has demonstrated a discernible upward trend, with notable superiority observed in the northern districts relative to the cases in their central, southern, and eastern counterparts.
2. Regarding the dynamic changes of the ECLU, the ECLU in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region showed a trend of rapid decline first and then slow and continuous rise. In the middle and late stages, there were fewer districts and counties in the rapid ECLU decline interval. The upward trend of districts and counties in Beijing and Tianjin was significantly weaker than that in most districts and counties in Hebei Province. The ECLU in the region is dynamically improved, with areas with low ECLU values exhibiting more rapid changes than those of areas with high ECLU values and the difference in ECLU in the region tending to narrow.
3. The improvement of the ECLU in the early stage mainly depends on technical efficiency, i.e., organizational optimization or scale expansion; subsequently, it starts depending more on technological progress. Owing to the law of diminishing returns to scale, the future improvement of the ECLU mainly depends on technological progress and investment. Increasing the investment in science and technology, promoting technological innovation in the agricultural field, improving resource utilization efficiency, and reducing environmental pollution are necessary steps toward further improving the ECLU.
4. The ECLU is mainly affected by the multiple cropping index, industrial structure, irrigation index, mechanized farming level, and per capita cultivated land. The ECLU was positively and negatively correlated with the multiple cropping index in the southern and northern regions, respectively. The industrial structure mainly shows a gradually increasing positive correlation through time. A higher proportion of the primary industry implies higher ECLU. The ECLU in was significantly negatively correlated with the irrigation index the central plain area, and the negative correlation in Zhangjiakou and Chengde mountainous areas was low for many years. The level of mechanized farming in the southern plain area was negatively correlated with the ECLU for a long time. The per capita cultivated land and the ECLU were significantly positively correlated, with the positive correlation in the plain area being higher. In the future, differentiated policy measures should be formulated according to the spatial–temporal differences of different factors to further improve the ECLU.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
XJ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Validation, Writing – original draft. JM: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft. GL: Investigation, Resources, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. YL: Supervision, Writing – original draft. CL: Project administration, Writing – original draft. XW: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019 M650823) and National Pre research Project of Hebei GEO University (KY2024YB16).
Conflict of interest
JM was employed by Hebei Geographic Information Group Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Bonfiglio, A., Arzeni, A., and Bodini, A. (2017). Assessing eco-efficiency of arable farms in rural areas. Agric. Syst. 151, 114–125. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2016.11.008
Cao, W., Zhou, W., Wu, T., Wang, X., and Xu, J. (2022). Spatial-temporal characteristics of cultivated land use eco-efficiency under carbon constraints and its relationship with landscape pattern dynamics. Ecol. Indic. 141:109140. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109140
Cecchini, L., Venanzi, S., Pierri, A., and Chiorri, M. (2018). Environmental efficiency analysis and estimation of CO2 abatement costs in dairy cattle farms in Umbria (Italy): a SBM-DEA model with undesirable output. J. Clean. Prod. 197, 895–907. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.06.165
Chen, Y., Li, S., and Cheng, L. (2020). Evaluation of cultivated land use efficiency with environmental constraints in the Dongting Lake eco-economic zone of Hunan Province, China. Land 9:440. doi: 10.3390/land9110440
Chen, Q., and Xie, H. (2019). Temporal-spatial differentiation and optimization analysis of cultivated land green utilization efficiency in China. Land 8:158. doi: 10.3390/land8110158
Chung, Y. H., Färe, R., and Grosskopf, S. (1997). Productivity and undesirable outputs: a directional distance function approach. J. Environ. Manag. 51, 229–240.
Cui, N. B., Wang, X. Y., and Yu, Z. (2021). Evaluation of ecological efficiency of cultivated land and analysis of influencing factors in the major grain producing areas of Northeast China. Ecol. Econ. 37, 104–110.
Fan, Z., Deng, C., Fan, Y., Zhang, P., and Lu, H. (2021). Spatial-temporal pattern and evolution trend of the cultivated land use eco-efficiency in the National Pilot Zone for ecological conservation in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19:111. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19010111
Fei, R., Lin, Z. Y., and Chunga, J. (2021). How land transfer affects agricultural land use efficiency: evidence from China’s agricultural sector. Land Use Policy 103:105300. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2021.105300
Feng, L., Lei, G., and Nie, Y. (2023). Exploring the eco-efficiency of cultivated land utilization and its influencing factors in black soil region of Northeast China under the goal of reducing non-point pollution and net carbon emission. Environ. Earth Sci. 82:94. doi: 10.1007/s12665-023-10770-0
Foley, J. A., Ramankutty, N., Brauman, K. A., Cassidy, E. S., Gerber, J. S., Johnston, M., et al. (2011). Solutions for a cultivated planet. Nature 478, 337–342. doi: 10.1038/nature10452
Fukuyama, H., and Weber, W. L. (2010). A slacks-based inefficiency measure for a two-stage system with bad outputs. Omega 38, 398–409. doi: 10.1016/j.omega.2009.10.006
Gómez-Limón, J. A., Picazo-Tadeo, A. J., and Reig-Martínez, E. (2012). Eco-efficiency assessment of olive farms in Andalusia. Land Use Policy 29, 395–406. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2011.08.004
Gu, R., Li, C., Li, D., Yang, Y., and Gu, S. (2022). The impact of rationalization and upgrading of industrial structure on carbon emissions in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19:7997. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19137997
Han, H., and Zhang, X. (2020a). Exploring environmental efficiency and total factor productivity of cultivated land use in China. Sci. Total Environ. 726:138434. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138434
Han, H., and Zhang, X. (2020b). Static and dynamic cultivated land use efficiency in China: a minimum distance to strong efficient frontier approach. J. Clean. Prod. 246:119002. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119002
Hou, X., Liu, J., Zhang, D., Zhao, M., and Xia, C. (2019). Impact of urbanization on the eco-efficiency of cultivated land utilization: a case study on the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. J. Clean. Prod. 238:117916. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117916
Hou, X., Liu, J., Zhang, D., Zhao, M., and Yin, Y. (2021). Effect of landscape-scale farmland fragmentation on the ecological efficiency of farmland use: a case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28, 789–806. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-12523-7
Huang, K., Tang, W., and Zhou, F. (2024). Agricultural productive services and ecological efficiency of cultivated land use: evidence from Hunan Province, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 33, 5127–5140. doi: 10.15244/pjoes/182907
Ke, N., Zhang, X., Lu, X., Kuang, B., and Jiang, B. (2022). Regional disparities and influencing factors of eco-efficiency of arable land utilization in China. Land 11:257. doi: 10.3390/land11020257
Ke, X., Zhang, Y., and Zhou, T. (2023). Spatio-temporal characteristics and typical patterns of eco-efficiency of cultivated land use in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 33, 357–372. doi: 10.1007/s11442-023-2086-x
Kuang, B., Lu, X., Zhou, M., and Chen, D. (2020). Provincial cultivated land use efficiency in China: empirical analysis based on the SBM-DEA model with carbon emissions considere forecast change. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2019.119874
Kühling, I., Broll, G., and Trautz, D. (2016). Spatio-temporal analysis of agricultural land-use intensity across the Western Siberian grain belt. Sci. Total Environ. 544, 271–280. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.129
Li, J., Rodriguez, D., and Tang, X. (2017). Effects of land lease policy on changes in land use, mechanization and agricultural pollution. Land Use Policy 64, 405–413. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.03.008
Li, M., Tan, L., and Yang, X. (2023). The impact of environmental regulation on cultivated land use eco-efficiency: evidence from China. Agriculture 13:1723. doi: 10.3390/agriculture13091723
Li, Y., and Wenbo, L. I. (2017). Cultivated land's utilization efficiency and influencing factors in China under environmental constraints—based on global Malmquist–Luenberger index method. Agric. Econ. Manage. 6, 25–35.
Li, X., Zhao, L., Chang, X., Yu, J., Song, X., and Zhang, L. (2023). Spatial and temporal evolution of the eco-efficiency of cultivated land use in the region around Beijing–Tianjin based on the super-EBM model. Front. Ecol. Evol. 11:1297570. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2023.1297570
Lin, H. C., and Hülsbergen, K. J. (2017). A new method for analyzing agricultural land-use efficiency, and its application in organic and conventional farming systems in southern Germany. Eur. J. Agron. 83, 15–27. doi: 10.1016/j.eja.2016.11.003
Liu, Y., Fang, F., and Li, Y. (2014). Key issues of land use in China and implications for policy making. Land Use Policy 40, 6–12. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2013.03.013
Liu, Q., Qiao, J., Han, D., Li, M., and Shi, L. (2023). Spatiotemporal evolution of cultivated land use eco-efficiency and its dynamic relationship with landscape pattern change from the perspective of carbon effect: a case study of Henan, China. Agriculture 13:1350. doi: 10.3390/agriculture13071350
Liu, C., Song, C., Ye, S., Cheng, F., Zhang, L., and Li, C. (2023). Estimate provincial-level effectiveness of the arable land requisition-compensation balance policy in mainland China in the last 20 years. Land Use Policy 131:106733. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2023.106733
Liu, K., and Zhang, A. L. (2023). Research progress and hotspots of cultivated land use efficiency in China and internationally: based on a bibliometric analysis. Resour. Sci. 45, 494–511. doi: 10.18402/resci.2023.03.03
Liu, Y., Zou, L., and Wang, Y. (2020). Spatial-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of agricultural eco-efficiency in China in recent 40 years. Land Use Policy 97:104794. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104794
Lu, X., Qu, Y., Sun, P., Yu, W., and Peng, W. (2020). Green transition of cultivated land use in the Yellow River Basin: a perspective of green utilization efficiency evaluation. Land 9:475. doi: 10.3390/land9120475
Luo, X., Ao, X., Zhang, Z., Wan, Q., and Liu, X. (2020). Spatiotemporal variations of cultivated land use efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Belt based on carbon emission constraints. J. Geogr. Sci. 30, 535–552. doi: 10.1007/s11442-020-1741-8
Ma, Y., Wang, X., and Zhong, C. (2024). Spatial and temporal differences and influencing factors of eco-efficiency of cultivated land use in Main grain-producing areas of China. Sustain. For. 16:5734. doi: 10.3390/su16135734
Ma, Y., Zheng, M., Zheng, X., Huang, Y., Xu, F., Wang, X., et al. (2023). Land use efficiency assessment under sustainable development goals: a systematic review. Land 12:894. doi: 10.3390/land12040894
Oh, D. H. (2010). A global Malmquist–Luenberger productivity index. J. Prod. Anal. 34, 183–197. doi: 10.1007/s11123-010-0178-y
Qu, Y., Lyu, X., Peng, W., and Xin, Z. (2021). How to evaluate the green utilization efficiency of cultivated land in a farming household? A case study of Shandong Province, China. Land 10:789. doi: 10.3390/land10080789
Rosegrant, M. W., and Cline, S. A. (2003). Global food security: challenges and policies. Science 302, 1917–1919. doi: 10.1126/science.1092958
Smith, P. (2013). Delivering food security without increasing pressure on land. Glob. Food Secur. 2, 18–23. doi: 10.1016/j.gfs.2012.11.008
Tan, S., Hu, B., Kuang, B., and Zhou, M. (2021). Regional differences and dynamic evolution of urban land green use efficiency within the Yangtze River Delta, China. Land Use Policy 106:105449. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2021.105449
Tilman, D., Balzer, C., Hill, J., and Befort, B. L. (2011). Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 20260–20264.
Tone, K. (2002). A slacks-based measure of super-efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 143, 32–41. doi: 10.1016/S0377-2217(01)00324-1
Tone, K. (2004). Dealing with undesirable outputs in DEA: a slacks-based measure (SBM) approach. GRIPS Res. Report Series 2004, 44–45.
Tone, K. (2010). Variations on the theme of slacks-based measure of efficiency in DEA. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 200, 901–907. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2009.01.027
Wang, J., Su, D., Wu, Q., Li, G., and Cao, Y. (2023). Study on eco-efficiency of cultivated land utilization based on the improvement of ecosystem services and energy analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 882:163489. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.163489
Wang, J., Yin, S., Ma, L., Gan, T., and Xu, L. (2022). Spatio temporal evolution and influencing factors of cultivated land ecological efficiency in Hebei province based on SBM model. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 29, 81–89.
Xiang, H., Wang, Y. H., Huang, Q. Q., and Yang, Q. Y. (2020). How much is the eco-efficiency of agricultural production in West China? Evidence from the village level data. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 17:4049. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17114049
Xiao, P., Xu, J., Yu, Z., Qian, P., Lu, M., and Ma, C. (2022). Spatiotemporal pattern differentiation and influencing factors of cultivated land use efficiency in Hubei Province under carbon emission constraints. Sustain. For. 14:7042. doi: 10.3390/su14127042
Xie, H., Xhen, Q., Wang, W., and He, Y. (2018). Analyzing the green efficiency of arable land use in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 133, 15–28. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2018.03.015=
Yang, B., Wang, Y., Li, Y., and Mo, L. (2023). Empirical investigation of cultivated land green use efficiency and influencing factors in China. 2000–2020. Land 12:1589. doi: 10.3390/land12081589
Yang, B., Wang, Z., Zou, L., Zou, L., and Zhang, H. (2021). Exploring the eco-efficiency of cultivated land utilization and its influencing factors in China's Yangtze River Economic Belt, 2001–2018. J. Environ. Manag. 294:112939. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112939
Ye, S., Song, C., Gao, P., Cheng, F., Ren, S., Du, B., et al. (2023). Construction of the new cognitive system for arable land resources from geospatial perspective. Trans. Chinese Soc. Agric. Eng. 39, 225–240. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202211142
Ye, S., Song, C., Shen, S., Peichao, G., Changxiu, C., Feng, C., et al. (2020). Spatial pattern of arable land-use intensity in China. Land Use Policy 99:104845. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104845
Ye, S., Wang, J., Jiang, J., Gao, P., and Song, C. (2024). Coupling input and output intensity to explore the sustainable agriculture intensification path in mainland China. J. Clean. Prod. 442:140827. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.140827
Yin, Y., Hou, X., Liu, J., Zhou, X., and Zhang, D. (2022). Detection and attribution of changes in cultivated land use ecological efficiency: a case study on Yangtze River Economic Belt. Ecol. Indic. 137:108753. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108753
Zhou, C., Shi, C., Wang, S., and Zhang, G. (2018). Estimation of eco-efficiency and its influencing factors in Guangdong province based on super-SBM and panel regression models. Ecol. Indic. 86, 67–80. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.12.011
Zhou, X., Wu, D., Li, J., Liang, J., Zhang, D., and Chen, W. (2022). Cultivated land use efficiency and its driving factors in the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 144:109411. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109411
Keywords: eco-efficiency of cultivated land use, spatial–temporal evolution, influencing factors, super-efficiency slacks-based measure, global Malmquist-Luenberger index, geographically and temporally weighted regression, Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region
Citation: Jiao X, Ma J, Liu G, Li Y, Li C and Wang X (2024) Spatial–temporal evolution and influencing factors of the eco-efficiency of cultivated land-use in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region in the context of food security. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1462031. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1462031
Edited by:
Xueru Zhang, Hebei University of Economics and Business, ChinaReviewed by:
Piling Sun, Qufu Normal University, ChinaHuanyu Chang, Tianjin Normal University, China
Copyright © 2024 Jiao, Ma, Liu, Li, Li and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chenggang Li, bGljaGVuZ2dhbmc2MDNAbWFpbC5ndWZlLmVkdS5jbg==
 Xinying Jiao
Xinying Jiao Jingtao Ma4
Jingtao Ma4 Guoxiang Liu
Guoxiang Liu Chenggang Li
Chenggang Li