EDITORIAL
Published on 18 Feb 2025
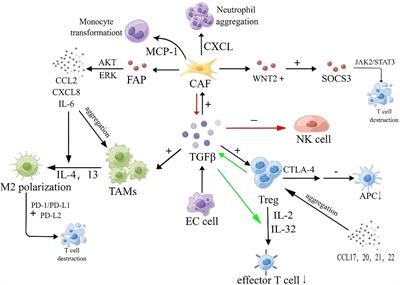
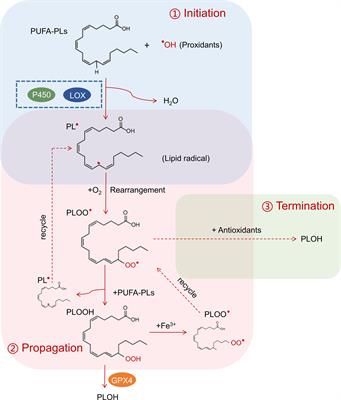
Editorial: Current insights in cancer metabolism and T cell based tumor immunity
doi 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1566491
- 306 views
8,841
Total downloads
27k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 18 Feb 2025
REVIEW
Published on 13 Feb 2024

REVIEW
Published on 08 Jan 2024
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 04 Jul 2023

REVIEW
Published on 08 Jun 2023