- 1Agroecology Theme, Center for International Forestry Research and World Agroforestry (CIFOR-ICRAF), Nairobi, Kenya
- 2Multifunctional Landscapes Lever, International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT), Nairobi, Kenya
- 3East Africa Hub, International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA), Nairobi, Kenya
- 4Drylands Natural Resources Centre (DNRC), Nairobi, Kenya
- 5Community Sustainable Agriculture and Healthy Environmental Program (CSHEP), Kiserian, Kenya
Agroecology, as a holistic approach to sustainable food systems, is gaining momentum globally as a key approach to addressing current challenges in agricultural and food production. In sub-Saharan Africa, despite numerous efforts to address declining soil productivity, water scarcity, and increasing pest pressure through agroecological soil, water, and integrated pest management (IPM) practices, the adoption of such practices remains low. As part of the CGIAR Agroecology Initiative, we conducted a collaborative rapid innovation assessment of existing soil, water, and pest management practices in two Agroecological Living Landscapes (ALLs) in Makueni and Kiambu counties, Kenya. The assessment also included an evaluation of the performance of these practices and identified farmer preferences. Using a multi-stage approach, we applied stratified random sampling to identify 80 farmers for farm assessments and in-depth interviews. A total of 31 practices were identified, of which 26 were further evaluated. The evaluation revealed a heterogeneous set of socio-economic and biophysical contextual factors influencing practice performance. Respondents identified 19 strengths, and 13 challenges associated with the practices, highlighting opportunities for innovation to improve or adapt performance. Farmers also expressed preferences for future adoption of 31 practices, 77% of which were listed in one of the three focus areas, namely soil management, water management, or IPM. The other 33% were associated with multiple functions and were listed under two or three of the focus areas. The results of the collaborative assessment informed a broader co-design cycle that included participatory prioritization and selection of innovative practices, experimental design, and monitoring protocols. This collaborative and systematic approach was taken because innovative practices often fail to be adopted due to a lack of co-design and inclusion of local perspectives in innovation design, and a disconnect between science and practice. Our study highlights the importance of integrating stakeholder input and transdisciplinary technical expertise in the co-design and implementation of agroecological innovations. It also emphasizes the importance of using a structured methodology to understand farmers’ options, context, and preferences while co-designing locally relevant agroecological practices, which promotes holistic and inclusive adoption, successful implementation and long-term sustainability of agroecological practices.
1 Introduction
The concept of agroecology is gaining traction globally as a key approach to comprehensively addressing the current challenges facing food production. Agroecology involves a synthesis of both agronomic and ecological principles that integrate social, environmental and economic dimensions. It emphasizes the promotion of biodiversity and associated ecosystem services to sustain agricultural production and promote resilient, environmentally sound and sustainable food systems (Wezel et al., 2009; Zanasi et al., 2020). It does so by harnessing biological interactions and seeking to optimize the relationships between plants, animals, soils and the surrounding ecosystems (Jones et al., 2022; Nicholls and Altieri, 2018). Agroecological practices include a range of methods and techniques through which the 13 agroecological principles are applied (HLPE, 2019; Wezel et al., 2020).
The agroecology principles are nested under three operational principles. The first category nests two principles, recycling and input reduction, which improve resource efficiency by optimizing resource use to increase economic returns and reduce negative environmental impacts. The second category nests five agroecological principles that strengthen resilience by improving the adaptive capacity, risk management, and response to changing conditions. This includes principles three through seven, namely soil health, animal health, biodiversity, synergy and economic diversification. The third operational principle consists of six principles that secure social equity by promoting fairness and accountability in addressing a broad spectrum of social and ethical concerns within societies. These principles include co-creation of knowledge, social values and diets, fairness, connectivity, land and natural resource governance and participation (HLPE, 2019). Consistent with the emphasis on principles to define what agroecology entails, there is no single set of farming practices that can be defined as agroecological in nature. Rather, agroecology is about the contextual operationalization of these 13 principles. However, it does point to relevant subsystems that should be considered, including soil, biodiversity, and others.
In this context, the importance of simultaneously adopting agroecological practices related to soil management, water management, and integrated pest management (IPM) has been emphasized. All three of these interrelated components are of paramount importance in promoting sustainable food systems (McIntyre et al., 2001). For example, poor and infertile soils with little or no organic matter have been found to not only retain little or no water and moisture that is necessary for plant growth but are also prone to erosion due to weak soil structure (Regelink et al., 2015). Further evidence shows that unhealthy and infertile soils lack diversity, biomass and abundance of beneficial soil macrofauna (Ayuke et al., 2011) and microfauna (Bolo et al., 2021, 2024). Schroth et al. (2000) further state that systems with low plant diversity are less resilient and are more susceptible to pests and diseases, leading to higher pesticide use. Deepika and MubarakAli (2020) note that there has been an increase in the use of synthetic fertilizers to address the high nutrient deficiencies in the soil. This reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides has been shown to result in the loss of beneficial soil macrofauna and contamination of water bodies and food crops (Solgi et al., 2018). Therefore, a holistic approach that integrates soil management, water management, and IPM is key to building resilient and sustainable agricultural systems.
In sub-Saharan Africa, there is a clear need to focus on and invest in integrated soil, water and pest management. For example, soil productivity is declining due to various factors such as land degradation, declining fertility, and poor health due to inefficient soil management practices (Raimi et al., 2017), including nutrient mining, removal of crop residues from the farm, and overcultivation without adding more organic matter to the soil (Blanco-Canqui and Lal, 2009; Majumdar et al., 2016). Agroecological soil management practices are therefore essential to maintain soil fertility, biodiversity, structure, and nutrient levels among other important requirements for optimal crop growth (Barrios et al., 2006; Chikowo et al., 2014). Such practices take advantage of ecological system interactions, including the use of ecosystem-friendly farm inputs, and prioritize nurturing healthy soils as the foundation for productive and resilient farming systems (Gliessman, 2018). They discourage the use of chemical inputs such as inorganic fertilizers and instead advocate for holistic, regenerative and sustainable practices that maintain or improve soil health over time (Hathaway, 2016; Wezel and Soldat, 2009). These include practices such as cover cropping, crop rotation, mulching, organic manure and soil amendments to improve soil fertility and structure (Alyokhin et al., 2020; Bolo et al., 2023).
Water management is equally critical in sub-Saharan African farming systems, where water scarcity is a persistent challenge that threatens livelihoods (Gaspard and Authority, 2013). Major causes of water insecurity include deforestation, climate-related drought and poor soil water management practices such as lack of rainwater harvesting and soil water conservation (Demeke, 2003; Mango et al., 2018; Shiferaw et al., 2014). Water scarcity and soil water deficit are particularly prevalent in arid and semi-arid areas that receive low rainfall amounts (Ong et al., 2007). Agroecological water management practices that prioritize the efficient and responsible use of water resources include rainwater harvesting, mulching, conservation agriculture, and the use of cover crops to enhance water retention in the soil and reduce water runoff (Altieri et al., 2015; Hermans et al., 2021). In addition, promoting diversity, including agroforestry, and integrating soil organic matter contribute to soil aggregate stability, increased water infiltration and retention, and reduced soil erosion (Bargués-Tobella et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2019; Winowiecki et al., 2021).
As a result of global warming, the sub-Saharan African region is experiencing increased temperatures and a concomitant increase in pest incidences, which contribute significantly to reduced agricultural productivity. Other factors contributing to increased pest incidences include declining biodiversity due to the promotion of monocropping systems, continuous cultivation without fallow periods, and the use of low-quality planting materials (Abate et al., 2000; Ratnadass et al., 2012). While conventional pest management promotes overreliance on chemical pesticides that kill rather than manage pests, and lead to the contamination and pollution of ecosystems (Barzman et al., 2015), IPM is an agroecological approach that provides a comprehensive and sustainable approach to pest management by integrating different strategies while maintaining ecosystem balance and minimizing health, environmental and economic risks. IPM typically combines biological, natural, cultural, mechanical, physical and host plant resistance technologies (Morales, 2004). It includes practices such as the use of natural predators, plant-based biopesticides, crop species diversification, and the use of companion planting to disrupt pest life cycles and pest-tolerant crop varieties (Deguine et al., 2021).
Despite practices falling under all three focus areas being implemented in sub-Saharan Africa (Debray et al., 2019; Nyantakyi-Frimpong et al., 2017), the region continues to experience low adoption of agricultural innovations, where adoption refers to the integration of an innovation into farmers’ normal farming activities over an extended period of time, preceded by a period of trial and adaptation to the local context (Loevinsohn and Sumberg, 2012; Ruzzante et al., 2021); and low crop productivity and food insecurity remain prevalent. One of the main reasons for this is the failure of external agents promoting such practices to elicit the participation of relevant stakeholders, including target adopters, in the co-design of context-specific agroecological practices (Chave et al., 2019; Magrini et al., 2019).
Co-design refers to the active and creative collaboration among stakeholders in the design and implementation of solutions to a pre-specified problem (Sanders and Stappers, 2008; Goodyear-Smith et al., 2015; Steen, 2013). Unlike user-centered approaches that incorporate the views and needs of end users of agricultural technologies (Ortiz-Crespo et al., 2021; Rose et al., 2018), or participatory action research where stakeholders participate in decision making throughout the design and implementation process (Baum et al., 2006; Cornish et al., 2023), co-design typically builds on the tradition of participatory design. Here, the roles of different stakeholders change throughout the co-design process, and the people who will ultimately benefit from the design process sometimes take on the role of “experts of their experience,” leading to the generation and sharing of knowledge and ideas (Sanders and Stappers, 2008). Consequently, co-design is a specific example of knowledge co-creation, where new knowledge is generated as stakeholders develop and experiment with new ideas resulting in new concepts and solutions that are context-specific and locally relevant (Mauser et al., 2013). Co-design processes thus promote transdisciplinary science, where stakeholders from different disciplines come together to co-create knowledge to solve complex social, political, environmental, educational and technological problems through the generation of new knowledge (Falconnier et al., 2017). Co-creation of knowledge, which refers to the collaborative generation of knowledge by different stakeholders, is described as more participatory, inclusive, holistic, and equitable for diverse actors, and as having better outcomes in adoption of and commitment to agroecological practices (Utter et al., 2021).
Our team adopted a rather broad definition of co-design as representing the highest level of participants’ engagement in design, decision-making, and implementation. We consider a continuum of consultation, involvement, participation, and co-production/co-design. The distinction between co-design and participatory design is often blurred in practice, and which term is most appropriate depends on the specific context. The term co-design itself has also evolved, resulting in different interpretations and applications, which contributes to terminological ambiguity. While the term co-design typically implies that a collaborative and iterative process is implemented, some focus more on creativity, exploration, and the discovery of new possibilities that emphasizes understanding user needs and fostering innovative solutions (Sanders and Stappers, 2008). Others use the term co-design in contexts that are more solution-oriented, focusing on the co-creation of practical, context-specific interventions through structured and goal-oriented processes aimed at implementation rather than exploration (Neef and Neubert, 2011). The structure and subsequent co-design process that we adopted are consistent with this latter interpretation: a participatory, solution-oriented co-design methodology aimed at co-developing actionable strategies with stakeholders. The rapid innovation assessment itself, which aimed to explore farmers’ practices and preferences, while conducted through a structured research-driven approach, focused on exploration and discovery as critical input for the more solution-oriented co-design workshops.
Our approach retains essential co-design elements such as collaboration, problem-focused, solution-oriented, inclusive, reflexive, iterative and stakeholder engagement (Rosendahl et al., 2015). In a recent meta-analysis of 88 publications, Busse et al. (2023) categorized intervention-oriented co-design approaches into four subtypes namely the “researcher-led and model-based” and “social science-driven intervention” studies that use a rigorous, predefined study design in which scientists are the dominant actors. The third subtype includes studies that develop “design-led and practice-oriented interventions” rather focus on practical outcomes than on scientific knowledge production. The fourth subtype, to which our current study aligns, is “transformative transdisciplinary interventions and living labs,” which have the strongest ties to transdisciplinary research philosophy, theory, methodology, and practice.
The concept and practice of co-design have been widely applied in different agricultural contexts. For example, Klerkx et al. (2012) advocate for a transdisciplinary and systems approach to address the complex socio-economic and natural context of farming systems by promoting participatory and co-design processes in the design and implementation of interventions. This is further supported by Berthet et al. (2018) who note that the complexity of agricultural innovations requires a systems thinking approach and facilitation process. However, despite their widespread application in agricultural systems, the optimal outcomes of agroecological transitions are often not fully realized. Therefore, for co-design processes to lead to responsible innovations in agricultural systems, human-centered design (HCD) approaches are required that promote four key dimensions namely inclusion, responsiveness, reflexivity and anticipation (McCampbell et al., 2022). This also requires ensuring that the co-design process is ethical and genuine by involving local communities in decision-making and shaping their current and future livelihoods (Sendra, 2024).
The adoption of generalized and top-down approaches and the lack of co-design of innovative agricultural practices can lead to a disconnect between scientific knowledge and the practical local realities of farming systems (Eilola et al., 2014). This is echoed by Reichelt and Nettle (2023) who observe that responsible innovation principles, which value the voices of diverse stakeholders, have not been widely applied to the adoption of innovative agricultural practices. The lack of local participation is often associated with an underestimation of the local heterogeneous and dynamic context of smallholder farming systems (Kuria et al., 2019; Vanlauwe et al., 2014) and an inadequate understanding of the context of their farming systems such as the nature, appropriateness and effectiveness of the agricultural practices and options they are already implementing (HLPE, 2019). It also leads to a limited understanding of the context-specific constraints and barriers that may hinder the success of agroecological practices (Sinclair and Coe, 2019). This can result in the promotion of agroecological options that are not locally appropriate, relevant, or adapted to the context of smallholder farming systems (Farrow et al., 2016), rather than using demand-driven and responsive approaches that are more likely to succeed in promoting actual behavior change (Fuchs et al., 2019a; Fuchs et al., 2022). Effective adoption of agroecology therefore requires a systems approach (Sinclair, 2017) and the integration of transdisciplinary perspectives and involves collaboration and co-creation of knowledge between farmers, researchers, and other stakeholders to develop context-specific agroecological practices (Calvet-Mir et al., 2018; Fernández González et al., 2021; Wezel et al., 2020). This also comes from documenting what people already know about agroecological practices and identifying knowledge gaps, which are then addressed.
In addition, the lack of local participation also results in a lack of consideration of farmers’ perspectives, preferences, and needs. Farmers’ preferences in agriculture are diverse and influenced by several factors, ranging from personal values, geographic and climatic conditions to Market trends and personal experiences (Duguma and Hager, 2011; Martin-Collado et al., 2015). These preferences include choices related to the crops they grow, whether they have livestock, land size, family size, their knowledge of agricultural techniques, their assessment of risk, and their future aspirations for their livelihoods (Knapp et al., 2021; Villacis et al., 2023). Fuchs et al. (2023a) posit that “communities will uptake and sustainably engage in such activities, if the practices promoted by the external actor are aligned with who they are, their livelihood activities, and what they like; and hence based on, and responsive to, local identities, interests, and preferences (IIP).” They define local IIP as “the quintessence of people’s complex life aspirations, influenced by their socio-cultural background, their rational calculations, and their personal taste” (p. 2). Therefore, in this study, we hypothesized that co-designing contextually relevant agroecological practices would lead to knowledge co-creation, which in turn would contribute to agroecological transitions by optimizing existing practices and innovating and redesigning smallholder systems to increase production efficiency and ecological resilience (Duru et al., 2015; Stratton et al., 2021).
Our study aimed to document all the existing agroecological farming practices in two so-called Agroecological Living Landscapes (ALLs) in Makueni and Kiambu counties, Kenya. Specifically, we investigated practices related to the three focus areas discussed above, namely soil management, water management and IPM (Kuria et al., 2023). After identifying existing options, the second objective was to understand the context of each practice’s performance, including by jointly identifying the strengths and weaknesses (barriers, gaps, and costs) of the agricultural practices that farmers were currently implementing, and third, to identify farmers’ preferences for innovative agroecological soil, water and IPM practices. After presenting the methods used in the rapid innovation assessment on which this study is based, and sharing and discussing the results in terms of options, context, and preferences, we contextualize the rapid innovation assessment in terms of how it informed the broader co-design cycle that led to a participatory prioritization of agroecological practices that were subsequently piloted and put under trial by ALL farmers in Kiambu and Makueni counties (Fuchs et al., 2023b).
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study area
The study was implemented in two agroecological living landscapes (ALLs), which are geographically bounded landscapes where smallholder farmers, agroecology practitioners, researchers, and other development actors have been engaged to identify, test and promote agroecological innovations across sectors and scales in Kenya. The two ALLs emerged from a comprehensive selection and engagement process conducted by the CGIAR Initiative on Agroecology (or Agroecology Initiative) beginning in September 2022 (Fuchs et al., 2023b). The targeted and purposive selection process included the identification of so-called ALL host centers, which provide a physical space where food system actors can meet and interact in the spirit of co-learning and knowledge co-creation. The Agroecology Initiative is a collaborative partnership of nine CGIAR entities, as well as CIFOR-ICRAF, the French research institute CIRAD, and the Agroecology Transformative Partnership Platform (TPP). Implemented in eight countries, the main objective of the Agroecology Initiative is to promote the application of contextually appropriate agroecological principles by farmers and communities in different contexts, with support from other food system actors.
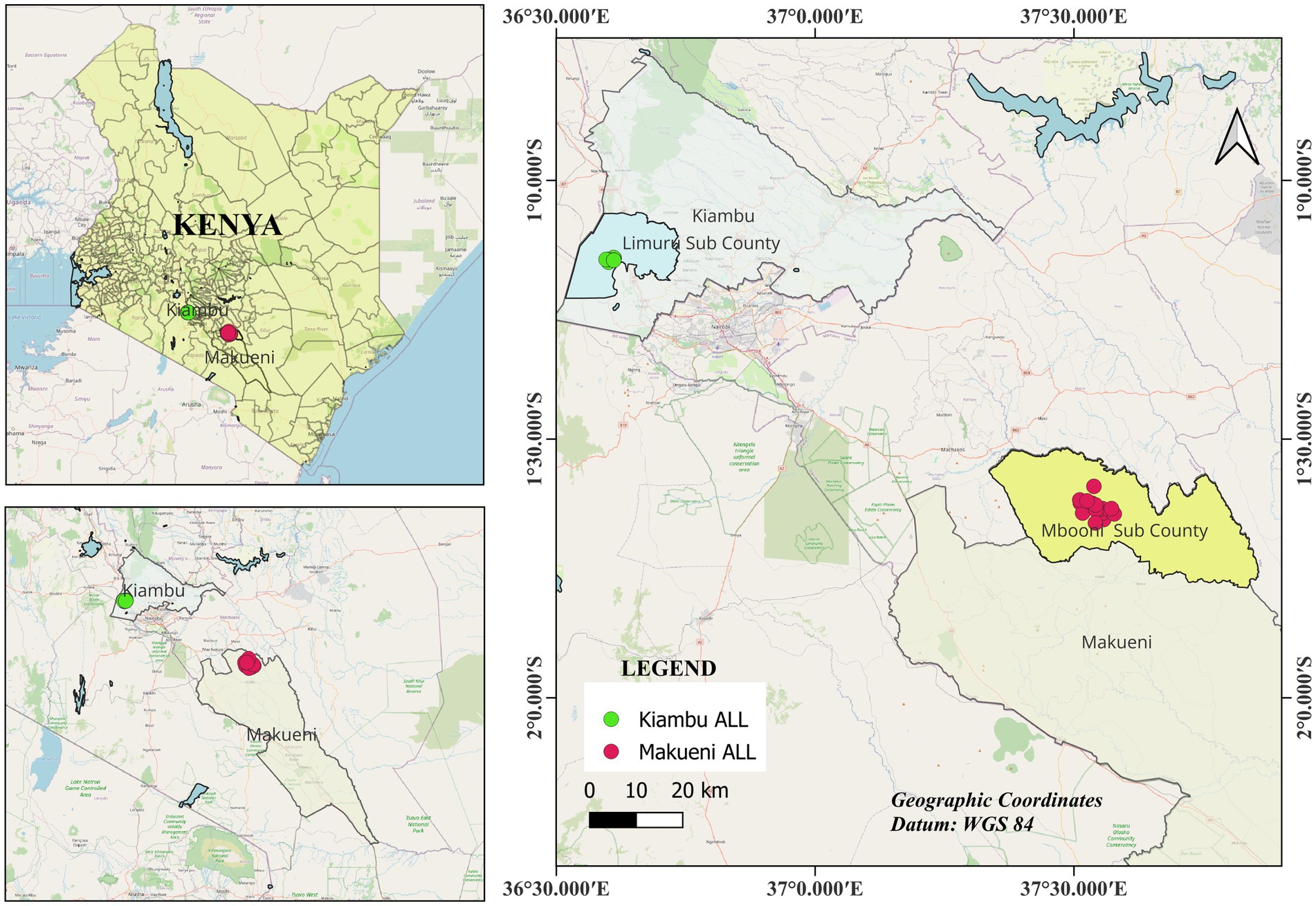
Specifically, the study focused on the two ALLs located in Makueni and Kiambu counties (Figure 1). Makueni County covers an area of 8,214 km2 between latitudes 1°35′ and 2°59′ south and longitudes 37°10′ and 38°30′ east, and has a population of 1,098,584, while Kiambu County covers an area of 2,543.5 km2 between latitudes 00°25′ and 10°20′ south and longitudes 36°31′ and 37°15′ east. Kiambu County has a population of 2,417,735, making it the second most populous county in Kenya after Nairobi, Kenya’s capital city. The two counties have different topography, climate, and soil conditions. Makueni County has a low-lying terrain with hilly areas receiving 800–1,200 mm of rainfall annually, while lower regions such as Kibwezi East receive 250–400 mm. Mean temperatures range from 20.2 to 35.8°C, with cooler temperatures in the hilly areas, and average annual rainfall of 500–750 mm of (Nyawira et al., 2023). The Drylands Natural Resources Center (DNRC) is the Makueni ALL host center. DNRC is a registered non-governmental organization (NGO) whose primary goal is to promote sustainable development of the resources of the drylands of Kenya through permaculture and agroecology. In Kiambu County, there are four topographic zones with different altitudes and agricultural activities. The upper highlands act as a water catchment area, while the lower highlands are suitable for tea and dairy farming. The midland zone faces challenges of soil erosion (ibid). Despite Kiambu’s generally humid climate, with annual rainfall ranging from 600 to 1,600 mm, semi-arid areas such as Ndeiya receive about 500 mm of rainfall annually, with April being the wettest month and July the driest. The Community Sustainable Agriculture and Healthy Environment Program (CSHEP), a registered community-based organization (CBO) in Ndeiya that focuses on training smallholder farmers in agroecological and organic practices, is the host center for the Kiambu ALL. The Agroecology Initiative’s agriculture-related activities in the early stages of implementation focused primarily on the areas surrounding the two ALL host centers, while other activities spread more widely across the ALLs.
2.2 Sampling strategy
A total of 80 farmers equally distributed between the two ALLs were interviewed in this collaborative rapid innovation assessment study. A stratified random sampling approach was used to ensure representation of the diverse and heterogeneous study areas. This approach aimed to create a sample that accurately reflects the biophysical and socioeconomic context and characteristics of the entire population. In doing so, the study enhances generalizability, promotes external validity, and mitigates research bias.
Stratified random sampling was conducted in collaboration with the ALL-host centers using a multi-stage approach based on five key factors: program participation (program and non-program farmers), geography (villages), gender, age, and land size. For example, in the Kiambu ALL, the study interviewed 27 farmers previously trained by Community Sustainable Agriculture and Healthy Environmental Program (CSHEP) host centers and 13 non-CSHEP farmers. In the Makueni ALL, 30 farmers affiliated with the Drylands Natural Resources Centre (DNRC) and 10 non-DNRC farmers were included in the sample. In the Kiambu ALL, farmers were selected from nine villages in Ndeiya sub-county and ward, including Gitutha, Makutano, Nderu, Boma, Gatarakwa, Kameria, Mirithu, Michofo, and Kiawanda (Figure 1). In the Makueni ALL, farmers were sampled from Mbooni East sub-county, with villages selected from two wards: Kiteta Kisau and Waiya Usalala. Overall, this rigorous sampling approach ensures that the study captures a representative sample from diverse backgrounds and contexts within the ALL regions.
2.3 Data collection and analysis
Prior to the commencing the study, ethical approval was sought to ensure that the rights, dignity, and welfare of participants are protected. We first submitted details of the planned research to the ICRAF Ethics Committee, outlining the study’s aims, methods, and potential impact of the study on participants, and obtained approval (Jordan and Gray, 2014). In addition, prior to interviewing the farmers, we obtained informed consent by providing each participant with comprehensive information about the study, including the study’s objectives, proceeding, data anonymization, voluntary participation, and the ability to withdraw at any time without penalty (Cooper et al., 2016; Singer, 2004). This ethical framework ensured transparency, demonstrated respect for participants’ autonomy, and maintained the integrity of the research process.
Data were collected in February 2023 through a survey consisting of semi-structured questionnaires administered by researchers who visited and interviewed the farmers at their homesteads and farms. The process involved the researchers asking the questions verbally and then recording the farmers’ responses on paper questionnaires. The survey tool was modeled on and informed by previous engagement activities, particularly the contours of the “mobilizing narratives” identified to operationalize the “communities of place” that would be engaged in the respective ALLs in November 2022, as well as subsequent engagements that generated community visions for desired future changes that could accelerate agroecological transitions in the ALLs (Fuchs et al., 2023a). The results of these transdisciplinary exercises helped to identify the key challenges that stakeholders were collectively interested in addressing in agroecological transitions and allowed categorizing them into the three main focus areas (soil, water, and integrated pest management) in which solutions were subsequently co-created. These focus areas served as a roadmap for developing tools for further research and became the conceptual vehicle for future co-design engagements.
The survey covered general farm and farmer characteristics, existing innovative agroecological practices, the context of their implementation and performance, availability of practice-specific materials, sources of knowledge related to their implementation, farmers’ understanding of the underlying scientific mechanisms, strengths and challenges, costs and labor requirements, associated crops, etc. Both open- and closed-ended questions were used. Questions related to socio-demographic and farming system characteristics were primarily closed-ended, while those assessing practices combined closed-ended and open-ended questions. The inclusion of open-ended questions, which refers to questions that do not have a set of response options (Züll, 2016), allowed farmers to provide detailed contextual information based on their personal experiences. To ensure that specific agroecological practices were correctly identified and mapped to their respective focus areas, keeping in mind that many practices serve multiple purposes and may be mapped to two or more focus areas depending on farmer’s practice, the team developed an initial complementary classification of all soil, water, and integrated pest management practices—including agroecological and non-agroecological (Kuria et al., 2023). A team of researchers from CIFOR-ICRAF, the Alliance of Bioversity International and the International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT), the International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA), and the ALL-host centers provided training and pre-testing, and administered the questionnaires.
The collected data were cleaned by removing outliers, correcting spelling errors, removing duplicate entries, and checking for errors and inconsistencies (Osborne, 2010). Next, qualitative data from open-ended questions were coded, either by assigning numerical codes or by reclassifying responses from open-ended questions into broader categories to facilitate statistical analysis (He and Schonlau, 2020). The data were then subjected to descriptive analysis and visualized in a variety of ways, for example, the socio-economic characterization of farmers and the results of the co-design trial prioritization were presented in tables. R software (R Core Team, 2020) was used to generate heat maps that were used to visualize cross-tabulation results, namely all agroecological practices found on farms, strengths, benefits and challenges associated with inventoried agroecological practices, while ggplots were used to visualize practices inventoried by farmers and costs associated with different practices. ATLAS.ti software (ATLAS.ti Scientific Software Development GmbH, 2023) was used to generate Sankey diagrams of farmer’s future preferred practices and to illustrate the multiple functions preferred in the three focus areas of soil management, water management, and IPM.
2.4 The co-design workshop process methodology
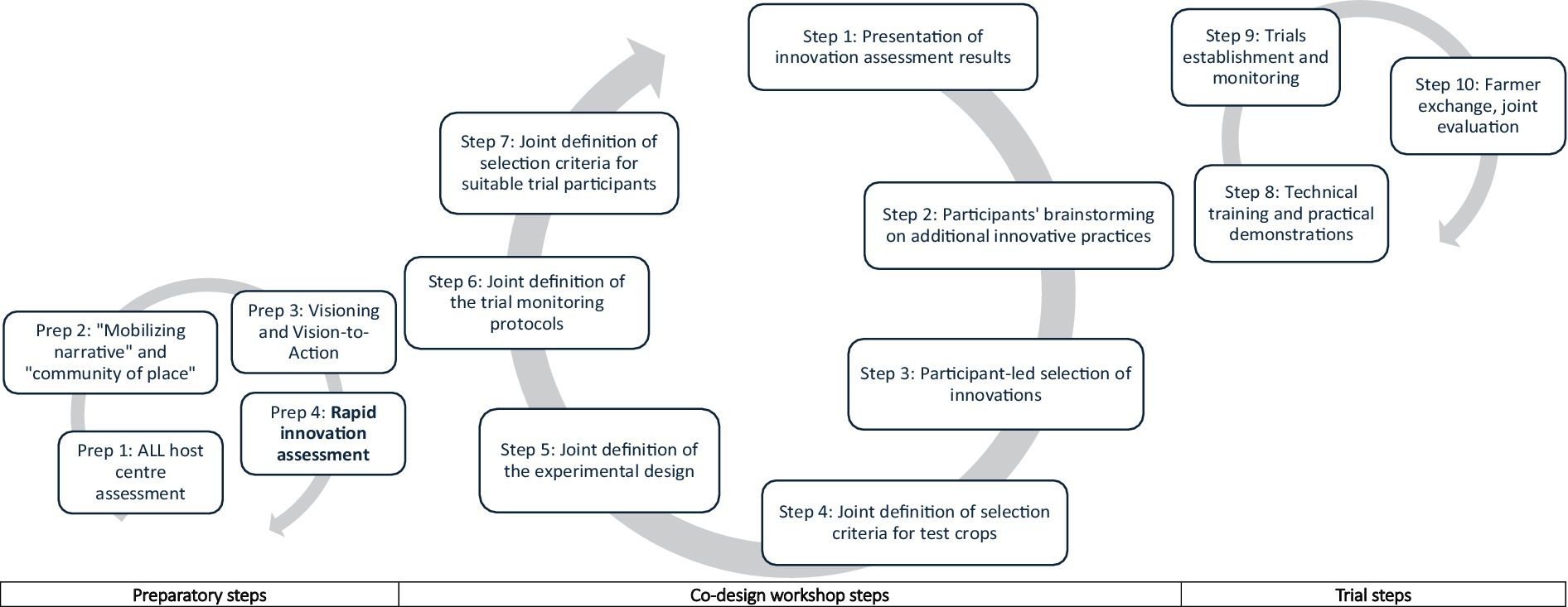
As mentioned above, the rapid innovation assessment was conducted in the context of a broader co-design cycle (Figure 2), the main objective of which was to test and put co-created innovative agroecological practices under trial in both ALLs (Fuchs et al., 2023b). The first actual co-design design workshop was highly methodical and followed a clear sequence. We held three-day integrated workshops in each of the ALLs between July and August 2023, bringing together farmers, ALL host centers, the Agroecology Initiative project team, and additional research, technical and extension stakeholders together to discuss the most appropriate and desired options to be tested through trials at the ALL centers and in farmers’ fields (Watts-Englert and Yang, 2021). Willing and agroecology-motivated participants were purposively selected to ensure broad representation, with 15 individual farmer groups selected and two members (a man and a woman) per group invited to the workshops. At least 50% of the farmers who participated in the co-design workshops had also been interviewed during the rapid assessment.
The co-design workshops consisted of seven steps. In step 1, the results of the rapid assessment, which included the participating farmers’ own views, were presented to the stakeholders. To visually support the data sharing, we prepared posters for each of the top three to five practices per focus area that provided a simple overview of the key findings from the innovation assessment. This included a broad set of existing soil, water and IPM options encountered and the context including benefits, challenges and preferred innovative practices identified. In Step 2, participants added other innovative practices that had not been identified or highlighted by the Agroecology Initiative team. Step 3 was to collectively narrow down the list of preferred innovations to a few agroecological innovations to be tested in monitored trials. After selecting the respective practices, Step 4 involved deliberations among participants on relevant selection criteria and the selection of the respective host test crops. Step 5 involved defining a strategy for setting up the trials for the selected agroecological innovations. Step 6 involved the development of appropriate protocols for the evaluation of the selected agroecological innovations, in which the farmers discussed desirable, measurable and observable criteria. Step 7 involved the collective identification of criteria for identifying the trial participants and a preselection of the participants. Once the co-design workshops were completed, two additional steps included Step 8, which involved technical training including practical demonstration of trial establishment in the ALL centers. After that the trials were established with the onset of the rains in a last step.
3 Results
3.1 Socio-economic characterization
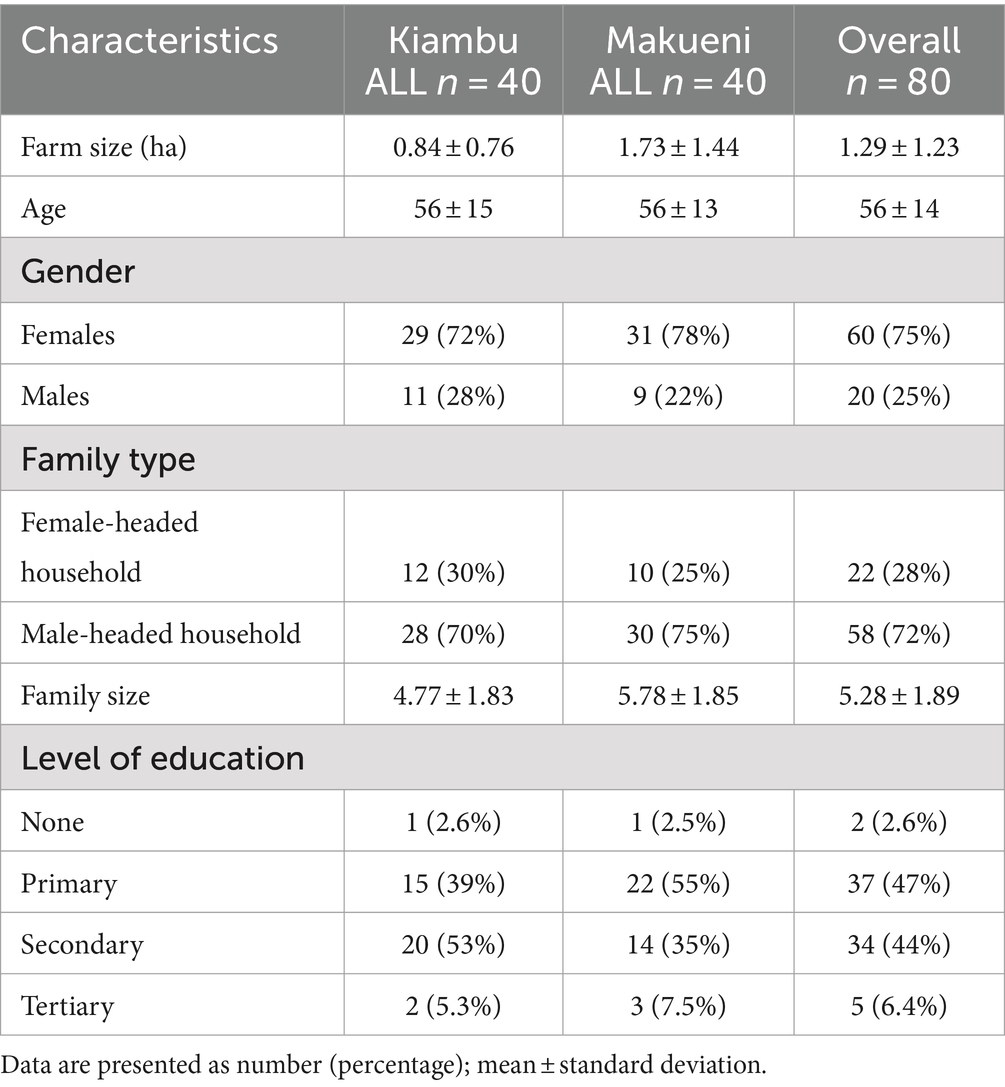
The average household land size was 1.73 ha in the Makueni ALL and 0.84 ha in the Kiambu ALL respectively, while the average age of the interviewed farmers was 56 years in both ALLs (Table 1). More than 70% of the farmers interviewed in both ALLs were female, while more than 72% of the households sampled were male headed. Almost all (96%) respondents indicated farming as their main source of livelihood. Food self-sufficiency was recorded at 8.2 ± 4.0 months in Kiambu and 6.6 ± 3.7 months in Makueni. The top four crops grown in Kiambu were maize, beans, vegetables, and Irish potatoes; while maize, beans, cowpeas, and pigeon peas were the top four crops grown in Makueni. Most respondents reported practicing natural or ecological farming (85% in Kiambu, 72% in Makueni), and agroforestry (85% in Kiambu, and 98% in Makueni). Soil quality was described as “medium” by most farmers (78% in Kiambu, 51% in Makueni), with a considerably higher percentage in Makueni (28%) describing it as “low.” In both the Makueni ALL and the Kiambu ALL, all farmers reported experiencing climate and yield changes in their main crops over the past 5–10 years. The two most common climate-related changes identified by farmers were drought due to low rainfall (52 respondents; 65%) and poor yield (29 respondents; 36%).
3.2 Existing soil, water and integrated pest management practices identified by farmers
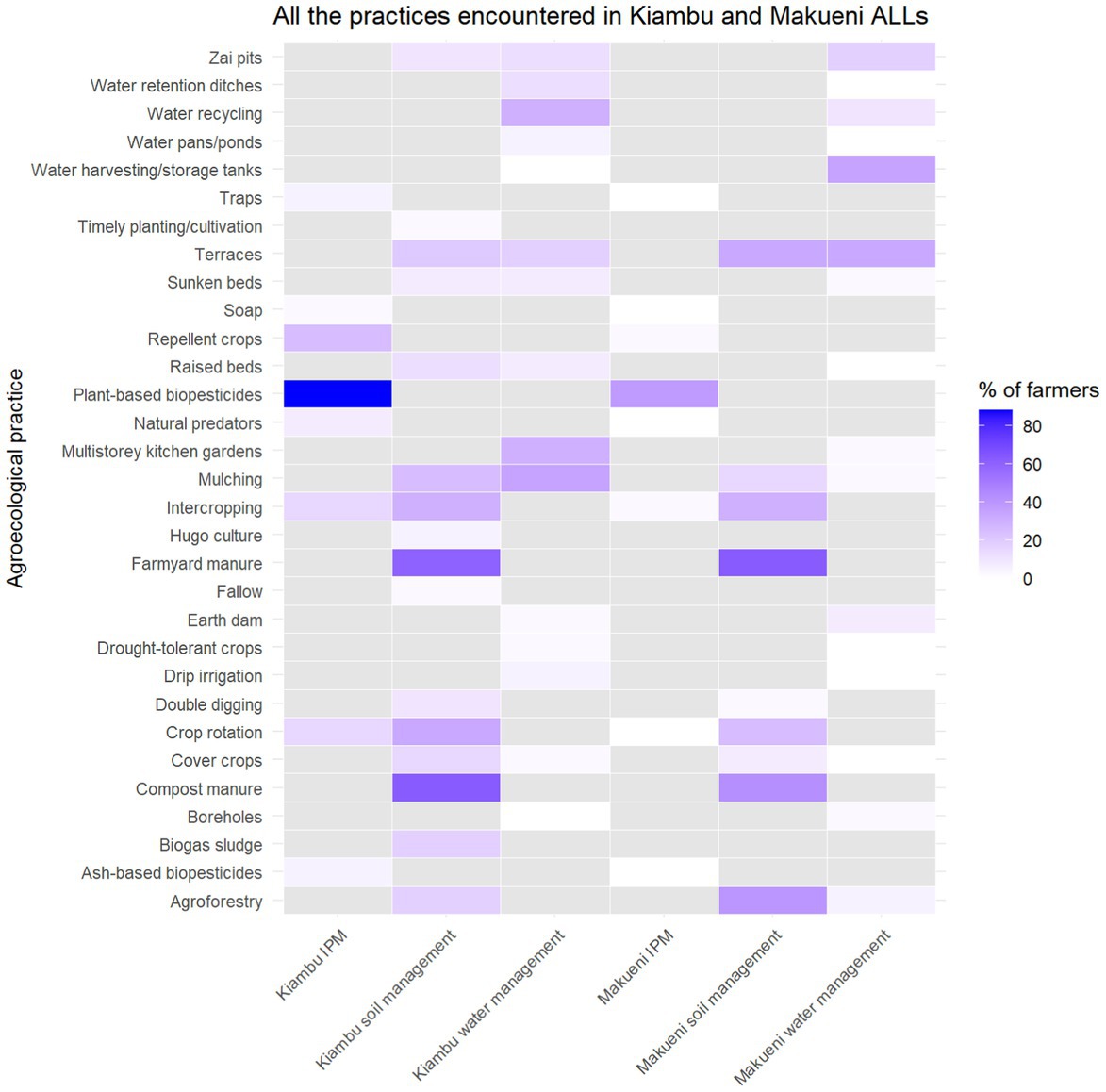
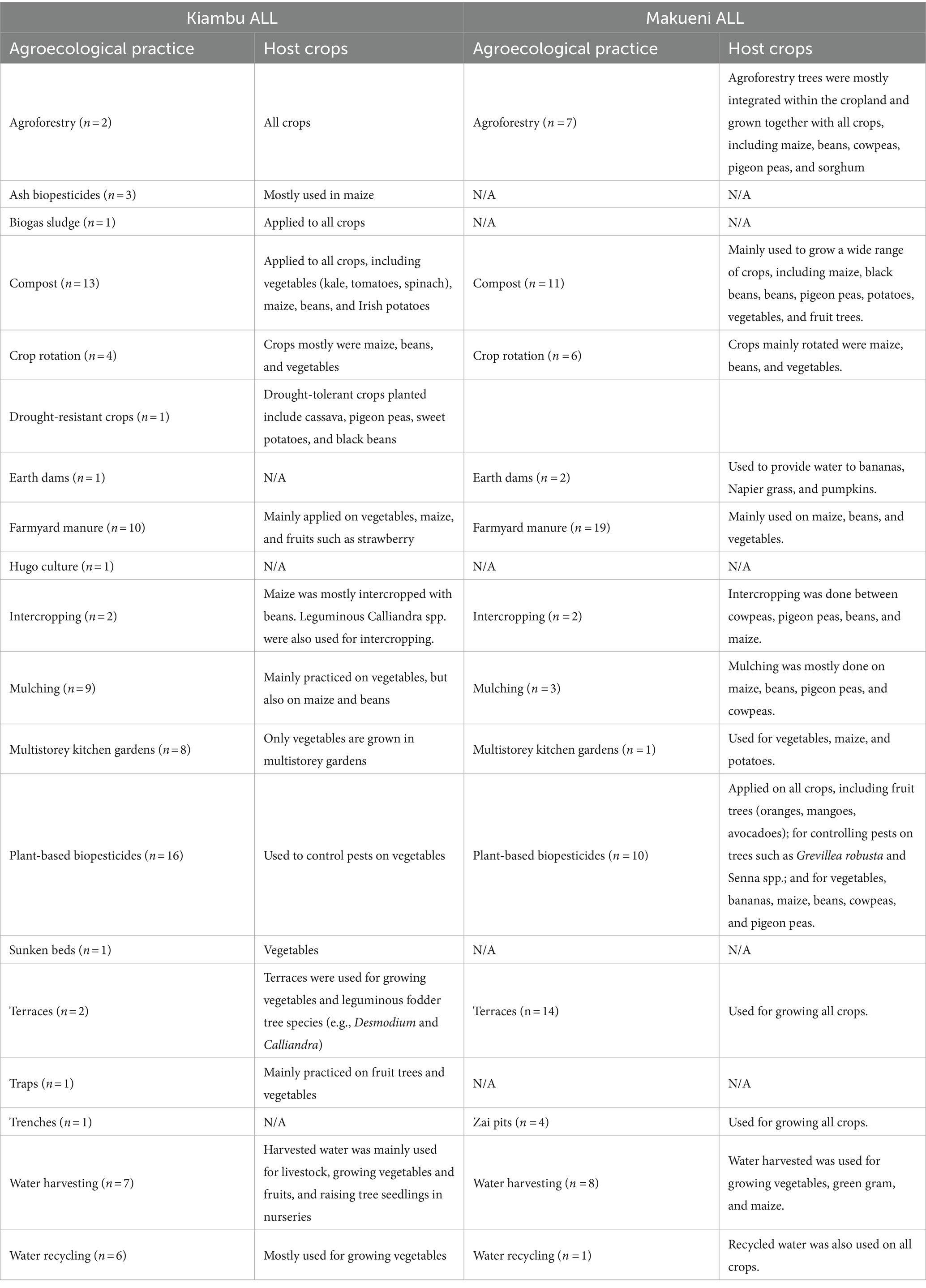
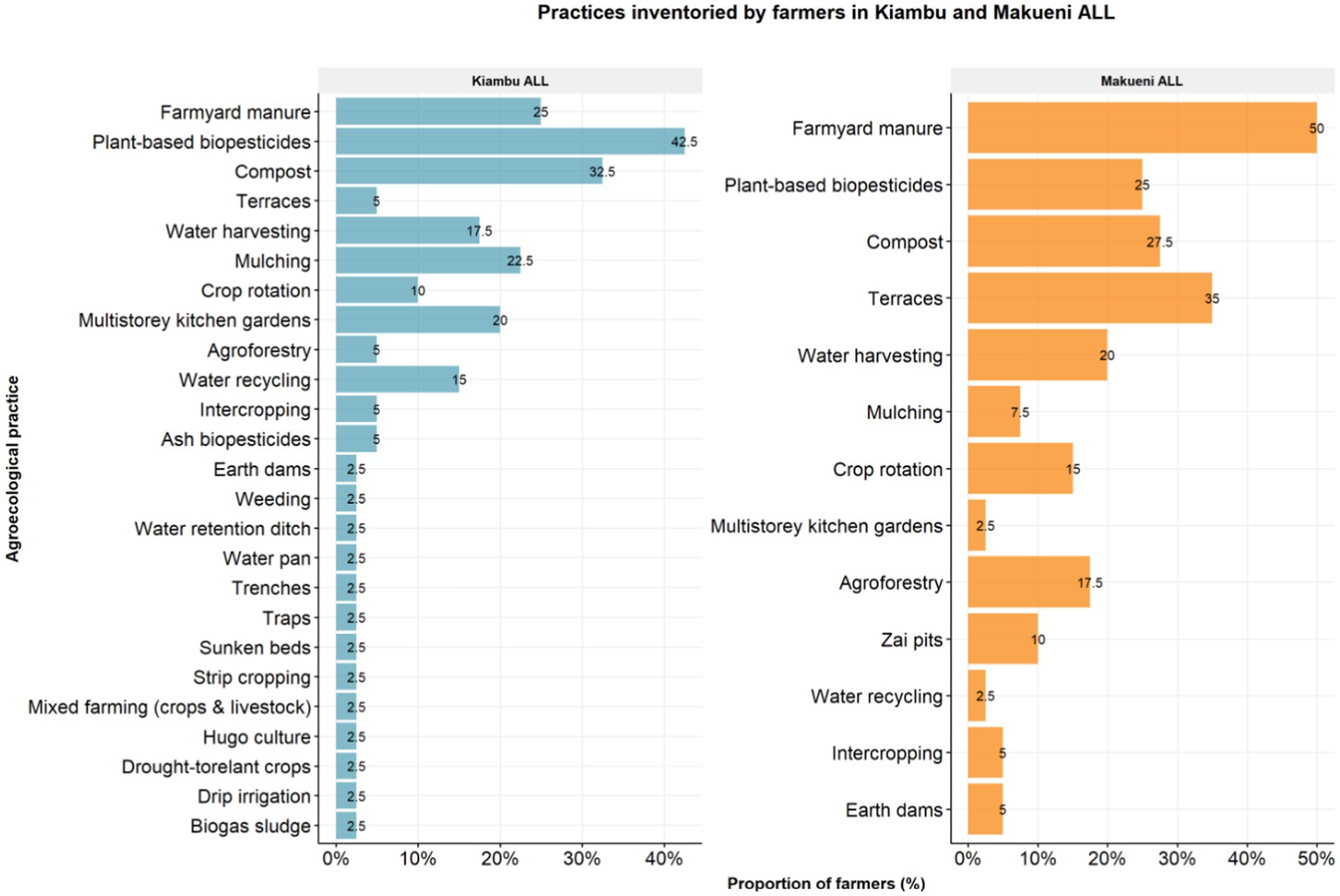
A total of 31 agroecological practices were identified on respondents’ fields in both ALLs, with 29 and 18 practices being mentioned in Kiambu and Makueni, respectively. There were 18 common practices, while 13 were unique to the sites. While many practices do serve multiple purposes, no practice was mentioned in all three focus areas during the options inventory. Practices that farmers reported implementing for both soil and water management were agroforestry, mulching, raised beds, sunken beds, terraces and zai pits. Practices that farmers implemented for both soil management and IPM were crop rotation and intercropping.
A total of 16 soil management practices were classified by farmers as being used for soil management, with all 16 reported by the farmers in the Kiambu ALL and 9 in the Makueni ALL (Figure 3). Farmyard manure (61%) and compost manure (53%) were the most reported soil management practices mentioned in both ALLs. Crop rotation (33%) and intercropping (30%) were more frequently mentioned in Kiambu while agroforestry (40%) and terraces (33%) were more commonly mentioned as serving soil management functions in Makueni. Similarly, 16 practices were reported to have water management functions. Thirteen of these were mentioned in Kiambu and 10 in Makueni. In Kiambu, the main water management practices reported by farmers were mulching (35%), multistorey kitchen gardens (30%), and water recycling (30%). In Makueni, water harvesting/storage tanks (35%), terraces (33%), and Zai pits (17%) were most frequently mentioned. Finally, a total of eight practices were mentioned as serving integrated pest management functions on the farms visited in both ALLs. Eight practices were mentioned in Kiambu, while only three were reported in Makueni. The use of plant-based biopesticides was the most common practice in both ALLs, mentioned by 88 and 38% of farmers in Kiambu and Makueni, respectively. Further, farmers in Kiambu used repellent plants (25%) and practiced crop rotation (15%) and intercropping (15%) to manage pests.
In addition to specific host crops, several agroecological practices were implemented on the surveyed farms (Table 2). In Kiambu, practices applied to all crops included: agroforestry, compost, biogas sludge; while those applied mostly to vegetables were farmyard manure, mulching, multistorey kitchen gardens, plant-based biopesticides, sunken beds, traps, water harvesting and water recycling. The practices used for maize and beans were crop rotation, intercropping, mulching and farmyard manure, while the practices used for fruit trees were terraces and water harvesting. In contrast, in Makueni, the practices applied to all crops included: plant-based biopesticides, compost, terraces, zai pits and water recycling; while the practices applied mostly to vegetables were compost, crop rotation, farmyard manure, mulching, multistorey kitchen gardens, and plant-based biopesticides. The practices applied to cereals (maize, sorghum) and legumes (beans, cowpeas, pigeon peas, green grams) were agroforestry, compost, crop rotation, intercropping, mulching, and water harvesting; while the practices applied to fruit trees were: plant-based biopesticides and compost.
3.3 Context: performance and evaluation of inventoried soil, water, and IPM practices
After inventorying existing practices, respondents assessed the context in which the existing agroecological practices were implemented and their performance in the respective settings. Farmers were asked to document at least two practices that were of high importance to them. Thus, the in-depth contextual study does not provide information on all practices, but only on those that were prioritized.
3.3.1 Soil, water, and IPM practices included in additional contextual analysis
Respondents provided additional contextual information on a total of 26 of the 31 practices that cut across the three functions, of which 25 were inventoried in the Kiambu ALL, and 13 in the Makueni ALL (Figure 4). A total of 12 common practices were evaluated in both ALLs, with the main ones in Kiambu being plant-based biopesticides, compost manure, farmyard manure, mulching, and multistorey kitchen gardens. In Makueni, farmers mainly discussed farmyard manure, terraces, compost manure, plant-based biopesticides, water harvesting, and agroforestry. Zai pits were unique to Makueni farmers.
3.3.2 Benefits and functions associated with soil, water, and IPM practices
In their open-ended responses, respondents identified a total of 19 benefits and functions associated with the agroecological practices, which fell under 10 of the 13 agroecological principles across all the three broad operational principles for sustainable food systems (Figure 5). Eleven of the 19 benefits belonged to the operational principle of strengthening resilience agroecology, five benefits belonged to securing social equity and three benefits to improving resource efficiency.
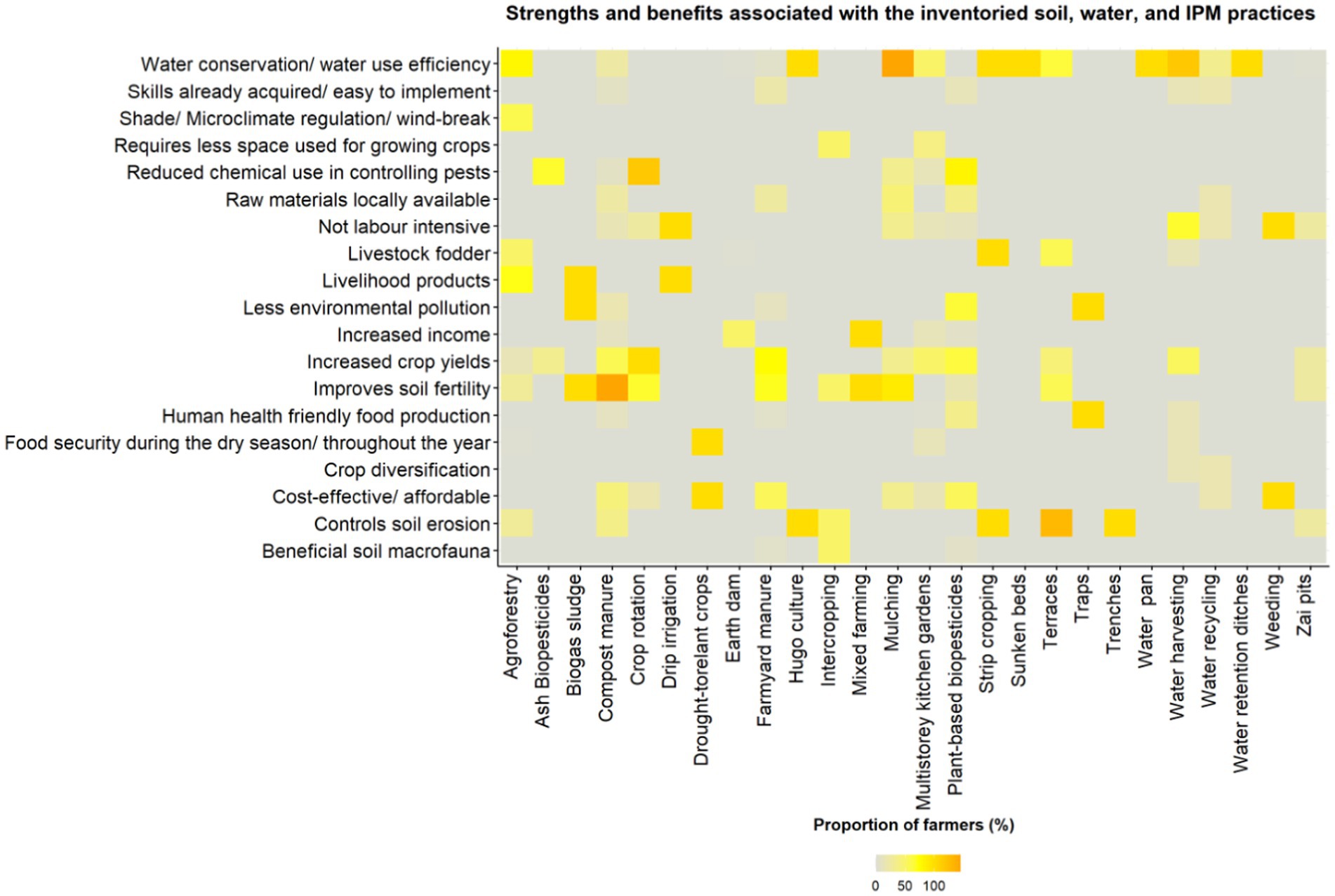
Figure 5. Benefits and strengths associated with inventoried soil, water and IPM agroecological practices.
Most of the benefits were associated with the broader operational principle of strengthening resilience, which includes agroecological principles 3 to 7. Under soil health, for example, biogas sludge (100%), compost manure (73%) and crop rotation (67%) were highly associated with improving soil fertility; while strip cropping, trenches, sunken beds (100%), terraces (79%) were perceived as beneficial in controlling soil erosion control; biogas sludge and traps (100%) were associated with reduced environmental pollution, while intercropping (50%) was seen as enhancing beneficial soil macrofauna. Several practices were said to contribute to the synergy principle through water conservation and water use efficiency, such as hugo culture, strip cropping, sunken beds, water pans and water retention ditches (100%) and water harvesting (88%); while agroforestry was said to contribute to microclimate regulation by providing shade (59%). The principle of economic diversification was mainly associated with practices that provide income and additional livelihood products diversification mainly biogas sludge, drip irrigation (100%), and agroforestry (71%). Improved animal health was associated with livestock fodder from strip cropping (100%), agroforestry and vegetation planted along terraces (50%).
Key benefits associated with the operational principle of securing social equity included: fairness through practices perceived as being cost effective such as weeding and planting of drought-tolerant crops (100%), farmyard manure (35%) and mulching (33%); while some practices were perceived as not being labor intensive such as drip irrigation, weeding (100%), water harvesting (34%) and mulching (33%). Social values and diets benefits included increased food security through drought-tolerant crops (100%); while practices associated with producing healthy and safe foods included the use of traps (100%) and plant-based biopesticides (18%). Finally, the operational principle on improving resource efficiency was mainly associated with input reduction through practices such as: reduced use of chemical pesticides through the use of ash-based biopesticides (67%), crop rotation (59%), and plant-based biopesticides (41%); while practices associated with the use of locally available raw materials that contribute to both input reduction and the use of local renewable resources included compost manure (23%), mulching (22%), plant-based biopesticides (18%), water recycling (17%), and farmyard manure (15%).
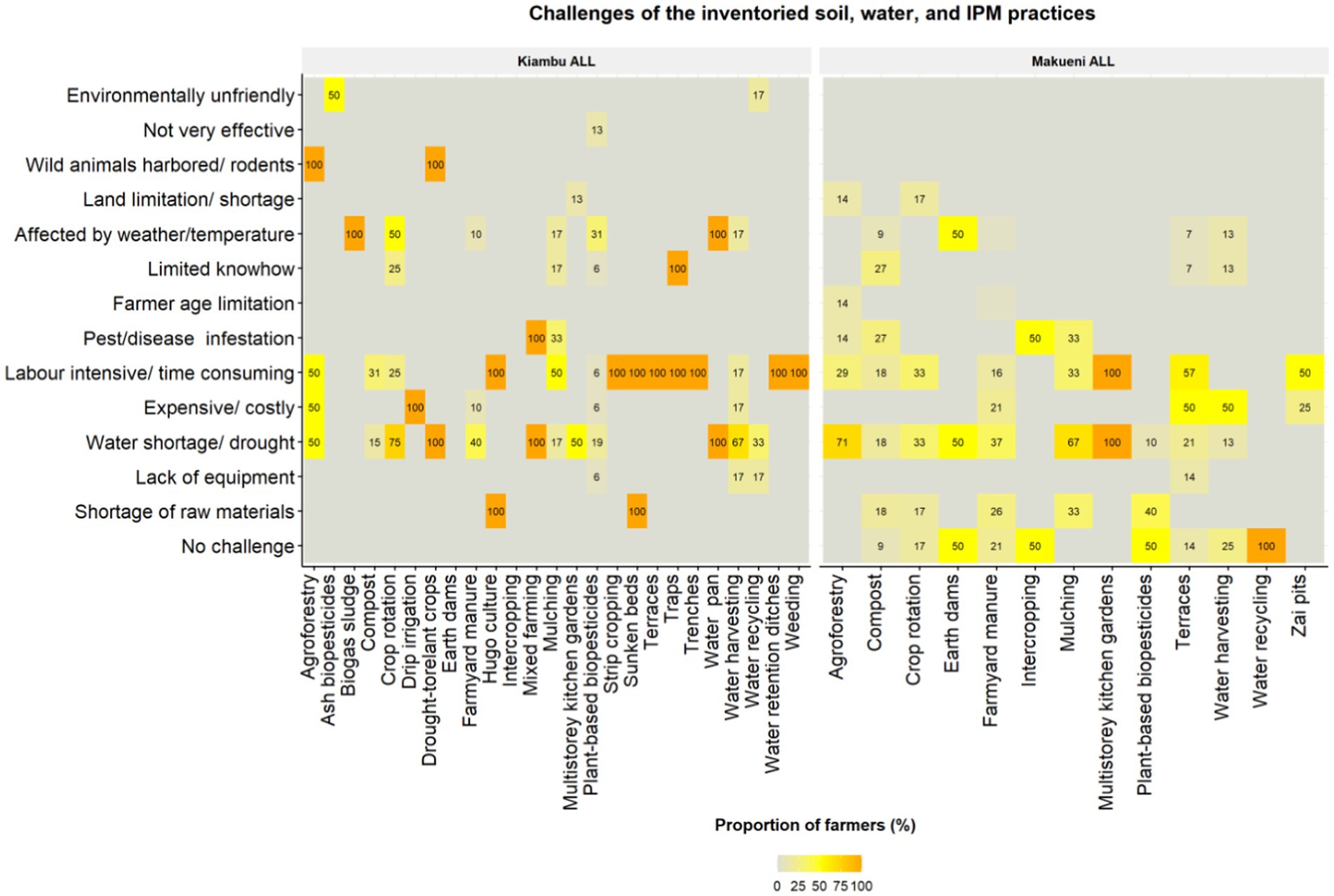
3.3.3 Challenges associated with soil, water, and IPM practices
In response to an open-ended question, farmers mentioned 13 challenges that limit the success or effectiveness of the soil, water and IPM practices they use (Figure 6). The most common challenges included: drought and water scarcity, being labor intensive, being costly and unaffordable, limited know-how, shortage of raw materials, being susceptibility to weather variability, and susceptibility to pest infestation. These challenges are discussed in subsequent sections. Drought and the water shortage was the most serious challenge, reported to affect numerous practices namely: multistorey kitchen gardens (100%) and agroforestry in both Makueni (71%) and Kiambu (50%); crop rotation (75%) and water harvesting (67%) in Kiambu; and mulching (67%) in Makueni.
Another challenge widely mentioned across both ALLs was that many practices were labor intensive. Some of the key practices perceived as labor intensive and time consuming were mentioned mainly in Kiambu and include construction and maintenance of structural practices such as terraces, trenches, sunken beds, and water retention ditches (100%), hugo culture (100%), multistorey gardens (100%) and weeding (100%), mulching and agroforestry (50%). In Makueni, fewer practices were perceived as labor intensive, including terraces (57%) and zai pits (50%). Some farmers reported having limited know-how of how to implement or do some practices, for example in Kiambu namely traps (100%), crop rotation (25%), and mulching (17%); while in Makueni, farmers had limited knowledge of compost manure (27%). Scarcity of raw materials was also mentioned especially in Makueni, namely for plant-based biopesticides (40%), mulching (33%), farmyard manure (26%), and compost (18%). In Makueni, pests were also reported in practices such as intercropping (50%), mulching (33%), compost (27%) and tree seedling establishment in agroforestry (14%). In Kiambu, agroforestry (trees) was blamed for harboring wild animals (100%) that would consume the planted crops.
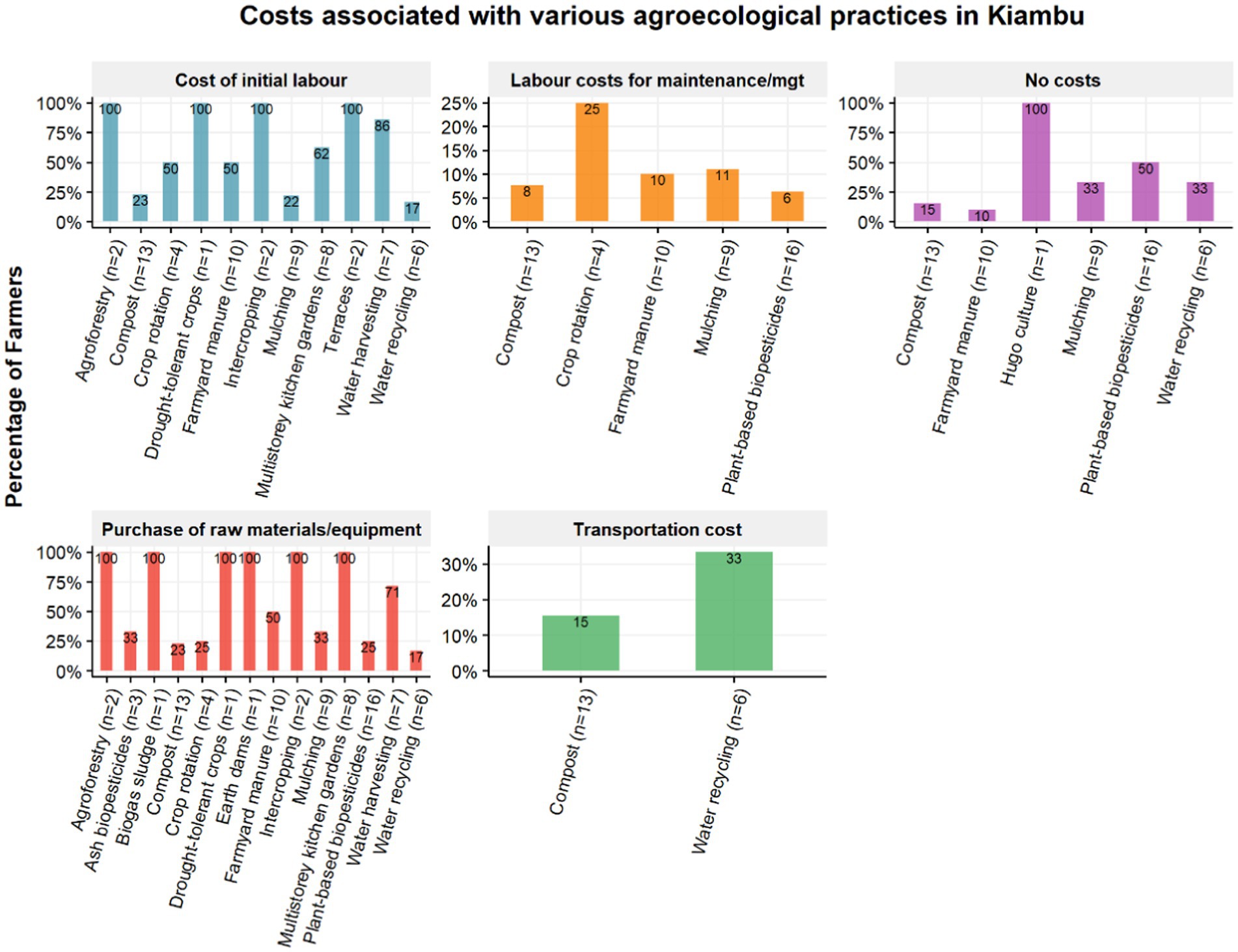
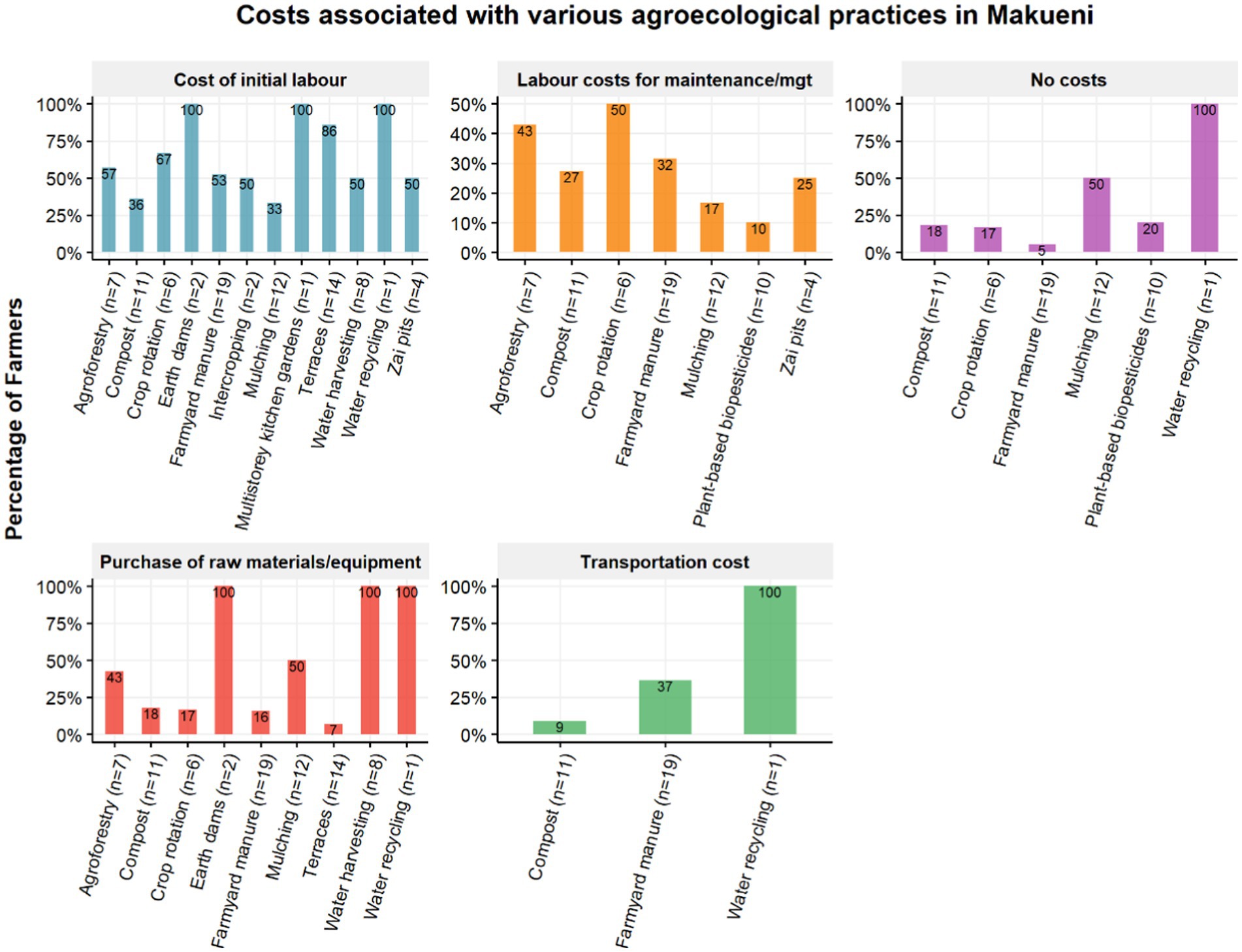
Another challenge mentioned in both ALLs was that some practices were considered as being costly and therefore farmers could not afford to implement them. Farmers identified four types of costs associated with the inventoried soil, water, and IPM practices: the cost of initial labor to implement the practices, the cost of purchasing raw materials and equipment, the cost of labor to maintain the practices, and the cost of transportation. The analysis showed that the highest costs in implementing the practices were associated with the initial labor required. In Kiambu, practices with high initial labor cost include agroforestry (100%), drought-tolerant crops (100%), intercropping (100%), terraces (100%), and water harvesting (86%) as shown in Figure 7. Maintenance labor costs were mostly incurred in crop rotation (25%), while the costs associated with raw material purchases included biogas sludge (100%), agroforestry (100%), drought-tolerant crops (100%), earth dams (100%), and multistorey kitchen gardens (100%). On the other hand, practices such as hugo culture (100%) and plant-based biopesticides (50%) were found to be the most cost-effective and affordable to install.
In the Makueni ALL, practices that were perceived to have the highest initial labor costs included earth dams, multistorey kitchen gardens and water recycling (100%), as shown in Figure 8. Practices incurring maintenance costs included crop rotation (50%) and agroforestry (43%), while practices that incurred high costs of purchasing raw materials included earth dams (100%), water harvesting (100%), and water recycling (100%). Water recycling further incurred transportation costs (100%). In addition, the analysis identified several practices that were perceived as easy to implement without the need for financial resources. These practices were plant-based biopesticides, mulching, crop rotation, farmyard manure (if sourced from own animals), and compost.
3.4 Farmer preferences in soil, water, and integrated pest management practices
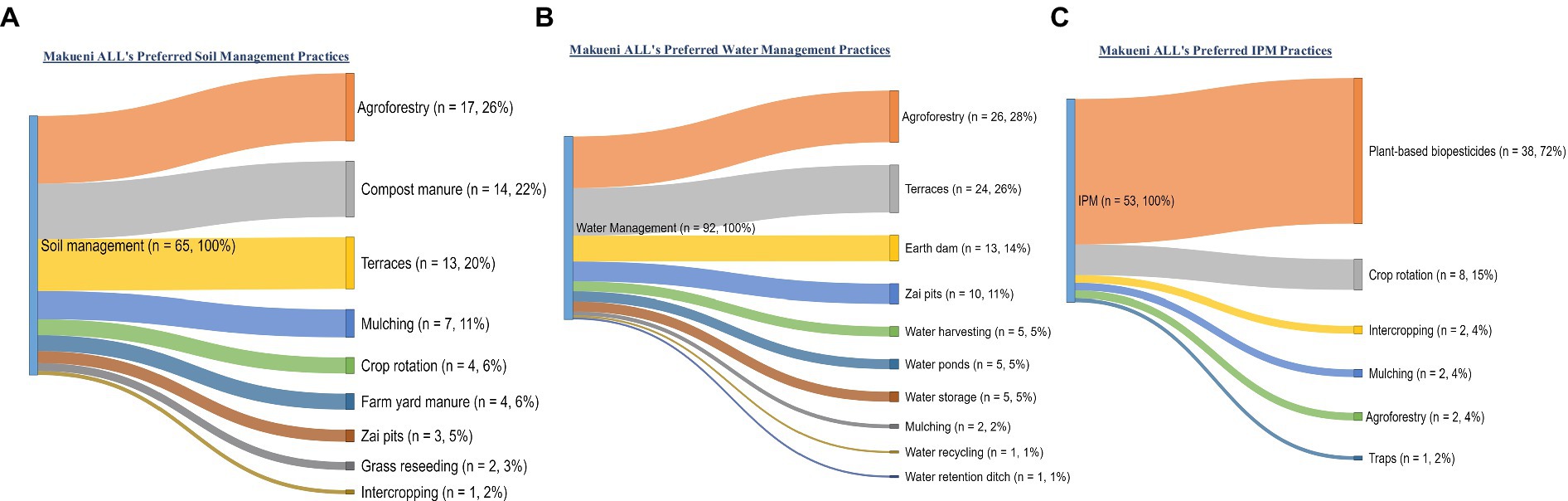
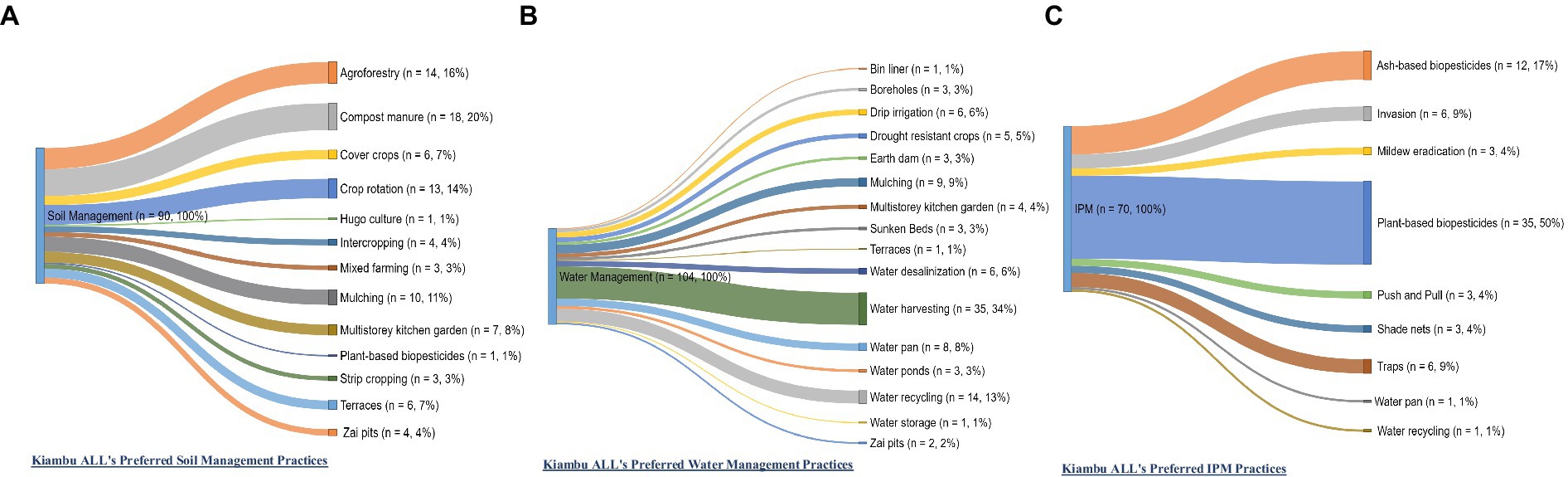
Looking specifically at practices that the respondents would like to implement in the future, respondents in Makueni preferred to implement nine individual soil management practices (Figure 9A), with the most preferred ones being agroforestry (26%), compost manure (22%), and terraces and mulching (22%). Farmers preferred to implement 10 water management practices (Figure 9B), with the most preferred being agroforestry (26%), terraces (26%), earth dams (14%), and zai pits (11%). Farmers preferred to use six IPM practices (Figure 9C), with the most preferred being plant-based biopesticides (72%), crop rotation (15%), and intercropping (4%). In Kiambu, respondents preferred to implement 13 individual practices for soil management, with the most preferred ones being compost manure (20%), agroforestry (16%), crop rotation (14%) and mulching (11%) as shown in Figure 10A. Farmers preferred to implement 16 water management practices (Figure 10B), with the most preferred being water harvesting (34%), water recycling (13%), mulching (9%) and water pans (8%). Farmers preferred to implement nine IPM practices (Figure 10C), with the most preferred being plant-based biopesticides (50%), ash-based biopesticides (17%), and traps (9%).
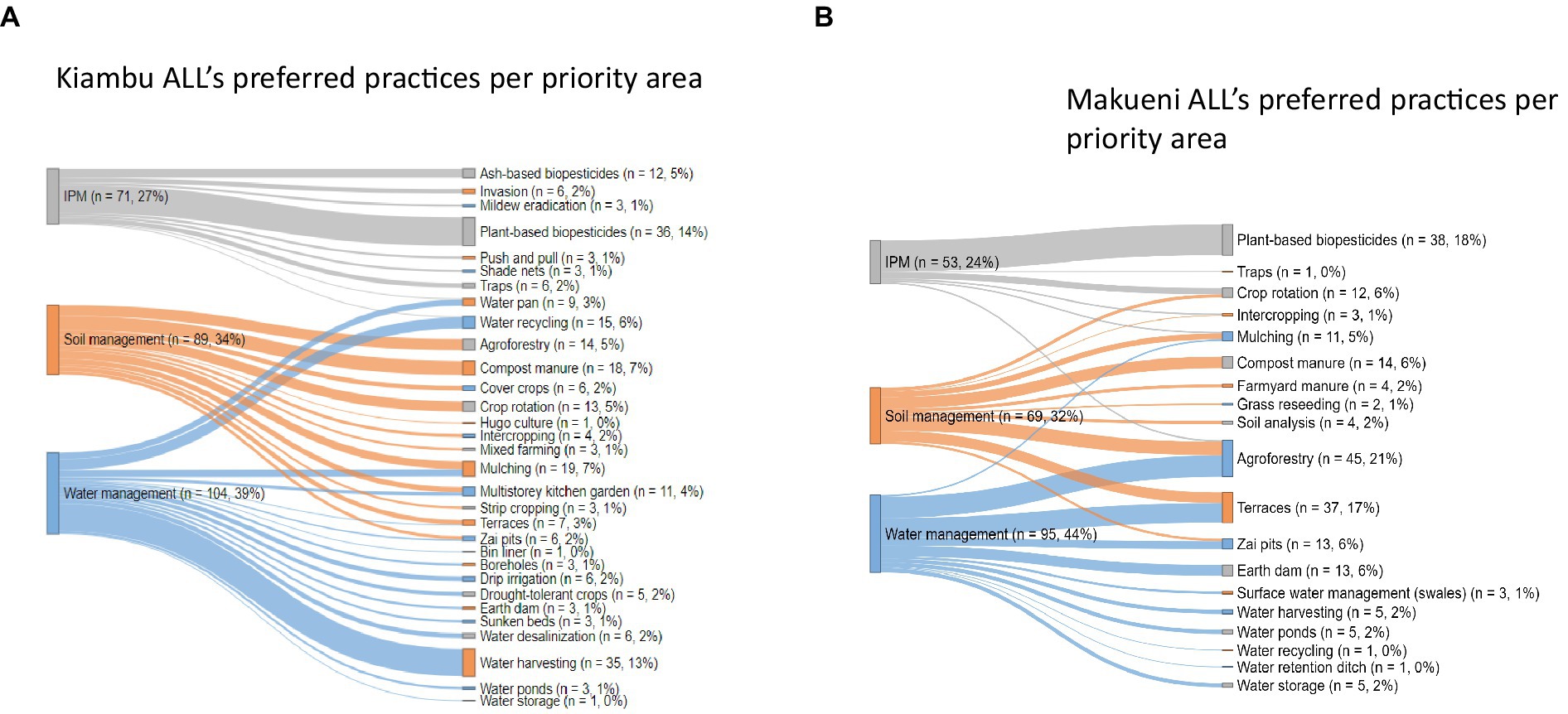
The assessment results showed that several practices were mentioned as preferred practices under two or all three focus areas. In Makueni, practices that could address all three functions were agroforestry (21%), and mulching (5%) as shown in Figure 11A. In addition, practices that were preferred to address both soil and water management needs were terraces (17%) and zai pits (6%). Practices mentioned under both soil management and IPM were crop rotation (6%) and intercropping (1%). On the other hand, in Kiambu, the preferred practices mentioned under both soil and water management were mulching (7%), multistorey gardens (4%), terraces (3%), and zai pits (2%); while the preferred practices for water management and IPM were water recycling (6%) and water pans (3%) as shown in Figure 11B.
3.5 Co-design and implementation of soil, water and IPM agroecological innovations
As mentioned previously, the co-design workshops consisted of seven steps (Figure 2). Resulting from steps 1, 2, and 3 of the co-design workshops, three specific innovative practices were chosen for farmer experimentation in each ALL. In the Kiambu ALL, participants selected to implement the integration of compost manure for soil management, mulching for water management and plant-based biopesticides for IPM (Table 3). In the Makueni ALL, participants selected farmyard manure for soil management, terraces for water management and plant-based biopesticides for IPM.
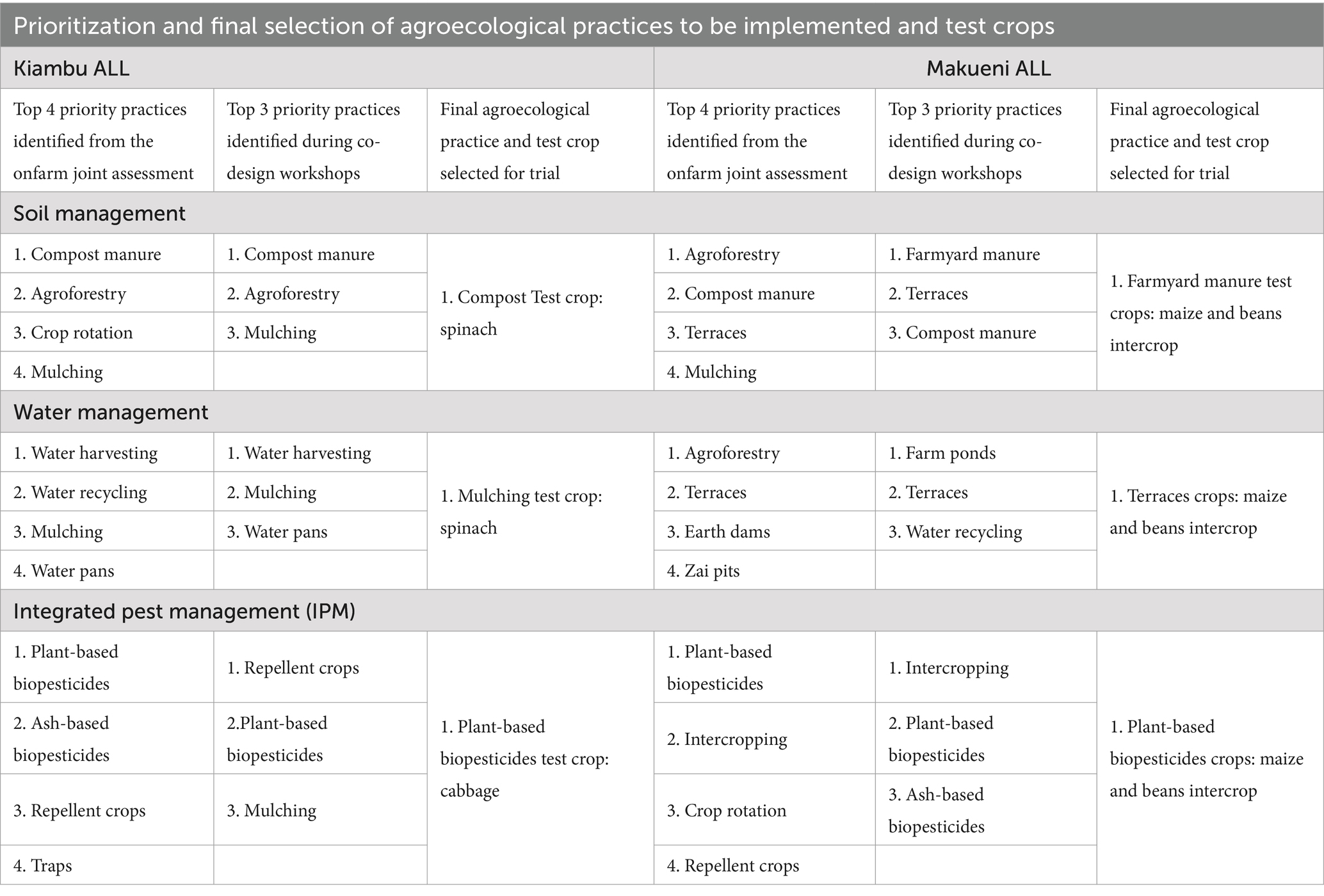
Table 3. Prioritization and final selection of agroecological practices to be implemented and associated test crops.
In step 4, farmers in both ALLs developed comprehensive crop selection criteria. Although conducted separately, participants identified five common criteria: the proposed crop had to be adaptable to local conditions, mature within the project period, have a readily available market, have low water requirements, and have high nutrient content. Additional unique criteria identified by Kiambu stakeholders included availability of seeds and planting materials, high yield potential, high susceptibility to pests for effective biopesticide testing, contribution to household food security and nutrition, economic significance to the local community, potential for value addition, and social acceptability. Stakeholders in Makueni identified additional unique criteria, namely the most popular and commonly used crops that most local farmers can adopt, crops that are disease resistant and tolerant, crops with local varieties, and crops that would be appropriate for the available space and farm sizes. As a result, in Makueni, due to limited space and farmers’ familiarity with intercropping, farmers unanimously agreed to intercrop two test crops, namely maize (Zea Mays) and beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) to experiment with all three practices. Based on the above criteria, farmers in Kiambu agreed to test the selected soil and water management practices on spinach (Spinacia oleracea), while cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata) was chosen for IPM due to its high susceptibility to pests (Table 2).
In step 5, which involved defining the experimental design strategy, the participants decided to maintain their conventional practice on the control plots for each of the selected innovative practices to be tested, rather than adopting a uniform control protocol. It was decided that both the test plot for the agroecological innovation and the control plot would be located adjacent to each other. This proximity was essential to minimize any potential variation due to differences in soil fertility and landscape orientation by maintaining similar slope characteristics for both plots. Step 6 involved the development of monitoring protocols in which farmers deliberated on and agreed to measurable and observable criteria to be monitored and recorded at two-week intervals. These included quantifiable parameters such as crop yield, growth rate, leaf surface area, plant nutrient content and shelf life; and observable parameters such as plant color, plant vigor, size of produce or leaves/biomass, presence of pests and diseases, weed density and maturity period. Additional factors to be considered included production costs (including labor), marketability of the crop, and rainfall frequency, timing and intensity. The technical team recommended that data collection be conducted in two phases. First, initial baseline data was collected, which included soil sampling prior to land preparation and recording of the farm management history. Once established, the actual trial data were collected through three levels of monitoring and data collection by participating trial farmers, ALL host center staff, and Agroecology Initiative researchers.
Step 7 involved the joint definition of selection criteria for trial farmers, followed by their selection according to the criteria. In each ALL, participants first discussed the selection criteria for potentially eligible trial participants. In Kiambu, five criteria were identified, including: possession of physical assets, namely ownership of at least two plots of land measuring 6 m by 5 m; interest in participating in the trials; openness to innovation and adopting new practices; communication skills and willingness to share knowledge; and possession of desirable personal attributes, such as high integrity and hospitality. The Makueni participants also came up with five selection criteria for trial farmers, namely: ownership of a farm with at least one plot (5 m × 6 m) and having the necessary resources such as animal manure; willingness to carry out the trials; keeping timely records; willingness to host field day participants and researchers in their homes for measurements and demonstrations; and willingness to provide labor. Other criteria were openness to innovation and implementing new knowledge and skills; good communication skills; and positive personal attributes, namely strong family relationships with the community and no existing conflicts.
To make the process inclusive and fair, the trial participants decided to report back to their respective farmer groups, and then inform the Agroecology Initiative team on the selected persons, rather than deciding at the workshops. In the end, a total of 63 willing farmers were selected (30 in Kiambu, and 33 in Makueni; that is, 10+ farmers per focus area). In Makueni, 73% of the selected trial participants were female and 27% were male farmers, and in Kiambu, 50% were male and 50% were female farmers. Upon completion of the co-design workshops, Step 8 involved the Agroecology Initiative technical team conducting integrated technical trainings and practical field demonstrations for all three identified practices at the respective ALL host centers with all selected trial participants in each ALL. The trainings focused on sharing technical skills, with an additional focus on trial establishment and monitoring. To build capacity as broadly as possible, all 63 trial participants were trained in all three practices in integrated three-day workshops facilitated by the Agroecology Initiative team and technical experts. This was followed by Step 9, the trial establishment on farms. Farmers were given hard copies of the co-designed monitoring sheets to be able to record observations and crop performance (using the indicators listed in Step 6) to build their observation and record keeping skills and knowledge, which are critical for assessing the performance of cropping systems over time and for timely adaptation of agroecological practices based on contextual needs to achieve optimal crop production. In Step 10, intra-ALL and inter-ALL farmer-to-farmer knowledge exchanges were organized to foster peer learning, joint reflection, strengthen social networks among farmers, which, in turn, support the development and refinement of sustainable and contextualized farmer-led agricultural innovations.
4 Discussion
4.1 Understanding household dynamics in agroecological design
The results showed distinct differences in land size, gender dynamics and other household demographics between the Makueni and Kiambu ALLs, highlighting the importance of considering household characteristics when designing agroecological practices (Liani et al., 2023). For example, there were differences in average household land size in the two ALLs (1.73 ha in Makueni and 0.84 ha in Kiambu), which may have influenced the most planted crops beyond agroclimatic factors (Manjunatha et al., 2013). While farmers in Makueni mainly planted maize, beans, cowpeas and pigeon peas, 75% of respondents in Kiambu planted vegetables in addition to maize, beans, and potatoes. This can be interpreted as farmers in Makueni adopting more traditional farming practices compared to more intensive and market-oriented practices in Kiambu. This has been observed elsewhere, with additional influencing factors being access to ready markets, access to economic resources and, of course, agro-climatic conditions (Esquivel et al., 2021).
The average age of farmers in both ALLs was 56 years, highlighting the generational continuity of farming, with older farmers dominating. Older age may have posed a challenge in terms of farmers’ inability to engage in labor-intensive agricultural activities (Benin et al., 2004), as evidenced by the fact that several practices, including terraces, zai pits, mulching and multistorey kitchen gardens were described as labor-intensive. This emphasizes the need to design and implement agroecological practices that are less labor intensive and easy to implement (Mekuria et al., 2022); or to find innovative ways to adapt existing practices to reduce labor requirements and enable effective and sustainable adoption of such interventions. The average age of our respondents may also indicate that fewer youths are engaging in agricultural activities. This is particularly true as more youth in sub-Saharan Africa migrate to urban areas in search of paid labor (Castañeda-Navarrete, 2021; Crossland et al., 2021a); although our results may partly be related to the sampling framework and the relatively small sample size overall.
Furthermore, although 72% of households surveyed in both ALLs were male headed, the majority of farmers interviewed (70%) were women. The low number of men interviewed was mainly due to factors such as men migrating to towns in search of better livelihood opportunities and engaging in off-farm activities such as petty trading (Crossland et al., 2021b; Greiner and Sakdapolrak, 2013). In Kenya, as in most sub-Saharan countries, even though agricultural activities are mostly undertaken by women and low agricultural productivity is mostly experienced by women (Awiti, 2022), men typically hold most of the land and are the main decision makers (Errico, 2021; Holden and Tilahun, 2020). Therefore, women have limited or no control or access to the productive resources on which agricultural activities depend (Valencia et al., 2021). To creatively address this potential conflict, during the co-design workshops, both men and women were encouraged to participate, and they were sensitized on the need for collective decision making and participation in agricultural innovation design, implementation and management (Madzorera et al., 2023; Sariyev et al., 2021). Other approaches that have been used to close the gender gap include implementing policy reforms that are gender-inclusive, transformative and responsive, and that take into account the unique gender differences that exist such as differences in gender roles, knowledge, skills, experiences, constraints and opportunities, access to resources, rights to resources and decision-making (Lopez et al., 2022; McGuire et al., 2022). Examples of practical approaches include promoting equity by empowering women with skills and access to economic resources to improve the food security outcomes of their farming activities (Farnworth et al., 2023; Shrestha et al., 2023). Other approaches relevant to the sub-Saharan context include involving both men and women, or husbands and wives, in the selection, design, and implementation of agroecological practices so that innovations to have more gender-responsive and inclusive outcomes (Crossland et al., 2021a; Paudyal et al., 2019).
4.2 Farmers’ knowledge and priorities inform co-design of multifunctional and inclusive agroecological practices
The results showed that farmers identified 31 practices (29 in Kiambu and 13 in Makueni), of which 18 and 13 were unique to Kiambu and Makueni, respectively. The results further showed that farmers preferred a diverse range of 26 soil, water and IPM agroecological practices that they were interested in adopting and/or maintaining on their farms, with more practices mentioned in Kiambu compared to Makueni. This highlights the underlying high heterogeneity of the farming systems and the different needs and priorities of farmers (Kihoro et al., 2021; Vanlauwe et al., 2014). Furthermore, while Makueni was dominated by farmyard manure, terraces, and water harvesting techniques reflecting a greater emphasis on soil conservation and water scarcity, Kiambu was dominated by organic input-based practices mainly plant-based biopesticides, compost manure, and mulching. The contextual variations highlight the need to understand the local context and thus tailor agroecological interventions to the context (Coe et al., 2014; Mutemi et al., 2017).
This study also found that farmers prefer agroecological practices that address multiple functions of soil, water and integrated pest management on their farms. For example, in Makueni, agroforestry and mulching were highlighted as preferred practices that address all three functions of soil, water and integrated pest management simultaneously. However, farmers preferred terraces and zai pits for meeting the soil and water management functions; and crop rotation and intercropping serving both soil management and pest management functions, in line with (Lasco et al., 2014). In Kiambu, farmers’ preference for compost manure and water harvesting in meeting their soil and water management needs is in line with previous studies that have demonstrated the benefits of practices that enhance water use efficiency and organic soil amendments (Adugna, 2016). These findings are consistent with the concept of multifunctional and multipurpose agriculture (Sivini and Vitale, 2023), and highlight the need to promote agroecological practices that serve multiple functions through synergies and complementary ecological interactions (Stefanovic et al., 2020).
Despite the inventoried agroecological practices contributing to multiple benefits, farmers identified only 20 distinct benefits that aligned with 10 of the 13 agroecology principles they derived, highlighting the need for awareness raising as part of co-designing agroecological practices. The benefits were derived from open-ended questions. Open-ended formats allow respondents to express their views (Reja et al., 2003). In terms of the three broader operational principles of agroecological sustainable food systems, 11 benefits reported by farmers fall under the seven agroecological principles that are categorized under the broader principle of strengthening resilience (Wezel et al., 2020). Consistent with the literature, many benefits were associated with the soil health principle, which received significant attention, with practices such as compost manure and crop rotation understood as contributing to increased soil fertility; terraces and strip cropping to soil erosion control while intercropping was viewed as enhancing beneficial soil macrofauna and promoting biodiversity (Singh et al., 2023). Contrary to existing literature, majority of farmers did not associate practices such as mulching and agroforestry with improving soil fertility or controlling soil erosion (Nzeyimana et al., 2013; Rosenstock et al., 2014).
Other practices were found to be beneficial in strengthening resilience by creating synergies such as conserving soil water, including as farmyard manure, hugo culture, sunken beds, mulching and strip cultivation, in line with Ndiso et al. (2018), while agroforestry was found to regulating microclimate, improve animal health through fodder and provide livelihood products (Gicheru et al., 2004; Mbow et al., 2014; Muthuri et al., 2023). Furthermore, resilience is further enhanced by increasing the diversity and abundance of such agroecological practices (Gachuiri et al., 2017; Magaju et al., 2020). Few farmers mentioned benefits related to the principle of economic diversification, which may indicate low knowledge, productivity or diversity of existing practices (van Zonneveld et al., 2020). Overall, only a few practices such as farmyard manure, plant-based biopesticides and water recycling were associated with the knowledge co-creation principle, where farmers reported already having and sharing existing knowledge about their implementation and performance amongst themselves. This highlights the need to address knowledge gaps on how to operationalize agroecological principles through specific agroecological practices as a prerequisite for promoting their adoption on farms (Bellamy and Ioris, 2017; Mottet et al., 2020). Doing so can increase their adoption rate, performance, and sustainability (Dumont et al., 2021).
Second, benefits related to securing social equity were evident as reported by farmers. For example, the fairness principle was addressed by many farmers who used organic material amendments that were low-cost and not labor-intensive, such as mulching and farmyard manure, in line with Maja et al. (2017). On the other hand, other practices, especially structural ones such as terraces, sunken-beds and water-retention ditches, were considered costly and unaffordable due to farmers’ resource constraints, as well as labor intensive. This contrasts with other studies that have observed that farmers’ perception of interventions being costly discourages their adoption due to the risks and uncertainties of outcomes against financial investments (Barry et al., 2021; Greiner et al., 2009). Cumulatively, these characteristics discourage farmers from widely adopting such innovations and threaten the long-term sustainability and success of agroecological practices (Panpatte and Jhala, 2019). Furthermore, in line with the literature, the social values and diets principle was addressed through practices that were perceived to promote food production in a human health-friendly manner, such as the use of plant-based biopesticides and physical traps to control pests (Rana et al., 2019), and achieving food security throughout the year by planting drought-tolerant crops (Atube et al., 2021). Such agroecological practices play a role in ensuring access to dietary diversity, thereby promoting nutritional security (Chakona and Shackleton, 2018; Kansanga et al., 2021) and increased access to multiple ecological services (Dissanayaka et al., 2023). These findings are consistent with previous studies highlighting the social dimensions of agroecology, emphasizing its potential to address inequalities and enhance the well-being of local communities (Gliessman, 2018).
Finally, three benefits related to promoting resource efficiency were identified. These mainly focused on input reduction through practices that were considered to reduce chemical use, such as ash-based biopesticides, plant-based biopesticides, compost manure and crop rotation. It has been reported that chemical use leads to multiple harmful forms of pollution, not only to soil/ land, but also to water bodies and air (Rana et al., 2019). This is in line with the broader need to move towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly agricultural systems (Pretty, 2009). In addition, practices such as compost manure and mulching utilize locally available materials in line with the principle of recycling. However, some studies indicate that for soil nutrient recycling to be effective and sustainable, there is a need for diversity and a wide range of organic input sources to meet the many soil macro- and micro-nutrients regularly required by crops (Falconnier et al., 2023). This implies the need to build farmer capacity and promote diverse agroecological practices to holistically meet these needs, thereby improving and sustaining crop productivity.
4.3 Agroecological transitions require addressing existing contextual limitations to soil, water and pest management
Constraints to agroecological transition are diverse and vary across contexts, underscoring the need to document and address constraints before or during the implementation of agroecological practices. Farmers identified numerous challenges that currently limit the successful implementation of agroecological soil, water, and integrated pest management practices, drawing attention to the complex and multifaceted nature of the transition required for such farming systems (Mekuria et al., 2022). One of the major challenges identified was the recurrent drought and water scarcity, which constrained practices more than two-thirds of all inventoried practices in both Kiambu and Makueni. This finding underscores the vulnerability of agricultural systems to climate change and highlights the need to design resilient and adaptive water conservation innovations (Lobell et al., 2011; Mpala and Simatele, 2023), as well as the general need to understand contextual constraints when designing interventions (Abu-Elsamen et al., 2019; Andersson and D’Souza, 2014).
Other examples include the importance of using appropriate mulching materials in the right proportions, which not only reduce soil evapotranspiration and control weeds that compete with crops for water, but also decrease soil compaction through increased aeration. This increases the retention of green water in the macro-aggregates, making it available for crop growth over a longer period of time (Chukalla et al., 2015). Another example is the use of shade netting structures to control water evaporation from water storage structures such as earth dams, trenches, water pans and water retention ditches (Craig et al., 2005; Muriuki et al., 2014). In this way, the harvested water can last longer and can even be used for irrigation to bridge the gap between one rainy season and the next.
In addition, the labor-intensive nature of many practices poses a significant barrier to adoption and scalability, as reported by farmers in both ALLs, highlighting the importance of considering labor constraints in the design and implementation of agroecological practices. Examples include designing and experimenting with different designs and variations of practices, such as different sizes of zai pits, which are labor intensive (Crossland et al., 2021b). Furthermore, some practices were perceived to be costly and unaffordable for resource-constrained households, which discourages farmers from adopting such practices (Bizoza and Graaff, 2012; Gillian et al., 2016). We found that the two most significant costs incurred were the initial labor costs of implementing practices such as terraces and water harvesting, and the cost of purchasing raw materials and equipment, in line with Mouratiadou et al. (2024). Economic barriers to the adoption of agroecological practices have been widely reported, especially for resource-constrained households (Yagi and Garrod, 2018). Some approaches to overcome financial barriers include the use of innovations that promote efficient use of locally available materials (Piñeiro et al., 2020). In addition, farmers have identified cost-effective and affordable practices such as mulching, suggesting potential opportunities to promote accessible and sustainable solutions that align with farmers’ financial capabilities (Carolan, 2018).
The constraints of scarcity of raw materials and inputs identified by farmers point to the need to address the systemic drivers and promote circular economy that reduces the inflow of inputs while ensuring increased recycling and reuse of locally generated raw materials, wastes and residues for practices such as mulching, composting, farmyard manure and gray water (Velasco-Muñoz et al., 2021). This includes exploring innovations such as the use of biochar to improve soil fertility, structure and aeration, to increase soil water-holding capacity, and control pest and diseases (Alkharabsheh et al., 2021; Safaei Khorram et al., 2016). Pest infestation was also mentioned to affect multiple practices such as mulching, agroforestry and compost, further highlighting the need for a systems approach that integrates different pest management strategies within existing practices, such as the use of clean raw materials, coupled with biological, cultural and mechanical practices (Dara, 2019; Rathee et al., 2018). The widespread challenge of limited knowledge on the benefits and scientific mechanisms and functions of different agroecological practices underscores the need for co-design processes that address knowledge gaps through capacity building and the establishment of on-farm demonstrations for co-learning and showcasing of agroecological best practices (Adamsone-Fiskovica and Grivins, 2022). Overall, addressing the above challenges requires a multifaceted and holistic approach that integrates integration of local knowledge with technical knowledge.
4.4 Supporting evidence-based stakeholder engagement and co-design: employing a methodical approach for selecting and testing agroecological innovations
As mentioned above, the rapid innovation assessment was conducted in the context of a broader co-design cycle, the main objective of which was to test innovative agroecological practices through trials on farmers’ fields in both ALLs (Fuchs et al., 2023b). The actual co-design design workshops were highly methodical and followed a clear sequence, and included different food system actors, including purposively selected male and female farmers from 15 farmer groups per ALL.
As described, the co-design workshops themselves involved seven steps (Figure 2). The results of the innovation assessment were presented to participants in step 1. To render insights into options, contexts, and preferences more accessible and intelligible for participants, we prepared posters for each of the top three to five practices per focus areas to visually support the data sharing. The posters provided simple overviews of the main results drawn from the innovation assessment. This helped participants in the identification, selection, and contextual adaptation of appropriate and suitable innovative practices. Addressing farmers’ needs, priorities and preferences has been reported to be a major driver of adoption of agri-food innovations (Antwi-Agyei et al., 2021; Fuchs et al., 2023b; Roussy et al., 2019).
These steps included identifying selection criteria for the innovations and the host crops. Other steps involved co-designing participatory trial protocols to ensure that participating farmers document the performance of their trials and play the role of actual farmer-scientists. Participants then discussed selection criteria for participating farmers that would ensure proper implementation, and documentation, while recognizing their responsibilities to their community to ensure that the experience and knowledge gained is shared with others. The final step involved the establishment of the trials, where the Agroecology Initiative technical team conducted integrated technical trainings and demonstrations for all three identified practices at the respective ALL host centers with all selected trial participants in each ALL. The training focused on sharing technical skills, with an additional focus on trial establishment and monitoring. In order to strengthen capacity as broadly as possible, all 30 trial participants per ALL were trained in all three practices in integrated three-day workshops facilitated by the Agroecology Initiative team and technical experts. This was followed by trial implementation on farms, accompanied by regular monitoring, co-learning and adaptation of the agroecological practices to suit the local context. The flexibility granted to farmers to implement, observe, experiment with and adapt agroecological practices to suit their context has been reported as a key driver for continued adoption of innovations (Falconnier et al., 2017).
The process of selecting, prioritizing and co-designing agroecological innovations for implementation involved a systematic approach aimed at ensuring diverse stakeholder engagement and representation (Fraser et al., 2006; Pagella and Sinclair, 2014; Triomphe et al., 2022). Through purposive selection (Tongco, 2007), participants were chosen to ensure broad representation, promote inclusive decision-making, and enhance the relevance of the selected innovations to local contexts (Jones-Garcia and Krishna, 2021). Each workshop served as a platform for stakeholders to deliberate on the most suitable and desired options to be tested through monitored trials, thereby facilitating knowledge exchange and consensus building among participants. The co-design workshops encompassed seven sequential steps designed to systematically guide stakeholders through the process of innovation selection and co-design process. This provided the basis for subsequent discussions on preferred innovative practices, informed by farmers’ expressed preferences and priorities (Gliessman, 2018). Subsequent steps focused on the selection of agroecological innovations for trial testing, with participants collaboratively narrowing down options based on the priority farmer preference list generated in earlier stages of the process. The culmination of this deliberative process resulted in the unanimous selection of practices to be implemented, tailored to the specific needs and contexts of each ALL.
The joint definition of criteria for selecting test crops to accompany the chosen innovations illustrates the importance of co-design (Dawson et al., 2008). Common criteria that motivated the selection of crops in both ALLs included adaptability to local conditions, high nutritional content and high economic value and readily available markets. Similar criteria have been reported elsewhere as motivating farmers to adopt innovations (Ahmed and Tetteh Anang, 2019; Singha et al., 2012). In Kiambu, these included seed availability and household food security, while in Makueni, the focus was on crop disease resistance and local farmers’ familiarity. This approach highlights the need to understand and consider farmers’ motivations, both intrinsic and extrinsic, when designing agrifood innovations, as this further increases the likelihood that they will adopt and sustain such innovations (Greiner et al., 2009; Jambo et al., 2019). The decision to intercrop maize and beans in Makueni reflects a pragmatic approach to maximize space use and leverage farmers’ existing knowledge and practices (Altieri, 1999). Such tailored strategies for crop selection demonstrate a nuanced understanding of local agricultural contexts and participants’ priorities.
In discussing the experimental design, participants emphasized the importance of positioning control plots adjacent to innovative practice plots to minimize potential variation in soil fertility and environmental factors. This approach ensures robust comparisons between treatment and control plots, thereby increasing the reliability and validity of experimental results (Pretty et al., 2003). The co-design of participatory monitoring protocols allowed combining variables that are of interest to farmers and those required by the research more broadly (Parwada et al., 2022). The monitoring sheets containing the crop performance parameters to be monitored (including when, how and why to monitor) are used for simultaneous trial monitoring by farmers, our research team, and the ALL-host centers. Participatory monitoring aims to build their capacity to sustain agroecological best practices in the future and to take timely and effective remedial actions to improve overall performance through the practical skills they gain from the process (Junge et al., 2009; Rossi et al., 2023). This supports their transformation into farmer-scientists as they can experiment with different management practices while monitoring crop progress and performance based on the pre-defined parameters (Marchant et al., 2019; Oliver et al., 2010) to identify the contextual factors that enhance or limit crop performance. Collaborative monitoring also ensures that challenges are identified early and addressed quickly (González-Orozco et al., 2023). This is an important step towards agroecological transition and promotes a sense of ownership of the innovations by implementers, which supports the adoption rate, success, and sustainability of such agroecological practices (Li et al., 2019; Sapbamrer and Thammachai, 2021). It also ensures that farmers’ local knowledge is fully utilized to adapt practices to address local challenges (Puppo et al., 2023). Finally, the joint definition of selection criteria for trial participants, and their participatory selection, is likely to strengthen participants’ sense of responsibility and duty to their fellow farmers, and also likely to strengthen demand from other farmers for knowledge exchange (Fuchs et al., 2019b). Farmer-to-farmer extension and other co-learning opportunities have been heralded as an effective approach for scaling up agroecological practices (Gliessman, 2018). Moreover, collective learning and shared knowledge systems, coupled with the shared commitment, are not only a catalyst for the successful adoption of innovations (Waarts et al., 2002), but also for diffusion and scaling of innovations (Chen and Li, 2022).
By integrating farmer knowledge and preferences into decision-making processes, the co-design approach held a promise for promoting sustainable agricultural transitions rooted in local expertise and community empowerment. This transdisciplinary approach aimed to integrate farmer preferences and knowledge with scientific knowledge to develop and test agroecological practices that are locally understood, relevant, appropriate and inclusive (HLPE, 2019; Sinclair et al., 2019). This participatory approach is consistent with the principles of co-design, which emphasize the involvement of diverse stakeholders in decision-making processes to ensure the relevance and feasibility of interventions and helped to create a sense of ownership of the co-design process and outcomes by all stakeholders (Dumont et al., 2017; Fuchs et al., 2019b).
5 Conclusion
The Agroecology Initiative team facilitated a comprehensive co-design process to support on-farm experimentation with and generation of evidence on the performance of contextually suitable innovative agroecological practices in the Kenyan ALLs in Kiambu and Makueni counties. The team conducted a rapid innovation assessment to gain insights into existing innovation options, contexts and preferences. This assessment informed the team’s scientific input to the actual co-design workshops where participants co-created innovative practices, experimental designs, and selection criteria for participating farmers. The collaborative assessment identified and evaluated the existing agroecological practices in three priority areas, namely soil management, water management, and integrated pest management. The assessment mapped 31 agroecological practices that were identified on respondents’ fields in both ALLs, with 29 practices found in Kiambu and 18 practices being inventoried in and Makueni. The assessment of the inventoried options highlighted the heterogeneity of the socio-economic and biophysical contexts between the Kiambu and Makueni ALLs, which influenced the performance of each practice. Respondents expressed a preference for a total of 31 practices, of which 77% were associated with one of the three focus areas (soil management, water management, or IPM), while 33% were assigned multiple functions in at least two of the three areas simultaneously.
Overall, the assessment provided insights into existing options, their contextual evaluation, and preferences for both function-specific and multifunctional practices. The assessment also highlighted gaps and potential opportunities for the improvement and contextual adaptation of specific innovation practices to enhance their performance. In addition, the process itself allowed participants to introduce and discuss potential additional practices that had not yet been popularized in the ALLs that had been tested and implemented elsewhere in a similar context. The methodical and iterative co-design cycle allowed for the mobilization of different types and sources of knowledge and fostered the co-creation of criteria, priorities, and the joint selection of options, experimental designs, monitoring protocols and participants. This collaborative and structured approach responds to the importance of understanding and considering farmers’ options, context and preferences in co-designing locally relevant and inclusive agroecological practices to promote greater adoption, successful implementation and long-term sustainability of agroecological practices, thereby promoting sustainable agrifood systems.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found at: https://dataverse.harvard.edu/dataset.xhtml?persistentId=doi:10.7910/DVN/8V4G7M.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by CIFOR-ICRAF research ethics committee. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
AK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PB: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. BA: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. HK: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. MS: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. PG: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. MM: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. LO: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. WN: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. NS: Conceptualization, Project administration, Validation, Writing – review & editing. EK: Conceptualization, Project administration, Validation, Writing – review & editing. LF: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported and funded by the Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR) through the Agroecology Initiative: Transforming Food, Land, and Water Systems Across the Global South project. Grant Number: CGIAR Initiative on Agroecology (INIT-31).
Acknowledgments
This study was conducted jointly with partner and host organizations and farmers. We are grateful for the support, team effort, and commitment of all persons involved. We thank our partners from the Drylands Natural Resources Centre (DNRC), a locally registered non-government organization (NGO) whose primary goal is to promote sustainable development of resources of the drylands regions of Kenya, and from Community Sustainable Agriculture Healthy Environmental Program (CSHEP), a registered community-based organization (CBO) focused on training small-scale farmers on agroecological and organic practices in Ndeiya, Kiambu County; and the Participatory Ecological Land Use Management (PELUM Kenya) team, and specifically Patrick Ngunjiri Kihoro, Zonal coordinator for Lower Eastern and Coast zone, for taking part in the data collection exercise and codesign workshops. Lastly, we thank Victor Mutugi (CIFOR-ICRAF) for supporting with data analysis for some results.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abate, T., Van Huis, A., and Ampofo, J. K. O. (2000). Pest management strategies in traditional agriculture: an African perspective. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 45, 631–659. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ento.45.1.631
Abu-Elsamen, A. A., Akroush, M. N., Asfour, N. A., and Al Jabali, H. (2019). Understanding contextual factors affecting the adoption of energy-efficient household products in Jordan. Sustain. Account. Manag. Policy J. 10, 314–332. doi: 10.1108/SAMPJ-05-2018-0144
Adamsone-Fiskovica, A., and Grivins, M. (2022). Knowledge production and communication in on-farm demonstrations: putting farmer participatory research and extension into practice. J. Agric. Educ. Ext. 28, 479–502. doi: 10.1080/1389224X.2021.1953551
Adugna, G. (2016). A review on impact of compost on soil properties, water use and crop productivity. Agric. Sci. Res. J. 4, 93–104. doi: 10.14662/ARJASR2016.010
Ahmed, H., and Tetteh Anang, B. (2019). Impact of improved variety adoption on farm income in tolon district of Ghana. Agric. Soc. Econ. J. 19, 105–115. doi: 10.21776/ub.agrise.2019.019.2.5
Alkharabsheh, H. M., Seleiman, M. F., Battaglia, M. L., Shami, A., Jalal, R. S., Alhammad, B. A., et al. (2021). Biochar and its broad impacts in soil quality and fertility, nutrient leaching and crop productivity: a review. Agronomy 11:993. doi: 10.3390/agronomy11050993
Altieri, M. A. (1999). The ecological role of biodiversity in agroecosystems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 74, 19–31. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-50019-9.50005-4
Altieri, M. A., Nicholls, C. I., Henao, A., and Lana, M. A. (2015). Agroecology and the design of climate change-resilient farming systems. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 35, 869–890. doi: 10.1007/s13593-015-0285-2
Alyokhin, A., Nault, B., and Brown, B. (2020). Soil conservation practices for insect pest management in highly disturbed agroecosystems – a review. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 168, 7–27. doi: 10.1111/eea.12863
Andersson, J. A., and D’Souza, S. (2014). From adoption claims to understanding farmers and contexts: a literature review of conservation agriculture (CA) adoption among smallholder farmers in southern Africa. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 187, 116–132. doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2013.08.008
Antwi-Agyei, P., Abalo, E. M., Dougill, A. J., and Baffour-Ata, F. (2021). Motivations, enablers and barriers to the adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices by smallholder farmers: evidence from the transitional and savannah agroecological zones of Ghana. Region. Sustain. 2, 375–386. doi: 10.1016/j.regsus.2022.01.005
ATLAS.ti Scientific Software Development GmbH (2023). ATLAS.ti qualitative data analysis software (version 23.2.1).
Atube, F., Malinga, G. M., Nyeko, M., Okello, D. M., Alarakol, S. P., and Okello-Uma, I. (2021). Determinants of smallholder farmers’ adaptation strategies to the effects of climate change: evidence from northern Uganda. Agric. Food Secur. 10, 1–14. doi: 10.1186/s40066-020-00279-1
Awiti, A. O. (2022). Climate change and gender in Africa: a review of impact and gender-responsive solutions. Front. Clim. 4:895950. doi: 10.3389/fclim.2022.895950
Ayuke, F. O., Brussaard, L., Vanlauwe, B., Six, J., Lelei, D. K., Kibunja, C. N., et al. (2011). Soil fertility management: impacts on soil macrofauna, soil aggregation and soil organic matter allocation. Appl. Soil Ecol. 48, 53–62. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2011.02.001
Bargués-Tobella, A., Winowiecki, L. A., Sheil, D., and Vågen, T. G. (2024). Determinants of soil field-saturated hydraulic conductivity across sub-Saharan Africa: texture and beyond. Water Resour. Res. 60:5510. doi: 10.1029/2023WR035510
Barrios, E., Delve, R. J., Bekunda, M., Mowo, J., Agunda, J., Ramisch, J., et al. (2006). Indicators of soil quality: a south-south development of a methodological guide for linking local and technical knowledge. Geoderma 135, 248–259. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2005.12.007
Barry, F., Sawadogo, M., Bologo, M., Ouédraogo, I. W. K., and Dogot, T. (2021). Key barriers to the adoption of biomass gasification in Burkina Faso. Sustainability 13, 1–14. doi: 10.3390/su13137324
Barzman, M., Bàrberi, P., Birch, A. N. E., Boonekamp, P., Dachbrodt-Saaydeh, S., Graf, B., et al. (2015). Eight principles of integrated pest management. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 35, 1199–1215. doi: 10.1007/s13593-015-0327-9
Baum, F., MacDougall, C., and Smith, D. (2006). Participatory action research. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 60, 854–857. doi: 10.1136/jech.2004.028662
Bellamy, A. S., and Ioris, A. A. R. (2017). Addressing the knowledge gaps in agroecology and identifying guiding principles for transforming conventional agri-food systems. Sustainability 9, 1–17. doi: 10.3390/su9030330
Benin, S., Smale, M., Pender, J., Gebremedhin, B., and Ehui, S. (2004). The economic determinants of cereal crop diversity on farms in the Ethiopian highlands. Agric. Econ. 31, 197–208. doi: 10.1016/j.agecon.2004.09.007
Berthet, E. T., Hickey, G. M., and Klerkx, L. (2018). Opening design and innovation processes in agriculture: insights from design and management sciences and future directions. Agric. Syst. 165, 111–115. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2018.06.004
Bizoza, A. R., and Graaff, J. D. E. (2012). Financial cost–benefit analysis of bench terraces in Rwanda. Land Degrad. Dev. 23, 103–115. doi: 10.1002/ldr.1051
Blanco-Canqui, H., and Lal, R. (2009). Crop residue removal impacts on soil productivity and environmental quality. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 28, 139–163. doi: 10.1080/07352680902776507
Bolo, P., Kihara, J., Mucheru-Muna, M., Njeru, E. M., Kinyua, M., and Sommer, R. (2021). Application of residue, inorganic fertilizer and lime affect phosphorus solubilizing microorganisms and microbial biomass under different tillage and cropping systems in a Ferralsol. Geoderma 390:114962. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2021.114962
Bolo, P., Mucheru-Muna, M. W., Mwirichia, R. K., Kinyua, M., Ayaga, G., and Kihara, J. (2023). Influence of farmyard manure application on potential zinc solubilizing microbial species abundance in a Ferralsol of Western Kenya. Agriculture (Switzerland) 13:2217. doi: 10.3390/agriculture13122217
Bolo, P., Mucheru-Muna, M., Mwirichia, R. K., Kinyua, M., Ayaga, G., and Kihara, J. (2024). Soil bacterial community is influenced by long-term integrated soil fertility management practices in a Ferralsol in Western Kenya. J. Sustain. Agric. Environ. 3:e12090. doi: 10.1002/sae2.12090
Busse, M., Zscheischler, J., Zoll, F., Rogga, S., and Siebert, R. (2023). Co-design approaches in land use related sustainability science – a systematic review. Land Use Policy 129:6623. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2023.106623
Calvet-Mir, L., Benyei, P., Aceituno-Mata, L., Pardo-de-Santayana, M., López-García, D., Carrascosa-García, M., et al. (2018). The contribution of traditional agroecological knowledge as a digital commons to agroecological transitions: the case of the CONECT-e platform. Sustainability 10:3214. doi: 10.3390/su10093214
Carolan, M. (2018). Lands changing hands: experiences of succession and farm (knowledge) acquisition among first-generation, multigenerational, and aspiring farmers. Land Use Policy 79, 179–189. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2018.08.011
Castañeda-Navarrete, J. (2021). Homegarden diversity and food security in southern Mexico. Food Secur. 13, 669–683. doi: 10.1007/s12571-021-01148-w
Chakona, G., and Shackleton, C. M. (2018). Household food insecurity along an agro-ecological gradient influences Children’s nutritional status in South Africa. Front. Nutr. 4:72. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2017.00072
Chave, M., Angeon, V., Paut, R., Collombet, R., and Tchamitchian, M. (2019). Codesigning biodiversity-based agrosystems promotes alternatives to mycorrhizal inoculants. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 39:48. doi: 10.1007/s13593-019-0594-y
Chen, X., and Li, T. (2022). Diffusion of agricultural technology innovation: research progress of innovation diffusion in Chinese agricultural science and technology parks. Sustainability 14:15008. doi: 10.3390/su142215008
Chikowo, R., Zingore, S., Snapp, S., and Johnston, A. (2014). Farm typologies, soil fertility variability and nutrient management in smallholder farming in sub-Saharan Africa. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 100, 1–18. doi: 10.1007/s10705-014-9632-y
Chukalla, A. D., Krol, M. S., and Hoekstra, A. Y. (2015). Green and blue water footprint reduction in irrigated agriculture: effect of irrigation techniques, irrigation strategies and mulching. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 19, 4877–4891. doi: 10.5194/hess-19-4877-2015
Coe, R., Sinclair, F., and Barrios, E. (2014). Scaling up agroforestry requires research “in” rather than “for” development. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 6, 73–77. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2013.10.013
Cooper, T. L., Kirino, Y., Alonso, S., Lindahl, J., and Grace, D. (2016). Towards better-informed consent: research with livestock-keepers and informal traders in East Africa. Prev. Vet. Med. 128, 135–141. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2016.04.008
Cornish, F., Breton, N., Moreno-Tabarez, U., Delgado, J., Rua, M., De-Graft Aikins, A., et al. (2023). Participatory action research. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 3:34. doi: 10.1038/s43586-023-00214-1
Craig, I., Green, A., Scobie, M., and Schmidt, E. (2005). Controlling evaporation loss from water storages rural water use efficiency Initiative Queensland Department of Natural Resources and Mines. 1000580. Available at: http://www.ncea.org.au/Evaporation%20Resources/index_files/Page1668.htm (Accessed on April 04, 2024).
Crossland, M., Valencia, A. M. P., Pagella, T., Magaju, C., Kiura, E., Winowiecki, L., et al. (2021a). Onto the farm, into the home: how intrahousehold gender dynamics shape land restoration in eastern Kenya. Ecol. Restor. 39, 90–107. doi: 10.3368/er.39.1-2.90
Crossland, M., Valencia, A. M. P., Pagella, T., Mausch, K., Harris, D., Dilley, L., et al. (2021b). Women’s changing opportunities and aspirations amid male outmigration: insights from Makueni County, Kenya. Eur. J. Dev. Res. 33, 910–932. doi: 10.1057/s41287-021-00362-8
Dara, S. K. (2019). The new integrated Pest management paradigm for the modern age. J. Integrat. Pest Manag. 10:10. doi: 10.1093/jipm/pmz010
Dawson, J. C., Murphy, K. M., and Jones, S. S. (2008). Decentralized selection and participatory approaches in plant breeding for low-input systems. Euphytica 160, 143–154. doi: 10.1007/s10681-007-9533-0
Debray, V., Wezel, A., Lambert-Derkimba, A., Roesch, K., Lieblein, G., and Francis, C. A. (2019). Agroecological practices for climate change adaptation in semiarid and subhumid Africa. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 43, 429–456. doi: 10.1080/21683565.2018.1509166
Deepika, P., and MubarakAli, D. (2020). Production and assessment of microalgal liquid fertilizer for the enhanced growth of four crop plants. Biocat. Agric. Biotechnol. 28:101701. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101701
Deguine, J. P., Aubertot, J. N., Flor, R. J., Lescourret, F., Wyckhuys, K. A. G., and Ratnadass, A. (2021). Integrated pest management: good intentions, hard realities. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 41:38. doi: 10.1007/s13593-021-00689-w
Demeke, A. B. (2003). Factors influencing the adoption of soil conservation practices in Northweastern Ethiopia. Agric. Econ. 37:82.
Dissanayaka, D. M. N. S., Dissanayake, D. K. R. P. L., Udumann, S. S., Nuwarapaksha, T. D., and Atapattu, A. J. (2023). Agroforestry—a key tool in the climate-smart agriculture context: a review on coconut cultivation in Sri Lanka. Front. Agron. 5:1162750. doi: 10.3389/fagro.2023.1162750
Duguma, L. A., and Hager, H. (2011). Farmers’ assessment of the social and ecological values of land uses in Central Highland Ethiopia. Environ. Manag. 47, 969–982. doi: 10.1007/s00267-011-9657-9
Dumont, E. S., Bonhomme, S., Pagella, T. F., and Sinclair, F. L. (2017). Structured stakeholder engagement leads to development of more diverse and inclusive agroforestry options. Exp. Agric. 55, 1–23. doi: 10.1017/S0014479716000788
Dumont, A. M., Wartenberg, A. C., and Baret, P. V. (2021). Bridging the gap between the agroecological ideal and its implementation into practice. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 41:32. doi: 10.1007/s13593-021-00666-3
Duru, M., Therond, O., and Fares, M. (2015). Designing agroecological transitions; A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 35, 1237–1257. doi: 10.1007/s13593-015-0318-x
Eilola, S., Käyhkö, N., Fagerholm, N., and Kombo, Y. H. (2014). Linking farmers’ knowledge, farming strategies, and consequent cultivation patterns into the identification of healthy agroecosystem characteristics at local scales. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 38, 1047–1077. doi: 10.1080/21683565.2014.923800
Errico, S. (2021). Women’s right to land between collective and individual dimensions. Some insights from sub-Saharan Africa. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 5, 1–15. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2021.690321
Esquivel, K. E., Carlisle, L., Ke, A., Olimpi, E. M., Baur, P., Ory, J., et al. (2021). The “sweet spot” in the middle: why do mid-scale farms adopt diversification practices at higher rates? Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 5, 1–16. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2021.734088
Falconnier, G. N., Cardinael, R., Corbeels, M., Baudron, F., Chivenge, P., Couëdel, A., et al. (2023). The input reduction principle of agroecology is wrong when it comes to mineral fertilizer use in sub-Saharan Africa. Outl. Agric. 52, 311–326. doi: 10.1177/00307270231199795
Falconnier, G. N., Descheemaeker, K., Van Mourik, T. A., Adam, M., Sogoba, B., and Giller, K. E. (2017). Co-learning cycles to support the design of innovative farm systems in southern Mali. Eur. J. Agron. 89, 61–74. doi: 10.1016/j.eja.2017.06.008
Farnworth, C. R., Bharati, P., and Galiè, A. (2023). Empowering women, challenging caste? The experience of a dairy cooperative in India. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 7:1114405. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2023.1114405
Farrow, A., Ronner, E., Van Den Brand, G. J., Boahen, S. K., Leonardo, W., Wolde-Meskel, E., et al. (2016). From best fit technologies to best fit scaling: incorporating and evaluating factors affecting the adoption of grain legumes in sub-Saharan Africa. Exp. Agric. 55, 1–26. doi: 10.1017/S0014479716000764
Fernández González, C., Ollivier, G., and Bellon, S. (2021). Transdisciplinarity in agroecology: practices and perspectives in Europe. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 45, 523–550. doi: 10.1080/21683565.2020.1842285
Fraser, E. D. G., Dougill, A. J., Mabee, W. E., Reed, M., and McAlpine, P. (2006). Bottom up and top down: analysis of participatory processes for sustainability indicator identification as a pathway to community empowerment and sustainable environmental management. J. Environ. Manag. 78, 114–127. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2005.04.009
Fuchs, L.E., Adoyo, B., Orero, L., Korir, H., Sakha, M., Anyango, E., et al. (2023a). Transition pathways and vision-to-action in the Agroecological living landscapes (ALLs) in Kenya. Available at: https://hdl.handle.net/10568/138753 (Accessed on June 17, 2024).
Fuchs, L.E., Korir, H., Adoyo, B., Bolo, P., Kuria, A., Sakha, M., et al. (2023b). Co-designing on-farm innovations in the agroecological living landscapes (ALLs) in Kenya. Available at: https://hdl.handle.net/10568/138714 (Accessed on June 19, 2024).
Fuchs, L. E., Orero, L., Namoi, N., and Neufeldt, H. (2019a). How to effectively enhance sustainable livelihoods in smallholder systems: a comparative study from Western Kenya. Sustain. For. 11:1564. doi: 10.3390/su11061564
Fuchs, L. E., Orero, L., Ngoima, S., Kuyah, S., and Neufeldt, H. (2022). Asset-based adaptation project promotes tree and shrub diversity and above-ground carbon stocks in smallholder agroforestry Systems in Western Kenya. Front. For. Glob. Change 4:773170. doi: 10.3389/ffgc.2021.773170
Fuchs, L. E., Peters, B., and Neufeldt, H. (2019b). Identities, interests, and preferences matter: fostering sustainable community development by building assets and agency in western Kenya. Sustain. Dev. 27, 704–712. doi: 10.1002/sd.1934
Gachuiri, A. N., Carsan, S., Karanja, E., Makui, P., and Kuyah, S. (2017). Diversity and importance of local fodder tree and shrub resources in mixed farming systems of Central Kenya. For. Trees Livelihoods 26, 143–155. doi: 10.1080/14728028.2017.1316216
Gaspard, R., and Authority, R. (2013). Climate change effects on food security in Rwanda: case study of wetland rice production in Bugesera District. Rwanda J. 1, 35–51. doi: 10.4314/rj.v1i1.3E
Gicheru, P., Gachene, C., Mbuvi, J., and Mare, E. (2004). Effects of soil management practices and tillage systems on surface soil water conservation and crust formation on a sandy loam in semi-arid Kenya. Soil Tillage Res. 75, 173–184. doi: 10.1016/S0167-1987(03)00161-2
Gillian, K., Hugh, B., and Ross, C. (2016). Why is adoption of agroforestry stymied in Zambia? Perspectives from the ground-up. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 11, 4704–4717. doi: 10.5897/AJAR2016.10952
Gliessman, S. (2018). Scaling-out and scaling-up agroecology. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 42, 841–842. doi: 10.1080/21683565.2018.1481249
González-Orozco, C. E., Diaz-Giraldo, R. A., and Rodriguez-Castañeda, C. (2023). An early warning for better planning of agricultural expansion and biodiversity conservation in the Orinoco high plains of Colombia. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 7:1192054. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2023.1192054
Goodyear-Smith, F., Jackson, C., and Greenhalgh, T. (2015). Co-design and implementation research: challenges and solutions for ethics committees. BMC Med. Ethics 16:78. doi: 10.1186/s12910-015-0072-2
Greiner, R., Patterson, L., and Miller, O. (2009). Motivations, risk perceptions and adoption of conservation practices by farmers. Agric. Syst. 99, 86–104. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2008.10.003
Greiner, C., and Sakdapolrak, P. (2013). Rural-urban migration, agrarian change, and the environment in Kenya: a critical review of the literature. Popul. Environ. 34, 524–553. doi: 10.1007/s11111-012-0178-0
Hathaway, M. D. (2016). Agroecology and permaculture: addressing key ecological problems by rethinking and redesigning agricultural systems. J. Environ. Stud. Sci. 6, 239–250. doi: 10.1007/s13412-015-0254-8
He, Z., and Schonlau, M. (2020). Automatic coding of open-ended questions into multiple classes: whether and how to use double coded data. Survey Res. Methods 14, 267–287. doi: 10.18148/srm/2020.v14i3.7639
Hermans, T. D. G., Dougill, A. J., Whitfield, S., Peacock, C. L., Eze, S., and Thierfelder, C. (2021). Combining local knowledge and soil science for integrated soil health assessments in conservation agriculture systems. J. Environ. Manag. 286:112192. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112192
HLPE (2019). Agroecological and other innovative approaches for sustainable agriculture and food systems that enhance food security and nutrition. A Report by the High Level Panel of Experts on Food Security and Nutrition of the Committee on World Food Security, July, 162. Available at: https://agritrop.cirad.fr/604473/1/604473.pdf (Accessed on May 10, 2024).
Holden, S. T., and Tilahun, M. (2020). Farm size and gender distribution of land: evidence from Ethiopian land registry data. World Dev. 130:4926. doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2020.104926
Jambo, I. J., Groot, J. C. J., Descheemaeker, K., Bekunda, M., and Tittonell, P. (2019). Motivations for the use of sustainable intensification practices among smallholder farmers in Tanzania and Malawi. NJAS - Wageningen J. Life Sci. 89:306. doi: 10.1016/j.njas.2019.100306
Jones, S. K., Bergamini, N., Beggi, F., Lesueur, D., Vinceti, B., Bailey, A., et al. (2022). Research strategies to catalyze agroecological transitions in low- and middle-income countries. Sustain. Sci. 17, 2557–2577. doi: 10.1007/s11625-022-01163-6
Jones-Garcia, E., and Krishna, V. V. (2021). Farmer adoption of sustainable intensification technologies in the maize systems of the global south. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 41:8. doi: 10.1007/s13593-020-00658-9
Jordan, S. R., and Gray, P. W. (2014). Reporting ethics committee approval in public administration research. Sci. Eng. Ethics 20, 77–97. doi: 10.1007/s11948-013-9436-5
Junge, B., Deji, O., Abaidoo, R., Chikoye, D., and Stahr, K. (2009). Farmers’ adoption of soil conservation technologies: a case study from Osun state, Nigeria. J. Agric. Educ. Ext. 15, 257–274. doi: 10.1080/13892240903069769
Kansanga, M. M., Kangmennaang, J., Bezner Kerr, R., Lupafya, E., Dakishoni, L., and Luginaah, I. (2021). Agroecology and household production diversity and dietary diversity: evidence from a five-year agroecological intervention in rural Malawi. Soc. Sci. Med. 288:3550. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2020.113550
Kihoro, E. M., Schoneveld, G. C., and Crane, T. A. (2021). Pathways toward inclusive low-emission dairy development in Tanzania: producer heterogeneity and implications for intervention design. Agric. Syst. 190:103073. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2021.103073
Klerkx, L., Van Mierlo, B., and Leeuwis, C. (2012). “Farming systems research into the 21st century: the new dynamic” in Evolution of systems approaches to agricultural innovation: Concepts, analysis and interventions. eds. I. Darnhofer, D. Gibbon, and B. Dedieu (Dordrecht: Springer), 457–483.
Knapp, L., Wuepper, D., and Finger, R. (2021). Preferences, personality, aspirations, and farmer behavior. Agric. Econ. 52, 901–913. doi: 10.1111/agec.12669
Kuria, A., Barrios, E., Pagella, T., Muthuri, C. W., Mukuralinda, A., and Sinclair, F. L. (2019). Farmers’ knowledge of soil quality indicators along a land degradation gradient in Rwanda. Geoderma Reg. 16:e00199. doi: 10.1016/j.geodrs.2018.e00199
Kuria, A., Bolo, P., Ntinyari, W., Orero, L., Adoyo, B., Korir, H., et al. (2023). Assessment of existing and preferred agroecological soil, water, and integrated pest management practices in the Makueni and Kiambu Agroecological living landscapes, Kenya. November. Available at: https://hdl.handle.net/10568/137726 (Accessed on March 28, 2024).
Lasco, R. D., Delfino, R. J. P., Catacutan, D. C., Simelton, E. S., and Wilson, D. M. (2014). Climate risk adaptation by smallholder farmers: the roles of trees and agroforestry. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 6, 83–88. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2013.11.013
Li, Q., Zeng, F., Mei, H., Li, T., and Li, D. (2019). Roles of motivation, opportunity, ability, and trust in the willingness of farmers to adopt green fertilization techniques. Sustainability 11:6902. doi: 10.3390/su11246902
Liani, M. L., Cole, S. M., Mwakanyamale, D. F., Baumung, L., Saleh, N., Webber, A., et al. (2023). Uneven ground? Intersectional gender inequalities in the commercialized cassava seed system in Tanzania. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 7:1155769. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2023.1155769
Liu, Y., Miao, H. T., Chang, X., and Wu, G. L. (2019). Higher species diversity improves soil water infiltration capacity by increasing soil organic matter content in semiarid grasslands. Land Degrad. Dev. 30, 1599–1606. doi: 10.1002/ldr.3349
Lobell, D. B., Schlenker, W., and Costa-Roberts, J. (2011). Climate trends and global crop production since 1980. Science 333, 616–620. doi: 10.1126/science.1204531
Loevinsohn, M., and Sumberg, J. (2012). Under what circumstances and conditions does adoption of technology result in increased agricultural productivity? Available at: http://eppi.ioe.ac.uk/ (Accessed on July 31, 2024).
Lopez, D. E., Frelat, R., and Badstue, L. B. (2022). Towards gender-inclusive innovation: assessing local conditions for agricultural targeting. PLoS One 17:e0263771. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263771
Madzorera, I., Bliznashka, L., Blakstad, M. M., Bellows, A. L., Canavan, C. R., Mosha, D., et al. (2023). Women’s input and decision-making in agriculture are associated with diet quality in rural Tanzania. Front. Public Health 11:1215462. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1215462
Magaju, C., Winowiecki, L. A., Crossland, M., Frija, A., Ouerghemmi, H., Hagazi, N., et al. (2020). Assessing context-specific factors to increase tree survival for scaling ecosystem restoration efforts in east africa. Land 9, 1–20. doi: 10.3390/land9120494
Magrini, M., Martin, G., and Magne, M. (2019). “Agroecological transitions: from theory to practice in local participatory design” in Agroecological transitions: From theory to practice in local participatory design. eds. J. E. Bergez, A. Elise, and T. Olivier (Springer Nature).
Maja, M., Ranko, Č., Ljiljana, N., Dejana, D., Srdan, Š., and Bavec, M. (2017). Ground cover management and farmyard manure effects on soil nitrogen dynamics, productivity and economics of organically grown lettuce (Lactuca sativa L. subsp. secalina). J. Integr. Agric. 16, 947–958. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(16)61565-4
Majumdar, K., Sanyal, S. K., Dutta, S. K., Satyanarayana, T., and Singh, V. K. (2016). “Nutrient mining: addressing the challenges to soil resources and food security” in Biofortification of food crops. eds. U. Singh, C. S. Praharaj, S. S. Singh, and N. P. Singh (India: Springer), 177–198.
Mango, N., Makate, C., Mapemba, L., and Sopo, M. (2018). The role of crop diversification in improving household food security in Central Malawi. Agric. Food Secur. 7, 1–10. doi: 10.1186/s40066-018-0160-x
Manjunatha, A. V., Anik, A. R., Speelman, S., and Nuppenau, E. A. (2013). Impact of land fragmentation, farm size, land ownership and crop diversity on profit and efficiency of irrigated farms in India. Land Use Policy 31, 397–405. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2012.08.005
Marchant, B., Rudolph, S., Roques, S., Kindred, D., Gillingham, V., Welham, S., et al. (2019). Establishing the precision and robustness of farmers’ crop experiments. Field Crop Res. 230, 31–45. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2018.10.006
Martin-Collado, D., Byrne, T. J., Amer, P. R., Santos, B. F. S., Axford, M., and Pryce, J. E. (2015). Analyzing the heterogeneity of farmers’ preferences for improvements in dairy cow traits using farmer typologies. J. Dairy Sci. 98, 4148–4161. doi: 10.3168/jds.2014-9194
Mauser, W., Klepper, G., Rice, M., Schmalzbauer, B. S., Hackmann, H., Leemans, R., et al. (2013). Transdisciplinary global change research: the co-creation of knowledge for sustainability. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 5, 420–431. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2013.07.001
Mbow, C., van Noordwijk, M., Prabhu, R., and Simons, T. (2014). Knowledge gaps and research needs concerning agroforestry’s contribution to sustainable development goals in Africa. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 6, 162–170. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2013.11.030
McCampbell, M., Schumann, C., and Klerkx, L. (2022). Good intentions in complex realities: challenges for designing responsibly in digital agriculture in low-income countries. Sociol. Rural. 62, 279–304. doi: 10.1111/soru.12359
McGuire, E., Rietveld, A. M., Crump, A., and Leeuwis, C. (2022). Anticipating gender impacts in scaling innovations for agriculture: insights from the literature. World Dev. Persp. 25:386. doi: 10.1016/j.wdp.2021.100386
McIntyre, B., Gold, C., Kashaija, I., Ssali, H., Night, G., and Bwamiki, D. (2001). Effects of legume intercrops on soil-borne pests, biomass, nutrients and soil water in banana. Biol. Fertil. Soils 34, 342–348. doi: 10.1007/s003740100417
Mekuria, W., Dessalegn, M., Amare, D., Belay, B., Getnet, B., Girma, G., et al. (2022). Factors influencing the implementation of agroecological practices: lessons drawn from the Aba-Garima watershed, Ethiopia. Front. Environ. Sci. 10, 1–15. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.965408
Morales, H. (2004). Pest Management in Traditional Tropical Agroecosystems: lessons for Pest prevention research and extension. Integr. Pest Manag. Rev. 7, 145–163. doi: 10.1023/b:ipmr.0000027502.91079.01
Mottet, A., Bicksler, A., Lucantoni, D., De Rosa, F., Scherf, B., Scopel, E., et al. (2020). Assessing transitions to sustainable agricultural and food systems: a tool for Agroecology performance evaluation (TAPE). Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 4:579154. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2020.579154
Mouratiadou, I., Wezel, A., Kamilia, K., Marchetti, A., Paracchini, M. L., and Bàrberi, P. (2024). The socio-economic performance of agroecology. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 44:19. doi: 10.1007/s13593-024-00945-9
Mpala, T. A., and Simatele, M. D. (2023). Climate-smart agricultural practices among rural farmers in Masvingo district of Zimbabwe: perspectives on the mitigation strategies to drought and water scarcity for improved crop production. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 7:1298908. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2023.1298908
Muriuki, J. K., Kuria, A. W., Muthuri, C. W., Mukuralinda, A., Simons, A. J., and Jamnadass, R. H. (2014). Testing biodegradable seedling containers as an alternative for polythene tubes in tropical small-scale tree nurseries. Small-Scale For. 13, 127–142. doi: 10.1007/s11842-013-9245-3
Mutemi, M., Njenga, M., Lamond, G., Kuria, A., Öborn, I., Muriuki, J., et al. (2017). “Using local knowledge to understand challenges and opportunities for enhancing agricultural productivity in Western Kenya” in Sustainable intensification in smallholder agriculture: an integrated systems research approach. eds. I. Öborn, B. Vanlauwe, M. Phillips, R. Thomas, W. Brooijmans, and K. Atta-Krah, (London, UK: Routledge), 177–195.
Muthuri, C. W., Kuyah, S., Njenga, M., Kuria, A., Öborn, I., and van Noordwijk, M. (2023). Agroforestry’s contribution to livelihoods and carbon sequestration in East Africa: a systematic review. Trees For. People 14:432. doi: 10.1016/j.tfp.2023.100432
Ndiso, J. B., Chemining, G. N., Olubayo, F. M., Saha, H. M., and Ndiso, J. B. (2018). Effect of different farmyard manure levels on soil moisture content. J. Adv. Stud. Agric. Biol. Environ. Sci. 2011, 5–21.
Neef, A., and Neubert, D. (2011). Stakeholder participation in agricultural research projects: a conceptual framework for reflection and decision-making. Agric. Hum. Values 28, 179–194. doi: 10.1007/s10460-010-9272-z
Nicholls, C. I., and Altieri, M. A. (2018). Pathways for the amplification of agroecology. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 42, 1170–1193. doi: 10.1080/21683565.2018.1499578
Nyantakyi-Frimpong, H., Kangmennaang, J., Bezner Kerr, R., Luginaah, I., Dakishoni, L., Lupafya, E., et al. (2017). Agroecology and healthy food systems in semi-humid tropical Africa: participatory research with vulnerable farming households in Malawi. Acta Trop. 175, 42–49. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2016.10.022
Nyawira, S., Bolo, P., Ntinyari, W., Orero, L., Onyango, K., Manjella, A., et al. (2023). A desk-top review of the context of agroecological principles of Kiambu and Makueni counties. The CGIAR Initiative Transformational Agroecology across Food, Land, and Water Systems.
Nzeyimana, I., Hartemink, A. E., and de Graaff, J. (2013). Coffee farming and soil management in Rwanda. Outl. Agric. 42, 47–52. doi: 10.5367/oa.2013.0118
Oliver, Y. M., Robertson, M. J., and Wong, M. T. F. (2010). Integrating farmer knowledge, precision agriculture tools, and crop simulation modelling to evaluate management options for poor-performing patches in cropping fields. Eur. J. Agron. 32, 40–50. doi: 10.1016/j.eja.2009.05.002
Ong, C. K., Anyango, S., Muthuri, C. W., and Black, C. R. (2007). Water use and water productivity of agroforestry systems in the semi-arid tropics. Ann. Arid Zone 46, 255–284.
Ortiz-Crespo, B., Steinke, J., Quirós, C. F., van de Gevel, J., Daudi, H., Gaspar Mgimiloko, M., et al. (2021). User-centred design of a digital advisory service: enhancing public agricultural extension for sustainable intensification in Tanzania. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 19, 566–582. doi: 10.1080/14735903.2020.1720474
Osborne, J. W. (2010). Data cleaning basics: best practices in dealing with extreme scores. Newborn Infant Nurs Rev 10, 37–43. doi: 10.1053/j.nainr.2009.12.009
Pagella, T. F., and Sinclair, F. L. (2014). Development and use of a typology of mapping tools to assess their fitness for supporting management of ecosystem service provision. Landsc. Ecol. 29, 383–399. doi: 10.1007/s10980-013-9983-9
Panpatte, D. G., and Jhala, Y. K. (2019). Soil fertility management for sustainable development. Singapore: Springer, 1–291.
Parwada, C., Micheal Okello, D., Mugonola, B., Awio, T., and Jan Stomph, T. (2022). Management practices and rice grain yield of farmers after participation in a joint experimentation. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 6:1009469. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2022.1009469
Paudyal, B. R., Chanana, N., Khatri-Chhetri, A., Sherpa, L., Kadariya, I., and Aggarwal, P. (2019). Gender integration in climate change and agricultural policies: the case of Nepal. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 3:66. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2019.00066
Piñeiro, V., Arias, J., Dürr, J., Elverdin, P., Ibáñez, A. M., Kinengyere, A., et al. (2020). A scoping review on incentives for adoption of sustainable agricultural practices and their outcomes. Nat. Sustain. 3, 809–820. doi: 10.1038/s41893-020-00617-y
Pretty, J. (2009). Can ecological agriculture feed nine billion people? Mon. Rev. 61:46. doi: 10.14452/MR-061-06-2009-10_5
Pretty, J. N., Morison, J. I. L., and Hine, R. E. (2003). Reducing food poverty by increasing agricultural sustainability in developing countries. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 95, 217–234. doi: 10.1016/S0167-8809(02)00087-7
Puppo, M., Gianotti, C., Calvete, A., Leal, A., and Rivas, M. (2023). Landscape, agrobiodiversity, and local knowledge in the protected area “Quebrada de los Cuervos y Sierras del Yerbal,” Uruguay. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 7, 1–24. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2023.1240991
R Core Team (2020). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing,.
Raimi, A., Adeleke, R., and Roopnarain, A. (2017). Soil fertility challenges and Biofertiliser as a viable alternative for increasing smallholder farmer crop productivity in sub-Saharan Africa. Cogent Food Agric. 3:933. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2017.1400933
Rana, A., Tyagi, M., and Sharma, N. (2019). Impact of chemical pesticides vs. biopesticides on human health and environment. Int. J. All Res. Writings 2, 45–51.
Rathee, M., Singh, N. V., Dalal, P. K., and Mehra, S. (2018). Integrated pest management under protected cultivation: a review. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 6, 1201–1208.
Ratnadass, A., Fernandes, P., Avelino, J., and Habib, R. (2012). Plant species diversity for sustainable management of crop pests and diseases in agroecosystems: a review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 32, 273–303. doi: 10.1007/s13593-011-0022-4
Regelink, I. C., Stoof, C. R., Rousseva, S., Weng, L., Lair, G. J., Kram, P., et al. (2015). Linkages between aggregate formation, porosity and soil chemical properties. Geoderma 247–248, 24–37. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.01.022
Reichelt, N., and Nettle, R. (2023). Practice insights for the responsible adoption of smart farming technologies using a participatory technology assessment approach: the case of virtual herding technology in Australia. Agric. Syst. 206:3592. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2022.103592
Reja, U., Manfreda, K. L., Hlebec, V., and Vehovar, V. (2003). Open-ended vs. close-ended questions in web questionnaires. Dev. Appl. Stat. 19, 159–177.
Rose, D. C., Parker, C., Fodey, J., Park, C., Sutherland, W. J., and Dicks, L. V. (2018). Involving stakeholders in agricultural decision support systems: improving user-centred design. Int. J. Agric. Manag. 6, 80–89. doi: 10.5836/ijam/2017-06-80
Rosendahl, J., Zanella, M. A., Rist, S., and Weigelt, J. (2015). Scientists’ situated knowledge: strong objectivity in Transdisciplinarity. Futures 65, 17–27. doi: 10.1016/j.futures.2014.10.011
Rosenstock, T. S., Tully, K. L., Arias-Navarro, C., Neufeldt, H., Butterbach-Bahl, K., and Verchot, L. V. (2014). Agroforestry with N2-fixing trees: sustainable development’s friend or foe? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 6, 15–21. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2013.09.001
Rossi, E. S., Materia, V. C., Caracciolo, F., Blasi, E., and Pascucci, S. (2023). Farmers in the transition toward sustainability: what is the role of their entrepreneurial identity? Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 7:1196824. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2023.1196824
Roussy, C., Ridier, A., Chaib, K., Roussy, C., Ridier, A., and Chaib, K. (2019). Farmers’ innovation adoption behaviour: role of perceptions and preferences. Int. J. Agric. Res. X:6439. doi: 10.1504/IJARGE.2017.086439
Ruzzante, S., Labarta, R., and Bilton, A. (2021). Adoption of agricultural technology in the developing world: a meta-analysis of the empirical literature. World Dev. 146:5599. doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2021.105599
Safaei Khorram, M., Zhang, Q., Lin, D., Zheng, Y., Fang, H., and Yu, Y. (2016). Biochar: a review of its impact on pesticide behavior in soil environments and its potential applications. J. Environ. Sci. (China) 44, 269–279. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2015.12.027
Sanders, E. B. N., and Stappers, P. J. (2008). Co-creation and the new landscapes of design. CoDesign 4, 5–18. doi: 10.1080/15710880701875068
Sapbamrer, R., and Thammachai, A. (2021). A systematic review of factors influencing farmers’ adoption of organic farming. Sustainability 13:3842. doi: 10.3390/su13073842
Sariyev, O., Loos, T. K., and Khor, L. Y. (2021). Intra-household decision-making, production diversity, and dietary quality: a panel data analysis of Ethiopian rural households. Food Secur. 13, 181–197. doi: 10.1007/s12571-020-01098-9
Schroth, G., Krauss, U., Gasparotto, L., Aguilar, J. A. D., and Vohland, K. (2000). Pests and diseases in agroforestry systems of the humid tropics. Agrofor. Syst. 50, 199–241. doi: 10.1023/A:1006468103914
Sendra, P. (2024). The ethics of co-design. J. Urban Des. 29, 4–22. doi: 10.1080/13574809.2023.2171856
Shiferaw, B., Tesfaye, K., Kassie, M., Abate, T., Prasanna, B. M., and Menkir, A. (2014). Managing vulnerability to drought and enhancing livelihood resilience in sub-Saharan Africa: technological, institutional and policy options. Weather Clim. Extrem. 3, 67–79. doi: 10.1016/j.wace.2014.04.004
Shrestha, G., Uprety, L., Khadka, M., and Mukherji, A. (2023). Technology for whom? Solar irrigation pumps, women, and smallholders in Nepal. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 7:1143546. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2023.1143546
Sinclair, F. L. (2017). “Systems science at the scale of impact: reconciling bottom-up participation with the production of widely applicable research outputs. In W. B” in Sustainable intensification in smallholder agriculture: An integrated systems research approach. eds. K. A.-K. I. Oborn, B. Vanlauwe, M. Phillips, and R. Thomas (London: Earthscan), 43–57.
Sinclair, F., and Coe, R. (2019). The options by context approach: a paradigm shift in agronomy. Exp. Agric. 55, 1–13. doi: 10.1017/S0014479719000139
Sinclair, F., Wezel, A., Mbow, C., Chomba, S., Robiglio, V., and Harrison, R. (2019). The Contribution of Agroecological Approaches To Realizing Climate-Resilient Agriculture. 46. Available at: www.gca.org (Accessed on May 14, 2024).
Singh, I., Hussain, M., Manjunath, G., Chandra, N., and Ravikanth, G. (2023). Regenerative agriculture augments bacterial community structure for a healthier soil and agriculture. Front. Agron. 5:1134514. doi: 10.3389/fagro.2023.1134514
Singha, A. K., Baruah, M. J., Bordoloi, R., Dutta, P., and Saikia, U. S. (2012). Analysis on influencing factors of technology adoption of different land based Enterprises of Farmers under diversified farming system. J. Agric. Sci. 4:139. doi: 10.5539/jas.v4n2p139
Sivini, S., and Vitale, A. (2023). Multifunctional and agroecological agriculture as pathways of generational renewal in Italian rural areas. Sustainability 15:5990. doi: 10.3390/su15075990
Solgi, E., Sheikhzadeh, H., and Solgi, M. (2018). Role of irrigation water, inorganic and organic fertilizers in soil and crop contamination by potentially hazardous elements in intensive farming systems: case study from Moghan agro-industry, Iran. J. Geochem. Explor. 185, 74–80. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.11.008
Steen, M. (2013). Co-Design as a Process of Joint Inquiry and Imagination (Vol. 29). Available at: http://direct.mit.edu/desi/article-pdf/29/2/16/1715163/desi_a_00207.pdf (Accessed on August 01, 2024).
Stefanovic, L., Freytag-Leyer, B., and Kahl, J. (2020). Food system outcomes: an overview and the contribution to food systems transformation. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 4:546167. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2020.546167
Stratton, A. E., Wittman, H., and Blesh, J. (2021). Diversification supports farm income and improved working conditions during agroecological transitions in southern Brazil. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 41:35. doi: 10.1007/s13593-021-00688-x
Tongco, M. D. C. (2007). Purposive sampling as a tool for informant selection. Ethnobot. Res. Appl. 5, 147–158.
Triomphe, B., Bergamini, N., Bioversity-Ciat, A., and Lisa,,), & Fuchs, E. (2022). Engaging with stakeholders for initiating agroecological transition in living landscapes Six guiding principles On behalf of the WP1 team CGIAR Initiative on Agroecology. Available at: https://www.sidalc.net/search/Record/dig-cgspace-10568-127414 (Accessed on June 19, 2024).
Utter, A., White, A., Méndez, V. E., and Morris, K. (2021). Co-creation of knowledge in agroecology. Elem. Sci. Anth. 9:00026. doi: 10.1525/elementa.2021.00026
Valencia, V., Wittman, H., Jones, A. D., and Blesh, J. (2021). Public policies for agricultural diversification: implications for gender equity. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 5:718449. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2021.718449
van Zonneveld, M., Turmel, M. S., and Hellin, J. (2020). Decision-making to diversify farm Systems for Climate Change Adaptation. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 4:32. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2020.00032
Vanlauwe, B., Coyne, D., Gockowski, J., Hauser, S., Huising, J., Masso, C., et al. (2014). Sustainable intensification and the African smallholder farmer. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 8, 15–22. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2014.06.001
Velasco-Muñoz, J. F., Mendoza, J. M. F., Aznar-Sánchez, J. A., and Gallego-Schmid, A. (2021). Circular economy implementation in the agricultural sector: definition, strategies and indicators. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 170:5618. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105618
Villacis, A. H., Bloem, J. R., and Mishra, A. K. (2023). Aspirations, risk preferences, and investments in agricultural technologies. Food Policy 120:2477. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2023.102477
Waarts, E., van Everdingen, Y. M., and van Hillegersberg, J. (2002). The dynamics of factors affecting the adoption of innovations. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 19, 412–423. doi: 10.1111/1540-5885.1960412
Watts-Englert, J., and Yang, E. (2021). Using a Codesign workshop to make an impact with Codesign research. Des. Manag. J. 16, 111–124. doi: 10.1111/dmj.12072
Wezel, A., Bellon, S., Doré, T., Francis, C., Vallod, D., and David, C. (2009). Agroecology as a science, a movement and a practice. Sustain. Agric. 2, 27–43. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-0394-0_3
Wezel, A., Herren, B. G., Kerr, R. B., Barrios, E., Gonçalves, A. L. R., and Sinclair, F. (2020). Agroecological principles and elements and their implications for transitioning to sustainable food systems. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 40, 1–13. doi: 10.1007/s13593-020-00646-z
Wezel, A., and Soldat, V. (2009). A quantitative and qualitative historical analysis of the scientific discipline of agroecology. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 7, 3–18. doi: 10.3763/ijas.2009.0400
Winowiecki, L. A., Bargues-Tobella, A., Mukuralinda, A., Mujawamariya, P., Ntawuhiganayo, E. B., Mugayi, A. B., et al. (2021). Assessing soil and land health across two landscapes in eastern Rwanda to inform restoration activities. Soil 7, 767–783. doi: 10.5194/soil-7-767-2021
Yagi, H., and Garrod, G. (2018). The future of agriculture in the shrinking suburbs: the impact of real estate income and housing costs. Land Use Policy 76, 812–822. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2018.03.013
Zanasi, C., Basile, S., Paoletti, F., Pugliese, P., and Rota, C. (2020). Design of a Monitoring Tool for eco-regions. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 4, 1–21. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2020.536392
Keywords: agroecology, soil management, water management, integrated pest management, options by context, farmer preference, participation, co-design
Citation: Kuria AW, Bolo P, Adoyo B, Korir H, Sakha M, Gumo P, Mbelwa M, Orero L, Ntinyari W, Syano N, Kagai E and Fuchs LE (2024) Understanding farmer options, context and preferences leads to the co-design of locally relevant agroecological practices for soil, water and integrated pest management: a case from Kiambu and Makueni agroecology living landscapes, Kenya. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1456620. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1456620
Edited by:
Simon Fielke, Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO), AustraliaReviewed by:
Stephen Snow, Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO), AustraliaZelalem Lema Moti, Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO), Australia
Copyright © 2024 Kuria, Bolo, Adoyo, Korir, Sakha, Gumo, Mbelwa, Orero, Ntinyari, Syano, Kagai and Fuchs. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Anne W. Kuria, YS5rdXJpYUBjaWZvci1pY3JhZi5vcmc=
 Anne W. Kuria
Anne W. Kuria Peter Bolo
Peter Bolo Beatrice Adoyo
Beatrice Adoyo Hezekiah Korir
Hezekiah Korir Michael Sakha
Michael Sakha Pius Gumo
Pius Gumo Machio Mbelwa
Machio Mbelwa Levi Orero
Levi Orero Winnie Ntinyari
Winnie Ntinyari Nicholas Syano
Nicholas Syano Esther Kagai5
Esther Kagai5 Lisa Elena Fuchs
Lisa Elena Fuchs