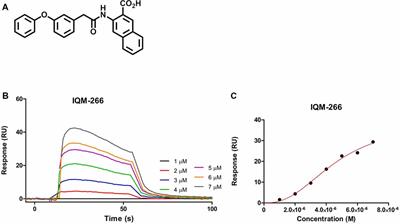
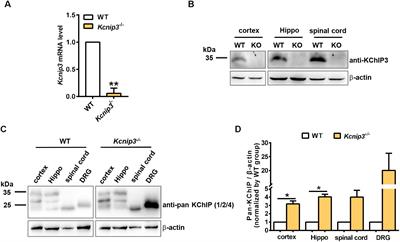
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 27 Nov 2019
NCS-1 Deficiency Affects mRNA Levels of Genes Involved in Regulation of ATP Synthesis and Mitochondrial Stress in Highly Vulnerable Substantia nigra Dopaminergic Neurons

doi 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00252
- 3,428 views
- 18 citations