- Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Key Laboratory of Respiratory Disease of Ningbo, The First Affiliated Hospital of Ningbo University, Ningbo, China
Background: Preserved Ratio Impaired Spirometry (PRISm) is increasingly recognized as a precursor to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). The impact of Ultra-Processed Foods (UPFs) intake on PRISm and lung function remains underexplored, and we aimed to explore their associations.
Methods: This study included 8,336 U.S. adults. Weighted logistic and linear regression models were employed for main analysis. Dose–response relationship was examined through restricted cubic spline (RCS) analysis, and subgroup analyses explored interactions with selected covariates.
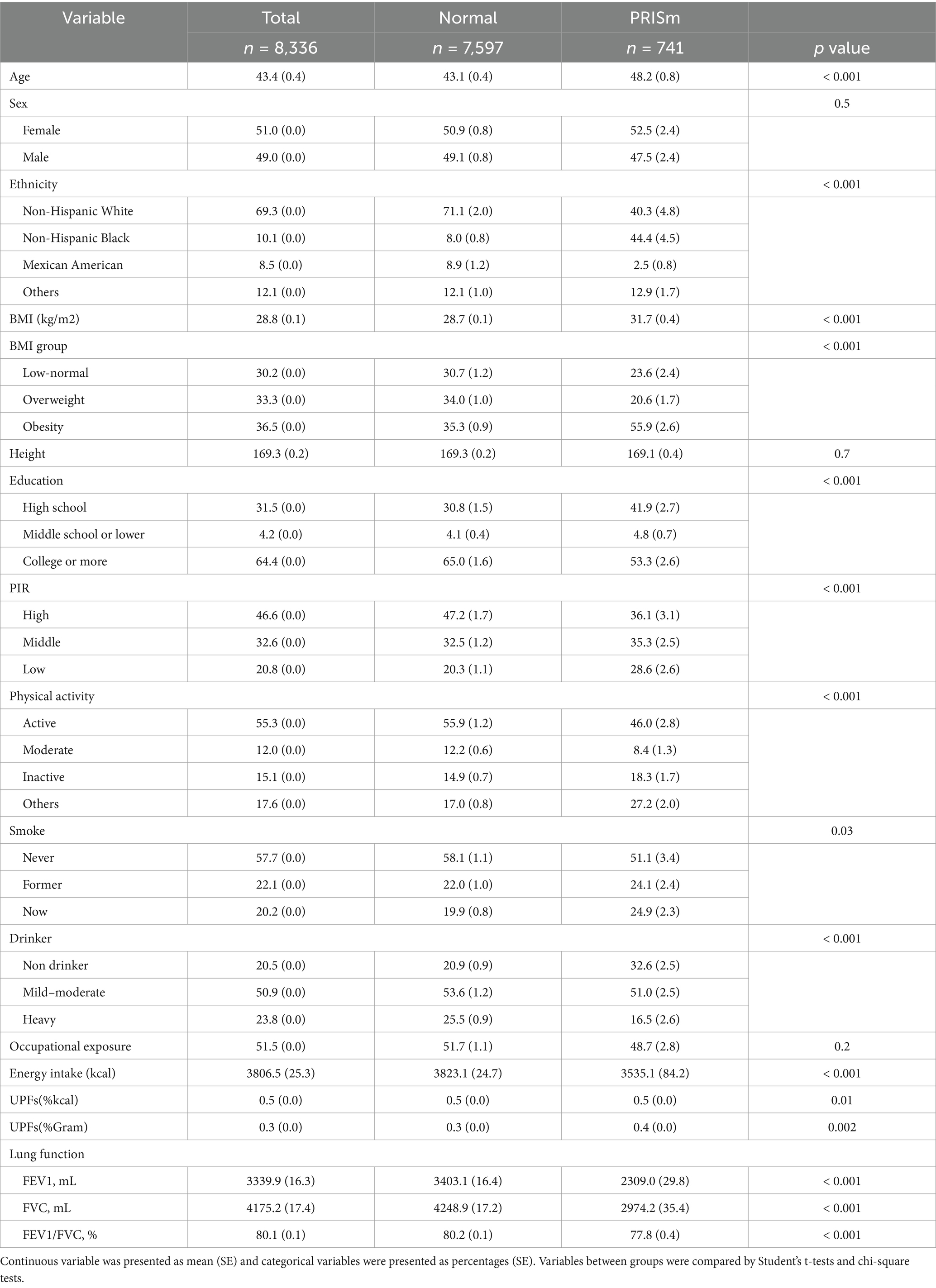
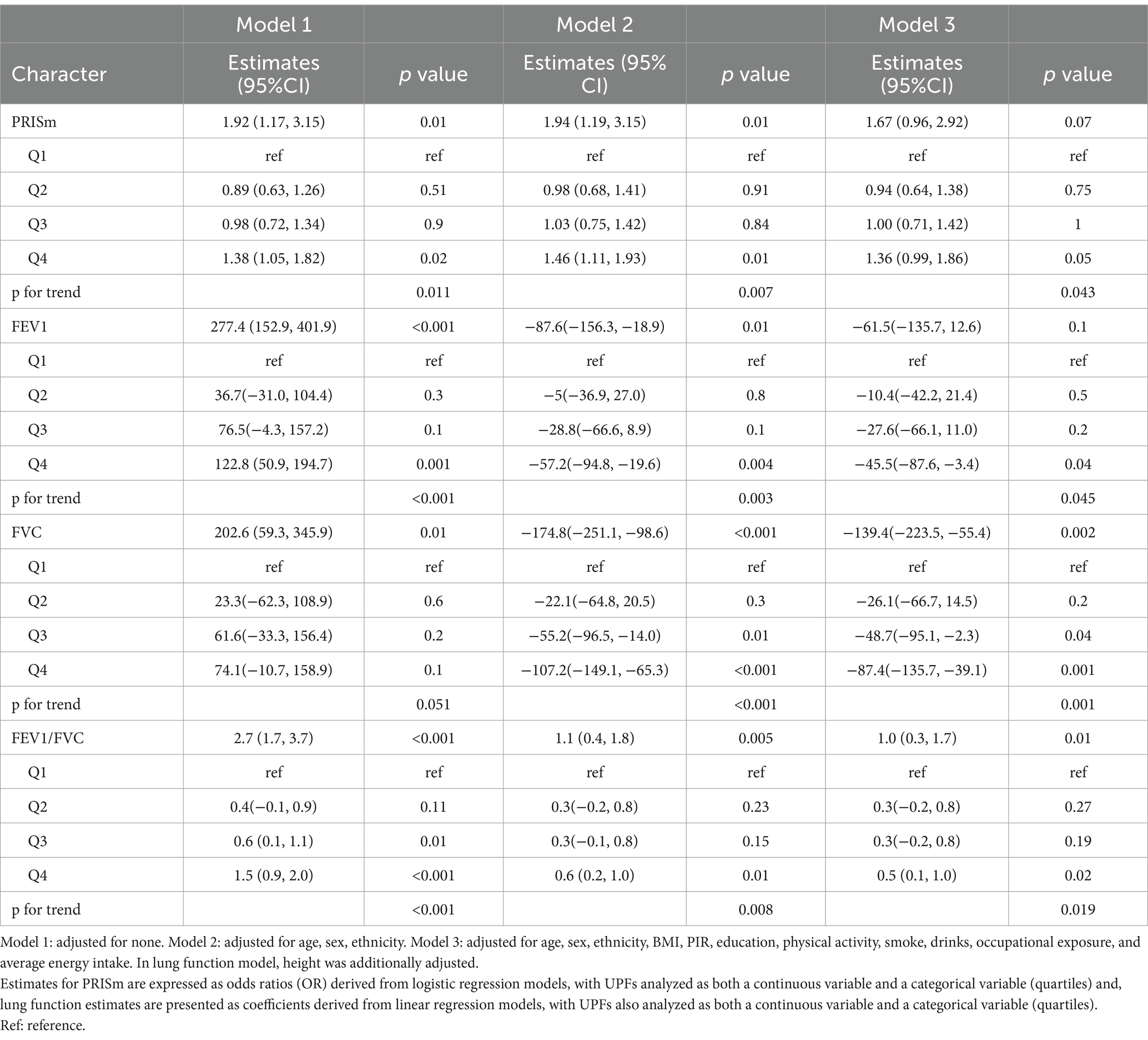
Results: Participants in the PRISm group were older and exhibited various adverse health characteristics. The percentage of total daily energy intake from UPFs (%Kcal) intake was associated with a non-significant increase in PRISm risk (OR 1.67, 95% CI: 0.96–2.92, p = 0.07). However, the highest quartile of UPFs (%Kcal) intake was significantly linked to increased PRISm risk (OR 1.36, 95% CI: 0.99–1.86, P for trend = 0.043). Furthermore, higher UPFs (%Kcal) intake negatively affected lung function, with participants in the highest quartile showing a significant reduction in forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1) of −45.5 mL (95% CI: −87.6 to −3.4, P for trend = 0.045) and a decrease in forced vital capacity (FVC) of −139.4 mL (95% CI: −223.5 to −55.4, p < 0.001) compared to those in the lowest quartile. RCS analysis demonstrated linear relationships for both PRISm and lung function. Subgroup analysis revealed increased susceptibility primarily among individuals with occupational exposure. Additionally, sensitivity analysis indicated that a higher percentage of total daily intake from UPFs (%Grams) intake was significantly associated with an increased risk of PRISm (OR 1.86, 95% CI: 1.07–3.25, p = 0.03).
Conclusion: Higher intake of UPFs is linked to an increased risk of PRISm and negatively affects lung function, particularly in individuals with occupational exposure.
1 Introduction
Ultra-processed foods (UPFs) are foods and beverages produced through a series of complex industrial processes, often with the addition of food additives to enhance taste, appearance, aroma, and shelf life. These products undergo numerous processing steps, most of which cannot be replicated at home, and the final product typically bears little resemblance to its original ingredients (1). These foods undergo multiple processing stages that alter their original composition, introducing additives and preservatives that enhance flavor, prolong shelf life, and increase convenience (2). In recent years, UPFs consumption has surged globally due to factors such as urbanization, aggressive marketing, and lifestyle changes. This trend raises significant public health concerns, as UPFs are associated with low dietary quality and linked to various adverse health outcomes (3). Numerous studies have established strong associations between high UPFs intake and the risk of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disorders (4), obesity (5), type 2 diabetes (6), certain cancers (7), and respiratory health (8).
Preserved ratio impaired spirometry (PRISm) is a respiratory condition characterized by a normal ratio of forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1) to forced vital capacity (FVC), despite a reduction in FEV1 (9). PRISm serves as an important indicator of early lung function decline and is frequently viewed as a precursor to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (9). Its prevalence is particularly high among adults, especially those who smoke or are exposed to environmental pollutants (10–12). Identifying PRISm and its associated risk factors is crucial, as this stage allows for timely intervention to prevent further deterioration of lung function and the progression to COPD, which can lead to symptoms such as shortness of breath and decreased physical ability, ultimately affecting quality of life and increasing healthcare demands (13).
Dietary is recognized as a critical factor in influencing the prognosis of respiratory diseases. Many studies have demonstrated that healthy dietary patterns, as measured by indices like the Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII) and the Composite Dietary Antioxidant Index (CDAI), can help reduce the risk of COPD and its mortality (14, 15). However, there is a notable lack of research exploring the relationship between dietary patterns and PRISm. Therefore, this study aims to explore the relationship between UPFs intake and PRISm among adults using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), providing valuable insights into how dietary influence PRISm and lung function.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Design
NHANES is an ethically approved, cross-sectional study that uses scientific sampling to ensure a representative sample of the U.S. population for health examinations and surveys. This analysis utilized data from three consecutive NHANES cycles (2007–2008, 2009–2010, and 2011–2012), each of which included lung function measurements. From an initial cohort of 30,442 participants, our analyses focused on 8,336 individuals after applying specific inclusion and exclusion criteria. Participants aged ≥20 years old underwent questionnaire interviews, physical examinations, and biospecimen collection at mobile examination centers, providing comprehensive information on demographics, socio-economic status, dietary information, and spirometry results. Further methodological details are presented in Figure 1.
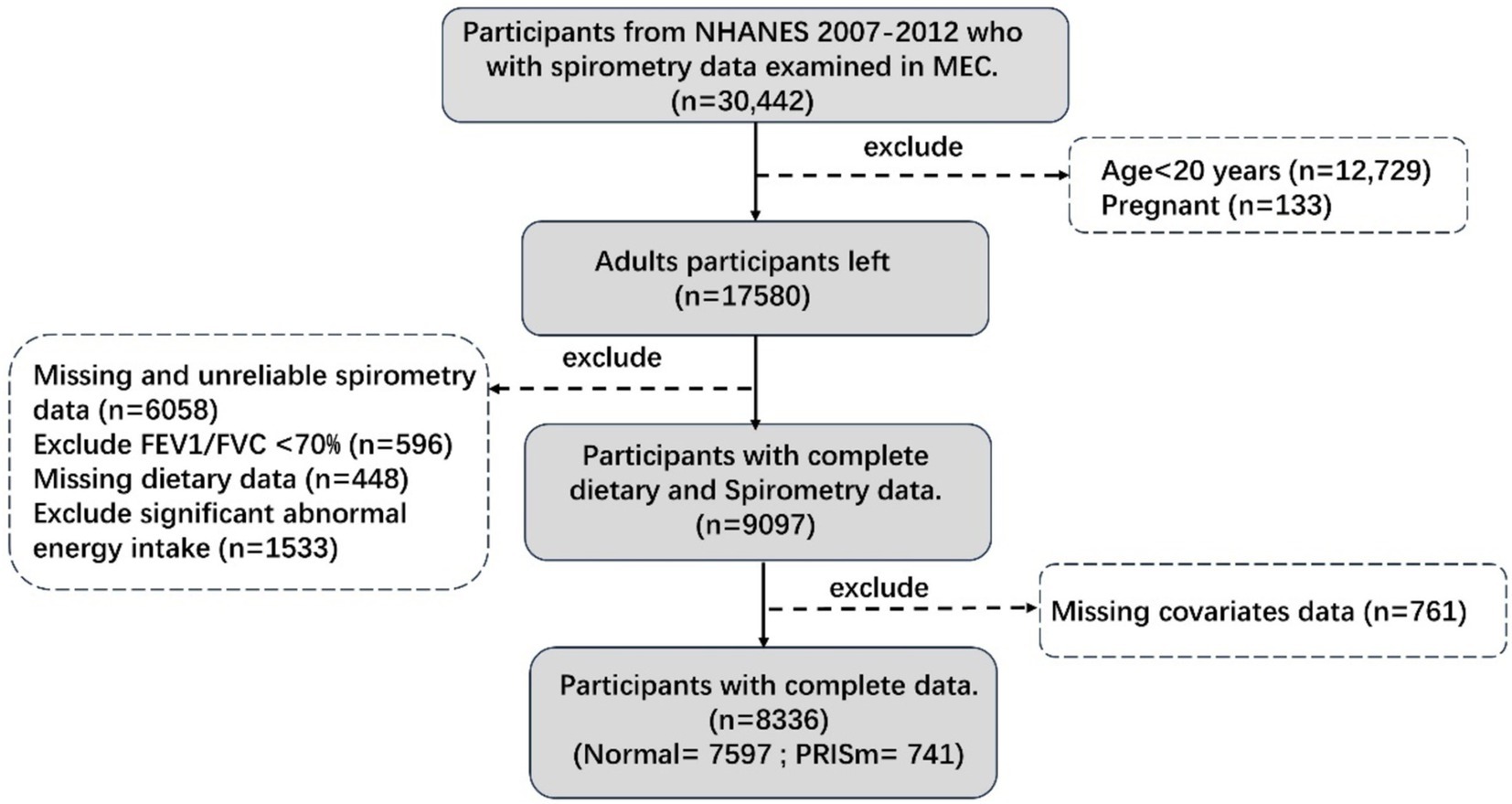
Figure 1. Participants flow chart. Unreliable spirometry: not exceeds or meets the American Thoracic Society data collection standards. Significant abnormal energy intake: total energy intake >5,000 kcal/d for women and > 8,000 kcal/d for men, or < 500 kcal/d.
2.2 UPFs
Individual 24-h dietary recalls were collected using the USDA Multiple-Pass Method, with detailed procedures available on the NHANES website. Based on the NOVA classification, we identified the composition of individual UPFs consumption, recording intake in both calories and grams. We then calculated the percentage of total daily energy intake from UPFs (%Kcal) and the percentage of total daily gram intake from UPFs (%Gram), which served as indicators of UPFs consumption. Further methodological details can be found in our previous publication (16).
2.3 Measurements of spirometry and PRISm definition
Using the pulmonary function parameters from the NHANES SPX dataset, we collected FEV1 and FVC as primary indicators and calculated the FEV1/FVC ratio. PRISm was defined as FEV1/FVC ≥ 0.7 with FEV1% < 80% of the predicted value, where the predicted values were calculated based on the NHANES III equations (17, 18).
2.4 Covariation
Our analysis included a range of covariates known or assumed to be associated with lung function and dietary quality. These covariates were age (as a continuous variable or categorized as <40, 40–59, and ≥ 60 years), sex (female, male), race/ethnicity (non-Hispanic Black, non-Hispanic White, Mexican American, and Others), poverty-to-income ratio (PIR: low <1.3, middle 1.3–3.5, high >3.5), and BMI based on WHO classifications (low-normal, overweight, obese). Education level was categorized as college or higher, high school, and middle school or lower. Alcohol intake was classified as nondrinkers, mild–moderate drinkers (1–3 drinks/day), and heavy drinkers (≥4 drinks/day) (19), while smoking status was divided into current, former, and never smokers. Physical activity level was classified as active, moderate, inactive, or other (20). Additionally, mean daily energy intake was calculated from 2 days’ dietary data. Height was also considered in the analysis of FEV1, FVC, and FEV1/FVC.
2.5 Statistical methods
To accommodate the NHANES complex sampling design, sample weights (Dietary day one sample weight) were applied to all analyses. Continuous variables were presented as weighted means with standard errors (SE), while categorical variables were reported as weighted percentages (SE). Differences in continuous variables between the normal and PRISm groups were analyzed using Student’s t-test, and differences in categorical variables were assessed with the Cochran–Mantel–Haenszel Chi-square test.
Weighted logistic regression was employed to evaluate associations between UPFs (%Kcal) intake and PRISm. Model 1 was unadjusted, while Model 2 adjusted for age, sex, and ethnicity. Model 3 included further adjustments for BMI, PIR, education, physical activity, smoking, alcohol intake, occupational exposure, and average energy intake. Weighted linear regression analyses were conducted to examine associations between UPFs (%Kcal) intake and lung function, utilizing the same three models; however, Model 3 additionally adjusted for height. Restricted cubic spline (RCS) analysis was performed to explore the dose–response relationships between UPFs (%Kcal) intake and both PRISm and lung function, adjusting for all potential confounders. Subsequent subgroup and interaction analyses were also conducted. Finally, a sensitivity analysis was performed to examine the relationships between UPFs (%Gram) intake and both PRISm and lung function parameters. All statistical analyses were conducted using R version 4.4.1.
3 Results
3.1 Participant characteristics
This study included a total of 8,336 U.S. adults, among whom 741 participants were classified in the PRISm group. Participants in the PRISm group were significantly older, with a mean age of 48.2 years, compared to 43.1 years in the normal group. This group was more likely to be non-Hispanic Black individuals, had a higher BMI, lower education levels, lower PIR, inactive physical activity, higher rates of active smoking, a greater proportion of non-drinkers, as well as lower occupational exposure and energy intake. Detailed characteristics are presented in Table 1.
3.2 Associations between UPFs and PRISm and lung function
Table 2 summarizes the associations between UPFs (%Kcal) intake and PRISm and lung function, as assessed through weighted logistic and linear regression analyses. After adjusting for all covariates, continuous UPFs (%Kcal) intake was associated with a non-significant increase in the risk of PRISm (OR 1.67, 95% CI: 0.96–2.92, p = 0.07). However, when categorized into quartiles, the highest quartile of UPFs (%Kcal) intake was significantly associated with an increased risk of PRISm compared to the lowest quartile (OR 1.36, 95% CI: 0.99–1.86, P for trend = 0.043). Additionally, higher UPFs (%Kcal) intake was negatively correlated with lung function. Specifically, participants in the highest quartile exhibited a significant reduction in FEV1 of −45.5 mL (95% CI: −87.6 to −3.4, P for trend = 0.045) and a decrease in FVC of −139.4 mL (95% CI: −223.5 to −55.4, p < 0.001) compared to those in the lowest quartile. The continuous analysis of UPFs (%Kcal) intake also revealed a significant reduction in FVC of −87.4 mL (95% CI: −135.7 to −39.1, P for trend <0.001). Furthermore, continuous UPFs (%Kcal) intake was associated with a modest increase in the FEV1/FVC ratio of 1.0 (95% CI: 0.3–1.7, p = 0.01), with significant associations noted in the highest quartile (0.5, 95% CI: 0.1–1.0, P for trend = 0.019).
3.3 Dose–response relationship
RCS analysis revealed linear relationships between UPFs, PRISm, and lung function (Figure 2). A linear association for PRISm was observed (P overall = 0.067, P nonlinearity = 0.196). Significant linear associations were found for FEV1 (P overall = 0.0411, P nonlinearity = 0.9942), FVC (P overall <0.001, P nonlinearity = 0.7524), and FEV1/FVC (P overall = 0.0008, P nonlinearity = 0.7941).
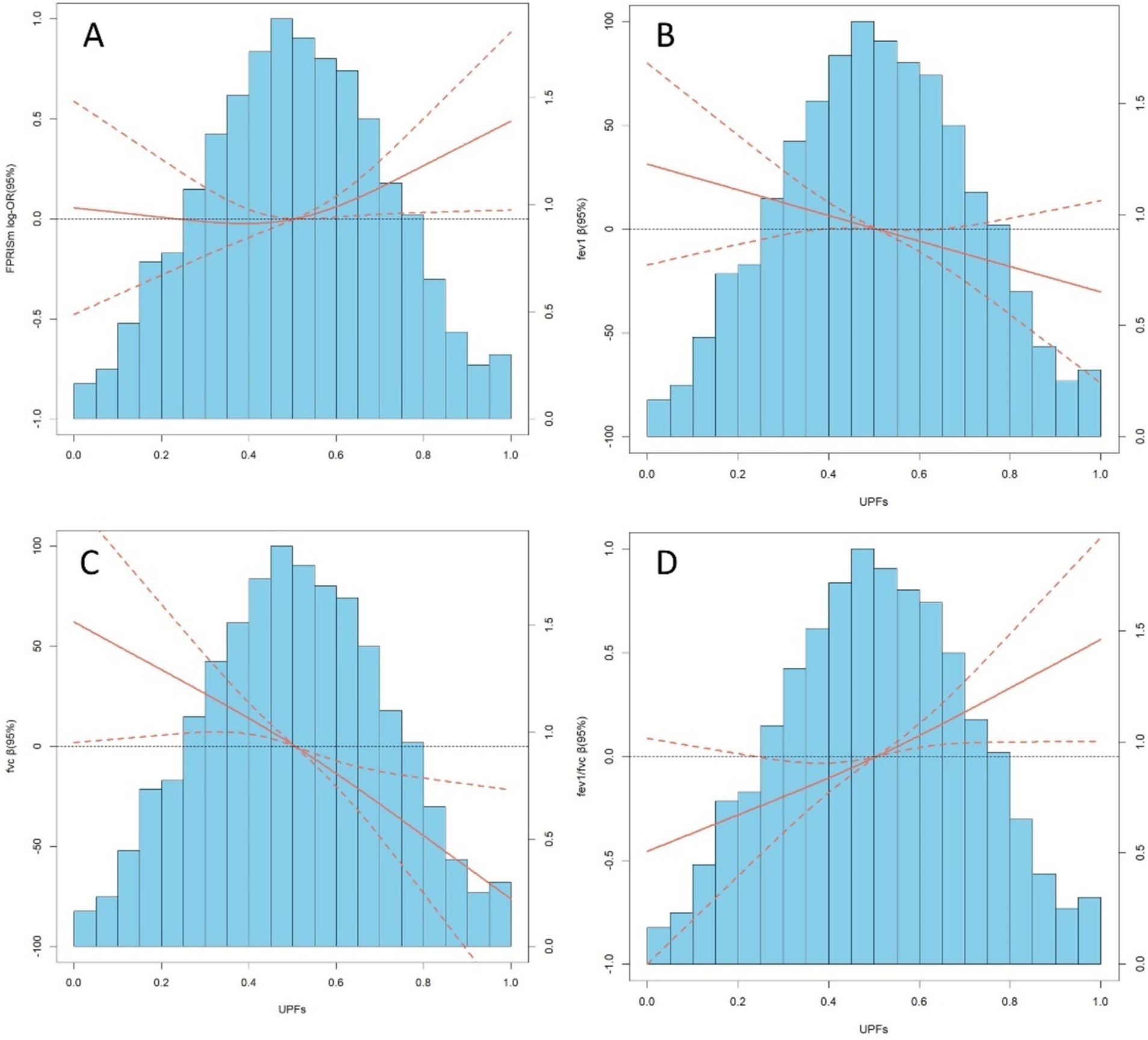
Figure 2. (A–D) depict distributions of frequency of UPFs (%Kcal) and dose–response relationship between UPFs (%Kcal) and PRISm and lung function in the sample of 8,336 U. S adults from NHANES 2007 to 2012. Red solid lines and Red dotted line represent RCS models and 95%CI, respectively. Multivariable linear regression model is used to estimate the fully adjusted estimates in PRISm and lung function and corresponding 95%CI. Models were adjusted by age, sex, ethnicity, BMI, PIR, education, physical activity, smoke, drinks, occupational exposure, and average energy intake. In lung function model, height was additionally adjusted.
3.4 Subgroup and interaction analysis
Stratified analysis by selected covariates revealed differential associations between UPFs (%Kcal) intake, PRISm, and lung function (Table 3). Individuals with occupational exposure demonstrated heightened susceptibility to the effects of UPFs (%Kcal) intake on PRISm, FVC, and FEV1/FVC, with significant interactions noted (P for interaction = 0.035, 0.036, and 0.023, respectively). Moreover, UPFs (%Kcal) showed a stronger impact on FEV1 among non-Hispanic Black individuals (P for interaction = 0.019). For FVC, the greatest effects were observed in males and both non-Hispanic White and Black populations, with interaction p-values of 0.024 and 0.039.
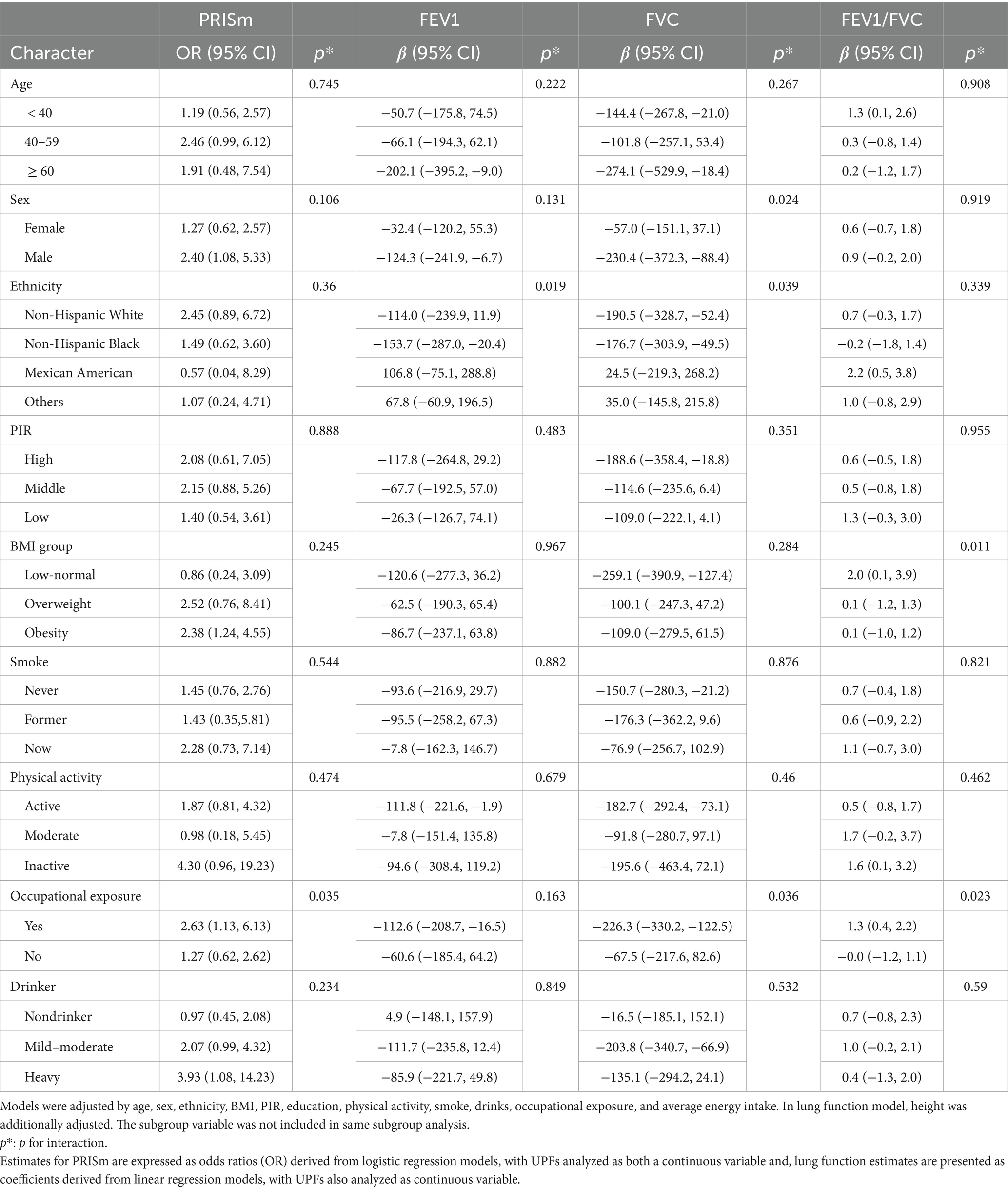
Table 3. Subgroup and interaction analyses between UPFs (%Kcal) and PRISm and lung function, stratified by selected covariates.
3.5 Sensitivity analysis
To account for the fact that some additives in UPFs may not be measured in calories, we also analyzed the relationship between UPFs (%Grams) intake and PRISm and lung function (Table S1). Our findings indicated that the results remained consistent, showing that UPFs (%Grams) intake were significantly associated with an increased risk of PRISm (OR 1.86, 95% CI: 1.07–3.25, p = 0.03).
4 Discussion
This study identified significant associations between UPFs intake and both PRISm and lung function. Participants with higher UPFs (%Kcal) consumption exhibited an increased risk of PRISm compared to those with lower intake levels. Additionally, a marked decline in critical lung function indicators, specifically FEV1 and FVC, was observed among individuals consuming greater amounts of UPFs (%Kcal). Stratified analyses and interaction tests further revealed a stronger association between UPFs and PRISm among individuals exposed to occupational environments. Notably, UPFs intake measured in grams was more strongly correlated with the increased risk of PRISm.
PRISm is an unstable classification and may serve as a precursor to COPD, preventing its progression is essential (13, 21, 22). Just as COPD requires nutritional support and management, the role of dietary patterns in PRISm is increasingly recognized (23). However, evidence regarding the impact of UPFs is lacking. Previous studies have primarily focused on the relationship between UPFs consumption and COPD risk, for instance, a prospective cohort study from the UK Biobank found a correlation between UPFs intake and increased COPD risk (24). Moreover, UPFs represent a typical western dietary pattern characterized by high consumption of processed meats, refined grains, desserts, and sugary foods, and evidence showed the western dietary pattern are associated with a higher risk of COPD (25–27). Notably, specific components related to UPFs, such as processed red meat, have been linked to a 26% increase in COPD risk (28). Recent investigations have begun to explore the association between the DII and CDAI with PRISm, highlighting the potential significance of anti-inflammatory and antioxidant diets in this context (29). Our study further enhances the understanding of dietary patterns’ effects on PRISm and extends the linkage between high UPFs consumption and respiratory health. The main results and sensitivity analyses indicated potential adverse impacts of UPFs on PRISm and lung function, regardless of whether intake was measured in grams or energy, underscoring concerns about the elevated risk of PRISm associated with high UPFs consumption. Specifically, UPFs were found to be negatively associated with both FEV1 and FVC, suggesting that managing the degree of food processing may be critical in the prevention and management of PRISm. Additionally, our findings indicate that individuals with occupational exposure may be at an increased risk of PRISm, likely due to from prolonged exposure, thereby calling for sufficient nutrient support to sustain immune defense responses (30). Furthermore, we observed variations in FEV1 and FVC related to race and sex, and the underlying reasons for these differences warrant further investigation.
Mechanistically, the adverse effects of UPFs on lung function are well-documented. Classified according to the NOVA classification, UPFs often lose a significant amount of nutrients during industrial processing and are characterized by high levels of added sugars and food additives, leading to their reputation for poor nutritional quality (31). Numerous studies have demonstrated that deficiencies in nutrients, including fruits, vegetables, and vitamins, negatively affect respiratory health (32, 33). The absence of these nutrients may compromise immune defense responses, contributing to inflammation and oxidative imbalance (34–36). Additionally, the high-fat, high-sugar, and low-quality protein characteristics of UPFs can adversely affect metabolic processes (37). Previous research has established the metabolic indicators such as the ratio of non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, Triglyceride-Glucose Index (TyG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and albumin can lead to chronic airway inflammation and sustained respiratory tissue damage (38–41). Moreover, the high sugar and fat content of UPFs, combined with exposure to food additives and microplastics from packaging, may disrupt gut microbiota. This dysbiosis can subsequently influence lung health through the gut-lung axis, thereby affecting pulmonary immune homeostasis—a concern that is increasingly being acknowledged in the literature (42–44).
Our research fills a critical gap by addressing the limitations of previous studies that focused on individual nutrients or food groups in relation to COPD. We have expanded the knowledge about the complex relationships between food processing, dietary combinations, and the risk of PRISm. However, this study still has limitations. As with all cross-sectional studies, it cannot establish causal relationships. Although we adjusted for multiple confounding factors and conducted sensitivity analyses, residual confounding cannot be entirely ruled out. Dietary assessments conducted through questionnaires may introduce measurement error, and since NHANES did not classify diets according to the NOVA classification, there may be bias in dietary categorization. Furthermore, our analysis relied on 24-h dietary recalls, which may not accurately reflect changes in dietary habits over time. Therefore, additional clinical trials or intervention studies are necessary to further explore and confirm these findings.
In conclusion, our study provides evidence that high UPFs consumption is associated with increased risks of PRISm, FEV1, and FVC decline. This research offers novel insights into the potential for dietary interventions aimed at preventing PRISm and mitigating its progression to COPD. However, the conclusion should be interpreted with caution due to the limitations of cross-sectional design. More prospective studies and mechanistic investigations are warranted to explore these relationships further.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: data from NHANES collection was sponsored by the CDC, and are publicly available (https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/Default.aspx).
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by National Center for Health Statistics. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
WK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Zhejiang Traditional Chinese Medicine Administration (2024ZF027), Medical Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Province (2024KY320), and Ningbo Municipal Bureau of Science and Technology (2023Y94).
Acknowledgments
The author thanks National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey for publicly available data.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1523736/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
NHANES, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; BMI, Body Mass Index (weight [kg]/height[m]2); CI, Confidence Intervals; COPD, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease; CDAI, Composite Dietary Antioxidant Index; DII, Inflammatory Index; DM, Diabetes Mellitus; FEV1, Forced expiratory volume in one second; FVC, Forced vital capacity; PRISm, Preserved ratio impaired spirometry; PIR, Poverty-to-Income Ratio; UPFs, Ultra-Processed Foods; %Kcal, the percentage of total daily energy intake from UPFs; %Gram, the percentage of total daily gram intake from UPFs; SE, Standard Errors; RCS, Restricted Cubic Spline; TyG, Triglyceride-Glucose Index.
References
1. Lawrence, M. Ultra-processed foods: a fit-for-purpose concept for nutrition policy activities to tackle unhealthy and unsustainable diets. Br J Nutr. (2023) 129:2195–8. doi: 10.1017/S000711452200280X
2. Robinson, E, Cummings, JR, Gough, T, Jones, A, and Evans, R. Consumer awareness, perceptions and avoidance of ultra-processed foods: A study of UK adults in 2024. Food Secur. (2024) 13:2317. doi: 10.3390/foods13152317
3. Wang, QH, Chen, H, Han, W, and Guo, XK. High ultra-processed foods consumption is unfavourable to health outcomes. Clin Nutr. (2024) 43:1812–3. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2024.06.011
4. Rauber, F, and Levy, RB. Ultra-processed foods and cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2024) 21:213–4. doi: 10.1038/s41569-024-00990-7
5. Zancheta, C, Rebolledo, N, Smith Taillie, L, Reyes, M, and Corvalán, C. The consumption of ultra-processed foods was associated with adiposity, but not with metabolic indicators in a prospective cohort study of Chilean preschool children. BMC Med. (2024) 22:340. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03556-z
6. Amirian, P, Zarpoosh, M, Najafi, F, Shakiba, E, Anvari, B, and Pasdar, Y. Ultra-processed foods and type 2 diabetes mellitus incidence in RaNCD project: a prospective cohort study. Acta Diabetol. (2024). doi: 10.1007/s00592-024-02385-z
7. Xiang, P, Yan, W, Liu, D, and Ping, H. The relationship between ultra-processed foods consumption and urological cancers risk. Clin Nutr. (2024) 43:1655–7. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2024.01.016
8. Li, H, Li, S, Yang, H, Zhang, Y, Ma, Y, Hou, Y, et al. Association of Ultra-Processed Food Intake with cardiovascular and respiratory disease multimorbidity: A prospective cohort study. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2023) 67:e2200628. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202200628
9. Siddharthan, T, Grealis, K, Robertson, NM, Lu, M, Liu, S, Pollard, SL, et al. Assessing the prevalence and impact of preserved ratio impaired spirometry in low-income and middle-income countries: a post-hoc cross-sectional analysis. Lancet Glob Health. (2024) 12:e1498–505. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(24)00233-X
10. Cadham, CJ, Oh, H, Han, MK, Mannino, D, Cook, S, Meza, R, et al. The prevalence and mortality risks of PRISm and COPD in the United States from NHANES 2007-2012. Respir Res. (2024) 25:208. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02841-y
11. Huang, J, Li, W, Sun, Y, Huang, Z, Cong, R, Yu, C, et al. Preserved ratio impaired spirometry (PRISm): A global epidemiological overview, radiographic characteristics, comorbid associations, and differentiation from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2024) 19:753–64. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S453086
12. Chen, C, Zhang, S, Yang, T, Wang, C, and Han, G. Associations between environmental heavy metals exposure and preserved ratio impaired spirometry in the U.S. adults. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. (2023) 30:108274–87. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-29688-y
13. Jo, YS, Rhee, CK, Kim, SH, Lee, H, and Choi, JY. Spirometric transition of at risk individuals and risks for progression to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in general population. Arch Bronconeumol. (2024) 60:634–42. doi: 10.1016/j.arbres.2024.05.033
14. Tian, TL, Zhi, TY, Xie, ML, Jiang, YL, and Qu, XK. Dietary inflammatory index and all-cause mortality in adults with COPD: a prospective cohort study from the NHANES 1999-2018. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1421450. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1421450
15. Liu, Z, Li, J, Chen, T, Zhao, X, Chen, Q, Xiao, L, et al. Association between dietary antioxidant levels and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a mediation analysis of inflammatory factors. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1310399. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1310399
16. Kong, W, Xie, Y, Hu, J, Ding, W, and Cao, C. Higher ultra processed foods intake is associated with low muscle mass in young to middle-aged adults: a cross-sectional NHANES study. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1280665. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1280665
17. Wan, ES, Balte, P, Schwartz, JE, Bhatt, SP, Cassano, PA, Couper, D, et al. Association between preserved ratio impaired spirometry and clinical outcomes in US adults. JAMA. (2021) 326:2287–98. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.20939
18. Bowerman, C, Bhakta, NR, Brazzale, D, Cooper, BR, Cooper, J, Gochicoa-Rangel, L, et al. A race-neutral approach to the interpretation of lung function measurements. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2023) 207:768–74. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202205-0963OC
19. Hicks, CW, Wang, D, Matsushita, K, Windham, BG, and Selvin, E. Peripheral neuropathy and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in U.S. adults: A prospective cohort study. Ann Intern Med. (2021) 174:167–74. doi: 10.7326/M20-1340
20. Kim, D, Vazquez-Montesino, LM, Li, AA, Cholankeril, G, and Ahmed, A. Inadequate physical activity and sedentary behavior are independent predictors of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. (2020) 72:1556–68. doi: 10.1002/hep.31158
21. Emily, SW, Spyridon, F, Elizabeth, AR, Hokanson, J, Han, MK, Casaburi, R, et al. Longitudinal phenotypes and mortality in preserved ratio impaired spirometry in the COPDGene study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 198:1397. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201804-0663OC
22. Wan, ES, Hokanson, JE, Regan, EA, Young, KA, Make, BJ, DL, DM, et al. Significant Spirometric transitions and preserved ratio impaired spirometry among ever smokers. Chest. (2021) 161:651–61. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2021.09.021
23. Heefner, A, Simovic, T, Mize, K, and Rodriguez-Miguelez, P. The role of nutrition in the development and Management of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Nutrients. (2024) 16:1136. doi: 10.3390/nu16081136
24. He, Q, Sun, M, Zhao, H, Sun, N, Han, Q, Feng, Z, et al. Ultra-processed food consumption, mediating biomarkers, and risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a prospective cohort study in the UK biobank. Food Funct. (2023) 14:8785–96. doi: 10.1039/D3FO02069J
25. Maldonado-Pereira, L, Barnaba, C, and Medina-Meza, IG. Oxidative status of ultra-processed foods in the Western diet. Nutrients. (2023) 15:4873. doi: 10.3390/nu15234873
26. Shaheen, SO, Jameson, KA, Syddall, HE, Aihie Sayer, A, Dennison, EM, Cooper, C, et al. The relationship of dietary patterns with adult lung function and COPD. Eur Respir J. (2010) 36:277–84. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00114709
27. Sorli-Aguilar, M, Martin-Lujan, F, Flores-Mateo, G, Arija-Val, V, Basora-Gallisa, J, and Sola-Alberich, R. Dietary patterns are associated with lung function among Spanish smokers without respiratory disease. BMC Pulm Med. (2016) 16:162. doi: 10.1186/s12890-016-0326-x
28. Kaluza, J, Larsson, SC, Linden, A, and Wolk, A. Consumption of unprocessed and processed red meat and the risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A prospective cohort study of men. Am J Epidemiol. (2016) 184:829–36. doi: 10.1093/aje/kww101
29. Zheng, Y, Liu, W, Zhu, X, Xu, M, Lin, B, and Bai, Y. Associations of dietary inflammation index and composite dietary antioxidant index with preserved ratio impaired spirometry in US adults and the mediating roles of triglyceride-glucose index: NHANES 2007-2012. Redox Biol. (2024) 76:103334. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103334
30. Zhang, FQ, Chen, J, and Fan, H. Eating for immunity: how diet shapes our defenses. Curr Opin Immunol. (2024) 91:102486. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2024.102486
31. Lauria, F, Dello Russo, M, Formisano, A, De Henauw, S, Hebestreit, A, Hunsberger, M, et al. Ultra-processed foods consumption and diet quality of European children, adolescents and adults: results from the I Family study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2021) 31:3031–43. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2021.07.019
32. Kaluza, J, Harris, HR, Linden, A, and Wolk, A. Long-term consumption of fruits and vegetables and risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a prospective cohort study of women. Int J Epidemiol. (2018) 47:1897–909. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyy178
33. Kaluza, J, Larsson, SC, Orsini, N, Linden, A, and Wolk, A. Fruit and vegetable consumption and risk of COPD: a prospective cohort study of men. Thorax. (2017) 72:500–9. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2015-207851
34. Gęgotek, A, and Skrzydlewska, E. Antioxidative and anti-inflammatory activity of ascorbic acid. Antioxidants (Basel). (2022) 11:1993. doi: 10.3390/antiox11101993
35. Ghalibaf, MHE, Kianian, F, Beigoli, S, Behrouz, S, Marefati, N, Boskabady, M, et al. The effects of vitamin C on respiratory, allergic and immunological diseases: an experimental and clinical-based review. Inflammopharmacology. (2023) 31:653–72. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01169-1
36. Xu, J, Zeng, Q, Li, S, Su, Q, and Fan, H. Inflammation mechanism and research progress of COPD. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1404615. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1404615
37. Poursalehi, D, Tirani, SA, Shahdadian, F, Hajhashemy, Z, Rouhani, P, and Saneei, P. Ultra-processed foods intake in relation to metabolic health status, serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor and adropin levels in adults. Nutr J. (2024) 23:121. doi: 10.1186/s12937-024-01024-1
38. Wu, R, and Gong, H. The association between non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the mediating role of dietary inflammatory index. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1427586. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1427586
39. Wu, TD, Fawzy, A, Brigham, E, McCormack, MC, Rosas, I, Villareal, DT, et al. Association of Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Lung Health: A population-based study. Chest. (2021) 160:1026–34. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2021.03.056
40. Freyberg, J, Landt, EM, Afzal, S, Nordestgaard, BG, and Dahl, M. Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and risk of COPD: Copenhagen general population study. ERJ Open Res. (2023) 9:00496–2022. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00496-2022
41. Cruthirds, CL, Deutz, NEP, Harrykissoon, R, Zachria, AJ, and Engelen, M. A low postabsorptive whole body protein balance is associated with markers of poor daily physical functioning in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin Nutr. (2022) 41:885–93. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2022.02.018
42. Whelan, K, Bancil, AS, Lindsay, JO, and Chassaing, B. Ultra-processed foods and food additives in gut health and disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2024) 21:406–27. doi: 10.1038/s41575-024-00893-5
43. Brichacek, AL, Florkowski, M, Abiona, E, and Frank, KM. Ultra-processed foods: A narrative review of the impact on the human gut microbiome and variations in classification methods. Nutrients. (2024) 16:1738. doi: 10.3390/nu16111738
Keywords: ultra-processed foods, PRISm, lung function, NHANES, pre-COPD
Citation: Kong W (2025) Associations between ultra-processed foods intake and preserved ratio impaired spirometry in U.S. adults. Front. Nutr. 12:1523736. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1523736
Edited by:
Sandra González-Palacios, Miguel Hernández University of Elche, SpainReviewed by:
Spyridon Fortis, The University of Iowa, United StatesSiew Tin Tan, International Medical University, Malaysia
Copyright © 2025 Kong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Weiliang Kong, TGl2ZWtvbmdAaG90bWFpbC5jb20=
 Weiliang Kong
Weiliang Kong