ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 17 Dec 2024
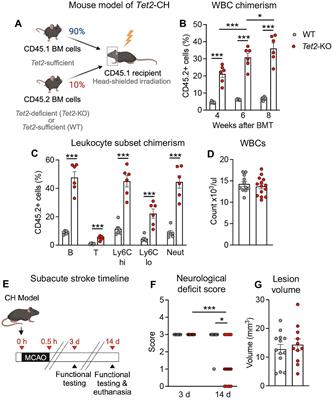
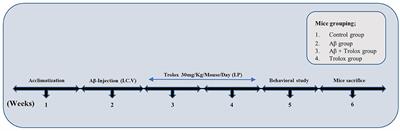
Tet2-mediated clonal hematopoiesis modestly improves neurological deficits and is associated with inflammation resolution in the subacute phase of experimental stroke
doi 10.3389/fncel.2024.1487867
- 785 views