ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 23 May 2018
β3GnT8 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Cells Invasion via CD147/MMP2/Galectin3 Axis
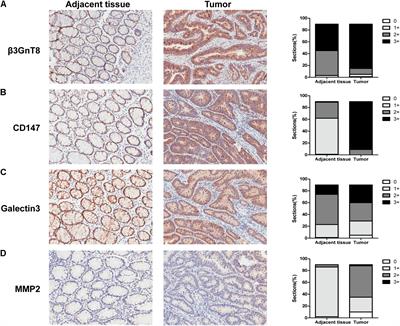
doi 10.3389/fphys.2018.00588
- 2,245 views
- 10 citations
11k
Total downloads
44k
Total views and downloads
You will be redirected to our submission process.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 23 May 2018

MINI REVIEW
Published on 03 May 2018
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 09 Mar 2018
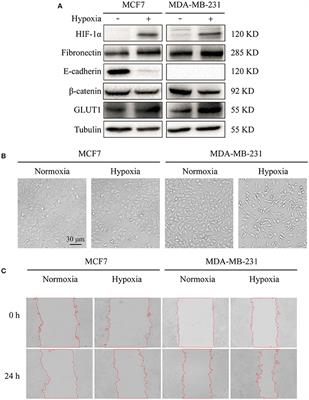
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 21 Aug 2017

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 02 Aug 2017
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 26 Jul 2017

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 07 Jul 2017

REVIEW
Published on 08 May 2017

