EDITORIAL
Published on 03 Dec 2019
Editorial: Mechanisms by Which SLE-Associated Genetic Variants Contribute to SLE Pathogenesis
doi 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02808
- 1,396 views
- 1 citation
21k
Total downloads
85k
Total views and downloads
You will be redirected to our submission process.
EDITORIAL
Published on 03 Dec 2019
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 20 May 2019

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 07 May 2019

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 02 Apr 2019

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 02 Apr 2019

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 26 Feb 2019

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 25 Jan 2019
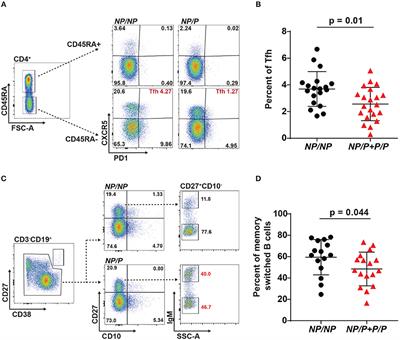
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 18 Dec 2018

REVIEW
Published on 16 Nov 2018

REVIEW
Published on 30 Oct 2018

MINI REVIEW
Published on 01 Oct 2018

