- 1Ecological Civilization Center, Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences, Beijing, China
- 2College of Economics and Management, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China
- 3College of Economics and Management, South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou, China
Background: Wetland restoration is an important measure for restoring wetland ecosystems and their ecological benefits, with the goal of restoring their ecological functions and resources. However, wetland restoration affects farmers' incomes and livelihoods. Although existing research has contributed to a deeper understanding of the relationship between wetland restoration and farmers' household incomes, some issues require further consideration. Therefore, here, we aimed to analyse the impact of wetland restoration on farmers' incomes and provide empirical evidence for the coordination mechanism of protection and development in the Poyang Lake Wetland in Jiangxi Province.
Methods: Based on 2 years of balanced panel data of 365 households around the Poyang Lake wetland, this study analysed the influence of policies related to wetland restoration and how variables such as the cultivated land area, labour force transfer, and location of nature reserves impact farmers' income. To this end, we used a two-way fixed-effect model to test the robustness by using propensity score matching, and the influence mechanisms of wetland protection policies, such as wetland restoration, wetland ecological compensation, and the Yangtze River fishing ban, on farmers' income interactions were explored.
Results and discussion: The results showed that, due to the policy of wetland restoration was implemented a long time ago, the negative impact of the policy on reducing farmers' household income is not significant now. Further, farmers' family livelihood strategies have changed, and choosing other types of agricultural production and off farm employment are currently the main choices for farmers. Wetland restoration has changed their income structures. Additionally, the two wetland restoration policies and banning of fishing have had synergistic effects. The findings of this study are helpful in understanding how wetland restoration around nature reserves influences farmers' household incomes. Further, they can provide policy insights for promoting an increase in income and the optimization of the income structure of communities around lake wetland nature reserves.
1 Introduction
Wetlands have long supported human communities worldwide (Murray, 2023). Wetland ecosystems are closely related to production and the lives of residents. More than one billion people rely on wetlands for their livelihoods worldwide. However, since 1700, wetlands have disappeared rapidly, with inland wetland loss mainly occurring in Europe, the United States, and China; further, the rate of decrease accelerated rapidly in the middle of the 20th century (Fluet-Chouinard et al., 2023). Their rate of disappearance is three times higher than that of forests, and the degradation of wetland functions poses a major threat to human survival and development. The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (2015–2030) include 17 aspects covering nearly 200 indicators, more than 70 of which are directly related to wetlands (United Nations, 2015). Correspondingly, the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands implemented its fourth Ramsar Strategic Plan (2016–2024) that consists of four goals and 19 targets aimed at enhancing wetland conservation, restoring wetlands, and ensuring informed usage. All these directly support the UN Sustainable Development Goals (Ramsar Convention Secretariat, 2016). The total area of wetlands in China is ~56.35 million hectares, and various types of wetland cover large areas.
Poyang Lake is in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. As the largest freshwater lake in China, it is an internationally important wetland resource. The Poyang Lake wetland plays an important role in providing large buffer zones for flood management in several provinces of central and eastern China, providing water resources for agricultural production, enriching fish diversity, mitigating climate change, and providing wildlife habitats (Jiang et al., 2015; Shi et al., 2009; Wang et al., 2019). Poyang Lake is one of the most important wintering habitats for migratory waterbirds in the East Asia–Australia migratory region, including Siberian cranes (Grus leucogeranus), White-naped cranes (Grus vipio), and Oriental White Storks (Ciconia boyciana) (Jia et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2019). It is the world's largest wintering ground for Siberian cranes, with more than 95% of their global population wintering there. Central and local governments have established several nature reserves in the Poyang Lake area to protect the Poyang Lake wetland ecosystem and the wildlife dominated by migratory birds. However, the decades-long reclamation of Poyang Lake has resulted in large-scale cultivated, which constitutes an important part of the grain production base and plays an important role in ensuring food security in China. Moreover, the sharp decrease in wetland areas has caused serious environmental impacts, such as frequent droughts and floods, loss of wildlife habitat, and destruction of wetland ecosystems. As a result, the ecosystem services and biodiversity of its watersheds are greatly threatened (Deng et al., 2016), especially in the Yangtze River Basin in 1998. It has caused great losses to people's lives and properties in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River and has drawn a significant amount of attention to ecological environmental problems and economic development models, which has preluded ecological projects, such as wetland restoration.
The purpose of wetland restoration (returning farmland to lakes1) is to provide certain funds or goods to relevant management institutions and rural residents who endure losses through financial transfer payments, guide and encourage farmers to withdraw from residential areas and cultivated land formed by reclaiming land from lakes for agricultural production, and restore these areas to natural lakes on a large scale to achieve the goal of improving wetland ecosystems. The original purpose of implementing the wetland restoration project was to strongly promote the protection of the ecological environment, improve the service capacity of wetland ecosystems, and reduce the disaster relief burden on the government and society in the polder area along the river or lake area, where the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River were destroyed by the 1998 flood. This is a large-scale project designed to decrease the risk of flooding by increasing the flood storage function of lake areas (Luguang et al., 2010). The number of households to be relocated in Jiangxi Province accounts for approximately half the total number of households in the four provinces,2 making it the most important ecological restoration policy in the Poyang Lake basin. The implementation of wetland restoration has significantly increased the scope of the Poyang Lake wetland (Liu Y. et al., 2017). After 1998, the resilience of the Poyang Lake area to flooding has gradually increased. Many major floods have occurred over the past two decades, but the losses of lives and properties have been relatively small. Wetland restoration not only guarantees flood control, but also adjusts the living environment. Due to its role in the production field of rural residents, the intensive use of cultivated land, transformation of rural residents' production activities and lifestyles, and ecological and food security of the Poyang Lake area have been guaranteed.
China has formulated relevant protection, utilisation, and restoration policies for multiple elements in wetlands, which have become an important basis for wetland ecosystem protection. The openness and public welfare characteristics of wetlands often lead to the underestimation of these areas in conservation decisions. Wetland restoration involves similar processes to those involved in returning farmland to forest, both of which have a wide range of contexts; however, previous research has explored this problem. Scholars have conducted detailed research on wetland restoration from different perspectives, mainly focusing on ecological benefit assessments of wetlands, the number of wetlands restored, and their spatial distributions (Lu et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2012; Yepsen et al., 2014; Zhang and Song, 2014; Zhang et al., 2021), including the benefits of the ecosystem at the city-wide scale, ecological compensation mechanism (Chen et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2015; Sun et al., 2016), farmers' willingness to participate (Lu and Chen, 2021; Wei et al., 2020; Zhu and Jiang, 2015; Zhu et al., 2015), farmers' responses (Zhang et al., 2009, 2008), and farmers' willingness to pay (WTP) and willingness to accept (WTA) (Bake and Sharma, 2019; Eskandari-Damaneh et al., 2020; Krishna et al., 2013; Nyongesa et al., 2016; Tabi and del Saz-Salazar, 2015). The relationship between wetland restoration and economic development has only begun to be considered in recent years (Browne et al., 2018; Ndebele and Forgie, 2017; Schroder et al., 2018; Yan et al., 2013), and studies have found that wetland restoration in Sanjiang Plain, China, increased the per capita GDP and degree of foreign capital introduction, as well as promoted the rapid development of social and ecological benefits. Most farmers believe that wetland restoration is conducive to maintaining the ecological environment and promoting the coordinated development of the local economy (Liao et al., 2009; Zhang and Tong, 2018). Researchers have investigated the reason for wetland restoration having a positive impact on the development of farmers. Some scholars believe that the goals of wetland restoration are not limited to solving ecological problems. Wetland restoration directly affects the residents' production activities and lifestyles, thus changing farmers' livelihood strategies. Wetland restoration also increases farmers' income, promotes non-agricultural employment, and adjusts rural production structures, which have positive impacts (Tian et al., 2016; Yu and Wu, 2022). By developing alternative livelihood activities, such as pig farming, cage fish farming, and organic vegetable cultivation, farmers' incomes and welfare have improved and their vulnerability has been reduced (Yu et al., 2006). Some authors believe that this may be attributable to government compensation funds for wetland restoration. For example, farmers hope to receive direct cash compensation when they are affected by the return of farmlands to wetlands (Zhang et al., 2009; Wei et al., 2020). Farmers involved in wetland restoration in Poyang Lake mainly choose to go out to work, do business, and develop animal husbandry as their main alternative livelihood strategies (Zhu and Kang, 2017).
The key to the success of wetland restoration lies in coordinating the redistribution of interest of the participants. However, when the economic losses of local residents have not been properly compensated for and local residents do not fully understand the importance of wetland restoration, the successful implementation of the program is often challenging. Gaining support from the public and locals is likely to improve the success of wetland restoration more successful (Herrera et al., 2019; Wilkins et al., 2019); therefore, understanding whether the policy of wetland restoration can increase the incomes of farmers' families is crucial. Although the household income of farmers cannot fully reflect the impact of development, the annual income reflects the actual value obtainable by the farmers (Cong et al., 2019). China fully achieved poverty eradication in 2020, but poor households in rural areas have limited ability to withstand production risks. This makes increasing income levels a key factor in achieving poverty reduction (He et al., 2021; Zhengxue et al., 2019). Given the large area of the Poyang Lake wetland and its important social, economic, and ecological functions, it has been the focus of China's wetland ecosystem restoration efforts.
Therefore, this study considered the communities around the Poyang Lake wetland in Jiangxi Province as the research area. First, a theoretical analysis framework for “wetland restoration–impact mechanism–farmers' incomes” is constructed. On this basis, the impact of wetland restoration on farmers' incomes was empirically analysed using a fixed-effects model with panel data from surveys distributed to farmers in 2018 and 2021. Robustness tests were also conducted to mitigate the endogeneity problem in the model. These aim to provide empirical evidence for the coordination mechanism between conservation and development. Compared with existing research, the contribution of this study is reflected in the following aspects: First, this study used the exogenous shock of wetland restoration in the Poyang Lake Basin in 1999 as a quasi-natural experiment and constructed a two-way fixed-effect model based on panel data to empirically test the impact on farmers' income. Second, this study analysed the heterogeneity of the impact on farmers' livelihood selection from the perspective of income structure. Third, this study analysed the interactive effects of multiple policies on income. The research results can provide new ideas and useful supplements for improving wetland protection policies around nature reserves and for coordinating the development of community farmers.
2 Material and methods
2.1 Study area
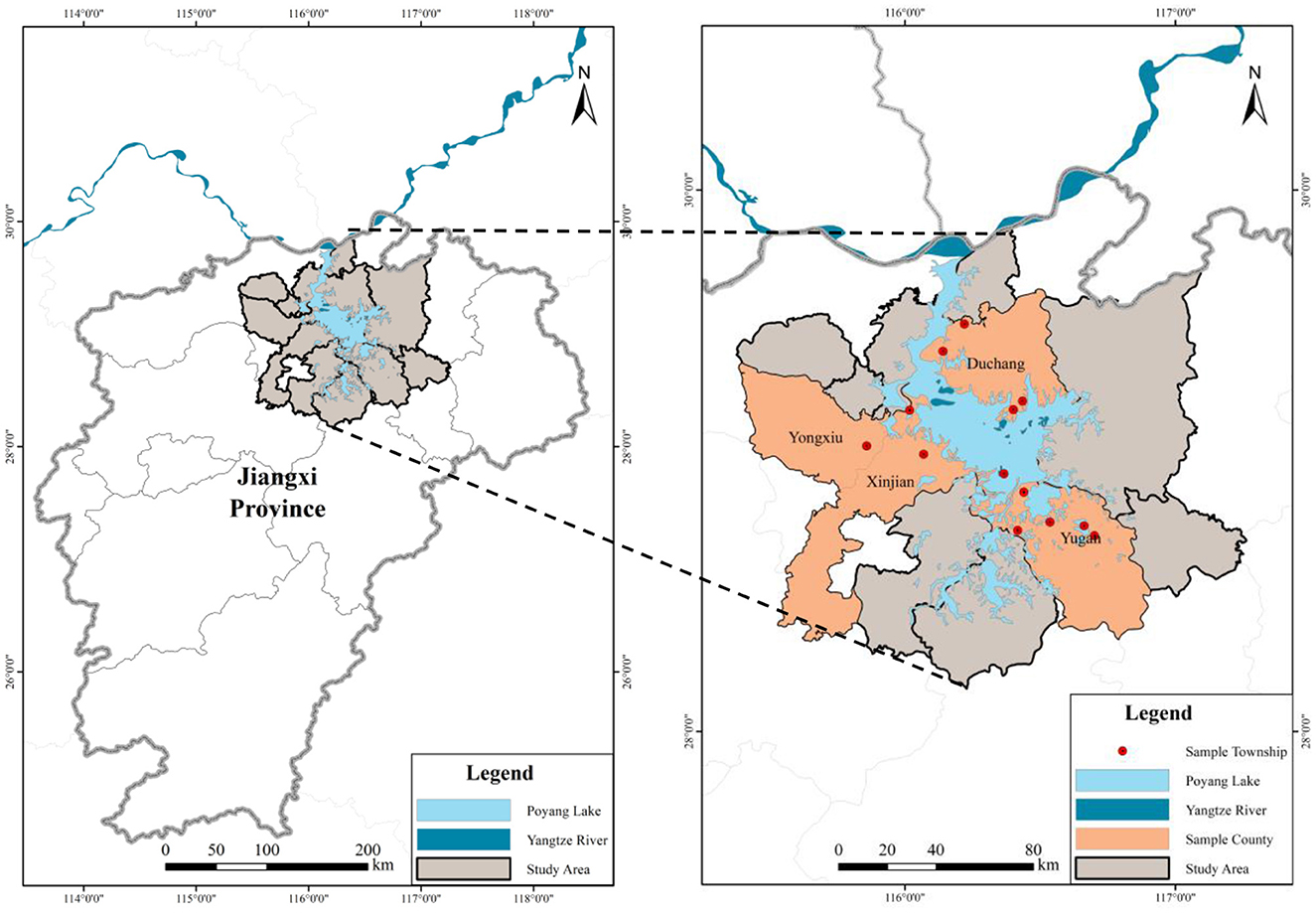
Poyang Lake is located on the south bank of the Yangtze River, north of Jiangxi Province (115°49′-116°46′E, 28°24′-29°46′N). It is the largest permanent freshwater riverine lake in China. Poyang Lake receives water resources (Wan et al., 2014) from the Xiuhe, Fuhe, Ganjiang, Xinjiang, and Raohe Rivers (hereinafter referred to as the “five rivers”) and other water systems, and flows into the Yangtze River from Hukou County, Jiujiang, forming a circular water system centred on Poyang Lake, which is seasonal. The boundaries of the Poyang Lake Basin coincide with the administrative boundaries of Jiangxi Province, with a drainage area of 15.67 × 104 km2, accounting for 94.1% of Jiangxi's land area, as shown in Figure 1.
The Poyang Lake area in this study refers to the complete administrative region near the core water body of Poyang Lake in Jiangxi Province as the connexion zone between the core water body and the five rivers. Second, the region is a complete lake–wetland ecosystem that combines land and water, and connects mountains, rivers, and lakes. It is an important ecological barrier for core water bodies and an important area for the implementation of ecological environmental protection. It is a traditional farming area and the most prominent area for protection and development. Therefore, this study focused on rural areas near the catchment area with the most prominent contradiction between protection and development in the Poyang Lake area.
2.2 Research design and data collection
This study used a questionnaire as the survey method to obtain data from farmers in the Poyang Lake area and followed conventional procedures for human research. Participants were invited to complete the survey voluntarily and anonymously, without compromising their privacy or raising ethical issues. By referring to several studies related to rural areas in the Poyang Lake area, consulting relevant experts in the field of wetland ecological protection, and conducting interviews with local farmers in Yongxiu County, Yugan County, and other sample counties, in combination with the characteristics of natural resources, agricultural production, wetland protection policies, and farmers' protection behaviours in Poyang Lake District, a questionnaire on the relationship between wetland restoration and farmers' livelihoods was designed for the Poyang Lake area, Jiangxi Province. Community surveys were conducted in 11 townships in 4 typical counties and districts in the Poyang Lake area.
The questionnaire designed in this study covers almost everything related to changes in natural resources around the community. For example, information on the head of the household, household plantations, fisheries, and other means of production or living, and household income. The time span was 2 years, 2018 and 2021, so the survey required the respondents to be familiar with the basic household information and have sufficient knowledge about planting, farming, fishery production, and other related information. The final respondents were mostly heads of households; therefore, the quality of the questionnaire was ensured. After eliminating questions that did not meet the standards, we ensured the accuracy and consistency of information acquisition, and finally obtained a total of 1,311 valid questionnaire samples over 2 years. Although the survey attempted to track all sample households, there were cases of withdrawal from the survey for various reasons, such as the relocation of the whole village, migrant work of the head of the household, and other factors. After the completion of the questionnaire and excluding farmers who could not be contacted, the two surveys from 2018 and 2021 totalled 365 households and 730 samples, which were still representative of the survey area. The empirical analysis of farmers in this study employed data from 365 households, as shown in Figure 2.
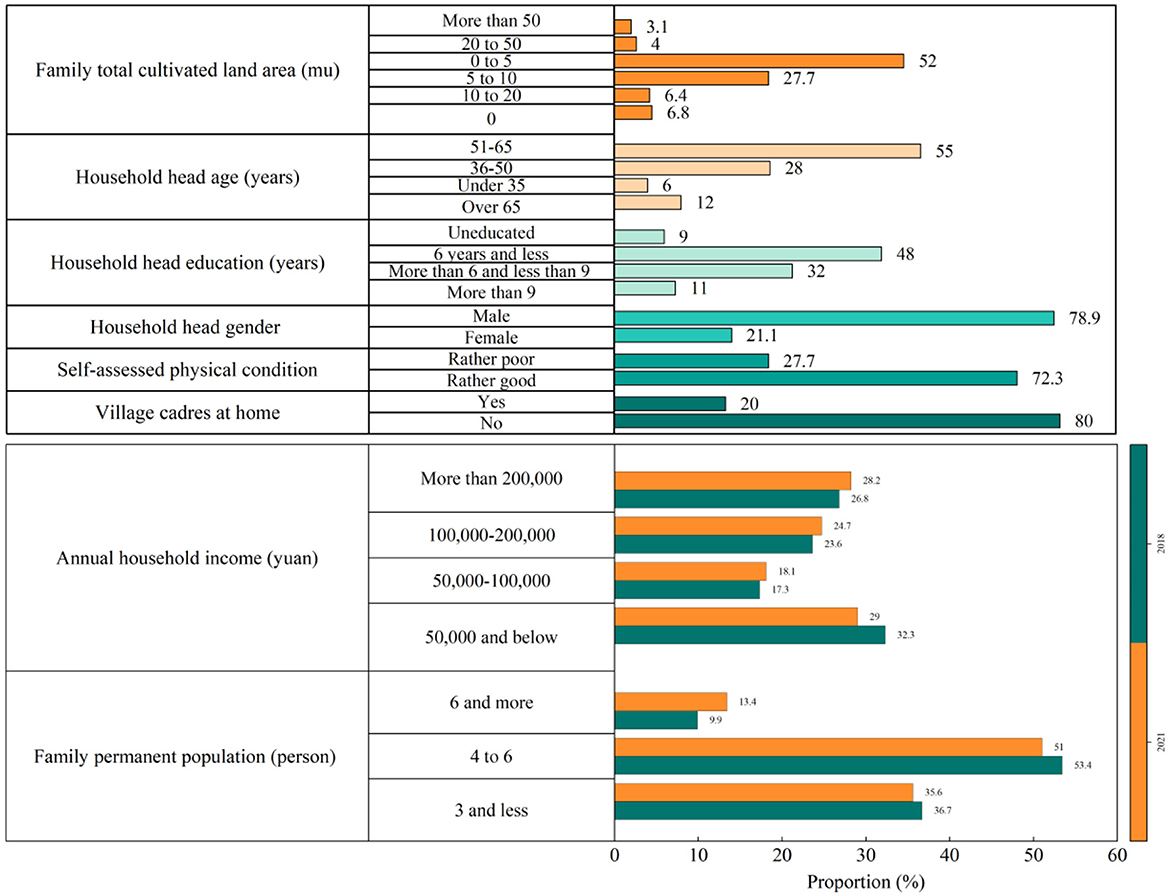
Figure 2. Descriptive statistics of households' socio-economic characteristics. Household head characterisation variables did not change over time, except for age, which was chosen to be that in 2018.
2.3 Analytical framework
Existing research has contributed to a deeper understanding of the relationship between wetland restoration and farmers' household incomes, providing valuable information for this study. However, there are still some issues that require further consideration. First, although some scholars have attempted to analyse the relationship between the exogenous impact of wetland restoration and farmers' income, an in-depth exploration of the internal mechanism of the impact of wetland restoration on farmers' household incomes is lacking, and research conclusions on the relationship between the two have not yet been unified. At present, the contribution of the ecosystem to the promotion of social development has gradually gained attention and has begun to be incorporated into the design of relevant public policies (Shuzhuo et al., 2021). The implementation of ecological protection policies has played an important role in ecosystem restoration in the Poyang Lake area; however, these policies may not be able to meet the ground-level practical needs of wetland protection. Can this compensate for the direct costs paid by farmers to protect wetlands and promote income growth?
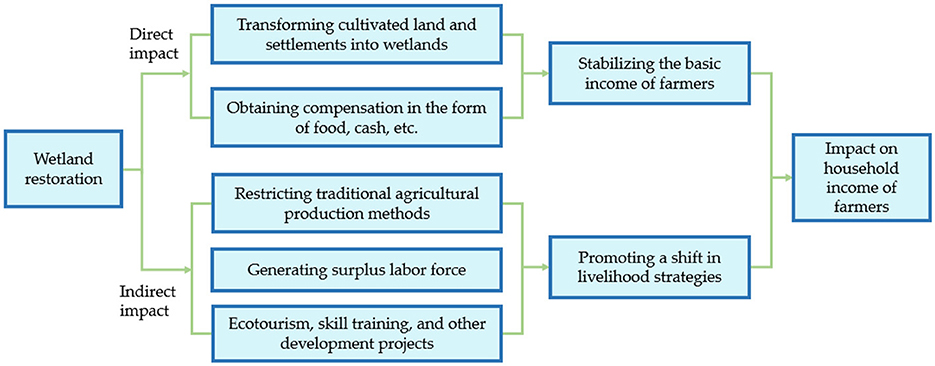
The return of farmland has two direct impacts on farmers: One is the ecological impact. Since 2000, the value of ecosystem services in the Poyang Lake Basin has continued to increase, and the sustainability of the entire basin has developed in a favourable direction. The richness of winter migratory birds and benthos species has increased, and the amount of water increased and then decreased in 2010. The annual maximum and average water supplies have rebounded, but the minimum water supply has continued to decline due to upstream impacts (Minkun and Xibao, 2021; Liu H. et al., 2017). The second policy involves farmers participating in farmland conversion projects receiving direct food or cash compensation. The original purpose of this policy was to compensate for the costs incurred due to losses of farmland or changes in residence. However, because the dikes in the policy of wetland restoration in the Poyang Lake area cannot be compensated for by flood storage, as stipulated by the State Council, most of the farmers surveyed have not been compensated continuously. Farmers participating in the conversion of farmland to wetland in Poyang Lake did not receive compensation and could not stabilise their basic agricultural income. However, farmers can increase their income by changing agricultural production types, going out to work, and other non-agricultural employment methods (Wang and Yue, 2017), as shown in Figure 3.
The indirect impact includes three aspects. First, wetland restoration has led to some farmers losing their farmland and being unable to continue planting and production (Wu et al., 2013), resulting in a shift towards other agricultural production practices, such as pond aquaculture and natural water harvesting. Second, owing to resource utilisation limitations and forced production and lifestyle changes, the agricultural labour force in the vicinity of wetlands is being transferred to non-agricultural sectors, engaging in non-agricultural production activities, such as part-time work and individual operations. Simultaneously, the development of secondary and tertiary industries in the region or other areas has attracted the agricultural labour force (Changhai et al., 2013; Pang et al., 2021; Mohapatra et al., 2007; Wu and Jing, 2018). Third, the local government relies on the unique landscape of large lakes, Wucheng Ancient Town, winter migratory bird habitats, and other ecological tourism resources to guide farmers in transferring their surplus labour and to fund ecological tourism or other operations. Field research has found that the local government is actively creating ecotourism projects related to migratory birds to encourage the rural labour force to participate in services and obtain economic returns (Feng et al., 2021).
In summary, although farmers have lost the opportunity to freely adjust production factors, such as land, labour adjustments can be made to encourage the concentration of household labour in production sectors with comparative advantages, increase the marginal return of production factors, and stimulate a continuous increase in household income for farmers. Therefore, hypothesis H1 can be proposed.
• H1: Wetland restoration does not have a significant impact on farmers' income.
Wetland restoration directly and indirectly affects the income of farmers, directly limiting their traditional planting and production behaviours, and prompting them to change their livelihood strategies. Some of the labour force has engaged in other agricultural production activities, while others have migrated to other areas to work. A small portion of the labour force and capital participates in ecotourism under the guidance of the local government. However, in the absence of reasonable compensation funds to stabilise the basic income of farmers after returning to their fields, it is crucial to transform their employment options and achieve income growth through livelihood transformation for the long-term implementation of the project. Therefore, we propose hypothesis H2.
• H2: Wetland restoration projects positively impact the diversity of farmer income structures.
2.4 Econometric modelling and estimation method
2.4.1 Benchmark model
As the wetland restoration policy was implemented in 1999, this study has no comparative data before the implementation of the policy, and the policy participation is invariant. Therefore, to investigate the impact of wetland restoration on the income of farmers' households and to further control for the possible unobservable variables, considering that income will be affected by regional and temporal changes, this study drew on the modelling ideas of existing research (Liu et al., 2020) by adding the joint effect of the amount of time taken to control the impact of the fixed unobservable variables and to analyse the policy effect on farmers' households in each township over time. This study also considered fixed effects in the robustness test. The specific income equation is as follows:
where ln Yit is the logarithm of the household income of the ith farmer in the tth year, indicating the income effect of participating in the conversion of farmland, and Xit is the family characteristic variable and resource endowment that affects the income of family i in the tth year. The family characteristic variables include whether the family has village cadres, family population size, labour force population, number of migrant workers, and family resource variables, such as cultivated land area and distance from Poyang Lake. Rit refers to whether a family participates in farmland conversion. Rit=1 indicates that it participated in the conversion of farmland in the tth year and Rit=0 indicates that it did not participate in the conversion of farmland. uy represents the fixed effect of time, vt represents the fixed effect of township; μit is a random error term.
2.4.2 Propensity score matching (PSM)
Farmers' participation in wetland restoration around Poyang Lake is not due to the random choice of the farmers' family's willingness to participate, nor is it a random distribution made by the relevant department in implementing policies, but a result of the choice made by the competent department according to ecological needs. Therefore, farmers' participation in the return of farmland was not an exogenous variable. Using the least-squares method to estimate the impact of policy participation on household income produces a self-selection bias. In addition to policy participation, household characteristics and household resource endowment are likely to have a more significant impact on household income. This leads to an endogeneity problem in estimating the impact of agricultural land conversion on household income. That is, household participation in agricultural land conversion is not only related to household income and income structure, but also to the error term.
Therefore, this study used propensity score matching (PSM) to solve the bias caused by self-selection and a robustness test was conducted. A counterfactual framework was constructed to approximate and randomise the non-random data of farmers participating in the policy of wetland restoration in the Poyang Lake area through this method; that is, due to the lack of data, the project was implemented earlier. In the survey, only the farmer's income after wetland restoration was considered; the income of the families affected by wetland restoration could not be observed before the land was returned, and comparative data could not be obtained. Therefore, referring to existing research, the matching score was used to determine whether the sample farmers were affected by the policy of wetland restoration (Rosenbaum and Rubin, 1983). The conditional probability fitting value of each farmer's participation in the wetland restoration policy was also the propensity score (PS, SP). The advantage of the PSM method is that, by matching the resampling method, a control group similar to the family participating in wetland restoration can be found in the families not participating. This method solves the problem that wetland restoration is not random participation via the construction of data close to randomisation and solving the problem of biassed estimation.
where Di = 1 indicates that the sample farmers participated in the conversion of farmland, Di = 0 indicates that the sample farmers have not returned farmland, and Xi represents the observable characteristics of rural households and resource endowments (control variables).
This study used two-way fixed effects to evaluate the impact of wetland restoration on farmers' incomes. Although this method can eliminate some endogenous problems through the fixed effects of township and time, the sample selection of farmers in each village group may not have been completely random for practical reasons; thus, selection bias was likely. Previous studies generally chose the PSM method to calculate and deal with endogenous problems caused by selection bias through different matching methods. If the matching results were similar to the original regression results, they were considered robust. Based on this, we used the PSM method to test robustness. Based on ecological protection research involving case studies similar to Poyang Lake or ecological protection coupled with the reality of farmers in typical counties in the Poyang Lake area, three common methods were used: K-nearest-neighbour matching, kernel matching, and radius matching in callipers. These methods can verify the effect of wetland restoration on the household income of farmers.
2.5 Definitions of the variables
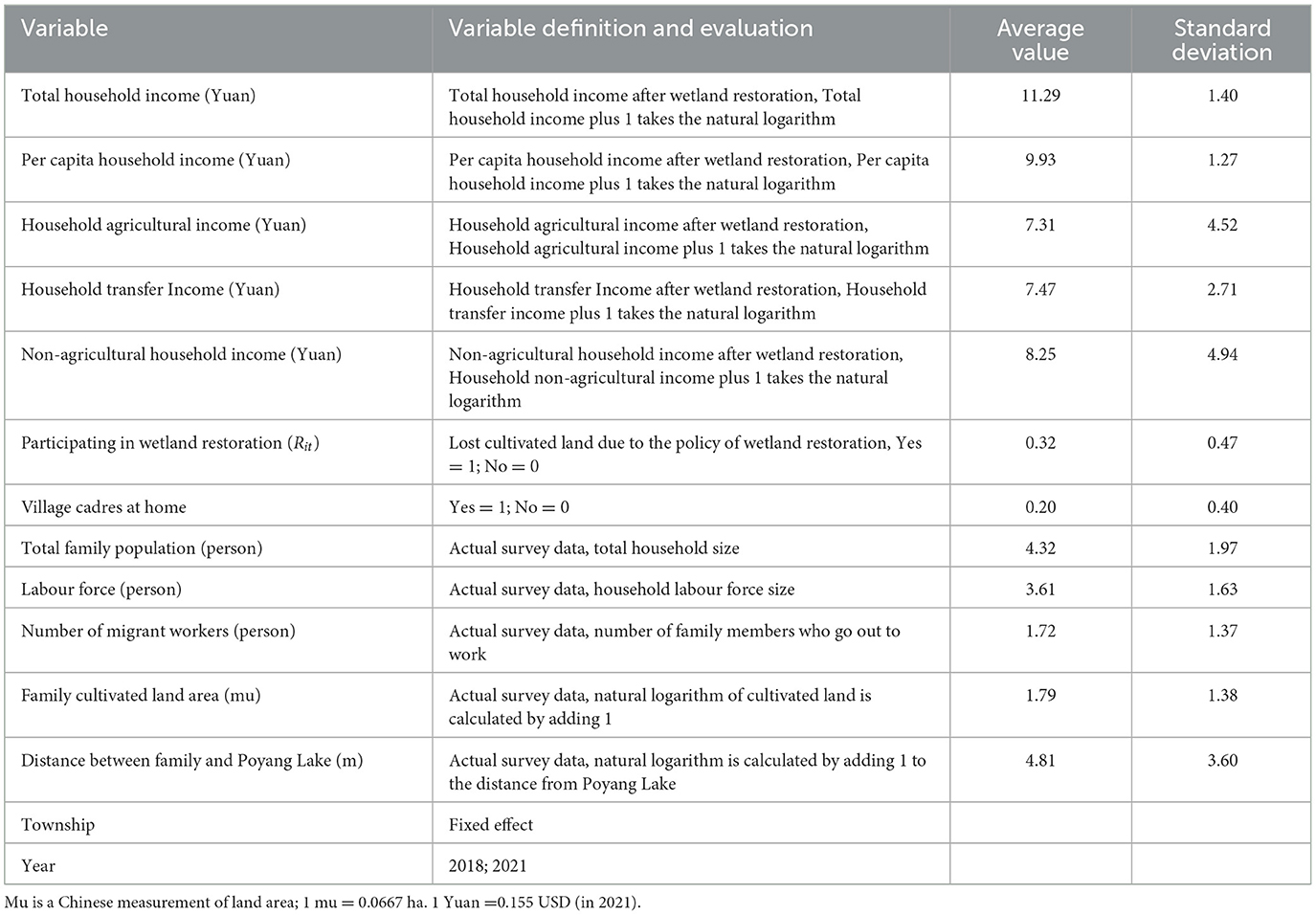
Variable yit represents the income of farmers in the lake area. The policy of wetland restoration deprives farmers of their most important means of production. Therefore, we selected household income as the core indicator to identify the impact of wetland restoration on farmers' income. We chose annual household income as an alternative indicator of the impact on farmers' development as it can have a specific regulatory effect. The total household income and per capita income represent the income of farmers, which can represent the overall and average situations of a family. Because changes in the means of production can have an impact on the income structure, therefore, we have discussed the impacts of wetland restoration on agricultural, transfer, and non-agricultural income. Among them, (1) agricultural income includes farmers' planting income, fishing income, pond and livestock breeding income, and wetland collection income; (2) transfer income refers to the transfer income of farmers in the lake area, such as pensions, agricultural subsidies, ecological compensation, and other compensation for winter migrant bird accidents; and (3) non-agricultural income refers to local or migrant income, rural tourism, tour guides, drivers, and other ecotourism or operating incomes. These three types of income represent the income structure. Before the regression analysis, we added one to each of the continuous variables to achieve natural logarithm processing via the elimination of the heteroscedasticity of the income data and other variables, as shown in Table 1.
The core explanatory variable Rit, representing whether and when farmers participate in wetland restoration, is defined here as the farmers who 'claimed to participate in wetland restoration' in the survey as returning farmland to households, that is, Rit=1; once those returning farmland to households are defined, the following years are also identified as those who returned farmland to households, incorporating the years of 2018 and 2021.
The control variable Xit considers that, in addition to wetland restoration, individual or family factors of farmers will have an impact on income; thus, six characteristic variables were selected from the household level of farmers (Zhang et al., 2008, 2009; Zhu and Kang, 2017; Lu and Chen, 2021; Wei et al., 2020; Yu and Wu, 2022), including family size, family labour force, number of migrant workers, family cultivated land area, and family distance from Poyang Lake, to control the above variables. The villages and towns where the farmers were located and the surveys in 2018 and 2021 were used as fixed effects.
3 Results
3.1 Effect of wetland restoration on increasing income of households
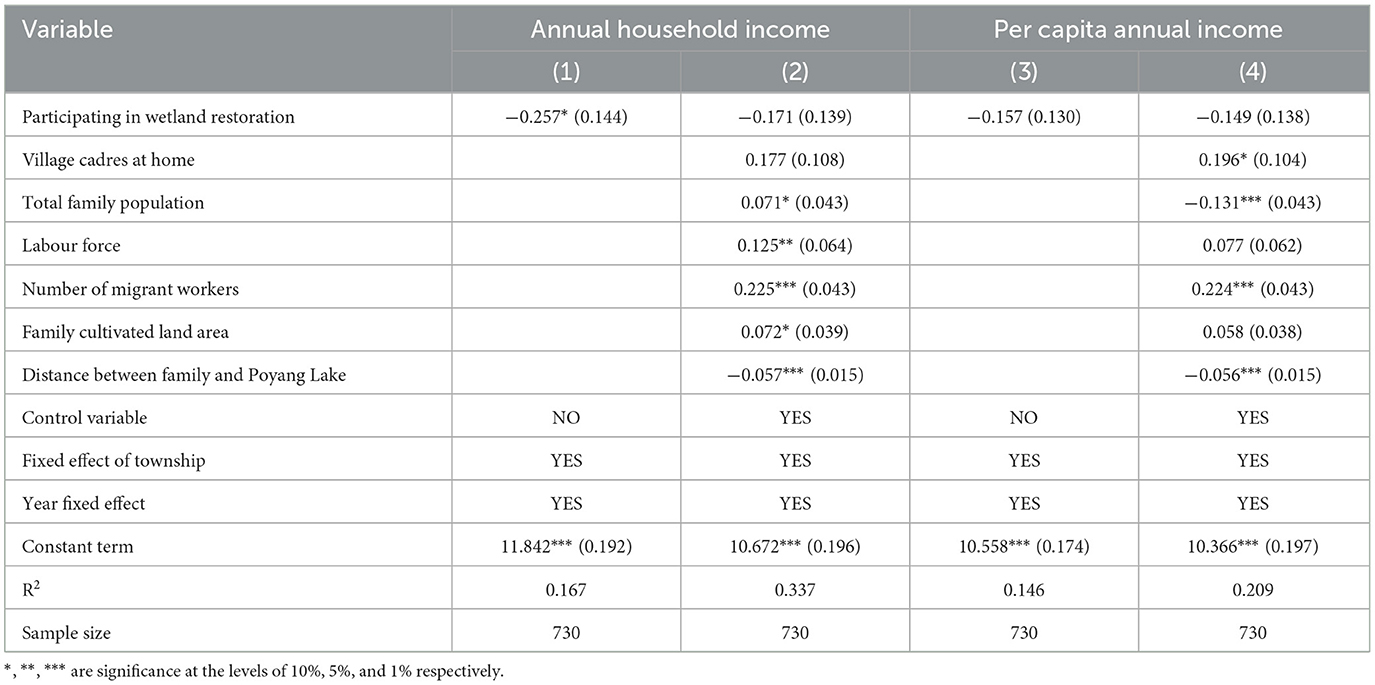
After completing the regression analysis by adding control variables, the original management rights and ownership of attachments to the land also changed due to the change in farmland usage rights. Although the project of wetland restoration in Poyang Lake area had a negative impact on family income and per capita income, there were significant differences. After a long period of wetland restoration without continuous subsidies, the participating farmers lost their cultivated land resources at home, but their incomes became relatively stable after adjusting their livelihood strategies. Most of the surveyed farmers did not receive compensation due to policy reasons, and those who received compensation could not recall the exact rate. Owing to the relatively long period of time, the compensation rate did not have a significant impact on the income of the farmers. In the field investigation, it was found that, owing to the current ecological protection policy and the decline in the economic benefits of traditional planting production, farmers in the lake area had no desire to reclaim land. This shows that, although it had an impact on farmers' incomes, it is not currently clear, which supports H1. Table 2 shows the joint fixed-effect regression results for the impact of wetland restoration on the household and per capita incomes of farmers.
In terms of the effect of control variables on farmers' incomes [columns (2) and (4)], the entry of village cadres into households had a positive effect on farmers' total and per capita incomes. Family size, family labour force, the number of migrant workers, and area of family arable land had significant positive impacts on total household income. Although the impact coefficient was low, it indicated that families with a large population may have had a larger labour force. More people can move to other developed areas to work, which can avoid the risk of losing traditional agricultural income, thereby enriching the sources of household income and improving the household income level. Similarly, the number of migrant workers also has a positive impact on the per capita income of the family at the 1% level.
The closer the family is to Poyang Lake, the more significant it is in promoting the growth of the total and per capita incomes of farmers' households. Although farmers who have returned farmland have lost part of their cultivated land resources and planting income, they have more water resources near Poyang Lake than farmers close to cities and towns. Therefore, their land can be transformed from planting practises to aquaculture and fishing practices. With changes in the ecological environment of Poyang Lake, local ecological tourism resources are also increasing. Farmers in lakeside areas may have more opportunities to participate in ecological tourism, such as migratory bird guides, drivers, and farms, or to participate in ecological protection public welfare positions. Opportunities, such as becoming the guardians of nature reserves and civil public welfare associations, all help farmers to obtain more employment opportunities in the local area.
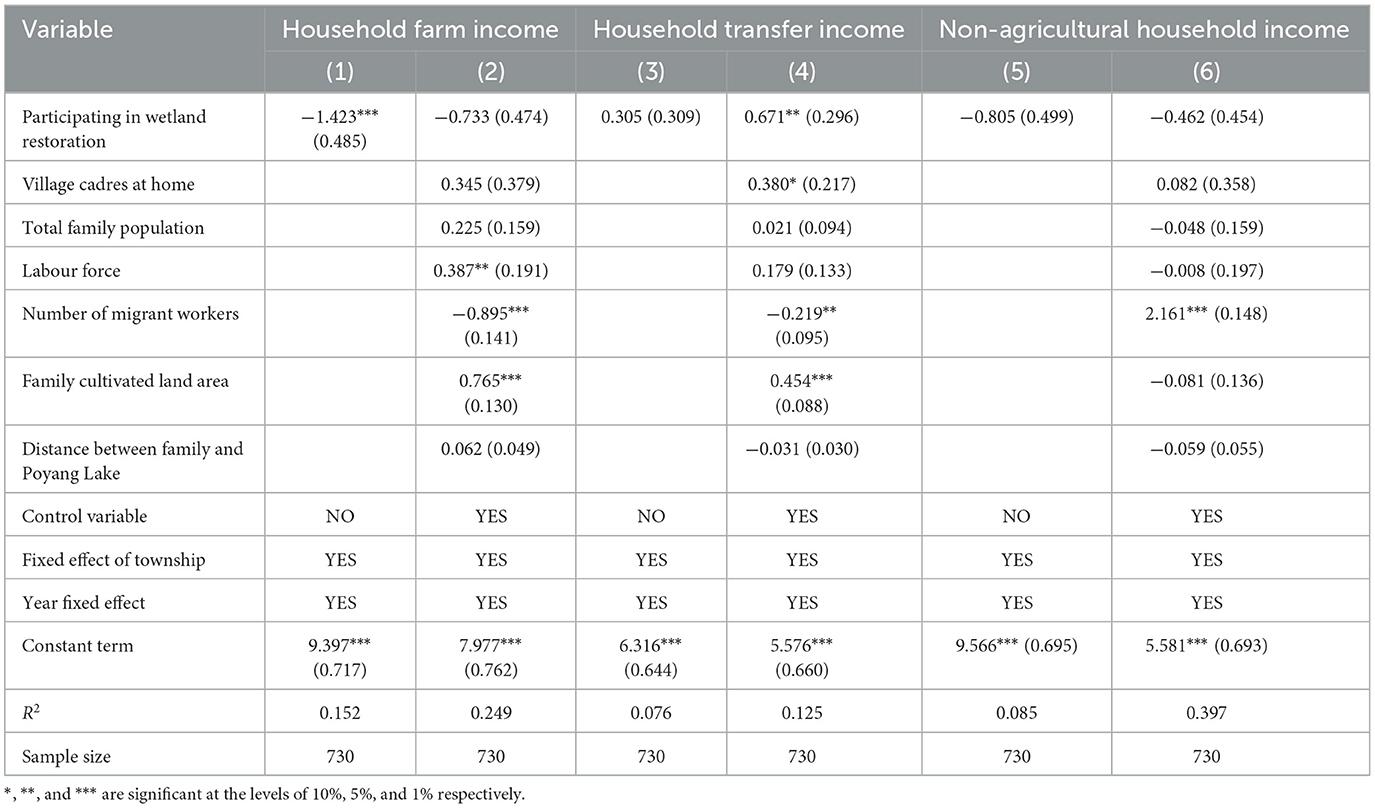
3.2 Impact of wetland restoration on the income structure of households
As farmers who participated in the policy of wetland restoration have responded to the national policy of increasing the wetland area of the Poyang Lake or decreasing the cultivated land area, they are limited by the change in their family's natural capital and can only decrease long-term farming; thus, agricultural income is reduced. Therefore, the impact of returned farmland on agricultural income was negative. However, owing to the long implementation time of the policy, it had no significant impact on agricultural income. Wetland restoration had a significant positive impact on family transfer income. The field survey revealed that, although farmers participating in the return of farmland did not receive special continuous subsidies, they did receive subsidies through other types of agricultural production. This shows that the labour force had not completely left agricultural production, which may be the reason for the stage of social development at that time. Farmers are more inclined to shift from traditional farming to other forms of agriculture instead of engaging in other types of employment. Therefore, H2 was supported, as shown in Table 3 below.
Regarding the impact of the control variables on income [Columns (2), (4), and (6)], the village cadres in the family had a significant positive impact on transfer income, indicating that higher social capital will bring more information channels to farmers, resulting in a higher transfer income, such as subsidies. The number of family labourers had a significant positive impact on agricultural income at the 5% level, indicating that more labour can engage in more agricultural production and thus obtain more agricultural income. The number of migrant workers significantly increased the non-agricultural income of farmers, but simultaneously decreased the agricultural and transfer incomes. Household cultivated land areas can significantly increase agricultural and transfer incomes. According to field surveys, although the yield rate of agricultural income was low, multiple planting behaviours significantly increased agricultural income. Therefore, a large area of cultivated land may enable farmers to increase their planting varieties and obtain responsive subsidies, thereby increasing their agricultural and transfer incomes.
3.3 Robustness test
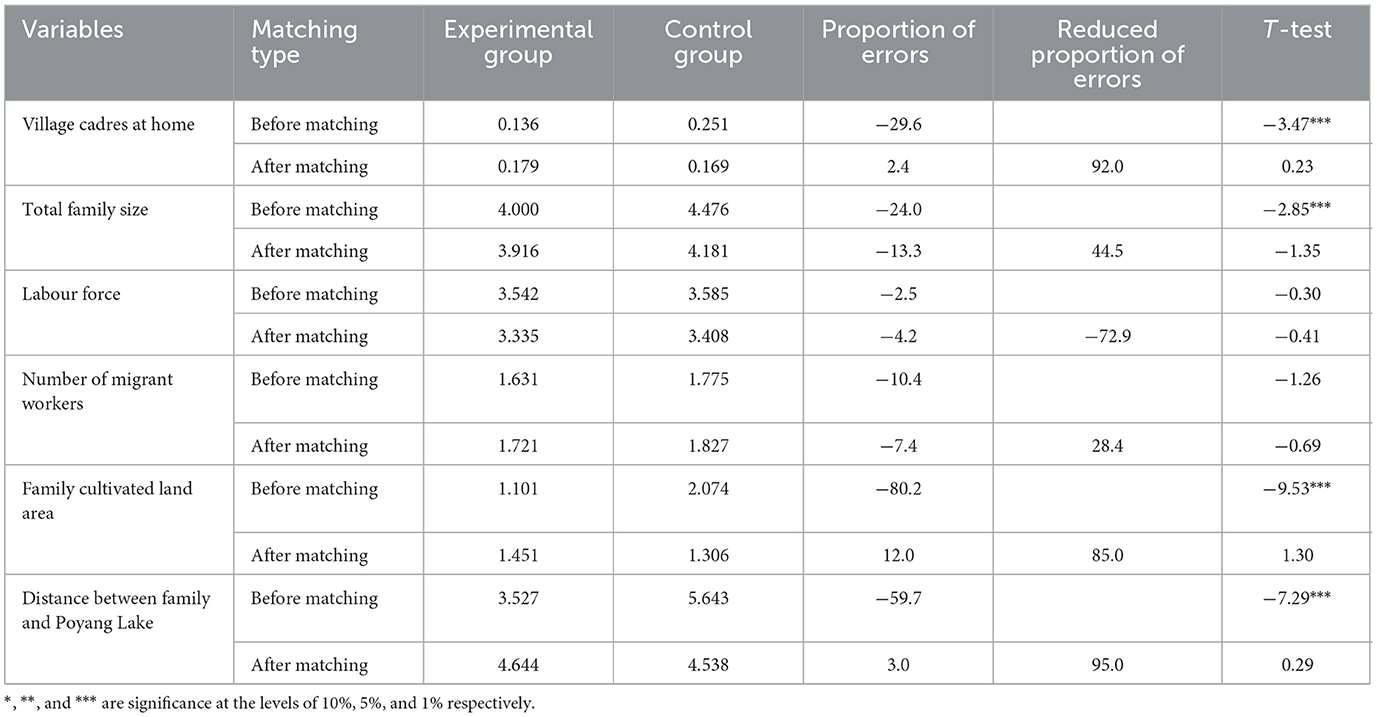
3.3.1 Balancing test results of control variables
Owing to space limitations, Table 4 lists only the balance test results of the total household income under the wetland restoration project using the nearest-neighbour matching (k-nearest-neighbour matching number is 3) method. The T-test showed that the difference between the two groups (those who participated in the conversion of farmland and those who did not) after matching was not statistically significant; that is, the samples selected in this paper passed the balance test after PSM matching.
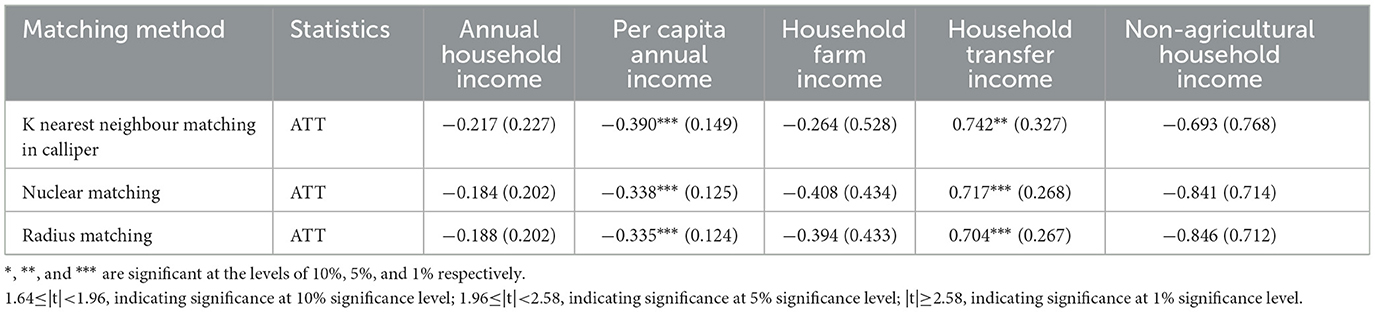
3.3.2 Treatment effect obtained by PSM method
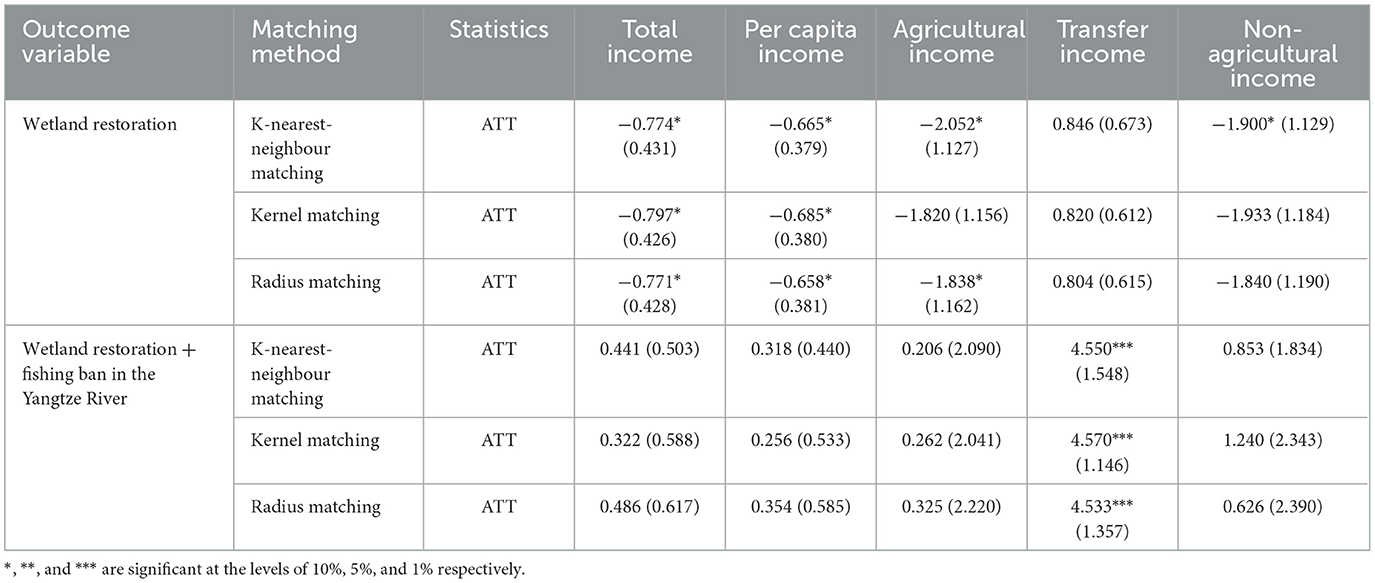
Table 5 lists the average treatment effect (ATT) of the impact of the project on the household income and income structure of the farmers in the lake area using the three PSM methods. In the calculation results of the three methods, taking kernel matching as an example, after controlling the selection bias, the total income of the households participating in the conversion of farmland decreased by 0.184, which could decrease the agricultural income by 0.264. After using the PSM method to control a series of observable variables, the total household income, per capita income, agricultural income, and non-agricultural income of the participating farmers decreased, while the transfer income increased, which is similar to the regression analysis results calculated in Section 3.1. The policy of wetland restoration had a negative impact on the household income of farmers and a significant negative impact on their per capita income. In summary, after correcting the endogenous problem, it can still be concluded that the conversion of farmland has decreased the household income of farmers.
3.4 Further discussion: interactive response of policy
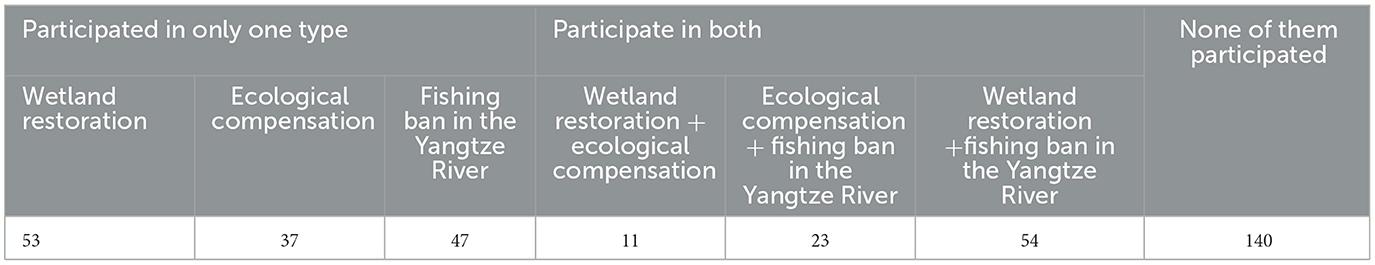
At present, Jiangxi Province is implementing a hybrid policy of “command control + economic incentive” for the protection of the Poyang Lake wetland. This policy has the characteristics of a strong binding force and quick response. Driven by a series of “command control + economic incentive” hybrid policies, it promotes the protection and utilisation of the Poyang Lake wetland ecosystem. In addition to the policy of wetland restoration, which is the focus of this study, it has the most extensive impact on farmers in the lake area; the most direct restrictions on farmers are the three policies of wetland ecological compensation and Yangtze River prohibition and withdrawal. Through the strict restriction and control of resource utilisation and according to the characteristics of resource ownership, a certain standard of economic compensation is given to farmers who pay protection costs to compensate for their losses and to coordinate the contradiction between protection and development. This study will continue to explore the specific impact of the interaction between wetland restoration and other wetland protection policies on farmers' most important income sources. The early implementation of the policy of wetland restoration and ecological compensation (engineering) has had a continuous impact on farmers. Therefore, only 365 farmers in 2021 were selected for statistical analysis. As shown in Table 6, most farmers did not participate in the three policies, and no farmers affected by all three policies were investigated.
These three policies are in three stages of long-term implementation, being widely implemented and just implemented, and their effects on farmers are also different. Due to the small number of farmers who participated in both wetland restoration + ecological compensation and ecological compensation + prohibition of capture, further analysis could not be conducted. This is consistent with the actual situation. The cultivated land of those who participated in wetland restoration was expropriated, thus changing the livelihood strategy based on planting to choose fishery production or other production methods. Fishery-based farmers are also less involved in planting production, so there are fewer samples for compensation. From a methodological perspective, the interaction effect of these three policies should be reflected in the unified model, which does not meet the calculation needs due to the realities of survey data collection. Therefore, only two cases—wetland restoration and wetland restoration + the prohibition of capture—were selected for discussion.
The propensity distribution method was used based on data from 365 households in 2021, which is only briefly explained here. According to the research characteristics and previous related research, k-nearest neighbour matching, kernel matching, and radius matching were performed to analyse the impact of wetland protection policies on farmers' incomes and the interaction between policies. The income effect of the protection policy is expressed by the total household income, per capita income, and income structure. In addition, due to data limitations, only three ecological protection policies were distinguished here, and other protection and development policies, such as food subsidies, were not distinguished individually.
The income effect of community participation in the Poyang Lake Wetland Protection Policy is shown in Table 7. First, wetland restoration had a significant negative impact on the household income of farmers, resulting in significant changes in the development of livelihood strategies; thus, income was significantly reduced. Second, from the perspective of income structure, wetland restoration reduced farmers' agricultural incomes. Compared with the non-participation group, the farmers in the policy participation group lost their cultivated land and thus lost their agricultural income. Third, the transfer income of farmers who participated in land withdrawal and capture simultaneously increased significantly, i.e., their household income did not decrease in 2021. Previous analysis revealed that, in recent years, farmers in the lake area have diversified their livelihoods, choosing to work outside as an important alternative livelihood strategy. Therefore, the income of the policy participation group improved and the two policies had a synergistic effect. When the two policies act on the community simultaneously, the income level of the community can be better improved through compensation and changes in livelihood strategies. However, direct compensation covers only 1 year, and more forms of diversified compensation and alternative livelihoods are needed to maintain the effect of increasing income.
Compared with the previous analysis of the impact of a single policy, the impact of wetland restoration on participating farmers remains significant, and the impact of the loss of cultivated land on traditional agriculture in the lake area is also significant. Farmers in lake areas regard fishing as an important source of income. Some farmers are professional fishermen with government-issued fishing licenses, while some fishermen do not have fishing licenses, but still make a living from fisheries. Therefore, fishermen with government-issued fishing licences were compensated for their loss of income compared to farmers without fishing licenses, and this one-off compensation made up for the loss of 1 year's income.
4 Discussion
Based on balanced panel data of 365 farmer households in 2018 and 2021, this study considered the Poyang Lake Wetland in Jiangxi Province as the research area and wetland restoration as a quasi-natural experiment. From the perspective of implementing wetland restoration policies, this study examined the impact of wetland restoration on farmers' incomes and non-agricultural employment. This study draws the following conclusions: Firstly, when only a single policy is considered, due to the long implementation period, the negative impact of wetland restoration policy on farmers' household income is no longer significant, the conclusion that still holds after the robustness test of the parallel trend assumption. Second, this study further confirms the impact of wetland restoration on farmers' livelihood strategy choices, as wetland restoration is not subsidised and therefore does not have a direct income enhancing effect. Despite the fact that cultivated land is an important means of production for farmers, after adjusting livelihood strategies, traditional cultivation is no longer the main source of household income, and farmers' household income can be increased by fishing and working outside the home, which reduces some of the income loss due to wetland restoration. This is one of the reasons why the negative impact of wetland restoration on farmers' incomes is no longer significant. However, the implementation of the 10-year fishing ban in the priority waters of the Yangtze River basin has prompted farmers to look for alternative livelihoods. Farmers who received the fishing ban compensation offset some of the income loss, but the relief was not sustainable.
There is still room for improvement in wetland restoration, and the topic of ecological effects is beyond the scope of this study. In terms of the effect of control variables on farmers' incomes [columns (2) and (4)], the entry of village cadres into households has a positive effect on farmers' total and per capita incomes. The effect on per capita income is significant at the 10% level. This indicates that the indirect income from social capital can mitigate the direct income loss from retiring farmland, to a certain extent. Second, if the farmland is returned to woodland or grassland instead of wetland, the nature of the land, right to use, right to manage, and ownership of the attachments are different. The original land and natural boundaries no longer exist. In addition to the purpose of ecological restoration, farmers have lost their right to use land, right to manage land, and ownership of attachments. Farmers may lose their right to obtain income from the land. Farmers cannot properly develop other agricultural products to increase income and maintain livelihoods while considering ecological restoration. Third, in the future, the lake area will implement the wetland restoration project again, returning farmland to forest and grassland, and provide farmers with corresponding compensation. In areas with rich wetland resources, relying on good ecological advantages, exploring the mechanism by which the value of ecological products can be realised, and promoting the coordinated development of ecological protection and the regional economy are all feasible; on the other hand, in urban areas and areas where industry and commerce can be developed, attention should be paid to further developing industry and commerce, absorbing the agricultural labour force withdrawn due to wetland restoration and the Yangtze River fishing ban, increasing farmers' incomes, and promoting the balanced development of urban and rural areas in the region.
Finally, the limitations of this study are as follows. First, although this study uses 2-year survey data from farmers to construct a model to solve the above problems, it is difficult to carry out parallel trend tests for short-term data. The level of bias of the model estimation results is still debatable, and they cannot fully reveal the long-term dynamic effect of wetland restoration on the specific production behaviour of farmers. Therefore, a method to solve the above endogenous problems is worth further consideration. It is necessary to use long-term panel data at the farmer level over a larger range to verify the main conclusions of this study. Second, the results of this study only preliminarily discuss the overall effect of wetland restoration in the Poyang Lake area, and the effect of policy interactions on farmers' household incomes needs to be further explored.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary file, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
JF: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YW: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – original draft. HZ: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – original draft. WD: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. HH: Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by the project of the National Social Science Foundation of China (23BGL197).
Acknowledgments
For their constructive suggestions and help in this research, we are grateful to Poyang Lake National Nature Reserve, Nanji Wetland National Nature Reserve, and Duchang Migratory Bird Provincial Nature Reserve for their help in the research process.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
1. ^After the severe flood disaster in 1998, the central government initiated the “Dike Construction, Farmland Return to Lake, and Resettlement” project (collectively known as the Farmland Return to Lake project) in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. Jiangxi Province contains a total of 417 embankments in the Farmland Return to Lake project, including 177 embankments involving both the relocation of residents and the return of farmland (“double return”) and 240 embankments involving only the relocation of residents without the return of farmland (“single return”). Among the 240 single-return embankments, 185 were located in the Poyang Lake area.
2. ^Hubei, Hunan, Jiangxi, and Anhui Provinces in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River.
References
Bake, H., and Sharma, R. (2019). “Estimating visitors' willingness to pay for lake conservation: a contingent valuation study of Pasha lake, Pune, India,” in Environmental Impacts of Tourism in Developing Nations, eds. R. Sharma, and P. Rao (London: IGI Global), 234–251. doi: 10.4018/978-1-5225-5843-9.ch013
Browne, M., Fraser, G., and Snowball, J. (2018). Economic evaluation of wetland restoration: a systematic review of the literature. Restor. Ecol. 26, 1120–1126. doi: 10.1111/rec.12889
Changhai, W., Yali, W., Wei, D., and Feng, H. A. N. (2013). Coupling relationship analysis on households' production behaviors and their influencing factors in nature reserves: a structural equation model. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 23, 506–518. doi: 10.1007/s11769-013-0608-7
Chen, K. Y., Qiu, S. R., Zhao, X. D., Huang, S. X., Gao, H. Y., He, Y. J., et al. (2021). Study on ecological compensation standard of wetland in Beijing. Acta Ecol. Sin. 41, 4786–4794. (in Chinese). doi: 10.5846/stxb201910222219
Cong, L. I., Manman, G., and Ping, L. (2019). Effect of relocation and settlement program: Analysis on the coupling model of “household welfare and ecosystem reliance”. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 33, 97–105. (in Chinese). doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2019.322
Deng, H., Shao, J. A., Wang, J. L., Gao, M., and Wei, C. F. (2016). Land use driving forces and its future scenario simulation in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area using CLUE-S model. Acta Geogr. Sin. 71, 1979–1997. (in Chinese). doi: 10.11821/dlxb201611009
Eskandari-Damaneh, H., Noroozi, H., Ghoochani, O. M., Taheri-Reykandeh, E., and Cotton, M. (2020). Evaluating rural participation in wetland management: a contingent valuation analysis of the set-aside policy in Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 747, 1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141127
Feng, J., Zhao, Z., Wen, Y. L., and Hou, Y. L. (2021). Organically linking green development and ecological environment protection in Poyang Lake, China using a social-ecological system (SES) framework. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18:2572. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18052572
Fluet-Chouinard, E., Stocker, B. D., Zhang, Z., Malhotra, A., Melton, J. R., Poulter, B., et al. (2023). Extensive global wetland loss over the past three centuries. Nature 614, 281–286. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05572-6
He, W. J., Zhao, Q. Y., and Zhang, H. X. (2021). Income-increasing effect of the collective Forest Tenure reform : mechanism discussions and empirical evidences. Chin. Rural Econ. 03, 46–67. (in Chinese).
Herrera, D., Cunniff, S., Dupont, C., Cohen, B., Gangi, D., Kar, D., et al. (2019). Designing an environmental impact bond for wetland restoration in Louisiana. Ecosyst. Serv. 35, 260–276. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoser.2018.12.008
Jia, Y., Zhang, Y., Lei, J., Jiao, S., Lei, G., Yu, X., et al. (2019). Activity patterns of four cranes in Poyang Lake, China: INDICATION of habitat naturalness. Wetlands 39, 45–53. doi: 10.1007/s13157-017-0911-7
Jiang, B., Wong, C. P., Chen, Y., Cui, L., and Ouyang, Z. (2015). Advancing wetland policies using ecosystem services – China's way out. Wetlands 35, 983–995. doi: 10.1007/s13157-015-0687-6
Krishna, V. V., Drucker, A. G., Pascual, U., Raghu, P. T., and King, E. D. I. O. (2013). Estimating compensation payments for on-farm conservation of agricultural biodiversity in developing countries. Ecol. Econ. 87, 110–123. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2012.12.013
Liao, Y. J., Song, C., Guo, Y. D., Wang, L., and Wang, L. L. (2009). Responses of farmers to wetland ecosystem stability and grain for wetland program based on participatory rural appraisal. J. Nat. Resour. 24, 1041–1048. (in Chinese).
Liu, H., Yin, J., Lin, M., and Chen, X. L. (2017). Sustainable development evaluation of the Poyang Lake Basin based on ecological service value and structure analysis. Acta Ecol. Sin. 37, 2575–2587. (in Chinese). doi: 10.5846/stxb201510102045
Liu, R. M., Mayo, Y., and Kang, Y.K. (2020). Deregulation, market vitality and tourism economy development: evidence from Chinese cultural system reform. Econ. Res. J. 55, 115–131. (in Chinese).
Liu, Y., Feng, J., Zheng-Lei, X. I. E., Jun-Bang, W., Fu-Qiang, L., Shu-Hua, Q. I., et al. (2017). Study on land reclamation around Poyang lake in the abandoned farmland in the context of the policy for converting farmland to lake. China Land Sci. 31, 44–50. (in Chinese).
Liu, Z. Y., Wang, H., Huo, L. Y., Cui, S. B., and Yuan, Z. N. (2015). Mechanism of ecological compensation of wetland protection in Songhua River Basin. Wetland Sci. 13, 202–206. (in Chinese). doi: 10.13248/j.cnki.wetlandsci.2015.02.011
Lu, C., Wang, Z., Liu, M., Ouyang, L., Jia, M., Mao, D., et al. (2015). Analysis of conservation effectiveness of wetland protected areas based on remote sensing in West Songnen Plain. China Environ. Sci. 35, 599–609. (in Chinese).
Lu, M. Q., and Chen, L. J. (2021). The contribution willingness of community residents' protection of wetlands based on MNL discrete selection model: a case study of Daqing wetland. J. Nat. Resour. 36, 449–458. (in Chinese). doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20210214
Luguang, J., Zhiming, F., Xiubo, Y. U., Lin, Z., and Heqing, H. (2010). Scenario analysis on the flood regulation service of the Poyang lake region. Resour. Sci. 32, 817–823. (in Chinese).
Minkun, C., and Xibao, X. (2021). Lake Poyang ecosystem services changes in the last 30 years. J. Lake Sci. 33, 309–318. (in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2021.0126
Mohapatra, S., Rozelle, S., and Goodhue, R. (2007). The rise of self-employment in rural China: development or distress? World Dev. 35, 163–181. doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2006.09.007
Murray, N. J. (2023). The extent and drivers of global wetland loss. Nature 614, 234–235. doi: 10.1038/d41586-023-00268-x
Ndebele, T., and Forgie, V. (2017). Estimating the economic benefits of a wetland restoration programme in New Zealand: a contingent valuation approach. Econ. Anal. Pol. 55, 75–89. doi: 10.1016/j.eap.2017.05.002
Nyongesa, J. M., Bett, H. K., Lagat, J. K., and Ayuya, O. I. (2016). Estimating farmers' stated willingness to accept pay for ecosystem services: case of Lake Naivasha watershed Payment for Ecosystem Services scheme-Kenya. Ecol. Processes 5, 1–15. doi: 10.1186/s13717-016-0059-z
Pang, J., Xu, K., and Jing, L. S. (2021). Research on the impact of wetland ecocompensation on farmers' livelihood strategies and income: an empirical analysis of Poyang Lake. China Land Sci. 35, 72–80, 108. (in Chinese). doi: 10.11994/zgtdkx.20210415.085006
Ramsar Convention Secretariat. (2016). The Fourth Ramsar Strategic Plan 2016–2024. Ramsar Handbooks for the Wise Use of Wetlands, 5th ed. Gland: Ramsar Convention Secretariat.
Rosenbaum, P. R., and Rubin, D. B. (1983). The central role of the propensity score in observational studies for causal effects. Biometrika 70, 41–55. doi: 10.1093/biomet/70.1.41
Schroder, S., Lang, Z., and Rabotyagov, S. (2018). Forward-looking farmers owning multiple potential wetland restoration sites: implications for efficient restoration. Environ. Manag. 61, 577–596. doi: 10.1007/s00267-018-1002-0
Shi, N., Zhan, J., Wu, F., and Du, J. (2009). Identification of the core ecosystem services and their spatial heterogeneity in Poyang Lake area. Front. Earth Sci. China 3, 214–220. doi: 10.1007/s11707-009-0008-6
Shuzhuo, L., Bofa, G., Cong, L., and Jie, L. (2021). Issues of conservation, development and well-being from the perspective of public policy——the proposal and application of an interdisciplinary research framework. J. Public Manag. 18, 23–33 + 165–166. (in Chinese). doi: 10.16149/j.cnki.23-1523.2021.02.002
Sun, B., Xie, Y., and Wen, Y. L. (2016). Advance in ecological compensation mechanism for wetlands in China. Wetland Sci. 14, 89–96. (in Chinese). doi: 10.13248/j.cnki.wetlandsci.2016.01.014
Tabi, A., and del Saz-Salazar, S. (2015). Environmental damage evaluation in a willingness-to-accept scenario: a latent-class approach based on familiarity. Ecol. Econ. 116, 280–288. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2015.05.010
Tian, Q., Guo, L., and Zheng, L. (2016). Urbanization and rural livelihoods: a case study from Jiangxi Province, China. J. Rural Stud. 47, 577–587. doi: 10.1016/j.jrurstud.2016.07.015
United Nations (2015). Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Washington, DC: United Nations.
Wan, R. R., Yang, G. S., Wang, X. L., Qin, N. X., and Dai, X. (2014). Progress of research on the relationship between the Yangtze River and its connected lakes in the middle reaches. J. Lake Sci. 26, 1–8. (in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2014.0101
Wang, S., and Yue, X. M. (2017). The Grain-For-Green Project. Nonfarm employment, and the growth of farmer income. Econ. Res. J. 52, 106–119. (in Chinese).
Wang, X., Yu, J., Zhou, D., Dong, H., Li, Y., Lin, Q., et al. (2012). Vegetative ecological characteristics of restored reed (phragmites australis) wetlands in the Yellow River Delta, China. Environ. Manag. 49, 325–333. doi: 10.1007/s00267-011-9757-6
Wang, Y., Molinos, J. G., Shi, L., Zhang, M., Wu, Z., Zhang, H., et al. (2019). Drivers and changes of the Poyang Lake wetland ecosystem. Wetlands 39, 35–44. doi: 10.1007/s13157-019-01180-9
Wei, X., Khachatryan, H., and Zhu, H. (2020). Poyang lake wetlands restoration in China: an analysis of farmers' perceptions and willingness to participate. J. Cleaner Prod. 284:125001. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125001
Wilkins, E. J., Sinclair, W., Miller, H. M., and Schuster, R. M. (2019). Does proximity to wetlands matter? A landscape-level analysis of the influence of local wetlands on the Public's concern for ecosystem services and conservation involvement. Wetlands 39, 1271–1280. doi: 10.1007/s13157-018-1076-8
Wu, J., Gong, Y., Zhou, J., Wang, X., and Gao, J. A, Y. (2013). The Governance of integrated ecosystem management in ecological function conservation areas in China. Reg. Environ. Change 13, 1301–1312. doi: 10.1007/s10113-013-0445-3
Wu, L., and Jing, L. S. (2018). Influence of eco-compensation on peasant households' livelihood in poverty-stricken regions in Guizhou Province. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 32, 1–7. (in Chinese). doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2018.228
Yan, D., Schneider, U. A., Schmid, E., Huang, H. Q., Pan, L., Dilly, O., et al. (2013). Interactions between land use change, regional development, and climate change in the Poyang Lake District from 1985 to 2035. Agric. Syst. 119, 10–21. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2013.04.001
Yepsen, M., Baldwin, A. H., Whigham, D. F., McFarland, E., LaForgia, M., and Lang, M. (2014). Agricultural wetland restorations on the USA Atlantic Coastal Plain achieve diverse native wetland plant communities but differ from natural wetlands. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 197, 11–20. doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2014.07.007
Yu, H. Y., and Wu, J. (2022). Rural households income-enhancing effect of wetland restoration based on the Lashihai watershed, Yunnan. China Environ. Sci. 42, 982–992. (in Chinese). doi: 10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.2022.0033
Yu, X. B., Zhang, C., and Pan, M. Q. (2006). Economic assessment of alternative livelihood in the context of wetland restoration. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin. 15, 632–637. (in Chinese).
Zhang, C. L., Tong, L. J., and Liu, J. B. (2008). Response of farmers to conversion of cultivated land to wetland and substitute livelihood-a case of Sanjiang Reserve. J. Nat. Resour. 23, 568–574. (in Chinese).
Zhang, C. L., Tong, L. J., Liu, J. B., Li, M. S., and Zhang, H. M. (2009). Farmers' response to policy of wetland protection and restoration in Sanjiang Reserve. Acta Ecol. Sin. 29, 946–952. (in Chinese).
Zhang, L. L., and Tong, G. J. (2018). Benefit evaluation of returning farmland to wetland based on fuzzy model analysis-taking the Sanjiang Plain wetland in Heilongjiang Province as an example. For. Econ. 40, 39–44. (in Chinese). doi: 10.13843/j.cnki.lyjj.2018.07.007
Zhang, S. Q., Zhang, P. Y., Pan, B. H., Zou, Y., Xie, Y., Zhu, F., et al. (2021). Wetland restoration in the East Dongting Lake effectively increased waterbird diversity by improving habitat quality. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 27, 1–17. doi: 10.1016/j.gecco.2021.e01535
Zhang, X. L., and Song, Y. Q. (2014). Optimization of wetland restoration siting and zoning in flood retention areas of river basins in China: a case study in mengwa, Huaihe River Basin. J. Hydrol. 519, 80–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.06.043
Zhengxue, H., Guoli, G., Fei, T., Biao, P., and Jianj, S. (2019). Where is the way for China to reduce poverty for a long Time? Prospects for poverty reduction strategies after the completion of poverty alleviation in 2020. Chin. Rural Econ. 09, 2–14. (in Chinese).
Zhu, H. G., and Jiang, H. Z. (2015). Influence of rights and interests protection and village cadres features on farmers' willingness of wetland restoration: based on survey data in Poyang Lake. J. Agro For. Econ. Manag. 14, 296–301. (in Chinese). doi: 10.16195/j.cnki.cn36-1328/f.2015.03.011
Zhu, H. G., Jiang, H. Z., and Kang, L. Y. (2015). An empirical analysis of wetland restoration compensation standards based on farmers' WTA: survey data from 1009 farmers in Poyang Lake. Fin. Trade Res. 26, 57–64. (in Chinese). doi: 10.19337/j.cnki.34-1093/f.2015.05.008
Keywords: Poyang Lake, wetland restoration, income increase effect, two-way fixed-effect model, interactive influence
Citation: Feng J, Wen Y, Zhang H, Duan W and Hao H (2024) Wetland restoration, household income, and livelihood structure of farmers. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1256115. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1256115
Received: 10 July 2023; Accepted: 24 October 2024;
Published: 13 November 2024.
Edited by:
Tom Langen, Clarkson University, United StatesReviewed by:
Nalini Rao, Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI), United StatesYanan Guan, Hebei Normal University, China
Copyright © 2024 Feng, Wen, Zhang, Duan and Hao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yali Wen, d2VueWFsaUBiamZ1LmVkdS5jbg==; Huiyuan Zhang, emhhbmdoeUBjcmFlcy5vcmcuY24=
 Ji Feng
Ji Feng Yali Wen2*
Yali Wen2*