- 1College of Economics and Management, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China
- 2College of Accounting, Inner Mongolia University of Finance and Economics, Hohhot, China
Introduction: The lack of trust in eco-labels is a significant reason for the slow growth in demand for sustainable food, and reducing the information gap between relevant parties is a crucial means to improve consumer trust in eco-labels.
Methods: In order to investigate the influence and driving pathways of consumers' information acquisition abilities on their trust in eco-labels, a total of 1,072 urban and rural consumers in Inner Mongolia, China were surveyed in this study, with an analysis conducted using the structural equation model.
Results: It was found that information acquisition ability, institutional trust, and label knowledge have significant direct impacts on eco-label trust, with impact effects of 0.270, 0.351, and 0.357, respectively. Additionally, information acquisition ability has indirect effect of 0.085 and 0.127 on label trust through institutional trust and label knowledge. Furthermore, information discernment awareness has a significant negative moderating effect between information acquisition ability and label trust.
Discussion: Therefore, when publicizing the certification system and label knowledge, cultivating consumers' information acquisition ability effectively enhances eco-label trust. Moreover, strengthening media supervision to ensure the authenticity and objectivity of information transmission is an important measure to protect trust in eco-labels. This study enriches relevant research in the field of food sustainability and provides valuable recommendations to promote sustainable food consumption.
1 Introduction
Food consumption satisfies basic human survival needs, constituting a crucial field that is closely linked to personal consumption and environmental sustainability. Food systems have great potential to contribute to public health and maintain environmental sustainability, but the current development patterns pose potential risks and threats to both. A growing realization is that promoting sustainable food production and consumption is crucial for sustainable development. In addition, food sustainability exhibits an attribute of trust. Therefore, although compared to traditional food, sustainable food presents such advantages as environmental benefits, food safety, and animal welfare, consumers cannot experience their processes and results no matter before purchasing or after consumption, resulting in the complete failure of the market in transferring the trust attribute of food (Nelson, 1970). Eco-labels aim to deliver the relevant attribute of sustainable food to consumers, thus addressing the market failure problem by reducing consumer information asymmetry (Gorton et al., 2021). Therefore, eco-labels play an increasingly important role in promoting green consumption and achieving the goal of sustainable development. Eco-labels provide a visual assurance for the attribute of trust, thus being regarded as an important instrument for consumers to evaluate food sustainability (Van Loo et al., 2015; Annunziata et al., 2019). Many countries and regions have introduced eco-label systems to guide consumers' food choices, such as USDA Organic in the US, Bio-Siegel in Germany, Euro-leaf in EU, and Agriculture Biologique in France. These labels both provide consumers with a basis for choosing sustainable foods and encourage food companies to adopt a more environmentally friendly production approach.
However, eco-labels are not always effective to reduce the information asymmetry between suppliers and consumers and promote sustainable consumption (Asioli et al., 2020). As a pioneering field in the food sector for transitioning to more sustainable production and consumption (Vittersø and Tangeland, 2015), the organic food market is currently the biggest market for sustainable food and eco-labels (Gorton et al., 2021). Research on consumer preferences and trust attribute assessment based on organic food shows that label trust is an important driving force of purchase decisions among consumers (Nuttavuthisit and Thøgersen, 2017; Britwum et al., 2021), increasing their willingness to pay (Zanoli et al., 2015; Ha et al., 2019). Nevertheless, the concern is that consumers are losing their confidence in eco-labels (Vittersø and Tangeland, 2015; Gorton et al., 2021). A survey showed that only 37.6% of European consumers were able to correctly recognize the EU eco-label (Gorton et al., 2021), and more than half of US consumers expressed distrust in the environmental information on eco-labels (Yang et al., 2023a). Particularly in transitional economies like China, consumers generally lack trust in their domestic eco-labels (Yang, 2015; Yang et al., 2023a), leading to slow growth in the demand for sustainable food among these economie (Nuttavuthisit and Thøgersen, 2017; Vega-Zamora et al., 2019). For instance, organic food has a market share of 10.8% in Switzerland and 6% in the United States, but <1% in China (Yuan et al., 2023). Therefore, trust building constitutes a core objective of sustainable behaviors, and it is of crucial importance to understand the determining factors of eco-label trust among consumers.
Trust is a complex social concept consisting of emotional and rational aspects (Lewis and Weigert, 1985). It is proposed in the Trust Building Model (TBM) that at the early stage of trust establishment, emotional factors based on human nature (general trust) and subjective perception exert a more significant effect on consumer decisions. With the increase in transition frequency, rational trust based on knowledge and institutions starts to come into play (McKnight et al., 1998). In the domain of sustainable food consumption, Thorsøe et al. (2016) found that Danish consumers demonstrate high trust in organic labels and that institutional and general trust play a crucial role in establishing label trust. Gorton et al. (2021) studied trust in organic labels among consumers in seven European countries. They found that institutional trust and certification knowledge of consumers exert a significantly positive effect on their label trust. Truong et al. (2021) argued that complex interactions between consumers' institutional trust in food systems and their interpersonal trust in food suppliers determine their trust in certified food. Yin et al. (2017) investigated the behaviors of Chinese consumers and found that food safety awareness, organic food knowledge, and institutional trust can all affect trust in organic labels among consumers. With varying degrees, these studies have verified that institutional trust and certification knowledge of consumers can positively affect their trust in eco-labels. Therefore, institution publicity and knowledge dissemination can be two powerful measures for improving consumers' trust in certification labels.
However, consumers' trust in eco-labels is established through two-way communication. Effective information transmission cannot solely depend on information suppliers' disclosure and transfer efforts but requires information search and acquisition activities on the demand side of information (Gu and Yi, 2020). It is hard to fundamentally change the trust configuration in the food system only by emphasizing the information supply. Only through efforts to promote information absorption and conversion among consumers can their trust in eco-labels be enhanced (Thorsøe et al., 2016). Unfortunately, current studies on consumers' trust in eco-labels have paid insufficient attention to the demand sides of information, neglecting the role of information acquisition in the communication process at the consumer level. A study conducted in China revealed that the ability to acquire information can positively impact consumers' trust in organic agricultural products (Yuan and Xiao, 2021). However, the mechanism of consumers' information acquisition abilities affecting their trust in products remains unclear. Based on this, micro-survey data from 1,072 urban and rural consumers in Inner Mongolia were utilized in this study to construct a determination model of eco-label trust among consumers by incorporating the factor of information acquisition ability into the trust-building model. Subsequently, structural equation modeling was employed to investigate the influencing factors of label trust and empirically measure the influence of information acquisition ability on the label trust of consumers and its underlying mechanism. Compared with previous studies, the possible contribution of this study is to investigate the role of consumers' information acquisition ability on eco-label trust from the information demand side and provide valuable suggestions for promoting the development of a sustainable food market.
2 Theoretical analysis framework
2.1 Analysis framework
The trust-building model has guided studying the formation mechanism of trust. This paper used the model as a basis to categorize eco-label trust influences into the following aspects: general trust, food safety awareness, institutional trust, and label knowledge. To investigate the important role of information search and acquisition at the consumer demand level in information transmission, the consumer information acquisition ability factor was incorporated into the trust-building model in this study to explore further the influence of information acquisition ability on label trust and its underlying mechanism. It is worth noting that the food certification system in China involves Green Food Certification and Organic Food Certification. The development of green food and organic food can improve the environmental sustainability in agriculture and reduce the incidence of food-borne diseases, potentially increasing the incomes of Chinese farmers (Yu et al., 2014). Therefore, the eco-labels discussed in this paper refer to the “Green Food” and the “Organic Food” labels.
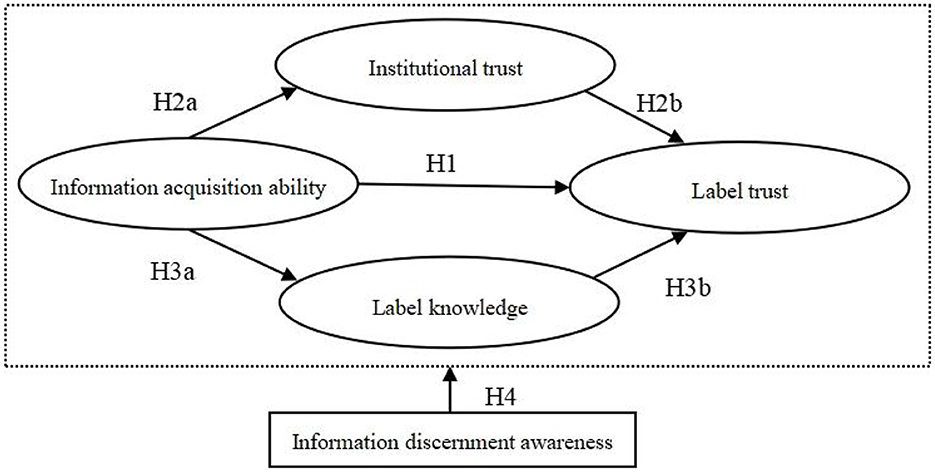
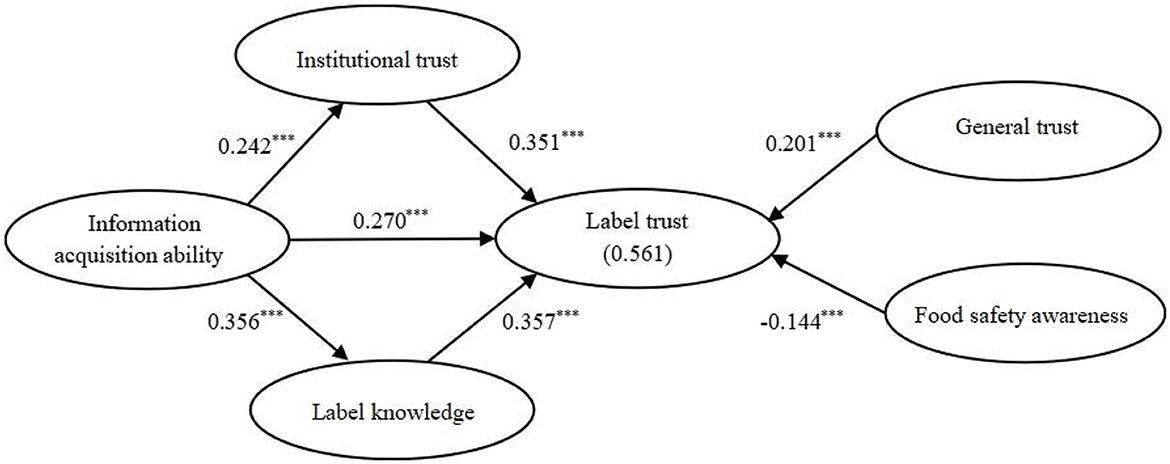
As an important signal screening mechanism, the eco-label certification system aims to reduce the information gap between producers and consumers. Effective information transmission cannot solely rely on information disclosure and transfer efforts on the information supply side; it also requires information search and acquisition activities on the information demand side. Consumers ' information acquisition abilities can improve their information exchange efficiency, thus promoting their trust in eco-labels. People form cognition through information observation and interpretation, affecting their attitudes and behaviors (Salancik and Pfeffer, 1978). It is difficult for food certification information acquired by consumers to affect their emotional cognition, such as general trust and food safety awareness. However, consumers' information acquisition abilities could affect their label trust in two ways (see Figure 1). One is to affect the institutional trust among consumers, thus further influencing their trust in eco-labels. The other is to affect consumers' label knowledge, thus further influencing their trust in eco-labels. Information discernment awareness refers to a consumer's subjective willingness and propensity to “critically” analyze the information obtained. During the transmission process of market information on sustainable food, consumers play a role not only in information acquisition but also in information screening. Heterogeneity in consumer information discernment awareness could affect the degree of information acquisition abilities and their trust in eco-labels. Based on the above analysis, the theoretical framework of this paper is shown in Figure 1.
2.2 Research hypotheses
Information acquisition ability refers to the comprehensive ability of a consumer to value information, master the use of information tools, actively acquire information, and utilize information resources to solve problems. An eco-label serves as an information cue that transforms the trust attribute of a product into a quasi-search attribute. Label trust is established during the communication processes between suppliers and consumers (Tung et al., 2012), and information acquisition at the consumer level plays a critical role in the effective transmission of quality signals. Therefore, consumers with stronger abilities to acquire relevant information about “green food” and “organic food” and more comprehensive information acquired can achieve information communication and promote eco-label trust among them. Therefore, Hypothesis 1 (H1) is proposed in this paper.
H1: Information acquisition ability can positively affect consumer trust in eco-labels.
Information acquisition ability can indirectly affect consumer label trust through institutional trust. Firstly, consumers with stronger information acquisition abilities are more capable of acquiring detailed information relating to eco-label certification systems, including certification standards, certification authorities, and regulatory measures. This kind of transparency can enhance public understanding and acceptance of eco-labels. With smooth information channels and accurate and reliable information, people are more likely to perceive systems as stable, fair, and effective, thus enhancing institutional trust among them. Secondly, when a third-party certification body issues eco-labels with public credibility and authority, consumers are more inclined to believe that products bearing these labels have met high-standard environmental or quality requirements. In other words, once trust in the certification system is established among consumers, it will be extended to certification products associated with the system (Jiang et al., 2008; Gorton et al., 2021). This indicates that institutional trust positively influences eco-label trust in the certification system. Therefore, the following hypotheses are proposed in this paper.
H2: Information acquisition ability indirectly affects consumer label trust through institutional trust.
H2a: Information acquisition abilities of consumers positively affect their institutional trust.
H2b: Consumer institutional trust positively affects consumer label trust.
It is easier for consumers with stronger information acquisition abilities to acquire more information relating to certified food from diversified information acquisition channels, making it convenient for consumers to understand the certification process of eco-labels and their underlying production standards. Therefore, it helps break down information barriers and accumulate consumer knowledge and experiences (Luh et al., 2014). At the same time, improved information acquisition abilities can help people understand newly established ecological standards and revoked certifications in a timely manner, thus ensuring the timeliness and accuracy of knowledge among them. Trust is based on cognition and is enhanced with the accumulation of knowledge (De Jonge et al., 2007). Consumers with rich label knowledge can better understand the meaning behind labels, presenting a greater acceptance of their authenticity and value with an improved sense of trust. Therefore, label knowledge relating to production standards, production processes, or food-system participants can lead to trust in certified food (Daugbjerg et al., 2014; Thorsøe et al., 2016; Yuan and Xiao, 2021). Based on this, the following hypotheses are proposed in this paper.
H3: Information acquisition ability indirectly affects label trust through label knowledge.
H3a: Consumer information acquisition ability positively affects consumer label knowledge.
H3b: Consumer label knowledge positively affects consumer label trust.
During the transmission process of market information on sustainable food, consumers need to acquire and convey information and screen information. However, under the influence of individual characteristics, consumers “embedded into” society exhibit significant differences in their awareness of information discernment. Lacking critical awareness and initiative in critical analysis, some consumers are inclined to passively accept external information and make their decisions primarily relying on external information. On the contrary, consumers with strong information-screening awareness tend to critically analyze and process biased and misleading market information to form their own “rational” judgments. With relatively stable cognitive structures, these consumers will not easily yield to the influences and persuasion of external information (Zhao, 2015). It indicates that information discernment awareness can somewhat weaken the positive effect of information acquisition ability on label trust. Therefore, Hypothesis 4 (H4) is proposed in this paper.
H4: Information discernment awareness can weaken the influence of information acquisition ability on label trust.
In addition, considering that general trust and food safety awareness play an important role in the establishment of consumer trust, these two variables were used as the control variables in this study.
3 Materials and methods
3.1 Data source
This study collected data from urban and rural consumers in the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region through a survey activity conducted from December 2021 to January 2022. According to data released by the National Bureau of Statistics, the per capita disposable income of residents in Inner Mongolia in 2020 was CNY 31,497, ranking 10th among 31 provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities in the country. This figure is slightly lower than the national average of CNY 32,189, making samples collected in this study present certain representativeness. Chifeng and Hohhot in Inner Mongolia were selected as the specific research areas in this study. These two cities were selected in this study for the following two reasons. Firstly, in terms of geographical location, Chifeng and Hohhot are located in the eastern and western regions of Inner Mongolia, respectively. Secondly, regarding the economic development level, the total GDP of Chifeng in 2020 was CNY 176.3 billion, and the total GDP of Hohhot in the same year was CNY 280 billion. Among all 12 leagues and cities in Inner Mongolia, these two cities can represent high and low economic development situations.
Survey targets were urban and rural residents aged 20 years or above in Chifeng and Hohhot, and survey respondents were primarily family members responsible for food shopping in their daily lives. Respondents' basic characteristics and consumer trust-related issues were primarily surveyed in this study. In order to ensure the quality of survey data, a pre-survey was carried out in the Saihan district of Hohhot before the formal survey activities were initiated, and relevant questionnaire contents were adjusted according to the results of the pre-survey. This study adopted a combination of online surveys and household-investigation methods. Data on urban residents in Hohhot and Chifeng were collected online for cost reduction and time savings. Questionnaires were distributed and collected through the website “Wenjuanxing” (https://www.wjx.cn). With such factors as high aging populations and low response rates to electronic questionnaires in rural areas taken into consideration, face-to-face interviews were conducted on-site through household investigations to collect data on rural residents. Following the principle of random sampling and with a combination of the geographical characteristics of the research area, this study randomly selected four counties and banners, including Helin County and Togtoh County in Hohhot and Wengniute Banner and Kalaqin Banner in Chifeng, to conduct the household investigations. Two towns were randomly selected in each county or banner, one or two villages were randomly selected in each town, and 10–30 households were randomly selected in each village to perform the household interviews. In addition, with the vast territory of Chifeng city taken into consideration, college students returning home for winter vacation were employed to survey 20 households in the village that was individually selected in Ar Horqin Banner, Ningcheng County, or Aohan Banner. Considering the particularity of production activities among residents in pastoral areas, there are significant differences in their food consumption habits compared to urban and rural residents. To ensure the representativeness of the survey data, all rural areas involved in this survey are in agricultural areas, and do not involve villages such as sumu and gacha in pastoral areas. The training was conducted among all survey workers participating in face-to-face interviews before field research activities in rural areas were initiated. During the survey processes, interviewers explained questionnaire filling rules to respondents and read questionnaire content for those interviewees with reading difficulties. To ensure the security of the respondents' information and the protection of their privacy, all questionnaires were completed anonymously, and respondents were promised that the data obtained would be used only for academic research before answering.
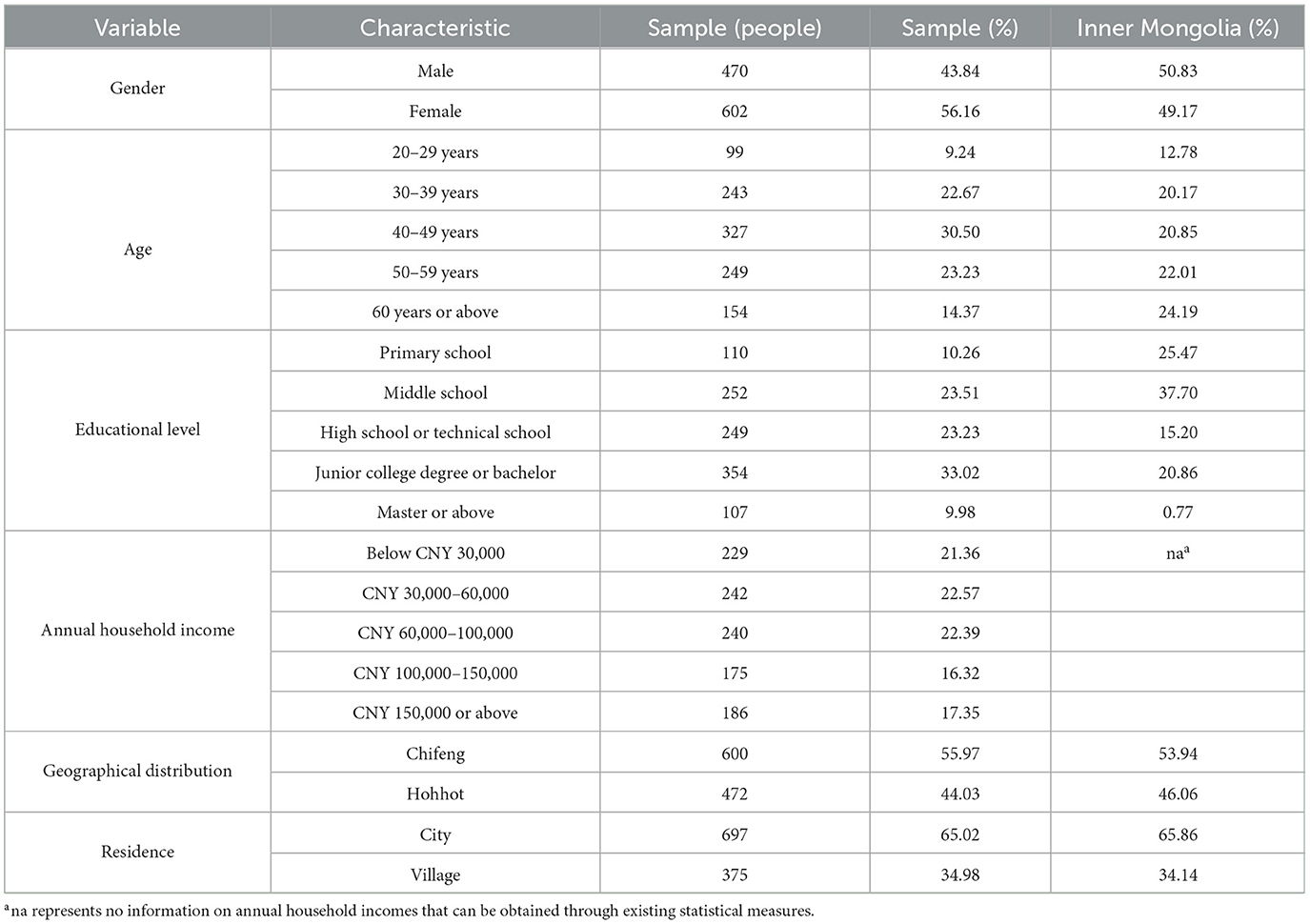
A total of 1,072 valid questionnaires were finally obtained in this study. Among them, 697 questionnaires were submitted by urban respondents, and rural respondents submitted 375 questionnaires. Questionnaires collected from urban respondents accounted for 65.02% of all valid questionnaires, which is consistent with the urbanization rate of 65.86% in Inner Mongolia. Questionnaires collected in Chifeng and Hohhot present a proportion ratio of 0.56:0.44, which is basically consistent with the proportion ratio (0.54:0.46) between resident populations in these two cities. The demographic characteristics of all survey respondents are listed in Table 1. In this study, data disclosed in the “Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Population Census Yearbook 2020” were used to calculate the demographic characteristics of the population aged 20 years or above in Inner Mongolia. The survey showed that female respondents slightly outnumbered male respondents, which is consistent with the situation in which female family members primarily do household food shopping. All respondents have an average age of about 45 years, with 76% of them aged 30–59 years old. These people are key decision-makers for household food consumption. Analysis of the educational status of the population aged 20 years or above in Inner Mongolia shows that respondents in the sampling area exhibited relatively high levels of education. This is due to the fact that the sampling area in this study is located in two major cities of Inner Mongolia with significant educational resources. In particular, Hohhot is the capital of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region and an important educational center in Inner Mongolia. Current statistical yearbooks provide no relevant information on the annual household incomes of Inner Mongolia residents. Based on the classification criterion for the middle-income population (with an annual household income of CNY 100,000–500,000) published by the National Bureau of Statistics, it is estimated that middle-income households account for 33.68% of all households that were surveyed in this study, which is lower than the proportion (36.80%) of the middle-income population in the whole country (Zhu and Wan, 2024). This is consistent with the relatively low economic development level in Inner Mongolia.
3.2 Variable setting and measurement
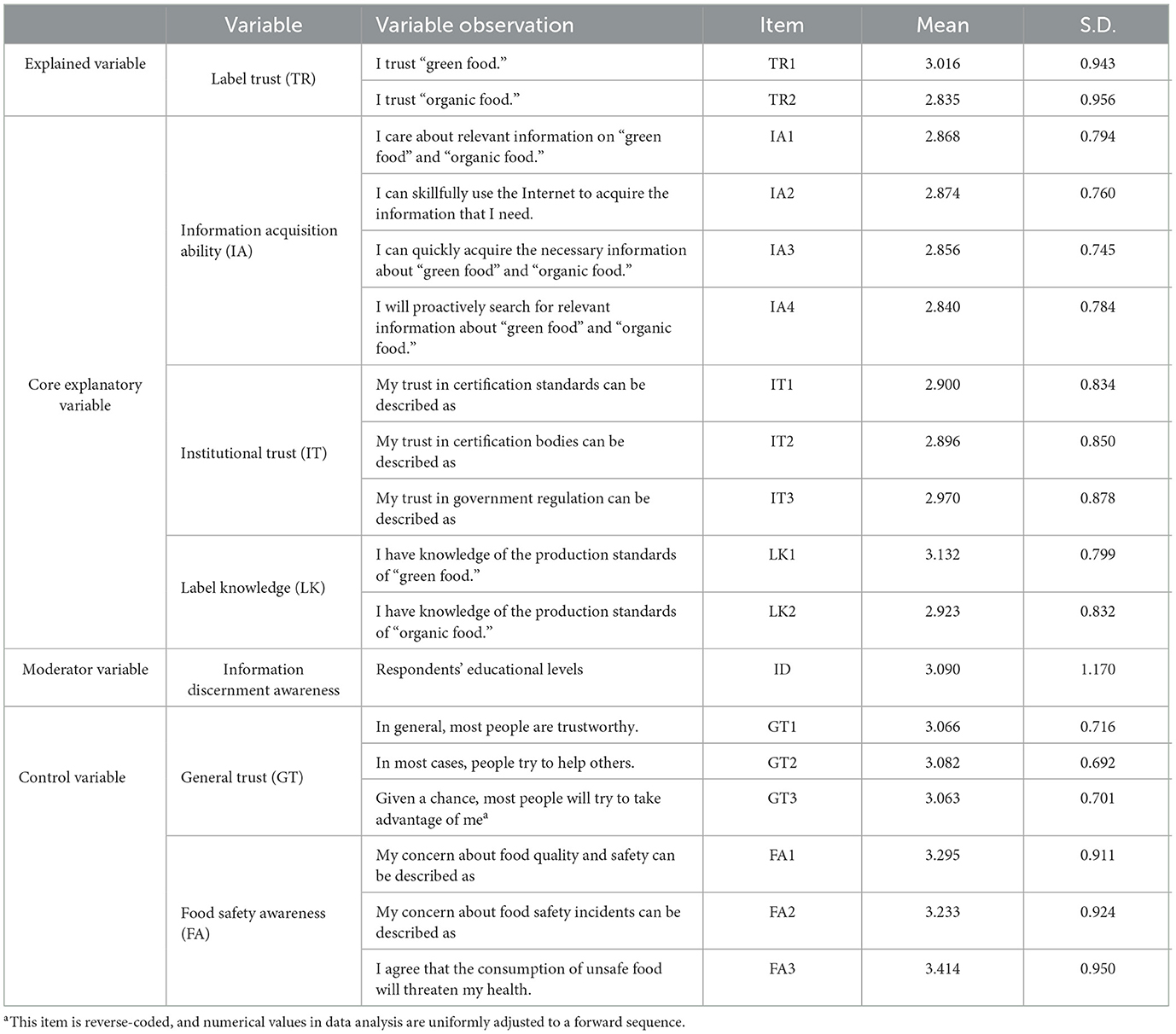
The scale used in this study was developed based on a comprehensive review of existing literature and with reference to mature scales established in relevant studies and the food certification system in China. All items were measured using a five-point Likert scale, with one representing “strongly disagree” and five representing “strongly agree.” In this study, the explained variable, label trust (TR), was measured with the degree of consumer trust in labels of “green food” and “organic food” (Zanoli et al., 2015; Gorton et al., 2021). The core explanatory variables used in this study include information acquisition ability (IA), institutional trust (IT), and label knowledge (LK). Four factors, namely, emphasis on information, mastery of information tools, and efficiency and initiative in information acquisition, were used to measure the information acquisition ability variable (Yin et al., 2017; Yang et al., 2023b). Three items, namely, trust in certification standards, trust in certification bodies, and trust in government regulation, were used to reflect the institutional trust variable (Yin et al., 2017; Ngo et al., 2020). Label knowledge involves subjective and objective label knowledge. In many cases, the attitudes of consumers toward certification labels are not built on the basis of their objective knowledge (Janssen and Hamm, 2012; Hsu et al., 2016). Therefore, this study focused on the subjective aspect of the label knowledge. Specifically, consumers' label knowledge was measured with their knowledge of the production standards for “green food” and “organic food” (Zingg et al., 2013; De Vocht et al., 2015).
Information discernment awareness (ID) is the moderator variable used in this research. It refers to a consumer's subjective willingness and propensity to critically analyze the information on certified food. In China, education has a significant enlightening effect. People with higher educational levels normally present more open and critical thinking (Im, 2014). Therefore, by borrowing the methods of existing studies, this study used the educational level as a substitute variable for the variable of information discernment awareness (Yuan and Xiao, 2021). Besides the abovementioned factors, the roles of general trust (GT) and food safety awareness (FA) played in consumer label trust should also be acknowledged. Therefore, this study used them as two control variables for further analysis. Among them, the general trust variable was measured using three question items, namely, “In general, most people are trustworthy,” “In most cases, people try to help others,” and “Given a chance, most people will try to take advantage of me (reverse coded) (Chen, 2013).” The food safety awareness variable was measured with three items, namely, worrying degrees of consumers about food safety, concern levels among consumers on food safety incidents, and consumers' perception of health risks associated with unsafe food consumption (Yin et al., 2017; Ngo et al., 2020). Detailed measurement results and descriptive statistics of variables are listed in Table 2.
3.3 Research methods
Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) was employed in this study to fit the influencing mechanism of information acquisition ability on eco-label trust. SEM presents unique advantages in multivariate data analysis (Hershberger, 2003). Therefore, this method has been widely used in relevant research on consumer trust (Ngo et al., 2020; Gorton et al., 2021). The specific procedure of data analysis is described as follows: (1) Reliability and validity test. A reliability and validity test was performed through the calculation of Cronbach's α, KMO, and Bartlett's chi-square values using SPSS26.0 software. Subsequently, AMOS26.0 software was used to perform the confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) to determine whether all variables can appropriately reflect the fitting status of their underlying structures and measurement models to data. (2) Hypothesis model test using AMOS 26.0. Specifically, this tests the structural model's fitting status to data and the pathway coefficients from independent variables to dependent variables. Sampling was repeatedly performed 5,000 times using the Bootstrap method to conduct the parallel mediation effect test. The multi-group analysis method was employed to perform the moderation effect test. (3) Common-method bias test. Common-method bias can occur among data measured using a self-report inventory (Podsakoff et al., 2003). Harman's single-factor test method was used in this study to perform the common-method bias test. An exploratory factor analysis was conducted on all measurement items using the SPSS26.0 software.
4 Data analysis results
4.1 Reliability and validity test
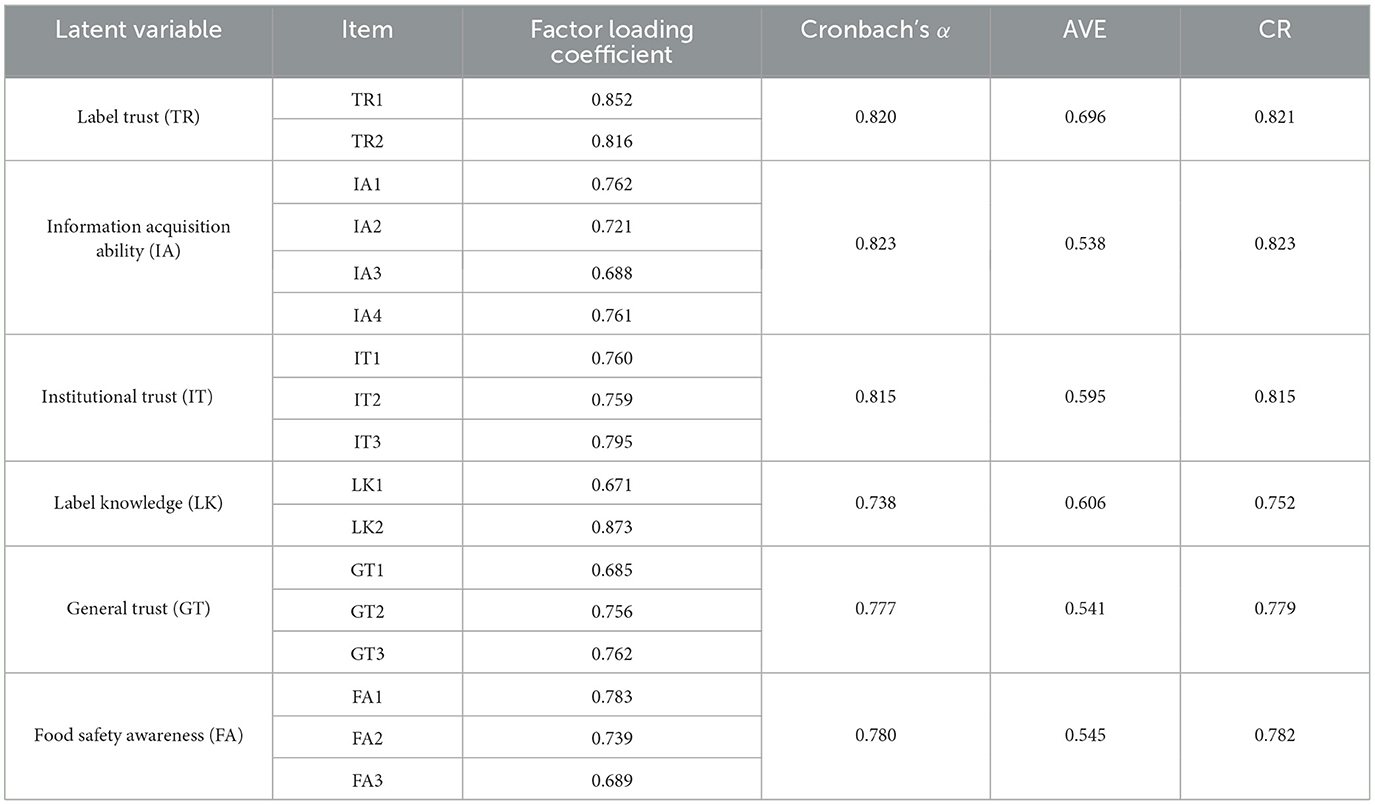
The overall Cronbach's α value of the scale used in this study is 0.787. The Cronbach's α values of variables label trust, information acquisition ability, institutional trust, label knowledge, general trust, and food safety awareness are 0.820, 0.823, 0.815, 0.738, 0.777, and 0.780, respectively (see Table 3). All these values are above 0.70, indicating good overall reliability and stability of questionnaire items. The KMO value is 0.8 (>0.5), and the Bartlett's test of sphericity is significant (p < 0.001), indicating good convergence of the scale and its suitability for factor analysis. The measurement model presents a value of 2.008 regarding the ratio of chi-square to the degree of freedom (χ2/df), which is lower than 3, and an RMSEA value of 0.031, which is lower than 0.05. In addition, the values of GFI, AGFI, and NFI obtained in the test are 0.978, 0.968, and 0.968, respectively, which are all higher than 0.9. The results of the confirmatory factor analysis are listed in Table 3. It can be seen that all standardized factor loading coefficients are significant, with values falling into the range of 0.671–0.873 (p < 0.001). Therefore, it can be preliminarily judged that all measurement variables exhibit good convergence validity. Meanwhile, the results show that all AVE values obtained are >0.5, and all CR values obtained are >0.7, indicating good variables' convergence validity. Furthermore, as shown in Table 4, the correlation coefficients of an individual variable with other variables are all lower than the square root of AVE, further indicating that all variables present good discriminant validity. Based on Harman's single-factor analysis, results of unrotated factors show that the first factor can explain 25.57% of the variance, below the critical standard of 40%, indicating no severe common-method bias in the measurement.
4.2 Correlation test of variables
The Pearson correlation analysis results show significant correlations among all variables (Table 4). Particularly, three core explanatory variables, namely, information acquisition ability, institutional trust, and label knowledge, exhibit correlation coefficients of 0.412, 0.432, and 0.434 with the label trust variable, respectively. Therefore, the research hypotheses previously mentioned in this paper have been preliminarily validated. In addition, the correlation coefficients among all variables are lower than 0.5, indicating no presence of potential multicollinearity among variables (Grewal et al., 2004).
4.3 Modle fit test
AMOS26.0 software was used to fit the model, with the following fit indices: chi-square value χ2 =282.171; degree of freedom df = 109; the ratio of chi-square to the degree of freedom χ2/df = 2.589 <3, and RMSEA value = 0.039 <0.05. The obtained GFI, AGFI, and NFI values are 0.970, 0.958, and 0.957, respectively. These values are all >0.9, indicating that the overall model fit indices can satisfy the fit standards. It shows that the model presents a good fit and excellent external quality, explaining 56.1% (see in Figure 2) of the variation in consumer trust.
4.4 Model result analysis
4.4.1 Influence of information acquisition ability on label trust
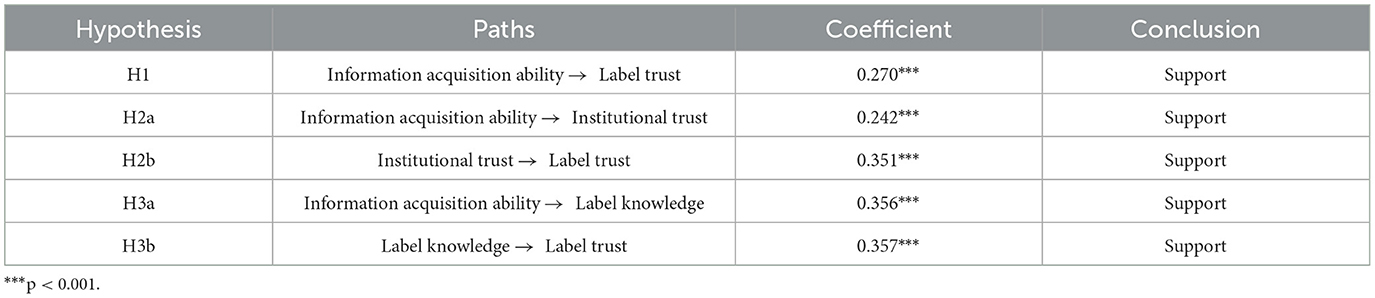
Structural equation modeling (SEM) analysis was conducted in this study to validate the research hypotheses previously proposed in this paper. The estimation results are listed in Table 5. It can be seen that the path coefficient from the information acquisition ability variable to the label trust variable has a value of 0.270, thus supporting H1; that is, information acquisition ability exerts a significantly positive effect on label trust. The path coefficient from the variable information acquisition ability to the variable institutional trust obtains a value of 0.242, thus supporting H2a; consumer information acquisition ability positively affects consumer institutional trust. The path coefficient from the variable institutional trust to the variable consumer label trust presents a value of 0.351, thus supporting H2b; that is, institutional trust has a significantly positive influence on label trust. The path coefficient from the variable information acquisition ability to the variable label knowledge obtains a value of 0.356, thus supporting H3a; information acquisition ability positively affects label knowledge. The path coefficient from the variable label knowledge to the variable label trust has a value of 0.357. Therefore, H3b has been proved; label knowledge positively affects label trust.
All path coefficients of core explanatory variables and control variables are shown in Figure 2. From the figure, it can be seen that general trust has a significantly positive influence on consumer label trust, with a path coefficient of 0.201. Food safety awareness exerts a significantly negative impact on label trust, with a path coefficient of −0.144. These results are consistent with the results of previous studies (Thorsøe et al., 2016; Yin et al., 2017; Ngo et al., 2020).
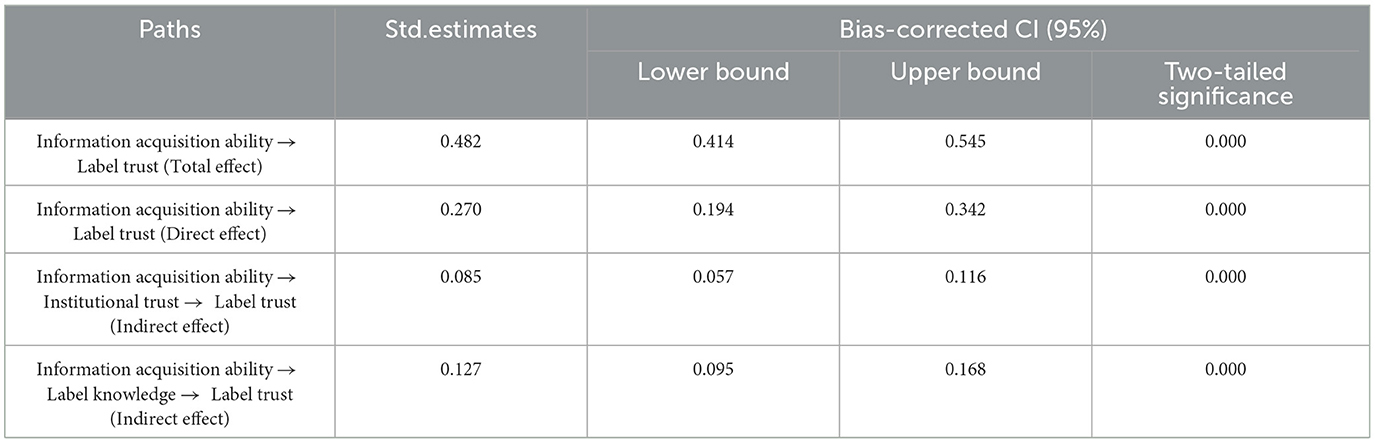
This study's theoretical analysis and path analysis results show that consumer information acquisition ability not only directly affects consumer label trust but also indirectly impacts consumer label trust through institutional trust and label knowledge. In order to test for the presence of mediation effect, sampling was performed repeatedly 5,000 times using the Bootstrap method for parallel mediation effect testing and confidence interval estimation. A 95% confidence interval not containing zero indicates a significant point estimation of the mediation effect (Zhao et al., 2010). Test results listed in Table 6 show that information acquisition ability indirectly affects consumer label trust through institutional trust, thus supporting H2. It can also be seen that information acquisition ability indirectly influences label trust through label knowledge, thus supporting H3.
4.4.2 Moderation effect of information discernment awareness
In order to analyze the moderation effect of information discernment awareness, overall samples were divided into the high-education group (N = 461) and the low-education group (N = 611) based on the mean value of educational level (3.090). Subsequently, structural equation modeling was employed for multi-group analysis. Firstly, the model-fitting status of the high-education and low-education groups was individually measured. The results show that the high-education group presents the following fitting indices: χ2/df = 1.839, RMSEA = 0.044, GFI = 0.949, AGFI = 0.928, and NFI = 0.922. Meanwhile, the fitting indices of the low-education group are as follows: χ2/df = 2.349, RMSEA = 0.047, GFI = 0.952, AGFI = 0.933, and NFI = 0.936. Overall, the ratio of chi-square degrees of freedom for both models are <3, RMSEA value are <0.05, and the remaining fitness indicators are all >0.9, all indices fall into an acceptable range, indicating the feasibility of multi-group analysis.
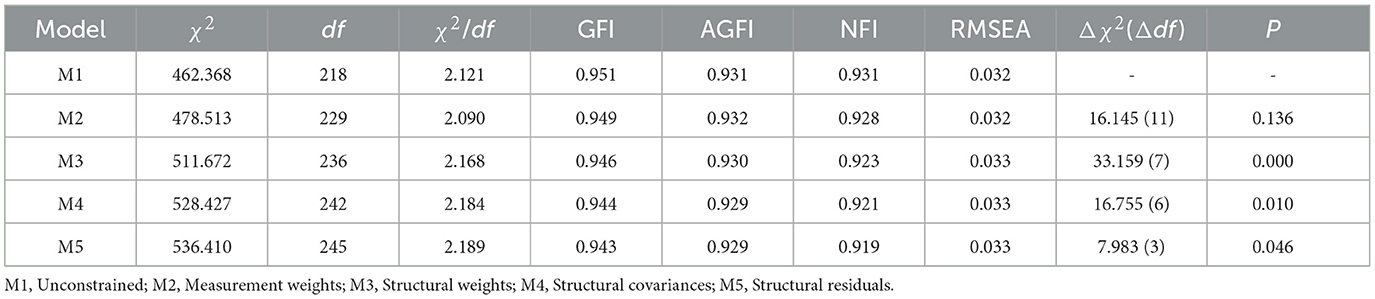
Then, regression coefficients were constrained successively; that is, the Measurement weights model, the Structural weights model, the Structural covariances model, and the Structural residuals model were successively constrained. The differences between the chi-square values of constrained and unconstrained models and the differences between their corresponding degrees of freedom were calculated. A significant chi-square difference (Δχ2) at the corresponding degree of freedom difference (Δdf) indicates a significant effect of the moderator variable on the model and a significant difference in the model under the corresponding constraint. The fitting indices of the multi-group model and the results of Δχ2 significance test are listed in Table 7. The results show that there is a significant Δχ2 between the constrained Structural weights model (M3) and the Measurement weights model (M2). Hence, it indicates that information discernment awareness presents a moderating effect.
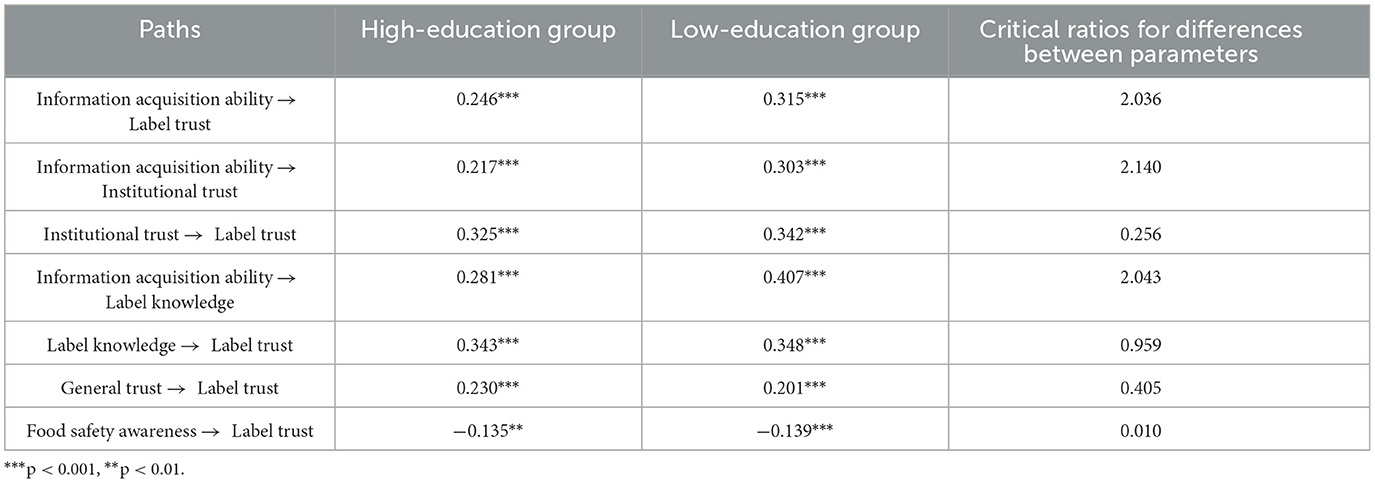
Further analysis (Table 8) shows that critical ratios for differences between parameters in the high-education and low-education groups on three pathways, namely, information acquisition ability → label trust, information acquisition ability → institutional trust, and information acquisition ability → label knowledge, are all >1.96, indicating the moderating effects of information discernment awareness on these three pathways. Among these three above-mentioned pathways with significant differences, samples in the high-education group present path coefficients of 0.246, 0.217, and 0.281, respectively. In terms of the low-education group, the corresponding path coefficients are 0.315, 0.303, and 0.407, respectively. The influence of information acquisition ability on label trust, institutional trust, and label knowledge in the high-education group is significantly lower than that of the low-education group. This indicates that information discernment awareness weakens the influence of information acquisition ability on label trust. Thus, H4 has been proved.
5 Discussion
5.1 Contributions and findings
As an information tool, eco-labels send signals to consumers to reduce information asymmetry, thus further affecting consumers' sustainable consumption decisions. Lack of trust in eco-labels will hinder the development of a sustainable food market. Therefore, it is important to enhance consumers' label trust for promoting their sustainable consumption behaviors. Label trust is established through a bidirectional communication process. The information disclosure and transmission on the supply side is a necessary but not sufficient condition for achieving consumer trust. The effectiveness of information is influenced and constrained by the information acquisition activities on the demand side, to which insufficient attention has been paid in existing studies. Compared to previous studies, this study has made the following marginal contribution. Firstly, this study has taken consumers in emerging markets as its survey objects to systematically investigate the influencing factors and degrees of eco-label trust and explore the theoretical logic behind the influences of institutional trust and label knowledge on label trust. Secondly, this research has filled the gap in the existing literature. Starting from the demand side of information, it has examined the influence and action mechanism of information acquisition abilities of consumers on their eco-label trust, enriching the research dimensions and perspectives of consumer eco-label trust.
Econometric analysis results in this study show that institutional trust and label knowledge significantly positively influence eco-label trust, with standardized path coefficients of 0.351 and 0.357, respectively. This indicates that the authority of certification systems and consumers' familiarity with the production standards of label products can affect the establishment of their label trust. This finding is consistent with research on consumer trust in Europe. Thorsøe et al. (2016) advocated the role of knowledge in the establishment of Danish consumers' trust in organic labels. Gorton et al. (2021) also confirmed the significant roles of institutional trust and certification knowledge in label trust in his study on the EU. The findings of this paper further confirm that, similar to developed countries, in emerging economies, both institutional trust and label knowledge have a significant impact on consumer eco-label trust. However, since institutional trust relies on industrial environments, including formal regulations and regulatory standards, its establishment conditions are more complex. Therefore, communication activities should focus on improving the certification knowledge of consumers (Gorton et al., 2021).
Consumer information acquisition ability presents a direct effect coefficient of 0.270 on label trust, indicating that during the consumption process of sustainable food, information acquisition on the demand side can enhance the efficiency of information transmission and help eliminate market uncertainty, thus promoting the establishment of consumer trust. This finding is consistent with the results obtained by Yuan and Xiao (2021) in their research. Information acquisition ability indirectly affects label trust through institutional trust and label knowledge, with effect coefficients of 0.085 and 0.127, respectively. This indicates that label trust can be enhanced among consumers who endeavor to acquire information and convert it into institutional recognition and knowledge (Thorsøe et al., 2016). Path coefficients from the variable information acquisition ability to institutional trust and label knowledge variables are 0.242 and 0.356, respectively. This indicates that compared to institutional trust, improved information acquisition ability on the demand side significantly affects label knowledge. Therefore, knowledge dissemination and promotion is the first necessary step to overcome label skepticism (Nuttavuthisit and Thøgersen, 2017; Gorton et al., 2021).
In addition, the results of the moderation effect analysis show that information discernment awareness plays a significantly negative moderating role between information acquisition ability and label trust. Compared with consumers with higher educational levels, consumers with lower educational levels exhibit more significant influences of their information acquisition abilities on label trust, institutional trust, and label knowledge, with statistically significant differences between these two groups. This is consistent with the results obtained by Wu et al. (2013). Their research found that when choosing food containing additives, consumers with lower educational levels are more likely to trust and follow government propaganda and guidance than consumers with higher levels of education (Wu et al., 2013). This implies that due to the lack of critical thinking, consumers with lower educational levels are more likely to build trust on the basis of external information. However, this kind of trust is more fragile and susceptible to being influenced and damaged by negative information.
Overall, our findings emphasize the degree of impact and mechanism of action of information acquisition ability on consumers' trust in Eco-labels regarding food sustainability, and the moderating role of information discernment awareness on the above relationships. Consequently, it becomes evident that cultivating consumers' information acquisition ability plays an important role in enhancing eco-labels trust and promoting sustainable food consumption.
5.2 Limitations and prospect
Systematic demonstration and analysis have been performed in this study on consumer eco-label trust. However, this study still has the following limitations. Firstly, it is implied in this study's analysis that all information consumers acquire is positive. However, in a diversified media environment, positive and negative information coexist. Future studies can attempt to utilize sentiment analysis tools to distinguish the positive and negative attributes of information and control the influences of negative information on the analytical conclusions. Secondly, in terms of the research scope, only survey data collected among urban and rural consumers in Inner Mongolia, China, were used in this study. In order to obtain a more comprehensive conclusion about consumer trust in sustainable food in emerging economies, future studies should further expand their research scopes. Lastly, although the survey objects of this study included both urban and rural residents, no in-depth analysis was conducted on the basis of heterogeneity between urban and rural consumers. In future studies, qualitative research methods such as in-depth interviews or focus group discussions can be employed to explore the specific differences in food consumption trust between rural and urban consumers. In this way, valuable insights can be gained into determining label trust among rural consumers.
6 Conclusions and recommendations
Based on the micro survey data of urban and rural consumers in Inner Mongolia, this study explored the influence and mechanism of consumers' information acquisition ability on eco-labels trust, and the moderating effect of information recognition awareness on the above relationship. The results show the institutional trust and label knowledge both positively affect eco-labels trust. There is a significant positive effect of information accessibility on labeling trust, both directly and indirectly through institutional trust and labeling knowledge. Compared with institutional trust, information acquisition ability plays a higher role in long-term trust through label knowledge. Information discernment awareness plays a significantly negative moderating role in the effect of information acquisition ability on label trust. Path coefficients from the variable information acquisition ability to variables of label trust, institutional trust, and label knowledge among consumers with higher educational levels are significantly lower than those among consumers with lower levels of education.
Based on the above conclusion, this paper proposes the following policy recommendations. Firstly, to address the current widespread lack of trust in eco-labels, it is of critical importance to enhance institutional credibility and popularize and promote certification knowledge. With complex establishment conditions of institutional trust taken into consideration, communication activities should focus more on the enhancement of label knowledge among consumers. For example, public education campaigns should be carried out to explain the meaning and standards of eco-labels. Concise and clear promotional materials using comprehensible language and symbols should be designed. Secondly, during the processes of information transmission and disclosure, relevant parties should focus more on cultivating consumers' information acquisition abilities and encouraging consumers to acquire information in a more proactive, purposeful, and effective way, thus enhancing digital literacy among consumers. Consumers should be educated to filter out irrelevant information and prevent information overload from affecting their information acquisition efficiency. In addition, consumers with weaker information discernment awareness are more likely to build their trust on the basis of external information. However, this kind of trust is very fragile. Therefore, governments should strengthen media regulation and purify the media environment to ensure authentic and objective information transmission to protect consumer trust.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
YY: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FX: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. GQ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant Number: 2021YFE0190200).
Acknowledgments
We thank students at the College of Accounting, Inner Mongolia University of Finance and Economics for their support in conducting household surveys, and also thank to the respondents for their active participation and cooperation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Annunziata, A., Mariani, A., and Vecchio, R. (2019). Effectiveness of sustainability labels in guiding food choices: analysis of visibility and understanding among young adults. Sustain. Product. Consumpt. 17, 108–115. doi: 10.1016/j.spc.2018.09.005
Asioli, D., Aschemann-Witzel, J., and Nayga, R. M. (2020). Sustainability-related food labels. Ann. Rev. Resour. Econ. 12, 171–185. doi: 10.1146/annurev-resource-100518-094103
Britwum, K., Bernard, J. C., and Albrecht, S. E. (2021). Does importance influence confidence in organic food attributes? Food Qual. Pref. 87:104056. doi: 10.1016/j.foodqual.2020.104056
Chen, W. (2013). The effects of different types of trust on consumer perceptions of food safety. China Agricult. Econ. Rev. 5, 43–65. doi: 10.1108/17561371311294757
Daugbjerg, C., Smed, S., Andersen, L. M., and Schvartzman, Y. (2014). Improving eco-labelling as an environmental policy instrument: knowledge, trust and organic consumption. J. Environ. Pol. Plan. 16, 559–575. doi: 10.1080/1523908X.2013.879038
De Jonge, J., Van Trijp, H. C. M., Jan Renes, R., and Frewer, L. J. (2007). Understanding consumer confidence in the safety of food: its two-dimensional structure and determinants. Risk Anal. 27:917. doi: 10.1111/j.1539-6924.2007.00917.x
De Vocht, M., Cauberghe, V., Uyttendaele, M., and Sas, B. (2015). Affective and cognitive reactions towards emerging food safety risks in Europe. J/ Risk Res. 18, 21–39. doi: 10.1080/13669877.2013.879486
Gorton, M., Tocco, B., Yeh, C.-H., and Hartmann, M. (2021). What determines consumers' use of eco-labels? Taking a close look at label trust. Ecol. Econ. 189:107173. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2021.107173
Grewal, R., Cote, J. A., and Baumgartner, H. (2004). Multicollinearity and measurement error in structural equation models: implications for theory testing. Market. Sci. 23, 519–529. doi: 10.1287/mksc.1040.0070
Gu, C., and Yi, Y. (2020). Can disclosed information acquisition improve food trust?—based on survey data of fresh food in Changsha City. J. Agrotech. Econ. 1, 68–79. doi: 10.13246/j.cnki.jae.2020.01.005
Ha, T. M., Shakur, S., and Pham Do, K. H. (2019). Rural-urban differences in willingness to pay for organic vegetables: evidence from Vietnam. Appetite 141:104273. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2019.05.004
Hershberger, S. L. (2003). The growth of structural equation modeling: 1994–2001. Struct. Eq. Model. 10, 35–46. doi: 10.1207/S15328007SEM1001_2
Hsu, S.-Y., Chang, C.-C., and Lin, T. T. (2016). An analysis of purchase intentions toward organic food on health consciousness and food safety with/under structural equation modeling. Br. Food J. 118, 200–216. doi: 10.1108/BFJ-11-2014-0376
Im, D.-K. (2014). The legitimation of inequality: psychosocial dispositions, education, and attitudes toward income inequality in China. Sociol. Perspect. 57, 506–525. doi: 10.1177/0731121414536883
Janssen, M., and Hamm, U. (2012). Product labelling in the market for organic food: consumer preferences and willingness-to-pay for different organic certification logos. Food Qual. Pref. 25, 9–22. doi: 10.1016/j.foodqual.2011.12.004
Jiang, P., Jones, D. B., and Javie, S. (2008). How third-party certification programs relate to consumer trust in online transactions: an exploratory study. Psychol. Market. 25, 839–858. doi: 10.1002/mar.20243
Lewis, J. D., and Weigert, A. J. (1985). Trust as a social reality. Soc. Forces 63, 967–985. doi: 10.2307/2578601
Luh, Y. H., Jiang, W., and Chien, Y.-N. (2014). Adoption of genetically-modified seeds in Taiwan: the role of information acquisition and knowledge accumulation. China Agricult. Econ. Rev. 6, 669–697. doi: 10.1108/CAER-03-2013-0037
McKnight, D. H., Cummings, L. L., and Chervany, N. L. (1998). Initial trust formation in new organizational relationships. Acad. Manag. Rev. 23, 473–490. doi: 10.2307/259290
Nelson, P. (1970). Information and consumer behavior. J. Polit. Econ. 78, 311–329. doi: 10.1086/259630
Ngo, H. M., Liu, R., Moritaka, M., and Fukuda, S. (2020). Urban consumer trust in safe vegetables in Vietnam: the role of brand trust and the impact of consumer worry about vegetable safety. Food Control 108:106856. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2019.106856
Nuttavuthisit, K., and Thøgersen, J. (2017). The importance of consumer trust for the emergence of a market for green products: the case of organic food. J. Bus. Ethics 140, 323–337. doi: 10.1007/s10551-015-2690-5
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Lee, J. Y., and Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: a critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 88, 879–903. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.88.5.879
Salancik, G. R., and Pfeffer, J. (1978). A social information processing approach to job attitudes and task design. Admin. Sci. Quart. 23, 224–253. doi: 10.2307/2392563
Thorsøe, M. H., Christensen, T., and Povlsen, K. K. (2016). “'Organics' are good, but we don't know exactly what the term means!” Trust and knowledge in organic consumption. Food Cult. Soc. 19, 681–704. doi: 10.1080/15528014.2016.1243767
Truong, V. A., Conroy, D. M., and Lang, B. (2021). The trust paradox in food labelling: an exploration of consumers' perceptions of certified vegetables. Food Qual. Pref. 93:104280. doi: 10.1016/j.foodqual.2021.104280
Tung, S. J., Shih, C. C., Wei, S., and Chen, Y. H. (2012). Attitudinal inconsistency toward organic food in relation to purchasing intention and behavior. Br. Food J. 114, 997–1015. doi: 10.1108/00070701211241581
Van Loo, E. J., Caputo, V., Nayga, R. M., Seo, H.-S., Zhang, B., and Verbeke, W. (2015). Sustainability labels on coffee: consumer preferences, willingness-to-pay and visual attention to attributes. Ecol. Econ. 118, 215–225. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2015.07.011
Vega-Zamora, M., Torres-Ruiz, F. J., and Parras-Rosa, M. (2019). Towards sustainable consumption: keys to communication for improving trust in organic foods. J. Clean. Product. 216, 511–519. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.129
Vittersø, G., and Tangeland, T. (2015). The role of consumers in transitions towards sustainable food consumption. The case of organic food in Norway. J. Clean. Prod. 92, 91–99. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.12.055
Wu, L., Zhong, Y., Shan, L., and Qin, W. (2013). Public risk perception of food additives and food scares. The case in Suzhou, China. Appetite 70, 90–98. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2013.06.091
Yang, B. (2015). Consumer behavior selection and green food market operations under low consumer trust in eco-labels. Econ. Surv. 32, 73–78. doi: 10.15931/j.cnki.1006-1096.2015.03.013
Yang, D., Yu, Y., and Feng, Z. (2023a). Consumer behavior selection and green food market operations under low consumer trust in eco-labels. Chin. J. Manag. Sci. 31, 73–82. doi: 10.16381/j.cnki.issn1003-207x.2021.0734
Yang, Z., Zhang, Y., and Gu, X. (2023b). Internet use, social capital and employment quality of migrant workers: from the perspective of information acquisition. Northw. Popul. J. 44, 70–83. doi: 10.15884/j.cnki.issn.1007-0672.2023.05.006
Yin, S., Wang, X., and Lv, S. (2017). Brand, certification, and consumer trust propensity: a case study of organic milk. J. Huazhong Agricult. Univ. 4, 45–147. doi: 10.13300/j.cnki.hnwkxb.2017.04.007
Yu, X., Gao, Z., and Zeng, Y. (2014). Willingness to pay for the “Green Food” in China. Food Pol. 45, 80–87. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2014.01.003
Yuan, R., Jin, S., and Lin, W. (2023). Could trust narrow the intention-behavior gap in eco-friendly food consumption? Evidence from China. Agribusiness 2023:21886. doi: 10.1002/agr.21886
Yuan, X., and Xiao, Y. (2021). Information accessibility, cognition level and consumer trust of organic agricultural products. J. Manag. 34, 92–108. doi: 10.19808/j.cnki.41-1408/F.2021.0039
Zanoli, R., Naspetti, S., Janssen, M., and Hamm, U. (2015). Mediation and moderation in food-choice models: a study on the effects of consumer trust in logo on choice. NJAS Wageningen J. Life Sci. 72, 41–48. doi: 10.1016/j.njas.2015.01.001
Zhao, X. (2015). Perceptions of distributive justice and attributions for inequality in transitional China: an empirical analysis based on CGSS2010. J. Gansu Admin. Inst. 5, 101–128.
Zhao, X., Lynch Jr, J. G., and Chen, Q. (2010). Reconsidering Baron and Kenny: myths and truths about mediation analysis. J. Consum. Res. 37, 197–206. doi: 10.1086/651257
Zhu, L., and Wan, G. (2024). Scale measurement and characteristic analysis of China's middle-income groups. Wuhan Univ. J. 77, 133–146. doi: 10.14086/j.cnki.wujss.2024.03.014
Keywords: sustainable food, information acquisition ability, eco-label, trust, consumer
Citation: Yang Y, Xue F and Qiao G (2024) The impact of information acquisition ability on consumers' trust in eco-labels in China: insight of food sustainability. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1449848. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1449848
Received: 16 June 2024; Accepted: 30 August 2024;
Published: 23 September 2024.
Edited by:
Anwar Ali, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaReviewed by:
Shahzor Gul, Sindh Agriculture University, PakistanClaudia Terezia Socol, University of Oradea, Romania
Seydi Yikmiş, Namik Kemal University, Türkiye
Rai Naveed Arshad, University of Technology Malaysia, Malaysia
Zhi-Wei Liu, Hunan Agricultural University, China
Copyright © 2024 Yang, Xue and Qiao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guanghua Qiao, cWlhb19pbWF1QDEyNi5jb20=
 Yanyan Yang
Yanyan Yang Fang Xue2
Fang Xue2