EDITORIAL
Published on 12 Jul 2019
Editorial: Novel Concepts in Cardiac Energy Metabolism: From Biology to Disease
doi 10.3389/fcvm.2019.00097
- 2,696 views
- 2 citations
15k
Total downloads
82k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 12 Jul 2019
OPINION
Published on 23 Oct 2018
MINI REVIEW
Published on 12 Jun 2018

OPINION
Published on 11 Jun 2018
REVIEW
Published on 07 Jun 2018
REVIEW
Published on 07 Jun 2018

REVIEW
Published on 06 Jun 2018
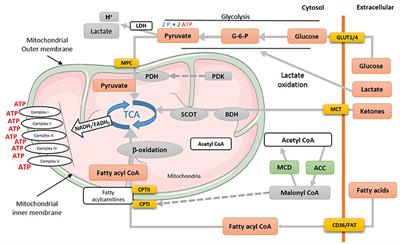
MINI REVIEW
Published on 03 May 2018
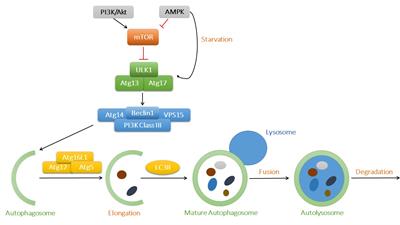
REVIEW
Published on 20 Apr 2018
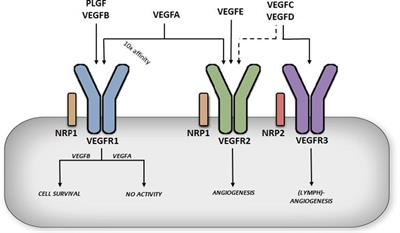
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 06 Mar 2018