
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Nutr. , 10 January 2025
Sec. Nutrition and Metabolism
Volume 11 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2024.1517087
This article is part of the Research Topic Marine Peptides: Unveiling Their Role in Bone Immunomodulation and Joint Health View all 3 articles
Diabetic cognitive dysfunction is one of the important comorbidities and complications of diabetes, which is mainly manifested by loss of learning ability and memory, behavioural disorders, and may even develop into dementia. While traditional anti-diabetic medications are effective in improving cognition and memory, long-term use of these medications can be accompanied by undesirable side effects. Therefore, there is an urgent need to find safe and effective alternative therapies. Accumulating evidence suggests that phytogenic bioactive peptides play an important role in the regulation of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes. In this review, we explored the relationship between diabetes mellitus and cognitive dysfunction, and the potential and underlying mechanisms of plant-derived bioactive peptides to improve diabetic cognitive dysfunction. We found that plant-derived active peptides alleviate diabetic cognitive impairment by inhibiting key enzymes (e.g., α-glucosidase, α-amylase) to improve blood glucose levels and increase antioxidant activity, modulate inflammatory mediators, and address intestinal dysbiosis. In conclusion, plant-derived active peptides show strong potential to improve diabetic cognitive impairment.
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disease characterised by insulin resistance and pancreatic β-cell dysfunction leading to disorders in glucose glucose metabolism, which can lead to chronic complications in the body such as cardiovascular disease, nephropathy, retinopathy and others (1). As the impact of diabetes pathogenesis has been intensively studied, there is growing evidence that people with impaired glucose tolerance and diabetes have an increased risk of developing cognitive dysfunction compared to healthy individuals, and a 50% increased risk of dementia in type 2 diabetes (T2DM) (2). The severity of cognitive impairment can significantly affect a patient’s daily life, and the global prevalence of diabetes is increasing year by year with an ageing population, changing dietary patterns, and the accelerated pace of modern life. The World Health organisation (WHO) estimates that approximately 552 million adults are expected to have diabetes by 2030, and diabetes-related cognitive dysfunction is likely to be a major challenge in terms of future health resource requirements (3, 4) (Figure 1).
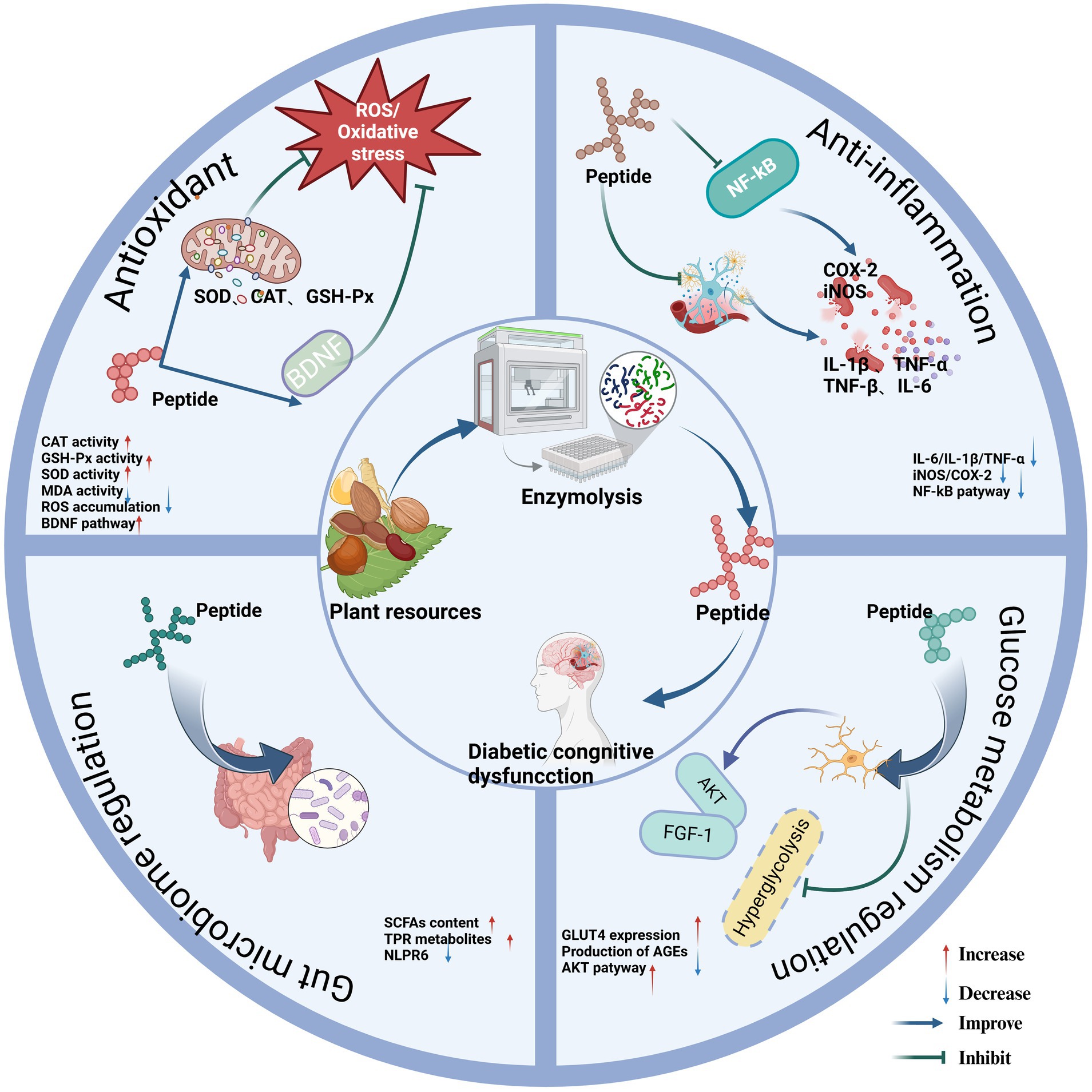
Figure 1. Regulatory mechanism of phytogenic bioactive peptides on diabetic cognitive dysfunction. Created in BioRender.com.
T2DM is the most common type of diabetes mellitus, and it is widely recognised that insulin resistance (IR) plays a key role in the development of T2DM and its organ-related complications, but the pathogenesis of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes mellitus is not yet fully understood (5). It is known that insulin is involved in neuronal survival, synaptic plasticity, memory, and cognitive function in the central nervous system (CNS), and existing hypotheses suggest that similar to diabetic neuropathy, impaired insulin signalling pathways due to elevated blood glucose and lipids may be the main metabolic mechanism that induces the occurrence of diabetic cognitive dysfunction (6). IR induced metabolic disturbances lead to degradation of brain function, and prolonged uncontrolled high blood glucose levels adversely affect a variety of metabolic pathways such as oxidative stress, formation of advanced glycosylation end products (AGEs), and protein kinase C activation, while metabolic disturbances inducing cerebral microvascular damage affect the extent of cognitive impairment (1, 7). The onset of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes is multifactorial. In addition to genetic factors, lifestyle habits (e.g., diet, sedentariness, and stress), and environmental factors (pesticides, heavy metals, and industrial by-products) have been linked to the progression of cognitive impairment, and these factors may further influence the signalling exchanges between the gut and the brain by affecting the abundance and diversity of gut flora. Traditionally, drugs used for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases have mainly consisted of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (ChEIs) and NMDA receptor antagonists (8). Although these drugs are effective in improving cognitive function and daily living abilities, they have limited efficacy in diabetic cognitive dysfunction, and available data suggest that antidiabetic drugs have the potential to improve cognitive dysfunction and dementia (9). The main antidiabetic drugs used clinically are thiazolidinediones (e.g., troglitazone, rosiglitazone), metformin, sulphonylureas and glinides (10). Although these drugs may slow the rate of cognitive decline by lowering blood glucose and enhancing central insulin signalling in the brain, patients can experience adverse effects such as decreased appetite, nausea, abdominal discomfort and diarrhoea while taking them (11). Currently, due to the need for health and safety, dietary control to prevent or influence the development of pathological conditions rather than treatment with drugs after onset may be more consistent with the idea of pursuing a healthy lifestyle. Therefore, it has become a research hotspot to develop foodborne active substances to improve diabetes mellitus and prevent cognitive function decline (12).
A growing body of evidence suggests that dietary nutrients from natural foods have great potential to positively modulate diabetes and its cognitive dysfunction, providing opportunities for safe and cost-effective nutritional modifiers (13). Nutrients such as polyphenols, flavonoids, glycosides, phosphatidylserine, proteins and peptides have been reported to exhibit positive effects in the management of cognitive deficits (14, 15). Among them, several studies have found that bioactive peptides of plant origin not only have the potential to regulate diabetes, but importantly also have neuroprotective and cognitive improvement functions (16, 17). Bioactive peptides isolated from plant proteins, generally consisting of 2–20 amino acids, have attracted widespread attention in the academic and health care communities for their good tissue affinity, specificity, and bioactivities such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hypoglycemic properties (17, 18). In this paper, we summarise the research progress of phytogenic bioactive peptides in improving diabetes and cognitive dysfunction, and focus on the role of phytogenic peptides in improving diabetes and cognitive dysfunction and its molecular mechanism, aiming to provide systematic theoretical support for the effective implementation of phytogenic bioactive peptides in the intervention of diabetes and cognitive dysfunction.
Cerebral microvascular damage may be one of the mechanisms associated with cognitive dysfunction in diabetes (19). The brain performs cognition and modulates cardiovascular homeostasis. As an important channel of essential oxygen and energy sources for the brain, cerebral microvessels are an important component of the blood–brain barrier (BBB), and its disruption is an early pathophysiological mechanism in neurodegenerative diseases (20). BBB is a biological and physical barrier consisting of astrocytes, pericytes, and brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs) that maintains the dynamic between the peripheral circulation and the central nervous system (21). The persistent hyperglycaemic state of diabetes leads to the deposition of advanced glycosylation end-products (AEGs) in the vascular wall of diabetic patients. The accumulation of AEGs and their binding to the receptor for glycosylation end-products (RAGE) promotes oxidative stress, which activates the NF-κB signalling pathway, upregulates the expression of target genes and triggers inflammation (22). Excessive production of RAGE on brain microvascular endothelial cells increases Aβ transport into the brain tissue and decreases its removal, leading to the accumulation of Aβ in the brain tissue, which in turn triggers a series of neurodegenerative pathological changes, such as the formation of amyloid plaques, the formation of neurofibrillary tangles, and the loss of neurons (23). Insulin resistance as well as the hypertensive response can cause damage to the structural integrity and transport function of the blood–brain barrier, increase the permeability of the blood–brain barrier (24), and the entry of free fatty acids (FFA) and other plasma components into the brain tissue to disrupt the homeostatic balance of the brain, as well as the entry of immune cells and inflammatory factors in the peripheral circulation into the CNS, which can cause further neuronal damage, thus leading to cognitive dysfunction (19). On this basis, the presence of microvascular alterations in a pre-diabetic mouse model also suggests that early hyperinsulinaemia and insulin resistance are sufficient to induce vascular damage and that blood–brain barrier dysfunction precedes cognitive decline (25). Delaying the onset of diabetes by altering the chronic hyperglycaemic state through plant-derived bioactive peptides may be an effective way to improve the associated cognitive dysfunction.
Neuroinflammation itself is a defence mechanism against acute the CNS damage and ameliorates the effects of toxic substances produced in brain nerve cells, but persistent neuroinflammation inhibits nerve regeneration, leading to neurodegeneration making the patient cognitively impaired. Neurodegeneration has been observed in animal models of diabetes. Epidemiology suggests that mild cognitive impairment in diabetes is present in all age groups, but predominantly occurs in older adults (> 65 years) (26). Rohden et al. (27) found that the cellular and molecular mechanisms of neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease and diabetic cognitive dysfunction may have relevance, and that the cell types involved in the inflammatory response in CNS are predominantly astrocytes and microglia, and that glia and neurons interact with each other via synapses, neurotransmitters, and chemicals. In the brain, hyperglycaemia activates microglia, and microglia activation and polarisation can mediate central inflammatory responses, neuronal apoptosis and exacerbate central neuropathy leading to dementia (28). Moreover, persistent hyperglycaemia triggers activation of the (NF-κB) pathway and release of pro-inflammatory factors, leading to an imbalance between the pro- and anti-inflammatory networks, resulting in an increase in reactive oxygen species and the production of a large number of inflammatory mediators, which affects the functioning of the mitochondria and leads to neuronal damage and degeneration (29).
Neuroinflammation can damage neuron-associated axons and myelin fractions, Paul et al. (30) suggesting that insulin resistance and glucose toxicity within the CNS of patients with T2D damages axon integrity, inhibits nerve impulses, and degrades myelin in oligodendrocytes, leading to cognitive dysfunction. These inflammatory responses may be an important etiological factor in the development of memory impairment and behavioural changes in the nervous system. Meng et al. (31) showed that neurons in the brains of patients with T2DM secrete the regulatory factor angiopoietin-like protein 8 (ANGPTL8) into the hippocampus, which activates microglia to up-regulate pro-inflammatory factors and axonal damage, leading to cognitive impairment. Co-localisation of amyloid plaques and neuroprogenitor fibre tangles with activated glial cells in animal models and human brain tissue. Several studies have reported pathological astrogliosis and associated neuronal hypotrophic glucose metabolism in patients with neurodegenerative disease and diabetic model animals, showing increased glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and significant cellular hypertrophy (32), which has been correlated to some extent with the severity of cognitive impairment in patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Under diabetic conditions, disruption of the regulation of microglia activity by hyperglycaemia occurs through a number of mechanisms, including overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and glycosylation end products (AGEs), and reduced elimination of Aβ. Y. Li et al. (33) demonstrated that activation of microglial NLRP3 inflammatory vesicles by diabetic mice and BV2 cells via the ROS/JNK MAPKs/NF-κB pathway leads to neuroinflammation. It follows that diabetes-related neuroinflammation exacerbates neurodegenerative disease and is an important regulatory mechanism for cognitive dysfunction.
The development of neuroinflammatory processes in the brain involves the activation of microglia and astrocytes, which is usually triggered by tissue damage and Aβ plaque deposition (34). Aβ attracts and activates microglia and astrocytes, leading to the release of pro-inflammatory mediators such as TNFα, IL-6, IL-2, and IL-1β, as well as reactive oxygen and nitrogen species produced by oxidative stress, which ultimately leads to neuronal cell death (35). In turn, these mediators have the ability to damage neurons while promoting Aβ synthesis and further enhancing microglia activation. In addition, it is known that Aβ induces the expression of enzymes such as nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and reactive oxygen species (ROS), which may lead to neighbouring neuronal damage. These pro-inflammatory mediators, along the lines of ROS, also stimulate γ-secretase activity and enhance the expression of amyloid precursor protein (APP), which promotes the processing of APP into the amyloid form (36). When neurons are damaged or die, they release immune signalling molecules that can exacerbate the inflammatory response, thereby increasing the neurotoxic effects of inflammation. These neurons also release the glutamate produced into the surrounding area, which may have a detrimental effect on the health of nearby neurons (37). Notably, there is evidence that the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1β plays a role in exacerbating tau pathology by accelerating tau phosphorylation (38).
The brain is the most oxygen-consuming organ in the human body, with the normal human brain accounting for more than 20 to 30 percent of the body’s total oxygen consumption, but the brain is low in antioxidants, making it more susceptible to the effects of oxidative stress (39). When oxidative stress is excessive or prolonged, the free radicals produced can cause lipid peroxidation, protein denaturation, and nucleic acid base damage, and different biomarkers can reflect oxidative damage to various biomolecules. For example, the levels of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (4-HNE) and malondialdehyde (MDA) in the brain reflect the extent of lipid peroxidation (40). Similarly, in microglia mitochondria, levels of 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) have been shown to be regarded as a marker of DNA/ RNA oxidation due to the lack of protection of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) by histone proteins and its own limited repair capacity (41). Using targeted proteomics, ENPP-2 was increased in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of AD patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI), and ENPP-2 directly reflects the brain glucose steady state (42, 43). Hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, or hypoinsulinemia can cause oxidative stress, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) produced by excessive oxidative stress can disrupt the BBB and further affect central nervous system (CNS) function. Studies have shown that oxidative stress promotes brain insulin resistance, and central nervous system (CNS) insulin resistance can affect neuronal development and increase the risk of neurodegenerative diseases (44).
Oxidative stress has a common role and key link in multiple mechanisms of diabetic cognitive dysfunction and neurodegenerative diseases, and is a bridge between different pathogenic mechanisms of diabetes and cognitive dysfunction, as well as an important link in the pathogenesis of diabetic cognitive impairment. Excessive oxidative stress produces ROS and RON, which mainly include superoxide anion (O2−), hydroxyl radical (.OH), H2O2, nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) and peroxynitrite (ONOO−), these deriving mainly from the mitochondrial electron transport chain, changes in metal valence states and enzymatic processes (e.g., MAO-B, NADPH oxidase) (45). Blood glucose levels affecting antioxidant levels of superoxide dismutase and antioxidants such as catalase or glutathione peroxidase for antioxidant defence, Cardoso et al. (46) analysed cerebral cortex and hippocampal mitochondria from hyperglycaemic and recurrently hypoglycaemic animals and found that cerebral cortical mitochondria exhibited high levels of MDA and α-tocopherol and increased glutathione disulphide reductase activity. Reduced manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) activity, reduced glutathione to glutathione disulphide (GSH/GSSG) ratios, and an impaired oxidative phosphorylation system were accompanied by an increase in caspase 9 activity in hippocampal homogenates. Numerous studies have shown that neurogenic fibre tangles (NFTs), which are observed in the brains of patients with AD and diabetic encephalopathy, consist of hyperphosphorylated tau (pTau) (47). In the brain, in order to induce tau phosphorylation, oxidative stress can directly interact with protein kinases, particularly glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK 3), increasing GSK-3β activity, which subsequently further disrupts its ability to bind to microtubules, accelerating their depolymerisation and interrupting neural signalling (48).
Human gut microbial communities promote host health through reciprocal relationships between them, and gut ecological dysbiosis is characterised by a reduction in microbially dominant strains and inadequate exposure to beneficial substances leading to poor gut microbial colonisation (49). Whereas the microbe-gut-brain axis connects the gut to the brain, and the enteric nervous system (ENS) exists at the interface between the microbiota and the host, the ENS is structurally and neurochemically similar to the CNS, and thus the pathogenic mechanisms that give rise to ENS disorders may also lead to CNS dysfunction and the nerves connecting the ENS to the CNS may act as a conduit for disease transmission (50). Thus, the ENS is regarded as a second brain that can directly or indirectly respond to the microbiota and its metabolites influencing cognitive functions through gut bacteria (51). The study found that the intestinal microbial imbalance in T2D was characterised by a decrease in the abundance of Bifidobacteria, Bacteroides, Faecalis, Akkermansia and Byrysia ross, while an increase in Rumen coccus, Fusobacterium and Blautella (52). One of the significant changes was a decrease in the number of Gram-positive organisms (53). Increased abundance of Gram-negative microorganisms leads to increased release of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), which disrupts the integrity of the intestinal mucosal barrier and triggers neuroinflammation and neuronal death through a series of steps (54). In addition to this, the brain receives information from the gut through a continuous flow of microbial, endocrine, metabolic and immune factors. This is also considered one of the main factors that promote obesity, diabetes and neuropsychiatric disorders (55).
Studies have shown a complex interaction between the gut and the brain, and that gut ecological dysregulation disrupts nervous system homeostasis in two main ways. On the one hand are microflora-associated metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids, tryptophan metabolites, immunostimulants and endogenous cannabinoids that may play a mediating role. On the other hand signalling molecules that operate mainly in the brain, in particular neuropeptide Y, brain-derived neurotrophic factor and γ-aminobutyric acid, which are disturbed by microbiological, obesity and diabetes, and are associated with psychiatric disorders (56, 57). The enteric nervous system transmits information from the gut to the brain via information carriers such as vagal afferent neurons, spinal afferent neurons, immune mediators and gut hormones. The influence of the gut microbiota is attributed to the host during disease, ageing, and lifestyle habits. High-sugar, high-fat (HSHF) diets significantly lead to an imbalance in the ratio of bacteria in the phylum Acidobacteria, Firmicutes and Thick-walled bacteria to those in the phylum Anaplasma, Aspergillus, Cyanobacteria, and Actinobacteria, which impairs the gut barrier function, and activates microglial cells in the brain, generating inflammation and affecting the cholinergic system to increase the risk of cognitive dysfunction (58, 59). Transplantation of faecal microorganisms (FMT) from healthy mice into male mice placed on a high-fat diet (HFD) can restore bacterial diversity, improves metabolism associated with poor dietary patterns and reduces hippocampal astrocyte hyperplasia, supporting the role of ecological dysregulation in mediating obesity-induced cognitive impairment (60). Moreover, microbial changes affect gastrointestinal (GIT) dysbiosis, which contributes to the gut-brain axis by increasing systemic LPS, reactive oxygen species, and inflammation. It has been reported that inflammation induced by direct injection of LPS can disrupt BBB and increase vascular permeability, increasing the infiltration of inflammatory mediators, leading to neuroinflammatory response and cognitive dysfunction (61) (Figure 2).
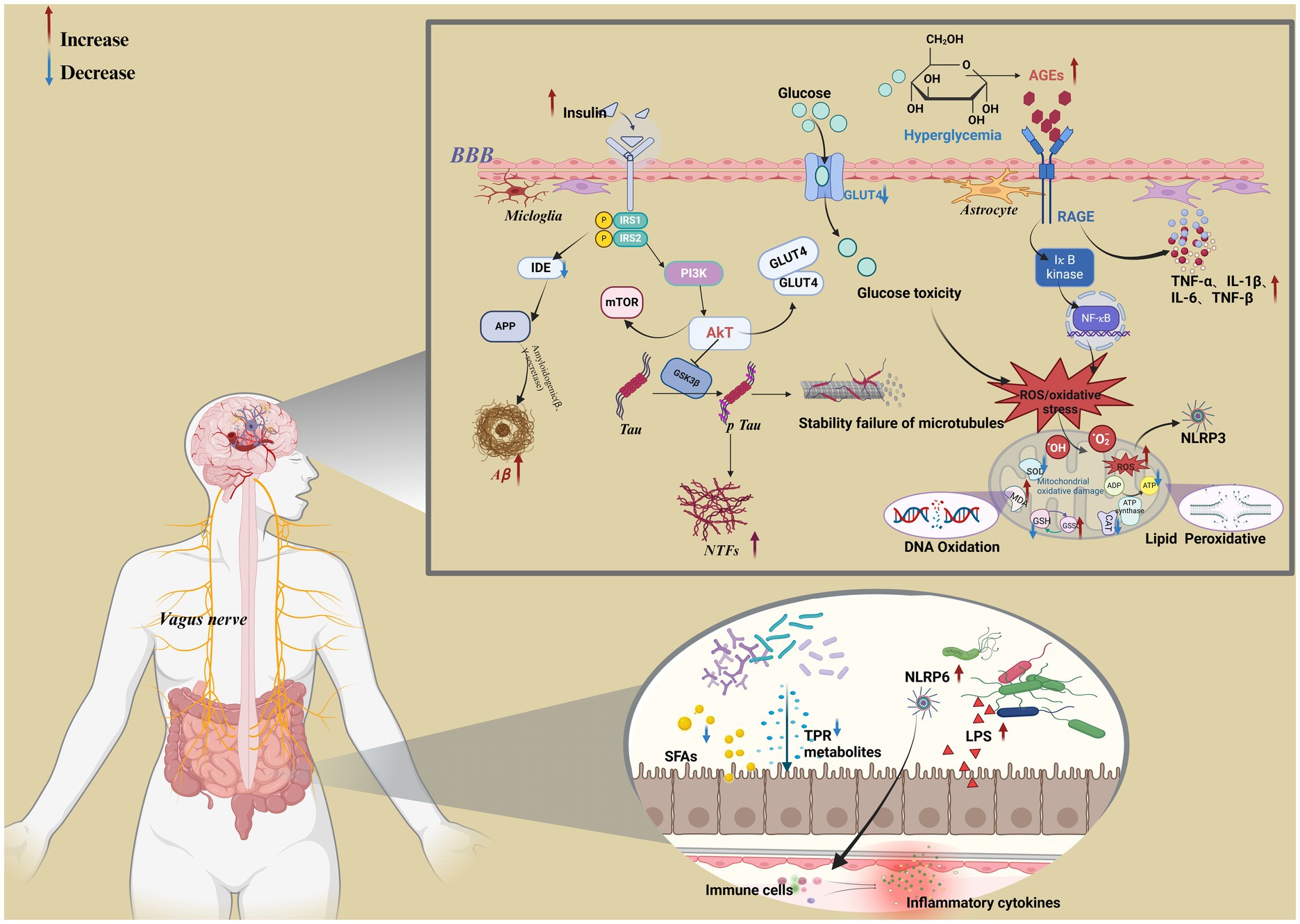
Figure 2. Metabolic mechanisms associated with cognitive dysfunction in diabetes. Created in BioRender.com.
A key aspect of diabetes management is the inhibition of enzymes involved in carbohydrate digestion, particularly α-glucosidase and α-amylase, which play a key role in blood glucose regulation, and inhibition of these enzymes delays the hydrolysis of dietary starch in the digestive system, lowering blood glucose levels, slowing glucose metabolism, and delaying glucose absorption (62, 63). Structural analyses indicate that α-amylase activity requires calcium ions to maintain structural integrity and is activated by chloride ions, and similarly, α-glucosidase operates via a Koshland double displacement reaction mechanism (64). At present, plant-active peptides with α-glucosidase inhibitory activity in legumes, cereals and nuts have been studied, and the inhibition effect of different enzymatically hydrolysed protein peptides α-glucosidase has been found to be significantly different. Compared with commonly used enzymes including pepsin, trypsin, neutral protease, acid protease, bromelain, and flavour protease etc., alkaline protease, as an endonuclease with broad specificity, the enzymatically digested plant protein peptides have the strongest inhibitory effect on α-glucosidase, therefore, alkaline proteases are widely used to hydrolyze a variety of plant proteins (65, 66).
Soy protein peptide peptides prepared with alkaline protease (AP) exhibited the highest α-glucosidase inhibitory activity compared to peptides prepared by papain and trypsin digestion. Three novel α-glucosidase inhibitory peptides identified in soy protein peptides, LLPLPVLK, SWLRL and WLRL, had IC 50 s of 237.43 ± 0.52, 182.05 ± 0.74 and 162.29 ± 0.74 μmol/L, respectively (67).Two novel peptides (WH and WS) with strong α-glucosidase inhibitory activity were isolated from hydrolysate of almond oil processing residues. Peptide WH was relatively stable in simulated gastrointestinal digestion and was able to maintain the IC 50 value for α-glucosidase inhibition (17.03 ± 0.05 μmol/L), whereas WS significantly increased the IC 50 value after simulated digestion (24.71 ± 0.02 μmol/L to 44.63 ± 0.03 μmol/L) (68). The walnut protein product-derived peptide LPLLR, hydrolysed by alkaline protease, exhibited in vitro inhibitory activity against alpha-amylase and attenuated insulin resistance in HepG2 cells. Currently, it has become increasingly common to screen potentially active peptides by predicting the binding mode and affinity of peptides and α-glucosidase through molecular modelling techniques. Deng et al. (69) identified three new potentially active peptides, RWPFFAFM (1101.32 Da), AAGRLPGY (803.91 Da) and VVRDFHNA (957.04 Da), from mulberry leaves by molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation. In vitro validation of RWPFFAFM and AAGRLPGY showed good IC50 values of α-glucosidase inhibition (1.299 mM and 1.319 mM). In addition, studies have shown that low molecular weight peptides have better stability and higher bioavailability, resulting in better biological functions in vivo. Kiwi enzymes hydrolyse wheat gluten proteins, where the smallest Mw fraction (< 1 kDa) of wheat alcohol soluble protein peptides showed the highest inhibitory capacity against α-glucosidase (18.4 ± 0.7%) and α-amylase (53.3 ± 1.9%) (70). According to previous studies, peptides with strong α-glucosidase inhibitory activity are short peptides with a relative molecular weight of less than 1 kDa, this is because lower molecular weight peptides can access and bind to the active site of α-glucosidase (71). Currently, acarbose is used as a glucosidase inhibitor, but long-term use of this drug can cause gastrointestinal side effects. Therefore, it is important to develop healthy, safe and efficient natural glucokinase inhibitors.
Biopeptides play a crucial role in enhancing insulin secretion, which is a central component of glucose regulation mediated by the pancreas through insulin and glucagon release. Enteric proinsulin hormones such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), GLP-1 promotes insulin production, reduces appetite, and maintains pancreatic β-cell health; whereas GIP enhances insulin secretion and affects fat metabolism and β-cell proliferation (72, 73). Rapid degradation of GLP-1 and GIP (DPP-IV) enzymes by dipeptidyl peptidase-IV emphasises the importance of DPP-IV inhibition. This inhibition extends the activity of these hormones, improves glucose control, maintains β-cell function, and ensures sustained postprandial insulin release for effective blood glucose reduction (74). Soymorphin-Soymorphin-5 (YPFVV), a β-opioid agonist peptide derived from the soybean β-glycin β-subunit, inhibits hyperglycemia in KKAy mice without increasing plasma insulin levels while decreasing plasma and hepatic triglyceride (TG) levels and liver weight, and promotes plasma adiponectin concentration and adiponectin receptor subtype AdipoR2 mRNA expression in the liver, PPAR in the liver after oral administration of soymorphin-5 The mRNA expression of γ and its target genes was also increased, effectively improving glucose and lipid metabolism in KKAy mice, a type 2 diabetes model animal (75). In vitro studies have shown that intraduodenal instillation of soy protein hydrolysate (SPH) in weaned piglets promotes the release of anorexigenic hormones such as peptide YY (PYY) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), stimulates insulin production in pancreatic islet cells by elevating the level of GLP-1 to inhibit short-term feed intake and triggers the secretion of cholecystokinin (CCK) in the liver through activation of the CaSR and the intracellular Ca2+/TRPM 5 pathway to reduce the appetite of pigs (76). Peptides RRDY and RL identified from yam diosgenin were used in oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) on normal ICR mice, and peptide RRDY reduced DPP-IV activity controlling blood glucose levels in normal mice (77). The use of a mixture of corn and wheat peptides can weaken the autoimmune process of pancreatic inflammation, reduce the degree of infiltration of β cells, improve the function of pancreatic β cells, treat and prevent the development of type 1 diabetes, reduce the incidence of diabetes (78). In most studies, in vivo or in vitro experiments are often used to investigate the physiological effects of peptides. However, in order to screen potential bioactive peptides more conveniently in the face of large and complex protein resources, researchers usually perform active peptide screening based on computer-analyzed molecular docking or quantitative conformational-activity relationship (QSAR) modelling indicative of the relationship between identified or known peptides and target proteins (79). R. Han et al. (80) reported that the application of Peptide Ranker web server and Pepsite 2 software confirmed that oilseed protein is a potentially important source of DPP-IV inhibitory peptides. Mudgil et al. (81) hydrolysed quinoa protein using food-grade enzymes, identified 136 peptides, 35 of which were predicted as potentially bioactive peptides (BAPs) based on the Peptide Ranker score, and have high potential for inhibition of DPP-IV, AG, and ACE, DPP-IV inhibition is a key target in the treatment of T2DM, and DPP-IV inhibitors were among the first oral hypoglycaemic agents prospectively designed as glucose-lowering agents. To date, more than a dozen DPP-IV inhibiting drugs have been developed and marketed around the world, which are classified as gliptins (82). However, these synthetic DPP-IV inhibitors have been reported to have a number of adverse effects, such as gastrointestinal adverse reactions, allergic reactions, skin-related side effects, and musculoskeletal disorders.
A key aspect of diabetes management is enhancing glucose uptake and regulating cellular metabolism. Glucose is the only source of energy in the brain because the brain cannot use fat or protein as alternative energy sources. In the brain, neurons have the highest energy requirements, but they cannot produce and store glucose, and therefore require a continuous supply of glucose to neurons via sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter family proteins (SGLT1 and SGLT2) and sodium-independent glucose transporter proteins (GLUT) across the BBB (83–85). In addition, glucose plays an important role in hippocampus-dependent learning and memory by upregulating the neurotrophic factors fibroblast growth factor-1 (FGF-1) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) through activation of the Akt signalling pathway (86). Neurons provide ATP mainly through mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), glycolysis, and patients with cognitive impairment are associated with abnormalities in cerebral glucose utilisation as well as glycolysis and OXPHOS metabolism. Autopsy studies in patients with neurodegenerative diseases have shown significant reductions in GLUT1 and GLUT3 in brain regions that are closely associated with the pathology of cognitive impairment (87). Clinical studies using fluorodeoxyglucose FDG and positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) imaging studies in subjects with AD have shown reduced glucose transport and glucose metabolism in the areas most affected by AD (88). Meanwhile, reduced expression and translocation of the high-volume insulin-sensitive glucose transporter protein GLUT4 has been found in hippocampal neurons of patients with T2DM, leading to reduced neuronal glucose and ultimately cognitive dysfunction (89).
Biopeptides derived from medicinal plants have been shown to activate specific signalling pathways, in particular the AMPK pathway, a serine/threonine kinase that is activated when cellular energy levels are low, and which signals to stimulate glucose uptake, fatty acid oxidation in adipose (and other) tissues (90), glucose transporter protein (GLUT)4 translocation and mitochondrial biosynthesis, while inhibiting protein and glycogen synthesis and improving insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis. GLUTs are proteins that aid in the transport of glucose to various tissues where it is efficiently used as an energy source (91). Among the GLUTs, GLUT4 is considered the major insulin-regulated glucose transporter protein and is essential for glucose uptake. Soya globulin peptides (IAVPGEVA, IAVPTGVA and LPYP) from soybean activate GLUT1 and GLUT4 by stimulating the Akt and AMPK pathways in HepG2 cells and consequently promote energy metabolism (92). Pea oligopeptides have also been found to have great potential to reverse the metabolic abnormalities associated with type 2 diabetes, Y. Zhu et al. (93) demonstrated that four polypeptides, VLP, LLP, LL and LL, derived from pea significantly regulated glucose metabolism and exerted an antioxidant effect in IR-HepG2 cells. Among them, LLP, VA and LL promote the expression of GLUT2 genes and proteins, while VLP and LL inhibit p38 MAPK phosphorylation, improve glucose tolerance, restore pancreatic function and enhance insulin signalling. The lupine seed protein congly-g stimulates the specific pathway PKC/Flotillin-2/caveolin-3/Cbl to activate glucose homeostasis and increase glucose transport (94). The active peptides HTL, FLSSTEAQQSY and TLVNPDGRDSY were isolated and characterised from mung bean, and these peptides promote translocation of (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane. The tripeptide HTL promotes glucose uptake through activation of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase, whereas the oligopeptides FLSSTEAQQSY and TLVNPDGRDSY promote glucose uptake through activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway, which is facilitated in L6 myotubes (95). Black bean-derived peptides (AKSPLF, ATNPLF, FEELN and LSVSVL) effectively reduced glucose uptake in Caco-2 cells, and molecular docking studies showed that these peptides strongly interacted with the glucose transport proteins SGLT-1 and GLUT-2. In a hyperglycaemic rat model, black bean hydrolysed protein isolate (HPI) reduced postprandial blood glucose in a dose-dependent manner in rats (Luis (96)). Taken together, these findings highlight the role of dietary biopeptides in regulating glucose metabolism, enhancing insulin sensitivity, and providing promising avenues for the regulation of diabetes.
Phyto-derived bioactive peptides play a potential therapeutic role as anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective agents, addressing excitotoxicity, which contributes to improved neuronal viability (97, 98). These approaches can be combined with improving targets related to glucose metabolism to collectively improve cognitive dysfunction in diabetes. Currently, the use of rational in vivo animal models and in vitro experimental assays is important in evaluating the effects of bioactive peptide use (99), however, it is difficult to take into account bioavailability-related factors such as gastrointestinal digestibility and peptide utilisation for the assessment of learning memory capacity using neuronal cells alone. The Morris water maze test and passive avoidance test are usually adopted to evaluate the bioavailability of peptides at the animal level (100), while in vitro experiments are used to explore the molecular mechanisms associated with the action of active peptides (101). Multiple implant-derived bioactive peptides were found to significantly improve neuroinflammation and effectively delay the development of cognitive dysfunction in the diet.
Walnut proteolytic digests are a potential source of bioactive peptides with improved cognitive function. S. Wang et al. (102) demonstrated that walnut protein hydrolysate (WPH) and its low molecular weight grades (WPHL) could attenuate LPS-induced memory deficits by normalising inflammatory responses and oxidative stress in the brain. Recent studies have shown that soy protein hydrolysates and their active peptides have an ameliorative effect on memory disorders. Oral administration of soy peptide (SP) has been reported to attenuate age-related cognitive decline in learning and memory in a mouse model of accelerated ageing (SAM), with increased expression of neurotrophic factors, such as BDNF and NT-3, observed in the brains of SP-fed mice at both the mRNA and protein levels (103). Improvement in cognitive function may be attributed to upregulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and neurotrophic factor-3 (NT-3) levels by cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) activation in the brain. BDNF and NT-3 are members of a family of neurotrophic factors that support neuronal development and survival and are involved in memory formation and neurogenesis. BDNF deficiency leads to age-related cognitive impairment (104, 105).Montserrat-de la Paz et al. (106) showed that the blue lupin peptide GPETAFLR can exhibit anti-inflammatory properties by reducing TNF-α expression and inhibiting inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-10). In addition, it effectively inhibited nitric oxide production in microglia (BV-2 cells) and hindered the expression of pro-inflammatory genes in microglial cells of mice on a high-fat diet, attributes that suggest that blue lupin has the ability to attenuate inflammation (107, 108), process that is at the core of neurodegenerative diseases, and also demonstrated to have an enhanced potential for cognitive function. Wattanathorn et al. (109) found that cashew protein hydrolysate inhibited the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the brain of rats with arterial occlusion-induced cerebral is chaemia, and by modulating the function of lipid metabolism, its modulation of serum cholesterol, TG, and LDL, and elevation of HDL, greatly improved spatial memory in rats. Oat peptides (DF-10), (HL-8) and (RW-9) have been shown to improve behavioural performance, reduce AChE activity, attenuate oxidative stress, and decrease the levels of inflammatory cytokines including TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in the brain of zebrafish exposed to scopolamine (110). Another study showed that the amino acid sequence and composition of peptides have a significant effect on neuroprotection and that the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of peptides are attributed to the presence of hydrophobic aromatic amino acids and essential amino acids implicated in neuroprotection, which can be involved in a number of cellular processes, transported via the BBB, and modulation of neuronal memory (111). The lipolysis-stimulating peptide VHVV obtained from flavoured enzyme-soy protein (SPI) hydrolysate (F-SPIH) is composed of two essential amino acids, valine and histidine, where valine is involved in many cellular processes, such as lipolysis, lipogenesis, glucose transport, and intestinal barrier glucose metabolism, and histidine regulates neurogenesis, astrocytes, and BBB integrity (112).
Most of the plant antioxidant peptides consist of 2–20 amino acids. It can effectively scavenge excessive reactive oxygen free radicals in the body, protect the normal structure and function of cells and mitochondria, and prevent the occurrence of lipid peroxidation, thus playing a role in preventing cognitive dysfunction in diabetes (113). In recent years, plant-derived antioxidant peptides have attracted much attention due to their significant neuroprotective potential and their ability to cross the gastrointestinal barrier or the BBB to reach their target sites associated with their molecular mode of action (114). N. Li et al. (115) found that wheat germ peptides have an important role in the endogenous antioxidant system by enhancing the activities of antioxidant enzymes, such as GSHPx, superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase (CAT), while decreasing the production of malondialdehyde (MDA), in order to protect the PC12 cells from H2O2-induced oxidative stress. AREGETVVPG reduces intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, inhibits phosphorylation of PKCζ, AKT, and Erk 1/2, and inhibits Nox 4 protein expression to protect hyperglucose-induced vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) oxidative stress (116). Walnut peptides have similar antioxidant properties. In a previous study, walnut peptides demonstrated a protective effect against H2O2 and Aβ-induced cellular damage, which was accompanied by a decrease in lipid peroxidation and an increase in antioxidant enzyme activity in rat PC12 and SH-SY5Y cell lines, as well as in primary cultured cortical neurons (117). Notably, compounding walnut peptide with ginseng saponin to feed senescence-accelerated mice (SAM) revealed that walnut peptide significantly increased the serum levels of antioxidant enzymes and reduced Aβ and p-tau in the hippocampus through activation of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)/TrkB-dependent PI3K/Akt signalling pathway, significantly improving the memory of rats with neurodegenerative disease capacity (118). H. Chen et al. (119) identified 77 peptides from the antioxidant fraction of defatted walnut meal hydrolysate (DWMH) that exhibited relatively strong hydroxyl scavenging and oxygen radical uptake. In an animal model of D-galactose-induced neurodegeneration, DWMH eliminates spatial learning memory deficits in the Morris water maze experiment and the dark/light avoidance experiment in mice. Among them, WSREEQEREE and ADIYTEEAGR significantly ameliorated H2O2-induced oxidative damage in PC12 cells. Feng et al. (120) smulated gastrointestinal digestion of SGGY tetrapeptide obtained from DWMH and exhibited high radical scavenging activity in both 2,2′-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazolino-6-sulfonic acid; ABTS) and oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC) assays, which protects neuroblastoma (SH-SY5Y) cells from H2O2-induced oxidative damage. In addition, Zheng et al. (121) found that tripeptides from defatted peanut (Arachis hypogaea) meal hydrolysate (DPMH) with Tyr-Gly-Ser (YGS) structure had a strong free radical absorbance capacity (ORAC), preventing linoleic acid peroxidation, and H2O2 induced oxidative damage to PC12 cells had a protective effect. Its antioxidant activity may be mediated through the mechanism of transferring hydrogen atoms and the presence of Tyr at the N-terminus, which constitutes a hydrogen donor. Notably, the isolation of PGCPST from peanut protein hydrolysate not only exhibited desirable antioxidant capacity, effectively increased cell viability and reduced apoptosis in 6-OHDA-induced PC12, but also exerted neuroprotective effects through sphingolipid metabolism-related pathways (122).
The intestinal flora, a complex community of microorganisms present in our gastrointestinal ecosystem, is an important protective barrier that maintains the integrity and structure of the intestinal layer, fights against harmful pathogens, and modulates host immunity, and imbalances in the intestinal flora can lead to impaired intestinal barrier function (123). Gut microbe-derived metabolites such as ROS and lipopolysaccharides can leak into the body circulation via a bidirectional microbe-gut-brain axis communication system, and these neurotoxin releases from the gut microbiota can elicit an inflammatory response and cross the blood–brain barrier to modulate neuronal activity, and neuroinflammation has been implicated in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus and its associated cognitive dysfunction (124). Y. Zhang et al. (125) used 16S rRNA gene sequencing to examine the composition of the intestinal flora in 154 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, 73 of whom had normal cognitive function and 81 of whom had impaired cognitive function. Tenericutes abundance is lower in patients with cognitive impairment. Comparisons at the genus level showed decreased abundance of Bifidobacterium and unranked-RF 39 and increased abundance of Digestive Cocci and unranked Leuconostocaceae in cognitively impaired patients with T2DM. In addition, the relative abundance of Veronococcus and Katococcus was reduced in cognitively impaired subjects, and the relative abundance of each of the seven subfunctions was significantly altered in the cognitively impaired group. Alterations in the gut microbiome have also been demonstrated in preclinical studies. H. Gao et al. (126) conducted a study on advanced type 1 diabetic (AST1D) rats with cognitive deficits and age-matched controls (AMC) to investigate the diversity of microbial populations. Microbiome alterations were found to be significant in ASTID rats. Relatively high abundance of Mycobacterium anisopliae and lower abundance of Mycobacterium anisopliae were observed in AST1D rats. Energy metabolism, which is critical for each organism, was significantly reduced in AST1D rats, especially in serum and hippocampus. Numerous findings have demonstrated that peptides can alleviate neuroinflammation and thereby ameliorate cognitive impairment by modulating the levels of reactive oxygen species in the gut and the composition of the intestinal flora, and that peptides with small molecular weights have higher antioxidant capacity compared to natural proteins and can be absorbed directly in the gut (126). Soy protein hydrolysates with molecular weight < 3 kDa not only attenuate the accumulation of reactive oxygen species ROS in H2O2-damaged human intestinal Caco-2 cells, but also inhibit lipid peroxidation and activate the cellular antioxidant defence system to protect the Caco-2 cells from oxidative stress, thereby maintaining the integrity of human intestinal mucosa (127). In addition, peptides can improve the composition of microbial communities by reducing the abundance of pathogenic organisms and protect the intestinal and mucosal immune systems, thereby exerting functional properties in neurodegenerative diseases. T2DM mice treated with ginseng polypeptide (GP) on a high-sugar and high-fat diet (including streptozotocin (STZ)) showed that GP could play a hypoglycemic role by restoring the SCFA-producing microbiota in the intestine, and enriched the microflora closely related to lipid metabolism, oxidative stress and inflammatory response, such as desalted bacilli, Bifidobacterium spp., and bacteroides (128). Targeting the insulin signalling pathway may provide new strategies for the prevention and treatment of cognitive impairment. Probiotic fermentation technology (PFT) has been reported to improve insulin signalling by modulating the gut microbiota, upregulating insulin receptor expression and activating PI3K/Akt signalling, followed by inhibition of GSK-3β and mTOR signalling, which leads to the downregulation of over-phosphorylated tau proteins in order to halt the development of memory and cognitive impairment (129). M. Wang et al. (130) reported that oral administration of PKNW enhanced learning and memory in APP/PS1 transgenic mice by reducing hippocampal Aβ plaque accumulation, and furthermore, PKNW treatment increased the relative abundance of the thick-walled phylum, whereas it decreased the relative abundance of the anamorphic phylum and the warty microphytobacterial phylum. Improved bidirectional communication between the gut-brain axis including the central and enteric nervous systems links the cognitive centres of the brain to peripheral gut function. Alterations in the gut microbiome are strongly associated with cognitive function. Further studies on interactions, metabolism and mechanisms of action are needed to develop effective neuroprotective agents (131). Given that peptides play an effective role in improving the composition of the gut microbiota, maintaining homeostasis of the gut microbiota prevents or delays the onset of neurodegenerative diseases. Thus, peptides may serve as a new research direction for future prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases through microbial targeting to reduce the dependence on synthetic drugs with severe side effects (Table 1).
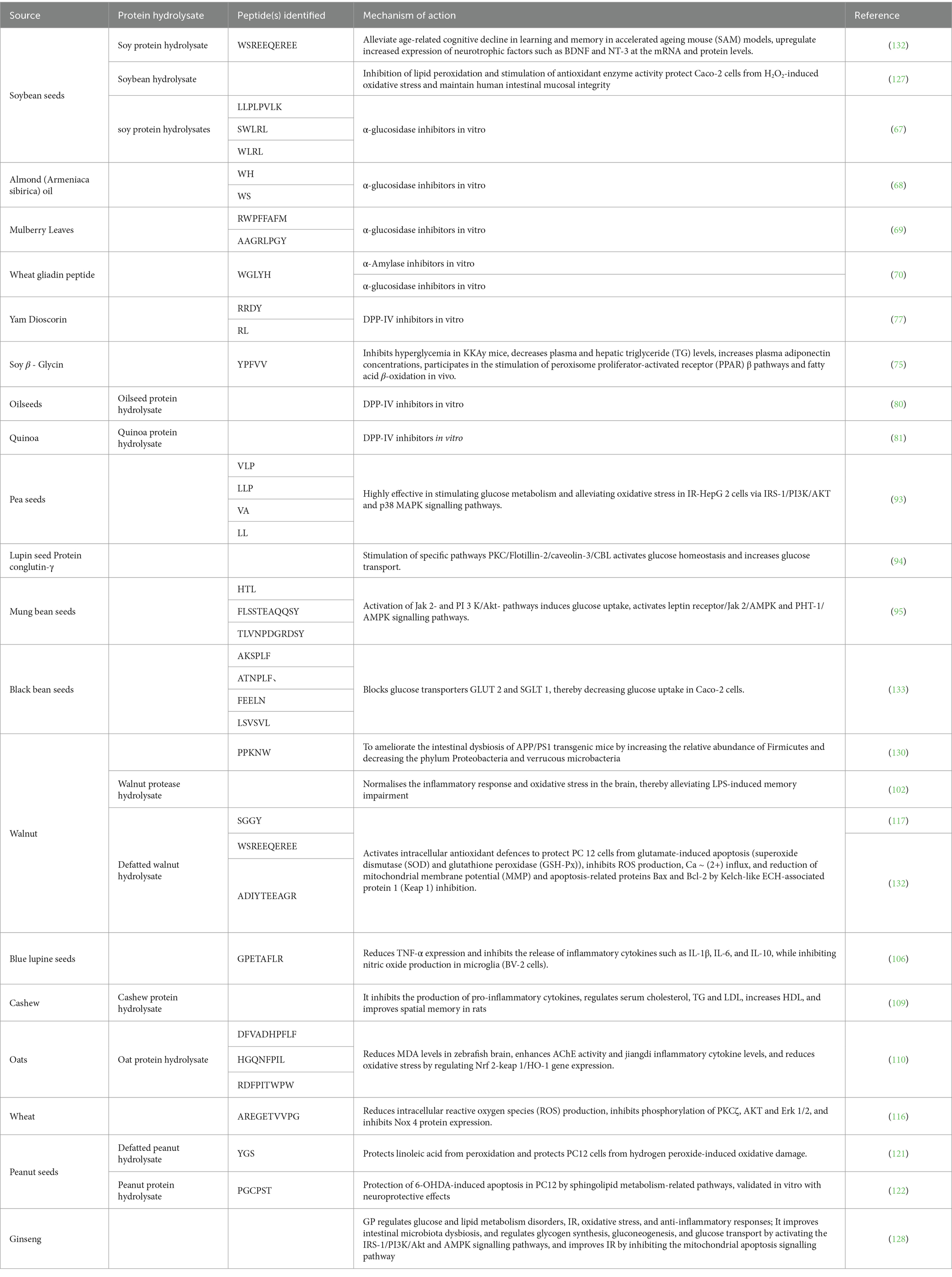
Table 1. Antidiabetic effects of peptides and protein hydrolysates identified from plants and their cognitive dysfunction.
Over the years, diabetic cognitive dysfunction has been extensively studied as a complication and comorbidity of diabetes, and although the specific pathogenesis is still unclear, a large number of studies have found that diabetic cognitive dysfunction and neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease) share common pathophysiological characteristics. With the progress of research, it has been found that chemical synthetic drugs that regulate diabetes may improve cognitive dysfunction and prevent the occurrence of dementia to a certain extent, however, these synthetic drugs have certain side effects that may bring inconvenience to patients’ lives. In contrast, phytogenic bioactive peptides have a wide range of sources, low molecular weight, high activity and specificity, easy absorption, high safety and low toxicity, and have broad application prospects in the prevention and treatment of various diseases. This article reviews the relevant mechanisms affecting the onset of cognitive dysfunction in diabetic patients, including oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, tau hyperphosphorylation, and amyloid precipitation. The development of these symptoms involves dysfunction of insulin signalling or synthesis, impaired glucose transporters. Here, we discuss potentially active peptides with antidiabetic properties that inhibit α-amylase, α-glucosidase, DPP-IV, and have inhibitory oxidative stress, apoptosis, and inflammatory and neuroprotective peptides isolated from plant sources. At present, additional work is needed to verify the efficacy and safety of phytogenic bioactive peptides in anti-diabetic and neuroprotective, so as to escort the further development of foods and drugs with the ability to prevent diabetic cognitive dysfunction.
XL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SM: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YY: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. ZW: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. YT: Project administration, Writing – review & editing. LT: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JD: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Validation, Writing – original draft and Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The financial support was provided by Yunnan Province agricultural joint special project (202101AK070243); Yunnan Province High-level Science and Technology Talent and Innovation Team Project (202305AS350025); Major science and technology special plan of Yunnan Province (202102AE090027-2).
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by Yunnan Province agricultural joint special project; Yunnan Province High-level Science and Technology Talent and Innovation Team Project; Major science and technology special plan of Yunnan Province.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Muriach, M, Flores-Bellver, M, Romero, FJ, and Barcia, JM. Diabetes and the brain: oxidative stress, inflammation, and autophagy. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2014) 2014:102158. doi: 10.1155/2014/102158
2. Luo, A, Xie, Z, Wang, Y, Wang, X, Li, S, Yan, J, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus-associated cognitive dysfunction: advances in potential mechanisms and therapies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. (2022) 137:104642. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104642
3. Okemah, J, Peng, J, and Quiñones, M. Addressing clinical inertia in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a review. Adv Ther. (2018) 35:1735–45. doi: 10.1007/s12325-018-0819-5
4. Stumvoll, M, Goldstein, BJ, and van Haeften, TW. Type 2 diabetes: principles of pathogenesis and therapy. Lancet. (2005) 365:1333–46. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)61032-X
5. Zhu, J, Hu, Z, Luo, Y, Liu, Y, Luo, W, du, X, et al. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: pathogenetic mechanisms and treatment. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1265372. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1265372
6. Bharadwaj, P, Wijesekara, N, Liyanapathirana, M, Newsholme, P, Ittner, L, Fraser, P, et al. The link between type 2 diabetes and neurodegeneration: roles for amyloid-beta, amylin, and tau proteins. J Alzheimers Dis. (2017) 59:421–32. doi: 10.3233/JAD-161192
7. Sáez-Orellana, F, Octave, JN, and Pierrot, N. Alzheimer's disease, a lipid story: involvement of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. Cells. (2020) 9:1215. doi: 10.3390/cells9051215
8. Majidazar, R, Rezazadeh-Gavgani, E, Sadigh-Eteghad, S, and Naseri, A. Pharmacotherapy of Alzheimer's disease: an overview of systematic reviews. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. (2022) 78:1567–87. doi: 10.1007/s00228-022-03363-6
9. Michailidis, M, Tata, DA, Moraitou, D, Kavvadas, D, Karachrysafi, S, Papamitsou, T, et al. Antidiabetic drugs in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:105–123. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094641
10. Hippisley-Cox, J, and Coupland, C. Diabetes treatments and risk of amputation, blindness, severe kidney failure, hyperglycaemia, and hypoglycaemia: open cohort study in primary care. BMJ. (2016) 352:i1450. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i1450
11. Jacob, RJ, Fan, X, Evans, ML, Dziura, J, and Sherwin, RS. Brain glucose levels are elevated in chronically hyperglycemic diabetic rats: no evidence for protective adaptation by the blood brain barrier. Metabolism. (2002) 51:1522–4. doi: 10.1053/meta.2002.36347
12. Sagud, M, Tudor, L, and Pivac, N. Personalized treatment interventions: nonpharmacological and natural treatment strategies in Alzheimer's disease. Expert Rev Neurother. (2021) 21:571–89. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2021.1906223
13. Admassu, H, Gasmalla, MAA, Yang, R, and Zhao, W. Bioactive peptides derived from seaweed protein and their health benefits: antihypertensive, antioxidant, and antidiabetic properties. J Food Sci. (2017) 83:6–16. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14011
14. Muttenthaler, M, King, GF, Adams, DJ, and Alewood, PF. Trends in peptide drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2021) 20:309–25. doi: 10.1038/s41573-020-00135-8
15. Pasinetti, GM, Iqbal, UH, and Rosenberg, PB. Effect of polyphenol treatment for mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and diabetes. Alzheimers Dement. (2020) 16. doi: 10.1002/alz.044062
16. Antony, P, and Vijayan, R. Bioactive peptides as potential nutraceuticals for diabetes therapy: a comprehensive review. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:9059. doi: 10.3390/ijms22169059
17. Chai, KF, Voo, AYH, and Chen, WN. Bioactive peptides from food fermentation: a comprehensive review of their sources, bioactivities, applications, and future development. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. (2020) 19:3825–85. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12651
18. Chakrabarti, S, Guha, S, and Majumder, K. Food-derived bioactive peptides in human health: challenges and opportunities. Nutrients. (2018) 10:1738. doi: 10.3390/nu10111738
19. van Sloten, TT, Sedaghat, S, Carnethon, MR, Launer, LJ, and Stehouwer, CDA. Cerebral microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes: stroke, cognitive dysfunction, and depression. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2020) 8:325–36. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(19)30405-X
20. Cashion, JM, Brown, LS, Morris, GP, Fortune, AJ, Courtney, JM, Makowiecki, K, et al. Pericyte ablation causes hypoactivity and reactive gliosis in adult mice. Brain Behav Immun. (2024) 123:681–96. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2024.10.014
21. Mayer, MG, and Fischer, T. Microglia at the blood brain barrier in health and disease. Front Cell Neurosci. (2024) 18:1360195. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1360195
22. Chen, Y, Meng, Z, Li, Y, Liu, S, Hu, P, and Luo, E. Advanced glycation end products and reactive oxygen species: uncovering the potential role of ferroptosis in diabetic complications. Mol Med. (2024) 30:141. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00905-9
23. Kosenko, E, Tikhonova, L, Alilova, G, Urios, A, and Montoliu, C. The Erythrocytic hypothesis of brain energy crisis in sporadic Alzheimer disease: possible consequences and supporting evidence. J Clin Med. (2020) 9:206. doi: 10.3390/jcm9010206
24. Gao, C, Liu, Y, Li, L, and Hölscher, C. New animal models of Alzheimer's disease that display insulin desensitization in the brain. Rev Neurosci. (2013) 24:607–15. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2013-0034
25. Bellavite, P, Fazio, S, and Affuso, F. A descriptive review of the action mechanisms of Berberine, quercetin and Silymarin on insulin resistance/hyperinsulinemia and cardiovascular prevention. Molecules. (2023) 28:4491. doi: 10.3390/molecules28114491
26. Biessels, GJ, and Despa, F. Cognitive decline and dementia in diabetes mellitus: mechanisms and clinical implications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2018) 14:591–604. doi: 10.1038/s41574-018-0048-7
27. Rohden, F, Ferreira, PCL, Bellaver, B, Aguzzoli, CS, Soares, C, Povala, G, et al. Astrocyte reactivity is associated with synaptic dysfunction across the aging and Alzheimer’s disease spectrum, whereas microglial reactivity is specifically associated with synaptic dysfunction related to cognitive impairment. Alzheimers Dement. (2023) 19. doi: 10.1002/alz.081975
28. Zhang, B, Song, C, Tang, X, Tian, M, Liu, Y, Yan, Z, et al. Type 2 diabetes microenvironment promotes the development of Parkinson's disease by activating microglial cell inflammation. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2024) 12:1422746. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1422746
29. Singh, MV, Wong, T, Moorjani, S, Mani, AM, and Dokun, AO. Novel components in the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB) signaling pathways of endothelial cells under hyperglycemic-ischemic conditions. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2024) 11:1345421. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1345421
30. Paul, S, Bhardwaj, J, and Binukumar, BK. Cdk5-mediated oligodendrocyte myelin breakdown and neuroinflammation: implications for the link between type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer's disease. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) - Mol Basis Dis. (2024) 1870:166986. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.166986
31. Meng, X, Li, D, Kan, R, Xiang, Y, Pan, L, Guo, Y, et al. Inhibition of ANGPTL8 protects against diabetes-associated cognitive dysfunction by reducing synaptic loss via the PirB signaling pathway. J Neuroinflammation. (2024) 21:192. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03183-8
32. Makarava, N, Chang, JCY, Kushwaha, R, and Baskakov, IV. Region-specific response of astrocytes to prion infection. Front Neurosci. (2019) 13:1048. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.01048
33. Li, Y, Zhang, H, Liu, M, Guo, W, and Yu, L. Microglia NLRP3 Inflammasomes activation involving diabetic Neuroinflammation in diabetic mice and BV2 cells. Curr Pharm Des. (2021) 27:2802–16. doi: 10.2174/1381612827666210716104606
34. Friedel, R, Huang, Y, Wang, M, and Wahane, S. Regulation of cell distancing in peri-plaque glial nets by Plexin-B1 affects glial activation and amyloid compaction in Alzheimer’s disease (2021) 27:1489–1504. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-967160/v1
35. Cardinal von Widdern, J, Hohmann, T, and Dehghani, F. Abnormal Cannabidiol affects production of pro-inflammatory mediators and astrocyte wound closure in primary astrocytic-microglial Cocultures. Molecules. (2020) 25. doi: 10.3390/molecules25030496
36. al-Atrache, Z, Lopez, D, Hingley, S, and Appelt, D. Astrocytes infected with Chlamydia pneumoniae demonstrate altered expression and activity of secretases involved in the generation of beta-amyloid found in Alzheimer disease. BMC Neurosci. (2019) 20:6. doi: 10.1186/s12868-019-0489-5
37. Li, YT, Jin, X, Tang, L, Lv, WL, Xiao, MM, Zhang, ZY, et al. Receptor-mediated field effect transistor biosensor for real-time monitoring of glutamate release from primary hippocampal neurons. Anal Chem. (2019) 91:8229–36. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b00832
38. Collins-Praino, LE, and Corrigan, F. Does neuroinflammation drive the relationship between tau hyperphosphorylation and dementia development following traumatic brain injury? Brain Behav Immun. (2017) 60:369–82. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2016.09.027
39. Dash, UC, Bhol, NK, Swain, SK, Samal, RR, Nayak, PK, Raina, V, et al. Oxidative stress and inflammation in the pathogenesis of neurological disorders: mechanisms and implications. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2024). doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.10.004
40. Zhang, X, Hou, L, Guo, Z, Wang, G, Xu, J, Zheng, Z, et al. Lipid peroxidation in osteoarthritis: focusing on 4-hydroxynonenal, malondialdehyde, and ferroptosis. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 9:320. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01613-9
41. Çalışkan, Z, Mutlu, T, Güven, M, Tunçdemir, M, Niyazioğlu, M, Hacioglu, Y, et al. SIRT6 expression and oxidative DNA damage in individuals with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Gene. (2018) 642:542–8. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.11.071
42. di, F, Pupo, G, Giraldo, E, Badìa, MC, Monllor, P, Lloret, A, et al. Oxidative signature of cerebrospinal fluid from mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease patients. Free Radic Biol Med. (2016) 91:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.12.004
43. McLimans, KE, and Willette, AAAlzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Autotaxin is related to metabolic dysfunction and predicts Alzheimer’s disease outcomes. J Alzheimers Dis. (2017) 56:403–13. doi: 10.3233/jad-160891
44. Rhea, E, and Banks, WA. Regulation of insulin transport across the blood-brain barrier by CNS insulin receptor signaling. Alzheimers Dement. (2020) 16. doi: 10.1002/alz.039508
45. Masuda, D, Nakanishi, I, Ohkubo, K, Ito, H, Matsumoto, KI, Ichikawa, H, et al. Mitochondria play essential roles in intracellular protection against oxidative stress-which molecules among the ROS generated in the mitochondria can escape the mitochondria and contribute to signal activation in cytosol? Biomol Ther. (2024) 14:128. doi: 10.3390/biom14010128
46. Cardoso, S, Santos, MS, Moreno, A, and Moreira, PI. UCP2 and ANT differently modulate proton-leak in brain mitochondria of long-term hyperglycemic and recurrent hypoglycemic rats. J Bioenerg Biomembr. (2013) 45:397–407. doi: 10.1007/s10863-013-9503-2
47. Drummond, E, Pires, G, MacMurray, C, Askenazi, M, Nayak, S, Bourdon, M, et al. Phosphorylated tau interactome in the human Alzheimer’s disease brain. Alzheimers Dement. (2020) 16:2803–2817. doi: 10.1002/alz.045492
48. Rana, AK, and Singh, D. Targeting glycogen synthase kinase-3 for oxidative stress and neuroinflammation: opportunities, challenges and future directions for cerebral stroke management. Neuropharmacology. (2018) 139:124–36. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.07.006
49. Dahlgren, AF, Pan, A, Lam, V, Gouthro, KC, Simpson, PM, Salzman, NH, et al. Longitudinal changes in the gut microbiome of infants on total parenteral nutrition. Pediatr Res. (2019) 86:107–14. doi: 10.1038/s41390-019-0391-y
50. Rao, M, and Gershon, MD. The bowel and beyond: the enteric nervous system in neurological disorders. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2016) 13:517–28. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2016.107
51. Zawada, A, Rychter, AM, Ratajczak, AE, Lisiecka-Masian, A, Dobrowolska, A, and Krela-Kaźmierczak, I. Does gut-microbiome interaction protect against obesity and obesity-associated metabolic disorders? Microorganisms. (2020) 9:18. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9010018
52. Gurung, M, Li, Z, You, H, Rodrigues, R, Jump, DB, Morgun, A, et al. Role of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology. EBioMedicine. (2020) 51:102590. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.11.051
53. Pham, TP, Tidjani, M, Bachar, D, Levasseur, A, Brah, S, Alhousseini, D, et al. Gut microbiota alteration is characterized by a Proteobacteria and Fusobacteria bloom in kwashiorkor and a Bacteroidetes paucity in marasmus. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:9084. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45611-3
54. Kalyan, M, Tousif, AH, Sonali, S, Vichitra, C, Sunanda, T, Praveenraj, SS, et al. Role of endogenous lipopolysaccharides in neurological disorders. Cells. (2022) 11:4038. doi: 10.3390/cells11244038
55. Lerner, A, Neidhöfer, S, and Matthias, T. The gut microbiome feelings of the brain: a perspective for non-microbiologists. Microorganisms. (2017) 5:66. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms5040066
56. Bonaz, B, Bazin, T, and Pellissier, S. The Vagus nerve at the Interface of the microbiota-gut-brain Axis. Front Neurosci. (2018) 12:49. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00049
57. Duve, K, Petakh, P, and Kamyshnyi, O. COVID-19-associated encephalopathy: connection between neuroinflammation and microbiota-gut-brain axis. Front Microbiol. (2024) 15:1406874. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1406874
58. Guo, Y, Zhu, X, Zeng, M, Qi, L, Tang, X, Wang, D, et al. A diet high in sugar and fat influences neurotransmitter metabolism and then affects brain function by altering the gut microbiota. Transl Psychiatry. (2021) 11:328. doi: 10.1038/s41398-021-01443-2
59. Wang, J, Cai, W, Yu, J, Liu, H, He, S, Zhu, L, et al. Dietary advanced glycation end products shift the gut microbiota composition and induce insulin resistance in mice. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. (2022) 15:427–37. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S346411
60. Pereira, LTG, Vilela, WR, Bellozi, PMQ, Engel, DF, de Paula, GC, de Andrade, RR, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation ameliorates high-fat diet-induced memory impairment in mice. J Neurochem. (2024) 168:2893–907. doi: 10.1111/jnc.16156
61. Zhao, Z, Ning, J, Bao, XQ, Shang, M, Ma, J, Li, G, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation protects rotenone-induced Parkinson's disease mice via suppressing inflammation mediated by the lipopolysaccharide-TLR4 signaling pathway through the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Microbiome. (2021) 9:226. doi: 10.1186/s40168-021-01107-9
62. Okuyama, M, Saburi, W, Mori, H, and Kimura, A. α-Glucosidases and α-1,4-glucan lyases: structures, functions, and physiological actions. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2016) 73:2727–51. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2247-5
63. Riyaphan, J, Jhong, CH, Lin, SR, Chang, CH, Tsai, MJ, Lee, DN, et al. Hypoglycemic efficacy of docking selected natural compounds against alpha-glucosidase and alpha-amylase. Molecules. (2018) 23:2260. doi: 10.3390/molecules23092260
64. Brás, N, Santos-Martins, D, Fernandes, P, and Ramos, M. Mechanistic pathway on human alpha-glucosidase maltase-Glucoamylase unveiled by QM/MM calculations. J Phys Chem B. (2018) 122:3889–99. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.8b01321
65. Arnal, M, Gallego, M, Talens, P, and Mora, L. Peptidomic profile and α-glucosidase inhibitory activity of cooked and gastrointestinal digested legumes. Lwt. (2024) 201:116283. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2024.116283
66. Lu, H, Xie, T, Wu, Q, Hu, Z, Luo, Y, and Luo, F. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitory peptides: sources, preparations, identifications, and action mechanisms. Nutrients. (2023) 15:4267. doi: 10.3390/nu15194267
67. Wang, R, Zhao, H, Pan, X, Orfila, C, Lu, W, and Ma, Y. Preparation of bioactive peptides with antidiabetic, antihypertensive, and antioxidant activities and identification of alpha-glucosidase inhibitory peptides from soy protein. Food Sci Nutr. (2019) 7:1848–56. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.1038
68. Gu, X, Gao, T, Hou, Y, Li, D, and Fu, L. Identification and characterization of two novel α-glucosidase inhibitory peptides from almond (Armeniaca sibirica) oil manufacture residue. Lwt. (2020) 134:110215. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110215
69. Deng, F, Liang, Y, Lei, Y, Xiong, S, Rong, J, and Hu, Y. Development and identification of novel alpha-glucosidase inhibitory peptides from mulberry leaves. Food Secur. (2023) 12:3917. doi: 10.3390/foods12213917
70. Mousavi, B, Azizi, MH, and Abbasi, S. Antidiabetic bio-peptides of soft and hard wheat glutens. Food Chem (Oxf). (2022) 4:100104. doi: 10.1016/j.fochms.2022.100104
71. Uraipong, C, and Zhao, J. In vitro digestion of rice bran proteins produces peptides with potent inhibitory effects on alpha-glucosidase and angiotensin I converting enzyme. J Sci Food Agric. (2018) 98:758–66. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.8523
72. Fisman, EZ, and Tenenbaum, A. The dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist tirzepatide: a novel cardiometabolic therapeutic prospect. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2021) 20:225. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01412-5
73. Holscher, C. Protective properties of GLP-1 and associated peptide hormones in neurodegenerative disorders. Br J Pharmacol. (2022) 179:695–714. doi: 10.1111/bph.15508
74. Rohani,, Febrina, E, Wahyuni, I, and Levita, J. Pharmacological and clinical studies of medicinal plants that inhibit dipeptidyl peptidase-IV. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2023) 17:3473–91. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S426870
75. Yamada, Y, Muraki, A, Oie, M, Kanegawa, N, Oda, A, Sawashi, Y, et al. Soymorphin-5, a soy-derived mu-opioid peptide, decreases glucose and triglyceride levels through activating adiponectin and PPARalpha systems in diabetic KKAy mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2012) 302:E433–40. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00161.2011
76. Wang, L, Ding, L, Zhu, W, and Hang, S. Soybean protein hydrolysate stimulated cholecystokinin secretion and inhibited feed intake through calcium-sensing receptors and intracellular calcium signalling in pigs. Food Funct. (2021) 12:9286–99. doi: 10.1039/d1fo01596f
77. Lin, YS, Han, CH, Lin, SY, and Hou, WC. Synthesized peptides from yam Dioscorin hydrolysis in silico exhibit dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory activities and Oral glucose tolerance improvements in Normal mice. J Agric Food Chem. (2016) 64:6451–8. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b02403
78. Sun, S, Zhang, G, Mu, H, Zhang, H, and Chen, YQ. The mixture of corn and wheat peptide prevent diabetes in NOD mice. J Funct Foods. (2019) 56:163–70. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.03.020
79. Bo, W, Chen, L, Qin, D, Geng, S, Li, J, Mei, H, et al. Application of quantitative structure-activity relationship to food-derived peptides: methods, situations, challenges and prospects. Trends Food Sci Technol. (2021) 114:176–88. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2021.05.031
80. Han, R, Maycock, J, Murray, BS, and Boesch, C. Identification of angiotensin converting enzyme and dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory peptides derived from oilseed proteins using two integrated bioinformatic approaches. Food Res Int. (2019) 115:283–91. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.12.015
81. Mudgil, P, Kilari, BP, Kamal, H, Olalere, OA, FitzGerald, RJ, Gan, CY, et al. Multifunctional bioactive peptides derived from quinoa protein hydrolysates: inhibition of α-glucosidase, dipeptidyl peptidase-IV and angiotensin I converting enzymes. J Cereal Sci. (2020) 96:103130. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2020.103130
82. Jackson, EK. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibition alters the hemodynamic response to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in humans with the metabolic syndrome. Hypertension. (2010) 56:581–3. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.158527
83. Głuchowska, K, Pliszka, M, and Szablewski, L. Expression of glucose transporters in human neurodegenerative diseases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2021) 540:8–15. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.12.067
84. Ida-Yonemochi, H, Otsu, K, Harada, H, and Ohshima, H. Functional expression of sodium-dependent glucose transporter in Amelogenesis. J Dent Res. (2020) 99:977–86. doi: 10.1177/0022034520916130
85. Raut, S, Bhalerao, A, Powers, M, Gonzalez, M, Mancuso, S, and Cucullo, L. Hypometabolism, Alzheimer's disease, and possible therapeutic targets: an overview. Cells. (2023) 12:2019. doi: 10.3390/cells12162019
86. Hossain, MS, Oomura, Y, and Katafuchi, T. Glucose can epigenetically Alter the gene expression of neurotrophic factors in the murine brain cells. Mol Neurobiol. (2017) 55:3408–25. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0578-3
87. Kyrtata, N, Emsley, HCA, Sparasci, O, Parkes, LM, and Dickie, BR. A systematic review of glucose transport alterations in Alzheimer's disease. Front Neurosci. (2021) 15. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.626636
88. Khrwat, A, and Saadawi, A. Generalized anxiety disorder among diabetic patients visiting Gharyan-polyclinic in Libya during COVID-19 pandemic. BJPsych Open. (2021) 7:S265–5. doi: 10.1192/bjo.2021.705
89. Yonamine, CY, Michalani, MLE, Moreira, RJ, and Machado, UF. Glucose transport and utilization in the Hippocampus: from neurophysiology to diabetes-related development of dementia. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:16480. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216480
90. Saha, A, Coughlan, KA, Valentine, RJ, and Ruderman, NB. AMPK activation: a therapeutic target for type 2 diabetes? Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy. (2014) 7:241–53. doi: 10.2147/dmso.S43731
91. Norton, L, Shannon, CE, Fourcaudot, M, Hu, C, Wang, N, Ren, W, et al. Sodium-glucose co-transporter (SGLT) and glucose transporter (GLUT) expression in the kidney of type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2017) 19:1322–6. doi: 10.1111/dom.13003
92. Lammi, C, Zanoni, C, and Arnoldi, A. IAVPGEVA, IAVPTGVA, and LPYP, three peptides from soy glycinin, modulate cholesterol metabolism in HepG2 cells through the activation of the LDLR-SREBP2 pathway. J Funct Foods. (2015) 14:469–78. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2015.02.021
93. Zhu, Y, Zhang, H, Wei, Y, Cai, M, Gu, R, Wang, Y, et al. Pea-derived peptides, VLP, LLP, VA, and LL, improve insulin resistance in HepG2 cells via activating IRS-1/PI3K/AKT and blocking ROS-mediated p38MAPK signaling. J Food Biochem. (2020) 44:e13454. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13454
94. Terruzzi, I, Senesi, P, Magni, C, Montesano, A, Scarafoni, A, Luzi, L, et al. Insulin-mimetic action of conglutin-γ, a lupin seed protein, in mouse myoblasts. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2011) 21:197–205. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2009.09.004
95. Yoshioka, Y, Zhang, Q, Wang, X, Kitakaze, T, Yamashita, Y, Kohno, M, et al. Mung bean peptides promote glucose uptake via Jak2 activation in L6 myotubes. Food Funct. (2023) 14:5375–90. doi: 10.1039/d3fo00836c
96. Mojica, L, Gonzalez de Mejia, E, Granados-Silvestre, MÁ, and Menjivar, M. Evaluation of the hypoglycemic potential of a black bean hydrolyzed protein isolate and its pure peptides using in silico, in vitro and in vivo approaches. J Funct Foods. (2017) 31:274–86. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.02.006
97. Dergunova, LV, Filippenkov, IB, Limborska, SA, and Myasoedov, NF. Neuroprotective peptides and new strategies for ischemic stroke drug discoveries. Genes (Basel). (2023) 14:953. doi: 10.3390/genes14050953
98. Toth, F, Cseh, EK, and Vécsei, L. Natural molecules and neuroprotection: Kynurenic acid, Pantethine and alpha-lipoic acid. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:403. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010403
99. Hasan, MM, Ahmed, QU, Mat Soad, SZ, and Tunna, TS. Animal models and natural products to investigate in vivo and in vitro antidiabetic activity. Biomed Pharmacother. (2018) 101:833–41. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.137
100. Cazarin, CA, Dalmagro, AP, Gonçalves, AE, Boeing, T, Silva, LM, Corrêa, R, et al. Usnic acid enantiomers restore cognitive deficits and neurochemical alterations induced by Abeta(1-42) in mice. Behav Brain Res. (2021) 397:112945. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2020.112945
101. Zasheva, D, Mladenov, P, Zapryanova, S, Gospodinova, Z, Georgieva, M, Alexandar, I, et al. Cytotoxic effects of plant secondary metabolites and naturally occurring bioactive peptides on breast Cancer model systems: molecular mechanisms. Molecules. (2024) 29:5275. doi: 10.3390/molecules29225275
102. Wang, S, Zheng, L, Zhao, T, Zhang, Q, Liu, Y, Sun, B, et al. Inhibitory effects of walnut (Juglans regia) peptides on Neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in lipopolysaccharide-induced cognitive impairment mice. J Agric Food Chem. (2020) 68:2381–92. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b07670
103. Katayama, S, Imai, R, Sugiyama, H, and Nakamura, S. Oral administration of soy peptides suppresses cognitive decline by induction of neurotrophic factors in SAMP8 mice. J Agric Food Chem. (2014) 62:3563–9. doi: 10.1021/jf405416s
104. Sheldrick, A, Camara, S, Ilieva, M, Riederer, P, and Michel, TM. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and neurotrophin 3 (NT3) levels in post-mortem brain tissue from patients with depression compared to healthy individuals - a proof of concept study. Eur Psychiatry. (2017) 46:65–71. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2017.06.009
105. Wu, L, Zhang, T, Chen, K, Lu, C, Liu, XF, Zhou, JL, et al. Rapid antidepressant-like effect of Fructus Aurantii depends on cAMP-response element binding protein/brain-derived neurotrophic facto by mediating synaptic transmission. Phytother Res. (2021) 35:404–14. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6812
106. Montserrat-de la Paz, S, Lemus-Conejo, A, Toscano, R, Pedroche, J, Millan, F, and Millan-Linares, MC. GPETAFLR, an octapeptide isolated from Lupinus angustifolius L. protein hydrolysate, promotes the skewing to the M2 phenotype in human primary monocytes. Food Funct. (2019) 10:3303–11. doi: 10.1039/c9fo00115h
107. Gao, Y, Zhang, X, Ren, G, Wu, C, Qin, P, and Yao, Y. Peptides from extruded Lupin (Lupinus albus L.) regulate inflammatory activity via the p38 MAPK signal transduction pathway in RAW 264.7 cells. J Agric Food Chem. (2020) 68:11702–9. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c02476
108. Li, F, Sun, X, Sun, K, Kong, F, Jiang, X, and Kong, Q. Lupenone improves motor dysfunction in spinal cord injury mice through inhibiting the inflammasome activation and pyroptosis in microglia via the nuclear factor kappa B pathway. Neural Regen Res. (2024) 19:1802–11. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.389302
109. Wattanathorn, J, Thukham-mee, W, Muchimapura, S, Wannanon, P, Tong-un, T, and Tiamkao, S. Preventive effect of cashew-derived protein hydrolysate with high Fiber on cerebral ischemia. Biomed Res Int. (2017) 2017:1–14. doi: 10.1155/2017/6135023
110. Rafique, H, Hu, X, Ren, T, Dong, R, Aadil, RM, Zou, L, et al. Characterization and exploration of the neuroprotective potential of oat-protein-derived peptides in PC12 cells and scopolamine-treated zebrafish. Nutrients. (2023) 16:117. doi: 10.3390/nu16010117
111. Xu, B, Dong, Q, Yu, C, Chen, H, Zhao, Y, Zhang, B, et al. Advances in research on the activity evaluation, mechanism and structure-activity relationships of natural antioxidant peptides. Antioxidants (Basel). (2024) 13:479. doi: 10.3390/antiox13040479
112. Tsou, MJ, Kao, FJ, Lu, HC, Kao, HC, and Chiang, WD. Purification and identification of lipolysis-stimulating peptides derived from enzymatic hydrolysis of soy protein. Food Chem. (2013) 138:1454–60. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.10.149
113. Tonolo, F, Grinzato, A, Bindoli, A, and Rigobello, MP. From in silico to a cellular model: molecular docking approach to evaluate antioxidant bioactive peptides. Antioxidants (Basel). (2023) 12:665. doi: 10.3390/antiox12030665
114. Galland, F, de Espindola, JS, Lopes, DS, Taccola, MF, and Pacheco, MTB. Food-derived bioactive peptides: mechanisms of action underlying inflammation and oxidative stress in the central nervous system. Food Chemistry Advances. (2022) 1:100087. doi: 10.1016/j.focha.2022.100087
115. Li, N, Wen, L, Wang, F, Wang, T, Li, T, Qiao, M, et al. Mechanism of mitigating effect of wheat germ peptides on lead-induced oxidative damage in PC12 cells. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2022) 246:114190. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.114190
116. Chen, S, Lin, D, Gao, Y, Cao, X, and Shen, X. A novel antioxidant peptide derived from wheat germ prevents high glucose-induced oxidative stress in vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro. Food Funct. (2017) 8:142–50. doi: 10.1039/c6fo01139j
117. Feng, L, Wu, Y, Wang, J, Han, Y, Huang, J, and Xu, H. Neuroprotective effects of a novel Tetrapeptide SGGY from walnut against H(2)O(2)-stimulated oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cells: possible involved JNK, p38 and Nrf2 signaling pathways. Food Secur. (2023) 12:1490. doi: 10.3390/foods12071490
118. Xu, M, du, Q, Hao, Y, Fan, R, and Li, Y. Long-term walnut oligopeptides prevents memory loss in aged SAMP8 mice by decreasing oxidative stress and Down-rRgulating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in Hippocampus. Current Develop Nutrit. (2020) 4:nzaa040_092. doi: 10.1093/cdn/nzaa040_092
119. Chen, H, Zhao, M, Lin, L, Wang, J, Sun-Waterhouse, D, Dong, Y, et al. Identification of antioxidative peptides from defatted walnut meal hydrolysate with potential for improving learning and memory. Food Res Int. (2015) 78:216–23. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2015.10.008
120. Feng, L, Peng, F, Wang, X, Li, M, Lei, H, and Xu, H. Identification and characterization of antioxidative peptides derived from simulated in vitro gastrointestinal digestion of walnut meal proteins. Food Res Int. (2019) 116:518–26. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.08.068
121. Zheng, L, Su, G, Ren, J, Gu, L, You, L, and Zhao, M. Isolation and characterization of an oxygen radical absorbance activity peptide from defatted peanut meal hydrolysate and its antioxidant properties. J Agric Food Chem. (2012) 60:5431–7. doi: 10.1021/jf3017173
122. Ma, R, Bai, J, Huang, Y, Wang, Z, Xu, Y, Huang, Y, et al. Purification and identification of novel antioxidant peptides from hydrolysates of peanuts (Arachis hypogaea) and their neuroprotective activities. J Agric Food Chem. (2023) 71:5861–6120. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c06075
123. Li, D, Tang, W, Wang, Y, Gao, Q, Zhang, H, Zhang, Y, et al. An overview of traditional Chinese medicine affecting gut microbiota in obesity. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1149751. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1149751
124. Peng, J, Tang, Y, and Huang, Y. Gut health: the results of microbial and mucosal immune interactions in pigs. Anim Nutr. (2021) 7:282–94. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2021.01.001
125. Zhang, Y, Lu, S, Yang, Y, Wang, Z, Wang, B, Zhang, B, et al. The diversity of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes with or without cognitive impairment. Aging Clin Exp Res. (2021) 33:589–601. doi: 10.1007/s40520-020-01553-9
126. Gao, H, Jiang, Q, Ji, H, Ning, J, Li, C, and Zheng, H. Type 1 diabetes induces cognitive dysfunction in rats associated with alterations of the gut microbiome and metabolomes in serum and hippocampus. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol basis Dis. (2019) 1865:165541. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.165541
127. Zhang, Q, Tong, X, Sui, X, Wang, Z, Qi, B, Li, Y, et al. Antioxidant activity and protective effects of Alcalase-hydrolyzed soybean hydrolysate in human intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells. Food Res Int. (2018) 111:256–64. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.05.046
128. Han, C, Kong, X, Xia, X, Huang, X, Mao, Z, Han, J, et al. Effects of ginseng peptides on the hypoglycemic activity and gut microbiota of a type 2 diabetes mellitus mice model. J Funct Foods. (2023) 111:105897. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2023.105897
129. el, N, Kandil, E, and Ghoneum, M. Enhancement of insulin/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and modulation of gut microbiome by probiotics fermentation technology, a kefir grain product, in sporadic Alzheimer's disease model in mice. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:666502. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.666502
130. Wang, M, Amakye, WK, Guo, L, Gong, C, Zhao, Y, Yao, M, et al. Walnut-derived peptide PW5 ameliorates cognitive impairments and alters gut microbiota in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2019) 63:e1900326. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201900326
131. Dong, TS, Shera, S, Peters, K, Gee, GC, Beltrán-Sánchez, H, Wang, MC, et al. Experiences of discrimination are associated with microbiome and transcriptome alterations in the gut. Front Microbiol. (2024) 15:1457028. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1457028
132. Wang, S, Zheng, L, Zhao, T, Zhang, Q, Su, G, and Zhao, M. The neuroprotective effect of walnut-derived peptides against glutamate-induced damage in PC12 cells: mechanism and bioavailability. Food Sci Human Wellness. (2022) 11:933–42. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2022.03.021
Keywords: cognitive improvement, cognitive function, diabetic cognitive dysfunction, diabetic disease, phytogenic bioactive peptides
Citation: Liu X, Mao S, Yuan Y, Wang Z, Tian Y, Tao L and Dai J (2025) Antin-diabetic cognitive dysfunction effects and underpinning mechanisms of phytogenic bioactive peptides: a review. Front. Nutr. 11:1517087. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1517087
Received: 25 October 2024; Accepted: 10 December 2024;
Published: 10 January 2025.
Edited by:
Qianqian Ouyang, Guangdong Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Zelin Li, Yunnan Academy of Agricultural Sciences, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Liu, Mao, Yuan, Wang, Tian, Tao and Dai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Liang Tao, dGFvd3VsaWFuZ0AxNjMuY29t; Jiahe Dai, ZGFpamlhaGUxMUAxNjMuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.