EDITORIAL
Published on 08 Oct 2024
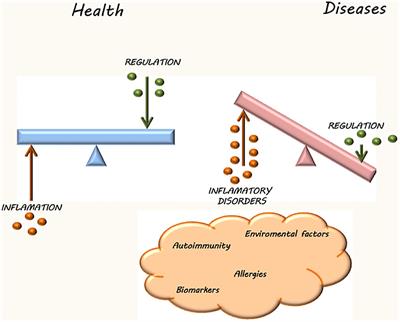
Editorial: Immune system disorders: from molecular mechanisms to clinical implications
doi 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1498830
- 546 views
32k
Total downloads
94k
Total views and downloads
You will be redirected to our submission process.
EDITORIAL
Published on 08 Oct 2024

REVIEW
Published on 12 Jul 2024
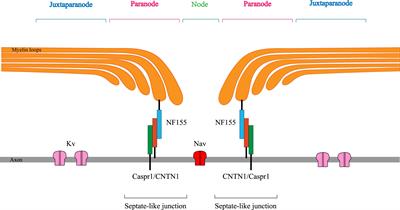
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 04 Jul 2024

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 25 Jun 2024
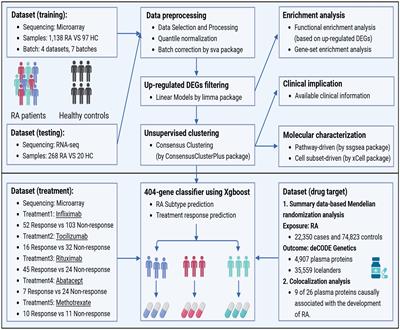
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Published on 14 Jun 2024

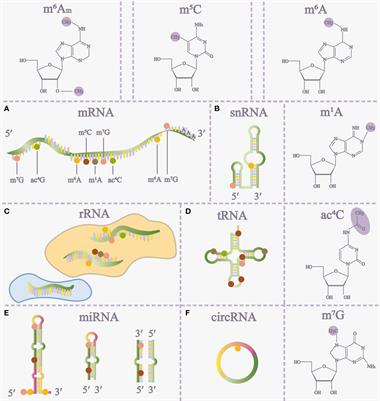
REVIEW
Published on 06 Jun 2024

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 28 May 2024

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 23 May 2024

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 14 May 2024

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 13 May 2024
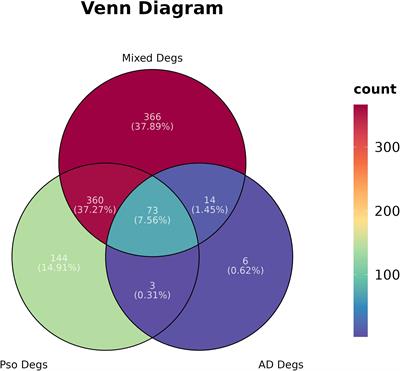
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 07 May 2024
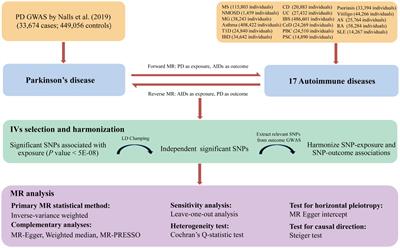
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 25 Apr 2024