- 1Shanxi Finance and Taxation College, Taiyuan, China
- 2Shanxi Intelligent Big Data Industry Technology Innovation Research Institute, Taiyuan, China
- 3Shanxi Provincial Digital Government Service Center, Taiyuan, China
Autonomous driving is the future trend. Accurate 3D object detection is a prerequisite for achieving autonomous driving. Currently, 3D object detection relies on three main sensors: monocular cameras, stereo cameras, and lidar. In comparison to methods based on stereo cameras and lidar, monocular 3D object detection offers advantages such as a broad detection field and low deployment costs. However, the accuracy of existing monocular 3D object detection methods is not ideal, especially for occluded targets. To tackle this challenge, the paper introduces a novel approach for monocular 3D object detection, denoted as SRDDP-M3D, aiming to improve monocular 3D object detection by considering spatial relationships between targets, and by refining depth predictions through a decoupled approach. We consider how objects are positioned relative to each other in the environment and encode the spatial relationships between neighboring objects, the detection performance is enhanced specially for occluded targets. Furthermore, a strategy of decoupling the prediction of target depth into two components of target visual depth and target attribute depth is introduced. This decoupling is designed to improve the accuracy of predicting the overall depth of the target. Experimental results using the KITTI dataset demonstrate that this approach substantially enhances the detection accuracy of occluded targets.
1 Introduction
Autonomous driving stands as a pivotal and forward-looking development in the realm of future transportation. Its significance extends beyond just technological advancements; it encompasses the realms of enhancing traffic safety, optimizing driving efficiency, conserving drivers’ time and energy, mitigating environmental pollution, and ultimately ushering in an era of intelligent transportation systems. At the heart of this transformative technology lies 3D object detection, a fundamental and indispensable component. This technology enables a precise perception of the environment, empowering vehicles to recognize, locate obstacles, and make informed decisions, thereby facilitating advanced driving strategies and path planning.
With the integration of multisensory data fusion and the ability to perform real-time, stable processing, 3D object detection establishes the essential groundwork for the realization of safer and more efficient autonomous driving systems. It is dedicated to the task of accurately pinpointing and identifying objects from images or point cloud data, extracting critical details such as their 3D position, orientation, and size. Unlike conventional 2D object detection, 3D object detection goes beyond mere object existence detection; it incorporates a nuanced modeling and estimation of an object’s physical properties within the real-world context. This calls for a fusion of depth perception and geometric computation technologies.
In the context of the various forms of sensor input data, the 3D object detection challenge can be broadly categorized into three types: LiDAR-based, stereo camera-based, and monocular camera-based 3D object detection. Each type leverages distinct sensor technologies and methods to address the intricacies of the autonomous driving environment (Qian et al., 2022).
LiDAR-based 3D object detection is a method that leverages point cloud data from LiDAR sensors to detect and classify objects in the surrounding environment. LiDAR technology excels at delivering precise, albeit somewhat sparse, scene point cloud data. Nonetheless, contemporary LiDAR instruments are constrained in their ability to accurately measure distances within a range typically spanning 1–200 m. This inherent limitation renders exclusive reliance on LiDAR for autonomous driving control precarious, especially in scenarios like high-speed highways.
Consequently, many autonomous driving enterprises, such as Tesla and Baidu Apollo, adopt a hybrid approach that combines LiDAR data with information from cameras to construct robust autonomous driving systems. This amalgamation addresses the shortcomings of LiDAR, including its cost-intensive nature and the range constraints. Overcoming these challenges is pivotal for the widespread adoption and acceptance of autonomous driving technologies.
Stereo camera-based 3D object detection (Chen et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2017; Li et al., 2019) is a sophisticated technique that harnesses the power of multiple precisely calibrated cameras mounted on a vehicle, each with known baselines, to achieve object detection. By concurrently capturing image data from diverse vantage points, this approach allows for the reconstruction of a scene’s 3D structure and object positions. The underlying principle of this algorithm is rooted in the stereo matching concept applied to images, using the baseline distance and corresponding pixel coordinates between the left and right cameras to compute the depth information of objects within the camera’s coordinate system. Through the meticulous matching and alignment of images from these different perspectives, precise depth estimation results are achieved, enabling accurate object detection.
For instance, Tesla’s autonomous driving system utilizes an entirely visual approach, employing eight cameras in total. While research on stereo camera-based algorithms has evolved into a more established and conventional field, the widespread adoption of this technology is impeded by the persistently high cost of stereo camera equipment. This economic barrier remains a challenge to its broader proliferation.
Monocular 3D object detection (Ding et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2021; Mousavian et al., 2017; Li et al., 2019; Shi et al., 2021; Simonelli et al., 2019) is a technique that leverages single-camera images, alongside camera calibration, to extrapolate 3D information from 2D data, ultimately culminating in the precise detection of a 3D object’s bounding box. Monocular 3D object detection methods offer a multitude of advantages, including an expansive measurement range, exceedingly economical equipment costs, making them ideal for broad-scale implementation, in stark contrast to LiDAR or stereo camera-based alternatives. However, it is essential to note that the current accuracy of monocular 3D object detection methods falls short of practical requirements, particularly when confronted with the task of detecting occluded targets.
Monocular 3D object detection using machine learning models for 2D image segmentation with depth predictions enables cost-effective and efficient autonomous driving systems. Models like Monodepth and DepthNet predict depth from 2D images, enhancing object recognition and navigation. However, challenges remain, particularly with occlusion and depth accuracy in dynamic environments. Research (Wijesekara, 2022) has improved depth estimation, but these models often struggle with generalizing across diverse real-world scenarios. The research gap lies in enhancing model robustness for real-time applications, improving accuracy under occlusions, and addressing computational efficiency for scalable deployment.
To address this inherent challenge, this paper proposes a monocular 3D object detection method based on the Spatial Relationships and Decoupled Depth Predictions (SRDDP-M3D). By encoding the spatial relationships between adjacent targets, the detection performance of occluded targets is improved. Additionally, the depth prediction for targets is decoupled into target visual depth and target attribute depth, enhancing the accuracy of target depth prediction.
2 Related work
Presently, existing monocular 3D object detection methods can be broadly categorized into three distinct groups: geometric projection model-based 3D object detection, pseudo-LiDAR-based 3D object detection, and 2D-to-3D feature-based object detection.
Geometric projection model-based 3D object detection methods rely on the application of geometric projection models to estimate depth from 2D object bounding boxes, subsequently allowing for the prediction of the 3D object bounding box (Lu et al., 2021). These models are constructed based on the geometric congruence between the object’s depth, camera focal length, actual object height, and the height as projected onto the image plane. Consequently, the prediction of object depth becomes synonymous with predicting the actual height of the object and its projected height in the image. Notably, Chen et al. (2020) introduced the MonoPair technique, an innovative monocular 3D object detection method that particularly excels in detecting partially obscured objects, thanks to its consideration of paired sample relationships and the application of spatial encoding constraints. Their experiments underscore the substantial enhancements in detecting occluded objects. Similarly, Liu et al. (2021) put forth MonoFlex, a versatile monocular 3D object detection method that effectively decouples truncated objects and merges various approaches for object depth estimation, thereby elevating detection performance while preserving real-time efficiency. Additionally, Zhou et al. (2019) identified an issue during the projection process, wherein the error in estimating height became magnified when inferring depth. This error escalation hindered the control over depth inference and disrupted the training efficiency. In response, they introduced the geometric uncertainty projection network, GUPNet, to rectify this magnification problem during inference and training phases. Furthermore, Shi et al. (2021) presented a method for geometric distance decomposition, which dissects the object’s distance into the physical height on the image plane and the visual height projected. This decomposition process enhances the interpretability, accuracy, and robustness of distance predictions. Motivated by these advancements, this paper embraces geometric projection models to offer a swift and precise preliminary depth estimation for object detection.
Pseudo-LiDAR-based 3D object detection methods leverage well-established monocular depth estimation techniques to generate dense depth maps corresponding to images (Fu et al., 2018). These dense depth maps are then transformed into 3D space to create a pseudo-LiDAR representation. Subsequently, 3D detection methods, reliant on point cloud data, are employed to detect objects. Notably, studies such as Weng and Kitani (2019), Wang et al. (2019), You et al. (2020), Guo et al. (2021), and Reading et al. (2021) have successfully implemented pseudo-LiDAR-based monocular 3D object detection, achieving commendable accuracy. However, it is important to note that these approaches necessitate the computation of point cloud data, which demands substantial memory resources, leading to slower processing speeds. Additionally, pseudo-LiDAR data often suffers from persistent noise interference, making its elimination a challenging task.
Hence, this paper adopts a different strategy by bypassing the direct calculation of intermediate point cloud data. Instead, it integrates the 3D geometric structure into the image-based network, allowing for the implicit learning of depth distribution within images in an end-to-end fashion.
2D-to-3D feature-based object detection methods aim to establish a mapping between 2D image features and their corresponding 3D spatial representations (Kumar et al., 2021, Yu et al., 2018, Liu et al., 2019, Woo et al., 2018, Hu et al., 2018). Unlike methods that directly generate pseudo-LiDAR point cloud data, these approaches rely on the utilization of features within 3D space for object detection.
For instance, Reading et al. (2021)) introduced the CaDDN method, a fully differentiable end-to-end monocular 3D object detection technique. CaDDN effectively projects abundant contextual feature information into the appropriate depth interval within 3D space, guided by the predicted class depth distribution for each pixel. Subsequently, a computationally efficient bird’s-eye view projection and a single-stage detector are employed to yield the ultimate 3D object detection results.
Furthermore, Zhang et al. (2021) proposed the DID-M3D network, which introduces the concept of instance depth as a combination of instance visual surface depth (visual depth) and instance attribute depth (attribute depth). This innovation enhances depth estimation accuracy. It is noteworthy that these methods avoid the direct computation of point cloud data for object detection. Instead, they enrich features with estimated depth information, subsequently facilitating the detection process. This approach not only enhances model efficiency and user-friendliness but also supports end-to-end training. In alignment with this methodology, our paper also follows suit.
Ma et al. (2021) conducted an extensive array of diagnostic experiments to assess the influence of various subtasks within monocular 3D object detection on the ultimate detection outcomes. Their findings underscored the pivotal role of “localization error” in constraining monocular 3D detection accuracy. Building upon this insight, we further discovered that distant objects exhibit notably larger localization errors in comparison to their close-range counterparts, leading to a considerable performance disparity between the two. Distant objects occupy fewer pixels in the image and offer limited informational cues, which naturally translates to more significant localization errors. Conversely, close-range objects encompass a richer pixel representation, contributing to heightened detection accuracy.
It is essential to acknowledge that distant and close-range objects manifest distinct characteristics. Utilizing a uniform detection methodology tends to inadequately extract features from distant objects, detrimentally impacting detection accuracy. As a solution, we advocate the implementation of differentiated processing techniques for distant and close-range objects, thereby effecting a substantial enhancement in the detection performance of distant objects while preserving the efficacy of close-range object detection. This strategic approach serves to ameliorate the overall performance of monocular 3D object detection.
The paper offers the following notable contributions:
1. We propose an innovative monocular 3D object detection method based on the Spatial Relationships and Decoupled Depth Predictions (SRDDP-M3D).
2. We propose to detect obscured targets by encoding the spatial relationships between adjacent targets. By considering how objects relate to each other in space, it enhances the detection of targets that might be hidden or obstructed in the scene by fully understanding and utilizing the spatial context between nearby targets for more effective 3D object detection.
3. We propose to separate the prediction of target depth into two components: visual depth and attribute depth. Visual depth is related to how the object appears in the image, considering its size and position. Attribute depth, on the other hand, represents the depth offset from the visible surface to the 3D center of the object, capturing intrinsic attributes. By decoupling these aspects, the method aims to improve the accuracy of predicting the overall target depth.
3 Proposed methods
We present an innovative monocular 3D object detection network tailored to the detection of occluded targets. This network takes an image as input to the backbone network, obtaining feature maps. Subsequently, based on these feature maps, 2D detection, 3D detection, and spatial constraint detection between adjacent targets are performed. The 2D detection head predicts the target’s 2D center and the dimensions of the 2D bounding box, yielding the target’s 2D bounding box. The 3D detection head predicts the target’s 3D center, yaw angle, 3D dimensions (length, width, height), target visual depth, and target attribute depth, resulting in the target’s 3D predicted bounding box. The spatial constraint detection between adjacent targets calculates the 3D distance between the target’s 3D center and the 3D center of adjacent targets. Finally, combining the spatial relationships between adjacent targets refines the results of the 3D predicted bounding box, making them more accurate (Figure 1).
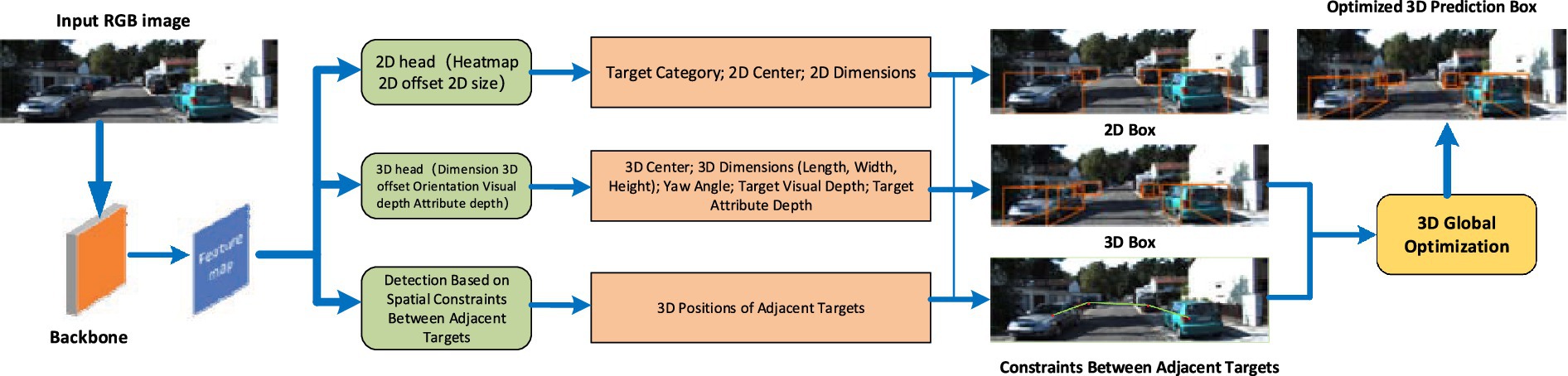
Figure 1. The proposed network architecture, in which “Backbone” signifies the primary network. “Feature map” denotes the feature map extracted by the backbone network. “2D head” represents the 2D detection head. “2D Box” is used to illustrate the predicted 2D bounding box. “3D head” is employed to label the 3D detection head. “3D Box” symbolizes the final predicted 3D bounding box.”3D head” signifies the 3D detection head.
The network flowchart is as follows:
This proposed method mainly consists of the five modules: Module 1: Backbone Network, Module 2: 2D Detection Head, Module 3: 3D Detection Head, Module 4: Spatial Constraints Between Adjacent Targets, Module 5: Spatial Optimization of 3D Predictive Boxes.
3.1 Module 1: Backbone network
We employ an improved DLA-34 network from CenterNet as the backbone network for feature extraction, as it can aggregate information across different levels. The network architecture is illustrated below:
Within Figure 2, the numerical values enclosed within the boxes denote the image stride. Figure 2a showcases the original DLA-34 network model, whereas Figure 2b illustrates the enhanced DLA-34 network model sourced from CenterNet. Notably, this improved DLA-34 network incorporates additional skip connections and elevates each convolution layer within the upsampling stage to deformable convolution layers, thereby enhancing its feature extraction capabilities.
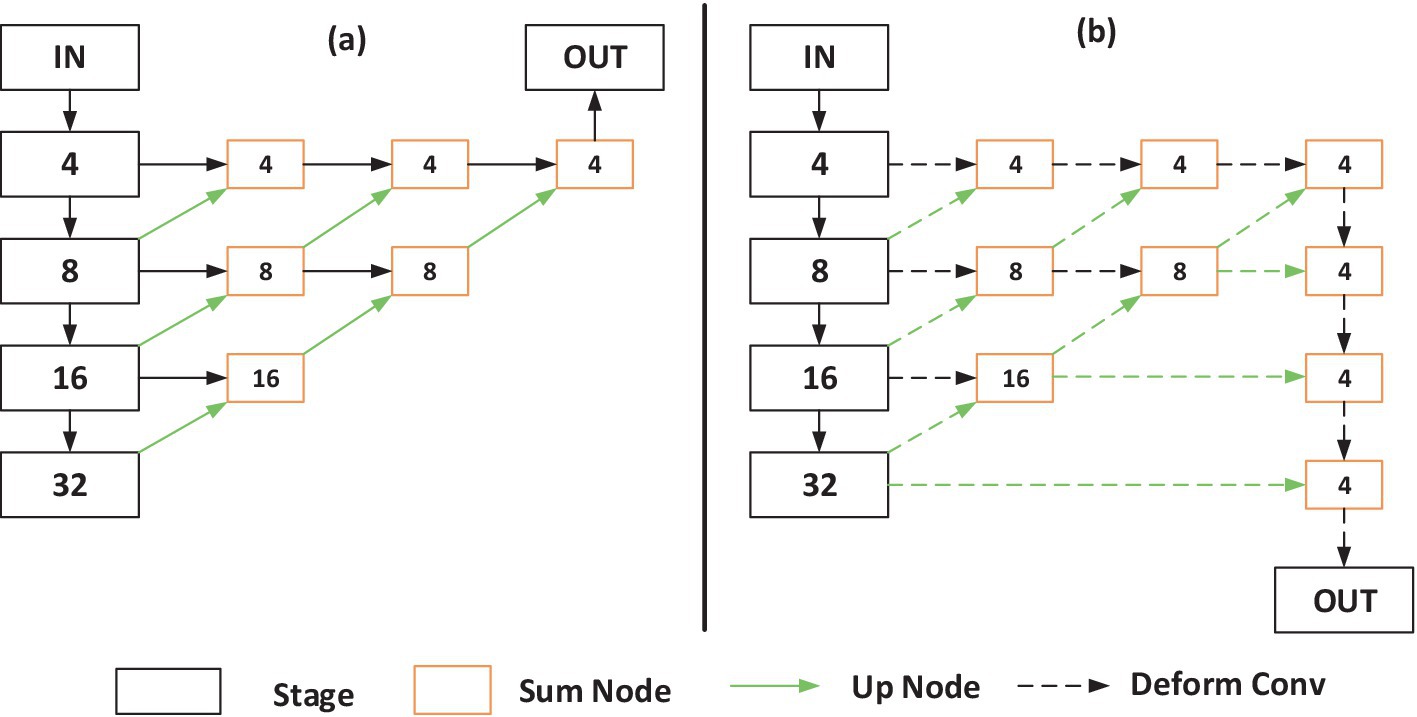
Figure 2. Schematic of the DLA-34 network model. (a) The original DLA-34 network model. (b) The enhanced DLA-34 network model.
The improved DLA-34 backbone network significantly enhances feature extraction by incorporating deformable convolution layers in the upsampling stage. These deformable layers allow the network to adaptively focus on relevant spatial regions, improving its ability to extract features even when parts of objects are occluded.
3.2 Module 2: 2D detection head
In the proposed network, we adopt the 2D detection head from CenterNet (Zhou et al., 2019), which comprises the HeatMap branch, 2D offset branch, and length-width branch. The HeatMap branch serves the purpose of identifying the approximate object position and its associated confidence in the image. Simultaneously, the 2D offset branch fine-tunes the approximate position by predicting the offset between the approximate position and the center of the 2D detection box. This results in a more precise localization of the 2D detection box’s center. Additionally, the length-width branch is responsible for predicting the dimensions of each object’s 2D detection box.
In the proposed network workflow, we input a monocular image into the improved DLA-34 network to generate a feature map. The 2D detection head then conducts 2D information detection on this feature map, extracting the object’s approximate position, 2D center offset, and dimensions. Subsequently, the object’s precise 2D detection box center is computed from the approximate position and 2D center offset, while the object’s 2D detection box dimensions are determined by the lengths and widths.
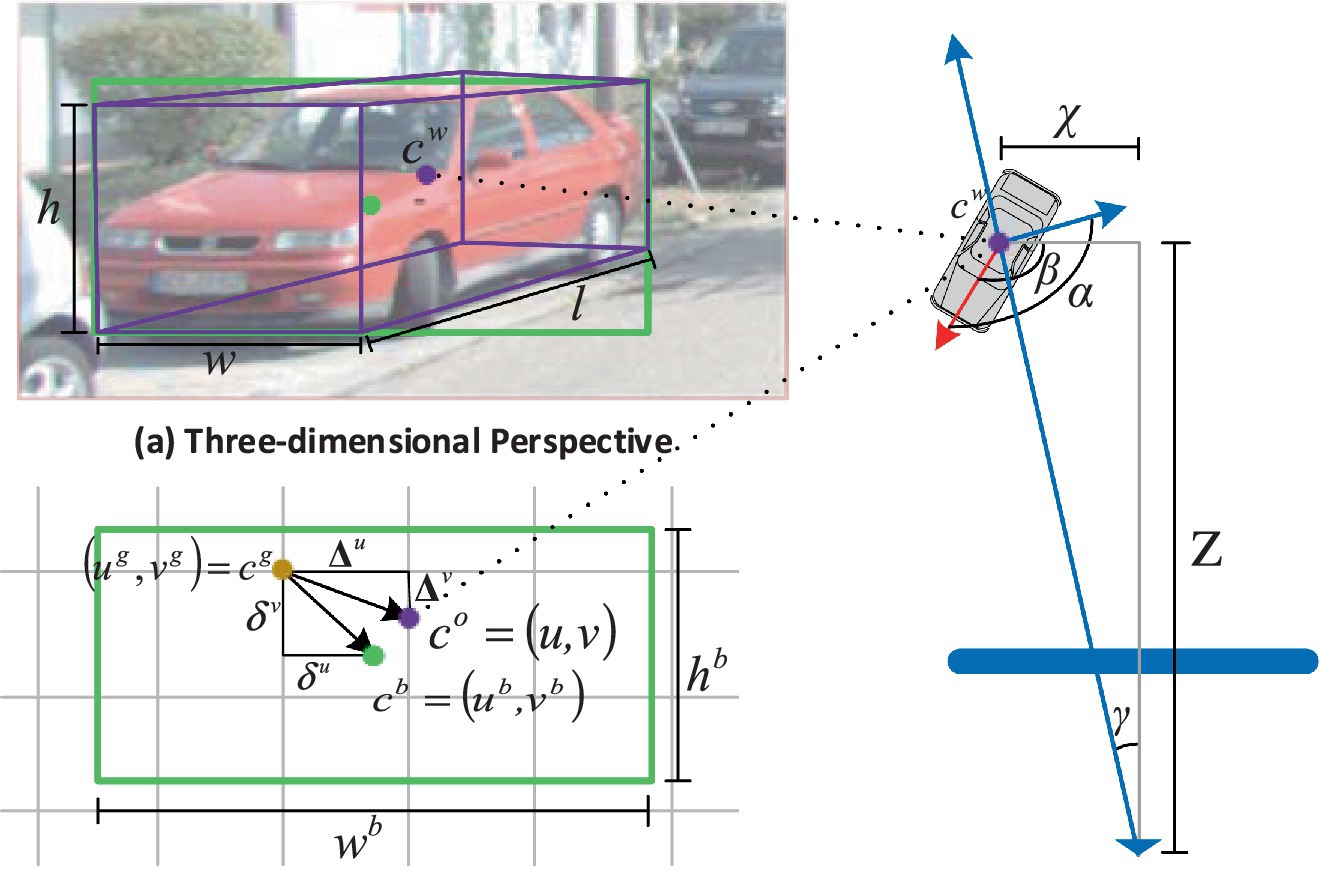
The 2D detection head has three output branches. Among them, a heat map of size (W × H × c) is used for the localization and classification of targets. In 3D object detection on the KITTI dataset, there are three target types, i.e., c = 3. Target positions, cg = (ug, vg), are extracted from the output feature map. The other two branches contain two channels, outputting the sizes of the bounding box (wb, hb) and the offset vector (δu, δv) from the located keypoint cg to the center of the bounding box cb = (ub, vb). This is illustrated in Figure 3.
3.3 Module 3: 3D detection head
The center point of the target in world space is represented as cw = (x, y, z). Its projection in the feature map is denoted as co = (u, v), as shown in Figure 3. We predict the offset (∆u, ∆v) of the target’s center point cw in world space relative to the keypoint position cg.
We decouple the target depth into visual depth and attribute depth. For monocular systems, visual depth highly depends on the object’s 2D bounding box size (objects far away appear small in the image, and vice versa) and its position on the image. Attribute depth is the depth offset from the visible surface to the 3D center of the object, as it is more likely related to the object’s inherent attributes. For example, when a car is oriented parallel to the z-axis (depth direction) in 3D space, the attribute depth at the car’s tail is half of the car’s length. Conversely, if the orientation is parallel to the x-axis, the attribute depth is half of the car’s width. Attribute depth depends on the target’s orientation and its intrinsic properties.
We use two separate detection heads to independently estimate target visual depth and attribute depth. The target depth is obtained by summing the visual depth and attribute depth. Decoupling the target depth has several advantages: (1) it is a rational and intuitive approach, allowing for a more comprehensive and accurate representation of objects; (2) it enables the network to extract different types of features for different depth types, facilitating learning.
Assuming the target depth is Z and the intrinsic matrix K of the camera is given by Equation (1):
then the target’s center in world space is given as Equation (2):
The three-dimensional size is represented as (w, h, l), indicating width, height, and length. As shown in Figure 3, to predict the yaw angle α of the target, we can first regress the global orientation β in the camera coordinate system. Then, calculate the relative rotation angle γ between the target and the camera’s perspective as γ = arctan (x/z). Finally, the yaw angle α of the target can be computed as α = β + γ.
The decoupling of target depth into visual and attribute depth enables a more precise estimation of the 3D center of occluded objects. Visual depth depends on observable cues, while attribute depth incorporates object-specific intrinsic properties, compensating for missing visual data caused by occlusion.
3.4 Module 4: Spatial constraints between adjacent targets
To further improve the detection accuracy of occluded targets, we propose a novel regression target prediction method, namely predicting spatial constraints between adjacent targets. The spatial constraint strategy between adjacent targets is illustrated in Figure 4a. For any pair of targets, we define a bounding circle by setting the distance between their 2D bounding box centers as the diameter. If the bounding circle contains the center of another target within it, we ignore that pair. Figure 4b displays an example image containing all valid pairs of targets.
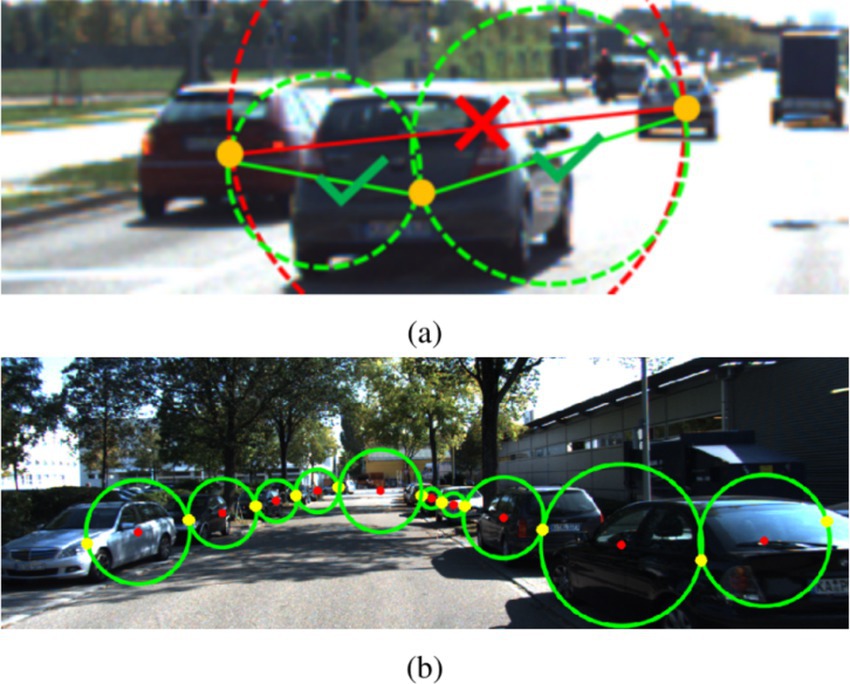
Figure 4. The spatial constraint strategy between adjacent targets. (a) The spatial constraint strategy between adjacent targets. (b) An example image containing all valid pairs of targets.
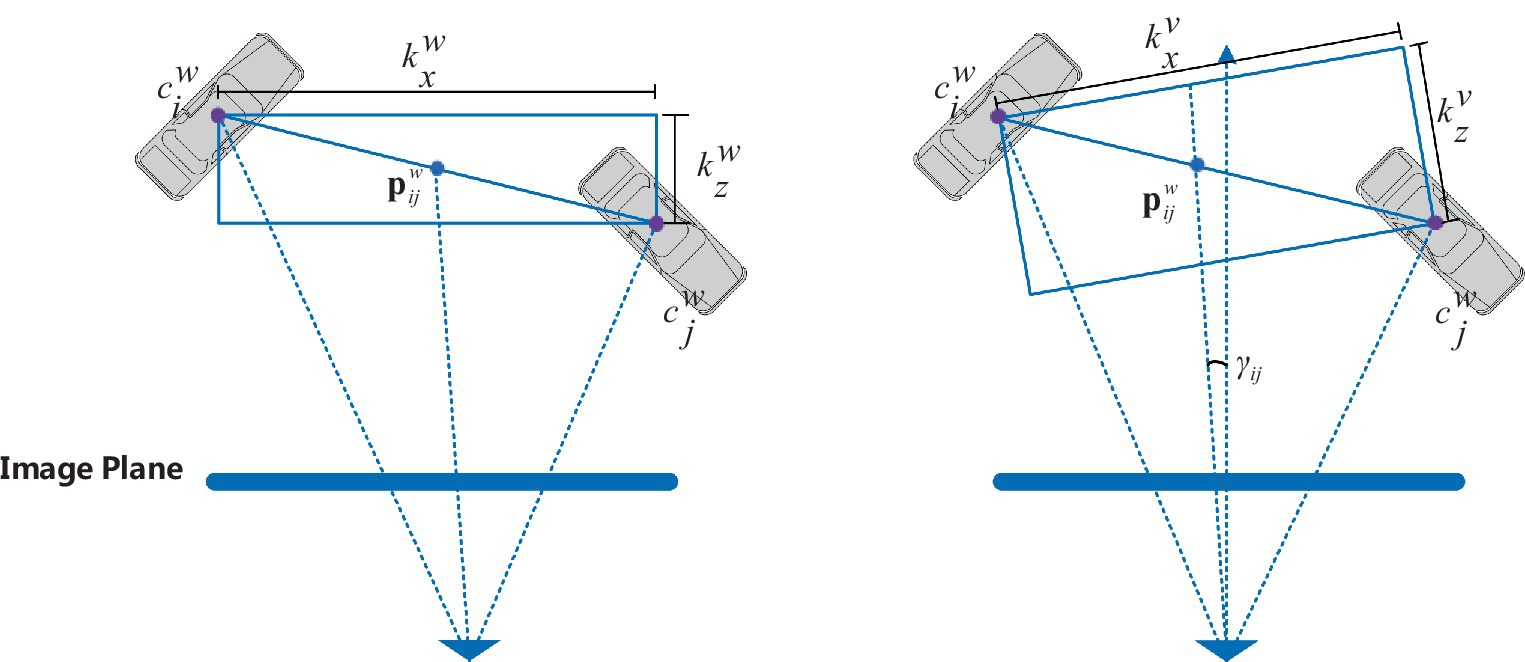
Given a selected pair of targets, with their three-dimensional centers in world space denoted as and , and their 2D bounding box centers on the feature map as and , the regression target for the spatial constraint between adjacent targets is the three-dimensional distance between these two targets. Firstly, locate the midpoint in three-dimensional space. Then, considering the viewpoint direction as the Z-axis, with as the origin, establish a local coordinate system using the left-hand coordinate system. The three-dimensional absolute distance between the adjacent targets and , as shown in Figure 5, serves as the regression target.
During the training process, it is straightforward to obtain from the training data through the actual 3D target centers, as described in Equation (3).
The can be obtained by taking the difference between the three-dimensional centers of two targets in the camera coordinate system, as described in Equation (4).
The is the rotation matrix from the camera coordinate system to the local coordinate system. In this work, we define the local coordinate system as a reference frame anchored to the object being analyzed. This coordinate system is used to express the position and orientation of object features in both 2D and 3D spaces. Unlike a global or world coordinate system, which relies on external references, the local coordinate system is intrinsic to the object itself. This approach ensures that the spatial properties of the object are described with precision, regardless of its placement or orientation within a larger environment.
The local coordinate system serves as the foundation for the feature map generated by the backbone network and the subsequent modules that estimate 2D and 3D object coordinates. By operating within this localized framework, our model improves its robustness to variations in global positioning and eliminates the need for complex transformations typically required in global coordinate systems. This design choice enhances both computational efficiency and prediction accuracy.
As shown in Figure 6, the three-dimensional distance kw between adjacent targets in the camera coordinate system remains invariant under different perspectives. However, the three-dimensional distance kv between adjacent targets in the local coordinate system varies with changes in the viewing angle. Therefore, the three-dimensional distance kv between adjacent targets in the local coordinate system is more meaningful.
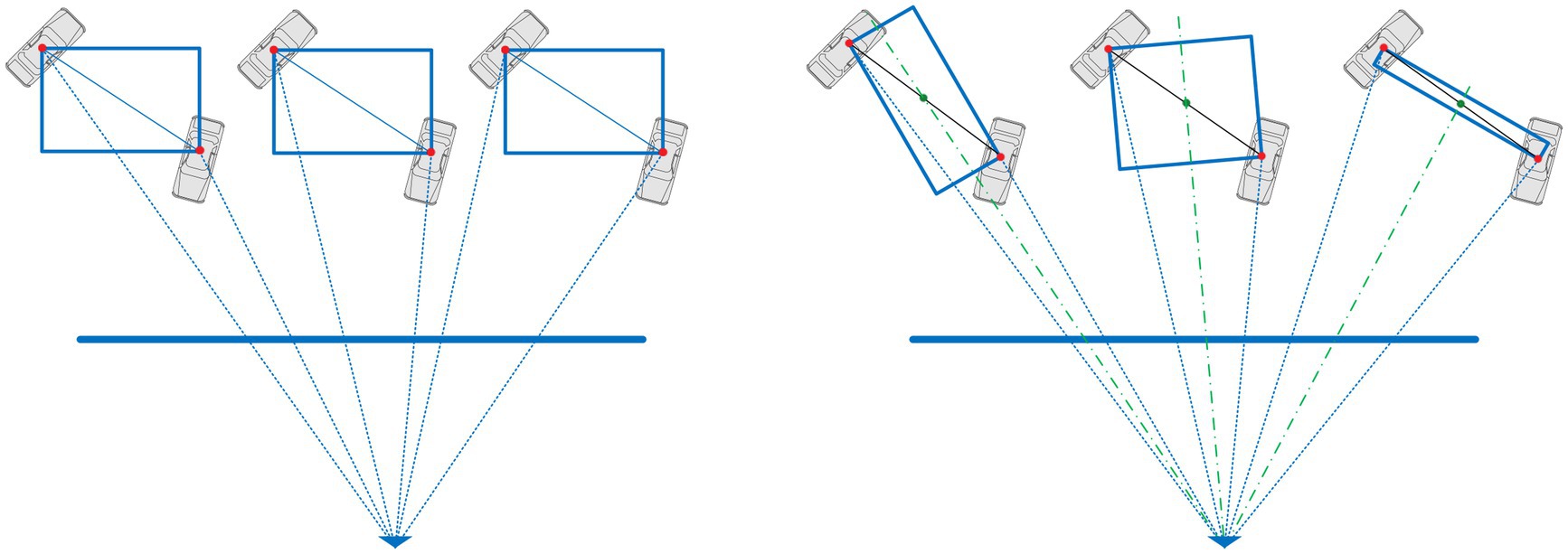
Figure 6. Spatial constraints between adjacent targets in the camera coordinate system and local coordinate system.
During the inference process, we first predict the two-dimensional position of the target, then find the nearest adjacent target to the center of the target’s 2D bounding box. Subsequently, we predict the three-dimensional distance kv between the two adjacent targets in the local coordinate system.
A key innovation lies in the spatial constraint detection between adjacent targets. By calculating the 3D distance between neighboring targets, the network captures spatial relationships, which are particularly valuable for inferring the location of partially occluded objects. This mechanism ensures that occluded targets are accurately localized by leveraging their contextual relationships with visible objects.
3.5 Module 5: Spatial optimization of 3D predictive boxes
In this module, we propose a three-dimensional bounding box spatial optimization method from a graph perspective to further improve the detection accuracy of occluded targets. Assuming that in a given image, the network outputs N targets, among which there are M pairs of spatial constraints between adjacent targets, we consider it as a graph with N vertices and M edges. Each vertex can be connected to multiple adjacent vertices. Targets that are not connected to other vertices do not require optimization.
3.5.1 Graph representation of targets
The detected targets are represented as a graph:
• Vertices (NNN) represent the detected targets in three-dimensional space.
• Edges (MMM) represent spatial constraints between adjacent targets, capturing the expected distance between their centers as estimated by the network.
Targets without shared edges (isolated vertices) are considered independent and do not undergo optimization, as no spatial constraints are applied.
3.5.2 Nonlinear least squares optimization
To refine the positions of the bounding box centers, we employ a nonlinear least squares optimization technique that minimizes spatial inconsistencies between the estimated three-dimensional distances and those predicted by the network.
1. Error Terms ( , ).
For each pair of adjacent targets connected by vertices Ci and Cj, the error terms quantify inconsistencies along the x, y, and z axes. These are defined as the absolute difference between:
• The predicted three-dimensional distance ( ).
• The actual distance ( ) derived from the estimated positions of the connected vertices Ci and Cj.
The mathematical expressions are presented in Equations (5, 6) as follows:
2. Rotation Matrix ( )
To ensure consistency across different orientations, a rotation matrix is applied, aligning spatial constraints for adjacent targets in the local coordinate system.
3. Optimization Process
For each target, error terms are calculated for all its adjacent targets. The optimization process adjusts the three-dimensional positions of bounding box centers to minimize the average error across all edges connected to a vertex, ensuring spatial consistency.
4. Output
The refined bounding box centers are obtained by minimizing the average error, replacing initial estimates for more accurate three-dimensional predictions.
3.5.3 Advantages of spatial optimization
1. Improved accuracy
The spatial consistency enforced by this method enhances the accuracy of bounding box predictions, particularly for occluded or overlapping targets.
2. Robustness to occlusions
The graph-based approach handles occluded objects effectively by leveraging spatial relationships between adjacent targets.
3. Scalability
The optimization process is computationally efficient and can handle dense scenes with a large number of targets.
The proposed graph-based spatial optimization further refines the 3D bounding boxes by minimizing inconsistencies in predicted spatial relationships. This approach is especially effective for occluded objects, as the optimization integrates global spatial information, ensuring that predictions remain consistent even when direct visual information is limited.
4 Experiments
4.1 Experimental setup
The experiments were carried out on the Ubuntu 16.04 operating system, utilizing 8 NVIDIA RTX 2080Ti GPUs, each equipped with 16GB of memory. The PyTorch deep learning framework was employed, and a Hierarchical Task Learning (HTL) training strategy (Kingma and Ba, 2014) was utilized. For optimizing model parameters, this paper employed the Adam optimizer with a Batch Size of 16. An initial learning rate of 1 × 10^(−5) was used, alongside a linear warm-up strategy, which gradually increased the learning rate to 0.001 over the course of the first 5 epochs. Subsequently, the learning rate was decayed at a rate of 0.1 at the 90th and 120th epochs.
In line with the approach inspired by CaDDN (Reading et al., 2021), we projected the LiDAR point cloud onto the image to generate a sparse depth map. We then executed depth completion to derive depth values for every pixel in the image. During the training process, the depth map served as the basis for supervision.
4.2 Datasets and metrics
We conducted our experiments using the KITTI dataset (Geiger et al., 2012), a comprehensive evaluation dataset jointly established by the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology in Germany and the Toyota Technological Institute of America. The KITTI dataset is currently the largest evaluation dataset for computer vision algorithms within the context of autonomous driving. It serves as the benchmark for evaluating a variety of tasks, including stereo images, optical flow, visual odometry, 3D object detection, and 3D tracking in automotive scenarios. The dataset comprises real image data captured in urban, rural, and highway scenes. Each image features up to 15 cars and 30 pedestrians, often with various degrees of occlusion and truncation. The dataset is divided into 7,481 training samples and 7,518 testing samples for 3D object detection. While labels for training samples are publicly available, those for testing samples are kept confidential on the KITTI website and are solely used for online evaluation and ranking. To facilitate our experiments, we further divided the training set and conducted ablation studies. The initial 7,481 training samples were segmented into a new training set (consisting of 3,712 samples) and a validation set (comprising 3,769 samples).
The KITTI dataset categorizes objects into three evaluation levels: easy, moderate, and hard. This classification is based on factors such as the height of the object’s 2D bounding box (related to depth), occlusion, and truncation levels.
For evaluation purposes, we employed two main metrics: AP3D and APBEV. AP3D assesses the accuracy of 3D bounding boxes by calculating the Intersection over Union (IoU) between each 3D predicted box and the corresponding ground truth 3D box. If the IoU is greater than 0.7, the predicted box is deemed a positive sample; otherwise, it is considered a negative sample. Subsequently, predicted bounding boxes are sorted in descending order based on their confidence scores, and precision and recall rates are sequentially calculated, forming a precision-recall (PR) curve. The area under this curve is determined using interpolation at 40 interpolation points along the horizontal axis, yielding the AP3D value for the detection results within that category.
AP3D calculation: The area under the PR curve is computed using interpolation at 40 interpolation points along the horizontal axis (recall). The AP3D is the mean average precision (mAP) at these 40 points, as described in Equation (7):
Where Ri represents the recall at the i-th interpolation point, and P (Ri) is the corresponding precision at that recall.
APBEV, on the other hand, evaluates the accuracy of yaw angles. It also relies on IoU calculations between each 3D predicted box and the ground truth 3D box in the bird’s-eye view. Similar to AP3D, an IoU greater than 0.7 categorizes the predicted box as a positive sample, while anything below this threshold is regarded as a negative sample. The same methodology is applied to construct a precision-recall (PR) curve, and the area under this curve is computed through interpolation at 40 interpolation points along the horizontal axis, resulting in the APBEV value for the detection results within that category.
APBEV calculation: The area under the PR curve for APBEV is computed similarly to AP3D using interpolation at 40 points along the recall axis, as described in Equation (8):
Where PBEV (Ri) is the precision at the i-th recall point Ri.
4.3 Performance on the KITTI benchmark
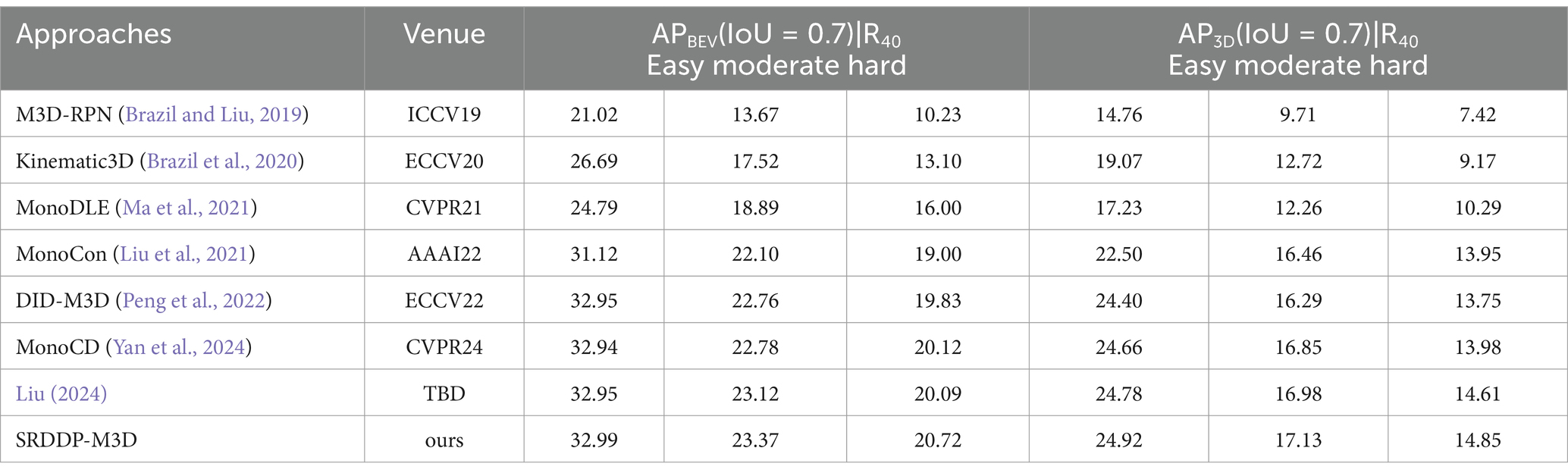
In our experiment, we conducted a comparative analysis of our method against five existing monocular 3D object detection approaches, namely M3D-RPN (Brazil and Liu, 2019), Kinematic3D (Brazil et al., 2020), MonoDLE (Ma et al., 2021), MonoCon (Liu et al., 2021), and DID-M3D (Peng et al., 2022), using the KITTI dataset. We also compare its results with existing state-of-the-art methods published in 2024, MonoCD by Yan et al. (2024) and Liu’s scalable vision-based approach (Liu, 2024) on the KITTI 3D object detection benchmark.
The results of this comparison are summarized in Table 1, which showcases the performance of our method alongside that of the other methods on the KITTI database.
As depicted in Table 1, our SRDDP-M3D method has exhibited noticeable enhancements across various performance metrics when evaluated on the KITTI dataset. Compared to the most recent DID-M3D, our method shows a slight improvement in the detection performance for easy-class objects, with an increase of 0.04% in APBEV and 0.52% in AP3D for the easy-class category. However, the most significant improvements are observed in the detection accuracy for moderate and hard-class objects. Specifically, the APBEV for moderate-class objects saw an improvement of 0.61%, while AP3D increased by 0.84%. For hard-class objects, the improvements were even more pronounced, with APBEV increasing by 0.89% and AP3D rising by 1.1%.
In comparison with MonoCD (Yan et al., 2024; Liu, 2024), our SRDDP-M3D method shows competitive performance. MonoCD achieves a slight increase in performance for moderate-class and hard-class objects, with APBEV and AP3D results slightly behind ours in these categories. Liu (2024), while also competitive, exhibits similar performance trends but does not surpass our method, especially in the hard-class object detection, where SRDDP-M3D outperforms both in APBEV and AP3D.
This enhanced performance can be attributed to the more effective modeling of the three-dimensional distance between adjacent targets in the local coordinate system, which varies with changes in viewing angles. In contrast, the three-dimensional distance between adjacent targets in the camera coordinate system remains invariant under different perspectives, which makes the local coordinate system a more meaningful reference in our approach.
4.4 Ablation study
To assess the effectiveness of the SRDDP-M3D method, we conducted two sets of ablation experiments, each with a specific focus. These experiments are as follows:
The module of Spatial Constraints Between Adjacent Targets: This experiment seeks to evaluate the role of Spatial Constraints Between Adjacent Targets by excluding it from the pipeline. In this setup, no Spatial Constraints Between Adjacent Targets is performed, and all objects are trained using the modules of backbone network, 2D detection head, 3D detection head, and Spatial Optimization of 3D Predictive Boxes.
The module of Spatial Optimization of 3D Predictive Boxes: To assess the effectiveness of the module of Spatial Optimization of 3D Predictive Boxes, this experiment omits Spatial Optimization of 3D Predictive Boxes. All objects are trained using the modules of backbone network, 2D detection head, 3D detection head, and Spatial Constraints Between Adjacent Targets.
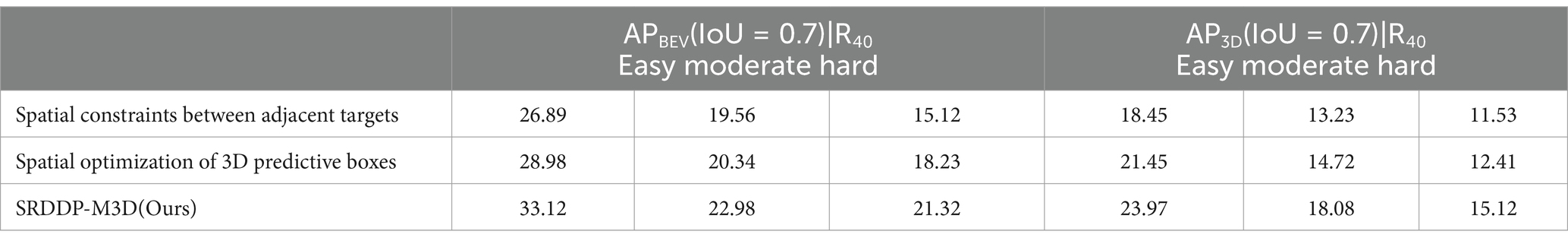
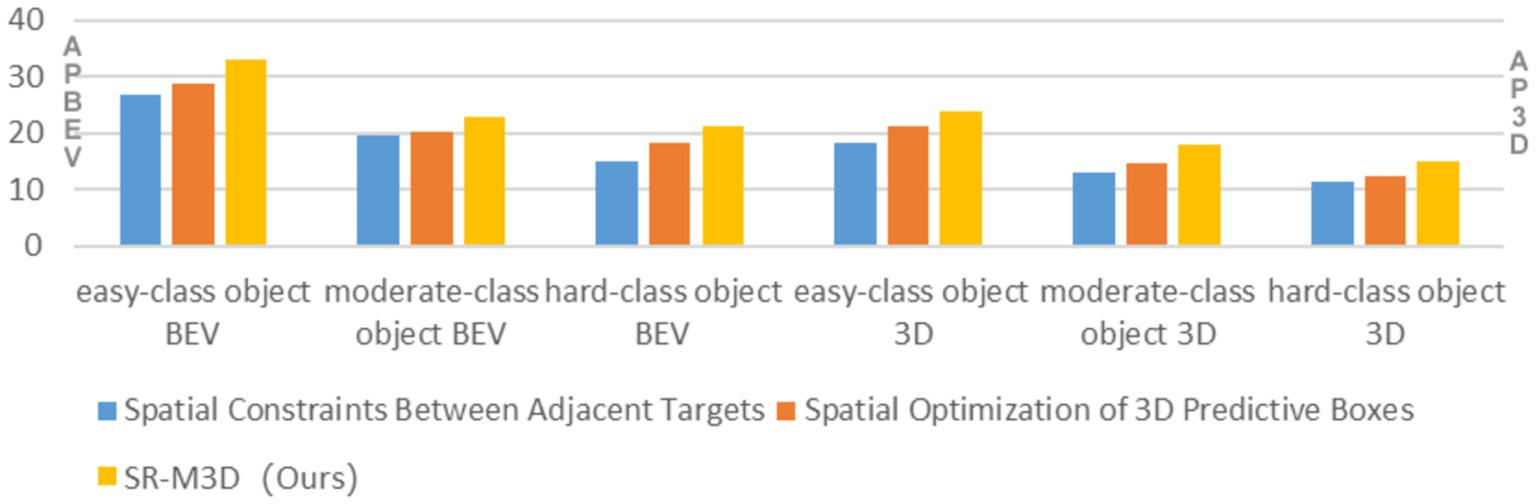
The results of these two experiments are presented in Table 2 for analysis and comparison.
The results presented in Table 2 offer valuable insights into the impact of various ablation experiments. The experiment omitting the module of Spatial Constraints Between Adjacent Targets revealed a notable decline in performance, with APBEV values for easy-class, moderate-class, and hard-class objects dropping by 6.23, 3.42, and 6.20%, respectively. The corresponding AP3D values also showed significant decreases of 5.52, 4.85, and 3.59% for easy-class, moderate-class, and hard-class objects, respectively. These findings underline the essential role of the module of Spatial Constraints Between Adjacent Targets and the significance of processing occluded targets separately.
In the case of the module of Spatial Optimization of 3D Predictive Boxes, the ablation experiment demonstrated a decrease in performance, with APBEV values for easy-class, moderate-class, and hard-class objects declining by 4.14, 2.64, and 3.09%, respectively. The corresponding AP3D values exhibited decreases of 2.52, 3.36, and 2.71% for easy-class, moderate-class, and hard-class objects, respectively. These results underscore the effectiveness of the module of Spatial Optimization of 3D Predictive Boxes improving the detection accuracy of occluded targets.
As illustrated in Figure 7, the results of the ablation experiments for the module of Spatial Constraints Between Adjacent Targets and the module of Spatial Optimization of 3D Predictive Boxes both exhibit lower performance compared to the SRDDP-M3D experiment results. This underscores the effectiveness of the SRDDP-M3D method, which entails Spatial Constraints Between Adjacent Targets and Spatial Optimization of 3D Predictive Boxes. In summary, the effectiveness of the SRDDP-M3D method is attributed to the integration of spatial constraints between adjacent targets and the spatial optimization of 3D predictive boxes. These elements contribute to the method’s ability to produce more accurate and reliable results in three-dimensional object detection.
Furthermore, the ablation experiment results for the module of Spatial Optimization of 3D Predictive Boxes outperform those of the module of Spatial Constraints Between Adjacent Targets, signifying that relying solely on the module of Spatial Optimization of 3D Predictive Boxes is more effective than relying solely on the module of Spatial Optimization of 3D Predictive Boxes. In addition, the ablation experiment results for both the feature enhancement and feature refinement modules fall short of the SRDDP-M3D experiment results, emphasizing the effectiveness of combining both modules for superior performance.
5 Conclusion
This paper proposes a novel monocular 3D object detection method based on Spatial Relationships and Decoupled Depth Predictions (SRDDP-M3D) for occluded targets, aiming to enhance their detection performance. The method improves the ability to detect targets that are partially or fully obscured by encoding the spatial relationships between adjacent targets. By considering how objects relate to each other in space, it enhances the detection of targets that might be hidden or obstructed in the scene. Furthermore, the proposed method introduces a Decoupled Depth Predictions Refining approach to improve the process of predicting the depth of targets. The conducted experiments have validated the effectiveness of our method.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found at: KITTI dataset: Geiger et al. (2012).
Author contributions
YG: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XM: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Software, Writing – review & editing. GZ: Investigation, Project administration, Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Brazil, G., and Liu, X. (2019). “M3d-rpn: monocular 3d region proposal network for object detection” in Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, 9287–9296.
Brazil, G., Pons-Moll, G., Liu, X., and Schiele, B. (2020). “Kinematic 3d object detection in monocular video” in Computer vision – ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part XXIII (Cham, Switzerland: Springer), 135–152.
Chen, X., Kundu, K., Zhu, Y., Ma, H., Fidler, S., and Urtasun, R. (2017). 3d object proposals using stereo imagery for accurate object class detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40, 1259–1272. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2706685
Chen, Y., Liu, S., Shen, X., and Jia, J. (2020). DSGN: Deep stereo geometry network for 3D object detection, in Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New Jersey, USA: IEEE, pp. 12533–12542.
Chen, Y., Tai, L., Sun, K., and Li, M. (2020). “Monopair: monocular 3D object detection using pairwise spatial relationships” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 12093–12102.
Ding, M., Huo, Y., Yi, H., Wang, Z., Shi, J., Lu, Z., et al. (2020). “Learning depth-guided convolutions for monocular 3d object detection” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 11672–11681.
Fu, H., Gong, M., Wang, C., Batmanghelich, K., and Tao, D. (2018). “Deep ordinal regression network for monocular depth estimation” in Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Piscataway, New Jersey, USA: IEEE), 2002–2011.
Geiger, A., Lenz, P., and Urtasun, R. (2012). “Are we ready for autonomous driving? The Kitti vision benchmark suite” in 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Piscataway, New Jersey, USA: IEEE), 3354–3361.
Guo, X., Shi, S., Wang, X., and Li, H. (2021). “LIGA-stereo: learning lidar geometry aware representations for stereo-based 3D detector” in International Conference on Computer vision (Piscataway, New Jersey, USA: IEEE), 3153–3163.
Hu, J., Shen, L., and Sun, G. (2018). Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 7132–7141.
Kingma, D. P., and Ba, J. (2014). Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv :1412.6980. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1412.6980
Kumar, A., Brazil, G., and Liu, X. (2021). “GrooMeD-NMS: grouped mathematically differen-tiable NMS for monocular 3D object detection” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 8973–8983.
Li, P., Chen, X., and Shen, S. (2019). “Stereo R-CNN based 3D object detection for autonomous driving” in Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Piscataway, New Jersey, USA: IEEE), 7644–7652.
Li, B., Ouyang, W., Sheng, L., Zeng, X., and Wang, X. (2019). “GS3D: an efficient 3D object detection frame-work for autonomous driving” in Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (Piscataway, New Jersey, USA: IEEE), 1019–1028.
Liu, Y. (2024). Scalable vision-based 3D object detection and monocular depth estimation for autonomous driving. arXiv:2403.02037.
Liu, S., Huang, D., and Wang, Y. (2019). Learning spatial fusion for single-shot object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1911.09516.Attentive contexts for object detection.
Liu, X., Xue, N., and Wu, T. (2021). Learning auxiliary monocular contexts helps monocular 3D object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv 36, 1810–1818. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v36i2.20074
Liu, Z., Zhou, D., Lu, F., Fang, J., and Zhang, L. (2021). “Autoshape: real-time shape-aware monocular 3d object detection” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 15641–15650.
Lu, Y., Ma, X., Yang, L., Zhang, T., Liu, Y., Chu, Q., et al. (2021). “Geometry uncertainty projection network for monocular 3d object detection” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 3111–3121.
Ma, X., Zhang, Y., Xu, D., Zhou, D., Yi, S., Li, H., et al. (2021). “Delving into localization errors for monocular 3d object detection” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 4721–4730.
Mousavian, A., Anguelov, D., Flynn, J., and Kosecka, J. (2017). “3D bounding box estimation using deep learning and geometry” in Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Piscataway, New Jersey, USA: IEEE), 5632–5640.
Peng, L., Wu, X., Yang, Z., Liu, H., and Cai, D. (2022). “DID-M3D: decoupling instance depth for monocular 3D object detection” in Computer Vision – ECCV 2022: 17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, October 23–27, 2022, proceedings, part I, 71–88.
Qian, R., Lai, X., and Li, X. (2022). 3D object detection for autonomous driving: a survey. Pattern Recogn. 130:108796. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2022.108796
Reading, C., Harakeh, A., Chae, J., and Waslander, S. L. (2021). “Categorical depth distribution network for monocular 3D object detection” in Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Piscataway, New Jersey, USA: IEEE), 8555–8564.
Shi, X., Ye, Q., Chen, X., Chen, C., Chen, Z., and Kim, T.-K. (2021). “Geometry-based distance decomposition for monocular 3D object detection” in International Conference on Computer Vision (Piscataway, New Jersey, USA: IEEE), 15172–15181.
Simonelli, A., Bulo, S. R., Porzi, L., L’Opez-Antequera, M., and Kontschieder, P. (2019). “Disen-tangling monocular 3d object detection” in Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 1991–1999.
Wang, Y., Chao, W.-L., Garg, D., Hariharan, B., Campbell, M., and Weinberger, K. Q. (2019). “Pseudo-lidar from visual depth estimation: bridging the gap in 3D object detection for autonomous driving” in Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Piscataway, New Jersey, USA: IEEE), 8445–8453.
Weng, X., and Kitani, K. (2019). “Monocular 3D object detection with pseudo-lidar point cloud” in International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (Piscataway, New Jersey, USA: IEEE), 857–866.
Wijesekara, P. A. D. S. N. (2022). Deep 3D dynamic object detection towards successful and safe navigation for full autonomous driving. Open Transport. J. 16:e2208191. doi: 10.2174/18744478-v16-e2208191
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J. Y., and Kweon, I. S. (2018). Cbam: convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 3–19.
Yan, L., Yan, P., Xiong, S., et al. Mono CD: Monocular 3D object detection with complementary depths in 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). (2024).
You, Y., Wang, Y., Chao, W., Garg, D., Pleiss, G., Hariharan, B., et al. (2020). “Pseudo-lidar++: Accurate depth for 3D object detection in autonomous driving” in International Conference on Learning Representations, Open Review.net.
Zhang, Y., Lu, J., and Zhou, J. (2021). “Objects are different: Flexible monocular 3D object detection” in Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (IEEE), 3289–3298.
Keywords: autonomous driving, computer vision, monocular 3D object detection, object detection (OD), spatial relationships, decoupled depth predictions
Citation: Gao Y, Miao X and Zhang G (2025) Monocular 3D object detection for occluded targets based on spatial relationships and decoupled depth predictions. Front. Comput. Sci. 6:1382080. doi: 10.3389/fcomp.2024.1382080
Edited by:
Marcello Pelillo, Ca’ Foscari University of Venice, ItalyReviewed by:
Yiming Qian, Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), SingaporePatikiri Arachchige Don Shehan Nilmantha Wijesekara, University of Ruhuna, Sri Lanka
Copyright © 2025 Gao, Miao and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yanfei Gao, MTM5MzQ1NDU5MTBAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Guoye Zhang, bGVjaWxAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Yanfei Gao
Yanfei Gao Xiongwei Miao2
Xiongwei Miao2