CORRECTION
Published on 19 Jun 2024
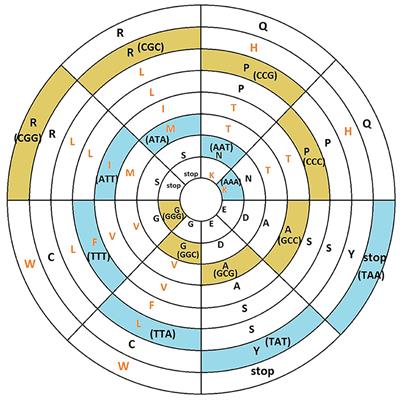
Corrigendum: Algebraic and toroidal representation of the genetic code
doi 10.3389/fams.2024.1445187
- 486 views
689
Total downloads
6,132
Total views and downloads
Select the journal/section where you want your idea to be submitted:
CORRECTION
Published on 19 Jun 2024

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 31 May 2024
HYPOTHESIS AND THEORY
Published on 30 May 2024

Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences