EDITORIAL
Published on 08 Jan 2020
Editorial: Recent Advances in Endothelial Progenitor Cells Toward Their Use in Clinical Translation
doi 10.3389/fmed.2019.00290
- 1,927 views
- 2 citations
15k
Total downloads
79k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 08 Jan 2020
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 11 Mar 2019
MINI REVIEW
Published on 30 Jan 2019
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 20 Dec 2018
MINI REVIEW
Published on 18 Dec 2018
BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT
Published on 27 Nov 2018
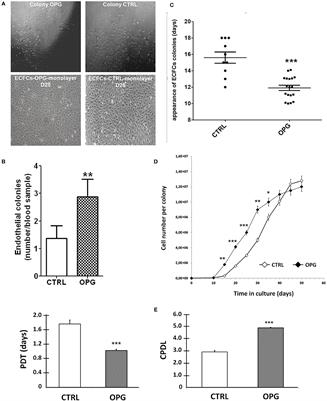
REVIEW
Published on 23 Oct 2018
REVIEW
Published on 16 Oct 2018
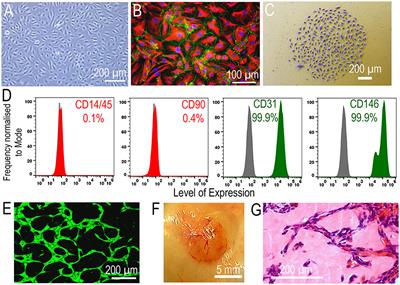
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 28 Sep 2018

REVIEW
Published on 10 Jul 2018