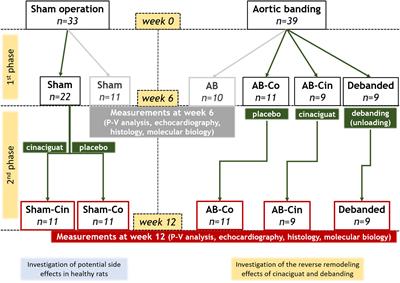
REVIEW
Published on 05 Nov 2019
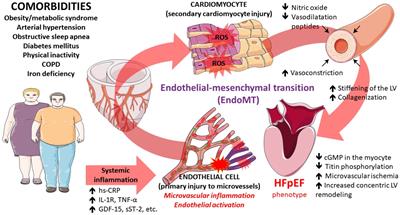
Microvascular Dysfunction in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction
doi 10.3389/fphys.2019.01347
- 18,301 views
- 100 citations
18k
Total downloads
68k
Total views and downloads
REVIEW
Published on 05 Nov 2019

OPINION
Published on 24 Oct 2019
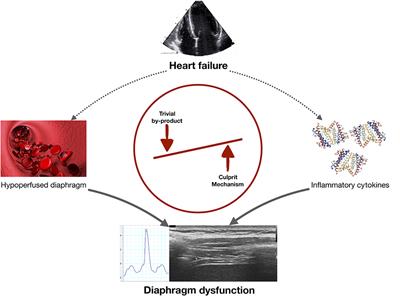
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 06 Sep 2019

REVIEW
Published on 04 Sep 2019
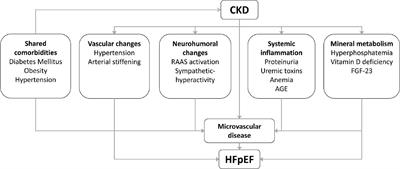
OPINION
Published on 05 Jul 2019
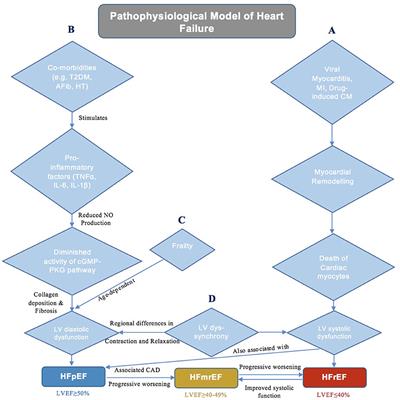
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 04 Jun 2019
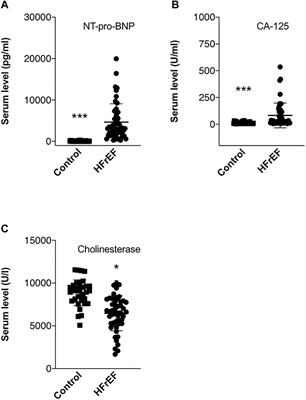
REVIEW
Published on 29 May 2019
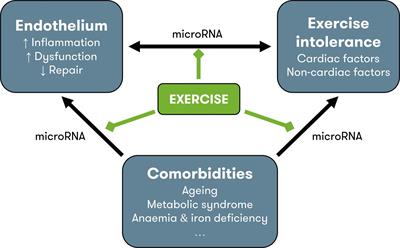
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 08 Jan 2019