EDITORIAL
Published on 21 Apr 2020
Editorial: IBD Management—Novel Targets and Therapeutic Perspectives
doi 10.3389/fphar.2020.00448
- 2,410 views
- 3 citations
32k
Total downloads
203k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 21 Apr 2020
REVIEW
Published on 18 Jun 2019
REVIEW
Published on 24 Apr 2019
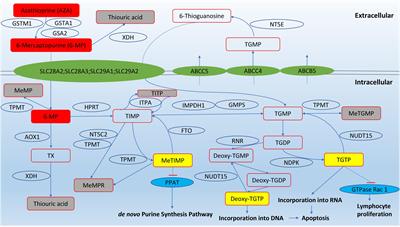
MINI REVIEW
Published on 29 Mar 2019
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Published on 19 Mar 2019

REVIEW
Published on 13 Mar 2019
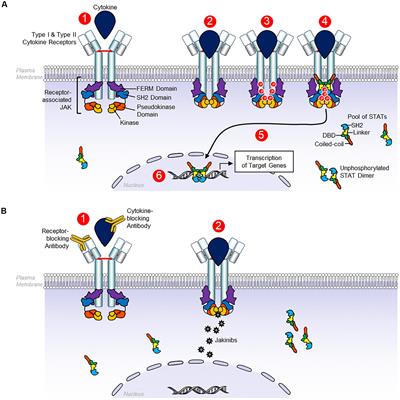
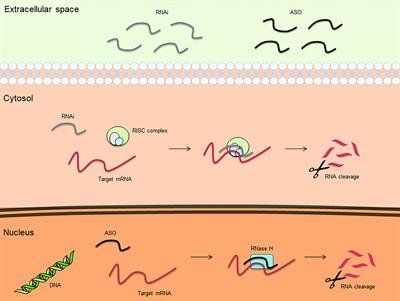
MINI REVIEW
Published on 08 Feb 2019
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 01 Feb 2019
REVIEW
Published on 10 Jan 2019
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 03 Dec 2018
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 31 Oct 2018
REVIEW
Published on 08 Oct 2018