ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 06 Mar 2018
Mechanical Strain Alters Cellular and Nuclear Dynamics at Early Stages of Oligodendrocyte Differentiation
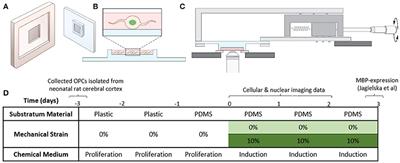
doi 10.3389/fncel.2018.00059
- 5,179 views
- 17 citations
13k
Total downloads
66k
Total views and downloads
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 06 Mar 2018

REVIEW
Published on 21 Feb 2018
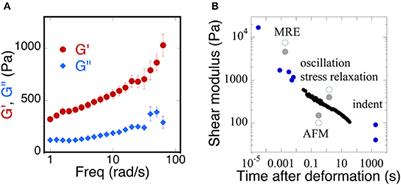
REVIEW
Published on 05 Jan 2018
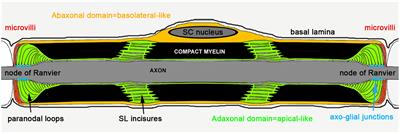
REVIEW
Published on 01 Nov 2017
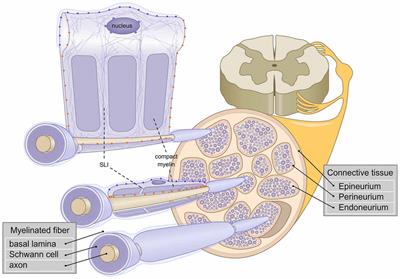
MINI REVIEW
Published on 25 Oct 2017

PROTOCOLS
Published on 30 Aug 2017

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 20 Apr 2017
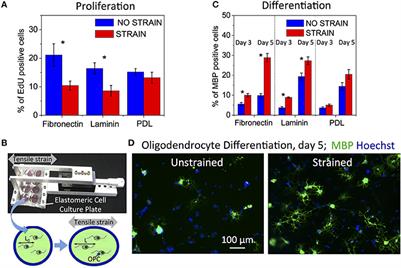
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 28 Mar 2017
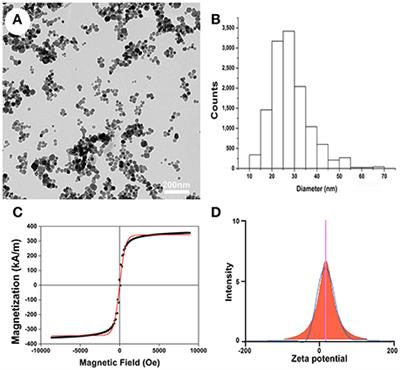
MINI REVIEW
Published on 29 Nov 2016
