EDITORIAL
Published on 10 Feb 2025
Editorial: The immune response to therapeutic antibodies
doi 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1554297
- 365 views
10k
Total downloads
44k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 10 Feb 2025
REVIEW
Published on 16 Dec 2024
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 11 Nov 2024
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 22 Aug 2024
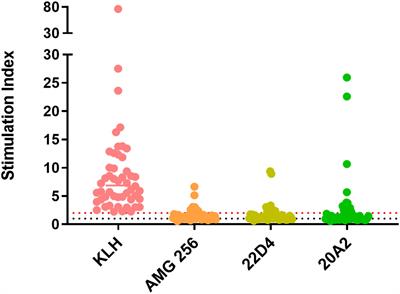
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 20 Aug 2024
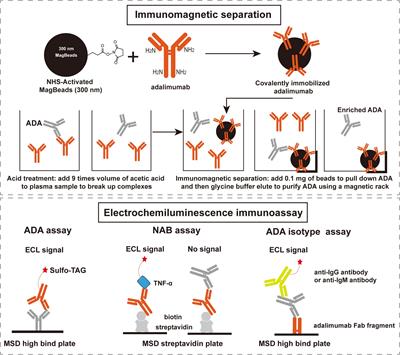
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 15 Jul 2024

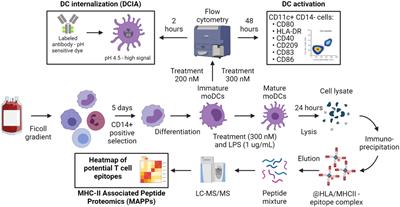
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 31 May 2024
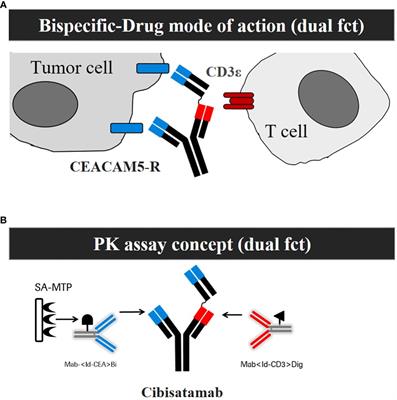
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 28 May 2024
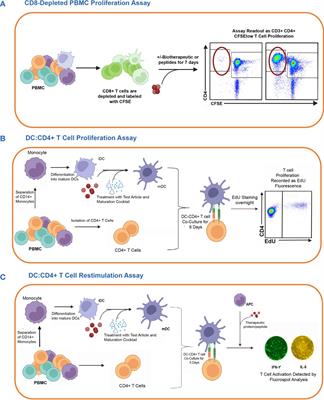
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 15 May 2024
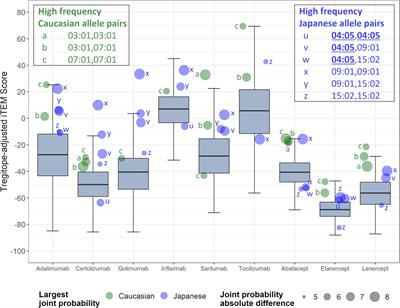
REVIEW
Published on 15 May 2024
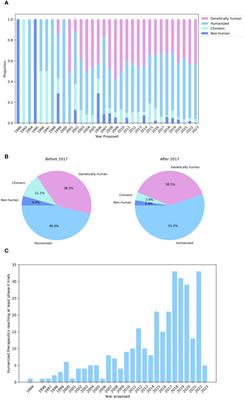
CORRECTION
Published on 27 Feb 2024
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 26 Jan 2024