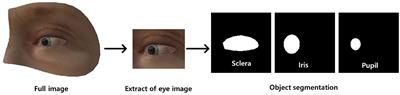
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 09 Jan 2025
Comparison of an AI-based mobile pupillometry system and NPi-200 for pupillary light reflex and correlation with glaucoma-related markers
doi 10.3389/fneur.2024.1426205
- 379 views
1,884
Total downloads
8,246
Total views and downloads
You will be redirected to our submission process.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 09 Jan 2025
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 09 Apr 2024
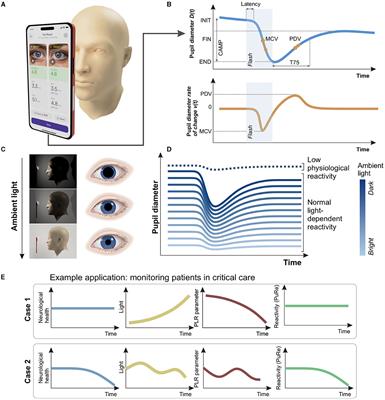
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 26 Mar 2024
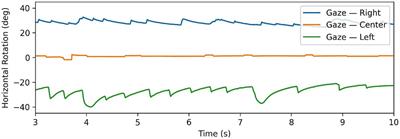
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 21 Feb 2024