ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 15 Jul 2024
Effects of Alhagi maurorum Medik polysaccharide derived from different regions on the intestinal immune functions of lambs
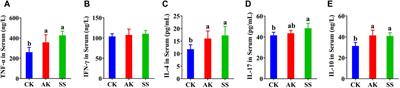
doi 10.3389/fphar.2024.1422461
- 703 views
- 1 citation
13k
Total downloads
43k
Total views and downloads
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 15 Jul 2024

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 24 Jun 2024

MINI REVIEW
Published on 19 Jun 2024

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 11 Jun 2024

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 10 Jun 2024

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 30 May 2024

REVIEW
Published on 15 May 2024
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 07 May 2024

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 01 May 2024

REVIEW
Published on 15 Apr 2024
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 08 Apr 2024

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 02 Apr 2024
