EDITORIAL
Published on 21 Aug 2020
Editorial: Intermittent Hypoxia: From Basic Mechanisms to Clinical Insights and Therapeutics
doi 10.3389/fneur.2020.00647
- 1,593 views
11k
Total downloads
52k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 21 Aug 2020
MINI REVIEW
Published on 03 Aug 2018
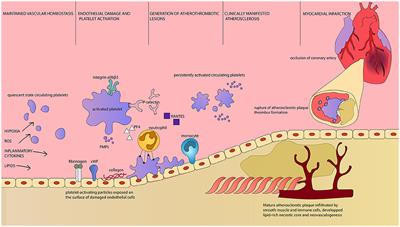
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 14 Jun 2018
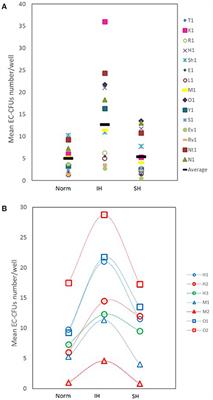
CLINICAL TRIAL
Published on 08 May 2018
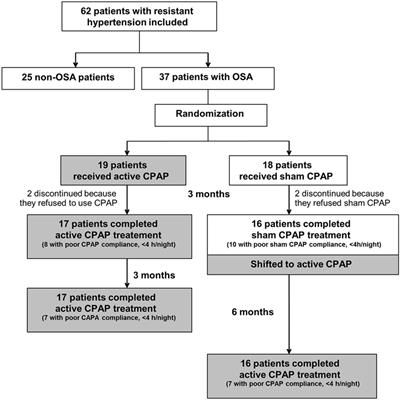
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 26 Apr 2018
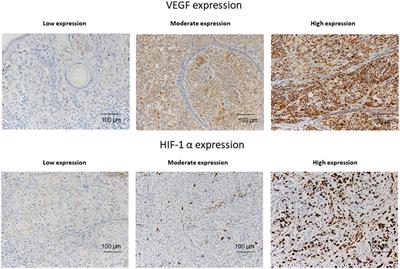
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Published on 22 Feb 2018
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 19 Jan 2018
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 22 Dec 2017

