EDITORIAL
Published on 12 Feb 2020
Editorial: Obesity and Diabetes: Implications for Brain-Immunometabolism
doi 10.3389/fnins.2020.00056
- 3,076 views
- 1 citation
44k
Total downloads
208k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 12 Feb 2020
REVIEW
Published on 22 May 2019
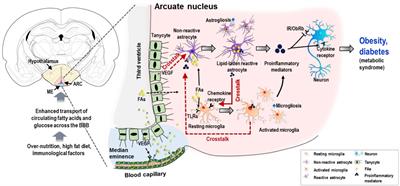
MINI REVIEW
Published on 24 Apr 2019
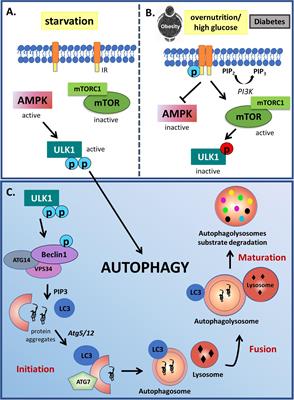
REVIEW
Published on 18 Apr 2019
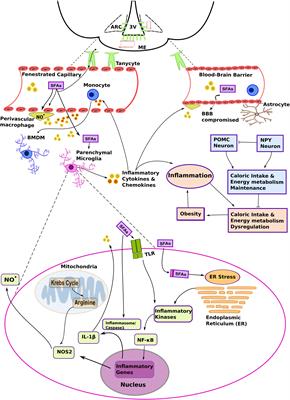
REVIEW
Published on 05 Apr 2019
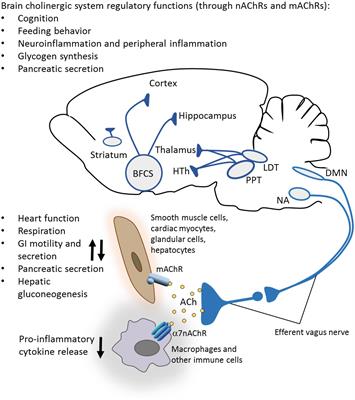
MINI REVIEW
Published on 29 Mar 2019
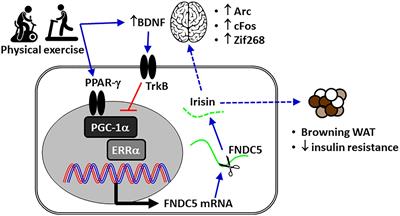
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 01 Mar 2019
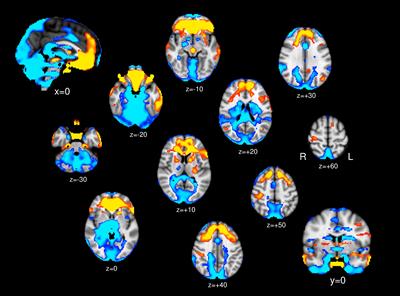
REVIEW
Published on 31 Jan 2019
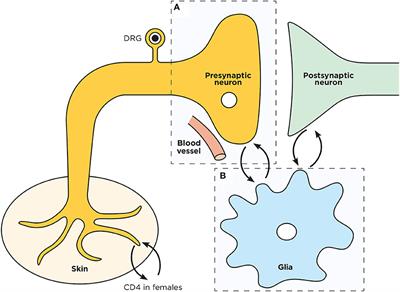
REVIEW
Published on 14 Jan 2019
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 09 Jan 2019
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 08 Jan 2019
REVIEW
Published on 13 Dec 2018