- 1School of Natural Sciences, University of Zambia, Lusaka, Zambia
- 2Faculty of Agriculture, Environment and Food Systems, University of Zimbabwe, Harare, Zimbabwe
- 3School of Health Sciences, University of Zambia, Lusaka, Zambia
The adoption of Sustainable Land Management (SLM) practices among smallholder farmers remains low, particularly among women farmers. Understanding the relationship between assets, gender, and SLM adoption and how their interaction impinges on household food self-sufficiency and livelihoods is essential for developing gender-responsive SLM programmes that effectively promote sustainable livelihoods and address household food insecurity. This study examines the effects of asset type on SLM practices adoption, women farmers, and their implications on household incomes and food self-sufficiency. Data was collected through a cross-sectional survey of 761 households selected from 11 chiefdoms across six districts in Eastern Zambia. Analysis involved Structural Equation System framework and Propensity Score Matching techniques to examine relationships between SLM adoption, food self-sufficiency, and household incomes, considering various socio-economic factors. Results showed marital status and household size as significant demographics, with education positively correlating with household income and SLM participation (p < 0.05). Gender disparities persisted, with male-headed households having higher incomes. Labour allocation analysis revealed women’s involvement in labour-intensive tasks, while smaller farms showed higher income probabilities, supporting sustainable agricultural intensification. Social capital significantly influenced SLM participation, and access to financial capital. Livestock assets, land size, and crop diversity predicted food security, while male decision-making influenced food security and income. Incomes were higher for women participating in SLM projects. This study underscores the importance of SLM practices in influencing household incomes and food security, especially for women. Addressing gender disparities and promoting women’s empowerment in agriculture are crucial for achieving equitable and sustainable rural development. Policymakers can foster sustainable livelihoods in rural communities by prioritizing SLM and empowering women.
1 Introduction
SLM encompasses agricultural practices that conserve water and soil and are environmentally non-degrading, technically appropriate, economically viable, and socially acceptable (Fowler and Rockstrom, 2001). It plays a crucial role in supporting the livelihoods of smallholder farmers by providing them with the necessary resources, such as land and water, to engage in agricultural production. Additionally, SLM practices can contribute to increased agricultural productivity and food self-sufficiency (McElwee et al., 2020). A review of 160 studies by Branca et al. (2013) found that SLM generally leads to higher and more stable crop yields, increased system resilience and, therefore, enhanced livelihoods and food security, and reduced production risk. Moreover, SLM can enhance food security by optimizing agricultural land and diversifying crops, thereby increasing the availability of locally produced food and reducing dependence on imports (Maponya, 2021; Oduniyi and Tekana, 2021; Andika et al., 2020). By implementing SLM, smallholder farmers can improve their profitability, leading to higher incomes. Efforts aimed at improving farm-related profitability are therefore important to improving livelihoods among smallholder farmers (Maponya, 2021; Ng’ang’a et al., 2021; Abegunde et al., 2019).
Smallholder farmers that depend on rain-fed agriculture face serious risks related to climate change and variability and soil degradation (Ng’ang’a et al., 2021). These risks directly impact agricultural productivity as unpredictable weather patterns and changes in precipitation affect crop growth and yield. This, in turn, threatens food self-sufficiency as farmers may struggle to produce enough food to meet their own needs and the needs of their communities (Müller et al., 2011). Additionally, climate change and soil degradation can disrupt the natural balance of ecosystems and reduce biodiversity, further compromising the resilience of agricultural systems. As a result, smallholder farmers may become more dependent on external sources for food, undermining their food sovereignty and increasing their vulnerability to price fluctuations and market instability. Furthermore, the risks associated with climate change and soil degradation also have a significant impact on the livelihoods of smallholder farmers (Huq et al., 2015). These risks can lead to decreased incomes and financial instability as farmers may experience crop failures or reduced yields. This can result in increased poverty and food insecurity among smallholder farmers, as their livelihoods are heavily reliant on agriculture. The livelihood and income of a large population of Sub Saharan Africa (SSA) depends on the natural resource base, and most of the poor people often live in marginalized lands and areas more prone to natural disasters (Hossain et al., 2012).
Over the recent decades, programmes aimed at channeling resources into SLM in order to mitigate the negative effects of climate change and variability on smallholder farmers’ livelihoods have been implemented. Proponents of such programmes have espoused that SLM practices have significant implications for the incomes and food self-sufficiency of smallholder farmers in SSA (Maponya, 2021; Ng’ang’a et al., 2021; Abideen et al., 2023). By implementing SLM practices, smallholder farmers in the region can enhance their productivity and profitability, attain higher incomes (Marques et al., 2016), improve soil quality, and mitigate the adverse effects of climate change. Overall, SLM practices have a positive impact on the livelihoods of smallholder farmers (Andersson Djurfeldt et al., 2019); and help address the problem of declining available farmlands by enhancing sustainable intensification, and therefore potentially increasing the value of harvest and incomes (Fuchs et al., 2019).
While the merits of SLM are widely acknowledged (Snapp et al., 2010; Ubochioma et al., 2012; Motavalli et al., 2013; FAO, 2017; Krah et al., 2019), several studies have shown that adoption of SLM practices by smallholder farmers in SSA has remained low (Ajayi et al., 2003; Ojiem et al., 2006; Bolliger, 2007; Mango et al., 2017; Cordingley et al., 2015; Kassie et al., 2015; Mutyasira et al., 2018), especially among female-headed households (Umar et al., 2019). Reasons advanced for the low adoption of SLM practices include risk aversion, logistical, financial and information barriers (Li et al., 2016; Krah et al., 2019). A recent review of empirical studies on agricultural technology adoption in SSA by Takahashi et al. (2020) revealed that assets, labour availability, social capital and networks, access to extension services, market and credits, soil conditions, rainfall, tenure security, education, and experience affect the adoption of SLM practices.
Employing a discrete choice-based experiment among smallholder farmers in Malawi, Krah et al. (2019) found evidence that the farmers’ propensity to adopt soil fertility management practices increases with improved access to mineral fertilizers, and when farmers receive relevant technical training on soil fertility improving technologies. A logistic regression model showed that farm management, ability to hire labour and months in a year households bought food for their families significantly influenced adoption of SLM practices in Kenya (Mugwe et al., 2009). A study of selected conservation agriculture (CA) households in Zimbabwe, Malawi and Mozambique found no significant impact of CA adoption on food security of farmers in Zimbabwe and Malawi, possibly due to the small land areas currently devoted to CA there, and the failure to implement the full complement of CA practices necessary to derive yield increases. Conversely, in Mozambique, CA was reportedly more effective as it was promoted together with complementary cropping management practices such as timely weeding and improved seed varieties (Mango et al., 2017).
For the case of Zambia, data from a sample of over 800 households and 3,000 plots showed that the adoption of a combination of SLM practices raises both maize yields and incomes of smallholder farmers in rural Zambia (Manda et al., 2015) while Abdulai (2016) found that the adoption of SLM increased maize output, and reduced household poverty and that farmers’ years of schooling, social networks, access to credit, extension services, and machinery as well as soil quality positively influence adoption of SLM technology. Khonje et al. (2018) demonstrated that in Zambia, the simultaneous adoption of SLM technologies (e.g. improved maize varieties and conservation agriculture practices) has a greater impact on farm output, income, and poverty than individual innovation package adoption. Similarly, Manda et al. (2015) reported that on average, adopters of a combination of SLM practices had between 43 and 75% more income per capita than non-adopters.
Due to gender gaps in asset ownership, women tend to be less resilient to agricultural shocks (Antwi-Agyei et al., 2013; Mphande et al., 2022; Umar, 2021). Assets of various types are central to the livelihoods of farming households as they determine what activities the households can engage in and the extent to which they can do so. Households have to make decisions on how to deploy their assets to address the numerous shocks and disturbances they face. The shocks and disturbances include risks linked to their bio-physical, economic and socio-cultural environments. Ultimately, their livelihood outcomes are mediated by a combination of assets, their context, and how resilient their livelihood strategies are to the stressors. We elaborate on these concepts in the next section.
1.1 Livelihoods, sustainable land management and food self sufficiency
Rural communities operate in a context which is characterized by shocks emanating from climate change and other unanticipated shocks (Ellis and Biggs, 2001). Such shocks may be intermittent (short-term) or chronic (long-term) and have implications on the socio-economic status of the household. Farming households depend on five types of capitals: social, natural, physical, human and financial capitals (DFID, 1999). The five capitals are crucial in developing livelihood strategies, which in turn, result in various outcomes observed at the farm level (Bebbington, 1999). The Sustainable Livelihood Framework (Figure 1) is commonly used to conceptualize the relationships between assets, context, exposure, livelihood strategies and outcomes.
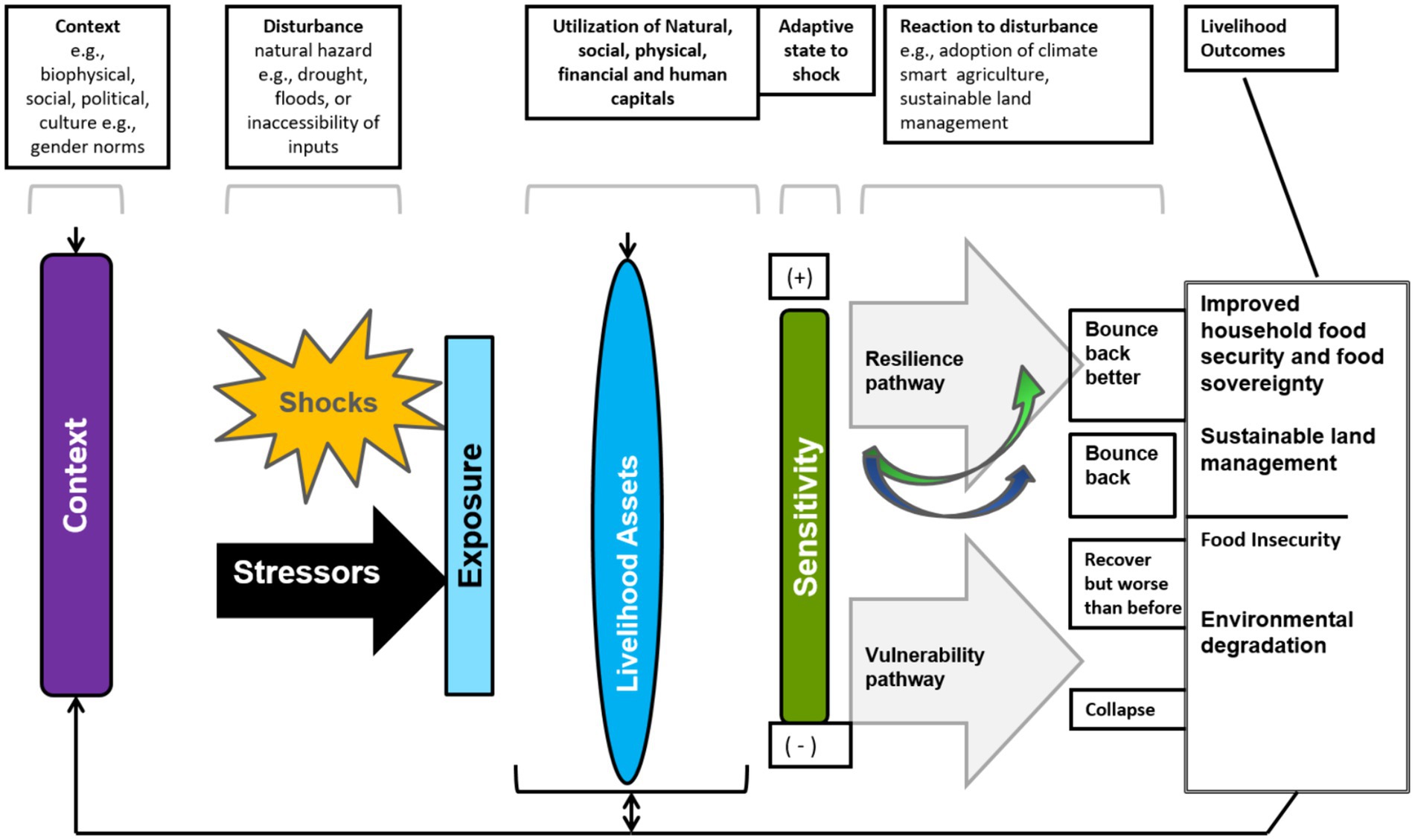
Figure 1. Sustainable livelihoods framework (adapted from DFID, 1999).
Assets are stocks of capital used to generate the means of living of the household. Essentially, they are the building blocks used by households to engage in production. They offer avenues to households to respond to shocks and stressors and determine their sensitivity to them. Upon exposure to a shock or stressor, a household may take the vulnerability or resilient pathway depending on its reaction to the disturbance. Whether it bounces back better, the same, or worse than before is affected by the context and its ability to draw upon assets. The resilient pathway leads to improved household food security, higher incomes and sustainable land management while the vulnerability pathway leads to food insecurity and environmental degradation.
The types of assets available to a household is mediated by the context. Among rural farming households of developing countries, the socio-cultural context invariably includes gender norms as a significant mediator of access to and control over assets, and consequently livelihood strategies and livelihood outcomes. Gender norms guide social relations between men and women, commonly resulting in lower access to the five different types of capital by women and higher vulnerability to shocks.
Although men and women may experience climate change and/or climate variability the same way, its effects on their agricultural production differs for various reasons including their engagement in the production of different crops and their differential access to assets needed to bounce back from disturbances (Mphande et al., 2022). Hence, women face more household food insecurity and environmental degradation than their male counterparts. Relatedly, they are less likely to adopt SLM practices. This creates a reinforcing feedback loop that leads back to less assets and increased vulnerability to shocks and stressors and food insecurity. Furthermore, the adoption of SLM is slowed down, with implications on incomes and food self-sufficiency.
Without SLM, the myriad challenges that smallholder farmers face persist, with potential for increased food insufficiency given the predicted growth in frequency and severity of extreme climatic events, and the low fertility of agricultural soils in Sub-Saharan Africa (Sánchez and Leakey, 1997). As women constitute almost half of the farmers in the region, it is important that the implications of SLM on their livelihoods are explored for increased understanding to help the design and implementation of SLM programmes that are gender responsive. Moreover, considering the existing and emerging trends in gender and rural livelihoods in developing countries, it is crucial to analyze how SLM can promote gender equality and sustainable livelihoods (Quisumbing and Pandolfelli, 2010). Academic research and practical understanding of SLM in relation to gender-responsive approaches is inadequate in many developing countries. Therefore, this study on gender-responsive SLM programmes will contribute to filling this research gap and provide valuable insights for policymakers, practitioners, and communities. It will help in identifying good practices and policies that work for promoting gender equality in rural livelihoods, and propose policy recommendations. Furthermore, the implementation of gender-responsive SLM programmes can have a positive impact on women’s access to and control over productive resources. These programmes can contribute to improving women’s economic status within households, especially in cases where agricultural land is acquired for urbanization. This article has three research questions: (1) What are the implications of participating in SLM on household incomes and food security? (2) What types of assets (social, economic, financial, natural and physical) are owned by women headed households for use in agricultural production? (3) How do these assets affect the choice of SLM practices among women?
2 Methods
2.1 Data collection
A total of 11 chiefdoms drawn from six districts in Eastern Zambia were selected for the study (Figure 2). A cross-sectional survey, during which questionnaires were administered to 761 households was conducted. Using an estimated population for the Eastern Province of 342,161 (Central Statistical Office, 2015), a confidence level of 99%, a sampling error of 5% and a 50% proportion, the sample size is adequate, as outlined in Israel (1992). The cross-sectional design provided the researchers with a snapshot view of all the study districts. This had the benefit that the data were collected during the same season from all study sites.
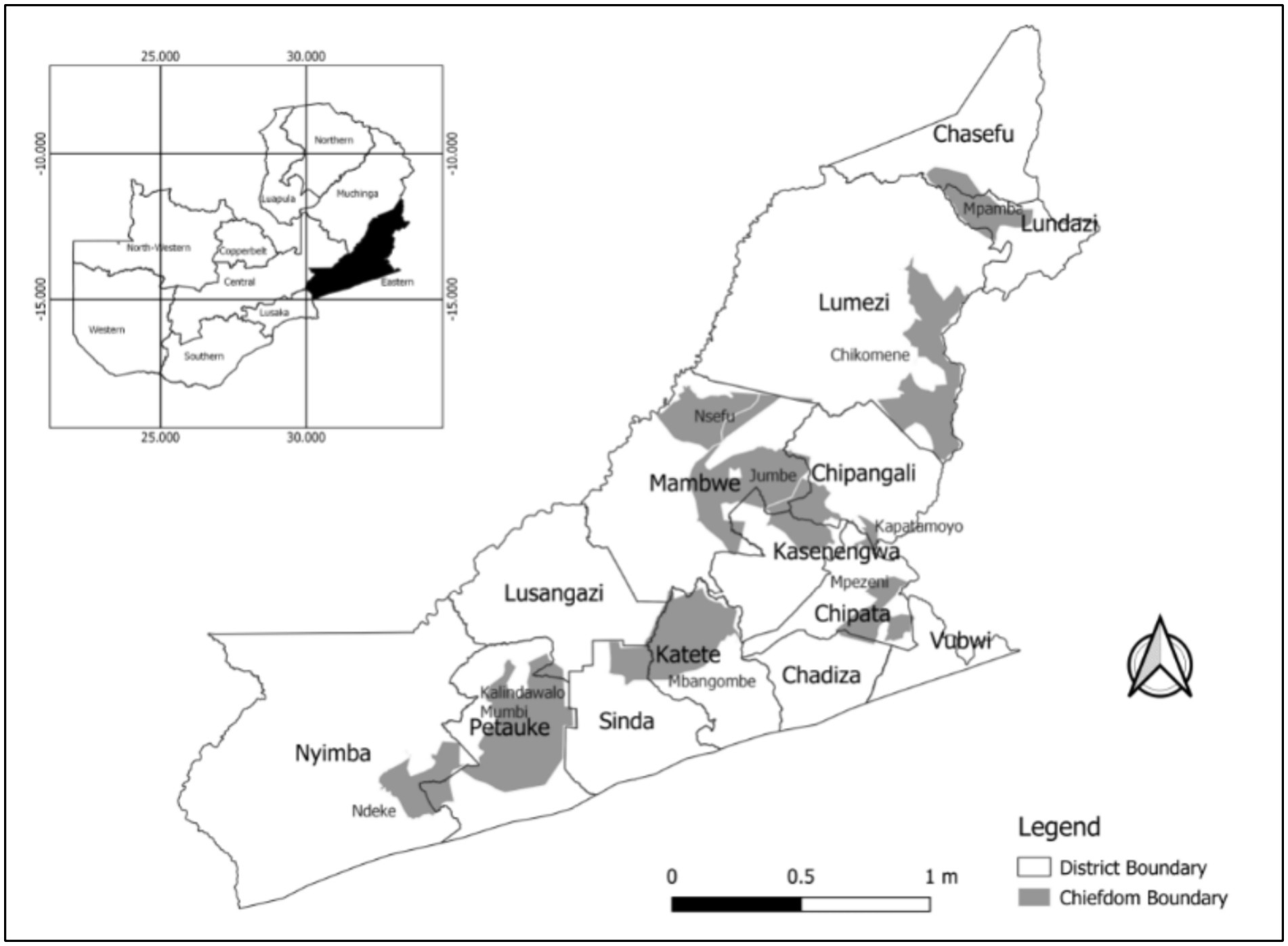
Figure 2. Map of Eastern Zambia showing study sites (Bwalya et al., 2023).
The 11 Chiefdoms were Chikomeni, Chikube, Jumbe, Kalindawalo, Kapatamoyo, Mbangombe, Mpamba, Mpenzeni, Mumbi, Ndake and Nsefu. The households were selected from lists of households that had previously participated in SLM projects in each chiefdom. The province has a rich history of SLM interventions, encompassing a wide array of practices, promoted by agricultural development actors. The common SLM practices promoted in the province are minimum tillage, leguminous crop rotations, agroforestry, intercropping, cover cropping, minimum tillage, zero tillage, terracing, use of crop residues and animal manure, cover-cropping, and soil and water conservation. Noteworthy is the high dis-adoption of SLM practices once projects that promote them end.
2.2 Model specification and data analysis
The study employs a Structural Equation System (SES) framework to investigate the intricate relationship between the adoption of SLM practices, food self-sufficiency, and household incomes within the study area. This model aims to elucidate how various socioeconomic factors influence the adoption of SLM practices and, subsequently, how these practices impact both food security and household income levels. Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) enables the simultaneous modeling and estimation of complex relationships among multiple dependent and independent variables, while accounting for measurement error in observable variable, thus providing a more precise measurement of the concepts of interest (Hair et al., 2021).
In the formulated model, the adoption of SLM practices serves as the focal point, represented as a binary variable denoted by i which denotes the household index. This binary variable takes the value of 1 if the household has adopted SLM practices and 0 if not. The adoption of SLM practices is posited to be influenced by a multitude of household-level predictors, including demographic characteristics (e.g., age, household size), educational attainment, access to credit, community membership, ownership of livestock, and land size. Mathematically, this relationship can be expressed as:
Where dichotomous Y1i takes values of 0 if the household is a non-adopter and 1 if the household has adopted SLM practices. Additionally, the model incorporates two key mediating variables: household income and food self-sufficiency. Food self-sufficiency is represented as a binary variable, denoted by indicating whether the household had sufficient food throughout the year.
Similarly, household income is dichotomized into high (1) and low (0) categories based on the sample mean household income earned per year. These mediating variables serve to capture the downstream effects of SLM adoption on household well-being. The hypothesized relationships between these variables can be conceptualized as follows:
To estimate the parameters of the model and test the proposed relationships, Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) techniques were employed. Logistic regression analysis was utilized to model the binary outcomes for the adoption of SLM practices and food self-sufficiency, and to model the binary outcome variable for household income. This model specification provides a comprehensive framework for examining the complex interplay between SLM adoption, food self-sufficiency, and household incomes, offering valuable insights into SLM practices and their socioeconomic implications for households within the study area.
2.3 Factors influencing farmers’ participation in sustainable land management—Equation 1
Table 1 provides a detailed description of the dependent and independent variables used to analyze factors influencing farmers’ participation in Sustainable Land Management (SLM) projects. The dependent variable, “Participationslm,” is binary, denoting whether farmers participated in SLM initiatives in the last 3 years. Independent variables include demographic and socio-economic factors such as gender, marital status, educational attainment, household size, and arable land size. Additionally, community involvement, access to credit, livestock and farm implement ownership, household structure, and tenure in the village are considered. These variables offer a comprehensive view of the factors affecting farmers’ engagement in SLM activities, enabling a nuanced understanding of the determinants of participation and informing targeted interventions to promote SLM practices.
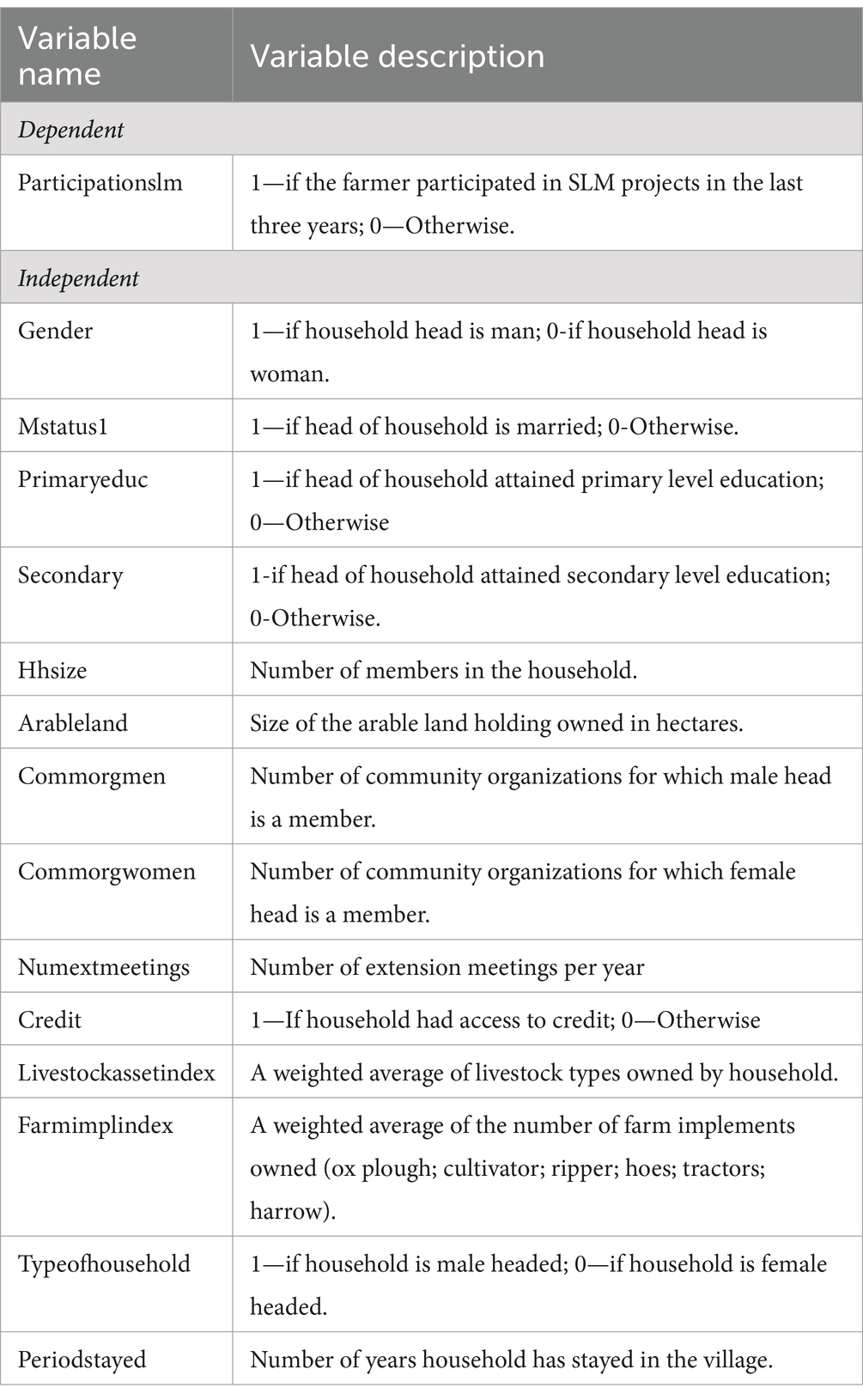
Table 1. Description of dependent and independent variables of factors affecting farmers’ participation in an SLM project.
2.4 Analysis of factors influencing household income—Equation 2
Table 2 provides a comprehensive description of the response and predictor variables utilized in Equation 2, focusing on the relationship between the five capitals and household income. The dependent variable, “Household income,” is dichotomized into high or low categories, reflecting financial capital. Independent variables encompass human, financial, social, physical, and natural capital factors. Human capital variables include gender, age of the household head, and educational attainment, with the expectation that men (gender), higher age, and higher education levels positively influence income. Financial capital is represented by access to credit, hypothesized to positively impact income. Social capital variables, such as the number of active community-based organizations for women and men, are expected to positively influence income. Physical capital factors include a weighted index of farm implements owned and a weighted index of livestock owned, both anticipated to positively impact income. Finally, natural capital is represented by the total area of arable land owned, expected to positively correlate with income. This comprehensive set of variables allows for a holistic exploration of the relationship between different forms of capital and household income, providing valuable insights for policymakers and researchers aiming to enhance household well-being and promote sustainable development.
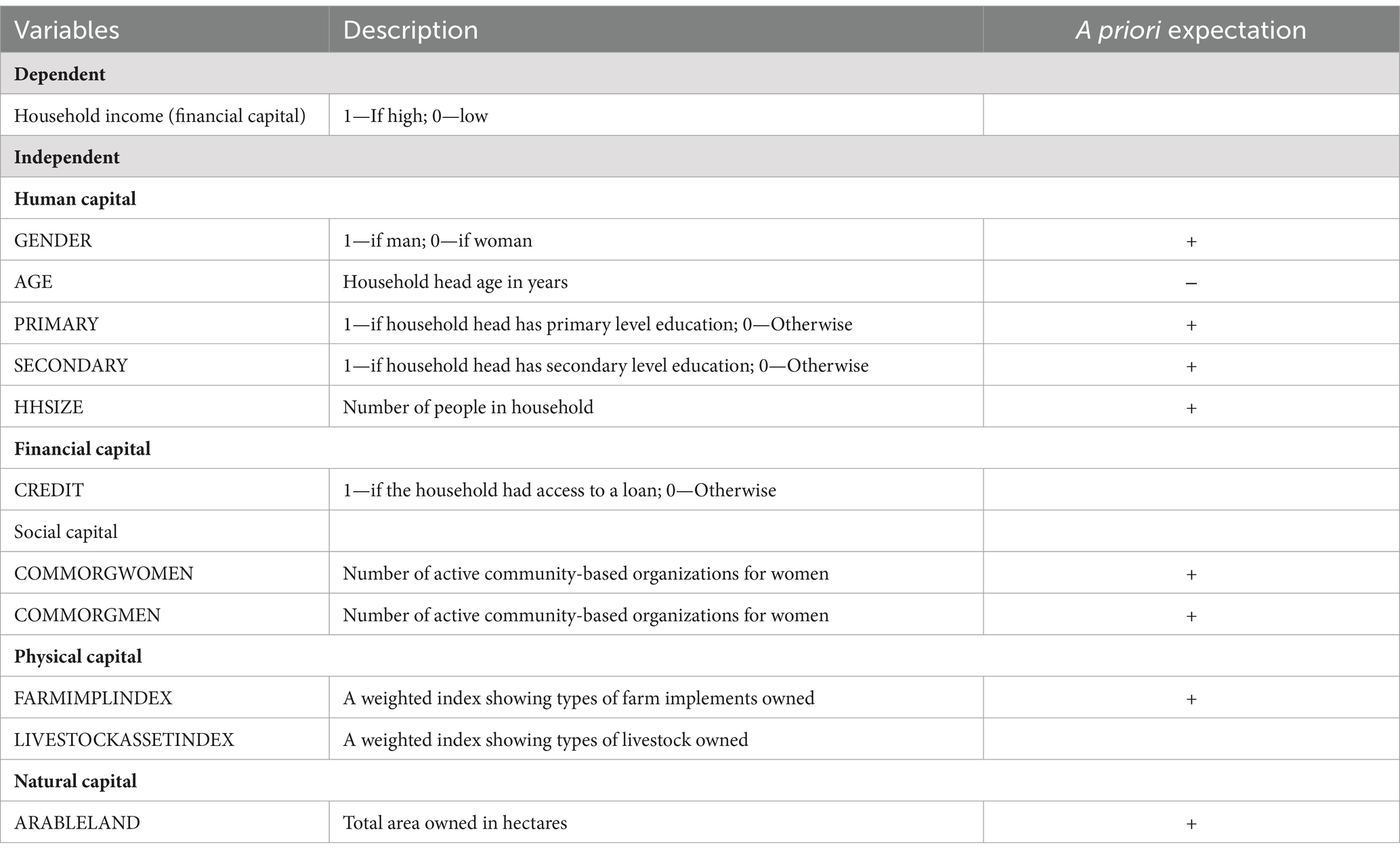
Table 2. Description of response and predictor variables in Equation 2 (Relationship between five capitals and SLM adoption).
Education has been shown to be an important variable in assimilation and understanding of different issues, concepts and themes that are related to SLM projects in the community. A priori, educated household heads would be expected to be aware and conversant of SLM projects and be more willing to participate and integrate an assortment of SLM innovations which may improve soil and water management as well as household livelihoods outcomes. Household size was used as a crude proxy variable for labour availability.
2.5 Factors influencing household food self-sufficiency—Equation 3
Table 3 provides a detailed description of the variables utilized in Equation 3, focusing on the key drivers of household food self-sufficiency. The dependent variable, “Household Food Self-Sufficiency,” is binary and indicates whether the household had enough food throughout the year. Independent variables encompass demographic, socio-economic, and agricultural factors, including gender, marital status, age of the household head, educational attainment, household size, and arable land size. Additionally, variables related to decision-making on land use, household structure, farm implement ownership, and crop diversity are considered. This comprehensive set of variables enables a nuanced exploration of the determinants of household food self-sufficiency, informing targeted interventions to enhance food security and promote SLM practices. Thus, the effect of SLM is expressed through the underlying structural correlation among the Equations 1–3.
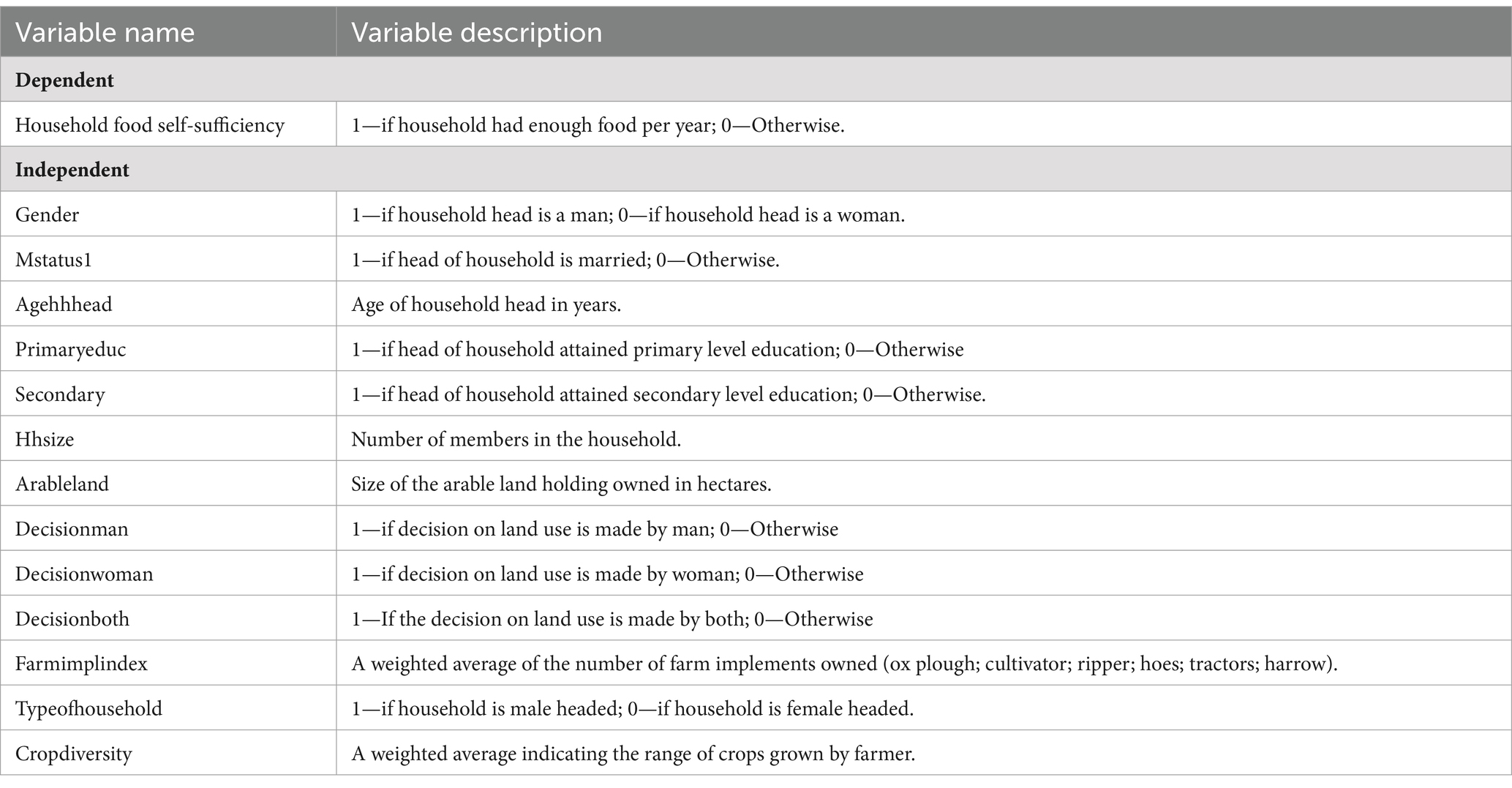
Table 3. Description of response and predictor variables in Equation 3 (key drivers of household food self-sufficiency).
2.6 Propensity score matching for SLM participants and non-participants
In many previous projects on SLM, rural communities have been encouraged to participate with the implicit assumption that their involvement will translate into benefits at the farm level. To assess whether there was a relationship between participation and incomes, propensity score matching (PSM) was used. The method entailed comparing annual incomes generated by women disaggregated by whether they had participated in an SLM initiative in the last 3 years.
PSM is used to address the potential biases that may exist in the selection of people who participate in projects. Individuals who are normally selected may be better off in terms of asset base, education levels and position in society (Rubin, 1997). Therefore, simply comparing “participants” versus “non-participants” is likely to give misleading results since the two groups may be naturally different prior to involvement in SLM. Thus, PSM estimates the average treatment effect as follows:
The counterfactual for individuals being “treated” is typically not observed in observational studies (Grilli and Rampichini, 2011). PSM therefore searches for similar non-treated individuals and compares them with similar treated cases (Caliendo and Kopeinig, 2008). In this context, the method compares individuals who participated in SLM with similar households (in terms of covariates) who did not participate in SLM, such that the difference can be largely attributed to the treatment or participation in SLM. A binary Probit model was used to generate the probability of participating in SLM projects as a function of several covariates.
2.7 Sustainable livelihood framework
The SLF was used to analyse whether the types of assets owned by the household had a relationship with the adoption, integration and use of SLM practices or not. Furthermore, the analysis considered whether there was a link between the use of these assets or capitals and food security and household incomes. The size of the farm was used as a proxy variable for natural capital. A priori, rural households that possessed larger landholdings were more likely to implement SLM practices, and thus achieve greater food security and incomes. The age, gender, educational status, and household size were used to identify the human capital element of the household. Given the patriarchal social structure, it was expected that male-headed households would have more assets, which would have a positive impact on household food security and household incomes. Membership to local community organizations was the main predictor of social capital while total livestock units, the farm implement index, and types of housing structures were used to predict physical capital. For financial capital, access to credit and remittances and annual household incomes were used.
Food security is commonly represented by an assessment of four interrelated areas (availability, access, nutrition and stability) (FAO, 2006). Due to a lack of a comprehensive set of variables, the number of months for which the household was food secure was used as a proxy for food self-sufficiency. Central to this exploration is the examination of the diverse array of assets owned by female-headed households and their utilization in agricultural production. Understanding how these assets are mobilized and leveraged by women in agricultural activities is essential for elucidating the pathways through which SLM innovations are adopted and integrated into farming practices. By analyzing the relationship between asset endowment and the uptake of SLM techniques among women, the study aims to shed light on the factors that drive or inhibit the adoption of SLM practices. Thus, the results of this study could be used as a basis for scaling-up current projects and the design of new projects.
3 Results and discussion
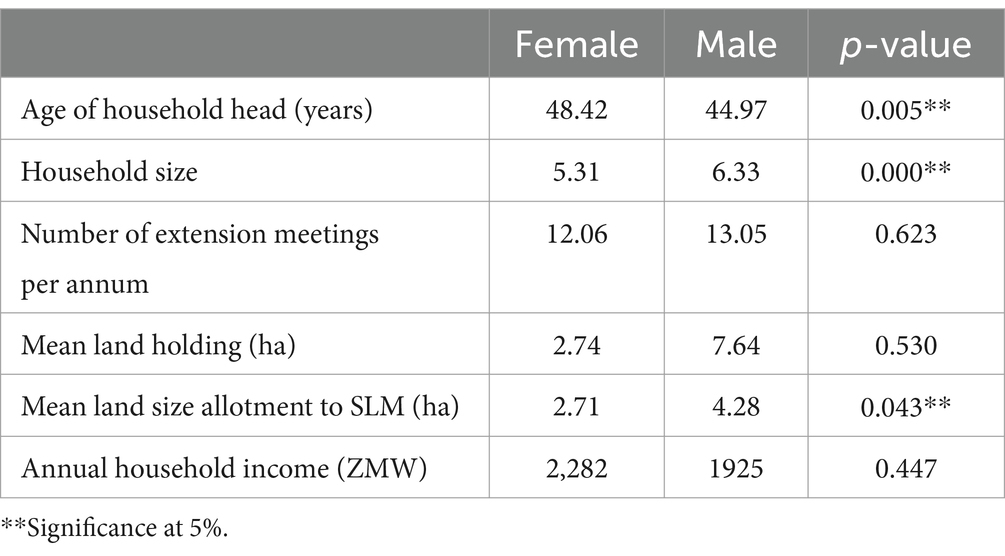
The basic socio-demographic characteristics of the male and female headed households included in the survey are shown in Table 4. Of the six descriptors, only three were statistically significant namely the age of the household head, household size and average land size allotted to SLM practices. Male headed households had a larger farms and allocated about 56% of their farms to SLM practices compared to 98% for females. This is largely attributed to the fact that the program had a deliberate focus on integrating SLM among female heads who are often not included in development initiatives.
About 78% of the household heads were married with an average of 6 members per household. Approximately 49 and 33% had primary and secondary level education, respectively. The mean age of the sample was 45 years, with a wide variation from 20 to 95 years. On average, household heads attended 12 agricultural extension meetings per year, with both men and women belonging to at least one community-based organization. The mean household income was ZMW2050.37. Only 12% of the households had received agricultural loans. About 70% of the households revealed that they had access to enough food throughout the year. Households were diversified in terms of cropping systems, with four crops on average being grown by each household.
3.1 The role of assets in income generation and food self sufficiency
The Log Likelihood ratio test (Wald Chi2 = 212.71, p < 0.05) indicated that there was a statistically significant relationship between the assets owned by the household, food self-sufficiency and household incomes. We report the role of the five types of assets or capital separately in the next sub-sections.
3.1.1 Human capital
Educational attainment had a positive effect on household income and participation in SLM (p < 0.05). Further, households headed by men were more likely to have a higher annual income compared with women headed households. The positive effect of educational attainment on household income corroborates findings from various studies emphasizing the role of education in improving livelihoods and breaking the cycle of poverty in rural areas (Vilorio, 2020). Education empowers individuals with knowledge and skills that enhance their productivity, earning potential, and ability to adopt innovative practices such as SLM (Adimassu et al., 2016). The finding that households headed by men tend to have higher annual incomes compared to those headed by women aligns with previous research from rural Zambia highlighting the mediating effect of gender in access to and control over resources (Namonje-Kapembwa and Chapoto, 2016; Ngoma-kasanda and Sichilima, 2016; Pelekamoyo and Umar, 2019; Ngoma et al., 2021). Using a nationally representative panel data set, Namonje-Kapembwa and Chapoto (2016) found that rural men in Zambia are more likely than women to access credit, own and cultivate large pieces of land, and have high productive asset value. Differences in access to education and credit between men and women have been identified as key factors contributing to agricultural income disparities in Ghana, Ethiopia and Malawi (Yokying and Lambrecht, 2020; Kang et al., 2020).
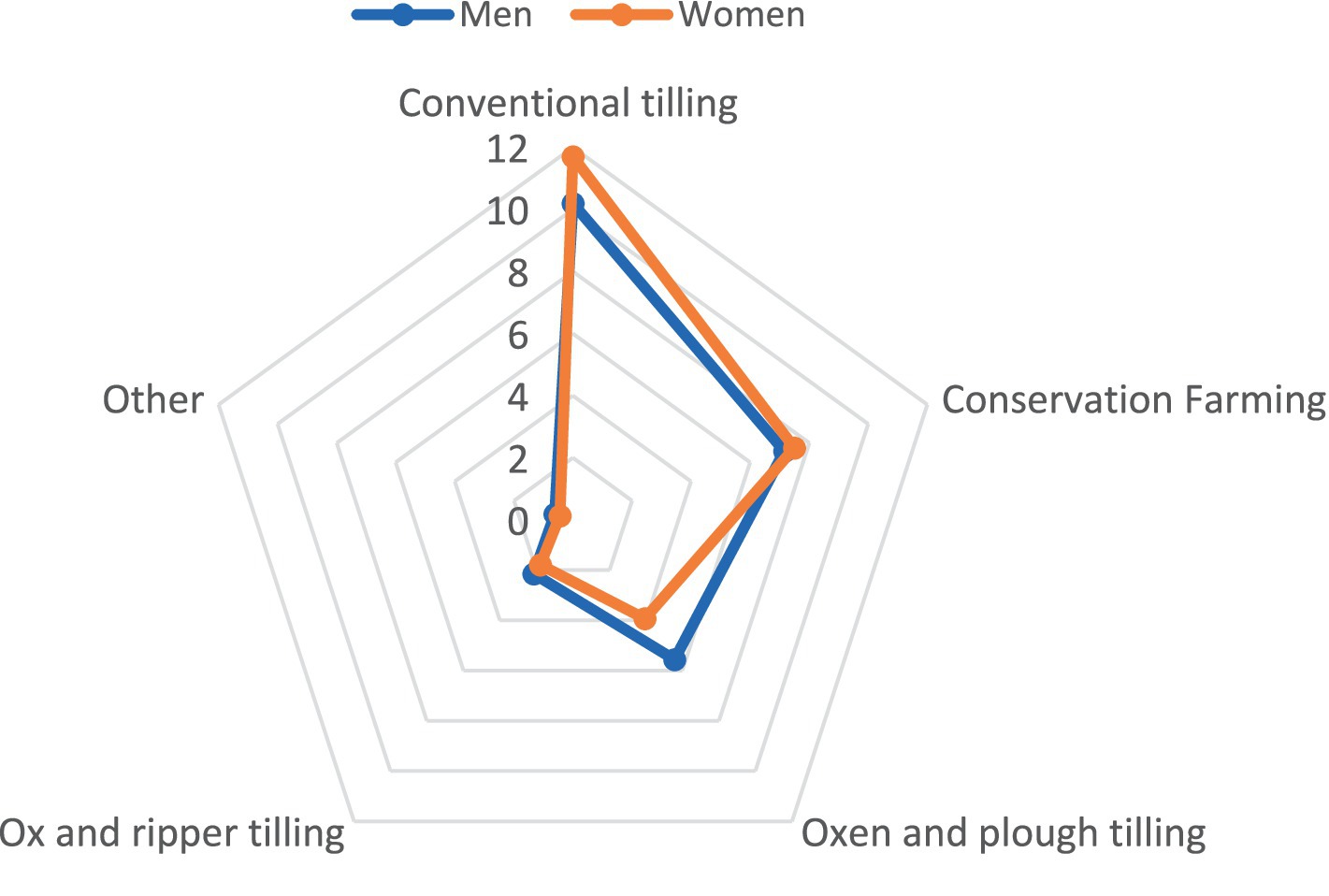
On average, each household had a total of 6 members. In addition, there were approximately three males and three females in each household. Human capital was further examined by comparing labour use by men and women in tillage activities. On average, 1 to 2 adult men were involved in providing labour for conventional tilling, ploughing with oxen or the use of a ripper. A similar pattern of labour allocation was evident for women for the same activities. A characterization of the mean number of days allocated for each of the main activities was made (Figure 3).
Women invested more days (11.7) under conventional tilling methods that relied on using hoes when compared to men (10.2). However, men allocated more labour days (5.6) to oxen and plough-based tillage compared to 3.9 days for women. Thus, women were involved in more menial and labour-intensive activities than men. Similarly, Nyanga et al. (2012) found that women were more engaged in hand-hoe based tillage while the men dominate animal draft powered tillage in their study of smallholder farmers in southern, eastern and central Zambia. In many agricultural communities, the use of manual labour and animal draught power in tillage plays a crucial role in crop production. Studies have shown that men and women have different roles and access to these sources of power, which can have various implications for their food self-sufficiency. This gender disparity in access to animal draught power can result from cultural norms and lower access to physical assets by women (Singh et al., 2013; Rao, 2012). In many societies, there are cultural norms that dictate gender roles and responsibilities. Women are often assigned household chores and caregiving tasks, while men take on roles that involve decision-making and control over productive resources (Pelekamoyo and Umar, 2019). These cultural norms restrict women’s access to physical assets such as land and livestock, which are essential for utilizing animal draught power in tillage. As a result, women are left to rely more on manual labour for tillage and other farming activities (Peterman et al., 2014).
3.1.2 Natural capital
The average land holding was 6.6 hectares. This is lower than the national average for rural households of 14.1 hectares but comparable for the average for the Eastern province which is 5 hectares (IAPRI, 2019). Decisions on land use were mostly made by men (55%). The probability of earning more income was higher amongst households with smaller farm sizes. The inverse relationship between farm size and household income, where smaller farms are associated with higher probabilities of earning more income, is consistent with the concept of sustainable agricultural intensification. Sustainable agricultural intensification focuses on maximizing productivity and profitability on limited land resources through efficient use of inputs, diversification of crops, and adoption of sustainable farming practices (Reich et al., 2021). Smallholder farmers often employ intensive farming methods to optimize yields per unit of land, contributing to higher incomes despite limited land holdings (Vanlauwe et al., 2014; Fuchs et al., 2019; Diao et al., 2023).
3.1.3 Physical capital
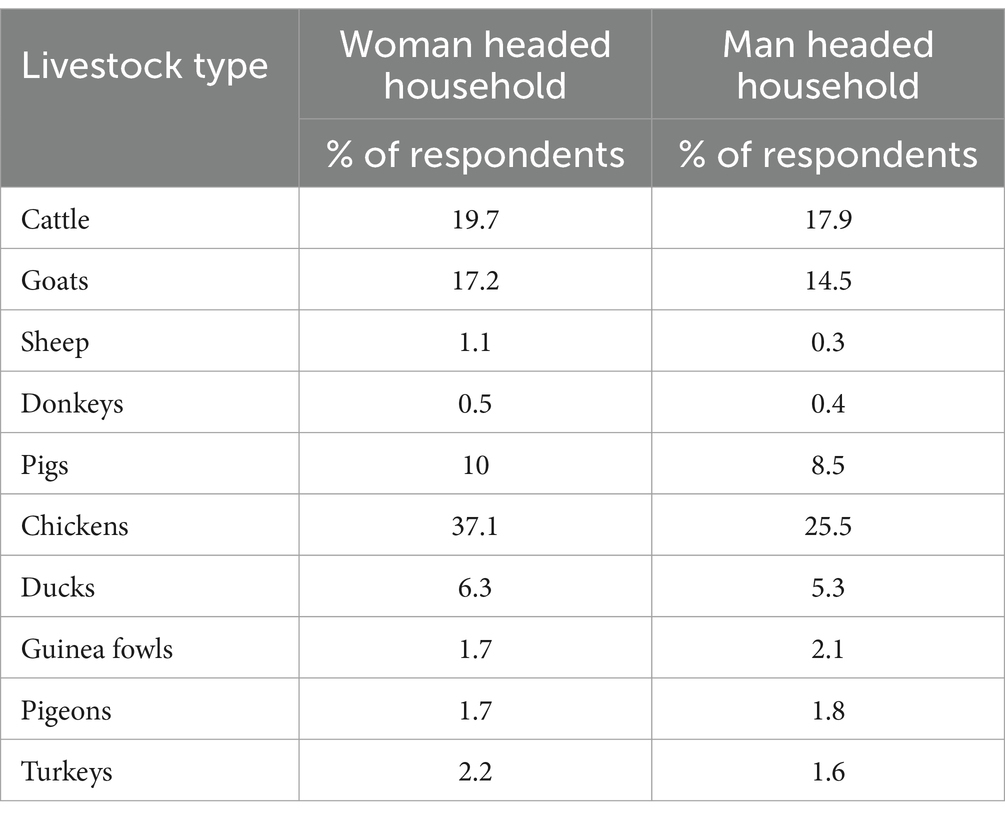
Livestock and farming implements were used to represent physical capital available to the farming households. Livestock rearing was less common than crop production with only about 20 and 18% of woman headed and man headed households, respectively, engaged in cattle production (Table 5) and lower percentages for other livestock types, except for chickens.
These percentages are lower than the national average which are 36, 43 and 16% for cattle, goats and pigs, respectively, for households headed by men and 23, 36 and 13% for cattle, goats and pigs for households headed by women. Noteworthy from our results are the slightly higher percentages of women headed households owning cattle, goats, pigs and chickens. We attribute this result to the recent trend by agricultural development interventions of targeting women headed households in projects that increasing include provision of such livestock types. While the numbers of livestock owned by women headed households are lower (6 for cattle and goats) than those for the men (8 for cattle and goats) (IAPRI, 2019), this trajectory of more women headed households owning livestock is likely to improve their household food self-sufficiency and incomes. To achieve this however, women’s access to animal draught powered implements such as ploughs, rippers, cultivators and ox-carts would have to be improved, from the very low current levels.
Livestock asset ownership and crop diversity were important drivers of household food self-sufficiency (p < 0.05). A previous study from Southern Zambia has similarly reported livestock incomes and ownership as important in moving towards household food Security (Nkomoki et al., 2018). Livestock assets are essential to the rural poor for affordable nutrition, animal draught power and improving soil health through animal manure amendments (Shackleton et al., 2005; Erdaw, 2023).
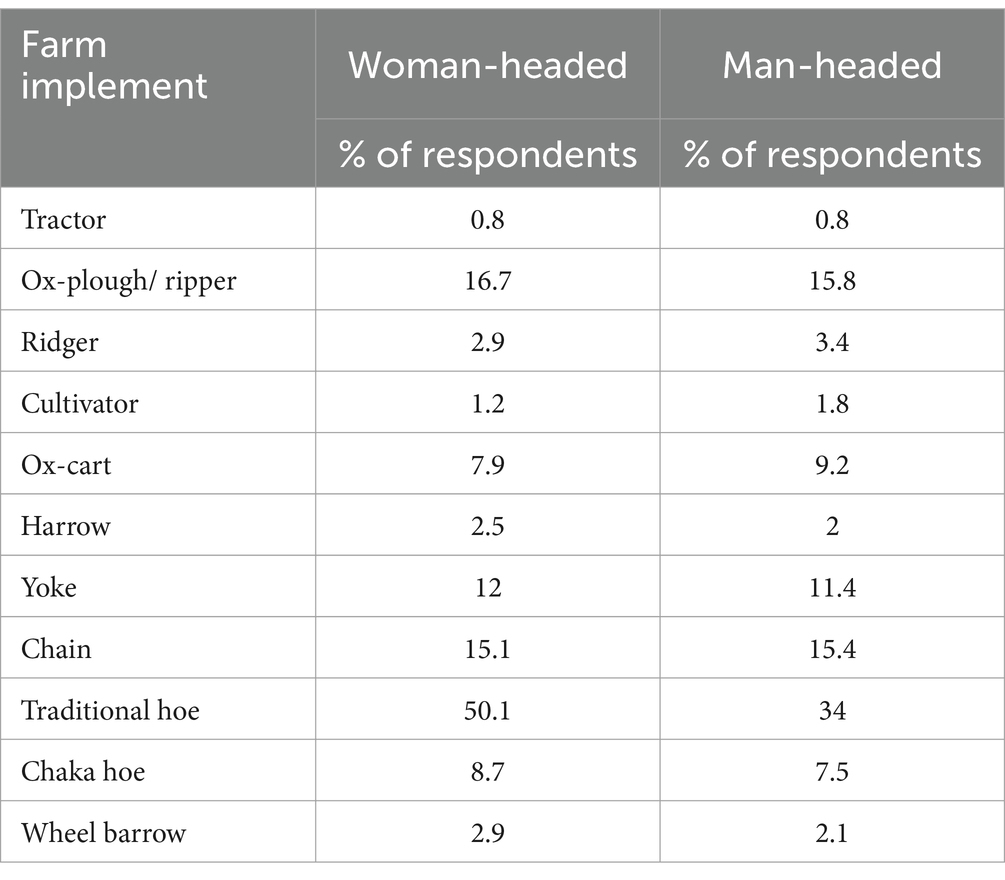
The most commonly owned farming implements were the traditional hoe and ploughs or rippers (Table 6).
The low ownership of animal draught powered implements has implications on the performance of agricultural activities such as tillage, weeding and transportation. Inadequate access to animal draught power limits the maximum land that farming households can till at the start of the farming season and delays farming operations for those that depend on borrowing such farm implements, with implications on crop yields and household food security.
3.1.4 Social capital
The social capital variables of local community membership by men and women had a statistically significant effect on participation in SLM initiatives and on accessing credit. In Zambia, provision of agricultural extension services to farmers is commonly done through groups. Thus, household members belonging to various community organizations are more likely to participate in training on SLM and subsequently adopt it, with cascading effects. For instance, community organization membership can provide networking opportunities and connections which may empower individuals or groups with various business ventures to enhance income generation, and nutritional programmes to address issues of food insecurity (Nkomoki et al., 2018). Further, such membership potentially leads to higher farm yields and household income (Ma and Abdulai, 2016). However, participation in community organizations is not costless. Requirements of membership fees and limits on the number of household members that can belong to a community organization curtails participation by the poorest farmers and by women. Community organizations commonly prescribe that only one household member can belong to the organization. It is invariably the man, culturally considered the indisputable household head who joins, depriving other household members of the benefits derived from participation.
3.1.5 Financial capital
3.1.5.1 Influence of participation in SLM projects on women’s incomes
On average, the probability of participating in an SLM project in the last 3 years was 66%, with a minimum of 6% and a maximum of 99%. Generally, there was overlap between treated and untreated cases indicating that there was common support (see Figure 4). Table 7 indicates the summary of the p-scores.
Furthermore, the T-tests also showed that there were no significant differences between the two groups except for the number of extension meetings, age of household head and household size (Table 8).
The results of the comparison between participants and non-participants is indicated in Table 9.
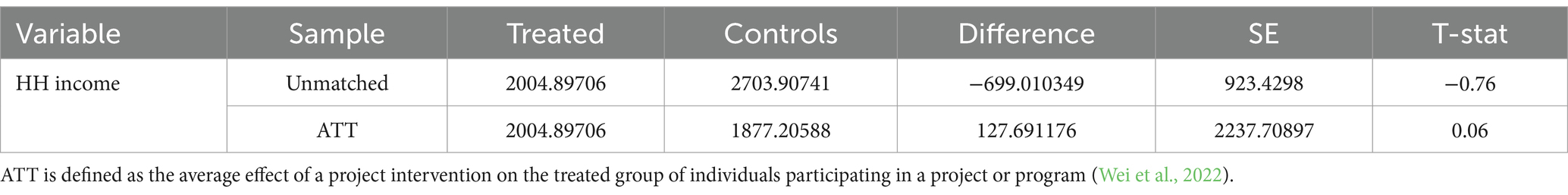
Generally, women that participated in SLM projects earned ZMW2004.89 compared to ZMW1877.21 among similar non-participating women. Thus, the average treatment effect (ATT) was positive indicating that there is an incentive for women to participate emanating from greater income streams (ZMW127.69). Clearly, the bias can be observed prior to matching of cases as the amount earned among participants (ZMW2004.89) was lower than that of non-participants (ZMW2703.91). This underscores the importance of matching across the two sub-groups.
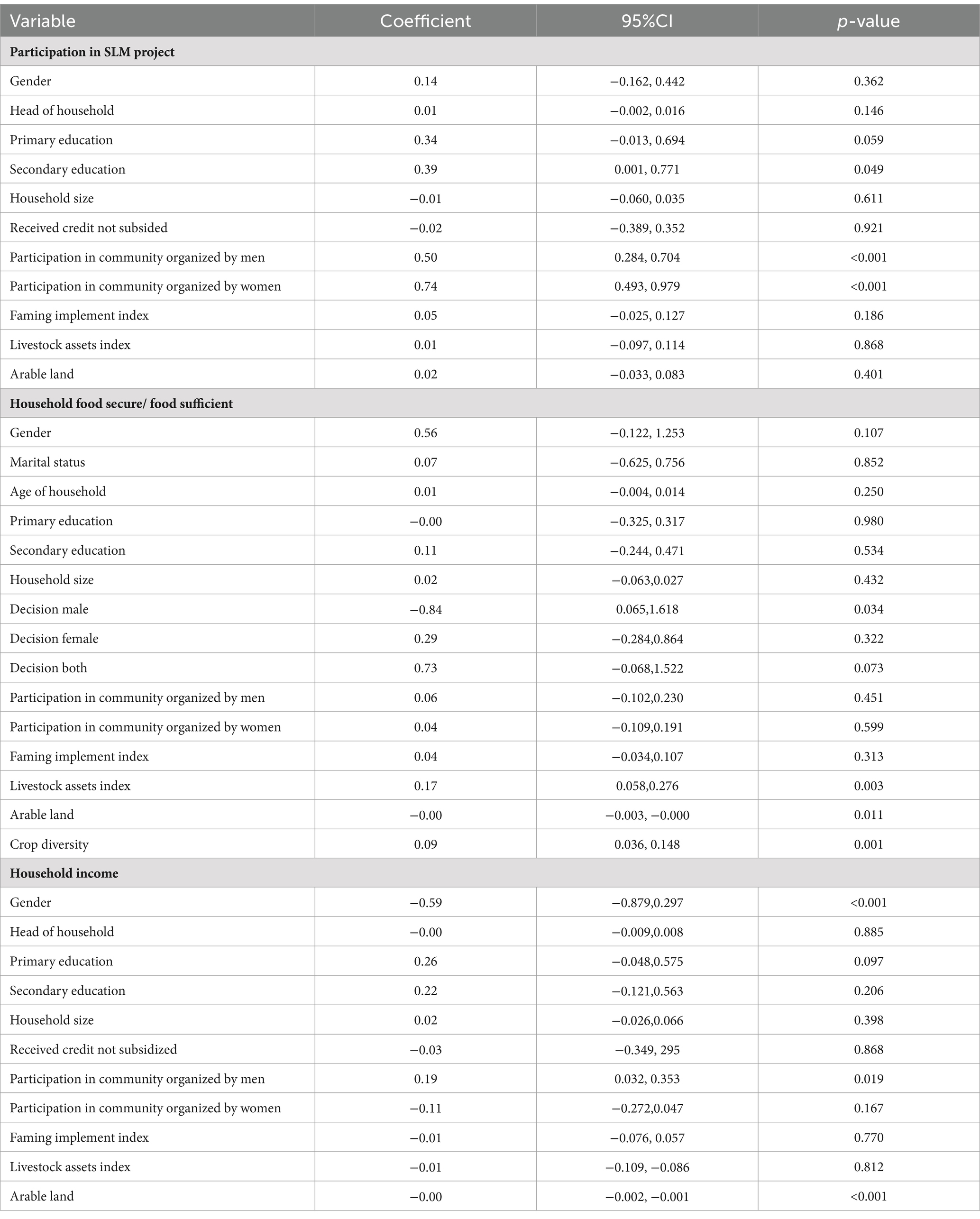
The mixed-process regression analysis revealed significant findings regarding the factors influencing farmers’ participation in SLM, household food security, and household income (Table 10). The Wald chi-square test statistic (37) yielded a value of 212.71, indicating a significant overall effect of the predictors on the outcomes. The log pseudo likelihood value of −909.39535 suggests a good fit of the model to the data. Additionally, the error terms atanhrh_12, atanhrh_13, and atanhrh_23 values of p = 0.898, p = 0.342, and p = 0.161, respectively, indicate the non-significant relationships between pairs of variables. For the participation in SLM projects, several significant predictors emerged. Participation in community organizations organized by men and women significantly influenced participation in SLM projects, with coefficients of 0.50 and 0.74, respectively (p < 0.001). Moreover, having secondary education (p = 0.049) and primary education (p = 0.059) showed significant positive associations with participation in SLM projects. Other factors such as gender, marital status, household size, access to credit, and ownership of farm implements and livestock did not show significant associations with participation in SLM projects.
Regarding household food security or food self-sufficiency, livestock assets index (p = 0.003), arable land (p = 0.011), and crop diversity (p = 0.001) were found to be significant predictors. Decision-making by men (p = 0.034) also significantly influenced household food security, while decision-making by both men and women showed a marginally significant association (p = 0.073). Other variables such as gender, marital status, age of household head, education levels, household size, and participation in community organizations did not show significant associations with household food security. In terms of household income, significant predictors included gender (p < 0.001), participation in community organizations organized by men (p = 0.019), and arable land (p < 0.001). Livestock assets index (p = 0.812) and participation in community organizations organized by women (p = 0.167) were not significant predictors of household income. Other factors such as educational attainment, household size, and ownership of farm implements did not show significant associations with household income.
3.2 Interplay of socio-economic factors and agricultural practices on farmers’ participation, food security, and income
The mixed-process regression analysis provides valuable insights into the complex interplay of factors influencing farmers’ participation in SLM projects, household food security, and household income, offering implications for policy and interventions aimed at promoting sustainable agricultural practices and enhancing rural livelihoods. These findings are consistent with previous studies that have highlighted the importance of various personal, economic, socio-institutional, and biophysical attributes in farmers’ decisions about the adoption of SLM practices (e.g., Gedefaw et al., 2018). Ensuring household food security is a crucial aspect of agricultural development and sustainable agricultural intensification. This requires understanding the factors that contribute to food security and identifying factors that can help improve it. The results from the study indicate that several factors have a significant influence on household food security. These factors include the livestock assets index, arable land, and crop diversity. This suggests that households with more livestock assets, larger amounts of arable land, and diverse crops are more likely to have food security.
Furthermore, the study found that decision-making by men significantly influenced household food security. This implies that households where men play a prominent role in decision-making are more likely to have better food security, as argued by Mwangi et al. (2020). These findings highlight the importance of livestock assets, arable land, and crop diversity in ensuring household food security. This study also examined predictors of household income and notes that gender, participation in community organizations by men, and arable land are significant predictors of household income. Other studies have suggested that promoting gender and participation in community organizations can have positive impacts on both household food security and income (Gazuma, 2018; Das and Singh, 2020).
4 Conclusion
Our study focuses on the critical intersection of SLM practices and their implications on household incomes and food self-sufficiency, particularly highlighting the role of women. Our analysis has revealed several significant insights. Firstly, SLM practices play a substantial role in shaping household incomes and food security outcomes. This highlights the importance of adopting environmentally friendly and sustainable farming techniques that not only conserve natural resources but also contribute to economic prosperity and food security for rural households. The mediating role of assets in pathways towards resilience and sustainable livelihoods is echoed. Human capital, in the form of education had a positive effect on income and participation in SLM. Households headed by men were more likely to have higher incomes compared to those headed by women. Households with less natural capital, that is, smaller land parcels earned more income from the land, through intensification. Access to motorized and animal draught power was low for both man and woman headed households, with a slightly higher percentage of women headed households owning cattle, goats and chickens but still more dependent on manual tillage and weeding. Men had more social capital as revealed by their higher participation in community organization, which positively impacted participation in SLM while women’s participation in SLM increased their incomes.
Secondly, our findings emphasize the disproportionate impact of SLM practices on women. Despite their pivotal role in agricultural production and food security, women often encounter systemic barriers that restrict their access to resources and decision-making authority within the agricultural sector. Addressing gender disparities and promoting women’s inclusion in SLM initiatives are crucial steps towards achieving climate resilient, equitable and sustainable livelihoods. Thirdly, our study highlights the necessity for targeted interventions and policy measures aimed at empowering women in agriculture. This includes initiatives to enhance women’s access to education, financial resources, and agricultural extension services, as well as promoting their involvement in decision-making processes related to SLM. Ultimately, our findings emphasize the transformative potential of SLM practices in fostering climate resilience, incomes, food security, and gender equality in rural communities. We recommend further research into the mediating effects of women empowerment programmes on SLM adoption, livestock ownership, and long term household food sufficiency.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by ERES Converge – a Nationally Accredited Review Board. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
BB: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. EM: Data curation, Formal analysis, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Resources. BC: Data curation, Formal analysis, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Software.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the World Bank Group and TERRAFRICA.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdulai, A. N. (2016). Impact of conservation agriculture technology on household welfare in Zambia. Agric. Econ. 47, 729–741. doi: 10.1111/agec.12269
Abegunde, V. O., Sibanda, M., and Obi, A. (2019). The dynamics of climate change adaptation in sub-Saharan Africa: a review of climate-smart agriculture among small-scale farmers. Climate 7:132. doi: 10.3390/cli7110132
Abideen, A. Z., Sundram, V. P. K., and Sorooshian, S. (2023). Scope for sustainable development of small holder farmers in the palm oil supply chain—a systematic literature review and thematic scientific mapping. Logistics 7:6. doi: 10.3390/logistics7010006
Adimassu, Z., Langan, S., and Johnston, R. (2016). Understanding determinants of farmers’ investments in sustainable land management practices in Ethiopia: review and synthesis. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 18, 1005–1023. doi: 10.1007/s10668-015-9683-5
Ajayi, O. C., Franzel, S., Kuntashula, E., and Kwesiga, F. (2003). Adoption of improved fallow technology for soil fertility management in Zambia: empirical studies and emerging issues. Agrofor. Syst. 59, 317–326. doi: 10.1023/B:AGFO.0000005232.87048.03
Andersson Djurfeldt, A., Djurfeldt, G., Hillbom, E., Isinika, A. C., Joshua, M. D. K., Kaleng’A, W. C., et al. (2019). Is there such a thing as sustainable agricultural intensification in smallholder-based farming in sub-Saharan Africa? Understanding yield differences in relation to gender in Malawi, Tanzania and Zambia. Dev. Stud. Res. 6, 62–75. doi: 10.1080/21665095.2019.1593048
Andika, A., Sari, F. A., Salam, R., Jufri, S. N., and Paradita, A. (2020). Sustainable agriculture: case study in Barebbo Village, bone regency. J. La Lifesci 1, 1–5. doi: 10.37899/journallalifesci.v1i1.30
Antwi-Agyei, P., Dougill, A., Fraser, E., and Stringer, L. (2013). Characterizing the nature of household vulnerability to climate variability: empirical evidence from two regions of Ghana. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 15, 903–926. doi: 10.1007/s10668-012-9418-9
Bebbington, A. (1999). Capitals and capabilities: a framework for analyzing peasant viability, rural livelihoods and poverty. World Dev. 27, 2021–2044.
Bolliger, A. (2007) Is zero-till an appropriate agricultural alternative for disadvantaged smallholders of South Africa? A study of surrogate systems and strategies, smallholder sensitivities and soil glycoproteins. PhD Thesis. University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, p. 67.
Branca, G., Lipper, L., McCarthy, N., and Jolejole, M. C. B. (2013). Food security, climate change, and sustainable land management. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 33, 635–650. doi: 10.1007/s13593-013-0133-1
Bwalya, B., Mutandwa, E., and Chiluba, B. C. (2023). Awareness and use of sustainable land management practices in smallholder farming systems. Sustain. For. 15:14660. doi: 10.3390/su152014660
Caliendo, M., and Kopeinig, S. (2008). Some practical guidance for the implementation of propensity score matching. J. Econ. Surv. 22, 31–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-6419.2007.00527.x
Central Statistical Office (2015). Living conditions monitoring survey report (LCMS). Lusaka, Zambia: CSO.
Cordingley, J. E., Snyder, K. A., Rosendahl, J., Kizito, F., and Bossio, D. (2015). Thinking outside the plot: addressing low adoption of sustainable land management in sub-Saharan Africa. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 15, 35–40. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2015.07.010
Das, J., and Singh, A. (2020). Women empowerment and its impact on livelihood and Food Security of households: a review. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 39, 19–28. doi: 10.9734/cjast/2020/v39i4031108
DFID (1999). Sustainable livelihoods governance sheets. London: Department of International Development.
Diao, X., Reardon, T., Kennedy, A., DeFries, R. S., Koo, J., Minten, B., et al. (2023). The future of small farms: innovations for inclusive transformation. In J. Braunvon, K. Afsana, L. O. Fresco, and M. H. A. Hassan (Eds.), Science and innovations for food systems transformation (pp. 191–205). Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing.
Ellis, F., and Biggs, S. (2001). Evolving themes in rural development 1950s-2000s. Dev. Policy Rev. 19, 437–448. doi: 10.1111/1467-7679.00143
Erdaw, M. M. (2023). Contribution, prospects and trends of livestock production in sub-Saharan Africa: a review. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 21. doi: 10.1080/14735903.2023.2247776
FAO (2006). Food Security. Policy brief. June 2006 Issue 2. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
FAO (2017). Sustainable land management (SLM) in practice in the Kagera Basin. Lessons learned for scaling up at landscape level – results of the Kagera transboundary agro-ecosystem management project (Kagera TAMP). Rome, Italy: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 440.
Fowler, R., and Rockstrom, J. (2001). Conservation tillage for sustainable agriculture: an agrarian revolution gathers momentum in Africa. Soil Tillage Res. 61, 93–108.
Fuchs, L. E., Orero, L., Namoi, N., and Neufeldt, H. (2019). How to effectively enhance sustainable livelihoods in smallholder systems: a comparative study from Western Kenya. Sustain. For. 11:1564. doi: 10.3390/su11061564
Gedefaw, M., Denghua, Y., Hao, W., Alemu, B., Chanie, M., Agitew, G., et al. (2018). Evaluation of adoption behavior of soil and water conservation practices in the Simein Mountain National Park, Highlands of Ethiopia. Cogent Food Agric. 4. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2018.1513782
Gazuma, E. G. (2018). An empirical examination of the determinants of Food insecurity among rural farm households: evidence from Kindo Didaye District of southern Ethiopia. Bus. Econ. J. 9. doi: 10.4172/2151-6219.1000345
Grilli, L., and Rampichini, C. (2011) Propensity scores for the estimation of average treatment effects in observational studies. Training Sessions on Causal Inference. June 28–29, 2011. University of Bristol, Bristol.
Hair, J. F., Hult, G., Tomas, M., Ringle, C. M., Sarstedt, M., Danks, N. P., et al. (2021). “An introduction to structural equation modeling” in Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) using R: A workbook. eds. J. F. Hair, G. T. M. Hult, C. M. Ringle, M. Sarstedt, N. P. Danks, and S. Ray (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 1–29.
Hossain, A. M., Reza, I. M., Rahman, S., and Kayes, I. (2012). “Climate change and its impacts on the livelihoods of the vulnerable people in the southwestern coastal zone in Bangladesh” in Climate change and the sustainable use of water resources. Climate change management. ed. W. Leal Filho (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer).
Huq, N., Hugé, J., Boon, E., and Gain, A. K. (2015). Climate change impacts in agricultural communities in rural areas of coastal Bangladesh: a tale of many stories. Sustain. For. 7, 8437–8460. doi: 10.3390/su7078437
IAPRI (2019). Rural Agricultural Livelihoods Survey Report. Lusaka, Zambia: Indaba Agricultural Research and Policy Institute.
Kang, M., Schwab, B., and Yu, J. (2020). Gender differences in the relationship between land ownership and managerial rights: implications for intra-household farm labor allocation. World Dev. 125:104669. doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2019.104669
Kassie, M., Teklewold, H., Jaleta, M., Marenya, P., and Erenstein, O. (2015). Understanding the adoption of a portfolio of sustainable intensification practices in eastern and southern Africa. Land Use Policy 42, 400–411. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2014.08.016
Khonje, M. G., Manda, J., Mkandawire, P., Tufa, A. H., and Alene, A. D. (2018). Adoption and welfare impacts of multiple agricultural technologies: evidence from eastern Zambia. Agric. Econ. 49, 599–609. doi: 10.1111/agec.12445
Krah, K., Michelson, H., Perge, E., and Jindal, R. (2019). Constraints to adopting soil fertility management practices in Malawi: a choice experiment approach. World Dev. 124:104651. doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2019.104651
Li, H., Qi, M., and Han, S. (2016). Understanding the effects of trust and risk on individual behavior toward social media platforms: a meta-analysis of the empirical evidence. Comput. Hum. Behav. 56, 34–44. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2015.11.011
Ma, W., and Abdulai, A. (2016). Does cooperative membership improve household welfare? Evidence from apple farmers in China. Food Policy 58, 94–102. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2015.12.002
Manda, J., Alene, A. D., Gardebroek, C., Kassie, M., and Tembo, G. (2015). Adoption and impacts of sustainable agricultural practices on maize yields and incomes: evidence from rural Zambia. J. Agric. Econ. 67, 130–153. doi: 10.1111/1477-9552.12127
Mango, N., Siziba, S., and Makate, C. (2017). The impact of adoption of conservation agriculture on smallholder farmers’ food security in semi-arid zones of southern Africa. Agric. Food Secur. 6:32. doi: 10.1186/s40066-017-0109-5
Maponya, P. (2021). An assessment of smallholder Farmer’s status in the Capricorn District in Limpopo Province, South Africa. Circ. Econ. Sustainability 1, 1401–1411. doi: 10.1007/s43615-021-00049-6
Marques, M. J., Schwilch, G., Lauterburg, N., Crittenden, S., Tesfai, M., Stolte, J., et al. (2016). Multifaceted impacts of sustainable land Management in Drylands: a review. Sustain. For. 8:177. doi: 10.3390/su8020177
McElwee, P., Calvin, K., Campbell, D., Cherubini, F., Grassi, G., Коротков, В. Н., et al. (2020). The impact of interventions in the global land and agri-food sectors on Nature’s contributions to people and the UN sustainable development goals. Glob. Chang. Biol. 26, 4691–4721. doi: 10.1111/gcb.15219
Motavalli, P., Nelson, K., Udawatta, R., Jose, S., and Bardhan, S. (2013). Global achievements in sustainable land management. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 1, 1–10. doi: 10.1016/S2095-6339(15)30044-7
Mphande, E., Umar, B. B., and Kunda-Wamuwi, C. F. (2022). Gender and legume production in a changing climate context: experiences from Chipata, Eastern Zambia. Sustainability 14:11901. doi: 10.3390/su141911901
Mugwe, J., Mugendi, D., Mucheru-Muna, M., Merckx, R., Chianu, J., and Vanlauwe, B. (2009). Determinants of the decision to adopt integrated soil fertility management practices by smallholder farmers in the central highlands of Kenya. Exp. Agric. 45, 61–75. doi: 10.1017/s0014479708007072
Müller, C., Cramer, W., Hare, W. L., and Lotze-Campen, H. (2011). Climate change risks for African agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 4313–4315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1015078108
Mutyasira, V., Hoag, D., Pendell, D., and Yildiz, F. (2018). The adoption of sustainable agricultural practices by smallholder farmers in Ethiopian highlands: an integrative approach. Cogent Food Agric. 4. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2018.1552439
Mwangi, V., Owuor, S., Kiteme, B., Giger, M., Jacobi, J., and Kirui, O. K. (2020). Linking household Food Security and Food value chains in north west Mt. Kenya. Sustainability 12:4999. doi: 10.3390/su12124999
Namonje-Kapembwa, T., and Chapoto, A. (2016). Improved agricultural technology adoption in Zambia: are women farmers being left behind? Working paper no. 106. Lusaka, Zambia: Indaba Agricultural Research Institute.
Ng’ang’a, S. K., Miller, V., and Girvetz, E. H. (2021). Is investment in climate-smart-agricultural practices the option for the future? Cost and benefit analysis evidence from Ghana. Heliyon 7:e06653. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06653
Ngoma, H., Finn, A., Kabisa, M., Machina, H., and Kuteya, A. N. (2021). Can agricultural subsidies reduce gendered productivity gaps? Panel data evidence from Zambia. Dev. Policy Rev. 39, 303–323.
Ngoma-Kasanda, E., and Sichilima, T. (2016). Gender and decision making in agriculture: A case study of the smallholder groundnuts sector in Zambia. Lusaka, Zambia: Musika Development Initiatives.
Nkomoki, W., Bavorova, M., and Banout, J. (2018). Adoption of sustainable agricultural practices and food security threats: effects of land tenure in Zambia. Land Use Policy 78, 532–538. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2018.07.021
Nyanga, P. H., Johnsen, P. H., and Kalinda, T. H. (2012). Gendered impacts of conservation agriculture and paradox of herbicide use among smallholder farmers. Int. J. Technol. Dev. Stud. 3, 1–24.
Oduniyi, O. S., and Tekana, S. S. (2021). The impact of sustainable land management practices on household welfare and determinants among smallholder maize farmers in South Africa. Land 10:508. doi: 10.3390/land10050508
Ojiem, J. O., de Ridder, N., Vanlauwe, B., and Giller, K. E. (2006). Socio-ecological niche: a conceptual framework for integration of legumes in smallholder farming systems. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 4, 79–93. doi: 10.1080/14735903.2006.9686011
Pelekamoyo, J., and Umar, B. B. (2019). Access to and control over agricultural labor and income in smallholder farming households: a gendered look from Chipata, Eastern Zambia. J. Gend., Agric. Food Secur. 4, 42–57.
Peterman, A., Behrman, J. A., and Quisumbing, A. R. (2014). A review of empirical evidence on gender differences in nonland agricultural inputs, technology, and services in developing countries. Springer eBooks, 145–186. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-8616-4_7
Quisumbing, A. R., and Pandolfelli, L. (2010). Promising approaches to address the needs of poor female farmers. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0305750X09001806
Rao, N. (2012). Male ‘providers’ and female ‘housewives’: a gendered co-performance in rural North India. Dev. Chang. 43, 1025–1048. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7660.2012.01789.x
Reich, J., Paul, S. S., and Snapp, S. S. (2021). Highly variable performance of sustainable intensification on smallholder farms: a systematic review. Glob. Food Sec. 30:100553. doi: 10.1016/j.gfs.2021.100553
Rubin, D. B. (1997). Estimating causal effects from large data sets using propensity scores. Ann. Intern. Med. 127, 757–763. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-127-8_part_2-199710151-00064
Sánchez, P. A., and Leakey, R. R. (1997). Land use transformation in Africa: three determinants for balancing food security with natural resource utilization. Eur. J. Agron. 7, 15–23. doi: 10.1016/s1161-0301(97)00034-8
Shackleton, C., Shackleton, S., Netshiluvhi, T., and Mathabela, F. (2005). The contribution and direct-use value of livestock to rural livelihoods in the Sand River catchment, South Africa. Afr. J. Range Forage Sci. 22, 127–140. doi: 10.2989/10220110509485870
Singh, K. M., Meena, M. L., Kumar, A., and Singh, R. K. (2013). An overview of gender issues in agriculture. Soc. Sci. Res. Netw. 1–9. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.2237993
Snapp, S. S., Blackie, M. J., Gilbert, R. A., Bezner-Kerr, R., and Kanyama-Phiri, G. Y. (2010). Biodiversity can support a greener revolution in Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 107, 20840–20845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1007199107
Takahashi, K., Muraoka, R., and Otsuka, K. (2020). Technology adoption, impact, and extension in developing countries’ agriculture: a review of the recent literature. Agric. Econ. 51, 31–45. doi: 10.1111/agec.12539
Ubochioma, C., Nnadi, F., Anaeto, F. C., Ejiogu-Okereke, N. E., and Anyoha, N. O. (2012). Analysis of the benefits of sustainable land management practices for climate change adaptation in Imo state Nigeria. Adv. Agric. Sci. Eng. Res. 2, 72–78. doi: 10.5707/aaser.v2i1.49
Umar, B. B. (2021). Adapting to climate change through conservation agriculture: a gendered analysis of eastern Zambia. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 5:5(456). doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2021.748300
Umar, B. B., Nyanga, P. H., Karki, S., Benitez, P., Mutandwa, E., Kristjanson, P., et al. (2019). Gender considerations in sustainable land management initiatives: Evidence from Zambia. Washington, DC: The World Bank Group and TerrAfrica.
Vanlauwe, B., Coyne, D., Gockowski, J., Hauser, S., Huising, J., Masso, C., et al. (2014). Sustainable intensification and the African smallholder farmer. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 8, 15–22. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2014.06.001
Vilorio, D. (2020). Education matters: career outlook. Available at: https://www.bls.gov/careeroutlook/2016/data-on-display/print/education-matters.htm.
Wei, S., Zhang, Z., and Li, G. (2022). Estimation of the average treatment effect on the treated with misclassified binary outcome. Stat 11:e422. doi: 10.1002/sta4.422
Keywords: Zambia, propensity score matching, sustainable livelihood framework, gender norms, social capital, agricultural credit
Citation: Bwalya B, Mutandwa E and Chiluba BC (2024) Sustainable land management and implications on incomes, food self-sufficiency and women. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1393489. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1393489
Edited by:
Luuk Fleskens, Wageningen University and Research, NetherlandsReviewed by:
Brenda Boonabaana, The University of Texas at Austin, United StatesMapenzie Tauzie, University of Leeds, United Kingdom
Copyright © 2024 Bwalya, Mutandwa and Chiluba. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bridget Bwalya, YnJpZ3QyMDAxQHlhaG9vLmNvLnVr
 Bridget Bwalya
Bridget Bwalya Edward Mutandwa2
Edward Mutandwa2 Brian Chanda Chiluba
Brian Chanda Chiluba