- Research Center for Agroindustry, National Research and Innovation Agency, Jakarta, Indonesia
In recent years, the drying of red chili peppers (Capsicum annuum) has garnered increasing attention in the global food industry, resulting in significant advances in drying techniques. This study presents a bibliometric analysis of red chili drying research from 2004 to 2023, using VOSviewer and Bibliometrix software. The analysis adopts a two-pronged approach: (1) research structure analysis, which maps collaborative networks among researchers, and (2) topic development analysis, which explores thematic evolution in this field. The results indicate a steady annual growth rate of 6.65% in publications, with major contributions from countries such as Turkey, India, and China. Drying technologies have advanced from traditional methods like sun drying to modern techniques, including solar, convective, infrared, ultrasound, radio-frequency, microwave, and freeze drying. These innovations not only improve efficiency but also help retain the sensory and bioactive qualities of chili peppers, such as color, texture, capsaicinoids, and antioxidants. Recent trends highlight the importance of optimizing processes to enhance product quality while minimizing energy consumption, contributing to food sustainability. Innovations in pre-treatment techniques, such as blanching and cold plasma, have also demonstrated potential in preserving bioactive compounds. Additionally, hybrid methods that combine drying techniques with pre-treatment strategies offer an optimal balance between efficiency and quality. The study recommends that future research focus on comparative analyses of different drying methods, examining their effects on product quality and energy efficiency. These insights aim to guide researchers, policymakers, and industry stakeholders in developing more sustainable and effective drying technologies for red chili.
1 Introduction
Drying of red chili peppers (Capsicum annuum) is a critical postharvest process that plays a key role in determining the quality, safety, and shelf life of the product (Jalgaonkar et al., 2022). With fresh chili peppers containing between 60 to 85% moisture at harvest (Majumder et al., 2021), they are highly susceptible to spoilage (Geng et al., 2022). The drying process lowers the moisture content to safe levels, inhibiting enzymatic and microbial activity, thereby extending the shelf life of chili peppers (Jin et al., 2018; Kurup et al., 2020).
Red chili peppers, renowned for their culinary and medicinal applications, require effective drying techniques to preserve their nutritional and sensory qualities. These qualities—such as color, texture, and capsaicinoid content—significantly influence both market prices and consumer acceptance (Duranova et al., 2022; Getahun and Ebissa, 2024). Consequently, the development of efficient drying technologies remains a focal point of research (Amit et al., 2017). In addition to being a preservation method, drying adds value to raw produce, enhances marketability, and supports the sustainable economic development of regions where chili peppers are a key commodity.
Color and pungency are the primary factors determining the quality of red peppers, influencing both market prices and consumer preferences (Kim et al., 2002; Gangadhar et al., 2012). However, drying methods vary significantly in efficiency and outcomes. Traditional methods, such as sun drying, are cost-effective but often result in inconsistent quality, extended drying times, and risks of contamination, including aflatoxins (Najmus et al., 2021). Modern methods, such as solar, convective, infrared, and microwave drying, offer greater efficiency and control but may compromise product quality—particularly in terms of color, texture, and bioactive content (Zhang et al., 2017). Moreover, these modern methods often require higher energy inputs, posing challenges for adoption in developing countries.
Recent trends emphasize the importance of optimizing drying processes to enhance product quality while minimizing energy consumption, contributing to food sustainability. One promising solution is the adoption of hybrid drying methods—systems that integrate multiple technologies (e.g., solar drying with microwave assistance) or pre-treatment strategies (e.g., blanching with cold plasma) to enhance efficiency. By balancing the strengths and limitations of individual techniques, these methods aim to improve both product quality and energy efficiency.
Despite significant progress, the field still requires cross-sector collaboration to overcome fragmentation and foster deeper synergies between research and practical applications. Many studies focus on specific drying methods and their impact on product quality, without providing a comprehensive view of global trends or emerging innovations. This bibliometric analysis, covering publications from 2004 to 2023, seeks to fill this gap by systematically analyzing the literature. Using VOSviewer and Bibliometrix software, this study maps research trends, identifies key contributors, and highlights underexplored areas.
A bibliometric approach offers valuable insights into the evolution of drying technologies by revealing research foci and neglected areas. It also allows for a systematic evaluation of the trade-offs between traditional and modern drying methods. For instance, hybrid methods that combine elements of both approaches may offer an optimal balance between efficiency and quality. By assessing the impact of various drying techniques on chili pepper attributes—such as color, taste, texture, and bioactive compound content—this study aims to provide evidence-based solutions for the adoption of sustainable drying technologies, especially in developing regions.
Furthermore, this analysis enhances global scientific communication by identifying key researchers and collaborative networks in the field. In addition to reviewing two decades of developments, the study offers strategic guidance for selecting the most appropriate drying technologies and highlights opportunities for future innovation.
Research Questions:
1. How has red chili drying technology evolved and the latest innovations over the past two decades?
2. What is the impact of drying method on product quality, including color, texture, and bioactive content?
3. How do modern drying technologies compare in terms of energy efficiency and bioactive retention?
4. What is the most effective and affordable drying method to implement in developing countries?
5. What are further research opportunities, especially in the development of hybrid methods?
The structure of this paper is described as follows: Initially, the methodology used in the bibliometric review is described. Next, results relevant to the research questions will be presented and evaluated. The main conclusions of this study will be summarized, and recommendations for future research in the field of red chili drying technology will be given.
2 Methodology
This quantitative study employs a bibliometric review, following the methodological model recommended by Zupic and Cater (2015). We utilized two bibliometric tools: VOSviewer and Bibliometrix. VOSviewer is particularly useful for constructing and visualizing bibliometric networks—such as citation networks, co-citations, and co-authorship patterns—making it ideal for mapping the research landscape (van Eck and Waltman, 2010). Bibliometrix, an R package, offers extensive capabilities for bibliometric analysis and visualization, including scientific mapping, collaboration networks, and thematic evolution (Aria and Cuccurullo, 2017).
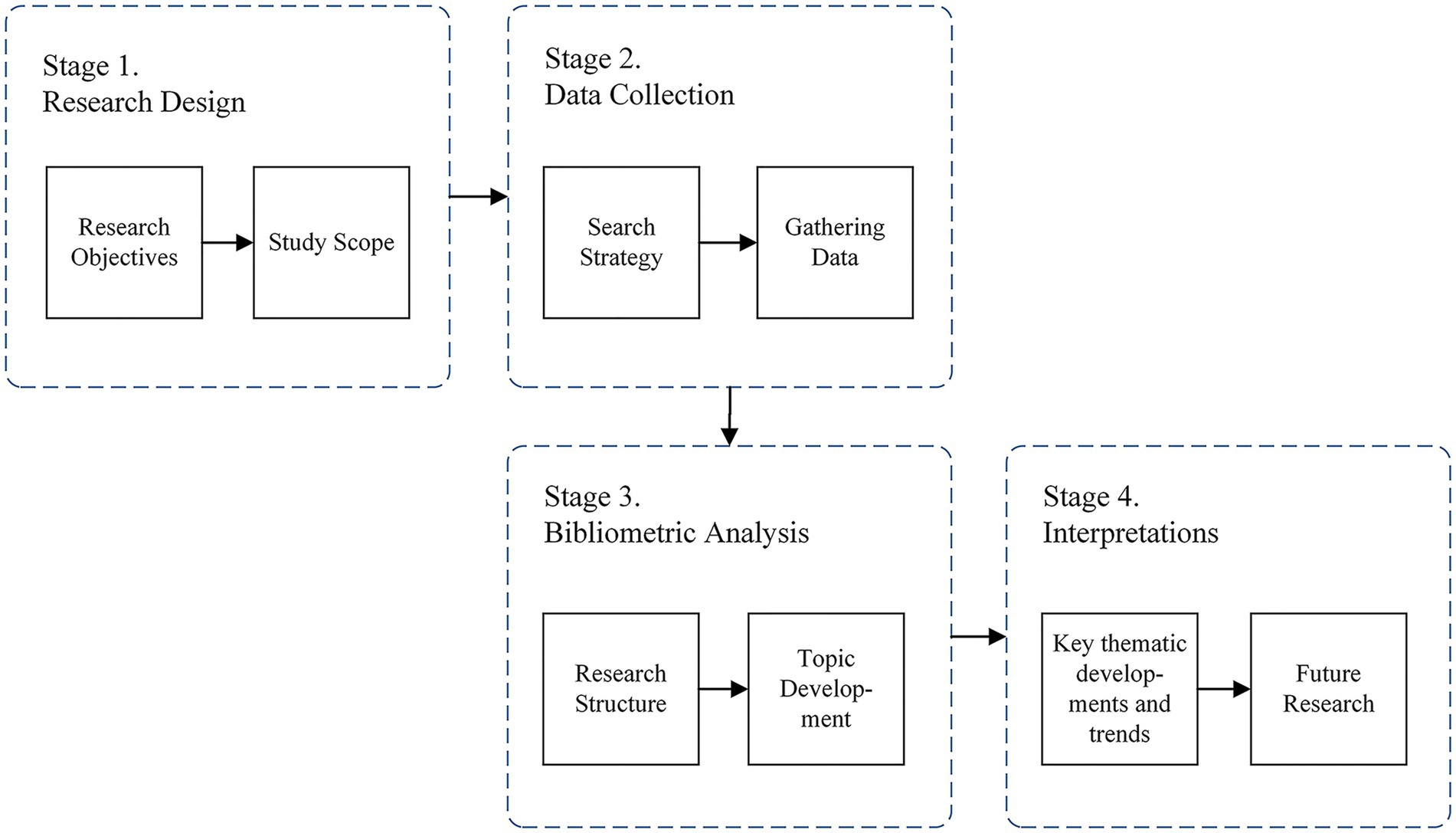
The research methodology follows a four-stage process to systematically analyze the evolution of research on red chili pepper drying. This approach ensures a comprehensive understanding of both the research structure and thematic developments.
Figure 1 illustrates the step-by-step research methodology, highlighting each phase in detail.
2.1 Stage 1: research design
We began by defining the study’s objectives and establishing its scope. The primary objective was to analyze global trends in red chili drying research, focusing on key contributors, collaborations, and thematic shifts over time. The scope was restricted to publications available in the Scopus database from 2004 to 2023, with a focus on scientific articles and conference proceedings written in English.
2.2 Stage 2: data collection
This stage involved developing a keyword-based search strategy. We used terms such as “red chili,” “Capsicum annuum,” and “drying” to retrieve relevant studies. Non-English articles and irrelevant publications were excluded to maintain consistency, ensuring that the collected dataset was suitable for bibliometric analysis.
2.3 Stage 3: bibliometric analysis
The dataset was analyzed to explore two aspects: (1) the research structure, focusing on publication growth, geographic contributions, and collaboration networks, and (2) topic development, tracking the evolution of research themes, emerging trends, and innovations in drying technologies.
2.4 Stage 4: interpretation
In the final stage, we synthesized the results to highlight key thematic developments and identify research gaps. These insights helped propose future research directions to advance the field further.
2.5 Research design
This research employs a bibliometric analysis framework to explore the intellectual and structural evolution of red chili drying research from 2004 to 2023. The two-decade span provides a comprehensive lens for identifying long-term research trajectories and capturing the transition from traditional to modern drying technologies. The selection of 2004 as the starting point is significant, marking a pivotal era in food processing research characterized by technological innovations, such as microwave-assisted drying, alongside a growing global focus on sustainability and food preservation. Additionally, this period aligns with the rapid expansion of digital databases like Scopus, offering a broader range of studies for in-depth analysis.
The primary objective of this study is to assess global research trends, identify key contributors, and track the thematic evolution of research topics through bibliometric tools. The analysis centers on two core components: Research Structure and Topic Development. Research Structure examines metrics such as publication growth, geographic contributions, and collaboration networks, while Topic Development employs keyword co-occurrence analysis to monitor shifts in research themes and highlight emerging trends. Key indicators include publication growth trends, Mean Total Citations per Article (MeanTCperArt), and the ratio of Single Country Publications (SCP) to Multiple Country Publications (MCP)—a metric that distinguishes between domestic and international research collaborations.
By analyzing co-authorship networks and keyword frequency patterns, the study identifies the most influential researchers, institutions, and regions, while mapping the thematic evolution of red chili drying research over time. The anticipated outcome is a comprehensive overview of the research landscape, shedding light on significant trends, collaborative networks, and emerging areas for future inquiry. This analysis aims to provide actionable insights that could guide future research directions and foster further collaboration in both traditional and cutting-edge drying technologies.
2.6 Data collection
2.6.1 Database selection
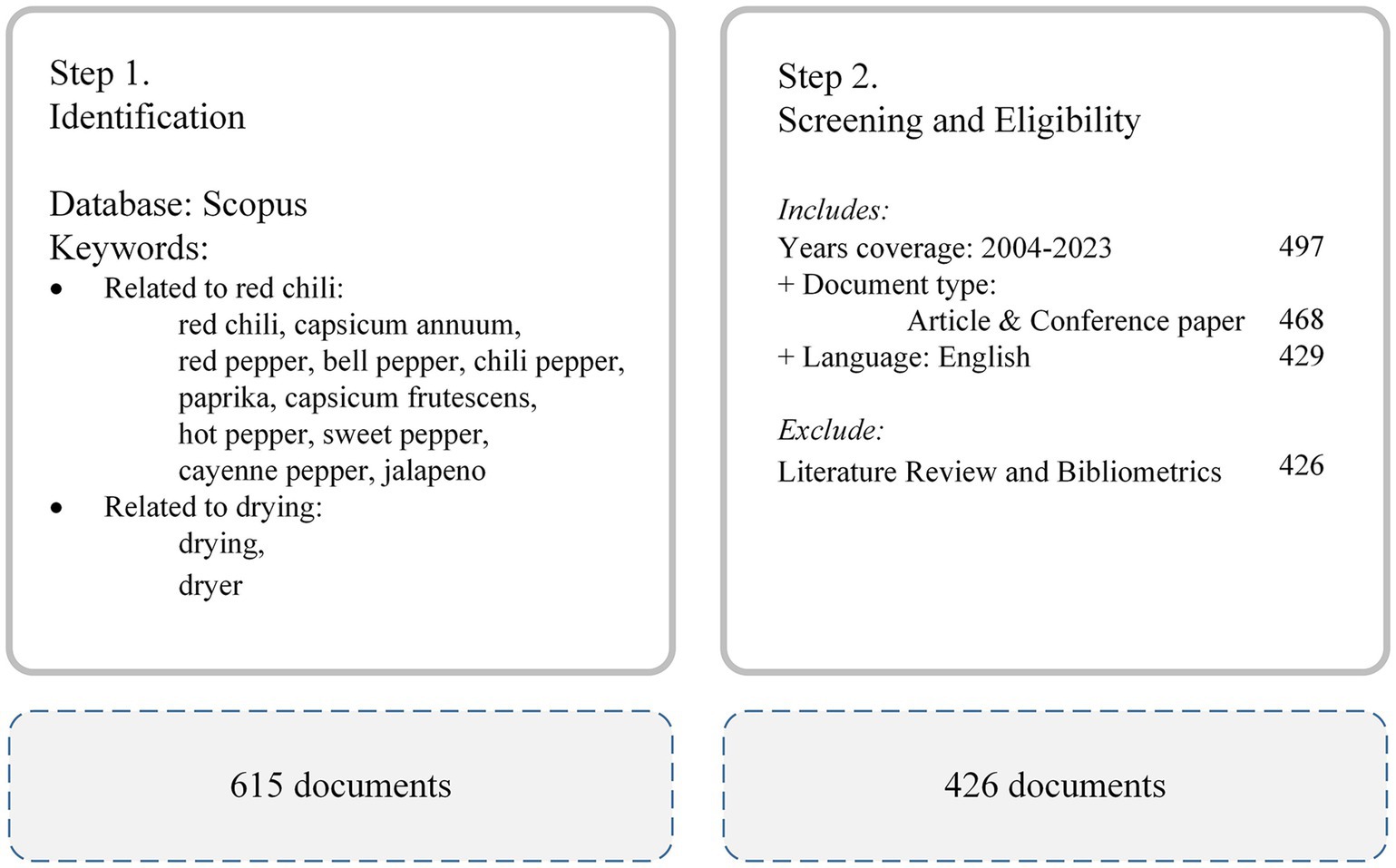
The data for this study were collected on October 1, 2024, using the Scopus database, as shown in Figure 2. Scopus, one of the largest and most comprehensive scientific literature databases, provides extensive coverage of high-quality publications across diverse disciplines. We selected Scopus because it offers reliable datasets that encompass a broad range of relevant studies (Baas et al., 2020). Compared to other databases, such as Web of Science and Google Scholar, Scopus provides a wider selection of indexed journals and more advanced citation analysis tools, making it particularly well-suited for bibliometric studies.
2.6.2 Search strategy
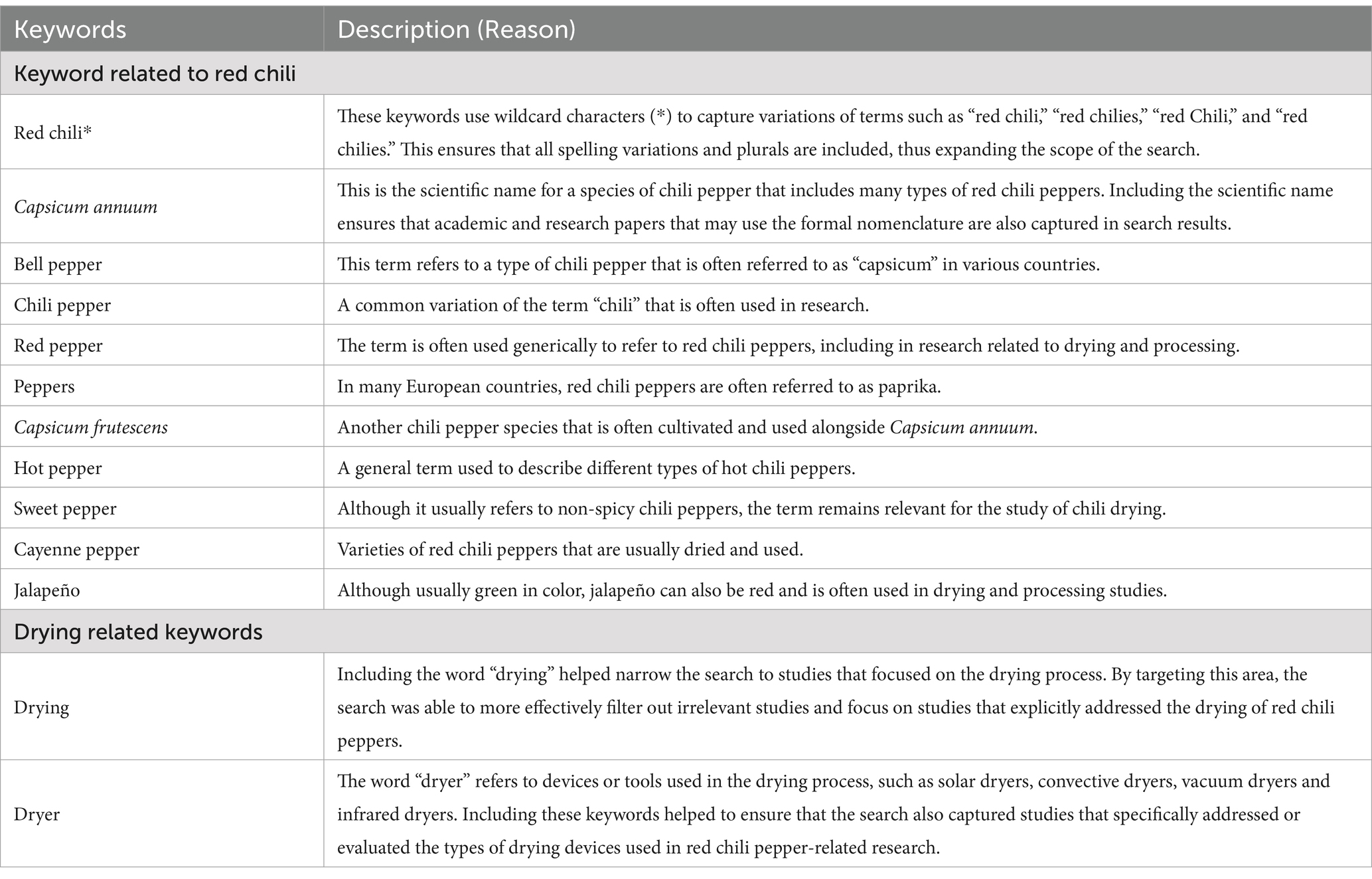
A keyword search is a crucial step in initiating research, enabling researchers to efficiently identify relevant literature and gather comprehensive information on a given topic. As MacDonald (2023) emphasizes, the effective use of keywords can greatly enhance the quality and breadth of research. For this study, we searched the database using a combination of keywords that reflect the core themes of our research, as outlined in Table 1.
A search with these keywords returned 615 papers.
2.7 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
To ensure the relevance and quality of the selected publications, we applied the following inclusion and exclusion criteria. The inclusion criteria were designed to capture studies that specifically addressed the impact of eligibility and exclusion criteria on non-English language papers.
• Inclusion Criteria:
o Publications from 2004 to 2023, resulting in 497 papers.
o Peer-reviewed journal articles and conference papers that explicitly addressed red chili drying. Resulting in 468 papers.
• Exclusion Criteria:
o Non-English articles were excluded to maintain consistency in analysis. 429 papers were produced.
o Moreover, we excluded review articles. Resulting in 426 papers.
2.8 Query string
• Query String:
• (TITLE-ABS-KEY (“red chili” OR “capsicum annuum” OR “red pepper” OR “bell pepper” OR “chili pepper” OR “paprika” OR “capsicum frutescens” OR “hot pepper” OR “sweet pepper” OR “cayenne pepper” OR “jalapeno”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (drying OR dryer)) AND PUBYEAR >2003 AND PUBYEAR <2024 AND NOT TITLE-ABS-KEY (“review” OR “SLR” OR “bibliometric”) AND (LIMIT-TO (DOCTYPE, “ar”) OR LIMIT-TO (DOCTYPE, “cp”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (LANGUAGE, “English”)).
• This phrase may refer to the use of certain search strings or syntax to extract relevant information from the Scopus database. For example, using advanced search operators and boolean expressions such as “AND,” “OR,” and appropriate phrases in quotes to refine search results. This method ensures that the search is comprehensive and topic-specific.
2.8.1 Feasibility
The bibliometric data collected included key variables such as the number of citations, authors, year of publication, and journal name. The data were extracted in BibTeX and CSV formats for efficient processing and analysis. To ensure a comprehensive understanding, we selected articles with high citation counts or those identified as particularly relevant through bibliometric evaluation for in-depth review. Additionally, recent publications were thoroughly analyzed to capture emerging trends and the latest developments in the field. This dual approach ensures that the study highlights both influential, well-established works and recent contributions, providing a balanced and up-to-date perspective on research advancements.
2.9 Bibliometric analysis
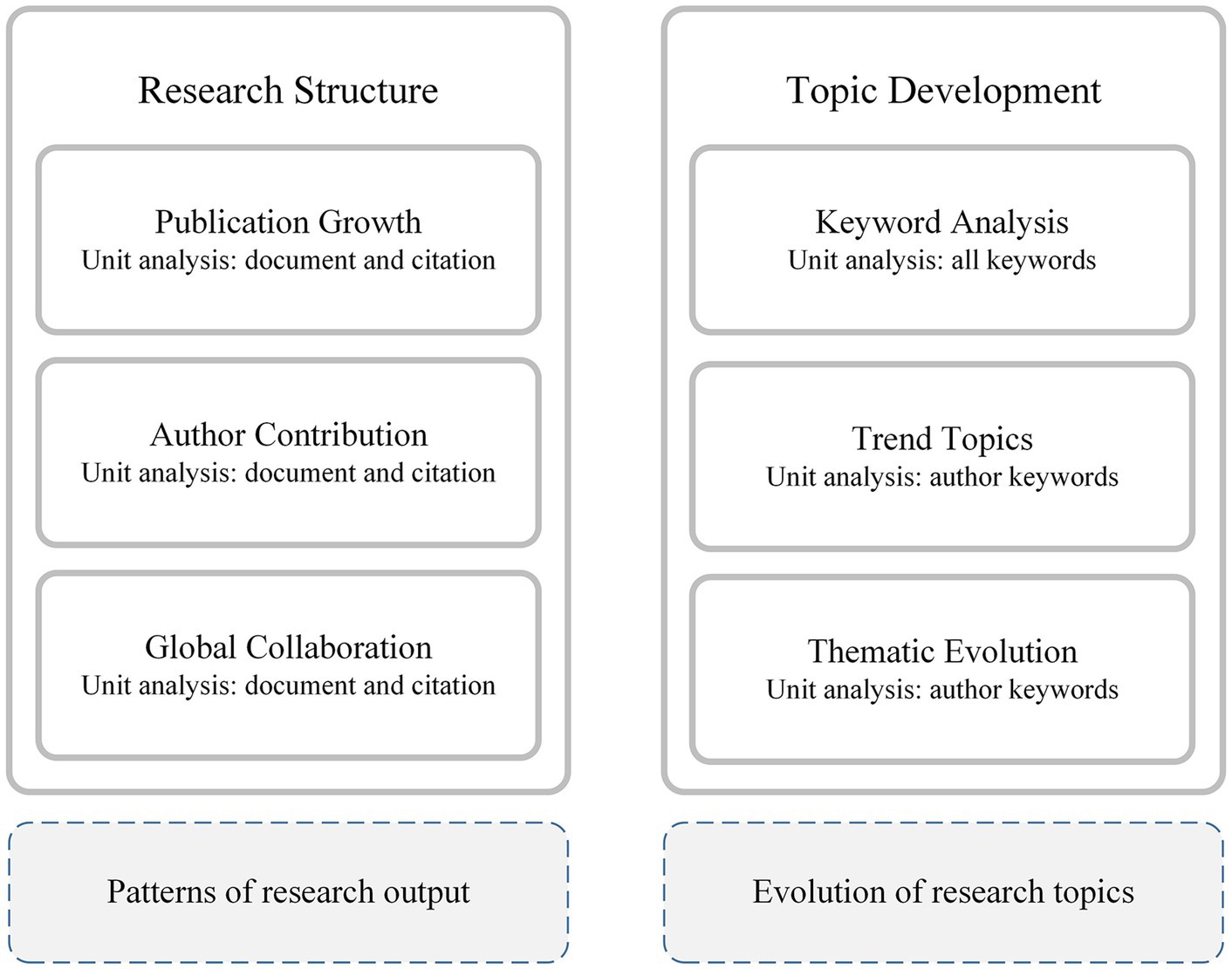
The bibliometric analysis in this study was designed to map the research structure and topic development of red chili drying research, as shown in Figure 3. The analysis was conducted to identify key trends, contributors, and research themes over the past two decades.
2.9.1 Research structures
The research structure analysis explored patterns in research output and collaboration within the field of red chili drying. Specifically, it focused on the following aspects:
1. Publication Growth: We tracked the annual distribution of publications to assess research growth and calculated Mean Total Citations per Article (MeanTCperArt) to measure the average impact. This combined analysis identified periods of significant output and high-impact research, indicated by high MeanTCperArt values (Hirsch, 2005).
2. Geographic Contributions: We mapped the global distribution of research by analyzing the origin of publications. Publications were categorized as Single Country Publications (SCP) or Multiple Country Publications (MCP) to assess domestic efforts and cross-border collaborations, highlighting the global research network (Sutherland et al., 2011).
3. Author Collaboration: Using co-authorship networks, we identified influential authors and key research groups. Metrics such as h-index and total citations further evaluated the impact of individual researchers and institutions (Ullah et al., 2022).
This analysis focuses on who conducts the research and where it is produced, emphasizing the structural components of the research ecosystem, including contributors, collaboration networks, and geographic distribution.
2.9.2 Topic development
The topic development analysis traced the evolution of research themes and identified emerging topics in red chili pepper drying. It included:
1. Co-occurrence of Keywords: Using VOSviewer, we analyzed keyword frequency and connections to identify main themes (Sampagnaro, 2023).
2. Thematic Mapping: A thematic map visualized keyword clusters representing research topics, such as traditional drying methods, advanced technologies, and bioactive compound preservation. Cluster size and density revealed unexplored areas and future research directions (Karakose et al., 2022).
3. Trends Over Time: We tracked shifts in research focus, such as the transition from solar drying to microwave-assisted drying, and identified increasing attention to sustainability and bioactive preservation (Nelis et al., 2022; Nguyen et al., 2021).
This analysis examines what is being studied, revealing emerging trends, popular topics, and shifts in focus over time. It highlights the intellectual evolution of the field, offering insights into current research themes and opportunities for future exploration.
2.10 Interpretation
This stage focuses on analyzing and interpreting the results in alignment with the research objectives and questions. It involves summarizing conclusions, discussing the implications and significance of the findings, and providing recommendations for future research.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Research structure
3.1.1 Publication growth
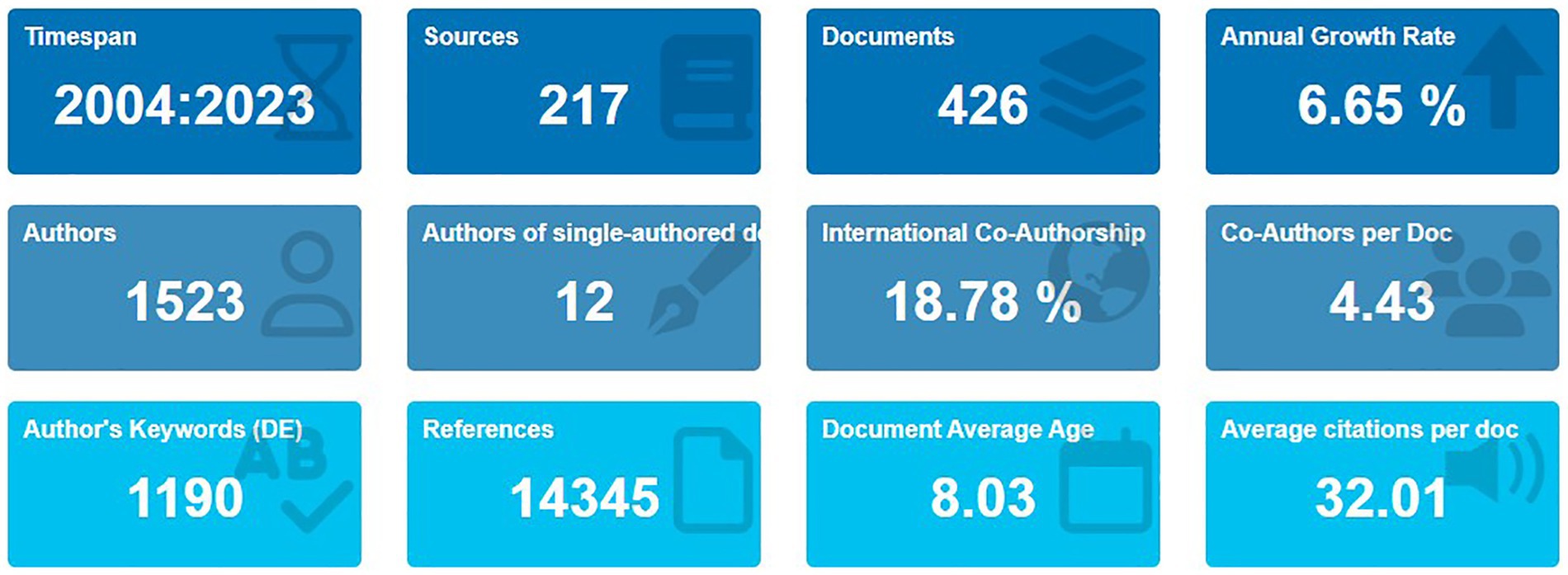
As summarized in Figure 4, research on red chili pepper drying has grown steadily, with an annual increase of 6.65% in publications over the past two decades. This growth reflects the increasing importance of the field in agriculture and food science. Contributions from 1,523 authors across 62 countries have resulted in 426 publications, comprising 394 research articles and 32 conference papers. On average, each document involves 4.43 co-authors, with 18.78% of papers representing international collaborations—highlighting the global interest and cooperative nature of research in this area. This broad participation underscores the role of red chili drying in both agriculture and cuisine worldwide.
The analysis identified 1,190 unique keywords and 14,345 references, demonstrating the depth and diversity of research. The average age of the documents is 8.03 years, indicating that much of the research remains relevant. Furthermore, with an average of 32.01 citations per document, the field has had a significant impact on the scientific community. These metrics underscore the influence of foundational research and its continued relevance in guiding new investigations and technological developments in drying methods.
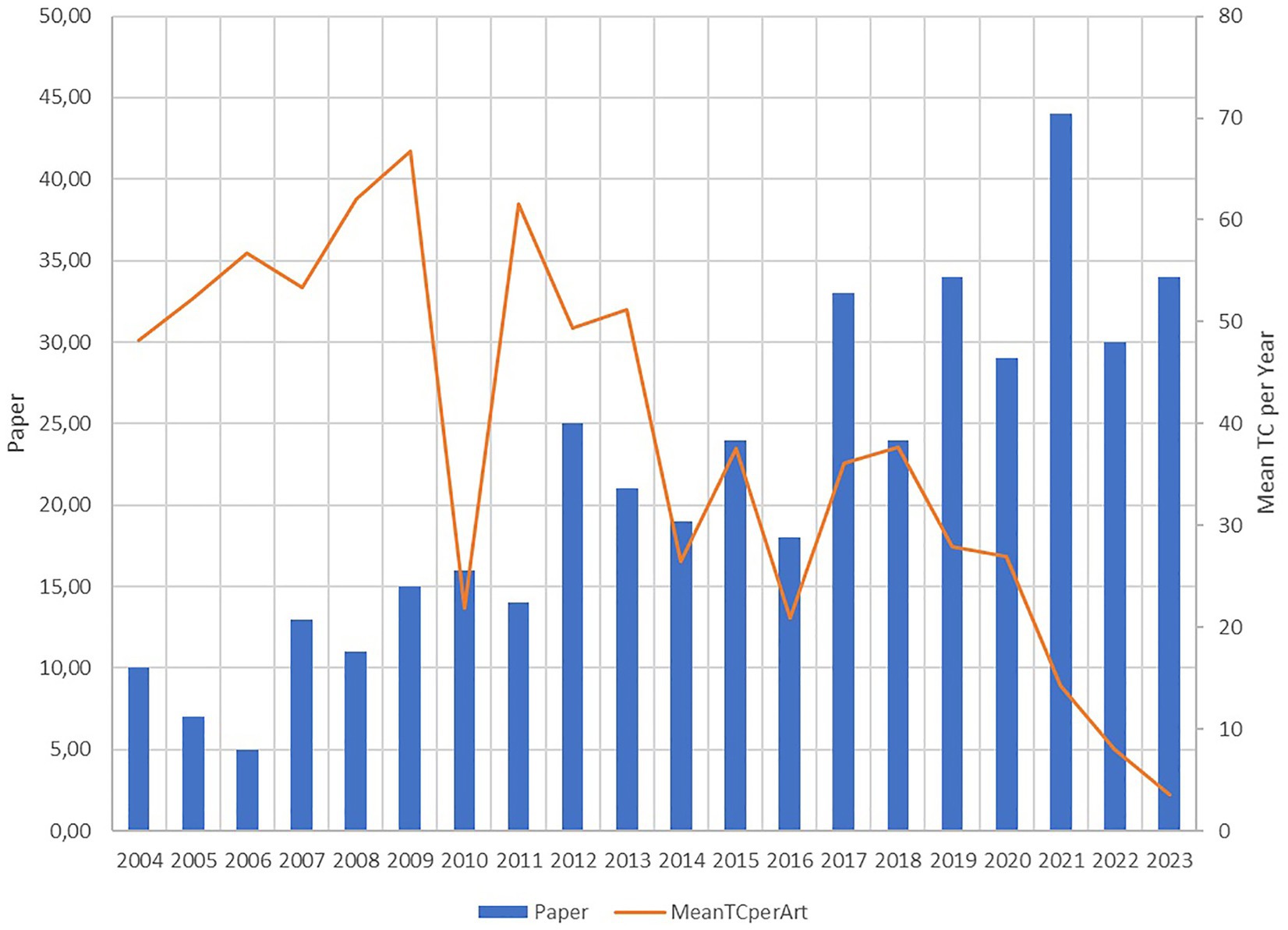
As illustrated in Figure 5, publication growth has been steady between 2004 and 2023, with several spikes indicating periods of heightened research activity. Notably, significant increases in publications occurred in 2012, 2017, 2019, and 2021. The surge in 2012 can be attributed to innovations in moisture removal technologies. Alonge and Adeboye (2012) demonstrated that direct passive solar dryers achieve superior drying rates compared to indirect methods. However, these dryers are weather-dependent, prone to contamination, and often result in inconsistent product quality. In response, Schössler et al. (2012) introduced a contact ultrasonic system, which reduced drying time without compromising product quality. Meanwhile, Swain et al. (2012) improved drying kinetics by applying osmotic pre-treatment to microwave-assisted drying.
The surge in publications during 2017 highlights a growing research focus on solar drying technology for red chili peppers. Studies by Rabha and Muthukumar (2017), Rabha et al. (2017a), and Castillo-Téllez et al. (2017) demonstrated the potential of solar drying in terms of energy efficiency, sustainability, and product quality. However, the effectiveness of this method remains constrained by geographical and climatic factors, which have not yet been fully explored. Although solar drying can maintain product quality, challenges such as the dependence on consistent sunlight and the high infrastructure costs limit its scalability, especially in developing countries with limited resources.
The surge in studies on drying red chili during 2019 and 2021 can be attributed to different aspects of red chili drying. Advancements in drying technologies, such as indirect solar dryer with air flow (Goud et al., 2019), vacuum assisted microwave system, cold plasma pretreatment, ultrasound, and hybrid methods (Guclu et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2019; Cárcel et al., 2019), have significantly contributed to increased research activity. Researchers have focused on optimizing these methods to enhance energy efficiency, maintain product quality, and reduce environmental impact (Ekka and Palanisamy, 2021). The emphasis on quality control—preserving the nutritional and sensory properties of dried chilies—has driven detailed studies on drying kinetics, degradation, and color preservation (Kheto et al., 2021). These technological and methodological innovations have sparked a wave of interest and collaboration among researchers from various fields, leading to a substantial increase in publications.
The growing number of publications during this period also reflects an effort to meet increasing consumer demand for high-quality dried chili peppers. However, the literature highlights the need to integrate sustainability into drying practices. While studies by Jalgaonkar et al. (2022) and Majumder et al. (2021) emphasize the benefits of pre-treatment techniques and renewable energy sources, further field trials are essential to validate their effectiveness at the industrial level. Critical evaluations are required to address the practical challenges associated with large-scale implementation.
Renewable energy initiatives in the drying process, such as those proposed by Getahun et al. (2021a,b) and Amjad et al. (2022), demonstrate the potential for significant environmental and economic benefits. Getahun et al. (2021a,b) reported that a two-stage solar tunnel dryer achieved a collector efficiency of 66.44–76.53% and an overall efficiency of 24.12–31.3%, while reducing carbon emissions by 13 tons annually. Additionally, the technology generated economic benefits through carbon credits worth USD 136,250–162,880 per year, with an energy payback period of 2.1–2.36 years—highlighting its long-term sustainability.
Amjad et al. (2022) further emphasized the importance of optimizing system components and operating conditions, particularly through the integration of solar tube collectors and gas burners. Their system achieved an advanced exergy efficiency of 97.41% in solar mode, minimizing energy losses and improving overall performance. Although these studies align with global sustainability trends, further research is necessary to assess the economic feasibility, energy consumption, and operational sustainability of these technologies on a larger scale. Ensuring their long-term viability will require careful analysis of cost structures and infrastructure needs.
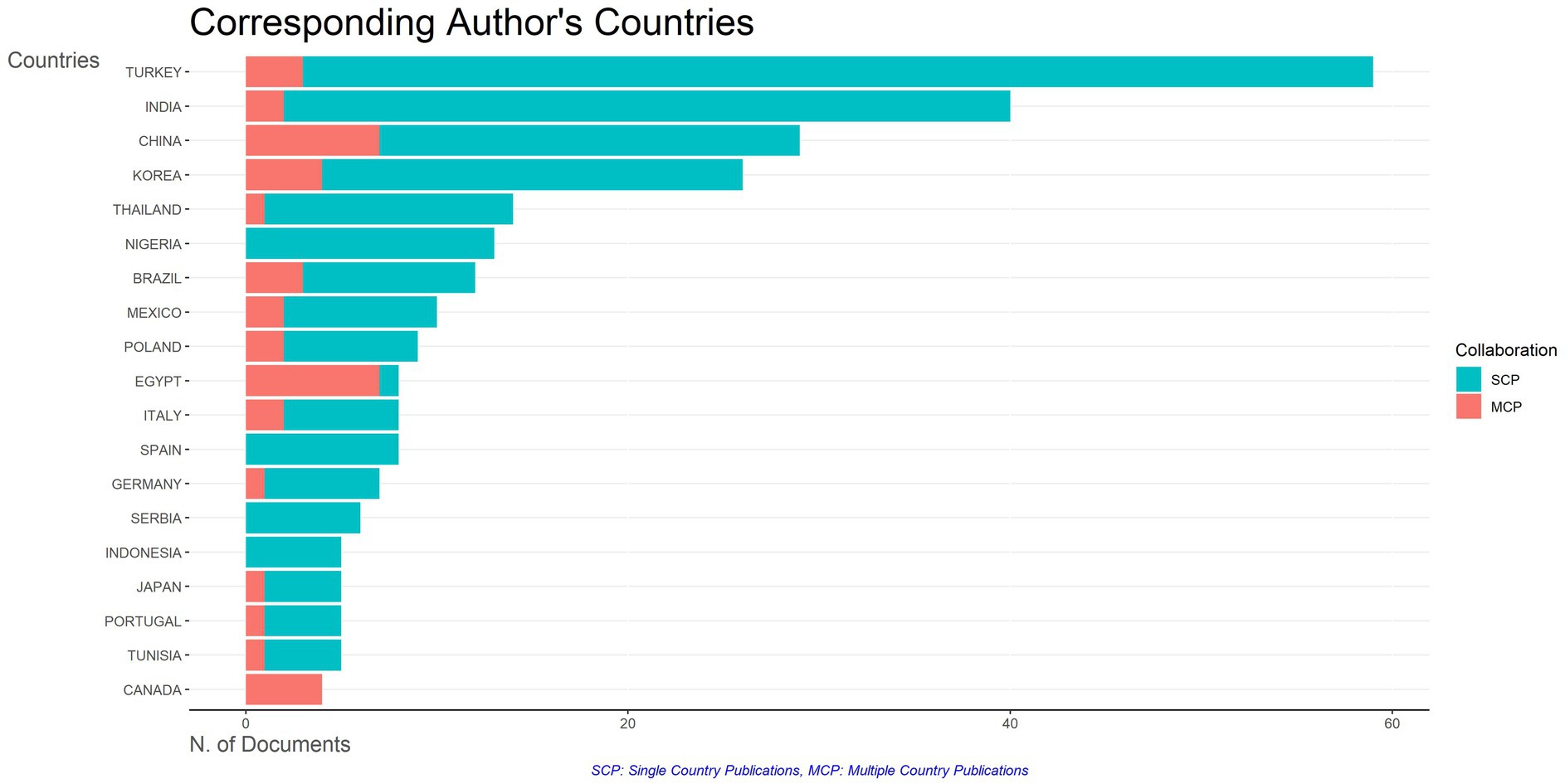
Figure 6 illustrates the geographical distribution of research articles on red chili drying by the corresponding author’s country, categorizing the data into single-country publications (SCP) and multiple-country publications (MCP). Countries with significant red chili production and consumption dominate the research landscape, demonstrates emerging synergies between national priorities and international cross-sector collaborations, advancing knowledge in red chili drying technology.
Turkey leads with 59 documents (13.85%), primarily SCPs, indicating strong domestic research initiatives. Key studies, such as those by Soysal et al. (2009) on microwave convective drying and Arslan and Özcan (2011) on the impact of drying on color and antioxidant retention, emphasize Turkey’s focus on reducing drying time while preserving quality. This focus aligns with Turkey’s culinary traditions and the economic significance of chili peppers in the region.
India follows with 40 publications (9.39%), also dominated by SCPs. Notable contributions include Rabha et al. (2017a,b) on solar dryer efficiency and Maurya et al. (2018) on drying techniques for multiple chili cultivars. India’s focus on solar drying reflects its commitment to utilizing abundant solar resources in line with global sustainability initiatives. However, ongoing challenges—such as the dependence on weather conditions and limited technological infrastructure—continue to raise concerns about the long-term viability and scalability of solar drying systems.
China and Korea also made significant contributions, with 29 and 26 publications, respectively, demonstrating a balance between SCPs and MCPs. China’s research stands out for exploring advanced techniques such as far-infrared, radio-frequency, and microwave drying (Guo and Zhu, 2014; Zhou et al., 2016). Researchers like Zhang et al. (2019) have also investigated cold plasma pre-treatment to enhance efficiency and product quality. Despite the promise of these technologies, unresolved challenges related to high energy costs and limited accessibility hinder their widespread adoption, particularly in developing regions.
Korea, in parallel, has advanced the use of pulsed electric field (PEF) technology to accelerate drying and improve color quality in chili peppers (Won et al., 2015). While these innovations are promising, concerns about their scalability beyond laboratory conditions persist, raising questions about their economic feasibility for industrial use.
Other countries, including Thailand, Nigeria, and Brazil, have also contributed to the field. Thailand has explored far-infrared microwave vacuum drying (Saengrayap et al., 2015), while Nigeria has focused on solar-powered drying systems to harness renewable energy (Tunde-Akintunde, 2011). Brazil has investigated freeze-drying techniques aimed at enhancing bioactive compounds such as capsaicin and dihydrocapsaicin (Aguiar et al., 2013).
The geographical distribution of red chili drying research highlights national strengths and collaborative efforts, with significant contributions from countries such as Turkey, India, China and Korea. While Turkey leads in single-country publications reflecting strong domestic research, other countries such as China and Korea show strong international collaboration, utilizing advanced technologies such as microwave-assisted drying and pulsed electric field (PEF) treatments. Thailand, Nigeria and Brazil also stand out for their innovative approaches in drying methods, such as infrared and solar drying. The research landscape clearly demonstrates the importance of national initiatives and global partnerships in advancing drying technologies and optimizing red chili quality. Going forward, increased international collaboration and cross-disciplinary research will be essential to unlock further innovations in this important area of food science.
3.1.2 Global collaboration
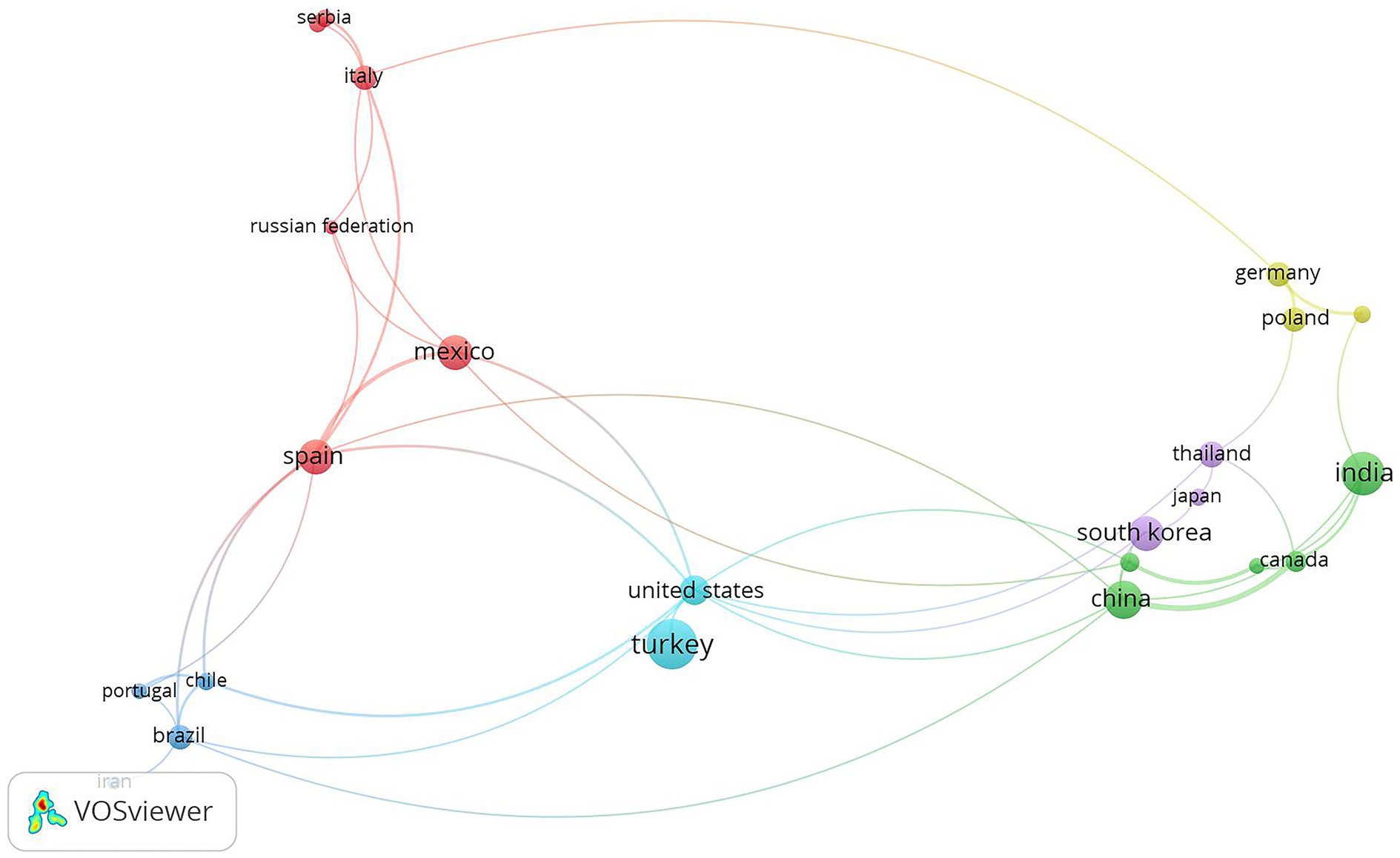
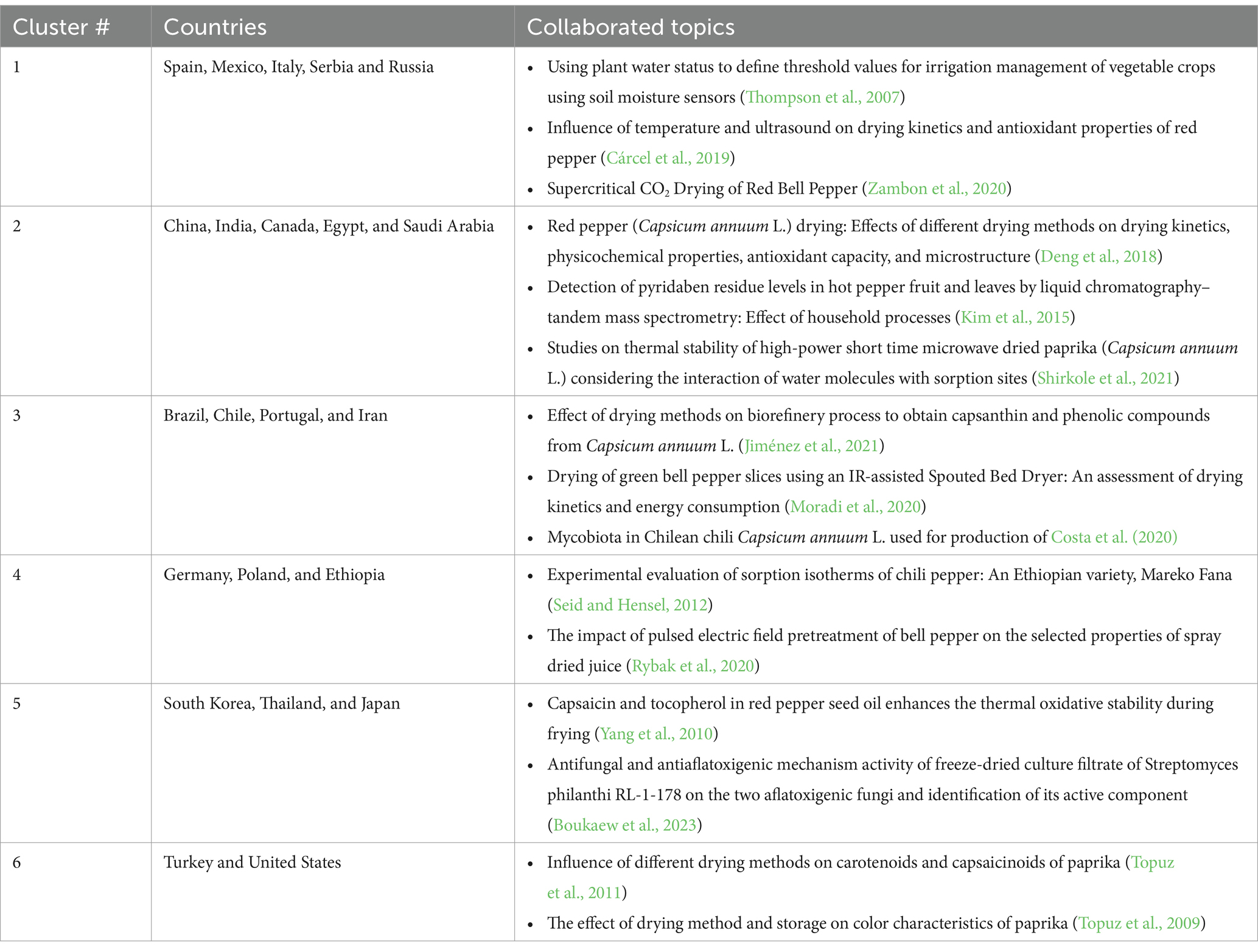
Global collaboration in red chili drying research shows a wide variety of partnerships, reflecting a concerted effort to innovate and share knowledge across different regions. Bibliometric analysis has identified six distinct groups within the author network, each with its own focus, yet collectively contributing to the broader field of red chili drying research, as depicted in Figure 7 and complemented by their collaborative studies in Table 2. These groups illustrate the range of priorities and approaches brought by different countries, highlighting both strengths and potential gaps in current research.
The international collaboration on red chili drying research reflects diverse partnerships, each focusing on distinct aspects of the field. European countries such as Spain, Italy, and Russia emphasize advanced techniques like ultrasound and supercritical CO2 drying to retain antioxidants and improve drying kinetics (Cárcel et al., 2019; Zambon et al., 2020). However, these studies often overlook energy efficiency and scalability, posing challenges for broader application. In parallel, China, India, and Canada explore various drying methods and food safety concerns, such as pesticide residue detection (Deng et al., 2018; Kim et al., 2015). Despite this well-rounded approach, much of the research remains at the laboratory scale, with limited focus on practical implementation for large-scale use.
Other clusters integrate regional relevance and sustainability. Brazil, Chile, and Iran investigate biorefinery processes for recovering valuable compounds from chili, such as capsanthin and phenolics, but they often neglect the energy costs associated with these advanced methods (Jiménez et al., 2021). In a complementary effort, Germany, Poland, and Ethiopia focus on drying kinetics and sorption properties of local chili varieties, using innovative pretreatments like pulsed electric fields (Rybak et al., 2020; Seid and Hensel, 2012). While these studies reflect important adaptations to local contexts, greater emphasis on consumer preferences and efficient drying systems for developing regions is still needed.
The research demonstrates notable advances across drying kinetics, chemical retention, and food safety. However, there are gaps in environmental sustainability, consumer-driven quality, and economic feasibility. Future collaboration should integrate efforts from different clusters, combining sustainable methods with scalable, energy-efficient drying solutions. This would help bridge the gaps and ensure that innovations benefit diverse regions and markets, making research more impactful globally.
3.2 Topic development
3.2.1 Keywords analysis
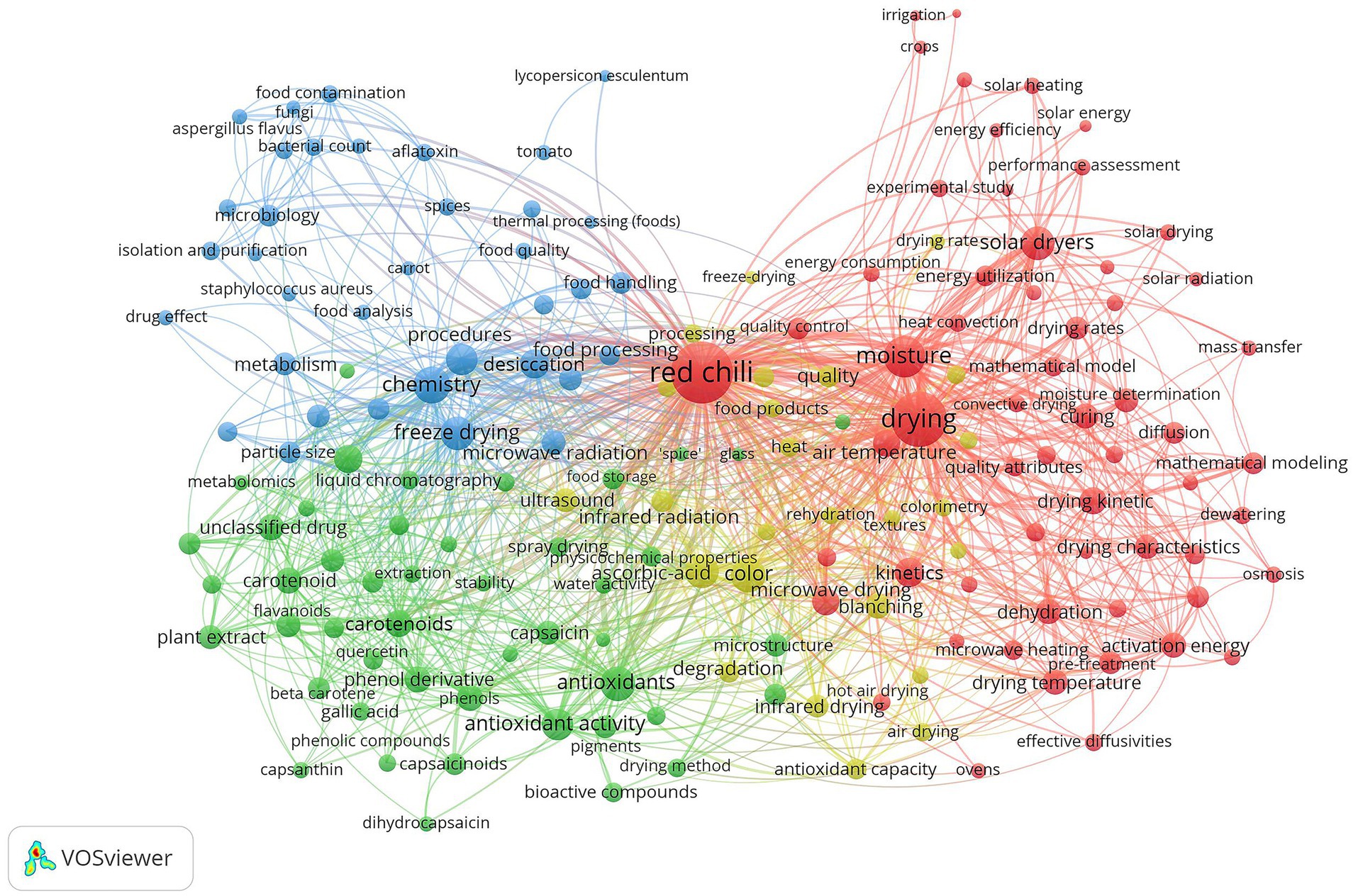
The co-occurrence map in Figure 8 provides a visual representation of how keywords related to red chili pepper drying are interlinked, forming distinct clusters that signify major research directions in this area. Through the use of VOSViewer, 3,794 keywords were analyzed, with 168 meeting the threshold of appearing at least six times. By setting the minimum group size to 20, these keywords were clustered into four main groups, each of which represents a unique aspect of red chili drying research.
3.2.1.1 Cluster 1 (red): drying methods and moisture control
Cluster 1 focuses on the technical and thermodynamic aspects of red chili drying, with particular attention to moisture content control and drying characteristics. In this research, scientists seek to optimize the drying process to efficiently remove moisture content, while maintaining product quality. Various drying techniques have been explored, including solar and convection methods that emphasize energy efficiency and sustainability, especially in regions with high solar energy access. As studies by Rabha and Muthukumar (2017) in India and Tunde-Akintunde (2011) in Nigeria highlighted the development of solar-based drying systems with a focus on optimizing drying time and energy use. These studies helped improve the efficiency of solar-powered drying, which is critical for large-scale applications in both countries. Fudholi et al. (2014) emphasized the need for innovations in solar drying that can improve the practicality and reliability of this technology under real-world conditions.
While in a different region with limited solar energy, research by Soysal et al. (2009) and Saengrayap et al. (2015) explored microwave and infrared methods, which were shown to reduce drying time and energy consumption while maintaining product quality. Topuz et al. (2009) and Won et al. (2015) also investigated the effect of this drying on quality parameters such as color, texture, and nutrient content, and showed that the freeze drying method proved to be more effective in maintaining the quality of dried red chili peppers than traditional methods, such as convection drying and hot air ovens.
Nevertheless, solar-based research is still being conducted by utilizing thermal energy storage to overcome the uncertain availability of solar resources. Solar-based drying innovation was continued by Azaizia et al. (2020), who introduced the use of Phase Change Material (PCM) in a greenhouse drying system, which successfully increased the drying temperature to 75°C at night and reduced the relative humidity significantly. This study showed that the use of PCMs not only accelerated the drying process, reducing the time from 55 h to 30 h, but also optimized the control of product moisture content. The application of mathematical models such as Midili and Two-term also helped to better clarify the drying kinetics, making a significant contribution to the development of more efficient drying technologies.
Complementing this research, Tuncer et al. (2020) developed a quadruple-pass solar air collector (QPSAC) combined with a pilot greenhouse scale dryer. The system showed an improved thermal efficiency of up to 80.66%, with a more stable drying temperature and better temperature control during the drying process. This research provides a more efficient solution in managing the moisture content of red chili peppers, especially through increasing the airflow rate and optimal temperature.
Research by Majumder et al. (2023) introduced osmosonication pretreatment combined with solar fluid bed and drying with humidified air. This pretreatment successfully reduced drying temperature by 10°C and energy consumption by 31.7%, while maintaining bioactive qualities such as capsaicin and red color of chili peppers. The technology demonstrates high efficiency in maintaining product moisture content and offers a solution to accelerate drying under dehumidified conditions, which is important in regions with limited energy access.
3.2.1.2 Cluster 2 (green): bioactive compounds and antioxidants
The green group focuses on the preservation of bioactive compounds in red chili peppers during the drying process, with keywords such as “antioxidants,” “antioxidant activity,” “capsaicin,” “capsaicinoids,” and “carotenoids.” This area of research concerns how various drying methods, including spray drying and others, affect the retention of key nutritional components such as beta carotene, flavonoids, capsantin and gallic acid, all of which contribute to the health benefits of red chili peppers. An important aspect of this group was the investigation into the stability and physicochemical properties of these bioactive compounds under different drying conditions. Studies assessed how factors such as water activity, food storage and drying environment affect the preservation of compounds such as dihydrocapsaicin and quercetin, which are important for the nutritional quality and shelf-life of the final product.
Research within this cluster, such as the studies by Vega-Gálvez et al. (2009) and Deng et al. (2018), delves into how various drying techniques impact the retention of these vital compounds. Deng et al. emphasize the importance of Pulsed Vacuum Drying (PVD) in achieving high-quality dried products, with superior rehydration capacity and pigment retention. This aligns with the broader trend toward adopting advanced and hybrid drying methods in the food industry. Vega-Gálvez et al. (2009), however, focused more on traditional air-drying techniques, which may limit the relevance of their findings to modern industrial applications.
These studies are particularly valuable because they provide insights into optimizing drying processes to maintain or even enhance the nutritional profile of red chili. Additionally, the cluster addresses safety concerns, notably the risk of aflatoxin contamination, as highlighted in the research by Gherbawy et al. (2015) and Gambacorta et al. (2018). The focus on aflatoxin underscores the importance of ensuring that dried chili products are not only nutritious but also safe for consumption, aligning with broader food safety standards.
Zhang et al. (2019) investigated cold plasma treatment as a non-thermal pretreatment for chili pepper drying. A 30-s exposure yielded optimal pigment retention and accelerated drying, while longer exposure negatively impacted quality. Microstructural analysis revealed the formation of micro-pores that enhanced moisture transfer. Notably, antioxidant activity increased with exposure time, with color and pigment quality preserved under optimal conditions. Cold plasma offers a chemical-free alternative to traditional treatments, reducing chemical residues (Geng et al., 2022). Unlike high-temperature methods such as HHAIB, HAD, and IR-HAD (Deng et al., 2018), cold plasma minimizes antioxidant and pigment degradation.
Recent breakthroughs by Zhang et al. (2023) and Lučić et al. (2023) showed that ultrasound-assisted drying increases phenolic content, carotenoids, and antioxidant activity through cavitation that breaks down cell structures and accelerates the release of bioactive compounds, while Sasikumar et al. (2023) demonstrated ultrasound-assisted drying retained essential nutrients such as vitamin C, carotenoids, polyphenols, and flavonoids. Zahoor et al. (2023) optimized microwave-assisted convective drying with Response Surface Methodology (RSM) to maximize nutrient retention during storage. This modern method balances efficiency and quality, reinforcing the importance of technological innovation in maintaining the nutrients and stability of dried red chili products.
3.2.1.3 Cluster 3 (yellow): physical quality attributes
The yellow cluster focuses on maintaining and improving the physical attributes of red chili during the drying process, especially color, texture, hardness, and ascorbic acid (vitamin C) content. These aspects are crucial for consumer acceptance and product market value. Researchers explored methods such as freeze-drying, infrared drying, and microwave-assisted drying, to maintain the physical and nutritional qualities of chili peppers, ensuring the attractiveness of the dried product when prepared for consumption.
Research by Ergüneş and Tarhan (2006) highlighted the chemical pretreatments such as NaOH and ethyl oleate solutions can maintain the color of chili peppers during drying, especially when optimal soaking temperatures are applied. Soysal et al. (2009) found that the intermittent mode of microwave-convective drying was better at preserving texture and color compared to continuous drying, highlighting the importance of power and temperature settings to maintain the physical attributes of the product.
Swain et al. (2014) developed a kinetics model to predict color degradation, confirming that microwave-convective drying requires precise control for optimal results to be achieved. Won et al. (2015) introduced pulsed electric field (PEF) as a pretreatment that accelerated drying by 34.7% and preserved the color and texture of the product, reducing the negative impact on the cell structure. These findings reinforce the importance of pretreatment to improve the efficiency and physical quality of dried red chili peppers.
More recent research by Hossain et al. (2018) showed that solar cabinet dryers are superior to direct sun drying as they reduce color degradation and speed up drying time. Zhang et al. (2023) emphasized the benefits of using ultrasound in improving antioxidant stability and maintaining color during storage. With these various techniques, the yellow cluster ensures that dried red chili peppers not only retain their physical and visual qualities, but also meet consumer needs and food industry standards.
3.2.1.4 Cluster 4 (blue): microbiology safety, food quality, and preservation
The blue group focused on microbiological safety and food quality during the red chili drying process. Keywords such as “microbiology,” “food contamination,” “bacterial count,” and specific pathogens such as staphylococcus aureus and aspergillus flavus highlighted the research emphasis on preventing microbial contamination and ensuring the safety of dried chili products. Aflatoxin contamination, a significant food safety issue, is another key area of focus, with research exploring how to reduce the risks associated with mold during the drying and storage process.
Research by Aydin et al. (2007) and Khan et al. (2014) found that 18–52.8% of chili powder samples from different regions had aflatoxin content that exceeded international tolerance limits. These findings underscore the importance of good storage and drying practices to prevent mold contamination during production and distribution. Ozilgen et al. (2013) emphasized that the washing and storage stages are critical points in chili production, and identified that preventive controls with FMEA and HACCP systems are essential to effectively reduce biological and chemical risks.
To improve microbiological safety, Cheon et al. (2015) tested a combination of UV-C irradiation and mild heat treatment, which was able to reduce pathogens such as E. coli and Salmonella typhimurium by up to 3 log CFU/g without affecting product color and aesthetics. This method proves that a combination of thermal and non-thermal treatments can significantly reduce microbiological risks without compromising the visual quality of dried chili products.
Furthermore, Choi et al. (2018) explored the combination of radio frequency thermal treatment (RF-TT) and dielectric barrier discharge plasma (DBD-PT) to reduce pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus. This technology not only eliminates microbes but also preserves the antioxidant content and color of the product, ensuring quality is maintained. These innovations emphasize that an approach based on a combination of modern technologies can improve product safety and stability in the long term, and strengthen the competitiveness of dried chili peppers in the international market.
Four distinct clusters show how red chili drying research covers a range of important areas, from technical optimization of drying methods (Red Cluster) to preserving nutrient content (Green Cluster), maintaining physical quality attributes (Yellow Cluster) and ensuring microbiological safety (Blue Cluster). Each cluster plays an important role in addressing the various challenges faced by the red chili drying industry, with the ultimate goal of producing safe, high-quality, nutrient-rich dried chili products. However, to move the field forward, there is potential for greater integration across these clusters-particularly by combining technological innovations in drying methods with deeper insights into nutrient preservation and safety, ensuring comprehensive solutions that meet industry standards and consumer demands.
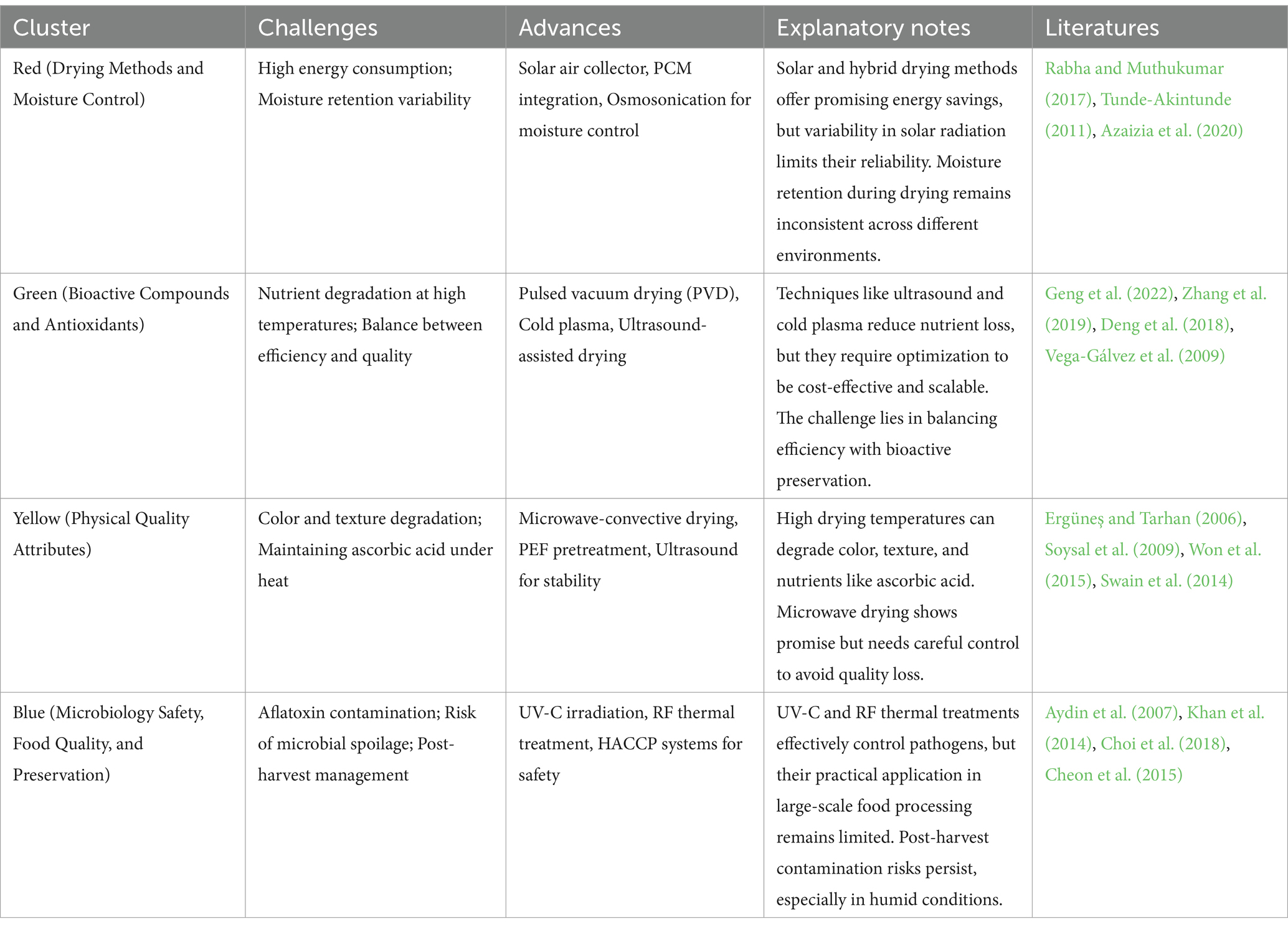
The challenges and advances across these four clusters are summarized in Table 3. Each cluster addresses key barriers and innovations in the drying process, such as moisture retention variability, nutrient degradation, and microbial safety. Table 3 provides an overview of the major challenges encountered and the technological advances that have been proposed to overcome them.
The key challenges across the clusters revolve around balancing efficiency, quality, and safety throughout the drying process. In the Red Cluster, researchers like Rabha and Muthukumar (2017) and Tunde-Akintunde (2011) focus on refining drying methods, including solar and microwave drying, to optimize energy consumption while maintaining ideal moisture levels. However, rapid moisture removal risks affecting the retention of bioactive compounds, a concern central to the Green Cluster. Maurya et al. (2018) showed that freeze-drying is the most effective method for preserving capsaicin, color, and β-carotene, outperforming other drying techniques (sun drying, hot air drying, and microwave vacuum drying). In the Yellow Cluster, Ergüneş and Tarhan (2006) and Soysal et al. (2009) highlighted the difficulty of maintaining color, texture, and firmness through high-temperature drying methods, underscoring the importance of controlled drying environments. Simultaneously, the Blue Cluster emphasizes the need for microbiological safety by addressing contamination risks, such as aflatoxin exposure, as documented by Aydin et al. (2007) and Khan et al. (2014).
Innovative solutions are being explored across clusters to overcome these challenges. Hybrid drying methods, such as PCM-based solar drying (Azaizia et al., 2020) and microwave-convective drying, provide better moisture control while reducing energy consumption. In the Green Cluster, Zhang et al. (2023) and Lučić et al. (2023) demonstrate how ultrasound-assisted drying improves bioactive retention by enhancing the release of antioxidants and carotenoids. Similarly, pretreatment methods such as PEF (Won et al., 2015) and cold plasma (Zhang et al., 2019) further accelerate the drying process, improving the texture and stability of the final product. To ensure microbiological safety, Cheon et al. (2015) showed how combining UV-C irradiation with mild heat treatments significantly reduces microbial load without degrading the product’s visual and sensory quality.
Advancements in each cluster reinforce progress in the others, creating an interconnected system that optimizes both product quality and process efficiency. Effective moisture control and optimized drying techniques from the Red Cluster enable better retention of antioxidants and pigments, benefiting the Green Cluster. Improvements in physical attributes, such as texture and color, addressed by the Yellow Cluster, align with safety goals from the Blue Cluster, ensuring that the dried chili not only meets consumer expectations but also complies with food safety standards. The synergy across these clusters provides a pathway for producing high-quality, long-lasting chili products that are nutritionally rich and safe for global markets.
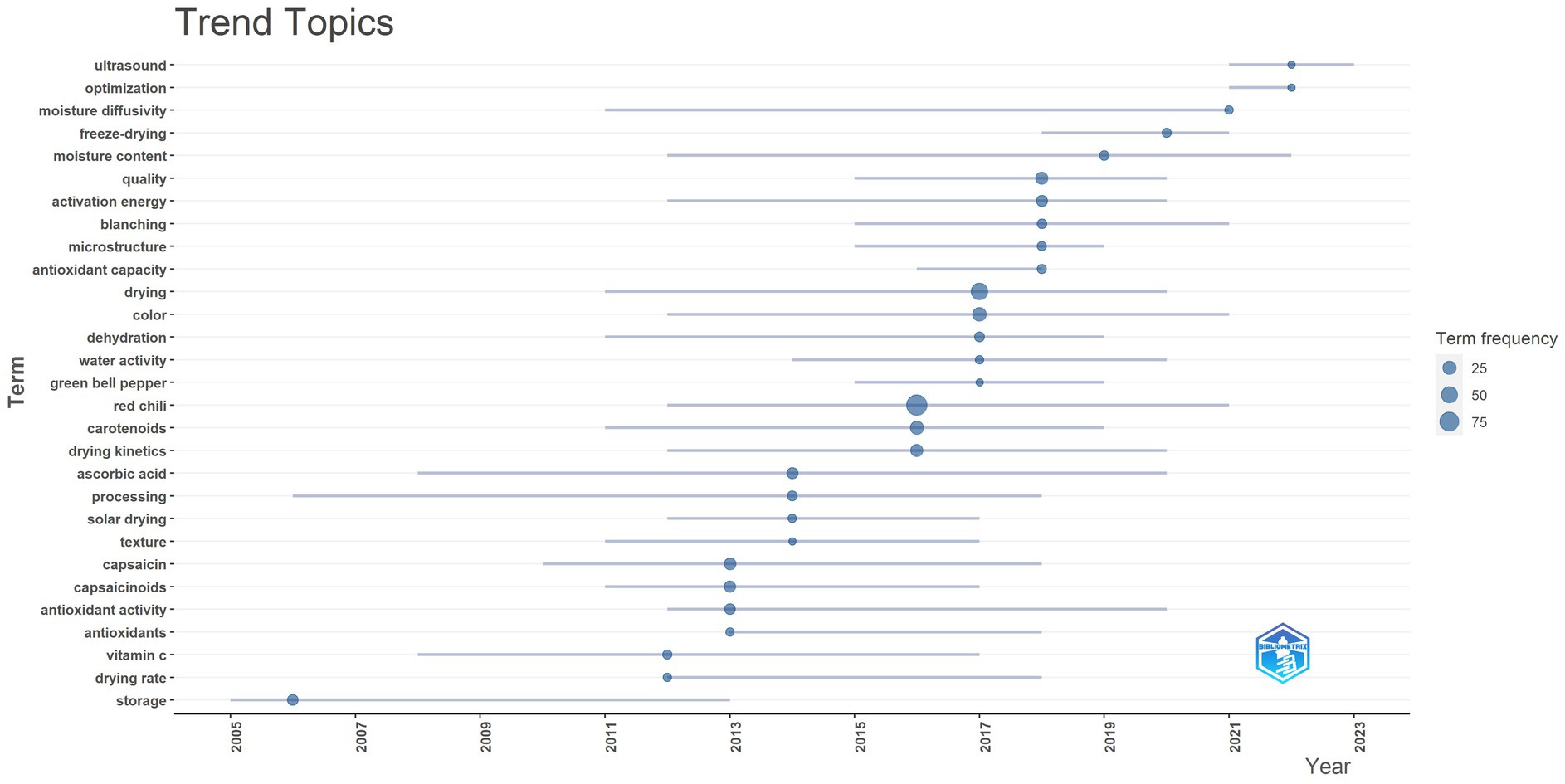
3.2.2 Trend topics
The literature survey on red chili drying technologies showed trends in topics from 2004 to 2023, as depicted in Figure 9. The graph illustrates the evolution of key research terms related to red chili drying over time. Each term is represented by a horizontal line, with the length indicating the range of years in which the term was frequently used in research publications. The size of the circle represents the frequency of the term, with larger circles indicating a higher frequency of use in a given year. Some topics appear and then fade away, while others continue to grow.
3.2.2.1 Early years (2004–2010)
In the early years, topics such as storage, processing, and drying kinetics were central, reflecting a fundamental focus on basic drying methods, storage techniques, and drying rate optimization (Topuz and Ozdemir, 2004; Martínez et al., 2005; Di Scala and Crapiste, 2008). There is a clear emphasis on understanding how drying and storage methods affect the shelf life, moisture content control, and storage stability of red pepper products (Kim et al., 2004; Topuz et al., 2009). Vitamin C and ascorbic acid are also major topics of research during this time, highlighting the interest in maintaining the nutritional quality of dried red chili peppers (Martínez et al., 2005; Kim et al., 2006; Vega-Gálvez et al., 2008, 2009). New Focus on Bioactive Compounds (2010–2015): As the field evolved, terms such as antioxidant activity, capsaicin, and carotenoids began to appear more frequently, signaling a shift toward studying the impact of drying on bioactive compounds in red chili peppers (Lutz et al., 2015; Caporaso et al., 2013; Daood et al., 2014). Research during this period has placed more emphasis on preserving the nutritional and medicinal properties of red chili peppers, particularly their antioxidants, capsaicinoids and carotenoids, which are critical to consumer health and product quality (González-Zamora et al., 2013). The increased focus on antioxidant capacity reflects the growing interest in ensuring that drying methods preserve the bioactive properties of chili peppers.
3.2.2.2 Advanced drying techniques (2015–2023)
More recent research has focused on advanced drying technologies and optimization techniques. Terms such as freeze drying, ultrasonic, far-infrared, microwave and moisture diffusivity became more prominent after 2015, reflecting the increasing focus on efficiency and quality retention in drying processes (Zhou et al., 2016; Szadzińska et al., 2017; Deng et al., 2018). Researchers have explored innovative methods such as ultrasonic and microwave-assisted drying to improve the drying rate and preservation of key nutritional components (Zahoor and Khan, 2021; Cárcel et al., 2019). Optimization is emerging as an important theme, indicating the need for refinement of drying conditions to maximize energy efficiency and product quality. Recent years have also seen an increased emphasis on solar drying, dehydration and quality, indicating a shift to sustainable practices in red chili pepper drying (ELkhadraoui et al., 2015). These terms indicate a concerted effort to reduce energy consumption and improve the environmental footprint of drying techniques, while still focusing on maintaining a high-quality dried product (Rabha et al., 2017a; Banout et al., 2011). Terms such as antioxidants, texture, and color that continue to stand out further support the idea that maintaining the sensory and nutritional attributes of red chili peppers remains a priority, such as innovative pre-treatments using high-humidity hot air impact blanching (HHAIB) (Wang et al., 2023).
Research developments in red chili drying have evolved from basic storage and quality maintenance to more complex issues such as nutrient retention, preservation of bioactive compounds, and process optimization, reflecting a holistic shift towards maximizing the quality and health benefits of dried chili products. The increasing focus on sustainable drying methods, such as solar drying, addresses environmental concerns; however, integrating these practices with advanced technological methods can further improve efficiency and product quality.
3.2.3 Thematic evolution
Figure 10 illustrates the development of the research themes, highlighting the evolution of the themes from 2004 to 2023. With keyword settings = 200, minimum cluster frequency = 5, clustering diagram = Walktrap, intersection points 2007, 2013, and 2019.
The thematic evolution of red chili drying research, as depicted in Figure 10, shows a clear progression from basic studies focused on storage and basic drying techniques (2004–2007) to more advanced and specialized research on energy efficiency, retention of bioactive compounds, and sustainability in recent years (2020–2023). Early research centered on improving the storage stability and shelf-life of dried red chili peppers, while later years saw the emergence of themes such as drying kinetics, activation energy, and mathematical models, reflecting a deeper technical focus on drying process optimization. In recent periods, there has been a strong emphasis on preserving bioactive compounds such as capsaicin and carotenoids, as well as exploring sustainable methods such as solar drying and energy-efficient techniques such as exergy. This shift illustrates the growing interest in balancing technical optimization of drying methods with the need to maintain nutritional quality and address environmental concerns.
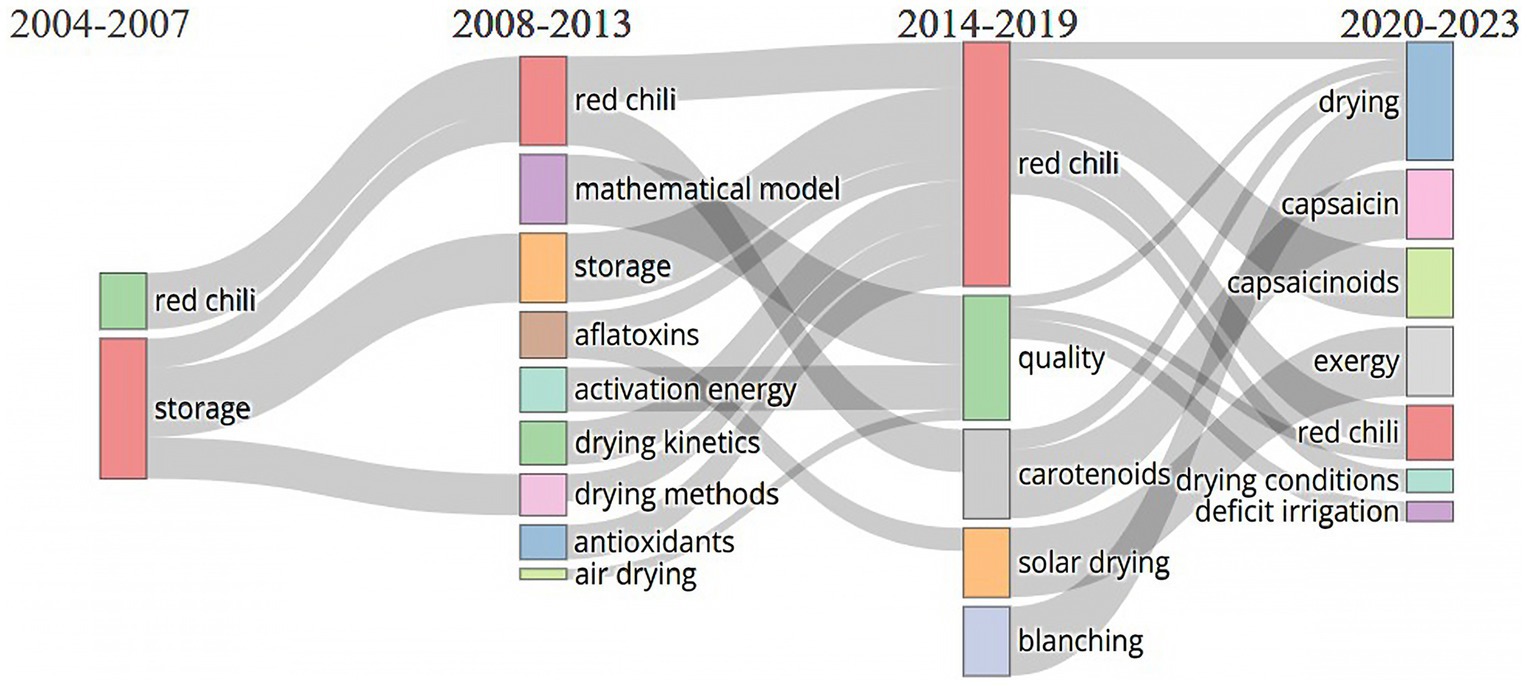
3.2.3.1 Period 2004–2007: understanding the fundamentals
As depicted in Figure 11, research from 2004 to 2007 was characterized by a fundamental exploration of red chili drying methods, focusing on key themes such as storage, drying methods, capsaicinoids, and color retention (Hossain and Bala, 2007; Ergüneş and Tarhan, 2006). These topics, positioned in the Motor Themes quadrant of the map, demonstrate their central role in the research landscape, with high relevance and density. The focus on storage indicates that maintaining product quality over time is a major concern, particularly in preserving key attributes such as color and capsaicinoid content, which are critical to consumer acceptance and market value (Park and Kim, 2007; Kim et al., 2004). The emphasis on drying methods reflects efforts to optimize traditional techniques, ensuring that the moisture removal process is efficient and effective. Including in these motor themes, color and capsaicinoids-important sensory and bioactive attributes-were also intensively studied, as maintaining these qualities is important for the nutritional and commercial value of red chili peppers. This initial research is likely to explore how different drying and pretreatment methods affect the color retention and stability of bioactive compounds such as capsaicinoids, which are known for their health benefits and their role in the spicy flavor of chili peppers.
Meanwhile, themes such as modeling and open sun drying were placed in the emerging or declining themes quadrant, indicating that while these topics were recognized, they had not yet reached full development in terms of relevance and impact. The emergence of modeling indicates an initial interest in developing mathematical or simulation models to predict drying outcomes, although this area has not been a dominant focus during this period.
This period laid the foundation for more advanced studies by establishing a clear understanding of fundamental drying principles, the critical role of storage in maintaining quality, and the need to optimize drying methods to retain important sensory and bioactive attributes.
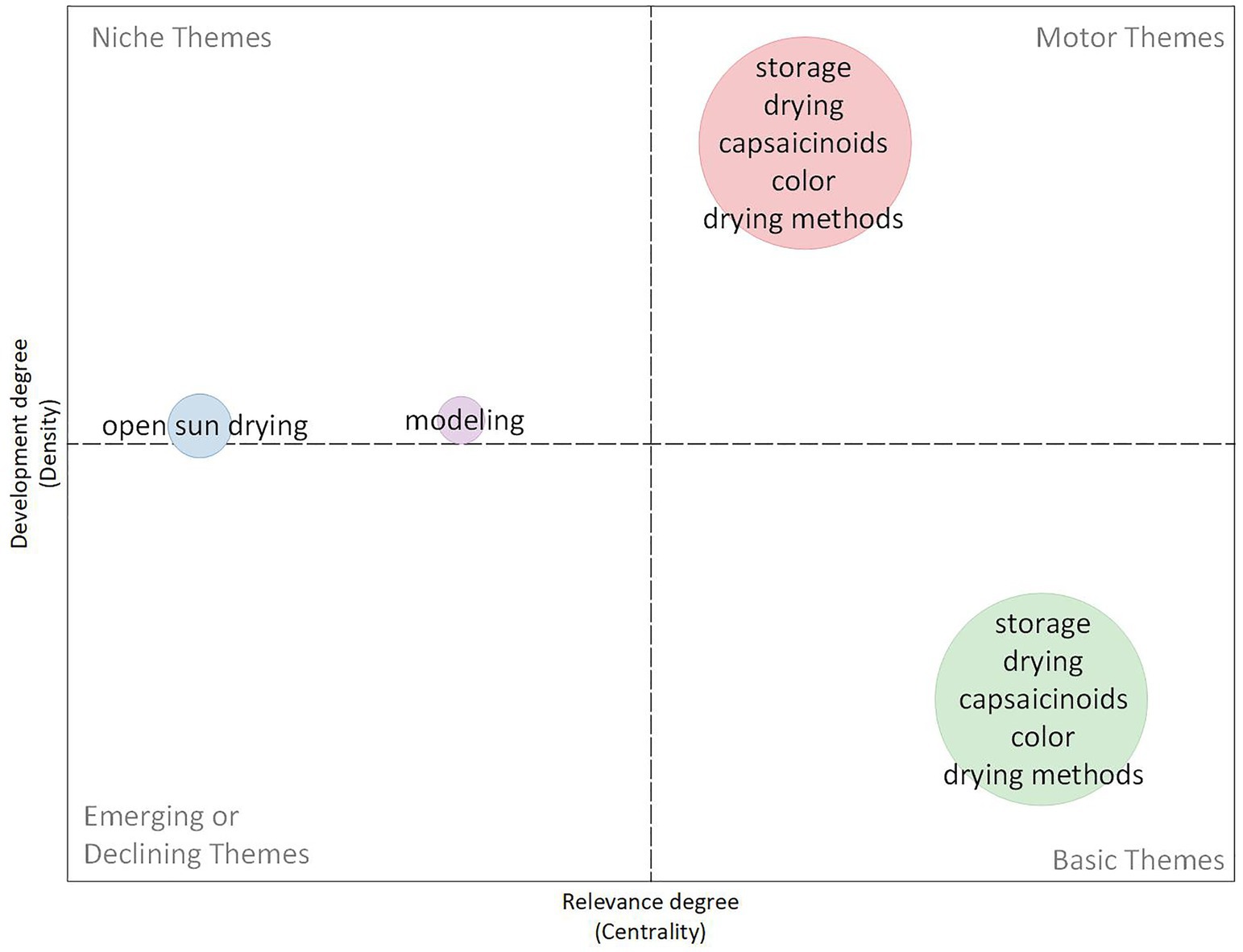
3.2.3.2 Period 2008–2013: advancing knowledge and techniques
The period from 2008 to 2013, as depicted in Figure 12, marked significant progress in red chili drying research, with the thematic map showing a clear shift towards more advanced drying techniques such as microwave drying, freeze drying, and osmotic dehydration, which were identified as motor themes. These methods became notable for their ability to increase drying efficiency and retention of essential nutrients such as capsaicinoids and carotenoids. Researchers during this period focused on optimizing drying kinetics and moisture diffusivity, key themes driving technological innovation, ensuring faster drying times while minimizing degradation of essential bioactive compounds. The development of techniques such as microwave-assisted drying and osmotic dehydration shows increasing interest in combining energy efficiency with product quality, as highlighted by Swain et al. (2012) and Arslan and Özcan (2011).
In addition to these motor themes, the research landscape expanded to incorporate other important aspects of the drying process, such as moisture content, drying rate, and the impact of various pretreatments such as blanching and sun drying. These themes, positioned in the upper quadrant, show a steady increase in relevance and density, indicating that the field is becoming more nuanced in its exploration of the physical and chemical changes that occur during drying. Air drying and solar drying, although still under development, reflect an emerging interest in sustainable drying methods. The emphasis on moisture content and water activity indicates efforts to control moisture content to extend shelf life while maintaining product quality, particularly in preventing spoilage.
New safety issues emerged during this period, particularly around aflatoxins-a toxic fungal by-product that can contaminate dried chili peppers. Although not yet fully developed, this theme reflects the increasing awareness of food safety risks, as shown by studies from Alonge and Adeboye (2012) and Marín et al. (2009). Ensuring the safety of dried chili peppers through appropriate drying and storage methods is becoming an important challenge, with researchers focusing on minimizing the risk of contamination while balancing the need for efficient drying. This period represents a maturation phase in red chili drying research, where innovation, quality control and safety issues are integrated into a more complex understanding of the field.
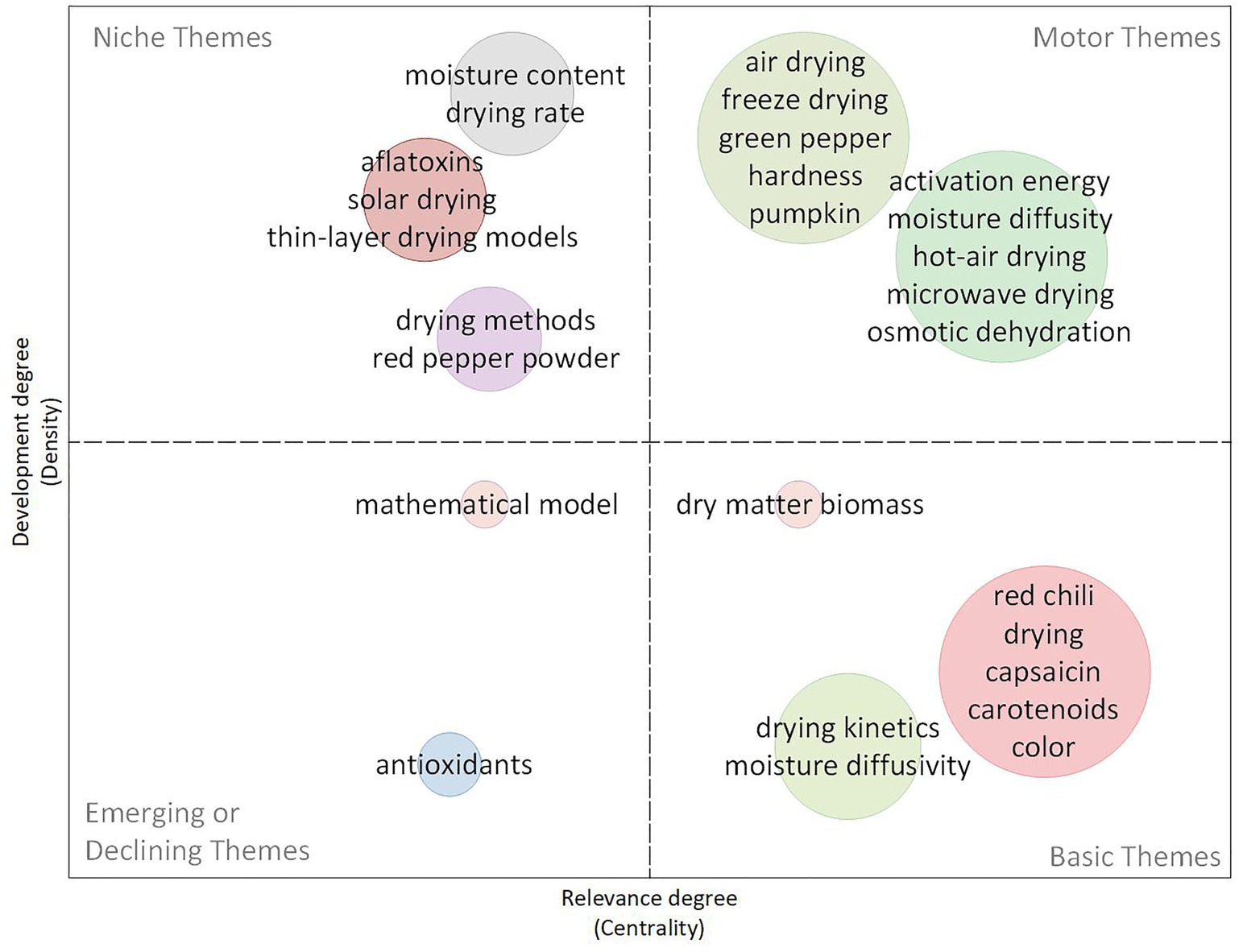
3.2.3.3 Period 2014–2019: quality optimization
Based on the thematic map from 2014 to 2019 (Figure 13), the research focus during this period shifted towards further optimizing drying methods and improving the overall quality of dried red chili peppers. The motor themes identified in the map include quality, activation energy, solar drying, and dehydration, indicating a strong emphasis on energy efficiency and preservation of product quality. This research aims to optimize drying techniques to maintain important attributes such as moisture content, nutrient retention, and color, which are critical for consumer acceptance and marketability. Research on blanching, solar drying, and microwave drying during this period showed a growing interest in sustainable and energy-efficient methods that preserve the bioactive compounds and color of red chili peppers. Innovations in pre-treatment, particularly blanching and encapsulation, were explored to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the drying process.
In addition, the period saw an increased focus on bioactive compounds such as carotenoids, capsaicin, and other antioxidants, reflecting their significance in maintaining the nutritional and health benefits of dried chili products. Themes such as drying kinetics, capsaicin, and carotenoids-positioned in the basic theme quadrant-highlight the ongoing efforts to perfect drying methods that retain these valuable compounds. Research by Deng et al. (2018) and others focuses on preserving these bioactive compounds through careful control of drying conditions, further driving innovation in drying technology.
At the same time, the thematic map reveals continued attention to safety issues, particularly those related to aflatoxins. Research on aflatoxin contamination and co-occurrence with other mycotoxins emerged as relevant topics, highlighting the need for better control measures during drying and storage to ensure product safety. Research by Gambacorta et al. (2018) emphasizes the importance of preventing aflatoxin contamination, which reinforces the need for comprehensive best practices throughout the supply chain to maintain the quality and safety of dried red chili products.
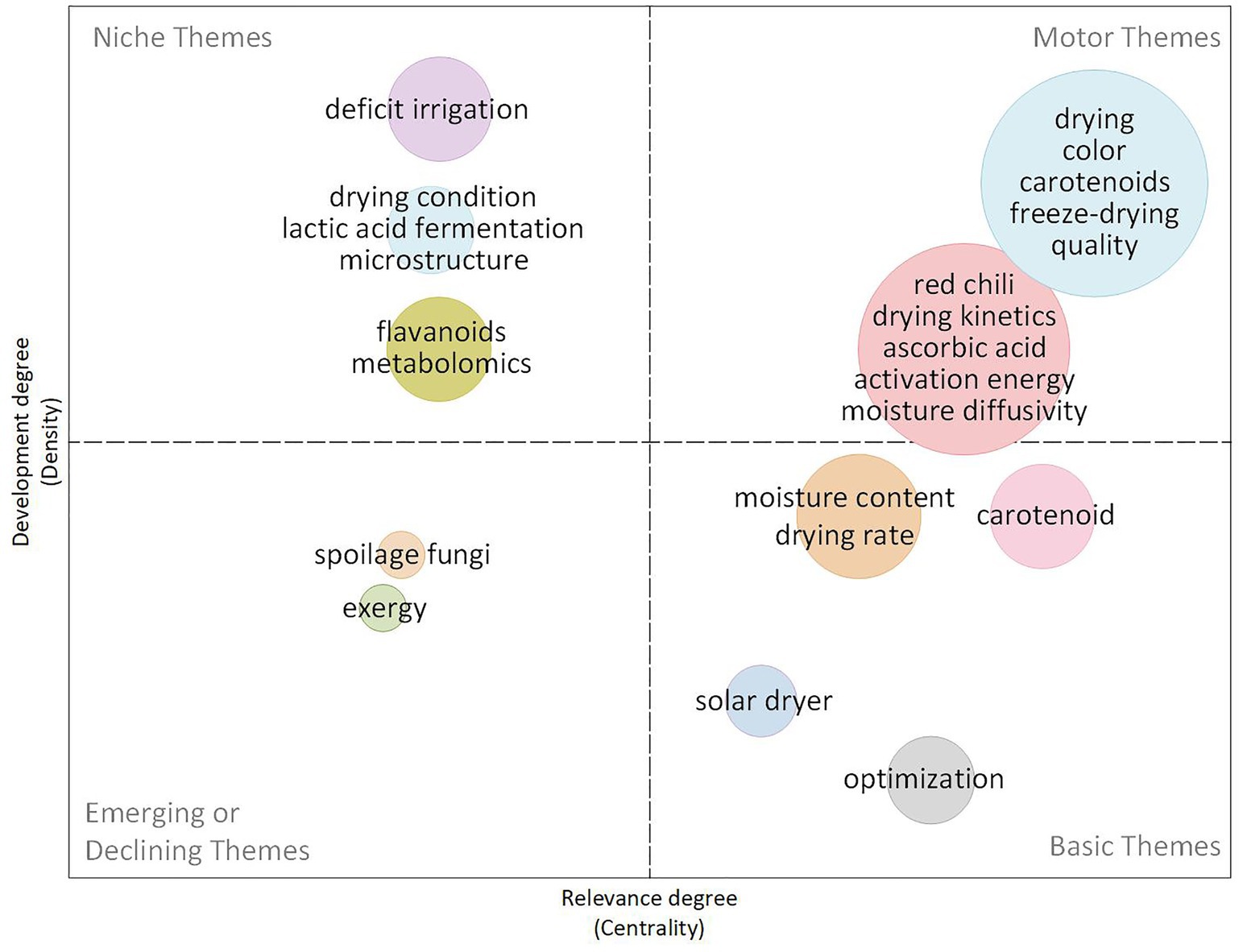
3.2.3.4 Period 2020–2023: innovations and sustainability
Based on the 2020 to 2023 thematic map (Figure 14), current research in red chili drying is increasingly focused on optimizing quality and sustainability, with particular attention to themes such as drying, color, carotenoids, freeze-drying, and overall product quality. These topics, positioned in the motor quadrant, are at the center of current research efforts. Meanwhile, drying kinetics, moisture diffusivity, and activation energy remain important for improving drying efficiency. Researchers are prioritizing the preservation of important quality attributes such as color and nutrient content, as these are key to consumer acceptance and marketability. Techniques such as freeze-drying have become renowned for their ability to preserve color, nutritional value, and bioactive compounds, such as carotenoids, as emphasized by Kheto et al. (2021).
Within the basic themes quadrant, research on moisture content and drying rates continues to play an important role in understanding basic drying principles, while solar drying and optimization remain important, albeit still evolving, areas of exploration for sustainable drying practices. The use of solar dryers and optimized drying conditions is in line with the increasing emphasis on reducing energy consumption and environmental impact, as seen in the work of Pochont et al. (2020) and Azaizia et al. (2020), which demonstrate the sector’s commitment to incorporating renewable energy into the agricultural drying process.
Emerging research areas in specialized quadrants, such as deficit irrigation, lactic acid fermentation, and microstructure analysis, indicate that there is growing interest in integrating agricultural practices and more advanced biochemical processes to further improve the efficiency and sustainability of red chili drying. Exploration of deficit irrigation and its effect on red chili drying, for example, underscores the need for water-efficient practices that can increase drying yields without compromising crop quality or yield. These themes demonstrate the expansion of ongoing research into more complex and sustainable approaches to red chili production and drying.
3.2.4 Red chili drying technology over 2 decades
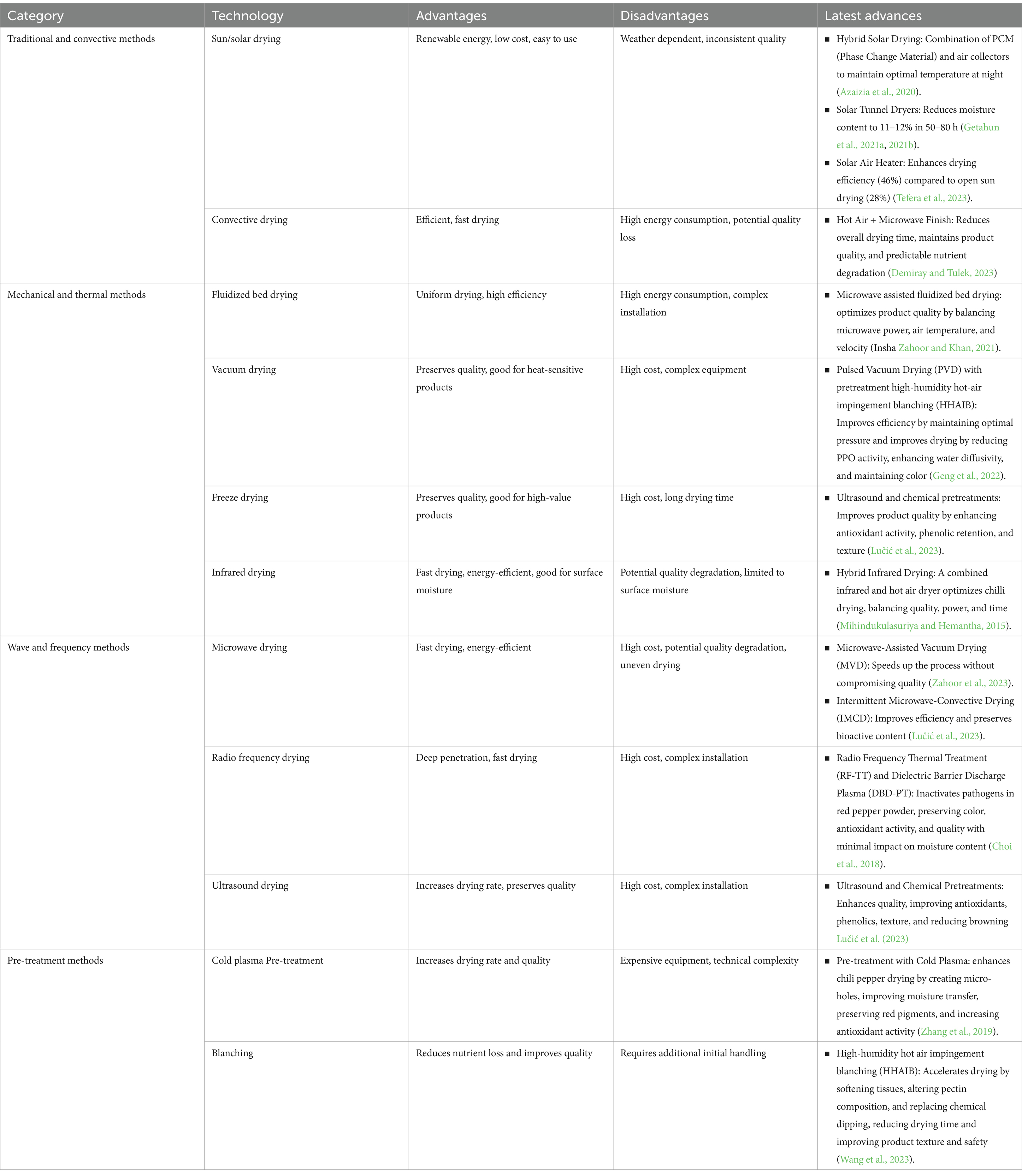
The advancement of red chili drying methods over the past two decades, as depicted in Table 4, highlights the important role this process plays in maintaining the quality, energy efficiency and extending the shelf life of high-value agricultural products. Traditional methods such as sun drying remain popular due to their convenience and low cost, especially in rural areas (Arslan and Özcan, 2010). However, dependence on sunlight intensity makes solar drying less than ideal in regions with high rainfall or erratic humidity, limiting its application in some tropical countries (Rabha and Muthukumar, 2017). In addition, although the initial investment for traditional methods is lower, hidden costs arise in the form of quality losses due to overexposure to sunlight and contamination risks. Energy efficiency is also low as the process is slow and uncontrollable.
Efforts to develop modern methods are seen in the innovative two-stage solar tunnel dryer (Getahun et al., 2021a) that can reduce moisture content to 11–12% in 50–80 h. The technology reduces energy consumption (2.1–2.44 kWh/kg) and carbon emissions, with mitigation potential of up to 13 tons of CO₂ per year and carbon credits worth 136.25 to 162.88 USD. Tefera et al. (2023) introduced a mixed-mode solar air heater that improves efficiency by 46%, is faster and more stable than open drying. Recent innovations include combining hot air drying with microwave finishing, a technique that shortens the drying process while maintaining product quality and offering more predictable nutrient degradation (Demiray and Tulek, 2023).
These innovations show that temperature control, energy efficiency, and sustainability are key in modern chili drying technology (Raghavan et al., 2022). However, while these innovations have successfully improved drying efficiency and quality, challenges remain, particularly regarding energy requirements and the risk of quality degradation under certain conditions. In response, hot air drying has been adopted to improve consistency and process control. However, this process is high energy demanding and can result in product quality degradation. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures leads to pigment and protein denaturation, as well as capsaicin and antioxidant degradation, which reduces the nutritional and sensory value of the product (Tavakolipour and Mokhtarian, 2016). Amid the need for more efficient drying processes, new technologies are being introduced to overcome the limitations of these traditional methods.
One solution that is starting to be widely used is microwave-based drying, which offers the advantages of much shorter drying times and increased energy efficiency (Hu et al., 2021). However, this drying process has the disadvantage that its physical mechanism involves rapid heating with deep penetration, which often triggers excessive water evaporation. Sudden temperature fluctuations can damage the structure of phenolics and capsaicin-two important compounds in red chili peppers-resulting in decreased antioxidant properties and spicy flavor (Wang et al., 2023). In addition, uneven drying is a frequent problem, where some parts of the product are overheated while other parts are not fully dried, risking accelerated spoilage when stored (Vadivambal and Jayas, 2007). While this technology has potential, especially for high-value products where drying speed is critical, further development is needed to address consistency issues and maintain product quality.
The ultrasonic drying technique (Chibuzo et al., 2021) overcomes most of those obstacles by using cavitation to accelerate water evaporation without causing thermal degradation. Ultrasonic waves create microbubbles that implode and break the water structure, thus allowing drying at lower temperatures and preserving the bioactive content such as carotenoids and flavonoids. However, high installation costs and the need for specialized equipment hinder its application on industrial scale.
One important breakthrough in the last decade is cold plasma as a pretreatment method (Kim et al., 2019). Cold plasma works by breaking molecular bonds on the product surface, reducing drying time and increasing color retention and antioxidant content. The process also helps in reducing the risk of microbial contamination without requiring high temperatures, making it an effective solution for products prone to thermal degradation. However, the biggest challenge in cold plasma technology is the high cost of equipment and technical complexity in its operation, so its use is still limited to research and small-scale production.
Recent innovations in hybrid drying (Sickert et al., 2023) have introduced a combination of methods to maximize the benefits of different drying techniques. For example, solar drying combined with microwave drying reduces weather dependency while speeding up the drying process. What’s more, hybrid drying was shown to retain bioactive content and improve color stability, two important attributes for consumers and industry. Industry-wide adoption challenges persist, as hybrid methods demand significant capital investment and precise control systems, posing difficulties for small and medium-sized enterprises.
One area that has received less attention is the adoption of hybrid methods on an industrial scale. While hybrid drying has shown great potential in improving energy efficiency and quality retention, its application on a large scale is still limited. The main challenges lie in installation costs and the need for precision control, which requires training and technical expertise to ensure the process is optimized.
Also, the accessibility of technology in developing countries is a major constraint. Modern equipment such as cold plasma and ultrasonic drying have the potential to improve productivity and quality, but high costs and technical complexity are often barriers for small and medium-sized producers in resource-constrained regions. Lack of infrastructure support also makes it difficult to consistently implement sustainable technologies such as solar drying in some tropical regions with unpredictable weather (Rabha et al., 2017b).
To overcome this challenge, further research is needed into more efficient and affordable hybrid operational models. In addition, the integration of digital technologies in the form of AI-based monitoring and machine learning is an important step that needs to be explored. With the use of AI, manufacturers can predict and optimize real-time drying parameters, such as temperature, humidity, and drying time, to ensure consistent product quality while minimizing energy consumption.
For example, AI and predictive models can help identify the best trade-off between time and temperature, thereby reducing the risk of quality deterioration such as capsaicin and antioxidant degradation. Automated monitoring technology integrated with sensors also enables the industry to continuously monitor the quality of bio-actives throughout the drying process, thus ensuring each batch meets the expected quality standards.
Future research also needs to explore sustainable solutions that combine renewable technology and renewable energy. The development of solar drying with thermal energy storage could be a solution for regions with unstable weather. In addition, cross-sector collaboration between academia, industry and policymakers is needed to create an innovation ecosystem that supports wider adoption of sustainable technologies.
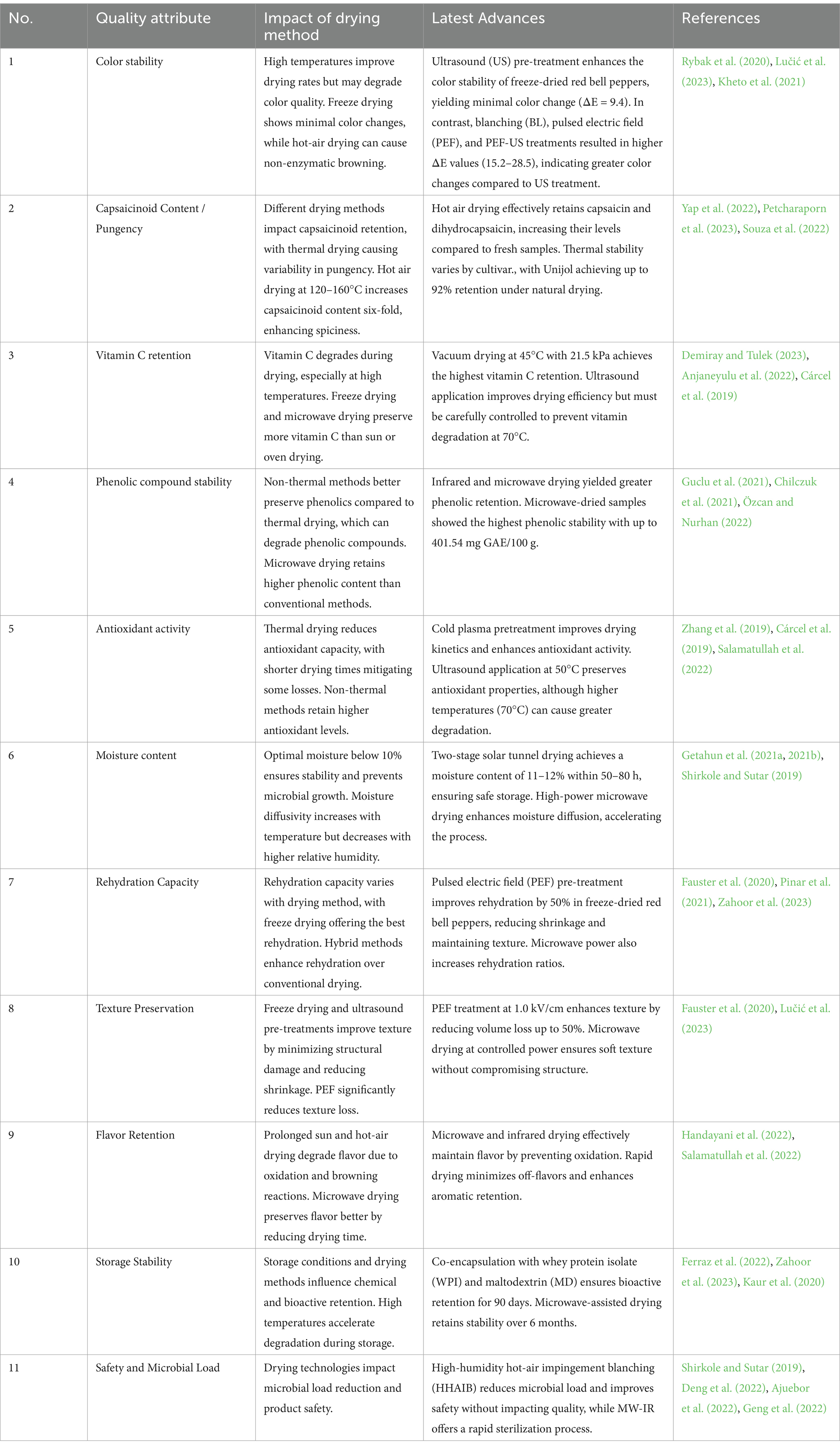
The continuous evolution of red chili drying techniques aims to produce high-quality dried chili peppers by combining advanced technology and sustainability considerations. This results in more efficient, cost-effective and environmentally friendly methods. Future advancements should integrate real-time monitoring systems to ensure consistent quality and maximum retention of nutritional and bioactive compounds. In addition, machine learning and AI for modeling and predicting drying behavior could revolutionize the industry. Table 5 summarizes the key quality attributes, impacts and advancements of various drying methods, enabling informed decisions for optimal dried red chili products.
The quality attributes of dried red chili peppers are strongly influenced by the drying method used, with each method having a significant impact on important aspects such as color, capsainoid retention, vitamin C content and overall product safety. Color is an important quality marker, especially as it affects consumer perception and market price. Recent studies have shown that hybrid methods such as microwave-assisted or infrared drying provide optimal results in retaining the color of chili peppers. However, a major challenge remains, which is how to ensure color consistency across batches during large-scale production (Zahoor et al., 2023; Lučić et al., 2023).
In addition to color, the retention of capsaicin as a pungency-determining compound is a critical factor. Hot-air drying methods can increase capsaicin content by up to six times, but this is only effective under certain varieties and proper drying conditions. The challenge in preserving pungency lies in the variability that arises due to differences in drying temperature and time. Innovations such as osmosonication and microwave-convective are able to preserve pungency while speeding up drying time (Majumder et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2023).
Vitamin C levels that are susceptible to degradation are also a major concern in the selection of drying methods. Freeze drying and vacuum methods have proven to be effective in maintaining vitamin C levels. However, the investment and energy required is often an obstacle for industrial application. Alternatives such as ultrasound-assisted drying have shown positive results in maintaining vitamin C levels at low temperatures, although adjustments are needed to keep the process energy efficient (Demiray and Tulek, 2023; Anjaneyulu et al., 2022).
Meanwhile, phenolic content and antioxidant activity are an important focus in maintaining the nutritional value of red chili peppers. Non-thermal methods such as cold plasma and ultrasonic pretreatment are proven to be better at maintaining these bioactive contents. Innovations in hybrid drying also open up opportunities to preserve phenolic and flavonoid content, although cost and installation complexity challenges remain (Zhang et al., 2023; Lučić et al., 2023).
In addition, rehydration ability and texture are important indicators of the physical quality of dried red chili peppers. Freeze drying excels in this regard, with a texture close to that of fresh product. However, this method has high cost and long time. PEF (pulsed electric field) pretreatment and combination with microwave drying can provide a solution in improving rehydration capacity without sacrificing texture (Fauster et al., 2020).
Preservation of aroma and flavor, especially in maintaining the volatility of flavoring compounds, is also a major concern in the industry. Infrared and microwave drying methods have been shown to retain flavor well, reducing the risk of oxidation of volatile compounds that can impair product flavor quality (Handayani et al., 2022; Salamatullah et al., 2022).
Durability during storage is also highly dependent on the drying method. Low residual moisture (<10%) is key to avoid microbial growth and ensure product safety during storage. The combination of drying with thermal energy storage systems shows great potential for regions with limited access to electricity (Getahun et al., 2021a; Ferraz et al., 2022).
Microbiological safety is an important focus, especially in reducing the risk of aflatoxin contamination. Modern methods such as RF-TT (Radio Frequency Thermal Treatment) and combination with DBD-PT (Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma Treatment) have shown effectiveness in reducing microbial load without affecting the visual quality of the product (Choi et al., 2018; Deng et al., 2022).
The application of hybrid technology provides a solution to overcome the limitations that exist in traditional and modern methods. Hybrid drying with a combination of microwave and infrared not only speeds up the process but also maintains color and flavor stability. However, the high initial investment and the need for technical expertise are barriers to the adoption of this technology in rural areas (Shirkole and Sutar, 2019; Getahun et al., 2021b).
Overall, the selection of red chili drying methods should consider energy efficiency, product quality, as well as infrastructure limitations and operational costs. The integration of digital technologies such as AI and sensor-based monitoring can be a solution to optimize the process in real-time and guarantee product consistency, making the red chili industry more competitive and sustainable.
3.3 Selection guide on drying technology for red chili
The selection of red chili drying technology should be done by considering energy efficiency, product quality, initial investment, and infrastructure limitations. The following is an in-depth analysis followed by steps to select the right technology.
3.3.1 Evaluation of environmental and infrastructure conditions
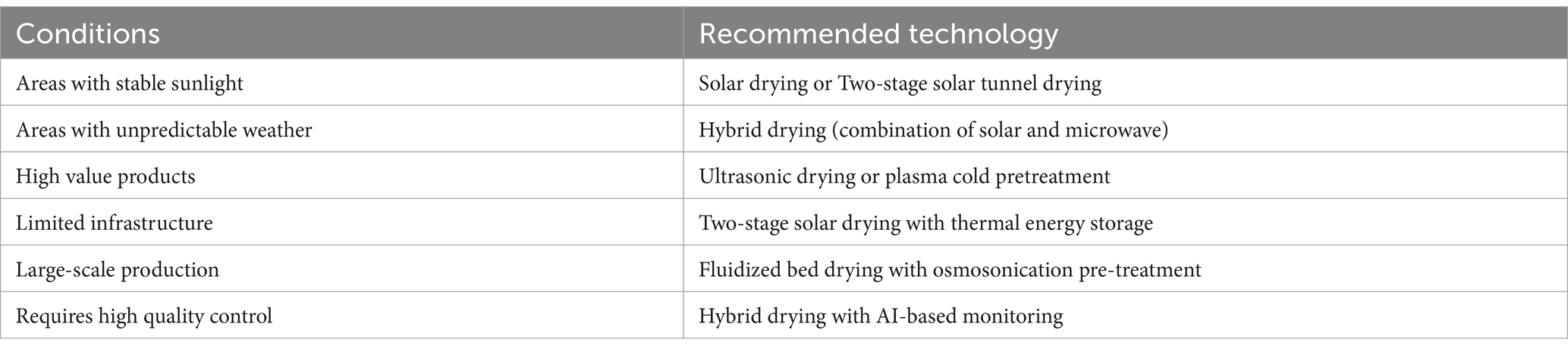
The first step is to evaluate the environmental conditions and infrastructure where the drying technology will be applied. In rural areas with abundant sunlight, solar drying or hybrid solar drying is an ideal choice as it is energy efficient and low cost. However, in areas with unpredictable weather or high rainfall, this method is less effective, making hot-air drying or microwave drying better options. In places with limited infrastructure, such as lack of access to electricity, renewable energy-based technologies such as solar dryers with thermal energy storage are highly recommended to overcome resource limitations.
3.3.2 Evaluation of production needs and product quality
The quality of the final product and the scale of production are also important considerations. If the product is of high value and the bioactive quality (such as capsaicin and β-carotene) must be maintained, hybrid drying or ultrasonic drying is the best option. Ultrasonic drying is effective as it preserves the bioactive compounds without the risk of thermal degradation. However, if the main goal is to maintain a large production capacity in a short time, microwave drying or fluidized bed drying can be used.
In addition, the scale of production also influences the technology selection decision. For small to medium-scale production, solar drying and hybrid drying are quite efficient with lower investment. On the other hand, for large-scale production, fluidized bed drying provides time efficiency and consistency of results.
3.3.3 Investment and energy efficiency considerations
Investment cost and energy efficiency are important aspects in choosing a technology. For low investment, solar drying and two-stage solar tunnel drying are economical as well as environmentally friendly solutions. However, if producers are looking for high ROI and are ready to spend more, advanced technologies such as ultrasonic drying and plasma cold pretreatment can be an option, especially since they produce premium product quality. On the other hand, hybrid drying with a combination of solar and microwave not only reduces dependence on weather conditions but also reduces carbon emissions and energy consumption.
3.3.4 Risk evaluation and implementation challenges
The risk of product quality degradation and operational challenges must be taken into account before adopting a particular technology. Microwave drying has the risk of overheating, which can damage the phenolic structure and capsaicin content, reducing the antioxidant properties and pungency of chili peppers. The same goes for hot-air drying, where prolonged high temperatures can cause degradation of pigments, proteins and antioxidants. Technologies such as ultrasonic drying and plasma cold pretreatment effectively reduce these risks, but the challenges of high cost and technical requirements remain.
3.3.5 Utilization of digital technology and AI
Digital technology and artificial intelligence (AI) can help improve the consistency and efficiency of the drying process. AI can be used to predict and optimize drying parameters such as temperature and time in real-time, reducing the risk of degradation of important compounds. With automated monitoring using smart sensors, the bioactive quality of each batch can be monitored continuously, ensuring consistent results and compliance with quality standards.
3.3.6 Selection of the right drying technology
In summary, the following red chili drying technology recommendations are presented based on environmental conditions and specific needs (Table 6).
3.3.7 Implementation and process monitoring
The selection of the right technology needs to be followed by a measured and consistent implementation process. This step is important so that the drying process always delivers products that meet the preferences of producers and consumers at all times. The implementation and monitoring process needs to follow the Standard Operational Procedure (SOP). Training and capacity building of the workforce (drying operators) is essential. More attention needs to be given especially to the use of advanced technology with AI-based systems. Aspects of energy management and process control to maximize efficiency are important topics in training.
Industry collaboration with academia is necessary for technology implementation. Academia can assist in research and development of more efficient methods, while the industry sector can support in the implementation and scalability of the technology. This collaboration will ensure continued innovation and wider application of technology in the agricultural sector.
Based on this analysis, hybrid drying emerges as the best option for developing future chili drying innovations because it combines the energy efficiency advantages of solar drying and the speed of microwave drying. Although it requires a higher initial investment, this method is suitable for high-value products and is able to provide consistent quality assurance. For areas with limited access to electricity, two-stage solar drying with thermal energy storage is an effective alternative.
3.4 Future research directions
Future research should explore emerging synergies between diverse drying technologies, paving the way for more sustainable and efficient hybrid systems, especially those that can overcome energy limitations and high costs. Utilizing renewable energy such as solar drying with thermal energy storage can be an effective solution for regions with limited access to electricity. In addition, the integration of AI and machine learning in drying systems will enable real-time monitoring and optimization, ensuring consistency of product quality while reducing energy consumption (Kaur et al., 2020).
More studies are also needed to understand the interaction between drying parameters and bioactive compounds such as capsaicinoids and phenolic compounds. Further research is needed to develop more accurate predictive models, so that producers can customize the drying process to maintain the nutritional and organoleptic quality of the product (Zhang et al., 2023).
In addition, non-thermal technologies such as cold plasma and PEF need to be further researched to make them more efficient and affordable for small producers. A focus on reducing drying time and increasing rehydration capacity is also high on the agenda to ensure better products with shorter process times (Fauster et al., 2020; Salamatullah et al., 2022).
Future research should also include the development of more efficient hybrid systems with a combination of non-thermal and thermal methods, such as microwave-infrared drying. Furthermore, the development of smart packaging technology with sensor integration for moisture monitoring can extend shelf life and improve product quality during distribution (Ferraz et al., 2022).
With increased collaboration between academia, industry and policymakers, technological innovations can be more quickly adopted. Regulatory support and incentives for the development of sustainable drying technologies will also accelerate the adoption of new methods in the industry, especially in developing countries that have great potential in red chili production.
4 Conclusion
This study provides an in-depth insight into the development of red chili pepper (Capsicum annuum) drying technology over the past two decades. Findings show that modern methods, such as microwave and cold plasma, improve the efficiency of the drying process, but face challenges in maintaining nutritional and sensory quality. These technologies offer significant solutions but need to be adapted to market needs and production capacity, especially in developing countries.
Hybrid methods have emerged as a potential solution to overcome the dilemma between efficiency and quality. The integration of these traditional and modern technologies allows for a more balanced process, improves the shortcomings of each method, and offers greater stability in preserving bioactive contents such as capsaicin and carotenoids. Nonetheless, the application of this technology still requires further research to ensure its adaptability in various local conditions.
In developing countries, cost-effective and environmentally friendly drying technologies are urgently needed. The adoption of sustainable drying methods can improve the economic welfare of farmers while extending the shelf life of the product. In addition, it is important for future research to focus on the adaptation of new technologies and enhance global collaboration within the agro-industrial sector. This will ensure that innovative developments in drying technology can be adopted quickly and efficiently to meet market needs and optimize product quality.
4.1 Limitations of the bibliometric study
This bibliometric study has limitations in the scope of data sources, as it only relies on publications available in certain databases and in English. As a result, some innovations from industry reports, patents or publications in other languages may be missed. Additionally, this study is likely to be affected by publication bias, where research from reputable journals is more visible, while contributions from limited access or lesser-known journals may be overlooked.
Reliance on metadata and keywords can result in relevant information being missed if not properly identified. Publication trends do not always reflect actual industry implementation, so a gap may exist between academic innovation and commercial practice. In addition, local or regional contexts in technology application may not be covered in this analysis, given the focus on global trends.
Data availability statement
The datasets generated/analyzed for this study can be found at: https://dx.doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.27925488.
Author contributions
HME: Conceptualization, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft. SJM: Supervision, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. BB: Project administration, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. AB: Methodology, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. HY: Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. MJD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft. NS: Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. EEK: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. AL: Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. LL: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. AA: Conceptualization, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aguiar, A. C., De, L. P., Sales, J. P., Coutinho, G. F., and Barbero, H. T. (2013). Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of Capsicum peppers: global yield and Capsaicinoid content. J. Supercrit. Fluids 81, 210–216. doi: 10.1016/j.supflu.2013.05.008
Ajuebor, F., Oluwafunmilayo, A. A., Oluseye, O. A., Samuel, E. A., Tinuade, J. A., and Oladipupo, O. O. (2022). Drying Process Optimization and Modelling the Drying Kinetics and Quality Attributes of Dried Chili Pepper (Capsicum Frutescens L.). Trends in Sciences 19, 1–21. doi: 10.48048/tis.2022.5752
Alonge, A. F., and Adeboye, O. A. (2012). Drying rates of some fruits and vegetables with passive solar dryers. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 5:504. doi: 10.3965/j.ijabe.20120504.00
Amit, S. K., Uddin, M. M., Rizwanur Rahman, S. M., Islam, R., and Khan, M. S. (2017). A review on mechanisms and commercial aspects of food preservation and processing. Agric. Food Security 6, 1–22. doi: 10.1186/s40066-017-0130-8
Amjad, W., Raza, M. A., Asghar, F., Munir, A., Mahmood, F., Husnain, S. N., et al. (2022). Advanced exergy analyses of a solar hybrid food dehydrator. Energies 15:505. doi: 10.3390/en15041505
Anjaneyulu, A., Sharangi, A. B., Upadhyay, T. K., Alshammari, N., Saeed, M., and Al-Keridis, L. A. (2022). Physico-chemical properties of red pepper (Capsicum Annuum L.) as influenced by different drying methods and temperatures. PRO 10:484. doi: 10.3390/pr10030484
Aria, M., and Cuccurullo, C. (2017). Bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informet. 11, 959–975. doi: 10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
Arslan, D., and Özcan, M. M. (2010). Study the effect of sun, oven and microwave drying on quality of onion slices. Lwt 43, 1121–1127. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2010.02.019
Arslan, D., and Özcan, M. M. (2011). Dehydration of red bell-pepper (Capsicum Annuum L.): change in drying behavior, colour and antioxidant content. Food Bioprod. Process. 89, 504–513. doi: 10.1016/j.fbp.2010.09.009
Aydin, A., Emin Erkan, M., Başkaya, R., and Ciftcioglu, G. (2007). Determination of aflatoxin B1 levels in powdered red pepper. Food Control 18, 1015–1018. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2006.03.013
Azaizia, Z., Sami Kooli, I., Hamdi, W. E., and Guizani, A. A. (2020). Experimental study of a new mixed mode solar greenhouse drying system with and without thermal energy storage for pepper. Renew. Energy 145, 1972–1984. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2019.07.055
Baas, J., Schotten, M., and Plume, A. (2020). Scopus as a curated, high-quality bibliometric data source for academic research in quantitative science studies. Quant. Sci. Stud. 1, 377–386. doi: 10.1162/qss_a_00019
Banout, J., Ehl, P., Havlik, J., Lojka, B., Polesny, Z., and Verner, V. (2011). Design and performance evaluation of a double-pass solar drier for drying of red Chili (Capsicum annum L.). Sol. Energy 85, 506–515. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2010.12.017
Boukaew, S., Zhang, Z., Prasertsan, P., and Igarashi, Y. (2023). Antifungal and Antiaflatoxigenic mechanism activity of freeze-dried culture filtrate of Streptomyces Philanthi RL-1-178 on the two Aflatoxigenic Fungi and identification of its active component. J. Appl. Microbiol. 134:91. doi: 10.1093/jambio/lxac091
Caporaso, N., Paduano, A., Nicoletti, G., and Sacchi, R. (2013). Capsaicinoids, antioxidant activity, and volatile compounds in olive oil flavored with dried chili pepper (Capsicum annuum). Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 115, 1434–1442. doi: 10.1002/ejlt.201300158
Cárcel, J. A., Castillo, D., Simal, S., and Mulet, A. (2019). Influence of temperature and ultrasound on drying kinetics and antioxidant properties of red pepper. Dry. Technol. 37, 486–493. doi: 10.1080/07373937.2018.1473417
Castillo-Téllez, M., Pilatowsky-Figueroa, I., López-Vidaña, E. C., Sarracino-Martínez, O., and Hernández-Galvez, G. (2017). Dehydration of the red Chilli (Capsicum Annuum L., Costeño) using an indirect-type forced convection solar dryer. Appl. Therm. Eng. 114, 1137–1144. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.08.114
Cheon, H.-L., Shin, J.-Y., Park, K.-H., Chung, M.-S., and Kang, D.-H. (2015). Inactivation of foodborne pathogens in powdered red pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) using combined UV-C irradiation and mild heat treatment. Food Control 50, 441–445. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.08.025
Chibuzo, N. S., Osinachi, U. F., James, M. T., Chigozie, O. F., Dereje, B., and Irene, C. E. (2021). Technological advancements in the drying of fruits and vegetables: a review. Afr. J. Food Sci. 15, 367–379. doi: 10.5897/AJFS2021.2113
Chilczuk, B., Beata, M., and Renata, K. (2021). Capsicum Annuum L. Extracts in Relation to Their Lipophilicity. Molecules 26, 1–11. doi: 10.3390/molecules26175215
Choi, E. J., Yang, H. S., Park, H. W., and Chun, H. H. (2018). Inactivation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Staphylococcus aureus in red pepper powder using a combination of radio frequency thermal and indirect dielectric barrier discharge plasma non-thermal treatments. LWT 93, 477–484. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.03.081
Costa, J., Rodríguez, R., Santos, C., Soares, C., Lima, N., and Santos, C. (2020). Mycobiota in Chilean Chili Capsicum annuum L. used for production of Merkén. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 334:108833. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108833
Daood, H. G., Palotás, G., Palotás, G., Somogyi, G., Pék, Z., and Helyes, L. (2014). Carotenoid and antioxidant content of ground paprika from indoor-cultivated traditional varieties and new hybrids of spice red peppers. Food Res. Int. 65, 231–237. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2014.04.048
Demiray, E., and Tulek, Y. (2023). Drying characteristics and quality of red pepper slices under hot air followed by microwave finish drying. Lat. Am. Appl. Res. 53, 241–250. doi: 10.52292/j.laar.2023.1106
Deng, L.-Z., Xiong, C.-H., Sutar, P. P., Mujumdar, A. S., Pei, Y.-P., Yang, X.-H., et al. (2022). An emerging pretreatment Technology for Reducing Postharvest Loss of vegetables-a case study of red pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) drying. Dry. Technol. 40, 1620–1628. doi: 10.1080/07373937.2022.2039934
Deng, L. Z., Yang, X. H., Mujumdar, A. S., Zhao, J. H., Wang, D., Zhang, Q., et al. (2018). Red pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) drying: effects of different drying methods on drying kinetics, physicochemical properties, antioxidant capacity, and microstructure. Dry. Technol. 36, 893–907. doi: 10.1080/07373937.2017.1361439
Di Scala, K., and Crapiste, G. (2008). Drying kinetics and quality changes during drying of red pepper. Lwt 41, 789–795. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2007.06.007
Duranova, H., Valkova, V., and Gabriny, L. (2022). Chili peppers (Capsicum Spp.): The spice not only for cuisine purposes: An update on current knowledge. Phytochem. Rev. 21:9789. doi: 10.1007/s11101-021-09789-7
Ekka, J. P., and Palanisamy, M. (2021). Performance assessments and techno and enviro-economic analyses on forced convection mixed mode solar dryer. J. Food Process Eng. 44, 1–13. doi: 10.1111/jfpe.13675
ELkhadraoui, A., Kooli, S., Hamdi, I., and Farhat, A. (2015). Experimental investigation and economic evaluation of a new mixed-mode solar greenhouse dryer for drying of red pepper and grape. Renew. Energy 77, 1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2014.11.090
Ergüneş, G., and Tarhan, S. (2006). Color retention of red peppers by chemical pretreatments during greenhouse and open sun drying. J. Food Eng. 76, 446–452. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2005.05.046
Fauster, T., Giancaterino, M., Pittia, P., and Jaeger, H. (2020). Effect of pulsed electric field pretreatment on shrinkage, rehydration capacity and texture of freeze-dried plant Materials. Lwt 121:108937. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108937
Ferraz, M. C., Procopio, F. R., de Figueiredo, G., and Hubinger, M. D. (2022). Co-encapsulation of paprika and cinnamon oleoresin by spray drying using whey protein isolate and maltodextrin as wall material: development, characterization and storage stability. Food Res. Int. 162:112164. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.112164
Fudholi, A., Sopian, K., Yazdi, M. H., Ruslan, M. H., Gabbasa, M., and Kazem, H. A. (2014). Performance analysis of solar drying system for red chili. Sol. Energy 99, 47–54. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2013.10.019
Gambacorta, L., Magistá, D., Perrone, G., Murgolo, S., Logrieco, A. F., and Solfrizzo, M. (2018). Co-occurrence of toxigenic Moulds, aflatoxins, Ochratoxin a, fusarium and Alternaria mycotoxins in fresh sweet peppers (Capsicum annuum) and their processed products. World Mycotoxin J. 11, 159–173. doi: 10.3920/WMJ2017.2271
Gangadhar, B. H., Mishra, R. K., Pandian, G., and Park, S. W. (2012). Comparative study of color, pungency, and biochemical composition in chili pepper (Capsicum annuum) under different light-emitting diode treatments. HortScience 47, 1729–1735. doi: 10.21273/hortsci.47.12.1729
Geng, Z., Huang, X., Wang, J., Xiao, H., Yang, X., Zhu, L., et al. (2022). Pulsed vacuum drying of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.): effect of high-humidity hot air impingement blanching pretreatment on drying kinetics and quality attributes. Food Secur. 11:318. doi: 10.3390/foods11030318
Getahun, E., Delele, M. A., Gabbiye, N., Fanta, S. W., and Vanierschot, M. (2021a). Studying the drying characteristics and quality attributes of chili pepper at different maturity stages: experimental and mechanistic model. Case Stud. Thermal Eng. 26:101052. doi: 10.1016/j.csite.2021.101052
Getahun, E., and Ebissa, D. T. (2024). Investigation of optimal drying conditions of red chili peppers in a hot air cabinet dryer. Case Stud. Thermal Eng. 59:104586. doi: 10.1016/j.csite.2024.104586
Getahun, E., Gabbiye, N., Delele, M. A., Fanta, S. W., and Vanierschot, M. (2021b). Two-stage solar tunnel chili drying: drying characteristics, performance, product quality, and carbon footprint analysis. Sol. Energy 230, 73–90. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2021.10.016
Gherbawy, Y. A., Shebany, Y. M., Hussein, M. A., and Maghraby, T. A. (2015). Molecular detection of Mycobiota and aflatoxin contamination of chili. Arch. Biol. Sci. 67, 223–234. doi: 10.2298/ABS141010028G
González-Zamora, A., Erick Sierra-Campos, J., Luna-Ortega, G., Pérez-Morales, R., Ortiz, J. C. R., and García-Hernández, J. L. (2013). Characterization of different Capsicum varieties by evaluation of their Capsaicinoids content by high performance liquid chromatography, determination of pungency and effect of high temperature. Molecules 18, 13471–13486. doi: 10.3390/molecules181113471
Goud, M., Reddy, M. V. V., Chandramohan, V. P., and Suresh, S. (2019). A novel indirect solar dryer with inlet fans powered by solar PV panels: drying kinetics of Capsicum annum and Abelmoschus Esculentus with dryer performance. Sol. Energy 194, 871–885. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2019.11.031
Guclu, G., Keser, D., Kelebek, H., Keskin, M., Sekerli, Y. E., Soysal, Y., et al. (2021). Impact of production and drying methods on the volatile and phenolic characteristics of fresh and powdered sweet red peppers. Food Chem. 338:128129. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128129
Guo, W., and Zhu, X. (2014). Dielectric properties of red pepper powder related to radiofrequency and microwave drying. Food Bioprocess Technol. 7, 3591–3601. doi: 10.1007/s11947-014-1375-x
Handayani, S. U., Mujiarto, I., Siswanto, A. P., Ariwibowo, D., Atmanto, I. S., and Mustikaningrum, M. (2022). Drying kinetics of Chilli under sun and microwave drying. Mater. Today Proc. 63, S153–S158. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2022.02.119
Hirsch, J. E. (2005). An index to quantify an Individual’s scientific research output. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 16569–16572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507655102
Hossain, M. Z., Alam, M. M., Hossain, M. F. B., Sarker, M. S. H., Awal, M. A., and Jahan, N. (2018). Performance evaluation of a cabinet solar dryer for drying red pepper in Bangladesh. J. Agric. Eng. 49, 100–109. doi: 10.4081/jae.2018.774
Hossain, M. A., and Bala, B. K. (2007). Drying of hot Chilli using solar tunnel drier. Sol. Energy 81, 85–92. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2006.06.008
Hu, Q., He, Y., Wang, F., Jing, W., Ci, Z., Chen, L., et al. (2021). Microwave technology: a novel approach to the transformation of natural metabolites. Chin. Med. 16, 87–22. doi: 10.1186/s13020-021-00500-8
Jalgaonkar, K., Mahawar, M. K., Girijal, S., and Hp, G. (2022). Post-harvest profile, processing and value addition of dried red Chillies (Capsicum annum L.). J. Food Sci. Technol. 61, 201–219. doi: 10.1007/s13197-022-05656-1
Jiménez, D., Vardanega, R., Salinas, F., Espinosa-Álvarez, C., Bugueño-Muñoz, W., Jenifer Palma, M., et al. (2021). Effect of drying methods on biorefinery process to obtain Capsanthin and phenolic compounds from Capsicum annuum L. J. Supercrit. Fluids 174:105241. doi: 10.1016/j.supflu.2021.105241
Jin, W., Mujumdar, A. S., Zhang, M., and Shi, W. (2018). Novel drying techniques for spices and herbs: a review. Food Eng. Rev. 10, 34–45. doi: 10.1007/s12393-017-9165-7
Kaur, R., Kaur, K., and Ahluwalia, P. (2020). Effect of Drying Temperatures and Storage on Chemical and Bioactive Attributes of Dried Tomato and Sweet Pepper. LWT 117. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108604
Karakose, T., Kocabas, I., Yirci, R., Papadakis, S., Ozdemir, T. Y., and Demirkol, M. (2022). The development and evolution of digital leadership: a bibliometric mapping approach-based study. Sustainability 14:171. doi: 10.3390/su142316171
Khan, M. A., Asghar, M. A., Iqbal, J., Ahmed, A., and Shamsuddin, Z. A. (2014). Aflatoxins contamination and prevention in red Chilies (Capsicum annuum L.) in Pakistan. Food Addit. Contaminants 7, 1–6. doi: 10.1080/19393210.2013.825330
Kheto, A., Dhua, S., Nema, P. K., and Sharanagat, V. S. (2021). Influence of drying temperature on quality attributes of bell pepper (Capsicum annuum L.): drying kinetics and modeling, rehydration, color, and antioxidant analysis. J. Food Process Eng. 44:880. doi: 10.1111/jfpe.13880
Kim, S. W., Abd El-Aty, A. M., Rahman, M. M., Choi, J. H., Choi, O. J., Rhee, G. S., et al. (2015). Detection of Pyridaben residue levels in hot pepper fruit and leaves by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: effect of household processes. Biomed. Chromatogr. 29, 990–997. doi: 10.1002/bmc.3383
Kim, S., Lee, K. W., Park, J., Lee, H. J., and Hwang, I. K. (2006). Effect of drying in antioxidant activity and changes of ascorbic acid and colour by different drying and storage in Korean red pepper (Capsicum annuum, L.). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 41, 90–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2006.01349.x
Kim, J. E., Oh, Y. J., Song, A. Y., and Min, S. C. (2019). Preservation of red pepper flakes using microwave-combined cold plasma treatment. J. Sci. Food Agric. 99, 1577–1585. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.9336
Kim, S., Park, J. B., and Hwang, I. K. (2002). Quality attributes of various varieties of Korean red pepper powders (Capsicum annuum L.) and color stability during sunlight exposure. J. Food Sci. 67, 2957–2961. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2002.tb08845.x
Kim, S., Park, J., and Hwang, I. K. (2004). Composition of Main carotenoids in Korean red pepper (Capsicum annuum, L.) and changes of pigment stability during the drying and storage process. J. Food Sci. 69, C39–C44. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2004.tb17853.x
Kurup, A. H., Deotale, S., Rawson, A., and Patras, A. (2020). Thermal processing of herbs and spices. Herbs Spices Med. Plants 21, –685. doi: 10.1002/9781119036685.ch1
Lučić, M., Potkonjak, N., Sredović Ignjatović, I., Lević, S., Dajić-Stevanović, Z., Kolašinac, S., et al. (2023). Influence of ultrasonic and chemical pretreatments on quality attributes of dried pepper (Capsicum Annuum). Food Secur. 12:468. doi: 10.3390/foods12132468
Lutz, M., Hernández, J., and Henríquez, C. (2015). Phenolic content and antioxidant capacity in fresh and dry fruits and vegetables grown in Chile. CYTA J. Food 13, 541–547. doi: 10.1080/19476337.2015.1012743
MacDonald, R. (2023). Successful keyword searching: Initiating research on popular topics using electronic databases. New York: Research Press.
Majumder, P., Deb, B., and Gupta, R. (2023). Investigation of Osmosonication pretreated chili (Capsicum Frutescens L.) drying in solar-assisted fluidized bed dryer utilizing dehumidified air. J. Food Process Eng. 46:351. doi: 10.1111/jfpe.14351
Majumder, P., Sinha, A., Gupta, R., and Sablani, S. S. (2021). Drying of selected major spices: characteristics and influencing parameters, drying technologies, quality retention and energy saving, and mathematical models. Food Bioprocess Technol. 14, 1028–1054. doi: 10.1007/s11947-021-02646-7
Marín, S., Colom, C., Sanchis, V., and Ramos, A. J. (2009). Modelling of growth of Aflatoxigenic A. flavus isolates from red Chilli powder as a function of water availability. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 128, 491–496. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2008.10.020
Martínez, S., López, M., González-Raurich, M., and Alvarez, A. B. (2005). The effects of ripening stage and processing systems on vitamin C content in sweet peppers (Capsicum Annuum L.). Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 56, 45–51. doi: 10.1080/09637480500081936
Maurya, V. K., Gothandam, K. M., Ranjan, V., Shakya, A., and Pareek, S. (2018). Effect of drying methods (microwave vacuum, freeze, hot air and sun drying) on physical, chemical and nutritional attributes of five pepper (Capsicum annuum Var. annuum) cultivars. J. Sci. Food Agric. 98, 3492–3500. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.8868
Mihindukulasuriya, S. D. F., and Hemantha, P. W. J. (2015). Drying of Chilli in a Combined Infrared and Hot Air Rotary Dryer. Journal of Food Science and Technology 52, 4895–4904. doi: 10.1007/s13197-014-1546-9
Moradi, M., Azizi, S., Niakousari, M., Kamgar, S., and Khaneghah, A. M. (2020). Drying of green bell pepper slices using an IR-assisted spouted bed dryer: An assessment of drying kinetics and energy consumption. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 60:102280. doi: 10.1016/j.ifset.2019.102280
Najmus, S., Yousaf, S., Shibli, S., Khurshid, S., Iqbal, H. M., Akbar, Q.-U.-A., et al. (2021). The impact of sun drying on the occurrence of aflatoxin in red chilies. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 13, 632–637. doi: 10.6000/1927-5129.2017.13.102
Nelis, J. L. D., da Silva, G. R., Ortuño, J., Tsagkaris, A. S., Borremans, B., Haslova, J., et al. (2022). The general growth tendency: a tool to improve publication trend reporting by removing record inflation Bias and enabling quantitative trend analysis. PLoS One 17, 1–17. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268433
Nguyen, V. T., Kravets, A. G., and Duong, T. Q. H. (2021). “Predicting Research Trend based on bibliometric analysis and paper ranking algorithm” in Cyber-physical systems: Digital technologies and applications. eds. A. G. Kravets, A. A. Bolshakov, and M. V. Shcherbakov (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 109–123.
Özcan, M. M., and Nurhan, U. (2022). Quantitative Changes of Bioactive Properties and Phenolic Compounds in Capia Pepper (Capsicum Annuum L.) Fruits Dried by the Air, Conventional Heater, and Microwave. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation 46. doi: 10.1111/jfpp.16897
Ozilgen, S., Bucak, S., and Ozilgen, M. (2013). Improvement of the safety of the red pepper spice with FMEA and post processing EWMA quality control charts. J. Food Sci. Technol. 50, 466–476. doi: 10.1007/s13197-011-0371-7
Park, J. H., and Kim, C. S. (2007). The stability of color and antioxidant compounds in paprika (Capsicum annuum L) powder during the drying and storing process. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 16, 187–192.
Petcharaporn, K., Kanittada, T., Pimporn, T., and Yuttana, S. (2023). Nutritional Composition, Capsaicin Content and Enzyme Inhibitory Activities from ‘Bang Chang’ Thai Cultivar Chili Pepper (Capsicum Annuum Var. Acuminatum) after Drying Process. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance 14, 707–11. doi: 10.25258/ijpqa.14.3.41
Pinar, H., Necati, Ç., Beyza, C., Kevser, K., and Mahmut, K. (2021). “Biochemical Composition, Drying Kinetics and Chromatic Parameters of Red Pepper as Affected by Cultivars and Drying Methods.” Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 102:103976. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2021.103976
Pochont, N. R., Mohammad, M. N., Pradeep, B. T., and Vijaya Kumar, P. (2020). A comparative study of drying kinetics and quality of Indian red Chilli in solar hybrid greenhouse drying and open sun drying. Mater. Today Proc. 21, 286–290. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2019.05.433
Rabha, D. K., and Muthukumar, P. (2017). Performance studies on a forced convection solar dryer integrated with a paraffin wax–based latent heat storage system. Sol. Energy 149, 214–226. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2017.04.012
Rabha, D. K., Muthukumar, P., and Somayaji, C. (2017a). Energy and exergy analyses of the solar drying processes of ghost Chilli pepper and ginger. Renew. Energy 105, 764–773. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2017.01.007
Rabha, D. K., Muthukumar, P., and Somayaji, C. (2017b). Experimental investigation of thin layer drying kinetics of ghost Chilli pepper (Capsicum chinense Jacq.) dried in a forced convection solar tunnel dryer. Renew. Energy 105, 583–589. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2016.12.091
Raghavan, V., Martynenko, A., and Shirkole, S. S. (2022). Role of drying in food quality, security, and sustainability. Dry. Technol. 40:1499. doi: 10.1080/07373937.2022.2089819
Rybak, K., Samborska, K., Jedlinska, A., Parniakov, O., Nowacka, M., Witrowa-Rajchert, D., et al. (2020). The impact of pulsed electric field pretreatment of bell pepper on the selected properties of spray dried juice. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 65:102446. doi: 10.1016/j.ifset.2020.102446
Saengrayap, R., Tansakul, A., and Mittal, G. S. (2015). Effect of far-infrared radiation assisted microwave-vacuum drying on drying characteristics and quality of red Chilli. J. Food Sci. Technol. 52, 2610–2621. doi: 10.1007/s13197-014-1352-4
Salamatullah, M., Ahmad, K. H., Husain, F. M., Ahmed, M. A., Arzoo, S., Althbiti, M. M., et al. (2022). Effects of different solvents extractions on Total polyphenol content, HPLC analysis, antioxidant capacity, and antimicrobial properties of peppers (red, yellow, and green (Capsicum annum L.)). Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2022, –101. doi: 10.1155/2022/7372101
Sampagnaro, G. (2023). Keyword occurrences and journal specialization. Scientometrics 128, 5629–5645. doi: 10.1007/s11192-023-04815-1
Sasikumar, R., Mangang, I. B., Vivek, K., and Jaiswal, A. K. (2023). Effect of ultrasound-assisted thin bed drying for retaining the quality of red bell pepper and compare the predictive ability of the mathematical model with artificial neural network. J. Food Process Eng. 46:468. doi: 10.1111/jfpe.14468
Schössler, K., Jäger, H., and Knorr, D. (2012). Novel contact ultrasound system for the accelerated freeze-drying of vegetables. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 16, 113–120. doi: 10.1016/j.ifset.2012.05.010
Seid, R. M., and Hensel, O. (2012). Experimental evaluation of sorption isotherms of chili pepper: An Ethiopian variety, Mareko Fana (Capsicum annum L.). Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 14, 163–172.
Shirkole, S. S., Mujumdar, A. S., and Sutar, P. P. (2021). Studies on thermal stability of high-power short time microwave dried paprika (Capsicum annuum L.) considering the interaction of water molecules with sorption sites. Dry. Technol. 39, 52–65. doi: 10.1080/07373937.2019.1693399
Shirkole, S. S., and Sutar, P. P. (2019). High power short time microwave finish drying of paprika (Capsicum annuum L.): development of models for moisture diffusion and color degradation. Dry. Technol. 37, 253–267. doi: 10.1080/07373937.2018.1454941
Sickert, T., Kalinke, I., Christoph, J., and Gaukel, V. (2023). Microwave-assisted freeze-drying with frequency-based control concepts via solid-state generators: a simulative and experimental study. PRO 11:327. doi: 10.3390/pr11020327
Souza, C. S., Hussein, G. D., Stella, A. D., Sergey, V., Gábor, P., András, N., et al. (2022). Stability of Carotenoids, Carotenoid Esters, Tocopherols and Capsaicinoids in New Chili Pepper Hybrids during Natural and Thermal Drying. Lwt 163. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113520
Soysal, Y., Ayhan, Z., Eştürk, O., and Arikan, M. F.. (2009). Intermittent microwave-convective drying of red pepper: drying kinetics, physical (colour and texture) and sensory quality. Biosyst. Eng. 103, 455–463. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2009.05.010
Sutherland, W. J., Goulson, D., Potts, S. G., and Dicks, L. V. (2011). Quantifying the impact and relevance of scientific research. PLoS One 6:e27537. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027537
Swain, S., Samuel, D. V. K., Bal, L. M., and Kar, A. (2014). Thermal kinetics of colour degradation of yellow sweet pepper (Capsicum annum L.) undergoing microwave assisted convective drying. Int. J. Food Prop. 17, 1946–1964. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2013.775150
Swain, S., Samuel, D. V. K., Bal, L. M., Kar, A., and Sahoo, G. P. (2012). Modeling of microwave assisted drying of osmotically pretreated red sweet pepper (Capsicum annum L.). Food Sci. Biotechnol. 21, 969–978. doi: 10.1007/s10068-012-0127-9
Szadzińska, J., Łechtańska, J., Kowalski, S. J., and Stasiak, M. (2017). The effect of high power airborne ultrasound and microwaves on convective drying effectiveness and quality of green pepper. Ultrason. Sonochem. 34, 531–539. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.06.030
Tavakolipour, H., and Mokhtarian, M. (2016). Drying of Chilli pepper in various conditions. Qual. Assurance Safety Crops Foods 8, 87–93. doi: 10.3920/QAS2014.0518
Tefera, E., Damtie, E. G., Bezzie, Y. M., and Admass, Z. (2023). Experimental testing of mixed-mode double pass solar air heater integrated with Aluminium cans for red pepper drying. Case Stud. Thermal Eng. 50:103379. doi: 10.1016/j.csite.2023.103379
Thompson, R. B., Gallardo, M., Valdez, L. C., and Fernández, M. D. (2007). Using plant water status to define threshold values for irrigation Management of Vegetable Crops Using Soil Moisture Sensors. Agric. Water Manag. 88, 147–158. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2006.10.007
Topuz, A., Dincer, C., Özdemir, K. S., Feng, H., and Kushad, M. (2011). Influence of different drying methods on carotenoids and Capsaicinoids of paprika (cv.; jalapeno). Food Chem. 129, 860–865. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.05.035
Topuz, A., Feng, H., and Kushad, M. (2009). The effect of drying method and storage on color characteristics of paprika. LWT 42, 1667–1673. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2009.05.014
Topuz, A., and Ozdemir, F. (2004). Influences of gamma irradiation and storage on the Capsaicinoids of sun-dried and dehydrated paprika. Food Chem. 86, 509–515. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2003.09.003
Tuncer, A. D., Sözen, A., Khanlari, A., Amini, A., and Şirin, C. (2020). Thermal performance analysis of a quadruple-pass solar air collector assisted pilot-scale greenhouse dryer. Sol. Energy 203, 304–316. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2020.04.030
Tunde-Akintunde, T. Y. (2011). Mathematical modeling of sun and solar drying of Chilli pepper. Renew. Energy 36, 2139–2145. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2011.01.017
Ullah, M., Shahid, A., Din, I., Roman, M., Assam, M., Fayaz, M., et al. (2022). Analyzing interdisciplinary research using co-authorship networks. Complexity 2022:491. doi: 10.1155/2022/2524491
Vadivambal, R., and Jayas, D. S. (2007). Changes in quality of microwave-treated agricultural products-a review. Biosyst. Eng. 98, 1–16. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2007.06.006
van Eck, N. J., and Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 84, 523–538. doi: 10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
Vega-Gálvez, A., Di Scala, K., Rodríguez, K., Lemus-Mondaca, R., Miranda, M., López, J., et al. (2009). Effect of air-drying temperature on Physico-chemical properties, antioxidant capacity, colour and Total phenolic content of red pepper (Capsicum annuum, L. Var. Hungarian). Food Chem. 117, 647–653. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.04.066
Vega-Gálvez, A., Lemus-Mondaca, R., Bilbao-Sáinz, C., Fito, P., and Andrés, A. (2008). Effect of air drying temperature on the quality of rehydrated dried red bell pepper (Var. Lamuyo). J. Food Eng. 85, 42–50. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2007.06.032
Wang, J., Pei, Y.-P., Chen, C., Yang, X.-H., An, K., and Xiao, H.-W. (2023). High-humidity hot air impingement blanching (HHAIB) enhances drying behavior of red pepper via altering cellular structure, pectin profile and water state. Innovative Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 83:246. doi: 10.1016/j.ifset.2022.103246
Won, Y. C., Min, S. C., and Lee, D.-U. (2015). Accelerated drying and improved color properties of red pepper by pretreatment of pulsed electric fields. Dry. Technol. 33, 926–932. doi: 10.1080/07373937.2014.999371
Yang, C. Y., Mandal, P. K., Han, K. H., Fukushima, M., Choi, K., Kim, C. J., et al. (2010). Capsaicin and tocopherol in red pepper seed oil enhances the thermal oxidative stability during frying. J. Food Sci. Technol. 47, 162–165. doi: 10.1007/s13197-010-0032-2
Yap, E. S. P., Apiradee, U., Natta, L., Pongphen, J., and Pongphen, J. (2022). Characterization of Volatiles and Non ‑ Volatiles as the Key Bioactive Compounds in Roasting Pre ‑ Dried Chilies. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization 16, 2131–43. doi: 10.1007/s11694-022-01308-2
Zahoor, I., Ganaie, T. A., and Wani, S. A. (2023). Effect of microwave assisted convective drying on physical properties, bioactive compounds, antioxidant potential and storage stability of red bell pepper. Food Chem. Adv. 3:100440. doi: 10.1016/j.focha.2023.100440
Zahoor, I., and Khan, M. A. (2021). Microwave assisted fluidized bed drying of red bell pepper: drying kinetics and optimization of process conditions using statistical models and response surface methodology. Sci. Hortic. 286:110209. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110209
Zambon, A., Tomic, N., Djekic, I., Hofland, G., Rajkovic, A., and Spilimbergo, S. (2020). Supercritical CO2 drying of red bell pepper. Food Bioprocess Technol. 13, 753–763. doi: 10.1007/s11947-020-02432-x
Zhang, Q., Chen, Y., Geng, F., and Shen, X. (2023). Characterization of spray-dried microcapsules of paprika oleoresin induced by ultrasound and high-pressure homogenization: physicochemical properties and storage stability. Molecules 28:75. doi: 10.3390/molecules28207075
Zhang, M., Chen, H., Mujumdar, A. S., Tang, J., Miao, S., and Wang, Y. (2017). Recent developments in high-quality drying of vegetables, fruits, and aquatic products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 57, 1239–1255. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2014.979280
Zhang, X. L., Zhong, C. S., Mujumdar, A. S., Yang, X. H., Deng, L. Z., Wang, J., et al. (2019). Cold plasma pretreatment enhances drying kinetics and quality attributes of chili pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). J. Food Eng. 241, 51–57. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2018.08.002
Zhou, L., Cao, Z., Bi, J., Yi, J., Chen, Q., Xinye, W., et al. (2016). Degradation kinetics of Total phenolic compounds, Capsaicinoids and antioxidant activity in red pepper during hot air and infrared drying process. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 51, 842–853. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.13050
Keywords: red chili, Capsicum annuum, drying techniques, bibliometric analysis, sustainable food processing, drying efficiency
Citation: Elmatsani HM, Munarso SJ, Benyamin B, Budiyanto A, Yohanes H, Djafar MJ, Sjafrina N, Koeslulat EE, Lukas A, Lanjar L and Arianto A (2024) Global perspective on red chili drying: insights from two decades of research (2004–2023). Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1456938. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1456938
Edited by:
Poonam Rani, Teagasc Food Research Centre, IrelandReviewed by:
Tobi Fadiji, Cranfield University, United KingdomMostafa Gouda, National Research Centre, Egypt
Copyright © 2024 Elmatsani, Munarso, Benyamin, Budiyanto, Yohanes, Djafar, Sjafrina, Koeslulat, Lukas, Lanjar and Arianto. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: S. Joni Munarso, c2pvbjAwMUBicmluLmdvLmlk
 Huda M. Elmatsani
Huda M. Elmatsani S. Joni Munarso
S. Joni Munarso Boni Benyamin
Boni Benyamin Agus Budiyanto
Agus Budiyanto Heryoki Yohanes
Heryoki Yohanes Mochammad Jusuf Djafar
Mochammad Jusuf Djafar Noveria Sjafrina
Noveria Sjafrina Ermi E. Koeslulat
Ermi E. Koeslulat Amos Lukas
Amos Lukas Lanjar Lanjar
Lanjar Lanjar Arief Arianto
Arief Arianto