EDITORIAL
Published on 25 Aug 2020
Editorial: TAVI and the Challenges Ahead
doi 10.3389/fcvm.2020.00149
- 3,056 views
- 5 citations
17k
Total downloads
76k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 25 Aug 2020
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 10 Jan 2020
REVIEW
Published on 23 Oct 2018
MINI REVIEW
Published on 17 Aug 2018
REVIEW
Published on 31 Jul 2018
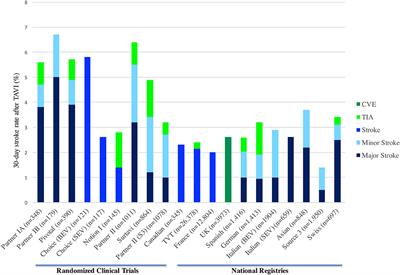
PERSPECTIVE
Published on 19 Jul 2018
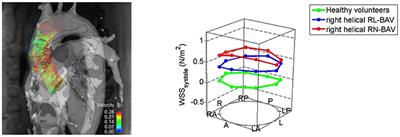
REVIEW
Published on 18 Jul 2018
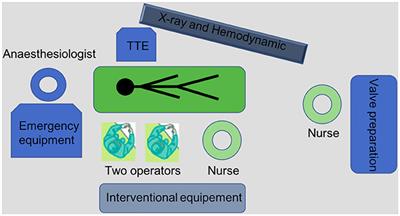
REVIEW
Published on 17 Jul 2018
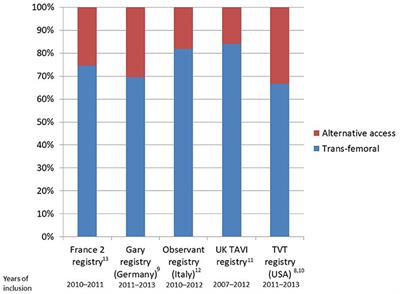
REVIEW
Published on 12 Jul 2018
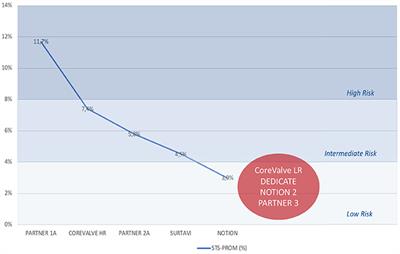
REVIEW
Published on 03 Jul 2018
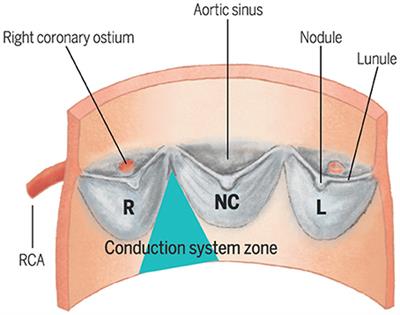
REVIEW
Published on 19 Jun 2018
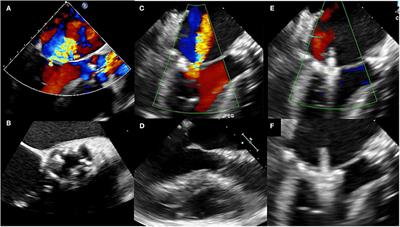
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 05 Jun 2018